Development of a Real-Time Recombinase-Aided Amplification Method for the Rapid Detection of Streptococcus equi subsp. equi
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains of Pathogens, Samples, and Extraction of DNA
2.2. Plasmid
2.3. Real-Time RAA Primer and Probe
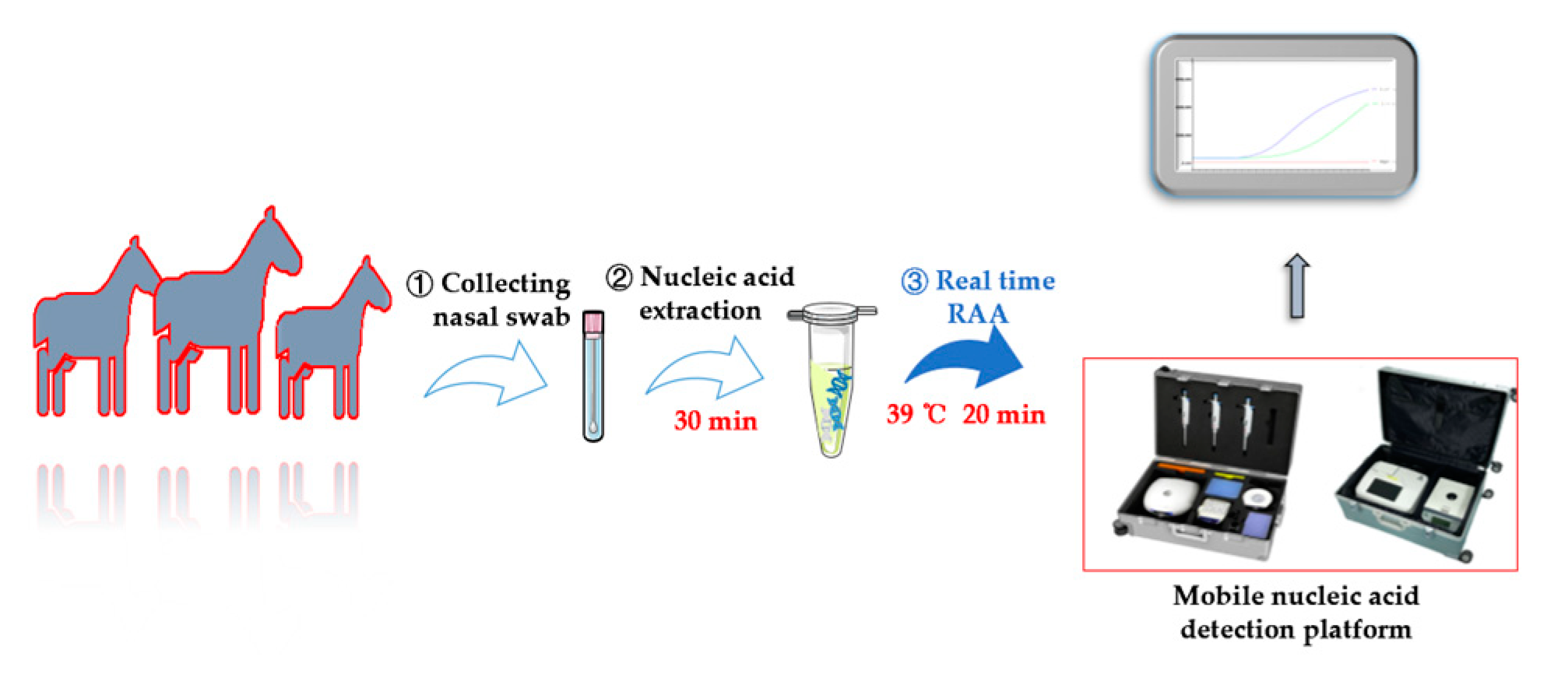
2.4. Real-Time RAA Assay
2.5. Real-Time PCR Assay
2.6. Analytical Specificity
2.7. Analytical Sensitivity
3. Results
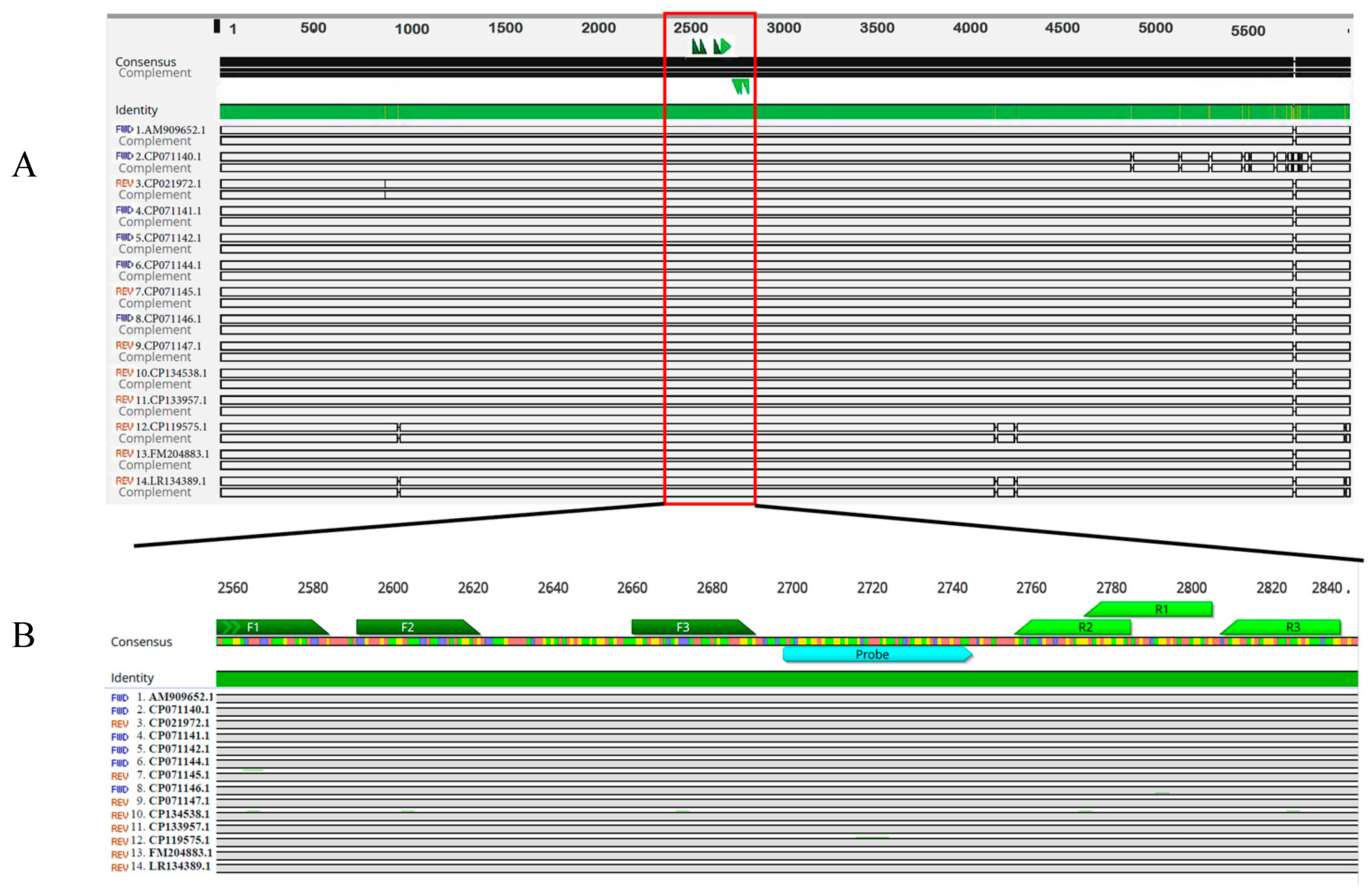
3.1. Design of the eqbE Real-Time RAA Primers and Probe
3.2. Reaction Optimization for Real-Time RAA Assays
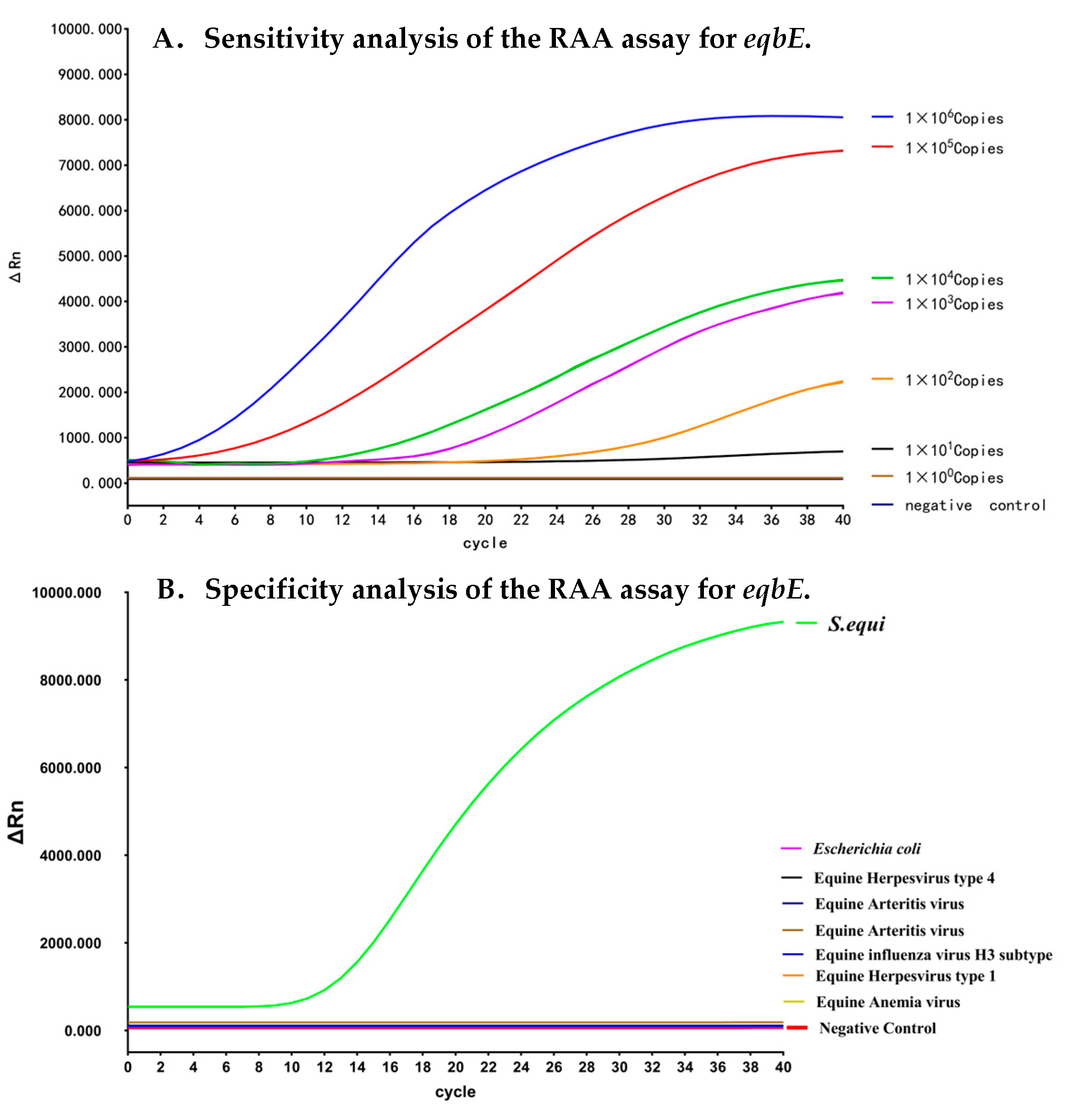
3.3. Analytical Sensitivity of the Real-Time RAA Assay
3.4. Analytical Specificity of the Real-Time RAA Assay
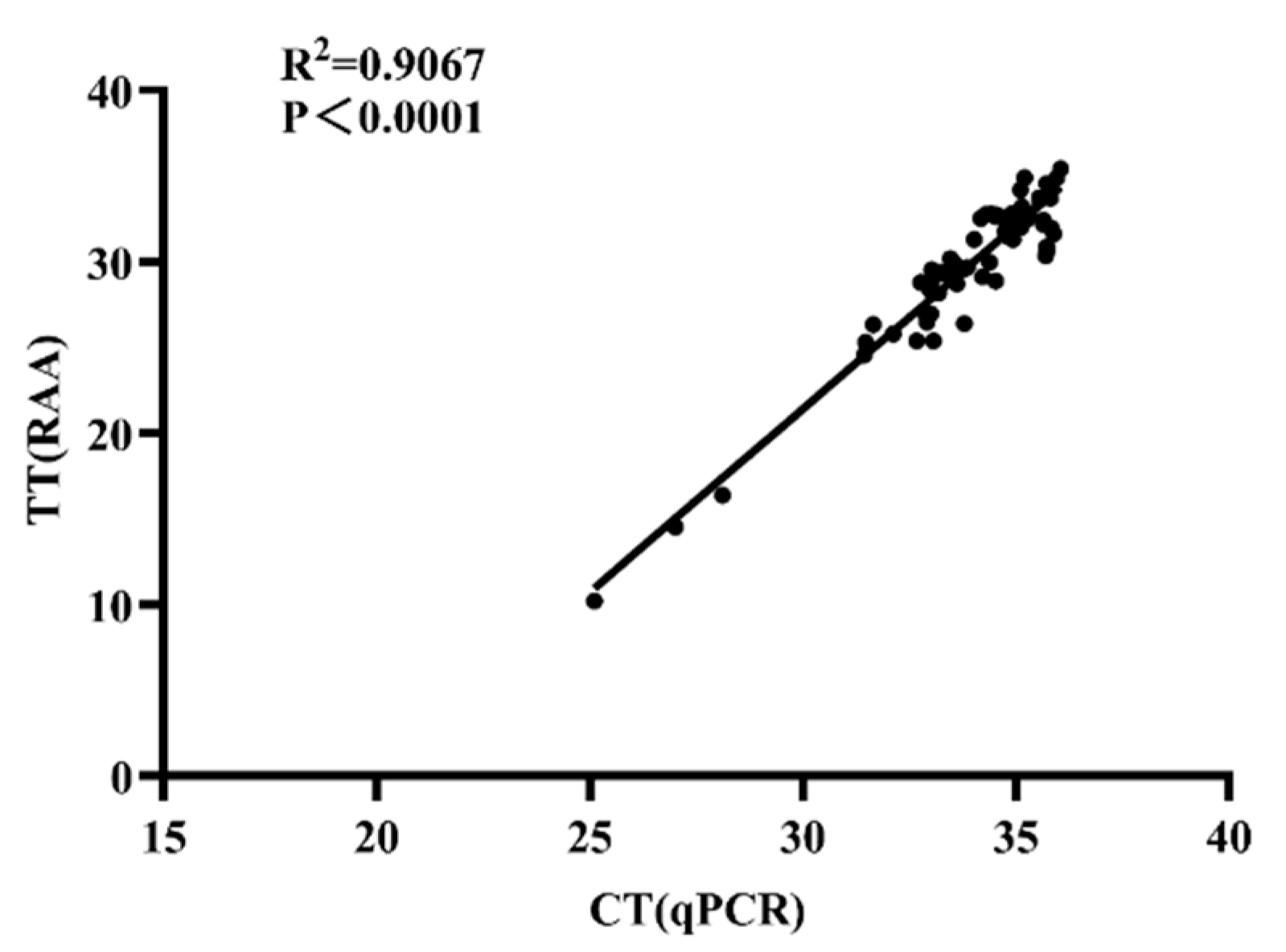
3.5. Diagnostic Performance of Real-Time RAA Using Clinical Nasal Swabs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newton, J.R.; Wood, J.L.N.; Dunn, K.A.; DeBrauwere, M.N.; Chanter, N. Naturally occurring persistent and asymptomatic infection of the guttural pouches of horses with Streptococcus equi. Vet. Rec. 1997, 140, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neamat-Allah, A.N.; Damaty, H.M. Strangles in Arabian horses in Egypt: Clinical, epidemiological, hematological, and biochemical aspects. Vet. World 2016, 9, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waller, A. Streptococcus equi: Breaking its strangles-hold. Vet. Rec. 2018, 182, 316–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikhuoso, O.A.; Monroy, J.C.; Rivas-Caceres, R.R.; Cipriano-Salazar, M.; Barbabosa Pliego, A. Streptococcus equi in Equine: Diagnostic and Healthy Performance Impacts. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2020, 85, 102870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendle, D.; de Brauwere, N.; Hallowell, G.; Ivens, P.; McGlennon, A.; Newton, R.; White, J.; Waller, A. Streptococcus equi infections: Current best practice in the diagnosis and management of ‘strangles’. UK-Vet Equine 2021, 5, S3–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallicote, M. Update on Streptococcus equi subsp equi infections. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2015, 31, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyum, F.; Mahendra, P. Clinical and microbiological observations on strangles in donkeys. Haryana Vet. 2015, 54, 64–66. [Google Scholar]
- Tonpitak, W.; Sornklien, C.; Wutthiwithayaphong, S. Characterization of a Streptococcus equi ssp. equi Isolate from a Strangles Outbreak in Thailand. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2016, 38, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torpiano, P.; Nestorova, N.; Vella, C. Streptococcus equi subsp. equi meningitis, septicemia and subdural empyema in a child. IDCases 2020, 21, e00808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlman, T.; Waddell, H.; Schumaker, B. A case of bacteremia and pneumonia caused by Streptococcus equi subspecies equi infection in a 70-year-old female following horse exposure in rural Wyoming. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2023, 22, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judy, C.E.; Chaffin, M.K.; Cohen, N.D. Empyema of the guttural pouch (auditory tube diverticulum) in horses: 91 cases (1977–1997). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1999, 215, 1666–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, A.G.; Timoney, J.F.; Newton, J.R.; Hines, M.T.; Waller, A.S.; Buchanan, B.R. Streptococcus equi Infections in Horses: Guidelines for Treatment, Control, and Prevention of Strangles-Revised Consensus Statement. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y. Identification of a Novel Genotype of Streptococcus equi Subspecies equi in a Donkey Suffering from Strangles. Pak. Vet. J. 2019, 39, 609–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusterla, N.; Bowers, J.; Barnum, S.; Hall, J.A. Molecular detection of Streptococcus equi subspecies equi in face flies (Musca autumnalis) collected during a strangles outbreak on a Thoroughbred farm. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2020, 34, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, C.; Waller, A.S.; Frykberg, L.; Flock, M.; Zachrisson, O.; Guss, B.; Flock, J.I. Intramuscular vaccination with Strangvac is safe and induces protection against equine strangles caused by Streptococcus equi. Vaccine 2020, 38, 4861–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGlennon, A.; Waller, A.; Verheyen, K.; Slater, J.; Grewar, J.; Aanensen, D.; Newton, R. Surveillance of strangles in UK horses between 2015 and 2019 based on laboratory detection of Streptococcus equi. Vet. Rec. 2021, 189, e948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo-Morales, C.; James, K.; Barnum, S.; Vaala, W.; Chappell, D.E.; Schneider, C.; Craig, B.; Bain, F.; Barnett, D.C.; Gaughan, E.; et al. Voluntary Biosurveillance of Streptococcus equi Subsp. equi in Nasal Secretions of 9409 Equids with Upper Airway Infection in the USA. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotinsulu, D.A.; Ewers, C.; Kerner, K.; Amrozi, A.; Soejoedono, R.D.; Semmler, T.; Bauerfeind, R. Molecular Features and Antimicrobial Susceptibilities of Streptococcus equi ssp. equi Isolates from Strangles Cases in Indonesia. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafa, A.A.; Hedia, R.H.; Ata, N.S.; Ibrahim, E.S. Vancomycin resistant Streptococcus equi subsp. equi isolated from equines suffering from respiratory manifestation in Egypt. Vet. World 2021, 14, 1808–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, D.S.H.; Goncalves, E. Diabetogenic effects of cardioprotective drugs. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, J.; Venner, M.; Tscheschlok, L.; Bachi, L.; Riihimaki, M. Long term silent carriers of Streptococcus equi ssp. equi following strangles; carrier detection related to sampling site of collection and culture versus qPCR. Vet. J. 2019, 246, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, A.E.; Kemp-Symonds, J. Failure of serological testing for antigens A and C of Streptococcus equi subspecies equi to identify guttural pouch carriers. Equine Vet. J. 2021, 53, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, M.C.; Goehring, L.S. Equine strangles: An update on disease control and prevention. Austral J. Vet. Sci. 2021, 53, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, A.G.; Stefanovski, D.; Rankin, S.C. Comparison of nasopharyngeal and guttural pouch specimens to determine the optimal sampling site to detect Streptococcus equi subsp equi carriers by DNA amplification. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöckle, S.D.; Winter, J.C.; Schöpe, S.S.; Gehlen, H. Possibilities and limitations of the prevention of strangles outbreaks on horse farms. Pferdeheilkunde 2019, 35, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindahl, S.; Båverud, V.; Egenvall, A.; Aspán, A.; Pringle, J. Comparison of sampling sites and laboratory diagnostic tests for S. equi subsp. equi in horses from confirmed strangles outbreaks. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2013, 27, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waller, A.S. New Perspectives for the Diagnosis, Control, Treatment, and Prevention of Strangles in Horses. Vet. Clin. N. Am.-Equine 2014, 30, 591–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, K.; Barker, C.; Harrison, T.; Heather, Z.; Steward, K.F.; Robinson, C.; Newton, J.R.; Waller, A.S. Detection of Streptococcus equi subspecies equi using a triplex qPCR assay. Vet. J. 2013, 195, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, C.; Mapes, S.; Akana, N.; Coatti Rocha, D.; Pusterla, N. Detection of modified-live equine intranasal vaccine pathogens in adult horses using quantitative PCR. Vet. Rec. 2014, 175, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordoni, G.; Williams, A.; Durham, A.; Florio, D.; Zanoni, R.G.; La Ragione, R.M. Rapid diagnosis of strangles (Streptococcus equi subspecies equi) using PCR. Res. Ve.t Sci. 2015, 102, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusterla, N.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Barnum, S.M.; Byrne, B.A. Use of quantitative real-time PCR to determine viability of Streptococcus equi subspecies equi in respiratory secretions from horses with strangles. Equine Vet. J. 2018, 50, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riihimaki, M.; Aspan, A.; Ljung, H.; Pringle, J. Long term dynamics of a Streptococcus equi ssp equi outbreak, assessed by qPCR and culture and seM sequencing in silent carriers of strangles. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 223, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.Z.; Chen, J.T.; Li, J.; Wu, X.J.; Wen, J.Z.; Liu, X.Z.; Lin, L.Y.; Liang, X.Y.; Huang, H.Y.; Zha, G.C.; et al. Reverse Transcription Recombinase-Aided Amplification Assay with Lateral Flow Dipstick Assay for Rapid Detection of 2019 Novel Coronavirus. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 613304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, G.; Zhang, R.; He, X.; Tian, F.; Nie, M.; Shen, X.; Ma, X. RAP: A Novel Approach to the Rapid and Highly Sensitive Detection of Respiratory Viruses. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 766411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Ren, W.C.; Xue, Z.T.; Miao, Y.D.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.X.; Yao, C.; Shang, Y.Y.; Li, S.S.; Mi, F.L.; et al. Real-time recombinase-aided amplification assay for rapid amplification of the gene of s. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2023, 42, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.H.; Fang, T.S.; Shen, J.L.; Zhang, G.D.; Guo, D.H.; Zhao, L.A.; Jiang, Y.; Zhi, S.; Zheng, L.; Lv, X.F.; et al. Development of Recombinase Aided Amplification (RAA)-Exo-Probe Assay for the Rapid Detection of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli. J. AOAC Int. 2023, 106, 1246–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Location | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| eqbE-F1 | CATCTATTTGGTCAAACCATTTGAATGTACCAAG | 1,226,818 to 1,226,852 | This study |
| eqbE-F2 | CCGAAAGATTGGATTTCCATTCCATATGGTAG | 1,226,859 to 1,226,890 | This study |
| eqbE-F3 | TGGTAGGATCTGCCCTAATTATGTTAAAGGTG | 1,226,830 to 1,226,861 | This study |
| eqbE-R1 | CTACCATTATCTCCAGTTCTATACCACCTCATC | 1226, 928 to 1,226,958 | This study |
| eqbE-R2 | TACCACCTCATCCCATCTTGTTCGAAGTAC | 1,226,947 to 1,226,979 | This study |
| eqbE-R3 | CCAAGAAACTCAATAATCCCATCATTCCATG | 1,226,982 to 1,226,912 | This study |
| Probe | TATCGGTGGAGTTGGTGTTGCTAAATGTTA/i6FAMdT//idSp/A/iBHQ1dT/GGTGACGAAGAATTA-3′C3 Spacer | 1,226,969 to 1,227,017 | This study |
| eqbE-F | ATGTAGCTATGGCAAATGTGGC | 1,223,599 to 1,223,620 | [26] |
| eqbE-R | AACACCCTTAGGAACACCTG | 1,223,689 to 1,223,708 | [26] |
| eqbE-probe | FAM-ATTGTTACTATGGCTGAAGGT-BHO1 | 1,223,966 to 1,223,987 | [26] |
| Method | Real-Time PCR | Kappa | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Total | ||||
| RAA | Positive | 64 | 2 | 66 | 0.931 | 0.0001 |
| Negative | 1 | 31 | 32 | |||
| Total | 65 | 33 | 98 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zu, H.; Sun, R.; Li, J.; Guo, X.; Wang, M.; Guo, W.; Wang, X. Development of a Real-Time Recombinase-Aided Amplification Method for the Rapid Detection of Streptococcus equi subsp. equi. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040777
Zu H, Sun R, Li J, Guo X, Wang M, Guo W, Wang X. Development of a Real-Time Recombinase-Aided Amplification Method for the Rapid Detection of Streptococcus equi subsp. equi. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(4):777. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040777
Chicago/Turabian StyleZu, Haoyu, Rongkuan Sun, Jiaxin Li, Xing Guo, Min Wang, Wei Guo, and Xiaojun Wang. 2024. "Development of a Real-Time Recombinase-Aided Amplification Method for the Rapid Detection of Streptococcus equi subsp. equi" Microorganisms 12, no. 4: 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040777
APA StyleZu, H., Sun, R., Li, J., Guo, X., Wang, M., Guo, W., & Wang, X. (2024). Development of a Real-Time Recombinase-Aided Amplification Method for the Rapid Detection of Streptococcus equi subsp. equi. Microorganisms, 12(4), 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040777







