Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Wastewater Associated with Scientific Stations in Antarctica and Possible Risk for Wildlife
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Virus Concentration
2.3. RNA Extraction and Virus Detection
2.4. Estimation of SARS-CoV-2 Genome Copy Number in Wastewater
2.5. Genome Sequencing and Variant Typing of SARS-CoV-2
2.6. Environmental Samples and SARS-CoV-2 Detection in Antarctic Wildlife
2.7. RNA Extraction from Wildlife Samples
2.8. RT-qPCR and RT-PCR Analysis
3. Results
3.1. SARS-CoV-2 RNA Detection in WWTPs
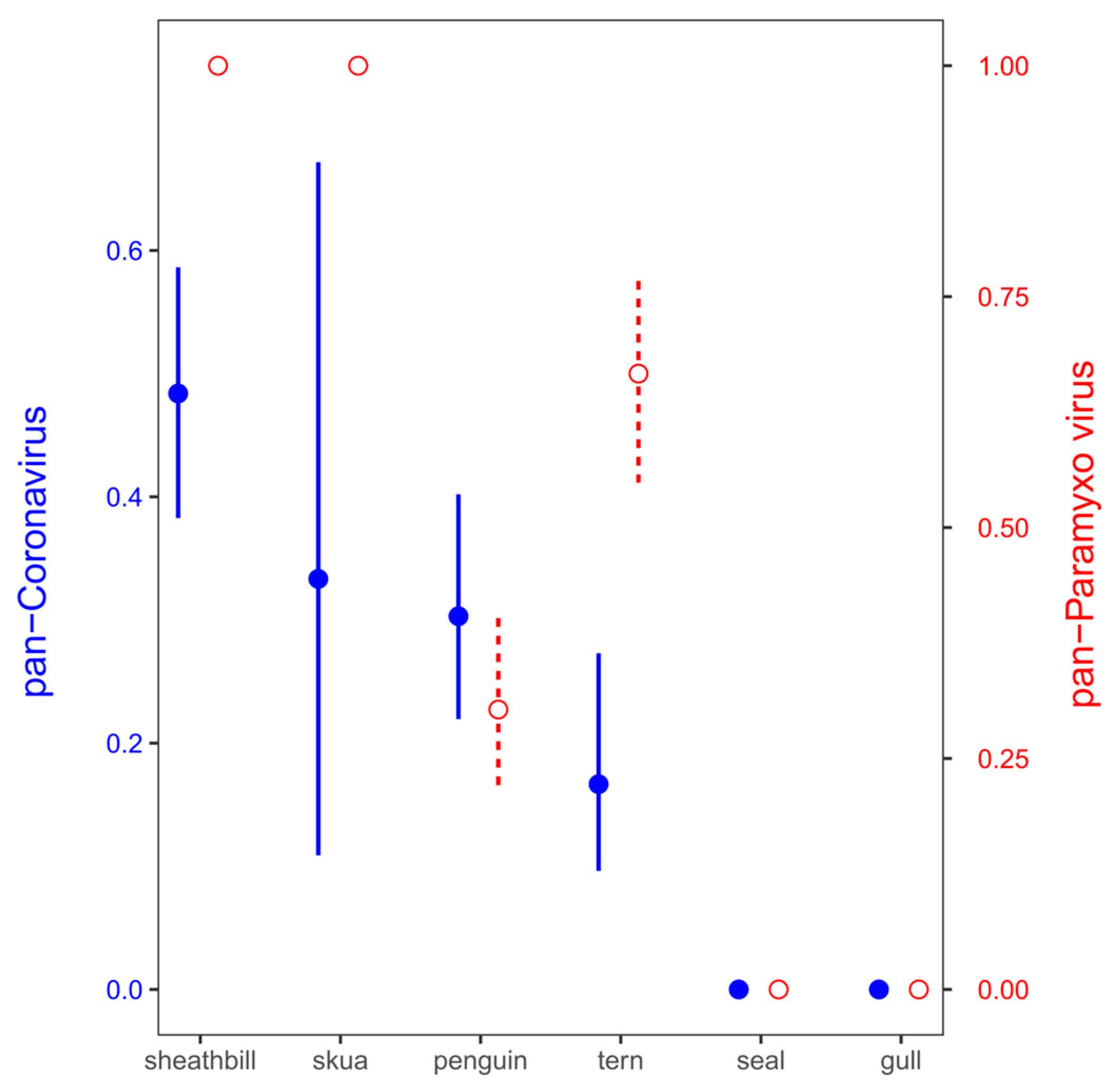
3.2. Environmental Animal Viral Detections by Real-Time RT-PCR Assays
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aronson, R.B.; Thatje, S.; McClintock, J.B.; Hughes, K.A. Anthropogenic impacts on marine ecosystems in Antarctica. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1223, 82–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwedorzewska, K.J.; Korczak-Abshire, M.; Znój, A. Is Antarctica under threat of alien species invasion? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 1942–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalonde, M.M.L.; Marcus, J.M. A global molecular phylogeny yields insights into the dispersal and invasion history of Junonia, a butterfly genus with remarkable dispersal abilities. Proc. R. Soc. 2022, 289, 20212801. [Google Scholar]
- Leihy, R.I.; Peake, L.; Clarke, D.A.; Chown, S.L.; McGeoch, M.A. Introduced and invasive alien species of Antarctica and the Southern Ocean islands. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelino, V.R.; Wille, M.; Hurt, A.C.; González-Acuña, D.; Klaassen, M.; Schlub, T.E.; Eden, J.S.; Shi, M.; Iredell, J.R.; Sorrell, T.C.; et al. Meta-transcriptomics reveals a diverse antibiotic resistance gene pool in avian microbiomes. BMC Biol. 2019, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, A.; Varsani, A.; Morandini, V.; Grimaldi, W.; Vanstreels, R.E.T.; Diaz, J.I.; Boulinier, T.; Dewar, M.; González-Acuña, D.; Gray, R.; et al. Risk assessment of SARS-CoV-2 in Antarctic wildlife. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 143352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, K.A.; Convey, P. Implications of the COVID-19 pandemic for Antarctica. Antarct. Sci. 2020, 32, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitajima, M.; Ahmed, W.; Bibby, K.; Carducci, A.; Gerba, C.P.; Hamilton, K.A.; Haramoto, E.; Rose, J.B. SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater: State of the knowledge and research needs. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosa, G.; Bonadonna, L.; Lucentini, L.; Kenmoe, S.; Suffredini, E. Coronavirus in water environments: Occurrence, persistence and concentration methods—A scoping review. Water Res. 2020, 179, 115899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares-Pacheco, J.; Adell, A.D.; Hepp, M.I.; Reis, A.S.; Echeverría, C.; Ibacache-Quiroga, C.; Assmann, P.; Gaggero, A. Detección y cuantificación de SARS-CoV-2 en plantas de tratamiento de aguas residuales de diferentes ciudades de Chile: Hacia la implementación de una vigilancia centinela permanente. Rev. Chil. Infectol. 2022, 39, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandukar, S.; Sthapit, N.; Thakali, O.; Malla, B.; Sherchan, S.P.; Shakya, B.M.; Shrestha, L.P.; Sherchand, J.B.; Joshi, D.R.; Lama, B.; et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater, river water, and hospital wastewater of Nepal. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouda, M.; Mustafa, F.; Maraqa, M.; Rizvi, T.; Aly Hassan, A. Wastewater surveillance for SARS-CoV-2: Lessons learnt from recent studies to define future applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Guo, J.; Møhlenberg, M.; Zhou, H. SARS-CoV-2 surveillance in medical and industrial wastewater—A global perspective: A narrative review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 63323–63334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carducci, A.; Federigi, I.; Balestri, E.; Lardicci, C.; Castelli, A.; Maltagliati, F.; Zhao, H.; Menicagli, V.; Valente, R.; De Battisti, D.; et al. Virus contamination and infectivity in beach environment: Focus on sand and stranded material. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 185, 114342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contrant, M.; Bigault, L.; Andraud, M.; Desdouits, M.; Rocq, S.; Le Guyader, F.S.; Blanchard, Y. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, surrogate for coronavirus decay measurement in French coastal waters and contribution to coronavirus risk evaluation. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e01844-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlknecht, J. Presence and persistence of SARS-CoV-2 in aquatic environments: A mini-review. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2022, 29, 100385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoa, B.; Ríos-Castro, R.; Otero-Muras, I.; Gouveia, S.; Cabo, A.; Saco, A.; Rey-Campos, M.; Pájaro, M.; Fajar, N.; Aranguren, R.; et al. Wastewater and marine bioindicators surveillance to anticipate COVID-19 prevalence and to explore SARS-CoV-2 diversity by next generation sequencing: One-year study. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Thongchankaew-Seo, U.; Yamazaki, W. Very low likelihood that cultivated oysters are a vehicle for SARS-CoV-2: 2021–2022 seasonal survey at supermarkets in Kyoto, Japan. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atoui, A.; Cordevant, C.; Chesnot, T.; Gassilloud, B. SARS-CoV-2 in the environment: Contamination routes, detection methods, persistence and removal in wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ash, K.T.; Joyner, D.C.; Williams, D.E.; Alamilla, I.; McKay, P.J.; Iler, C.; Green, B.M.; Kara-Murdoch, F.; Swift, C.M.; et al. Decay of enveloped SARS-CoV-2 and non-enveloped PMMoV RNA in raw sewage from university dormitories. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1144026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröndahl, F.; Sidenmark, J.; Thomsen, A. Survey of waste water disposal practices at Antarctic research stations. Polar Res. 2016, 28, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masindi, V.; Foteinis, S.; Nduli, K.; Akinwekomi, V. Systematic assessment of SARS-CoV-2 virus in wastewater, rivers and drinking water—A catchment-wide appraisal. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 800, 149298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calgua, B.; Fumian, T.; Rusinol, M.; Rodriguez-Manzano, J.; Mbayed, V.A.; Bofill-Mas, S.; Miagostovich, M.; Girones, R. Detection and quantification of classic and emerging viruses by skimmed-milk flocculation and PCR in river water from two geographical areas. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2797–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Latorre, L.; Ballesteros, I.; Villacrés-Granda, I.; Granda, M.G.; Freire-Paspuel, B.; Ríos-Touma, B. SARS-CoV-2 in river water: Implications in low sanitation countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgaço, F.G.; Corrêa, A.A.; Ganime, A.C.; Brandão, M.L.L.; Medeiros, V.D.M.; Rosas, C.D.O.; Lopes, S.M.D.R.; Miagostovich, M.P. Evaluation of skimmed milk flocculation method for virus recovery from tomatoes. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2018, 49, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio, D.C.; Ares, M.; Hannon, G.J.; Nilsen, T.W. Purification of RNA Using TRIzol (TRI Reagent). Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2010, pdb-prot5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randazzo, W.; Truchado, P.; Cuevas-Ferrando, E.; Simón, P.; Allende, A.; Sánchez, G. SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater anticipated COVID-19 occurrence in a low prevalence area. Water Res. 2020, 181, 115942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Davis, A.; Jones, D.; Lemeshow, S.; Tu, H.; He, F.; Ru, P.; Pan, X.; Bohrerova, Z.; Lee, J. Wastewater SARS-CoV-2 monitoring as a community-level COVID-19 trend tracker and variants in Ohio, United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraud-Billoud, M.; Cuervo, P.; Altamirano, J.C.; Pizarro, M.; Aranibar, J.N.; Catapano, A.; Cuello, H.; Masachessi, G.; Vega, I.A. Monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater as an epidemiological surveillance tool in Mendoza, Argentina. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 148887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosiles-González, G.; Carrillo-Jovel, V.H.; Alzate-Gaviria, L.; Betancourt, W.Q.; Gerba, C.P.; Moreno-Valenzuela, O.A.; Tapia-Tussell, R.; Hernández-Zepeda, C. Environmental Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in Wastewater and Groundwater in Quintana Roo, Mexico. Food Environ. Virol. 2021, 13, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, L.C.; Aubee, A.; Babahaji, L.; Vigil, K.; Tims, S.; Aw, T.G. Targeted wastewater surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 on a university campus for COVID-19 outbreak detection and mitigation. Environ. Res. 2021, 200, 111374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barriga, G.P.; Boric-Bargetto, D.; Cortez-San Martin, M.; Neira, V.; van Bakel, H.; Thompsom, M.; Tapia, R.; Toro-Ascuy, D.; Moreno, L.; Vasquez, Y.; et al. Avian influenza virus H5 strain with North American and Eurasian lineage genes in an Antarctic penguin. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomczynski, P.; Sacchi, N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 162, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijgen, L.; Moës, E.; Keyaerts, E.; Li, S.; Van Ranst, M. A pancoronavirus RT-PCR assay for detection of all known coronaviruses. In SARS-and Other Coronaviruses: Laboratory Protocols; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- van Boheemen, S.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Verhagen, J.H.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Pas, S.D.; Herfst, S.; Fouchier, R. A family-wide RT-PCR assay for detection of paramyxoviruses and application to a large-scale surveillance study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, V.L.; Dennis, P.M.; McBride, D.S.; Nolting, J.M.; Madden, C.; Huey, D.; Ehrlich, M.; Grieser, J.; Winston, J.; Lombardi, D.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection in free-ranging white-tailed deer. Nature 2022, 602, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharun, K.; Dhama, K.; Pawde, A.M.; Gortázar, C.; Tiwari, R.; Bonilla-Aldana, D.K.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.J.; De La Fuente, J.; Michalak, I.; Attia, Y.A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 in animals: Potential for unknown reservoir hosts and public health implications. Vet. Q. 2021, 41, 181–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoutzias, G.D.; Nikolaidis, M.; Tryfonopoulou, E.; Chlichlia, K.; Markoulatos, P.; Oliver, S.G. The Remarkable Evolutionary Plasticity of Coronaviruses by Mutation and Recombination: Insights for the COVID-19 Pandemic and the Future Evolutionary Paths of SARS-CoV-2. Viruses 2022, 14, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Peng, X.; Lu, G.; Shi, W.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, P.; Wang, Q. An Updated Review on SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Animals. Viruses 2022, 14, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.C.S.; Lam, S.D.; Richard, D.; Owen, C.J.; Berchtold, D.; Orengo, C.; Nair, M.S.; Kuchipudi, S.V.; Kapur, V.; van Dorp, L.; et al. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from humans to animals and potential host adaptation. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, A.; Bevins, S.; Chandler, J.; DeLiberto, T.J.; Ghai, R.; Lantz, K.; Lenoch, J.; Retchless, A.; Shriner, S.; Tang, C.Y.; et al. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in free-ranging white-tailed deer in the United States. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, F.P.; Noronha Souza, P.F.; Aragão, D.R.; Diógenes, E.M.; da Silva, E.L.; Amaral, J.L.; Freire, V.N.; de Souza Collares Maia Castelo-Branco, D.; Montenegro, R.C. In silico analysis of ACE2 from different animal species provides new insights into SARS-CoV-2 species spillover. Future Virol. 2023, 18, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryseels, S.; De Bruyn, L.; Gyselings, R.; Calvignac-Spencer, S.; Leendertz, F.H.; Leirs, H. Risk of human-to-wildlife transmission of SARS-CoV-2. Mamm. Rev. 2021, 51, 272–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, D.; Lois, M.; Fernández-Núñez, M.T.; Romalde, J.L. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in bivalve mollusks and marine sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanova, L.; Rutala, W.A.; Weber, D.J.; Sobsey, M.D. Survival of surrogate coronaviruses in water. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1893–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, D.; Kolar, P.; Hall, S.G. A review of the impact of environmental factors on the fate and transport of coronaviruses in aqueous environments. NPJ Clean Water 2021, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Taki, K.; Gahlot, R.; Sharma, A.; Dhangar, K.A. chronicle of SARS-CoV-2: Part-I—Epidemiology, diagnosis, prognosis, transmission and treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shutler, J.D.; Zaraska, K.; Holding, T.; Machnik, M.; Uppuluri, K.; Ashton, I.G.C.; Migdał, Ł.; Dahiya, R.S. Rapid assessment of SARS-CoV-2 transmission risk for fecally contaminated river water. ACS ES&T Water 2021, 1, 949–957. [Google Scholar]
- Sala-Comorera, L.; Reynolds, L.J.; Martin, N.A.; O’Sullivan, J.J.; Meijer, W.G.; Fletcher, N.F. Decay of infectious SARS-CoV-2 and surrogates in aquatic environments. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allinson, M.; Kadokami, K.; Shiraishi, F.; Nakajima, D.; Zhang, J.; Knight, A.; Gray, S.R.; Scales, P.J.; Allinson, G. Wastewater recycling in Antarctica: Performance assessment of an advanced water treatment plant in removing trace organic chemicals. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemnani, M.; Rodrigues, D.; Santos, N.; Santos-Silva, S.; Figueiredo, M.E.; Henriques, P.; Ferreira-e-Silva, J.; Rebelo, H.; Poeta, P.; Thompson, G.; et al. Molecular detection and characterization of coronaviruses in migratory ducks from Portugal show the circulation of Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavirus. Animals 2022, 12, 3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monchatre-Leroy, E.; Boué, F.; Boucher, J.M.; Renault, C.; Moutou, F.; Gouilh, M.A.; Umhang, G. Identification of Alpha and Beta Coronavirus in wildlife species in France: Bats, rodents, rabbits, and hedgehogs. Viruses 2017, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Talukder, A.; Chowdhury, M.M.H.; Talukder, R.; Akter, R. Coronaviruses in wild birds—A potential and suitable vector for global distribution. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 7, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wille, M.; Harvey, E.; Shi, M.; Gonzalez-Acuña, D.; Holmes, E.C.; Hurt, A.C. Sustained RNA virome diversity in Antarctic penguins and their ticks. ISME J. 2020, 14, 1768–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, G.; Aguilar Pierlé, S.; Loncopan, J.; Araos, L.; Verdugo, F.; Rojas-Fuentes, C.; Krüger, L.; Gaggero, A.; Barriga, G.P. Scavengers as Prospective Sentinels of Viral Diversity: The Snowy Sheathbill Virome as a Potential Tool for Monitoring Virus Circulation, Lessons from Two Antarctic Expeditions. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e03302-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damas, J.; Hughes, G.M.; Keough, K.C.; Painter, C.A.; Persky, N.S.; Corbo, M.; Hiller, M.; Koepfli, K.P.; Pfenning, A.R.; Zhao, H.; et al. Broad host range of SARS-CoV-2 predicted by comparative and structural analysis of ACE2 in vertebrates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 22311–22322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, M.R.D.; Hughes, K.A.; Morelli, E.; Convey, P. International response under the Antarctic treaty system to the establishment of a non-native fly in Antarctica. Environ. Manag. 2021, 67, 1043–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaraman, V.; Drolet, B.S.; Mitzel, D.N.; Wilson, W.C.; Owens, J.; Gaudreault, N.N.; Meekins, D.A.; Bold, D.; Trujillo, J.D.; Noronha, L.E.; et al. Mechanical transmission of SARS-CoV-2 by house flies. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cashman, J.S.; Cozier, G.E.; Harrison, C.; Isaac, R.E.; Acharya, K.R. Crystal structures of angiotensin-converting enzyme from Anopheles gambiae in its native form and with a bound inhibitor. Biochem. J. 2019, 476, 3505–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgs, S.; Huang, Y.J.S.; Hettenbach, S.M.; Vanlandingham, D.L. SARS-CoV-2 and Arthropods: A Review. Viruses 2022, 14, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Date | Source | Frei | Escudero | O’Higgins | Lineages Detected |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 December 2020 | I | n/s | (+) | n/s | B.1.1.451 |
| E | n/s | (+) | n/s | B.1.1 | |
| 10 February 2021 | I | (+) | n/d | n/s | B.1.1 |
| E | (+) | n/d | n/s | B.1.1 | |
| 17 February 2021 | I | n/d | n/d | n/s | n/s |
| E | n/d | (+) | n/s | No sequence | |
| 23 February 2021 | I | n/s | n/s | (+) | B.1.1 |
| E | n/s | n/s | (+) | B.1.1 | |
| 24 February 2021 | I | n/d | n/s | n/s | n/s |
| E | n/d | n/s | n/s | n/s | |
| 25 February 2021 | I | n/s | n/d | n/s | n/s |
| E | n/s | (+) | n/s | No sequence | |
| 2 March 2021 | I | n/s | n/s | (+) | B.1.1 |
| E | n/s | n/s | (+) | B.1.1 | |
| 3 March 2021 | I | n/s | n/d | n/s | n/s |
| E | n/s | n/d | n/s | n/s | |
| 9 March 2021 | I | n/s | n/s | (+) | B.1.1.409 |
| E | n/s | n/s | (+) | No sequence |
| Environmental Pool | Pan-Coronavirus | SARS-CoV-2 | Pan-Paramyxovirus | Influenza A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (−) | (−) | (−) | (−) |
| 2 | (−) | (−) | (−) | (−) |
| 3 | (−) | (−) | (−) | (−) |
| 4 | (−) | (−) | (−) | (−) |
| 5 | (−) | (−) | (+) | (−) |
| 6 | (+) | (−) | (+) | (−) |
| 7 | (−) | (−) | (+) | (−) |
| 8 | (−) | (−) | (+) | (−) |
| 9 | (+) | (−) | (+) | (−) |
| 10 | (−) | (−) | (−) | (−) |
| 11 | (−) | (−) | (−) | (−) |
| 12 | (+) | (−) | (−) | (−) |
| 13 | (−) | (−) | (−) | (−) |
| 14 | (−) | (−) | (−) | (−) |
| 15 | (−) | (−) | (+) | (−) |
| 16 | (−) | (−) | (+) | (−) |
| 17 | (+) | (−) | (+) | (−) |
| 18 | (+) | (−) | (+) | (−) |
| 19 | (−) | (−) | (+) | (−) |
| 20 | (+) | (−) | (+) | (−) |
| 21 | (−) | (−) | (+) | (−) |
| Negative control | (−) | (−) | (−) | (−) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Aravena, M.; Galbán-Malagón, C.; Castro-Nallar, E.; Barriga, G.P.; Neira, V.; Krüger, L.; Adell, A.D.; Olivares-Pacheco, J. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Wastewater Associated with Scientific Stations in Antarctica and Possible Risk for Wildlife. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040743
González-Aravena M, Galbán-Malagón C, Castro-Nallar E, Barriga GP, Neira V, Krüger L, Adell AD, Olivares-Pacheco J. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Wastewater Associated with Scientific Stations in Antarctica and Possible Risk for Wildlife. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(4):743. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040743
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Aravena, Marcelo, Cristóbal Galbán-Malagón, Eduardo Castro-Nallar, Gonzalo P. Barriga, Víctor Neira, Lucas Krüger, Aiko D. Adell, and Jorge Olivares-Pacheco. 2024. "Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Wastewater Associated with Scientific Stations in Antarctica and Possible Risk for Wildlife" Microorganisms 12, no. 4: 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040743
APA StyleGonzález-Aravena, M., Galbán-Malagón, C., Castro-Nallar, E., Barriga, G. P., Neira, V., Krüger, L., Adell, A. D., & Olivares-Pacheco, J. (2024). Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Wastewater Associated with Scientific Stations in Antarctica and Possible Risk for Wildlife. Microorganisms, 12(4), 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040743








