Captivity Shifts Gut Microbiota Communities in Plateau Zokor (Eospalax baileyi)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Data Profiling
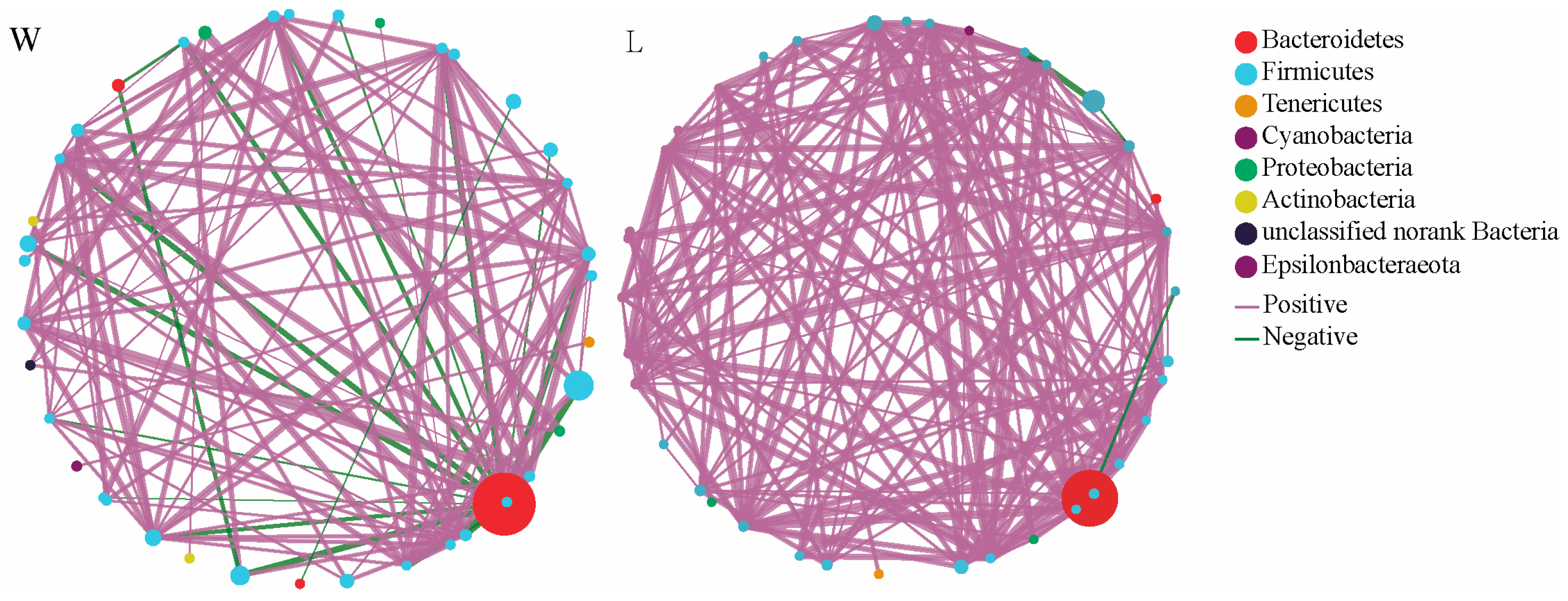
3.2. Correlation Network Analysis
3.3. Community Assembly of Gut Microbiota
4. Discussion
4.1. Captivity Affects the Stability of the Gut Microbiota in Plateau Zokors
4.2. Captivity Affects the Assembly Process of the Gut Microbiota in Plateau Zokors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.-B.; Hartemink, A.E.; Jiang, Z.-D.; Jin, N.-X.; Sun, Z.-X. Digital soil morphometrics of krotovinas in a deep Alfisol derived from loess in Shenyang, China. Geoderma 2017, 301, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. The biology and ecology of plateau zokors (Eospalax fontanierii). In Subterranean Rodents: News from Underground; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 237–249. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, B.; Hegab, I.M.; Kang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Su, J. Underground environment increases the differentiation of personality traits between male and female plateau zokors (Eospalax baileyi). Acta Ethologica 2023, 26, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Zhao, F.; Chen, H.; Deng, X.; Su, J.; Zhang, T. Comparative phylogeography of the plateau zokor (Eospalax baileyi) and its host-associated flea (Neopsylla paranoma) in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. BMC Evol. Biol. 2014, 14, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Pu, Q.; Shi, S.; Su, J. Plateau zokors (Eospalax baileyi) respond to secondary metabolites from the roots of Stellera chamaejasme by enhancing hepatic inflammatory factors and metabolic pathway genes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 258, 109368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Ji, W.; Li, H.; Yao, T.; Wang, J.; Nan, Z. Zokor disturbances indicated positive soil microbial responses with carbon cycle and mineral encrustation in alpine grassland. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 144, 105702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Su, J.; Yao, B.; Ji, W.; Hegab, I.M.; Hanafy, A.M.; Zhang, D. Geometric morphometric analysis of the plateau zokor (Eospalax baileyi) revealed significant effects of environmental factors on skull variations. Zoology 2020, 140, 125779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Van Hul, M.; Lefort, C.; Depommier, C.; Rastelli, M.; Everard, A. Microbial regulation of organismal energy homeostasis. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Doestzada, M.; Chen, L.; Andreu-Sanchez, S.; van den Munckhof, I.C.; Augustijn, H.E.; Koehorst, M.; Ruiz-Moreno, A.J.; Bloks, V.W.; Riksen, N.P. Characterization of gut microbial structural variations as determinants of human bile acid metabolism. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 1802–1814.e1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valles-Colomer, M.; Blanco-Míguez, A.; Manghi, P.; Asnicar, F.; Dubois, L.; Golzato, D.; Armanini, F.; Cumbo, F.; Huang, K.D.; Manara, S. The person-to-person transmission landscape of the gut and oral microbiomes. Nature 2023, 614, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yan, J.; Wang, H.; Jiang, F.; Song, P.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, T. Microbial biogeography along the gastrointestinal tract segments of sympatric subterranean rodents (Eospalax baileyi and Eospalax cansus). Animals 2021, 11, 3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Gao, H.; Wu, G.; Qin, W.; Song, P.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, T. Comparison of gut microbiota diversity between wild and captive bharals (Pseudois nayaur). BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Song, P.; Yan, J.; Wang, H.; Cai, Z.; Xie, J.; Zhang, T. Gut microbiome changes in captive plateau zokors (Eospalax baileyi). Evol. Bioinform. 2021, 17, 1176934321996353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Gao, H.; Song, P.; Liang, C.; Jiang, F.; Xu, B.; Liu, D.; Zhang, T. Captivity shifts gut microbiota communities in white-lipped deer (Cervus albirostris). Animals 2022, 12, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasimuddin; Menke, S.; Melzheimer, J.; Thalwitzer, S.; Heinrich, S.; Wachter, B.; Sommer, S. Gut microbiomes of free-ranging and captive Namibian cheetahs: Diversity, putative functions and occurrence of potential pathogens. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 5515–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, R.R.; Sommer, S. The amphibian microbiome: Natural range of variation, pathogenic dysbiosis, and role in conservation. Biodivers. Conserv. 2017, 26, 763–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberdi, A.; Martin Bideguren, G.; Aizpurua, O. Diversity and compositional changes in the gut microbiota of wild and captive vertebrates: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, K.D.; Dearing, M.D. Wild-caught rodents retain a majority of their natural gut microbiota upon entrance into captivity. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2014, 6, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ren, K.; Isabwe, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.; Yang, J. Stochastic processes shape microeukaryotic community assembly in a subtropical river across wet and dry seasons. Microbiome 2019, 7, 138. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Tang, X.; Ren, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Effects of captivity on the assembly process of microbiota communities of plateau pikas. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2022, 42, 519. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Mi, T.; He, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhen, Y.; Yu, Z. Active bacterial and archaeal communities in coastal sediments: Biogeography pattern, assembly process and co-occurrence relationship. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 142252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan, W.T.; Lunn, M.; Woodcock, S.; Head, I.M.; Nee, S.; Curtis, T.P. Quantifying the roles of immigration and chance in shaping prokaryote community structure. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzhov, T.V.; Mullen, K.M.; Spiess, A.-N.; Bolker, B.; Mullen, M.K.M.; Suggests, M. Package ‘minpack.lm’. Title R Interface Levenberg-Marquardt Nonlinear Least-Sq. Algorithm Found MINPACK Plus Support Bounds. 2016. Available online: https://github.com/cran/minpack.lm (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Harrell, F.E., Jr.; Harrell, M.F.E., Jr. Package ‘hmisc’. CRAN2018 2019, 2019, 235–236. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.-L.; Hu, H.-W.; Yan, Z.-Z.; Li, C.-Y.; Nguyen, B.-A.T.; Sun, A.-Q.; Zhu, Y.-G.; He, J.-Z. Deterministic selection dominates microbial community assembly in termite mounds. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 152, 108073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, V.L.; Smith, M.R.; Hall, L.J.; Cleare, A.J.; Stone, J.M.; Young, A.H. Perturbations in gut microbiota composition in psychiatric disorders: A review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Juan, P.A.; Castro, I.; Dhami, M.K. Captivity reduces diversity and shifts composition of the Brown Kiwi microbiome. Anim. Microbiome 2021, 3, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallas, J.W.; Warne, R.W. Captivity and animal microbiomes: Potential roles of microbiota for influencing animal conservation. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 85, 820–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Stombaugh, J.I.; Gordon, J.I.; Jansson, J.K.; Knight, R. Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 2012, 489, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, P.; Minoarivelo, H.O.; Brännström, Å.; Hui, C.; Dieckmann, U. Complexity and stability of ecological networks: A review of the theory. Popul. Ecol. 2018, 60, 319–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyte, K.Z.; Schluter, J.; Foster, K.R. The ecology of the microbiome: Networks, competition, and stability. Science 2015, 350, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevelline, B.K.; Fontaine, S.S.; Hartup, B.K.; Kohl, K.D. Conservation biology needs a microbial renaissance: A call for the consideration of host-associated microbiota in wildlife management practices. Proc. R. Soc. B 2019, 286, 20182448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Wang, Z. Studies on the population energetics of plateau zokor i. Average daily metabolic rate and burrowing metabolic rate. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2006, 12, 200. [Google Scholar]
- Kinlaw, A. A review of burrowing by semi-fossorial vertebrates in arid environments. J. Arid Environ. 1999, 41, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebensperger, L.A.; Blumstein, D.T. Sociality in New World hystricognath rodents is linked to predators and burrow digging. Behav. Ecol. 2006, 17, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, L.; Fan, C.; Wang, L.; Fu, H.; Ren, S.e.; Shen, W.; Jia, S.; Wu, G.; Zhang, Y. Dietary fiber influences bacterial community assembly processes in the gut microbiota of Durco × Bamei crossbred pig. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 688554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.-X.; Lin, G.-H.; Liu, C.-X.; Yang, C.-H.; Deng, X.-G.; Cui, X.-F.; Li, B.; Zhang, T.-Z.; Su, J.-P. Diet selection in overwinter caches of plateau zokor (Eospalax baileyi). Acta Theriol. 2014, 59, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.; Li, B.; Song, P.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, T. Captivity Shifts Gut Microbiota Communities in Plateau Zokor (Eospalax baileyi). Microorganisms 2024, 12, 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040789
Liu D, Li B, Song P, Jiang F, Zhang T. Captivity Shifts Gut Microbiota Communities in Plateau Zokor (Eospalax baileyi). Microorganisms. 2024; 12(4):789. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040789
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Daoxin, Bin Li, Pengfei Song, Feng Jiang, and Tongzuo Zhang. 2024. "Captivity Shifts Gut Microbiota Communities in Plateau Zokor (Eospalax baileyi)" Microorganisms 12, no. 4: 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040789
APA StyleLiu, D., Li, B., Song, P., Jiang, F., & Zhang, T. (2024). Captivity Shifts Gut Microbiota Communities in Plateau Zokor (Eospalax baileyi). Microorganisms, 12(4), 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040789





