Effectiveness of Biological Approaches for Removing Persistent Organic Pollutants from Wastewater: A Mini-Review
Abstract
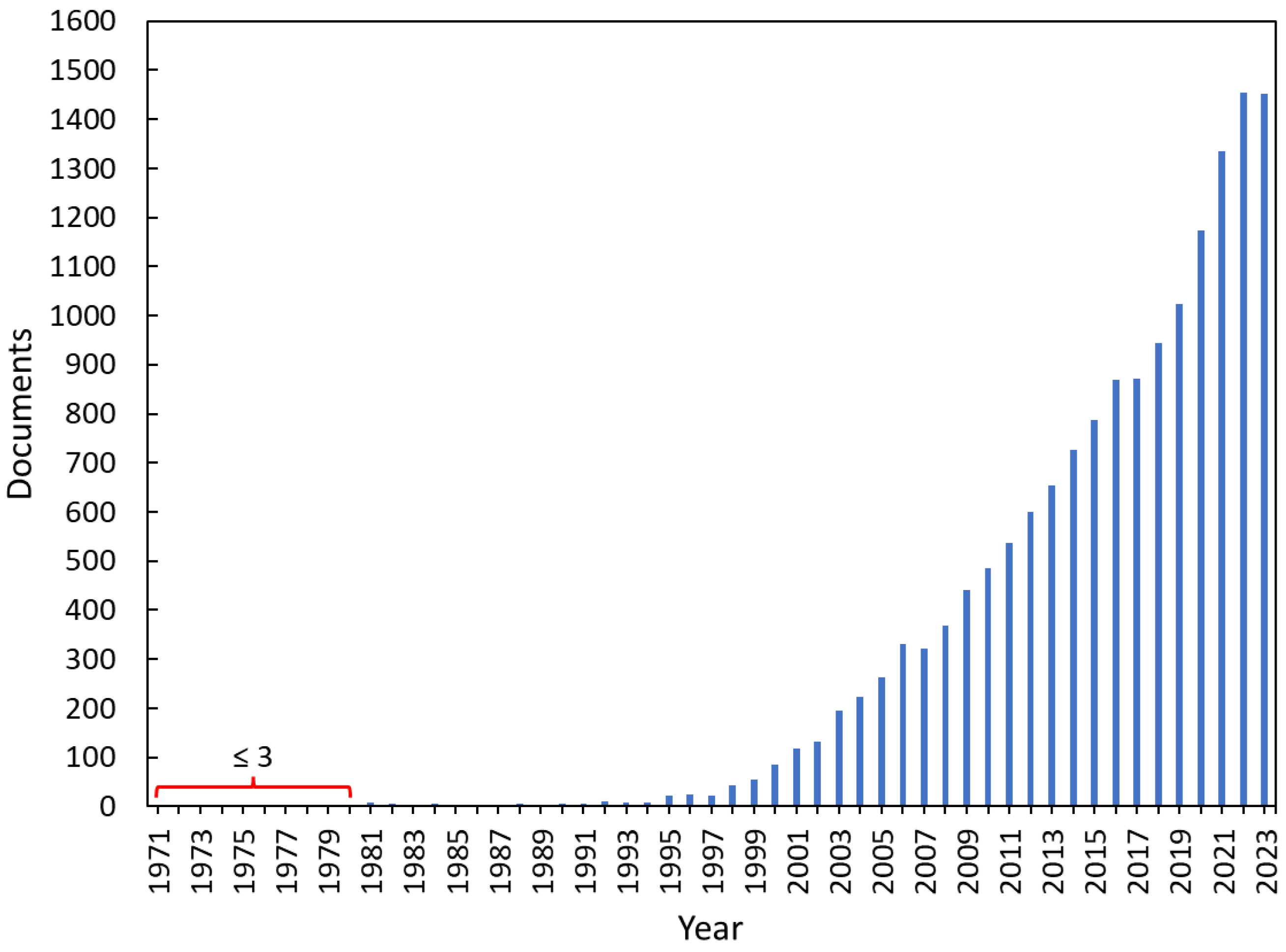
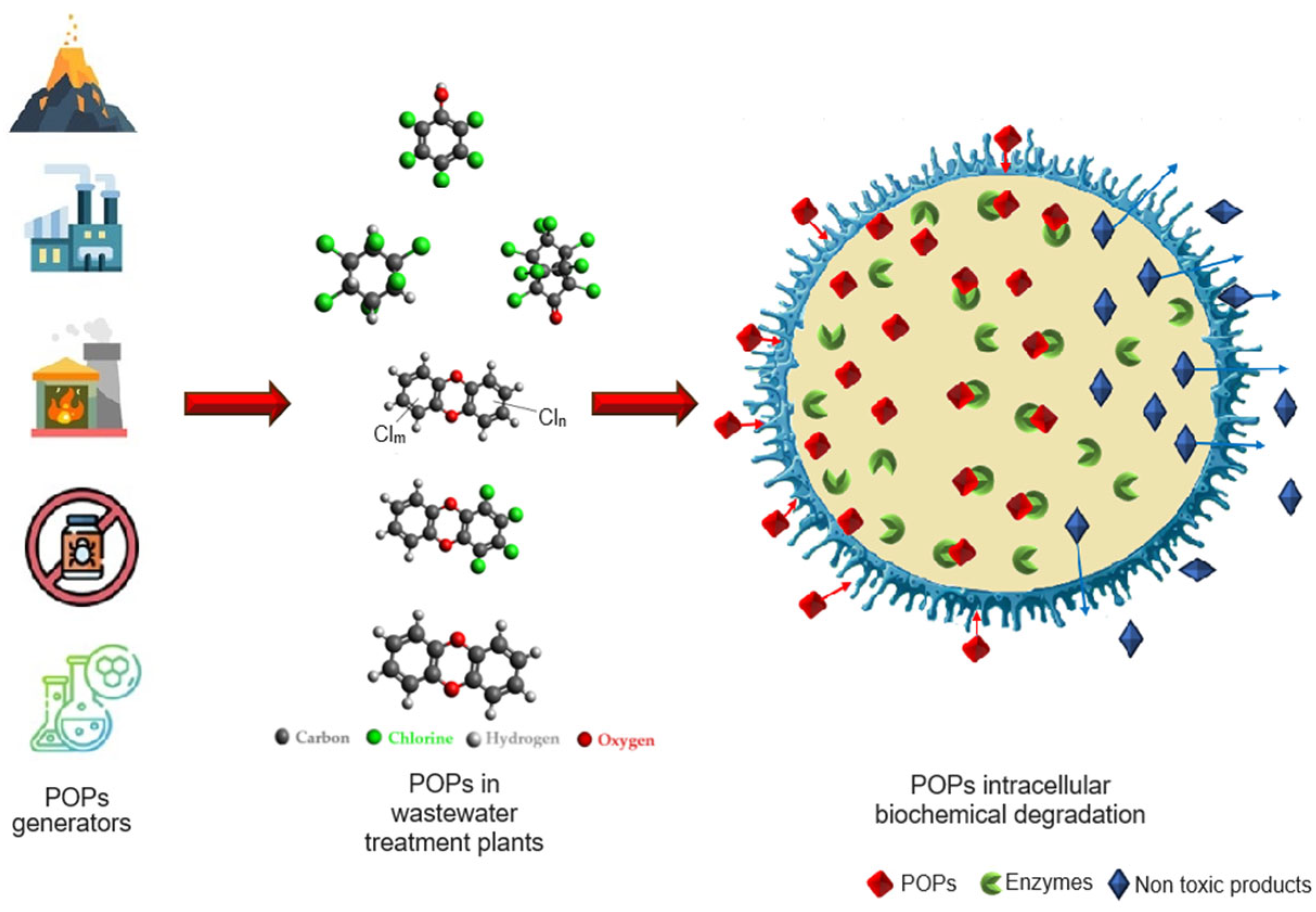
1. Introduction
2. Methodology and Results
- Problem (P): Challenges associated with the removal of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) using conventional treatment methods;
- Intervention (I): Biological treatment methods to effectively remove POPs from wastewater;
- Comparison (C): Conventional physicochemical treatment methods;
- Outcome (O): Outcomes in terms of POP concentration reduction, breakdown product formation, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impacts associated with biological POP removal.
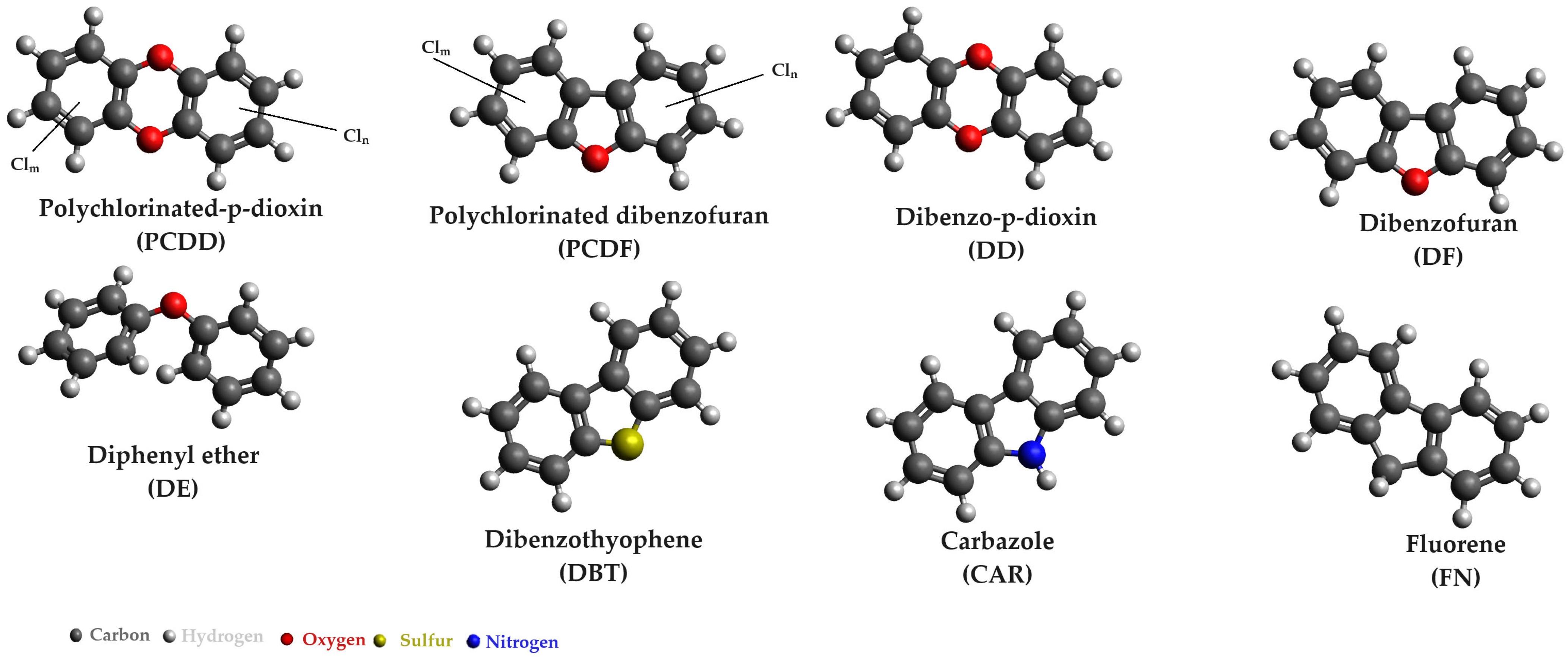
3. Microorganisms Employed for Removing POPs from Wastewaters
3.1. Bacteria-Assisted Biodegradation of POPs from Wastewaters
3.2. Fungus-Assisted Biodegradation of POPs from Wastewaters
4. Conclusions, Challenges and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaur, N.; Narasimhulu, K.; PydiSetty, Y. Recent advances in the bio-remediation of persistent organic pollutants and its effect on environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 1602–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, P.E.; Walls, M.P. The Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants. Nat. Resour. Environ. 2005, 19, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Gu, G.; Xia, C. Comparative study on catalytic hydrodehalogenation of halogenated aromatic compounds over Pd/C and Raney Ni catalysts. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Programme. Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs): A Global Assessment (2023). Nairobi, Kenya. Available online: https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/42503/Kenya_Country_Report_POPs.pdf?sequence=3 (accessed on 15 June 2024).
- James, T.Z. Degradation Pathways of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) in the Environment. In Persistent Organic Pollutants; Stephen Kudom, D., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2019; Chapter 3. [Google Scholar]
- Titchou, F.E.; Zazou, H.; Afanga, H.; El Gaayda, J.; Akbour, R.A.; Hamdani, M. Removal of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) from water and wastewater by adsorption and electrocoagulation process. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 13, 100575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badmus, K.O.; Tijani, J.O.; Massima, E.; Petrik, L. Treatment of persistent organic pollutants in wastewater using hydrodynamic cavitation in synergy with advanced oxidation process. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 7299–7314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, F.C.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Brillas, E.; Vilar, V.J.P. Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: A review on their application to synthetic and real wastewaters. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 202, 217–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Xiong, Y. Electrochemical oxidation technology: A review of its application in high-efficiency treatment of wastewater containing persistent organic pollutants. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 44, 102308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLU-IN. Persistent Organic Pollutants (pops). Treatment Technology Reports. Available online: https://cluin.org/contaminantfocus/default.focus/sec/persistent_organic_pollutants_(pops)/cat/Treatment_Technology_Reports/ (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Xia, Y.; Lin, X.D. Efficient biodegradation of straw and persistent organic pollutants by a novel strategy using recombinant. Bioresour Bioprocess 2022, 9, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanwell, M.D.; Curtis, D.E.; Lonie, D.C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Zurek, E.; Hutchison, G.R. Avogadro: An advanced semantic chemical editor, visualization, and analysis platform. J. Cheminformatics 2012, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
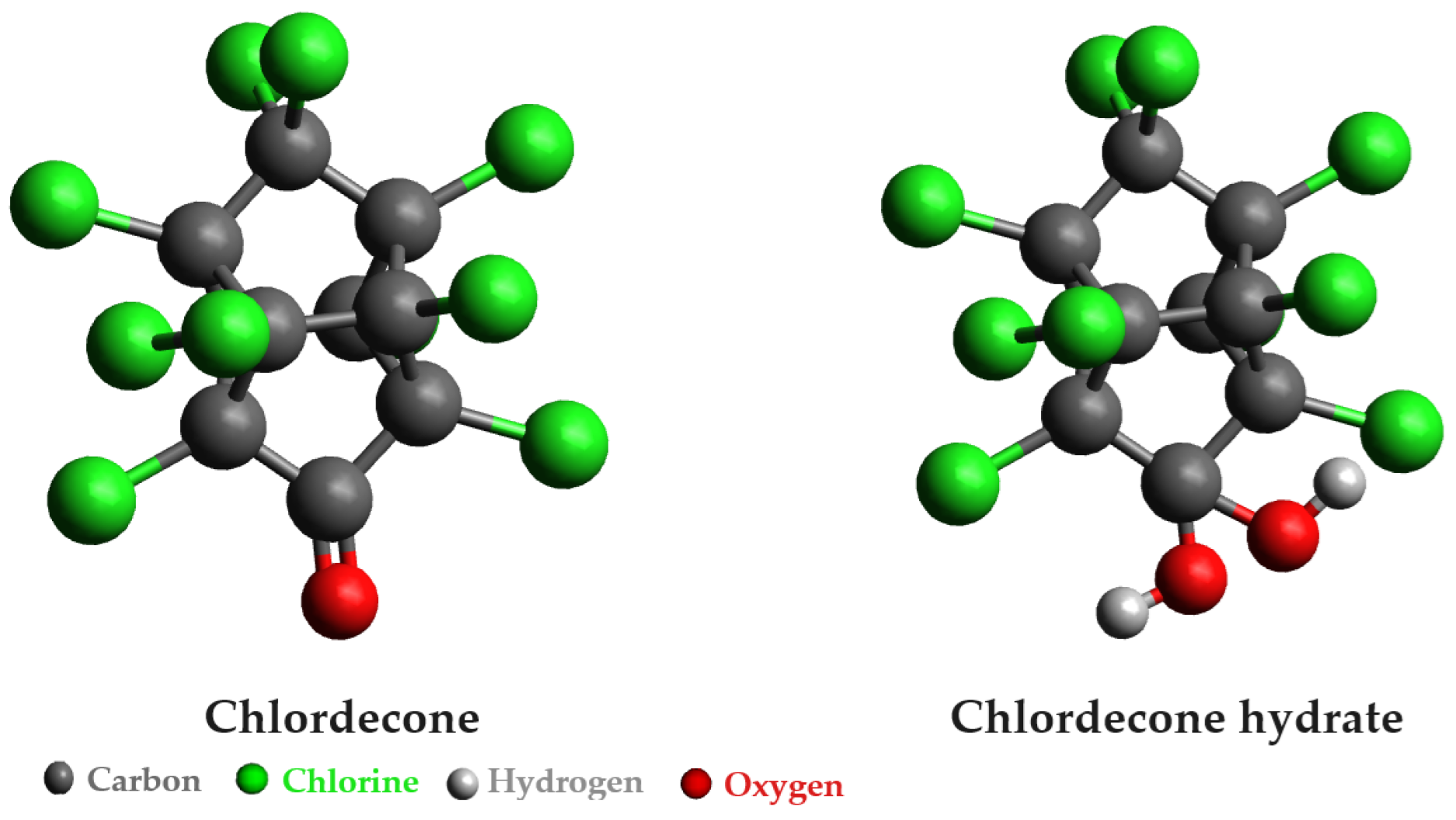
- Martin, D.E.; Alnajjar, P.; Muselet, D.; Soligot-Hognon, C.; Kanso, H.; Pacaud, S.; Le Roux, Y.; Saaidi, P.L.; Feidt, C. Efficient biodegradation of the recalcitrant organochlorine pesticide chlordecone under methanogenic conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Zhu, M.; Yuan, Y.; Dang, Z.; Yin, H. Bioremediation of PBDEs and heavy metals co-contaminated soil in e-waste dismantling sites by Pseudomonas plecoglossicida assisted with biochar. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 460, 132408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyetibo, G.O.; Miyauchi, K.; Huang, Y.; Chien, M.F.; Ilori, M.O.; Amund, O.O.; Endo, G. Biotechnological remedies for the estuarine environment polluted with heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 119, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergani, L.; Mapelli, F.; Marasco, R.; Crotti, E.; Fusi, M.; Di Guardo, A.; Armiraglio, S.; Daffonchio, D.; Borin, S. Bacteria associated to plants naturally selected in a historical PCB polluted soil show potential to sustain natural attenuation. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 01385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multigner, L.; Kadhel, P.; Rouget, F.; Blanchet, P.; Cordier, S. Chlordecone exposure and adverse effects in French West Indies populations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della-Negra, O.; Kouassi, A.E.; Dutasta, J.P.; Saaidi, P.L.; Martinez, A. Fluorescence Detection of the Persistent Organic Pollutant Chlordecone in Water at Environmental Concentrations. Chem. Eur. J 2023, 29, e202203887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esegni, V.A.; Kofa, G.P.; Koungou, S.N.; Kayem, J. Chlordecone dechlorination under aerobic conditions by Bacillus sp. Int. J. Innov. Appl. Stud. 2019, 26, 545–555. [Google Scholar]
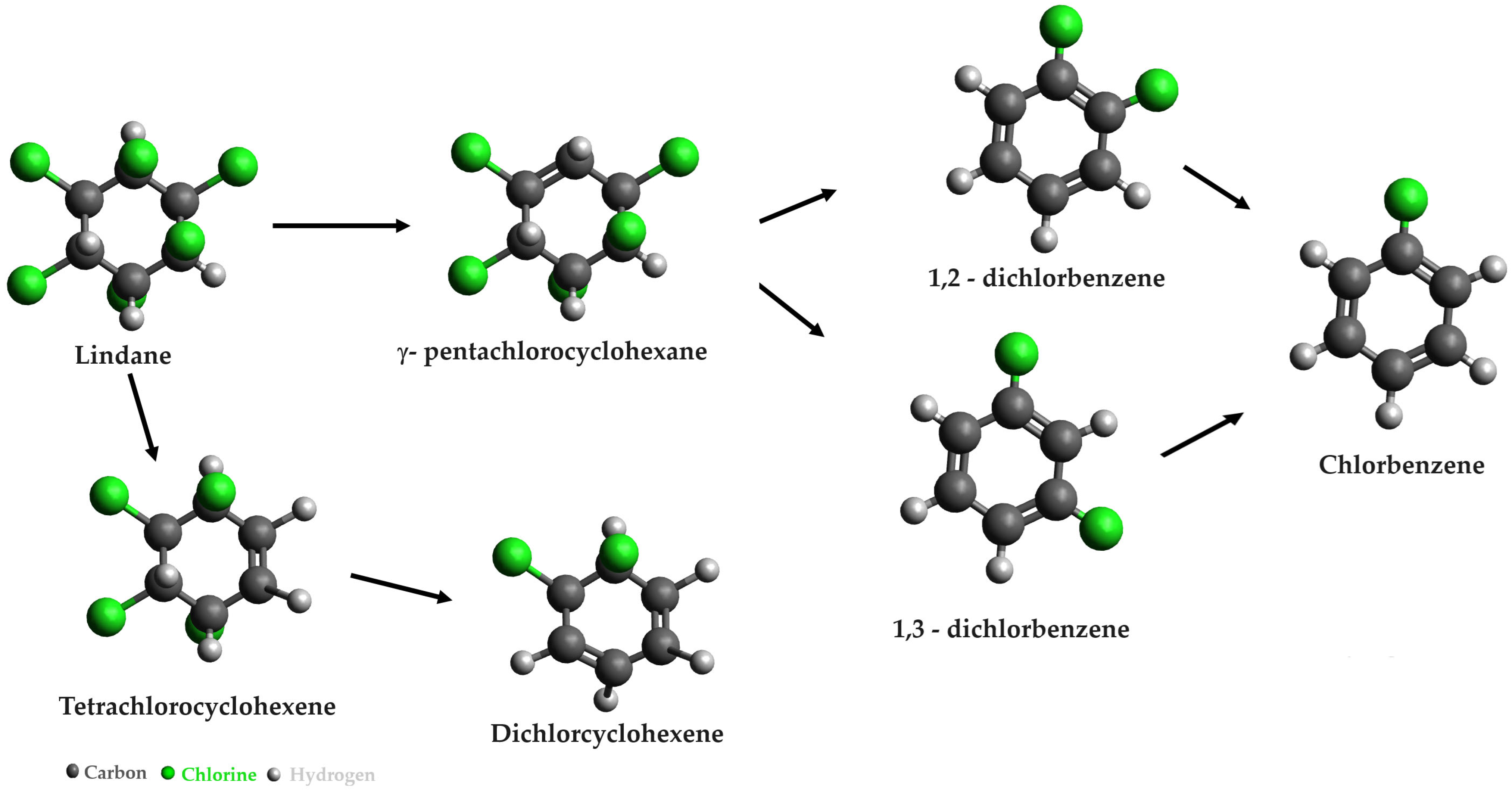
- Barbance, A.; Della-Negra, O.; Chaussonnerie, S.; Delmas, V.; Muselet, D.; Ugarte, E.; Saaidi, P.L.; Weissenbach, J.; Fischer, C.; Le Paslier, D.; et al. Genetic Analysis of Citrobacter sp. 86 Reveals Involvement of Corrinoids in Chlordecone and Lindane Biotransformations. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 590061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.P.; Lin, Z.Q.; Pang, S.M.; Bhatt, P.; Chen, S.H. Insights into the Biodegradation of Lindane (γ-Hexachlorocyclohexane) Using a Microbial System. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 00522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Kuntze, K.; Vogt, C.; Nijenhuis, I. Anaerobic biotransformation of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers by Dehalococcoides species and an enrichment culture. Biodegradation 2018, 29, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, R.; Pandey, G.; Sharma, P.; Kumari, K.; Malhotra, S.; Pandey, R.; Raina, V.; Kohler, H.P.E.; Holliger, C.; Jackson, C.; et al. Biochemistry of Microbial Degradation of Hexachlorocyclohexane and Prospects for Bioremediation. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.B.; Mahala, K.; Jain, K.; Madamwar, D. Development of mixed bacterial cultures DAK11 capable for degrading mixture of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 253, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulazhagan, P.; Vasudevan, N.; Yeom, I.T. Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon by a halotolerant bacterial consortium isolated from marine environment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 7, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steliga, T.; Wojtowicz, K.; Kapusta, P.; Brzeszcz, J. Assessment of Biodegradation Efficiency of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) and Petroleum Hydrocarbons (TPH) in Soil Using Three Individual Bacterial Strains and Their Mixed Culture. Molecules 2020, 25, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horváthová, H.; Lászlová, K.; Dercová, K. Bioremediation of PCB-contaminated shallow river sediments: The efficacy of biodegradation using individual bacterial strains and their consortia. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.W.; Capozzi, S.L.; Kjellerup, B.V.; Mahmood, S.; Mahmood, T.; Khalid, A. Simultaneous biotreatment of hexavalent chromium Cr(VI) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) by indigenous bacteria of Co-polluted wastewater. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2021, 161, 105249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, J.; Taleon, D.M.; Auresenia, J.; Gallardo, S. Polychlorinated biphenyls and their biodegradation. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 1999–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
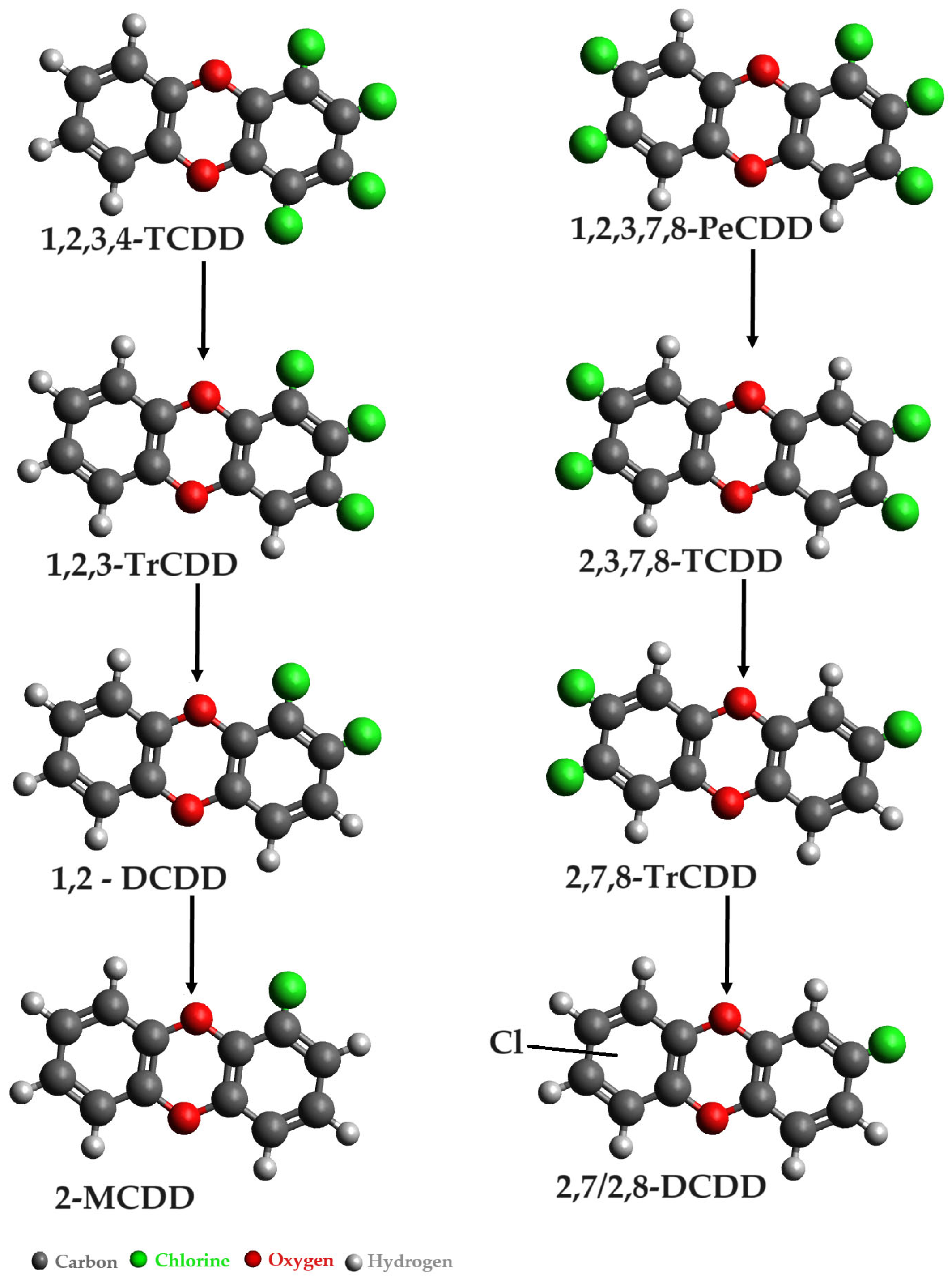
- Field, J.A.; Sierra-Alvarez, R. Microbial degradation of chlorinated dioxins. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 1005–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, H.T.; Sun, W.M.; McGuinness, L.; Kerkhof, L.J.; Häggblom, M.M. Identification of a Chlorodibenzo-dioxin Dechlorinating by Stable Isotope Probing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 14409–14419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunge, M.; Lechner, U. Anaerobic reductive dehalogenation of polychlorinated dioxins. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fennell, D.E.; Nijenhuis, I.; Wilson, S.F.; Zinder, S.H.; Häggblom, M.M. Dehalococcoides ethenogenes Strain 195 Reductively Dechlorinates Diverse Chlorinated Aromatic Pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 2075–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dam, H.T.; Vollmers, J.; Kaster, A.K.; Häggblom, M.M. Reconstructed genomes of novel strains from 1,2,3,4-tetrachlorodibenzo-dioxin-dechlorinating enrichment cultures reveal divergent reductive dehalogenase gene profiles. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraishi, A. Biodiversity of dioxin-degrading microorganisms and potential utilization in bioremediation. Microbes Environ. 2003, 18, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maucourt, F.; Cébron, A.; Budzinski, H.; Le Menach, K.; Peluhet, L.; Czarnes, S.; Melayah, D.; Chapulliot, D.; Vallon, L.; Plassart, G.; et al. Prokaryotic, Microeukaryotic, and Fungal Composition in a Long-Term Polychlorinated Biphenyl-Contaminated Brownfield. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 86, 1696–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
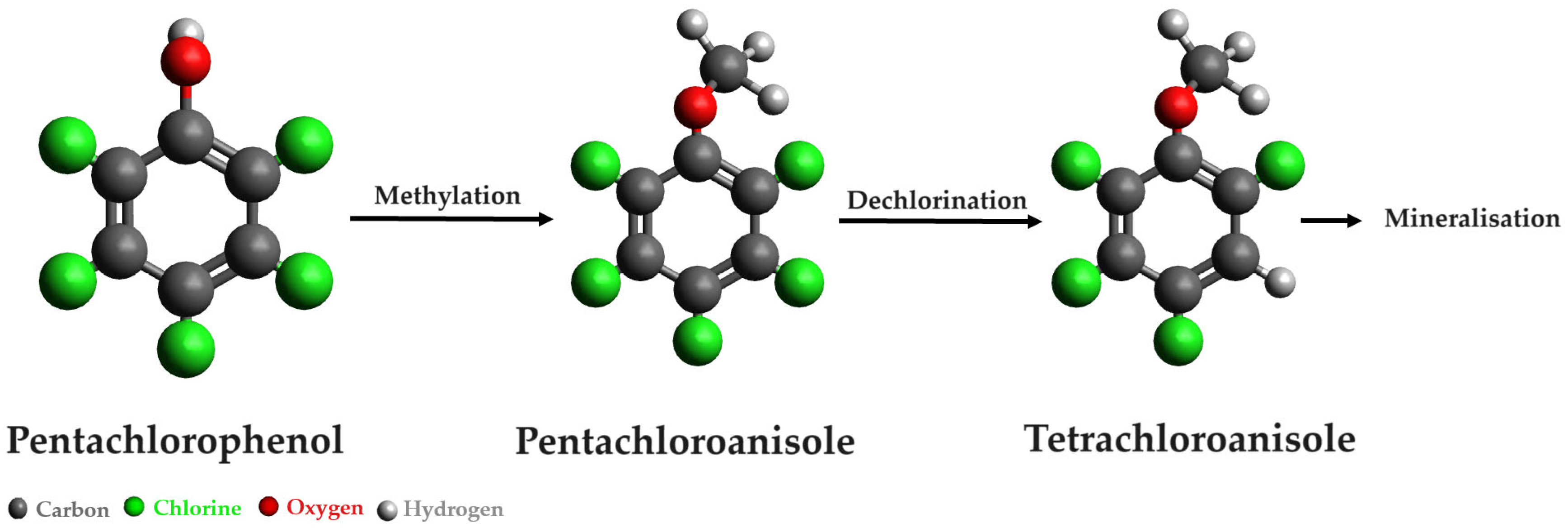
- Vacondio, B.; Birolli, W.G.; Ferreira, I.M.; Seleghim, M.H.R.; Gonçalves, S.; Vasconcellos, S.P.; Porto, A.L.M. Biodegradation of pentachlorophenol by marine-derived fungus Trichoderma harzianum CBMAI 1677 isolated from ascidian Didemnun ligulum. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2015, 4, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birolli, W.G.; Santos, D.D.; Alvarenga, N.; Garcia, A.C.F.S.; Romao, L.P.C.; Porto, A.L.M. Biodegradation of anthracene and several PAHs by the marine-derived fungus Cladosporium sp. CBMAI 1237. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, A.T.N.; Loenen, S.J.; Swart, K.; Dang, H.T.C.; Brouwer, A.; de Boer, T.E. Characterization of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin biodegradation by extracellular lignin-modifying enzymes from ligninolytic fungus. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Mao, H. Removal of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in the liquid culture of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Chemosphere 2023, 345, 140427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bumpus, J.A.; Tien, M.; Wright, D.; Aust, S.D. Oxidation of Persistent Environmental-Pollutants by a White Rot Fungus. Science 1985, 228, 1434–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Kondo, R. Degradation of 2,7-dichlorodibenzo-dioxin by wood-rotting fungi, screened by dioxin degrading ability. Fems Microbiol. Lett. 2002, 213, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, W.; Gong, A.; Li, J. Isolation and identification of a 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-P-dioxin degrading strain and its biochemical degradation pathway. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2021, 19, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, S.; Nakamura, M.; Matsueda, T.; Kondo, R.; Sakai, K. Degradation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans by the white rot fungus Phanerochaete sordida YK-624. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 4323–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benitez, S.F.; Sadañoski, M.A.; Velázquez, J.E.; Zapata, P.D.; Fonseca, M.I. Comparative study of single cultures and a consortium of white rot fungi for polychlorinated biphenyls treatment. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 1775–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mateescu, C.; Lungulescu, E.-M.; Nicula, N.-O. Effectiveness of Biological Approaches for Removing Persistent Organic Pollutants from Wastewater: A Mini-Review. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081632
Mateescu C, Lungulescu E-M, Nicula N-O. Effectiveness of Biological Approaches for Removing Persistent Organic Pollutants from Wastewater: A Mini-Review. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(8):1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081632
Chicago/Turabian StyleMateescu, Carmen, Eduard-Marius Lungulescu, and Nicoleta-Oana Nicula. 2024. "Effectiveness of Biological Approaches for Removing Persistent Organic Pollutants from Wastewater: A Mini-Review" Microorganisms 12, no. 8: 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081632
APA StyleMateescu, C., Lungulescu, E.-M., & Nicula, N.-O. (2024). Effectiveness of Biological Approaches for Removing Persistent Organic Pollutants from Wastewater: A Mini-Review. Microorganisms, 12(8), 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081632






