First Molecular Survey and Genetic Characterization of Rickettsia spp. in Haemaphysalis hystricis Ticks Infesting Dogs in Taiwan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tick Collection and Species Identification
2.2. Genomic DNA Extraction from Tick Specimens
2.3. Rickettsia Detection by Nested Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
2.4. Genetic Relatedness Determined by Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. GenBank Accession Numbers of Submitted Nucleotide Sequences
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Detection of Rickettsia Infection in H. hystricis Ticks of Taiwan
3.2. Genetic Relatedness of Rickettsia spp. Detected in H. hystricis Ticks
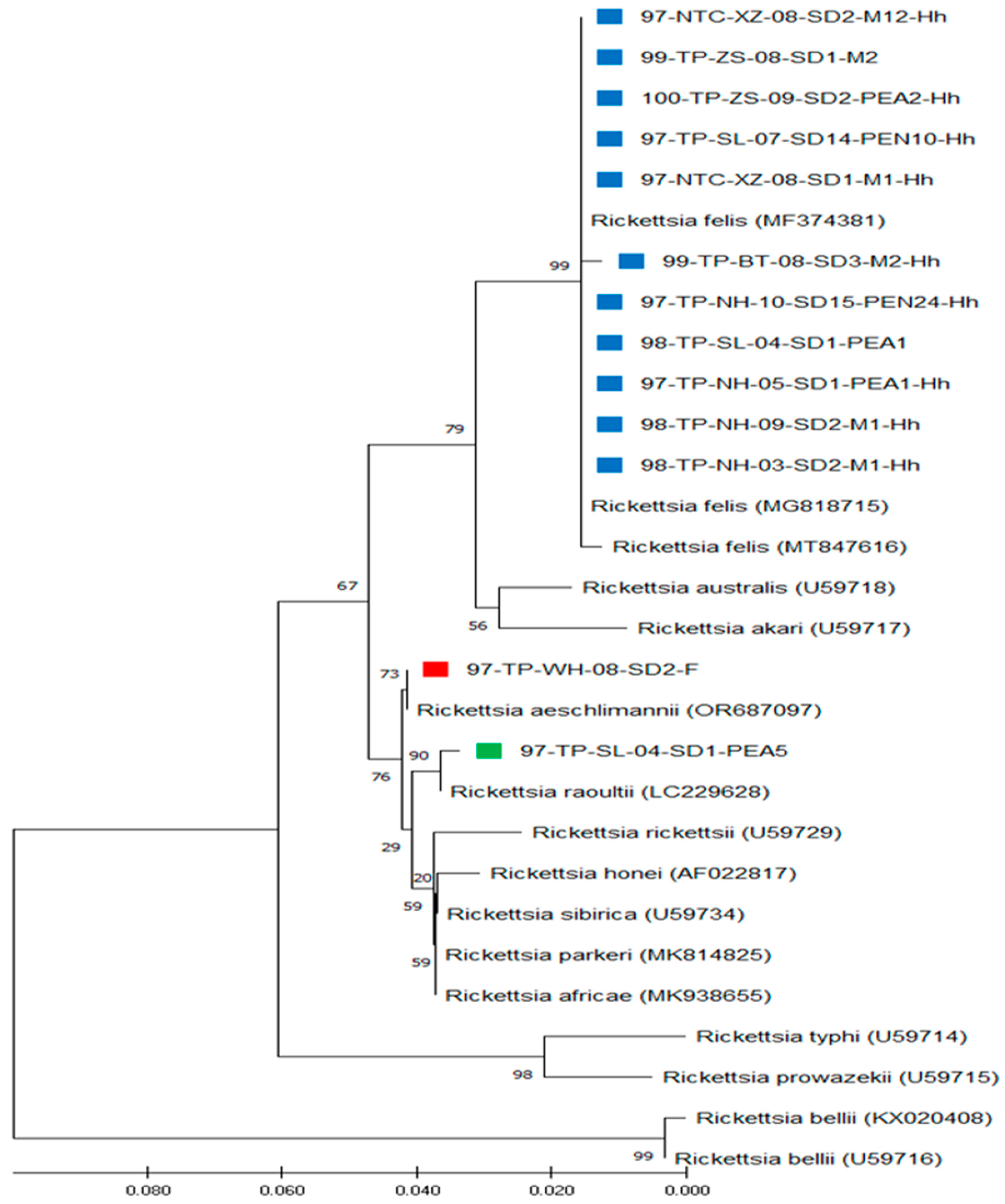
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of Rickettsia spp. Detected in H. hystricis Ticks
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balashov, Y.S. Bloodsucking ticks (Ixodoidea)-vectors of diseases of man and animals. Misc. Publ. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1972, 8, 268–305. [Google Scholar]
- Sonenshine, D.E.; Roe, R.M. Biology of Ticks, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; ISBN 9780199744060. [Google Scholar]
- Hoogstraal, H.; Trapida, H.; Kohls, G.M. Studies on southeast Asian Haemaphysalis ticks (Ixodoidea, Ixodidae). The identity, distribution, and hosts of H. (Kaiseriana) hystricis supino. J. Parasitol. 1965, 51, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatri-Chhetri, R.; Wang, H.C.; Chen, C.C.; Shih, H.C.; Liao, H.C.; Sun, C.M.; Khatri-Chhetri, N.; Wu, H.Y.; Pei, K.J.C. Surveillance of ticks and associated pathogens in free-ranging Formosan pangolins (Manis pentadactyla pentadactyla). Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2018, 7, 1238–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongejan, F.; Su, B.L.; Yang, H.J.; Berger, L.; Bevers, J.; Liu, P.C.; Fang, J.C.; Cheng, Y.W.; Kraakman, C.; Plaxton, N. Molecular evidence for the transovarial passage of Babasia gibsoni in Haemaphysalis hystricis (Acari: Ixodidae) ticks from Taiwan: A novel vector for canine babesiosis. Prasite Vectors 2018, 11, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Tian, J.H.; Yu, B.; Guo, W.P.; Holmes, E.C.; Zhang, Y.Z. Extensive diversity of rickettsiales bacteria in ticks from Wuhan, China. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2017, 8, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parola, P.; Cornet, J.P.; Sanogo, Y.O.; Miller, S.; Thien, H.V.; Gonzalez, J.P.; Raoult, D.; Telford, S.R., III; Wongsrichanalai, C. Detection of Ehrlichia spp., Anaplasma spp., Rickettsia spp., and other Eubacteria in ticks from the Thai-Myanmar border and Vietnam. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 1600–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Xuan, X.; Fu, R.; Tai, H.; Xu, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Jiang, J.; Wu, H.; Ma, H.; et al. Preliminary investigation of ixodid ticks in Jiangxi Province of eastern China. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2019, 77, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, L.L.; Hsieh, C.K.; Ho, T.Y.; Shih, C.M. First zootiological survey of hard ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) infesting dogs in northern Taiwan. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2019, 77, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, J.J.; Lim, F.S.; Chen, F.; Phoon, W.H.; Khor, C.S.; Pike, B.L.; Chang, L.Y.; AbuBakar, S. Coxiella detection in ticks from wildlife and livestock in Malaysia. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016, 16, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, J.J.; Lim, F.S.; Tan, K.K.; Chen, F.S.; Phoon, W.H.; Khor, C.S.; Pike, B.L.; Chang, L.Y.; AbuBakar, S. Detection in Malaysia of Borrelia sp. from Haemaphysalis hystricis (Ixodida: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, P.S.; Lai, Y.W.; Chung, H.H.; Chia, Y.T.; Wang, C.C.; Teng, H.J.; Chen, S.L. First molecular detection of a novel Babesia species from Haemaphysalis hystricis in Taiwan. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2024, 15, 102284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, P.E.; Dumler, J.S.; Greub, G.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Raoult, D. Gene sequence-based criteria for identification of new Rickettsia isolates and description of Rickettsia heilongjiangensis sp. nov. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 5456–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parola, P.; Paddock, C.D.; Raoult, D. Tick-borne rickettsioses around the world: Emerging diseases challenging old concepts. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 719–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillesoie, J.J.; Williams, K.; Shukla, M.; Snyder, E.E.; Nordberg, E.K.; Ceraul, S.M.; Dharmanolla, C.; Rainey, D.; Soneja, J.; Shallom, J.M.; et al. Rickettsia phylogenimics: Unwinding the intricacies of obligate intracellular life. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, K.E.; Patel, N.G.; Levy, M.A.; Storeygard, A.; Balk, D.; Gittleman, J.L.; Daszak, P. Global trends in emerging infectious diseases. Nature 2008, 451, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satjanadumrong, J.; Robinson, M.T.; Hughes, T.; Blacksel, S.D. Distribution and ecological drivers of spotted fever group Rickettsia in Asia. EcoHealth 2019, 16, 611–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, A.F.; Beard, C.B. Rickettsial pathogens and their arthropod vectors. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1998, 4, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraiva, D.G.; Nieri-Bastos, F.A.; Horta, M.C.; Soares, H.S.; Nicola, P.A.; Pereira, L.C.M.; Labruna, M.B. Rickettsia amblyommii infecting Amblyomma auricularium ticks in Pernambuco, Northeastern Brazil: Isolation, transovarial transmission, and transstadial perpetuation. Vector-Borne Zoonoic Dis. 2013, 13, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socolovschi, C.; Huynh, T.P.; Davoust, B.; Gomez, J.; Raoult, D.; Parola, P. Transovarial and transstadial transmission of Rickettsiae africae in Amblyomma variegatum ticks. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15 (Suppl. S2), 317–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazejak, K.; Janecek, E.; Strube, C. A 10-year surveillance of Rickettsiales (Rickettsia spp. and Anaplasma phagocytophilum) in the city of Hanover, Germany, reveals Rickettsia spp. as emerging pathogens in ticks. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Jang, W.J.; Kim, J.H.; Ryu, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Park, K.H.; Paik, H.S.; Koh, Y.S.; Choi, M.S.; Kim, I.S. Spotted fever group and typhus group rickettsioses in humans, South Korea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teglas, M.; Matern, E.; Lein, S.; Foley, P.; Mahan, S.M.; Foley, J. Ticks and tick-borne disease in Guatemalan cattle and horses. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 131, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unsworth, N.B.; Stenos, J.; Graves, S.R.; Faa, A.G.; Cox, G.E.; Dyer, J.R.; Boutlis, C.S.; Lane, A.M.; Shaw, M.D.; Robson, J.; et al. Flinders Island Spotted Fever rickettsiosis caused by marmionii strain of Rickettsia honei, Eastern Australia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, H.; Drebot, M.A.; Dewailly, E.; Dillon, L.; Dimitrova, K.; Forde, M.; Grolla, A.; Lee, E.; Loftis, A.; Makowski, K.; et al. Short Report: Seroprevalence of seven zoonotic pathogens in pregnant women from the Caribbean. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 91, 642–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, M.G.; Junior, J.M.; Foster, R.J.; Harmsen, B.J.; Sanchez, E.; Martins, T.F.; Quigley, H.; Marcili, A.; Labruna, M.B. Ticks and rickettsiae from wildlife in Belize, Central America. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Jin, Y.; Fan, M.; Xu, G.; Liu, Q.; Raoult, D. Genotypic and antigenic identification of two new strains of spotted fever group rickettsiae isolated from China. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, T.; Uchiyama, T.; Kumano, K.; Walker, D.H. Rickettsia japonica sp. nov., the etiological agent of spotted fever group rickettsiosis in Japan. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1992, 42, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenos, J.; Roux, V.; Walker, D.H.; Raoult, D. Rickettsia honei sp. nov., the aetiological agent of Flinders Island spotted fever in Australia. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1998, 48, 1309–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollars, T.M., Jr.; Tippayachai, B.; Bodhidatta, D. Short report: Thai tick typhus, Rickettsia honei, and a unique rickettsia detected in Ixodes granulatus (Ixodidae: Acari) from Thailand. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2001, 65, 535–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, H.; Fournier, P.E.; Takada, N.; Saito, T.; Raoult, D. Rickettsia asiatica sp. nov. isolated in Japan. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 2365–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Springer, A.; Montenegro, V.M.; Schicht, S.; Wolfel, S.; Schaper, S.R.; Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Siebert, S.; Strube, C. Detection of Rickettsia monacensis and Rickettsia amblyommatis in ticks collected from dogs in Costa Rica and Nicaragua. Ticks Tick. Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seva, A.d.P.; Martins, T.F.; Munoz-Leal, S.; Rodrigues, A.C.; Pinter, A.; Luz, H.R.; Angerami, R.N.; Labruna, M.B. A human case of spotted fever caused by Rickettsia parkeri strain Atlantic rainforest and its association to the tick Amblyomma ovale. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, V.; Rydkina, E.; Eremeeva, M.; Raoult, D. Citrate synthase gene comparison, a new tool for phylogenetic analysis, and its application for the rickettsiae. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1997, 47, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, P.E.; Takada, N.; Fujita, H.; Raoult, D. Rickettsia tamurae sp. nov. isolated from Amblyomma testudinarium ticks. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 1673–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Sun, Y.; Ju, W.; Wang, X.; Cao, W.; Wu, M. Vector competence of the tick Ixodes sinensis (Acari: Ixodidae) for Rickettsia monacensis. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, H.; Kadosaka, T.; Nitta, Y.; Ando, S.; Takano, A.; Watanabe, H.; Kawabata, H. Rickettsia sp. in Ixodes granulatus ticks, Japan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1963–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.M.; Chao, L.L. A Catalog of Ixodidae Ticks in Taiwan; National Science Council: Taipei, Taiwan, China, 2011; ISBN 978-957-41-85849. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, L.L.; Chen, T.H.; Lien, W.; Erazo, E.; Shih, C.M. Molecular and morphological identification of a reptile-associated tick, Amblyomma geoemydae (Acari: Ixodidae), infesting wild yellow-margined box turtles (Cuora flavomarginata) in northern Taiwan. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 101901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, P.A.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Bio. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 52, 1119–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, C.M.; Yang, P.W.; Chao, L.L. Molecular detection and genetic identification of Rickettsia infection in Ixodes granulatus ticks, an incriminated vector for geographical transmission in Taiwan. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, P.Y.; Tsai, K.H.; Weng, M.H.; Hung, Y.W.; Liu, Y.T.; Hu, K.Y.; Lien, J.C.; Lin, P.Y.; Shaio, M.F.; Wang, H.C.; et al. Molecular detection and characterization of spotted fever group Rickettsiae in Taiwan. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 77, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, L.L.; Erazo, E.; Robinson, M.; Liang, Y.F.; Shih, C.M. First detection and molecular identification of a pathogenic spotted fever group Rickettsia, R. massiliae, from Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides ticks infesting dogs in southern Taiwan. Acta Trop. 2022, 236, 106666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoult, D.; Fournier, P.E.; Abboud, P.; Caron, F. First documented human Rickettsia aeschlimannii infection. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 748–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, A.M.; Birtleas, R.J. Rickettsia aeschlimannii: A new pathogenic spotted fever group Rickettsia, South Africa. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, D. Effects of antibiotic treatment on the fecundity of Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides tick. Parasite Vectors 2018, 11, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Ogawa, M.; Brouqui, P.; Raoult, D.; Parola, P. Transmission of Rickettsia massiliae in the tick, Rhipicephalus turanicus. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2005, 19, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemtsova, G.; Killmaster, L.F.; Mumcuoglu, K.Y.; Levin, M.L. Co-feeding as a route for transmission of Rickettsia conorii israelensis between Rhipicephalus sanguineus ticks. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2010, 52, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraes-Filho, J.; Francisco, B.C.; Monize, G.; Herbert, S.S.; Marcelo, B.L. Rickettsia rickettsii co-feeding Transmission among Amblyomma aureolatum Ticks. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 2041–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
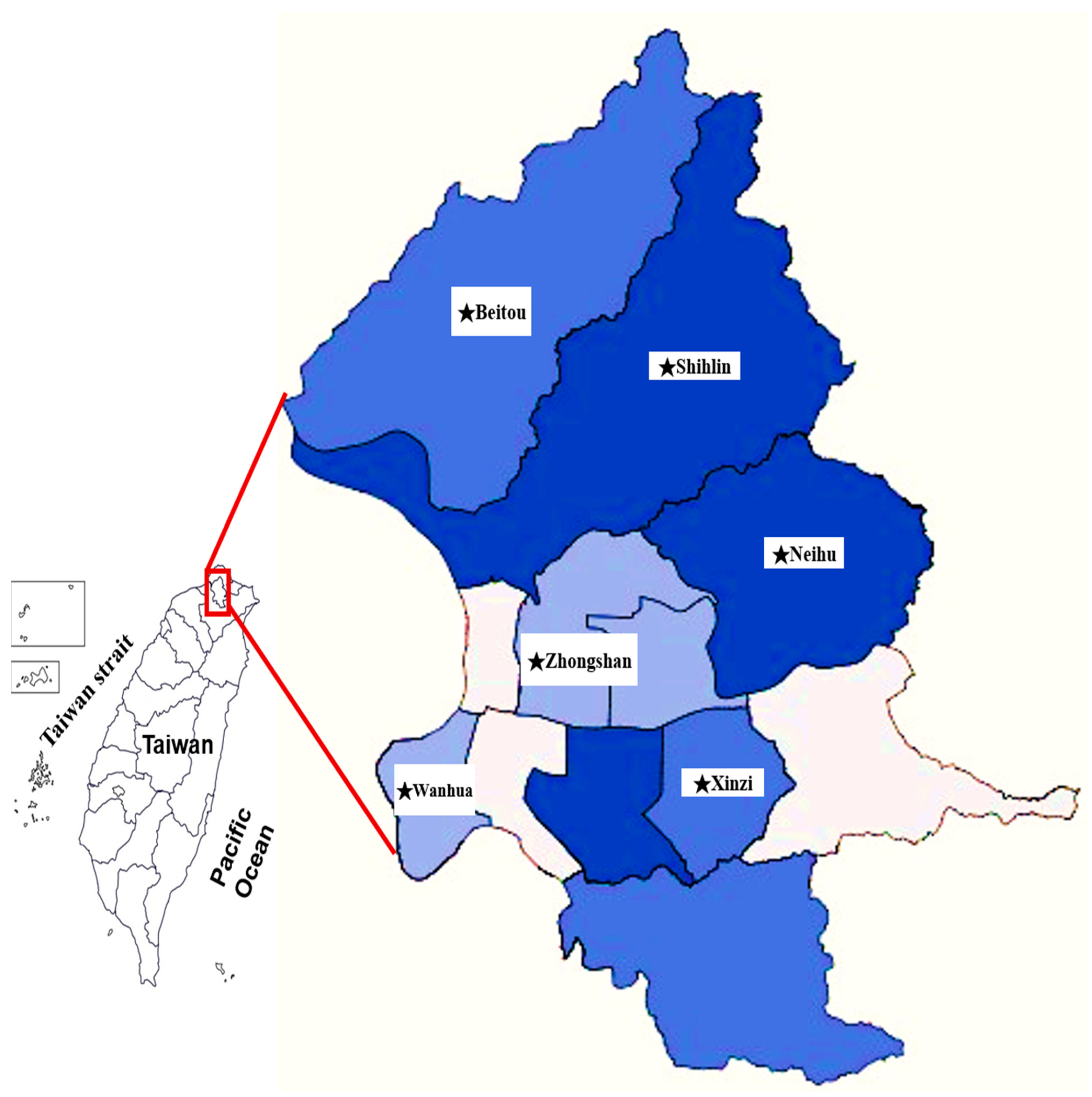

| Strain/Species | Origin of Rickettsia Strain | gltA Gene Accession Number a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biological | Geographic | ||
| Taiwan strain | |||
| 97-TP-SL-04-SD1-PEA5 | Haemaphysalis hystricis | Taiwan | PQ212712 |
| 97-TP-WH-08-SD2-F | Haemaphysalis hystricis | Taiwan | PQ212713 |
| 97-NTC-XZ-08-SD1-M1-Hh | Haemaphysalis hystricis | Taiwan | PQ212714 |
| 97-NTC-XZ-08-SD2-M12-Hh | Haemaphysalis hystricis | Taiwan | PQ212715 |
| 97-TP-NH-05-SD1-PEA1-Hh | Haemaphysalis hystricis | Taiwan | PQ212716 |
| 97-TP-NH-10-SD15-PEN24-Hh | Haemaphysalis hystricis | Taiwan | PQ212717 |
| 97-TP-SL-07-SD14-PEN10-Hh | Haemaphysalis hystricis | Taiwan | PQ212718 |
| 98-TP-NH-03-SD2-M1-Hh | Haemaphysalis hystricis | Taiwan | PQ212719 |
| 98-TP-NH-09-SD2-M1-Hh | Haemaphysalis hystricis | Taiwan | PQ212720 |
| 98-TP-SL-04-SD1-PEA1 | Haemaphysalis hystricis | Taiwan | PQ212721 |
| 99-TP-BT-08-SD3-M2-Hh | Haemaphysalis hystricis | Taiwan | PQ212722 |
| 99-TP-ZS-08-SD1-M2 | Haemaphysalis hystricis | Taiwan | PQ212723 |
| 100-TP-ZS-09-SD2-PEA2-Hh | Haemaphysalis hystricis | Taiwan | PQ212724 |
| Rickettsia felis | Ctenocephalides felis | Austria | MF374381 |
| Rickettsia felis | Booklice from herbals | China | MG818715 |
| Rickettsia felis | Rhipicephalus sanguineus | Taiwan | MT847616 |
| Rickettsia australis | Human | Australia | U59718 |
| Rickettsia akari | Human | USA | U59717 |
| Rickettsia aeschlimannii | Dermacentor reticulatus | Russia | OR687097 |
| Rickettsia raoultii | Hyalomma marginatum | Portugal | LC229628 |
| Rickettsia rickettsii | Dermacentor andersoni | USA | U59729 |
| Rickettsia parkeri | Amblyomma ovale | Mexico | MK814825 |
| Rickettsia africae | Diatom | Italy | MK938655 |
| Rickettsia honei | Human | Australia | AF022817 |
| Rickettsia sibirica | Dermacentor nuttalli | USSR | U59734 |
| Rickettsia typhi | Human | USA | U59714 |
| Rickettsia prowazeki | Human | Poland | U59715 |
| Rickettsia bellii | Amblyomma pseudoconcolor | Brazil | KX020408 |
| Rickettsia bellii | Dermacentor variabilis | USA | U59716 |
| Parasitized Host | Rickettsia spp. Detected in Various Life Stages of Tick | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Partially Engorged Female P/E a (%) | Flat Male P/E a (%) | Partially Engorged Nymph P/E a (%) | No. Positive/ No. Examined (%) | |
| Stray dogs | 11/302 (3.64) | 15/358 (4.19) | 12/255 (4.71) | 38/915 (4.15) b |
| Domestic dogs | 2/159 (1.26) | 1/86 (1.16) | 0/26 (0) | 3/271 (1.11) b |
| Total (%) | 13/461 (3.2) | 16/444 (3.6) | 12/281 (4.27) | 41/1186 (3.46) |
| Rickettsia Strains b | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Rickettsia felis (MF374381) | — | ||||||||||||||
| 2. 100-TP-ZS-09-SD2-PEA2-Hh (Taiwan) | 0.000 | — | |||||||||||||
| 3. 97-NTC-XZ-08-SD2-M12-Hh (Taiwan) | 0.000 | 0.000 | — | ||||||||||||
| 4. 98-TP-SL-04-SD1-PEA1 (Taiwan) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | — | |||||||||||
| 5. 98-TP-NH-09-SD2-M1-Hh (Taiwan) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | — | ||||||||||
| 6. 99-TP-BT-08-SD3-M2-Hh (Taiwan) | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | — | |||||||||
| 7. Rickettsia aeschlimannii (OR687097) | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.039 | 0.039 | 0.042 | — | ||||||||
| 8. 97-TP-WH-08-SD2-F (Taiwan) | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.039 | 0.039 | 0.042 | 0.000 | — | |||||||
| 9. Rickettsia raoultii (LC229628) | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.039 | 0.039 | 0.042 | 0.006 | 0.006 | — | ||||||
| 10. 97-TP-SL-04-SD1-PEA5 (Taiwan) | 0.041 | 0.042 | 0.042 | 0.042 | 0.042 | 0.046 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.003 | — | |||||
| 11. Rickettsia parkeri (MK814825) | 0.041 | 0.042 | 0.042 | 0.042 | 0.042 | 0.046 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.007 | — | ||||
| 12. Rickettsia sibirica (U59734) | 0.041 | 0.042 | 0.042 | 0.042 | 0.042 | 0.046 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.000 | — | |||
| 13. Rickettsia rickettsii (U59729) | 0.053 | 0.053 | 0.053 | 0.054 | 0.054 | 0.057 | 0.017 | 0.017 | 0.017 | 0.020 | 0.013 | 0.013 | — | ||
| 14. Rickettsia typhi (U59714) | 0.089 | 0.090 | 0.090 | 0.091 | 0.091 | 0.094 | 0.082 | 0.082 | 0.082 | 0.086 | 0.086 | 0.086 | 0.090 | — | |
| 15. Rickettsia bellii (KX020408) | 0.194 | 0.196 | 0.196 | 0.193 | 0.193 | 0.197 | 0.168 | 0.168 | 0.168 | 0.173 | 0.173 | 0.173 | 0.169 | 0.213 | — |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shih, C.-M.; Huang, X.-R.; Erazo, E.; Chao, L.-L. First Molecular Survey and Genetic Characterization of Rickettsia spp. in Haemaphysalis hystricis Ticks Infesting Dogs in Taiwan. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020424
Shih C-M, Huang X-R, Erazo E, Chao L-L. First Molecular Survey and Genetic Characterization of Rickettsia spp. in Haemaphysalis hystricis Ticks Infesting Dogs in Taiwan. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(2):424. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020424
Chicago/Turabian StyleShih, Chien-Ming, Xing-Ru Huang, Esmeralda Erazo, and Li-Lian Chao. 2025. "First Molecular Survey and Genetic Characterization of Rickettsia spp. in Haemaphysalis hystricis Ticks Infesting Dogs in Taiwan" Microorganisms 13, no. 2: 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020424
APA StyleShih, C.-M., Huang, X.-R., Erazo, E., & Chao, L.-L. (2025). First Molecular Survey and Genetic Characterization of Rickettsia spp. in Haemaphysalis hystricis Ticks Infesting Dogs in Taiwan. Microorganisms, 13(2), 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020424







