Abstract
The purple sulfur bacterium Thiocapsa roseopersicina BBS is interesting from both fundamental and practical points of view. It possesses a thermostable HydSL hydrogenase, which is involved in the reaction of reversible hydrogen activation and a unique reaction of sulfur reduction to hydrogen sulfide. It is a very promising enzyme for enzymatic hydrogenase electrodes. There are speculations that HydSL hydrogenase of purple bacteria is closely related to sulfur metabolism, but confirmation is required. For that, the full genome sequence is necessary. Here, we sequenced and assembled the complete genome of this bacterium. The analysis of the obtained whole genome, through an integrative approach that comprised estimating the Average Nucleotide Identity (ANI) and digital DNA-DNA hybridization (DDH) parameters, allowed for validation of the systematic position of T. roseopersicina as T. bogorovii BBS. For the first time, we have assembled the whole genome of this typical strain of a new bacterial species and carried out its functional description against another purple sulfur bacterium: Allochromatium vinosum DSM 180T. We refined the automatic annotation of the whole genome of the bacteria T. bogorovii BBS and localized the genomic positions of several studied genes, including those involved in sulfur metabolism and genes encoding the enzymes required for the TCA and glyoxylate cycles and other central metabolic pathways. Eleven additional genes coding proteins involved in pigment biosynthesis was found.
1. Introduction
The purple sulfur bacterium T. roseopersicina BBS belongs to the Chromatiaceae family from the class Gammaproteobacteria. This strain was isolated from the White Sea Estuary in 1969 [1]. Bacterial cells are spherical with a diameter of 1.0–1.5 microns. The color of the culture depends on the growth conditions and the composition of growth media and may range from pinkish red to light pink in cases of accumulating molecular sulfur. The bacteria are Gram negative. Despite the absence of flagella, the bacteria are capable of spontaneous impulse movements in wet microscopic samples. The culture grows in the pH range of 6.0–8.0 (optimum pH is 7.0–7.5) and in the presence of NaCl (up to 5%, the optimum content being 1–2%). T. roseopersicina BBS is a B12 auxotroph. It reproduces by a binary fission. The culture accumulates polyphosphate granules, poly-β-butyrate, and polysaccharides as storage compounds. It can grow under chemolithotrophic conditions [2]. Over the past years, the metabolism of hydrogen, sulfur, and carbon as well as the biosynthesis of the photosynthetic pigments in these bacteria have been extensively studied at both biochemical and physiological levels [3,4,5,6,7,8]. Special attention has been paid to the hydrogenases of this species, their structure, maturation, and cellular functions as well as the genes encoding the hydrogenases and the enzymes responsible for their synthesis [9,10,11,12,13,14]. However, for future research and practical application of this bacterium, the full genome sequence is important.
The aim of this work was to assemble the data of the whole genome of Thiocapsa sp. BBS; give a short description; analyze the genetic potential of this bacterium in sulfur metabolism, comparing it with the most studied purple sulfur bacterium, Allochromatium vinosum, for research into HydSL hydrogenase’s role in sulfur metabolism; present the genetic reason for the autotrophic growth of the bacterium; check for the presence of the citric acid cycle; and validate systematic position of the studied bacterium.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Growth Conditions
T. roseopersicina BBS was obtained from the culture collection of the Department of Microbiology, Moscow State University. The bacterium was cultivated at 28 °C in a modified Pfennig medium [1] containing NaHCO3 (0.2%), Na2S 9H2O (0.1%), sodium thiosulfate (0.2%), B12 (20 µg/ml), and NaCl (2%). Cells were cultivated under phototrophic conditions at an illumination intensity of 60 W/m2 in 250 ml flasks with stoppers.
2.2. Genome Sequencing, Assembly, and Annotation
Genomic DNA was isolated from the biomass of a fresh culture (a colony) of T. roseopersicina BBS grown under anaerobic photoheterotrophic conditions on modified Pfennig’s medium in the presence of 0.2% sodium acetate using the Monarch® HMW DNA Extraction Kit (T3050L, NEB). Sequencing was performed using the MinION sequencer with an R9.4.1 flow cell (Oxford Nanopore Technologies [ONT]) in the facilities of the State Research Center for Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (SRCAMB, Obolensk, Russia). The library was prepared using the Rapid Barcoding Kit (cat. # SQK-RBK00). Guppy version 3.2.4 software was used for base calling, which yielded a total of 338.5 Mb distributed in 179,494 reads. Reads were filtered based on the quality metric (Q > 10).
The same DNA sample was sequenced using the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform with an S2 reagent kit (catalog number 20012861; 2 × 100 bp; BioSpark, Moscow, Russia). A paired-end library was prepared with the Kapa HyperPlus kit (Roche, Basel, Switzerland).
Quality control of Illumina reads was carried out using FastQC. (http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc accessed on 1 June 2023). Illumina and Nanopore reads were used for hybrid assembly with SPAdes version 3.15.2 [15]. Nanopore reads were assembled into contigs using the Flye assembler version 2.6 [16]. SPAdes contigs were then combined into replicons using Flye data as a reference. Illumina reads were used to correct Nanopore errors using Bowtie2 version 2.3.5.1 [17] and Pilon version 1.23 [18] software. Default settings were used for all software. Circularization of the ends of a chromosome was confirmed by overlapping ends as well as by visualization in the Tablet program [19].
Data were submitted to the GenBank database under the following accession numbers: BioProject—PRJNA224116, BioSample—SAMN23799607, and GenBank—CP089309.1
The assembled genome was annotated using Prokka [20] and RAST [21]. The functions of some proteins were checked manually using BLAST. The phylogenetic tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method using the REALPHY service [22]. Genome sequences of Thiocapsa strains required for constructing the phylogenetic tree were taken from the WGS database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Traces/wgs/?view=wgs, accessed on 11 October 2021). The circular map was created using DNAPlotter [23].
The ANI value was calculated using the EzBioCloud service [24]. The DDH parameter was calculated using the Genome-to-Genome Distance Calculator 2.1 service [25]. We used the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) [26] to perform functional annotation using the blastp module.
Horizontal gene transfer regions (HGT regions) were searched using Alien Hunter [27]. CRISPR/Cas elements were searched using CRISPR/Cas Finder [28].
Metabolic pathways at the level of enzymes and their genes in T. roseopersicina BBS were analyzed using information from the KEGG Pathway database for prokaryotes, as well as records for substrates and products of biochemical reactions in KEGG Compounds. Searching for homologous genes in the T. roseopersicina BBS genome was performed using tBLASTn (by amino acid sequences of six open reading frames of the genome [29]). The best-characterized gene of a prokaryotic organism (i.e., having an experimentally proven function of interest) was chosen as a query for analysis. If highly homologous genes were absent, the test was repeated with less-characterized sequences (from purple bacteria only) as queries. The algorithm parameters were set to default values. The criteria for finding the gene of interest were as follows: for protein sequences, identity > 40% and alignment length > 100 Aa, Bit Score > 50, and e-value (the expectation value) ≤ 10−6 indicated the presence of the gene (provided that all other conditions were met); whereas e-value > 10−6 implied that the gene was absent. If this did not reveal the putative gene, the gene was considered as absent. We detected a small number of genes satisfying the search criteria. Amino acid sequences of the proteins from the UniProt database were used as search templates [30].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. General Characteristics of the T. roseopersicina BBS Genome
We sequenced and assembled the genome of T. roseopersicina BBS. Its main statistical features are shown in Table 1. The T. roseopersicina BBS DNA consists of a circular chromosome 5,649,927 bp long (with a GC content of 63.94%), and plasmids are absent (Figure 1). The chromosome contains 5036 genes, 2 rRNA clusters (5S, 16S, 23S), and 51 tRNAs. Of 4978 protein-coding sequences, 2468 (49.6%) were functionally annotated (Figure 2).

Table 1.
Comparative genome statistics for the purple sulfur bacteria T. roseopersicina BBS and Alc. vinosum DSM 180T.
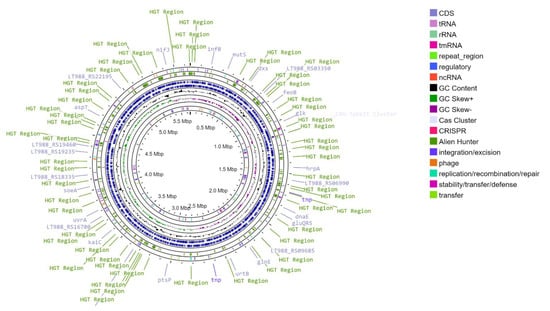
Figure 1.
Circular genomic map of T. roseopersicina BBS chromosome.
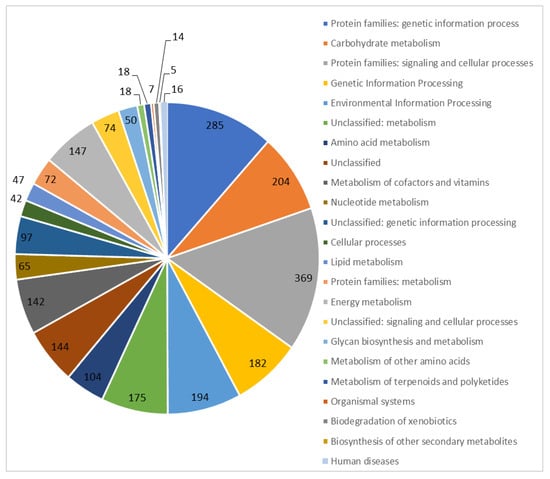
Figure 2.
Functional annotation of the genomic DNA of T. roseopersicina BBS.
3.2. Validating the Taxonomic Position of the BBS Strain
The genus Thiocapsa currently comprises nine species. Two of them have not been validated at the time of preparing this manuscript (LPSN - List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature, https://www.bacterio.net/, accessed on 1 June 2023). One of the two non-validated species includes the strain under consideration: the reclassification of the T. roseopersicina BBS species into a novel species T. bogorovii BBS was suggested by Tourova et al. in 2009 with BBS as a type (and single at the moment) strain [31]. However, these data require further validation using a full genome, since GenBank contains only fragmented data on small sequences of T. roseopersicina BBS genomic DNA up to 40,000 base pairs in size (AF528191.1, JF712872.1, etc.). Therefore, it has not previously been possible to determine the extent to which this bacterium differs from the typical T. roseopersicina strain.
Analyzing the obtained whole genome of T. roseopersicina BBS through an integrated approach that included calculating the ANI and DDH parameters resulted in validation of the systematic position of T. bogorovii BBS. This bacterium is not closely related to any typical strain of the species from the Thiocapsa genus (T. marina, T. rosea, T. imhoffii, and T. roseopersicina) (Table 2). Thus, for the first time, we obtained the assembled whole genome of T. bogorovii BBS and confirmed the relevance of its classification into a novel typical species of the Thiocapsa genus.

Table 2.
The level of similarity between the T. roseopersicina BBS genome and other typical species of the Thiocapsa genus *.
The systematic position of T. bogorovii BBS explains the existence of substantial differences in bacterial physiology from T. roseopersicina DSM 217T. In particular, T. bogorovii BBS is characterized by the absence of assimilatory sulfate reduction, vitamin B12 auxotrophy, and higher optimal values of growth medium salinity as well as the distinct range of utilized organic compounds [1].
3.3. A Comparison of the Whole Genomes of T. bogorovii BBS and Alc. Vinosum DSM 180T
To study the specificities of sulfur metabolism and the role of the involved hydrogenases in T. bogorovii BBS, the whole sequence of its genome was characterized and compared with the genome of another representative of the Chromatiaceae family, Alc. vinosum DSM 180 T, since its sulfur metabolism has been studied in detail. The whole sequence of Alc. vinosum DSM 180T consists of one circular chromosome and two plasmids [32]. Similar to T. bogorovii BBS, this bacterium is capable of phototrophic growth (anaerobic in the light) and chemotrophic growth (aerobic in the dark). Data on the major features of the genetic categories are given in Table 3. So, these bacteria belong to distinct families of purple sulfur bacteria and are very different in genome composition. Nevertheless, sulfur metabolism is the common features between them and it allows us to compare them in this respect.

Table 3.
Comparison of major gene categories * encoded by the genomes of T. bogorovii BBS and Alc. vinosum DSM 180 T.
3.3.1. Pigment Biosynthesis and Photocomplexes
The photosynthetic apparatus of many purple bacteria consists of three types of pigment-protein complexes: two light-harvesting antenna complexes (LHI and LHII) capture photons of different wavelengths and transfer the excitation energy to the reaction center (RC, complex III) [33]. The core antenna LH1 is adjacent to the RC, forming an open ring [34]. The LH2 peripheral antenna is located at the periphery. There are three structural types of RC–LH1 complexes in purple bacteria [35]. The gaps in the LH1 ring are considered to be necessary for the penetration of the ubiquinone that links RC with the cytochrome bc1 complex. In Cereibacter sphaeroides, the PufX protein is present in each monomer of the dimeric RC–LH1 [36]. In the purple non-sulfur bacterium Rhodopseudomonas palustris [37], RC exists in the form of the RC–LH1 monomer and contains the protein W (similar to PufX). The third structural type of RC–LH1 complex has been identified in the purple sulfur bacterium Thermochromatium tepidum [38]. In this bacterium, RC exists as the RC–LH1 monomer and does not comprise proteins similar to the PufX or W proteins (however, the LH1 ring is open containing channels). Recently, a fourth form of RC–LH1 with a closed ring has been reported in purple bacteria [39].
Gene clusters in T. bogorovii BBS related to photosynthesis have been investigated earlier. The localization of several genes is uncommon compared to other photosynthetic bacteria [8]. The obtained whole genome of these bacteria allowed for specification of the localization of the enzymes that belonged to the specific pathway of carotenoid synthesis in T. bogorovii BBS, the main carotenoid being spirilloxanthin [1,8]. It also allowed for identification of the genes of the light-harvesting photosynthetic complexes and the genes related to the synthesis of bacteriochlorophyll a, which are located outside of the previously studied genomic fragments (Table 4). Sequencing errors (substitutions and deletions) were detected in some previously characterized regions. According to the genomic analysis performed, the genes encoding the proteins W and PufX are absent from both T. bogorovii BBS and Alc. vinosum DSM 180T.

Table 4.
The genes encoding the enzymes of specific carotenoid synthesis, light-harvesting photosynthetic complexes, and genes related to bacteriochlorophyll a in T. bogorovii BBS.
3.3.2. Autotrophy and RuBisCO
In purple bacteria, the major pathway for CO2 assimilation under autotrophic conditions is the reductive pentose phosphate cycle (Calvin–Benson–Bassham cycle) [40]. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO), Phosphoribulokinase (PRK), and Sedoheptulose-bisphosphatase (SBP) are the enzymes that function exclusively in this cycle [41]. Together, RuBisCo and PRK can indicate that this cycle is present in the organism in question. Enzymes that differ from the typical plant form of RuBisCo have been identified in various microorganisms. There are four main forms of RuBisCO [42], with RuBisCO forms I, II, and III exhibiting carboxylase and oxygenase activity, but under potentially different physiological conditions. Form III has been found only in archaea and has therefore been allocated into a separate category. Form IV includes the RubisCO-like protein (RLP). This enzyme does not catalyze ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate-dependent CO2 fixation; however, it might be involved in sulfur metabolism and stress responses [43,44] as well as in the methionine salvage pathway [45]. The function of RLP is unknown in many organisms. RuBisCO activity has been detected in the T. roseopersicina DSM 217T and T. bogorovii BBS cultures [3,7,46]. The peculiarity of the BBS strain is the insensitivity of RuBisCO synthesis to molecular oxygen [3]. In contrast, RuBisCO synthesis is suppressed by oxygen in most purple bacteria [40].
The green-like form I RuBisCO was the only one obtained and sequenced using specific oligonucleotide primers in T. roseopersicina DSM 217T and T. bogorovii BBS [31], whereas Alc. vinosum DSM 180T was shown to contain two forms (the green-like form I RuBisCO and the red-like form II RuBisCO).
Analysis of the T. bogorovii BBS genome using the RAST 2 algorithm revealed two copies of the gene encoding the green-like RuBisCO form I. It is worth noting that the genes encoding the small subunits are different, and their nucleotide sequences have 70% identity (using standard settings of the Nucleotide BLAST algorithm). Using tBlastn, the bacterial genome was shown to contain a gene (LT988_08840, 1944337 to 1945626 base pairs) encoding a protein product with 71% identity of amino acid sequence of the form IV “RuBisCO-like” protein of Alc. vinosum DSM 180T. The role of RLP in T. bogorovii BBS has not yet been elucidated.
The structural genes encoding two enzymes of the RuBisCO form I are far apart, and their genetic neighborhoods are different, similar to the RuBisCO genes in Alc. vinosum DSM 180T [32]. In one case, the RuBisCO structural genes (LT988_02750, rubisco L 566332–567750 bp and LT988_02755, rubisco S 567908–568264 bp) were located upstream of the genes encoding RuBisCO activation proteins (LT988_02760, CbbQ 568387–569193 bp and LT988_02770, CbbO 569671–572049 bp), with the 23Sr gene (LT988_02765, 569275–569637 bp) encoding the four-helix bundle protein located in-between. The transcriptional regulator of the RuBisCO operon (LT988_RS02745, CbbR) is located within 566015–565080 bp. This gene has an inverted orientation relative to the other RuBisCO genes.
In another case, based on the classical RAST 2 annotation, the RuBisCO structural genes (LT988_RS07075, CbbL, 1573243–1574658 bp and LT988_RS07080, CbbS, 1574821–1575165 bp) were located upstream of the genes encoding carboxysome proteins (carboxysome shell proteins CsoS2 (LT988_07085) and CsoS3 (LT988_07090), putative carboxysome peptides A and B (LT988_07095 and LT988_07100, respectively), two carboxysome shell proteins CsoS1 (LT988_07105 and LT988_07110)), and bacteriopheophytin (suspected to be related to carboxysome, LT988_07115). The transcription regulator of the RuBisCO operon is located at some distance (LT988_07130, 1582292–1583305 base pairs). Carboxysomes are organelle-like protein microcompartments found in cyanobacteria and many chemoautotrophic bacteria. They elevate the efficiency of carbon fixation by abolishing oxygen access to RuBisCO, located under the protein envelope, as well as via the mechanism of carboanhydrase-dependent CO2 concentration [47,48]. In Alc. vinosum DSM 180T, low CO2 caused a preferential expression of the RuBisCO form flanked by carboxysomal genes, compared to the second RuBisCO form that dominates at high CO2. This is considered to support the role of the carboxysome-dependent CO2 concentration mechanism in this bacterium [32]. However, there is still no data regarding the existence of carboxysomes in T. boborovii BBS. Nevertheless, analysis of the genomes of Alc. vinosum DSM 180T and T. bogorovii BBS using RAST ver. 2.0 revealed 15 and 23 genes associated with the carboxysome system, 19 and 22 genes associated with photorespiration (involving RuBisCO oxygenase activity), and 13 and 17 genes associated with the Calvin–Benson–Bassham cycle, respectively.
Thus, the analysis of the genomic sequence of T. bogorovii BBS allowed us to detect several genes for different forms of RuBisCO and complemented the data obtained by Turova et al., who found only part of the single gene encoding the green-like RuBisCO form I in this bacterium using oligonucleotide primers specific to different types and forms of RuBisCO genes [31]. Further studies are needed to confirm the expression activity of the identified genes and to determine their physiological roles in metabolism in T. bogorovii BBS.
3.3.3. Heterotrophy
T. bogorovii BBS assimilates organic substrates during photoheterotrophic growth and can utilize them both as electron donors and also as carbon sources. The main metabolic pathways of carbon metabolism are the tricarboxylic acid cycle, the Entner–Doudoroff pathway, and the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway.
Organic acids and substrates metabolized through acetyl-CoA are assimilated via the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle). T. bogorovii BBS is categorized as a purple bacterium, in which neither tricarboxylic acid cycle functions, by its ability to consume few organic compounds from the growth medium and usually only as additional carbon sources. However, according to the results of KEGG-Pathway analysis of the complete genome of T. bogorovii BBS and the genome of Alc. vinosum DSM 180T, both bacteria possess genes of all enzymes necessary for the functioning of the tricarboxylic acid cycle [7].
The glyoxylate cycle genes required for the assimilation of acetate as the only source of organic compounds (isocitrate lyase (EC: 4.1.3.1) and malatesynthase (EC: 2.3.3.9)) are present in the genome of T. bogorovii BBS (LT988_08090 and LT988_06350) as well as in the genome of Alc. vinosum DSM 180T (isocitrate lyase, Alvin_1848 and malate synthase G, Alvin_2606).
The lack of beneficial effect after adding certain substrates to an inorganic medium can be explained by the lack of their intracellular transport. The revealed contradictions are the basis for further studies of the functional activity of genes of the considered metabolic pathways at the levels of transcription and proteomics.
Experimental research has shown that cell yield is elevated under the light if the inorganic growth medium is supplemented with acetate, pyruvate, lactate, glycerol, or glucose (0.1%) [31]. Meanwhile, adding the compounds that serve as TCA cycle intermediates (2-ketoglutarate, fumarate, succinate, or malate) and their precursors (propionate) induces a slight gain in the biomass, representing a difference between T. bogorovii BBS and Alc. vinosum DSM 180T [32]. Meanwhile, the biomass yield is not affected by such organic compounds as formate, butyrate, fructose, galactose, lactose, sorbose, arabinose, rhamnose, xylose, mannose, maltose, sucrose, methanol, ethanol, butanol, propanol, isopropanol, mannitol, sorbitol, and dulcitol. Some compounds (benzoic acid, isobutanol, and amyl and isoamyl alcohols) are known to inhibit the growth of T. bogorovii BBS [31].
Earlier works have shown that T. bogorovii BBS has an open reductive TCA cycle (rTCA) typical of bacteria lacking the full set of TCA enzymes [7,49]. Essentially, rTCA functions as a reverse oxidative TCA employed by bacteria as a pathway for autotrophic CO2 fixation and acetate assimilation. The full turn of the cycle under autotrophic conditions leads to the fixation of four CO2 molecules with the formation of one oxaloacetate molecule. Two irreversible TCA cycle reactions in the reductive cycle are catalyzed by the alternative enzymes. The formation of 2-oxoglutarate from succinyl-CoA and CO2 is catalyzed by 2-oxoglutarate synthase (EC: 1.2.7.3 1.2.7.11). The irreversible citrate synthase can be substituted by the reversible ATP-dependent citrate lyase (EC: 2.3.3.8) [50] or by two sequentially functioning enzymes: citryl-CoA synthetase (EC: 6.2.1.18) and citryl-CoA ligase (EC: 4.1.3.34) [51]. Analysis of the T. bogorovii BBS genome with KEGG revealed one of these key genes encoding 2-oxoglutarate synthase (EC: 1.2.7.3 1.2.7.11; LT988_18060, LT988_18065). However, the enzymes required to replace the irreversible citrate synthase involved in the oxidative TCA cycle have not been identified yet; therefore, this pathway has been termed the open rTCA cycle. The genes encoding the key rTCA cycle enzymes are absent in Alc. vinosum DSM 180T as well. The genes encoding the enzymes of TCA and rTCA cycles in T. bogorovii BBS are listed in Table 5.

Table 5.
The genes encoding the enzymes of the TCA cycle (reactions 1–13), unique enzymes of the rTCA cycle (reactions, 14,15,16), and the glyoxylate cycle (reactions 17,18) in T. bogorovii BBS.
Conversion of carbohydrates to phosphoenolpyruvate, pyruvate, and acetyl-CoA occurs via the Entner–Doudoroff and Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathways. According to the KEGG Annotation, the genomes of T. bogorovii BBS and Alc. vinosum DSM 180T contain the genes of glycolytic enzymes (Embden–Meyerhof pathway) and enzymes involved in pyruvate oxidation and gluconeogenesis (Table 6).

Table 6.
The genes encoding the enzymes of the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway (1–10), gluconeogenesis (reactions 10–1 with the reaction 3 substituting the reverse reaction 11), and pyruvate oxidation (reactions 12 or 13–15) in T. bogorovii BBS.
The Entner–Doudoroff pathway has no genetic potential for function in the bacteria when considered according to the KEGG Pathway database. This confirms the results previously obtained when studying T. bogorovii BBS at the physiological level.
According to KEGG, the genes required for the pentosophosphate pathway function are present in the genome of T. bogorovii BBS (Table 7).

Table 7.
The genes encoding the enzymes of the pentosophosphate pathway (1–7) in T. bogorovii BBS.
It should be noted that T. bogorovii BBS has the gene LT988_13700 encoding D-glucose permease of the phosphotransferase system (PTS, which is absent in the genome of Alc. vinosum DSM 180T). This enzyme (EC 2.7.1.199) is a component (known as enzyme II) of the phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)-dependent sugar transporting PTS.
Further research is required to confirm the functions of the proteins encoded by the identified genes.
3.3.4. Hydrogenases
Hydrogenases belong to a class of oxidoreductases that can catalyze molecular hydrogen activation. They are widely distributed in archaea, bacteria, and some unicellular eukaryotes. These enzymes are involved in highly diverse biological processes [52] where they perform different functions. In some cases, the organisms produce hydrogen to remove an excess of reducing equivalents; in other cases, they uptake hydrogen and utilize it as an electron source. Hydrogen uptake hydrogenases are used by nitrogen-fixing microorganisms to utilize the hydrogen generated by the nitrogenase system. A separate group of sensor hydrogenases is involved in the transcription induction of hydrogen uptake hydrogenases [52,53].
Following the current classification, hydrogenases are divided into 38 classes: 29 subclasses of Ni-Fe hydrogenases, 8 subtypes of Fe-Fe hydrogenases, and monophyletic Fe hydrogenases [54]. T. bogorovii BBS is known to have five genes encoding Ni-Fe hydrogenases belonging to different groups and performing different functions (HupSL, HydSL, hupUV, and two Hox hydrogenases) [11,12,13,55,56,57]. Membrane-bound-hydrogen-uptake hydrogenases in T. bogorovii BBS comprise HupSLC and HydSL hydrogenases.
HupSL hydrogenase is involved in the uptake of the exogenous and endogenous molecular hydrogen with the transfer of electrons to the ubiquinone pool. This enzyme is also known to participate in the reverse uptake of hydrogen produced by nitrogen fixation [52]. This hydrogenase is thought to ensure bacterial growth under photoautotrophic conditions as well as chemolithotrophic growth under microaerophilic conditions in the dark [10,57]. HupS (LT988_02910) and hupL (LT988_02915) encode the small and large subunits of HupSLC hydrogenase, respectively. HupC (LT988_02920) is the cytochrome of the b type. The genome of T. bogorovii BBS also contains the genes hupDHI required for the biosynthesis of HupSLC hydrogenase [55]: LT988_02925 (Hydrogenase expression/formation protein HupD), LT988_02930 hupH (comparison of the nucleotide sequence of hupH from the AY837591.1 (GenBank) with the sequence from the whole genome of T. bogorovii BBS using tBlastn revealed the differences reflected in 92% identity of amino acid sequences), and LT988_02935 (Rubredoxin Gene hupI).
Hyd hydrogenase can reversibly catalyze the reaction towards hydrogen production as well as hydrogen uptake [58,59]. However, to date, the only known major physiological cellular function of Hyd is to catalyze the reduction of elemental sulfur with hydrogen uptake in the dark [10]. HydSL is encoded by LT988_03130 (HydS subunit) and LT988_03145 (HydL subunit). The structural genes encoding the large and small subunits are separated by two open reading frames (LT988_03135 and LT988_03140) called isp1 and isp2. The Isp1 protein encoded by the gene with the same name is a heme-containing transmembrane protein of b type, whereas the sequence of Isp2 demonstrates a substantial level of similarity with heterosulfide reductases [11].
Despite the presence of HupUV genes (LT988_05045 and LT988_05050) in the genome of T. bogorovii BBS, this bacterium does not express this enzyme that commonly serves as a hydrogen sensor in other bacteria and is involved in the synthesis of HupSL hydrogenases [60].
Soluble hydrogenases belonging to the HoxEFUYH type of Ni-Fe hydrogenases and involved in NAD+ reduction or NADH oxidation, have been shown experimentally [13,61,62]. The activity of Hox hydrogenases is closely linked to sulfur metabolism. Elemental sulfur serves as an electron donor for hydrogen production under light [10]. The Hox1 hydrogenase consists of the HoxYH hydrogenase (LT988_09435 and LT988_09445) and HoxFU diaphorase (LT988_09425 and LT988_09430). HoxE (LT988_09420) is a fifth subunit that is thought to be involved in an electron transfer, followed by a gene (LT988_09450) encoding the hydrogenase maturation protein, namely HoxW.
In T. bogorovii BBS, Hox2 hydrogenase, which was later identified and characterized [13], is encoded by the genes Hox2YH (LT988_16220 and LT988_16225), Hox2FU (LT988_16210 and LT988_16215), and Hox2W (LT988_18265).
HydSL, HupSLC, and Hox1 enzymes have been identified and described in Alc. vinosum DSM 180T [32]; however, in contrast to T. bogorovii BBS, this bacterium lacks the genes of the sensor hydrogenase HupUV. The Alc. vinosum DSM 180T genome contains the genes of the other two hydrogenases. The sequences of one of the hydrogenases (Alvin_0807 to Alvin_0810) show a high degree of similarity with the hydrogenase/sulforeductases (EC: 1.12.98.4) of Thermodesulfovibrio yellowstonii DSM 11347 and Chlorobium tepidum [32]. Searching for the genes encoding this enzyme in the genome of T. bogorovii BBS using tBlastn revealed that the highest degree of similarity was between the sequences of the sulfhydrogenase and Hox2 hydrogenase genes.
According to the KEGG Orthology annotation, Alc. vinosum DSM 180T has another hydrogenase, Ech hydrogenase, which catalyzes H2-dependent reduction of 2[4Fe-4S] ferredoxin in Methanosarcina barkeri as well as hydrogen generation with the reduced ferredoxin as an electron donor [63]. This hydrogenase consists of the A (Alvin_0338, function number according to the KEGG Orthology: K14086), B (Alvin_0337; K14087), C (Alvin_0331; K14088),D (Alvin_0330; K14089), E (Alvin_0329; K14090), and F subunits (Alvin_0328; K14091).
Thus, analysis of the bacterial genome searching for known forms of hydrogenases revealed the presence of hydrogenase genes previously demonstrated experimentally.
3.3.5. Chemotrophic Metabolism
Upon photoautotrophic growth, sulfide, thiosulfate, sulfur, or H2 are utilized as electron donors. Chemoautotrophic growth in the dark under anaerobic conditions is possible due to thiosulfate used as a sulfur source as well as an electron donor and energy source for CO2 assimilation [2].
T. roseopersicina and T. bogorovii BBS are known to grow under chemolithotrophic conditions utilizing thiosulfate as an electron donor [2]. It should be noted that, in theory, CO2 fixation involving RuBisCO can occur in the presence of oxygen, since its synthesis is continued in the presence of O2 in both Thiocapsa species. It might be related to the presence of the RuBisCO carboxysome form described in the ‘Autotrophy and RuBisCO’ subparagraph.
Similar to Alc. vinosum DSM 180T [32], the genome of T. bogorovii BBS contains the genes encoding both oxidases required for the chemotrophic growth of the bacteria in the presence of oxygen. Cytochrome bd oxidase is encoded by the genes LT988_17870 (annotated as the ubiquinol oxidase subunit I, its amino acid sequence exhibits 85% identity with the sequence of the oxidase Alvin_2499 in Alc. vinosum DSM 180T), LT988_17865 (annotated as the cytochrome d ubiquinol oxidase subunit II, 80% identity with Alvin_2500 in Alc. vinosum DSM 180T), and LT988_17860 (annotated as the cytochrome bd-I oxidase subunit CydX, 73% identity with Alvin_2501 from Alc. vinosum DSM 180T). Cytochrome bd oxidase from Alc. vinosum DSM 180T is known to function mostly under microanerobic conditions, removing toxic oxygen generated during nitrogen fixation [64].
Cytochrome cbb3 oxidase from T. bogorovii BBS is encoded by the genes located between LT988_18880 and LT988_18925. Cytochrome cbb3 oxidase maintains its catalytic activity in the presence of low oxygen and is capable of proton translocating [32]. We demonstrated the presence of genes responsible for chemotrophic metabolism. Further research is required to confirm the functions of the proteins encoded by these genes.
3.3.6. Nitrogen Metabolism
According to genome annotation (Subsystem Technology (RAST; version 2.0) online genome analysis software), the fraction of genome involved in nitrogen metabolism in T. bogorovii BBS is 1.8 times greater than in Alc. vinosum DSM 180T (Table 2). Both bacteria are known to be diazotrophs [32,65]. Their ability to fix molecular nitrogen is provided by a Mo-containing-bicomponent complex of the metalloenzyme nitrogenase encoded by nifHDK genes. The genomic DNA of T. bogorovii BBS contains all the genes of the nitrogenase complex: LT988_07970 (NifH, nitrogenase iron protein), LT988_07975 (NifD, nitrogenase molybdenum-iron protein alpha chain), and LT988_07980 (NifK, nitrogenase molybdenum-iron protein beta chain). Similar to Alc. vinosum DSM 180T [32,65], in T. bogorovii BBS genes associated with nitrogen fixation are located in various genomic regions and organized in genetic clusters.
T. bogorovii BBS can utilize ammonium salts, urea, peptone, casein hydrolyzate, and arginine as nitrogen sources. However, it cannot grow in the presence of alanine or hydroxylamine [31]. Furthermore, T. bogorovii BBS does not grow when supplemented with glutamic acid or KNO3. According to the online analysis tools and KEGG Pathway database, this bacterium has a shortage of genes involved in assimilatory nitrate reduction (ferredoxin-nitrate reductase [EC:1.7.7.2]; nitrate reductase (NAD(P)H) [EC:1.7.1.1 1.7.1.2 1.7.1.3]; assimilatory nitrate reductase catalytic subunit [EC:1.7.99.-], catalyzing formation of nitrite from nitrate; and ferredoxin-nitrite reductase [EC:1.7.7.1], nitrite reductase (NAD(P)H) [EC:1.7.1.4]. However, it has a gene encoding the nitrite reductase [NAD(P)H] small subunit [EC:1.7.1.4] nirD, LT988_07740). The bacterium under scrutiny contains some genes required for denitrification (nitrite reductase (NADH) large subunit [EC:1.7.1.15], nitrite reductase (cytochrome c-552) [EC:1.7.2.2]), and nitrification (methane/ammonia monooxygenase subunit A [EC:1.14.18.3 1.14.99.39] and nitrate reductase/nitrite oxidoreductase, alpha subunit [EC:1.7.5.1 1.7.99.-]). At the genomic level, this bacterium has the potential for the first reaction of the dissimilatory nitrate reduction, conversion of nitrate into nitrite by nitrate reductase/nitrite oxidoreductase, alpha subunit [EC:1.7.5.1 1.7.99.-] (LT988_06635 encoding respiratory nitrate reductase subunit gamma; and LT988_07690 encoding nitrate reductase cytochrome c-type subunit). Analysis of the Alc. vinosum DSM 180T genome revealed the lack of the genes involved in the above processes mentioned above [32].
Thus, we have clearly demonstrated the presence of genes responsible for nitrogen metabolism, experimentally discovered here based on previous physiological data. Further studies are needed to confirm the functions of the proteins encoded by the identified genes.
3.3.7. Sulfur Metabolism
T. bogorovii BBS grows only in the presence of S0, S2–, or S2O3- [31]. It does not utilize cysteine and methionine as sulfur sources. Sulfide and thiosulfate are oxidized to sulfate via the formation of elemental sulfur accumulated in cells as granules. There are several known pathways for utilizing sulfur compounds as electron donors and acceptors for energy acquisition.
In contrast to Alc. vinosum DSM 180T [32], T. bogorovii BBS is not capable of assimilatory sulfate reduction [31]. This is confirmed by the results of KEGG Pathway genome analysis. This bacterium lacks the genes encoding the enzymes of phosphoadenosine phosphosulfate reductase [EC:1.8.4.8 1.8.4.10], sulfite reductase (NADPH) [EC:1.8.1.2], and alternative ferredoxin-sulfite reductase [EC:1.8.7.1].
Thiosulfate Oxidation
Thiosulfate oxidation can occur in the periplasm with the formation of tetrathionate (S4O62−) or in the periplasmic multi-enzyme sulfur oxidation system (Sox system) [66]. The main enzyme of the tetrathionate pathway in Alc. vinosum DSM 180T functions as tetrathionate reductase (TsdA, Alvin_0091 [67]). The electron transfer from TsdA to the photosynthetic or respiratory ETC upon thiosulfate oxidation involves the TsdB protein (diheme cytochrome c4 encoded by Alvin_2879 in Alc. vinosum) and possibly protein Alvin_2880 [66]. Another possible acceptor of electrons from TsdA in the purple sulfur bacteria is the high potential protein HiPIP (350 mV). In the T. bogorovii BBS genome, there is no gene encoding TsdA or the alternative archaeal enzyme AoxDA (thiosulfate/quinone oxidoreductase, which is absent in phototrophic prokaryotes).
The second pathway of thiosulfate oxidation is mediated by the Sox system involved in the disproportionation of thiosulfate with the formation of sulfate and molecular sulfur [66]. In this pathway, protein-bound sulfur atoms undergo oxidation. The genes involved in the Sox pathway are present both in Alc. vinosum DSM 180T [32] and T. bogorovii BBS (Table 8). LT988_16035 (SoxY), LT988_16040 (SoxZ), LT988_24235 (SoxB), LT988_24240 (SoxX), LT988_24245 (SoxA), and also LT988_24250 (61% identity with the amino acid sequence of the SoxXA-binding protein from Alc. vinosum DSM 180T (SoxK, Alvin_2170)); LT988_24255 and LT988_09460 (61% and 43% identity with the periplasmic sulfur transferase from Alc. vinosum DSM 180T (SoxL, Alvin_2171)). SoxL serves as an alternative to the SoxCD proteins and is typical of bacteria that do not accumulate sulfur. The SoxCD encoding genes are absent both in T. bogorovii BBS and Alc. vinosum DSM 180T.

Table 8.
The genes encoding the enzymes involved in Sox system thiosulfate oxidation (1–5), sulfide oxidation (sulfide/quinone oxidoreductase (SQR (6)), and flavocytochrome c sulfide dehydrogenase (FccAB (7,8)) in T. bogorovii BBS.
Sulfide Oxidation
Several enzymes can oxidize sulfides: sulfide/quinone oxidoreductase (SQR), flavocytochrome c sulfide dehydrogenase (FccAB), and the Sox system in bacteria that do not accumulate sulfur [66].
The described SQRs are single-subunit flavoproteins bound to the cytoplasmic membrane. They are classified into six types based on structural data. SQRA and SQRE types are not found in the purple sulfur bacteria, SqrF and SqrD proteins are widely distributed among the Chromatiaceae purple sulfur bacteria, and the ScrB type is common among the Ectothiorhodospirilaceae family members [66]. The primary product of the SQR reaction is polysulfide.
T. bogorovii BBS has the genes LT988_02950 and LT988_15980, annotated as the FAD-dependent oxidoreductase (Table 8, reaction 6) according to GenBank and homologous to the genes from Alc. vinosum DSM 180T encoding SqrD and SqrF proteins, respectively. In contrast to Alc. vinosum DSM 180T, T. bogorovii BBS lacks the genes Alvin_1196 and Alvin_1197 that are located downstream of SqrF and are possibly responsible for attaching the enzyme to the membrane in Alc. vinosum DSM 180T [32].
Sulfide oxidation can involve the flavocytochrome c sulfide reductase in the periplasmic space; however, the physiological role of this enzyme has not been clarified yet (the knockout bacteria oxidize sulfide with the same rates [32], whereas some species of green and purple sulfur bacteria do not produce the proteins). T. bogorovii BBS has two genes, LT988_00625 and LT988_00620 (Table 8, Nos. 7,8), that are homologous to the genes encoding the FccB and FccA subunits of flavocytochrome c sulfidereductase FccAB from Alc. vinosum DSM 180T.
Oxidizing Elemental Sulfur
Elemental sulfur is almost insoluble in water, and it has not been fully understood how phototrophic organisms bind, activate, and uptake this substrate [66]. Exogenous elemental sulfur mainly consists of S8 rings, chains of polymeric sulfur, and traces of S7 rings. The uptake of elemental sulfur by Alc. vinosum DSM 180T seems to require the direct interaction of cells with sulfur and, although unlikely, the action of secreted compounds towards the substrate outside the cell.
The purple sulfur bacteria of the Chromatiaceae family accumulate molecular sulfur in the periplasmic space in the form of globules surrounded by the protein coat. In Alc. vinosum DSM 180T, the protein coat is a monolayer consisting of four sulfur globule proteins, SgpABCD, that perform an exclusively structural function and that are required for sulfur formation and deposition. SgpA (Alvin_1905, annotated as Sulfur globule protein CV1) and SgpB (Alvin_0358, annotated as Sulfur globule protein CV2) are similar, have a weight of 10.5 kDa, and can partially substitute for each other. The SgpC protein encoded by Alvin_1325 (annotated as Sulfur globule protein CV3) is important for globule expansion. SgpD (Alvin_2515) is the most common protein of these globules, as shown by the proteomic studies. According to the sequencing genomic data, Sgp proteins are present in all members of purple sulfur bacteria from the Chromatiaceae family in variable combinations [32] and absent in the members of the Ectothiorhodospirilaceae family. Earlier, the protein sequences of two large Sgps isolated from Alc. vinosum strain ATCC 17899 (10.5 kDa) were demonstrated to be similar to one of the two isolated Sgp proteins from the T. roseopersicina strain SMG219. Likewise, the sequences of small Sgp proteins from these bacteria (8.5 and 8.7 kDa, respectively) were found to show a certain amount of similarity as well [68]. Three genes annotated as sulfur globule proteins were discovered in T. bogorovii BBS. They are LT988_04675, encoding sulfur globule protein CV3; LT988_09360, encoding sulfur globule protein CV1; LT988_19155, encoding sulfur globule protein CV1 LT988_19155; and two more genes that are classified as sulfur globule family proteins (LT988_08020 and LT988_19100). No associated KEGG Orthology function has been identified for these genes.
In Alc. vinosum, sulfur is present in the globules in the form of mono- and bis-organylsulfanes [69]. The sulfur accumulated in the globules can undergo oxidation after being activated and then translocated to the cytoplasm with a vehicle perthiol molecule. There are two known pathways of sulfur oxidation: the Dsr system (which involves reversible dissimilatory sulfite reductase DsrAB) and the sulfur oxidation pathway involving the system of enzymes similar to heterosulfide reductase [66].
Low-molecular-weight organic persulfides such as glutathion persulfide can serve as vehicle molecules translocating sulfur from periplamic or extracellular deposits to the cytoplasm [70]. As yet, the pathway mediating formation of possible molecules in persulfide vehicles has not been studied; it is not known whether there are specific enzymes and transporters involved in this process. In Alc. vinosum DSM 180T, sulfur from the globules is translocated to the active center of sulfite reductase DsrAB via the cascade of persulfide intermediates located on the rhodanese, TusA, and probably DsrE2A, DsrE, and DsrC [61]. Along with SoxL, six other genes that can encode rhodanese in Alc. vinosum DSM 180T have been annotated: Alvin_0258, Alvin_0866, Alvin_0868, Alvin_1587, Alvin_2599, and Alvin_3028. Currently, the role of these proteins in the dissimilatory sulfur metabolism is not clear. The T. bogorovii BBS genome contains seven genes encoding the products annotated as rhodanese-like domain-containing protein (LT988_07780, LT988_09460, LT988_12845, LT988_16050, LT988_19985, LT988_23355, and LT988_24255), some of which show similarity with rhodanese genes from Alc. vinosum DSM 180T. None of these proteins from T. bogorovii BBS have been assigned a function according to KEGG Orthology. Previously, the product of the Rhd_2599 gene (Sulfurtransferase Alvin_2599, rhodanese-like protein) has been experimentally shown to serve as a sulfur vehicle and to participate in sulfur transfer involved in oxidative-dissimilatory sulfur metabolism [71]. In Alc. vinosum, this protein provides sulfur mobilization and the transfer of sulfur from a low-molecular-weight thiol (probably from glutathion) to the TusA protein (Alvin_2600); TusA serves as a sulfur donor for DsrEFH (genes Alvin_1253, Alvin_1254, and Alvin_1255), which in its turn perform the persulfation of DsrC (Alvin_1256); persulfated DsrC is likely to serve as a direct substrate for reverse sulfite reductase DsrAB. Rhd_2599, TusA, and DsrE2 in Alc. vinosum DSM 180T have been shown to bind sulfur atoms via conserved cysteine residues.
The Dsr proteins of Alc. vinosum DSM 180T are encoded by the same gene cluster, dsrABEFHCMKLJOPNRS, which is located downstream of Alvin_1251 and upstream of Alvin_1265 and Alvin_2601 (DsrE2). T. bogorovii BBS has genes dsrABEFHCMKLJOPNRS (located in from LT988_06665 to LT988_06595 in the genome), but the only genes annotated in the same manner are dsrA (LT988_06665) and dsrB (LT988_06660); the other genes were identified using the tBlastn algorithm (Table 9). Furthermore, the genome contains several more genes annotated as TusE/DsrC/DsvC family sulfur relay protein (LT988_03825, LT988_03875, LT988_06640, LT988_06690, LT988_16185, LT988_16425, and LT988_19515) according to GenBank.

Table 9.
Genes encoding Dsr proteins of T. bogorovii BBS and Alc. vinosum DSM 180T.
The results obtained were compared with the data on the possible pathways of sulfate oxidation in purple sulfur bacteria summarized in the reviews [61]. Figure 3 shows the scheme demonstrating the reactions of sulfur metabolism that were revealed in T. bogorovii BBS at a genomic level.
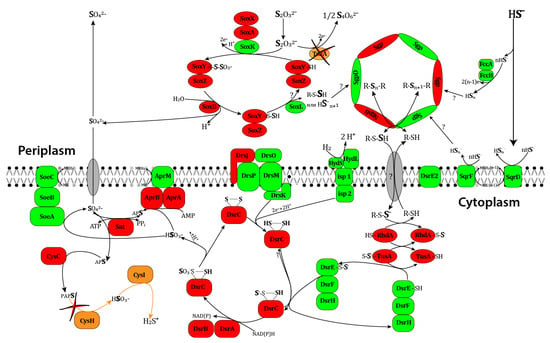
Figure 3.
The scheme of sulfur metabolic pathways in purple non-sulfur bacteria. The proteins encoded by genes from the annotated sequence of T. bogorovii BBS with names different from those in Alc. vinosum DSM 180T are shown in red; the proteins with the same names are shown in green; the proteins absent in T. bogorovii BBS are shown in brown; currently unidentified proteins are shown in gray.
4. Conclusions
The phototrophic purple sulfur bacterium T. bogorovii BBS belonging to the Chromatiaceae family was isolated from the White Sea Estuary in 1969 [1]. In this work, we have obtained, assembled, and published the whole genome of T. bogorovii BBS (GenBank: CP089309.1). Analysis of the genome sequence allowed us to validate the systematic position of the bacteria and to confirm the appropriateness of classifying it as a new typical species of the genus Thiocapsa, as proposed by Tourova et al. [31].
Some genes involved in pigment synthesis in T. roseopersicina BBS have been described previously, but identification of genes outside the genomic DNA fragment examined by the authors was required. Through mining the whole genome of T bogorovii sequence, we found eleven additional genes coding proteins involved in pigment biosynthesis.
We employed the functional gene annotation capabilities of the KEGG database, the Subsystem Technology software for genome analysis (RAST; version 2.0), performed a comparative analysis with the genome of the purple bacterium Alc. vinosum DSM 180T, and manually searched for several genes using the tBlastn algorithm. As a result, we both located and functionally characterized the genes in the genomic DNA that determine the function of central metabolic pathways in T. bogorovii BBS. Two copies of the RuBisCO green-like form I genes allow RuBisCO-mediated CO2 fixation in this bacterium. The genes are located far apart and have different neighborhoods. In one case, the gene is flanked by the genes encoding RuBisCO activation proteins. In the other case, the genes encoding carboxysome proteins and the regulator of the RuBisCO operon transcription are located downstream of the RuBisCO structural genes. Along with concentrating CO2, carboxysomes protect RuBisCO from O2, as O2 can compete with CO2. However, there is no information in the pertinent literature about carboxysomes in bacterial cells. The genome of the bacterium under scrutiny also contains a gene belonging to the type IV RuBisCO-like proteins that is not involved in CO2 fixation. According to the KEGG Pathway database, T. bogorovii BBS has all of the genes encoding the enzymes that are required for the TCA and glyoxylate cycles.
In earlier works, T. bogorovii BBS was demonstrated to have the reductive TCA cycle, which is supported by the genomic data in this present work. The cycle is open due to the absence of the enzymes required to substitute for irreversible citrate synthase from the oxidizing TCA cycle.
The T. bogorovii BBS genome contains the genes from the Embde–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway, pyruvate oxidation, and gluconeogenesis for the synthesis and conversion of carbohydrates to phoshoenolpyruvate, pyruvate, and acetyl-CoA. The Entner–Doudoroff pathway has no genetic potential in T. bogorovii BBS.
We manually searched for hydrogenase genes and determined their locations in the bacterial genome. These are in full accordance with previously published data.
We have identified the genes for the cytochromes bd and cbb3 of oxidases required for chemotrophic growth of the bacteria in the presence of oxygen.
The ability to fix atmospheric molecular nitrogen is ensured by the existence of genes for the Mo-containing nitrogenase complex nifHDK.
T. bogorovii BBS lacks some of the genes required for the assimilatory nitrate reduction, denitrification, and nitrification. However, it has the potential for dissimilatory nitrate reduction. This finding is new and not supported by previous biochemical data.
It is known that HydSL hydrogenase from T. bogorovii BBS can be simply immobilized on carbon electrodes with proper orientation between a distal FeS cluster and an electrode and the production of high current densities [72]. Taking into account the fact that that this hydrogenase is stable and can work even at 70°C, one can conclude that it is a very promising enzyme for use in enzymatic hydrogenase electrodes. Several schemes of HydSL hydrogenase participation in metabolism of T. bogorovii BBS exist [14,66,73]. All of them indicate that HydSL hydrogenase in purple bacteria is closely connected with sulfur metabolism but, unfortunately, none of them took into account all valid experimental data. We have genetically analyzed the sulfur metabolism of T. bogorovii BBS and compared it with the most studied sulfur metabolism of Alc. vinosum [66]. This knowledge is important for understanding the mechanisms involved in electron transfer between hydrogenases and native partners. The automatic annotation of the whole genome of the bacteria T. bogorovii BBS was refined and the genomic positions of several studied genes, including those involved in sulfur metabolism, were localized. The bacterium has no genetic potential for assimilatory sulfate reduction, but it has the genes required for dissimilatory sulfate reduction and thiosulphate oxidation by the SOX-complex. Figure 3 shows a scheme demonstrating the reactions of sulfur metabolism revealed in T. bogorovii BBS at a genomic level.
The functional potential of central metabolic pathways identified at the genome level in the bacterium undoubtedly requires further experiments to confirm their activity at the transcriptional and enzymatic levels. Some gene sequences are present in the T. bogorovii BBS genome in several copies. Further research is required to confirm the functions of the proteins encoded by the identified genes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.P. and A.T.; methodology, E.P., M.K., Y.D., A.B. and E.G.; validation, E.P., Y.D. and M.K.; formal analysis, E.P., M.K., Y.D. and E.M.; investigation, E.P., M.K., E.M., Y.D., E.F., A.B. and E.G.; writing—original draft preparation, E.P., Y.D. and A.T.; writing—review and editing, E.P., M.K. and A.T.; visualization, E.P., M.K. and Y.D.; supervision, A.T.; project administration, E.P., Y.D. and A.T.; funding acquisition, A.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was performed within the framework of the state assignment no. 122041200039-0 and was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, grant number 19-14-00255P, https://rscf.ru/project/19-14-00255/ accessed on 1 June 2023.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in financial or any other sphere.
Abbreviations
| Aa, aa—amino acids |
| Alc. vinosum—Allochromatium vinosum |
| ANI—Average Nucleotide Identity |
| ATCC—American Type Culture Collection |
| ATP—adenosine triphosphate |
| bp—base pairs |
| CRISPR—clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats |
| DDH—digital DNA-DNA hybridization parameter |
| DNA—deoxyribonucleic acid |
| e-value—the expectation value |
| FAD—flavin adenine dinucleotide |
| FccAB—flavocytochrome c sulfide dehydrogenase |
| FCSD—flavocytochrome c sulfide dehydrogenase |
| GC content—guanine-cytosine content |
| HiPIP—High potential iron–sulfur protein |
| kbp—kilobase pairs |
| kDa—kilodalton |
| KEGG—Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| LH—light-harvesting antenna complex |
| LPSN—List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature |
| Mb—megabase |
| Mo-containing—molybdenum-containing |
| NAD—nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
| NAD+—the oxidized form |
| NADH—the reduced form |
| NADP—nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate |
| NAD(P)H—the reduced form |
| ncRNAs—non-coding RNA |
| ONT—Oxford Nanopore Technologies |
| PEP—phosphoenolpyruvate |
| PRK—Phosphoribulokinase |
| PTS—phosphotransferase system |
| PufX—intrinsic membrane protein |
| RC—reaction center |
| Rhd—rhodanese-like protein |
| RLP—RubisCO-like protein |
| RNA—ribonucleic acid |
| rRNA—ribosomal RNA |
| rTCA—reductive tricarboxylic acid cycle |
| RuBisCO—Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase |
| SBP—Sedoheptulose-bisphosphatase |
| Sgp—sulfur globule proteins |
| Sox system—sulfur oxidation system |
| SQR—sulfide/quinone oxidoreductase |
| T. bogorovii—Thiocapsa bogorovii |
| T. imhoffii—Thiocapsa imhoffii |
| T. marina—Thiocapsa marina |
| T. rosea—Thiocapsa rosea |
| T. roseopersicina—Thiocapsa roseopersicina |
| TCA cycle—the tricarboxylic acid cycle |
| tRNA—transfer RNA |
| TsdA—tetrathionate reductase |
References
- Bogorov, L.V. The Properties of Thiocapsa Roseopersicina, Strain BBS, Isolated from an Estuary of the White Sea. Mikrobiologiia 1974, 43, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kondratieva, E.N.; Zhukov, V.G.; Ivanovsky, R.N.; Petushkova, Y.P.; Monosov, E.Z. The Capacity of Phototrophic Sulfur Bacterium Thiocapsa Roseopersicina for Chemosynthesis. Arch. Microbiol. 1976, 108, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhukov, V.G. Formation of Ribuloso-1,5-Diphosphate Carboxylase by Thiocapsa Roseopersicina under Different Growth Conditions. Mikrobiologiia 1976, 45, 915–917. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Petushkova, I.P.; Ivanovskiĭ, R.N. Enzymes Involved in Thiosulfate Metabolism in Thiocapsa Roseopersicina under Various Conditions of Growth. Mikrobiologiia 1976, 45, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Petushkova, Y.P.; Ivanovsky, R.N. Sulphite Oxidation by Thiocapsa Roseopersicina (Russian). Mikrobiologiya 1976, 45, 592–597. [Google Scholar]
- Gogotov, I.N. Hydrogenases of Phototrophic Microorganisms. Biochimie 1986, 68, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondratieva, E.N.; Ivanovsky, R.N.; Krasilnikova, E.N. Light and Dark Metabolism in Purpule Sulfur Bacteria. Sov. Sci. Rev. 1981, 13, 325–364. [Google Scholar]
- Kovács, A.T.; Rákhely, G.; Kovács, K.L. Genes Involved in the Biosynthesis of Photosynthetic Pigments in the Purple Sulfur Photosynthetic Bacterium Thiocapsa Roseopersicina. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 3093–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, K.L.; Kovács, Á.T.; Maróti, G.; Mészáros, L.S.; Balogh, J.; Latinovics, D.; Fülöp, A.; Dávid, R.; Dorogházi, E.; Rákhely, G. The Hydrogenases of Thiocapsa roseopersicina. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005, 33, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurinavichene, T.V.; Rákhely, G.; Kovács, K.L.; Tsygankov, A.A. The Effect of Sulfur Compounds on H2 Evolution/Consumption Reactions, Mediated by Various Hydrogenases, in the Purple Sulfur Bacterium, Thiocapsa Roseopersicina. Arch. Microbiol. 2007, 188, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palágyi-Mészáros, L.S.; Maróti, J.; Latinovics, D.; Balogh, T.; Klement, E.; Medzihradszky, K.F.; Rákhely, G.; Kovács, K.L. Electron-Transfer Subunits of the NiFe Hydrogenases in Thiocapsa Roseopersicina BBS. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maróti, G.; Fodor, B.D.; Rákhely, G.; Kovács, Á.T.; Arvani, S.; Kovács, K.L. Accessory Proteins Functioning Selectively and Pleiotropically in the Biosynthesis of [Nife] Hydrogenases in Thiocapsa Roseoporsicina. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 2218–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maróti, J.; Farkas, A.; Nagy, I.K.; Maróti, G.; Kondorosi, É.; Rákhely, G.; Kovács, K.L. A Second Soluble Hox-Type NiFe Enzyme Completes the Hydrosenase Set in Thiocapsa Roseopersicina BBS. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 5113–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tengölics, R.; Mészáros, L.; Gyori, E.; Doffkay, Z.; Kovács, K.L.; Rákhely, G. Connection between the Membrane Electron Transport System and Hyn Hydrogenase in the Purple Sulfur Bacterium, Thiocapsa Roseopersicina BBS. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2014, 1837, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolmogorov, M.; Yuan, J.; Lin, Y.; Pevzner, P.A. Assembly of Long, Error-Prone Reads Using Repeat Graphs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast Gapped-Read Alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An Integrated Tool for Comprehensive Microbial Variant Detection and Genome Assembly Improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, I.; Stephen, G.; Bayer, M.; Cock, P.J.A.; Pritchard, L.; Cardle, L.; Shawand, P.D.; Marshall, D. Using Tablet for Visual Exploration of Second-Generation Sequencing Data. Brief. Bioinform. 2013, 14, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid Prokaryotic Genome Annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid Annotations Using Subsystems Technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertels, F.; Silander, O.K.; Pachkov, M.; Rainey, P.B.; Van Nimwegen, E. Automated Reconstruction of Whole-Genome Phylogenies from Short-Sequence Reads. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carver, T.; Thomson, N.; Bleasby, A.; Berriman, M.; Parkhill, J. DNAPlotter: Circular and Linear Interactive Genome Visualization. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 119–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.H.; Ha, S.M.; Lim, J.; Kwon, S.; Chun, J. A Large-Scale Evaluation of Algorithms to Calculate Average Nucleotide Identity. Antonie Leeuwenhoek Int. J. Gen. Mol. Microbiol. 2017, 110, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Auch, A.F.; Klenk, H.P.; Göker, M. Genome Sequence-Based Species Delimitation with Confidence Intervals and Improved Distance Functions. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Sato, Y.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG for Integration and Interpretation of Large-Scale Molecular Data Sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D109–D114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernikos, G.S.; Parkhill, J. Interpolated Variable Order Motifs for Identification of Horizontally Acquired DNA: Revisiting the Salmonella Pathogenicity Islands. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2196–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couvin, D.; Bernheim, A.; Toffano-Nioche, C.; Touchon, M.; Michalik, J.; Néron, B.; Rocha, E.P.C.; Vergnaud, G.; Gautheret, D.; Pourcel, C. CRISPRCasFinder, an Update of CRISRFinder, Includes a Portable Version, Enhanced Performance and Integrates Search for Cas Proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W246–W251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A New Generation of Protein Database Search Programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: A Hub for Protein Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D204–D212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourova, T.P.; Keppen, O.I.; Kovaleva, O.L.; Slobodova, N.V.; Berg, I.A.; Ivanovsky, R.N. Phylogenetic Characterization of the Purple Sulfur Bacterium Thiocapsa Sp. BBS by Analysis of the 16S RRNA, CbbL, and NifH Genes and Its Description as Thiocapsa bogorovii sp. nov., a New Species. Microbiology 2009, 78, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissgerber, T.; Zigann, R.; Bruce, D.; Chang, Y.J.; Detter, J.C.; Han, C.; Hauser, L.; Jeffries, C.D.; Land, M.; Munk, C.; et al. Complete Genome Sequence of Allochromatium Vinosum DSM 180T. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2011, 5, 311–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchane, S.; Picaud, M.; Vernotte, C.; Astier, C. Photooxidative Stress Stimulates Illegitimate Recombination and Mutability in Carotenoid-Less Mutants of Rubrivivax Gelatinosus. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 4777–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, B.; Lunceford, C.; Lin, S.; Woronowicz, K.; Niederman, R.A.; Woodbury, N.W. Energy Transfer Properties of Rhodobacter Sphaeroides Chromatophores during Adaptation to Low Light Intensity. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 17133–17141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogdell, R.J.; Roszak, A.W. Structural Biology: The Purple Heart of Photosynthesis. Nature 2014, 508, 196–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, P.; Papiz, M.Z.; Jackson, P.J.; Brindley, A.A.; Ng, I.W.; Olsen, J.D.; Dickman, M.J.; Bullough, P.A.; Hunter, C.N. Three-Dimensional Structure of the Rhodobacter Sphaeroides Rc-Lh1-Pufx Complex: Dimerization and Quinone Channels Promoted by PufX. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 7575–7585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roszak, A.W.; Howard, T.D.; Southall, J.; Gardiner, A.T.; Law, C.J.; Isaacs, N.W.; Cogdell, R.J. Crystal Structure of the RC-LH1 Core Complex from Rhodopseudomonas Palustris. Science 2003, 302, 1969–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, S.; Yu, L.J.; Takeda, K.; Hirano, Y.; Kawakami, T.; Wang-Otomo, Z.Y.; Miki, K. Structure of the LH1-RC Complex from Thermochromatium Tepidum at 3.0 Å. Nature 2014, 508, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.N.; Bracun, L.; Li, M. Structural Diversity and Modularity of Photosynthetic RC−LH1 Complexes. Trends Microbiol. 2023, 32, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabita, F.R. The Biochemistry and Metabolic Regulation of Carbon Metabolism and CO2 Fixation in Purple Bacteria. In Anoxygenic Photosynthetic Bacteria; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, Germany, 1995; pp. 885–914. [Google Scholar]
- McFadden, B.A.; Shively, L.M. Variations in Autotrophic Life; Academic Press: London, UK, 1991; pp. 25–49. [Google Scholar]
- Tabita, F.R.; Hanson, T.E.; Li, H.; Satagopan, S.; Singh, J.; Chan, S. Function, Structure, and Evolution of the RubisCO-Like Proteins and Their RubisCO Homologs. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 576–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, T.E.; Tabita, F.R. Insights into the Stress Response and Sulfur Metabolism Revealed by Proteome Analysis of a Chlorobium Tepidum Mutant Lacking the Rubisco-like Protein. Photosynth. Res. 2003, 78, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, T.E.; Tabita, F.R. A Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase (RubisCO)-like Protein from Chlorobium Tepidum That Is Involved with Sulfur Metabolism and the Response to Oxidative Stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4397–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badger, M.R.; Bek, E.J. Multiple Rubisco Forms in Proteobacteria: Their Functional Significance in Relation to CO2 Acquisition by the CBB Cycle. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 1525–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purohit, K.; McFadden, B.A. Ribulose 1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase and Oxygenase from Thiocapsa Roseopersicina: Activation and Catalysis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1979, 194, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badger, M.R.; Price, G.D. CO2 Concentrating Mechanisms in Cyanobacteria: Molecular Components, Their Diversity and Evolution. J. Exp. Bot. 2003, 54, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerfeld, C.A.; Sawaya, M.R.; Tanaka, S.; Nguyen, C.V.; Phillips, M.; Beeby, M.; Yeates, T.O. Microbiology: Protein Structures Forming the Shell of Primitive Bacterial Organelles. Science 2005, 309, 936–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondratieva, E.N. Interrelation between Modes of Carbon Assimilation and Energy Production in Phototropic Purple and Green Bacteria. Int. Rev. Biochem. 1979, 21, 117–175. [Google Scholar]
- Takai, K.; Campbell, B.J.; Cary, S.C.; Suzuki, M.; Oida, H.; Nunoura, T.; Hirayama, H.; Nakagawa, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Inagaki, F.; et al. Enzymatic and Genetic Characterization of Carbon and Energy Metabolisms by Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Chemolithoautotrophic Isolates of Epsilonproteobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 7310–7320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoshima, M.; Ishii, M.; Igarashi, Y. A Novel Enzyme, Citryl-CoA Synthetase, Catalysing the First Step of the Citrate Cleavage Reaction in Hydrogenobacter Thermophilus TK-6. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 52, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignais, P.M.; Billoud, B.; Meyer, J. Classification and Phylogeny of Hydrogenases. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 25, 455–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.W.W.; Mortenson, L.E.; Chen, J.-S. Hydrogenase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Rev. Bioenerg. 1980, 594, 105–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, D.; Pedersen, C.N.S.; Greening, C. HydDB: A Web Tool for Hydrogenase Classification and Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, srep34212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colbeau, A.; Kovacs, K.L.; Chabert, J.; Vignais, P.M. Cloning and Sequences of the Structural (HupSLC) and Accessory (HupDHI) Genes for Hydrogenase Biosynthesis in Thiocapsa Roseopersicina. Gene 1994, 140, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fodor, B.; Rákhely, G.; Kovács, Á.T.; Kovács, K.L. Transposon Mutagenesis in Purple Sulfur Photosynthetic Bacteria: Identification of HypF, Encoding a Protein Capable of Processing [NiFe] Hydrogenases in α, β, and γ Subdivisions of the Proteobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 2476–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kovács, K.L.; Fodor, B.; Kovács, Á.T.; Csanádi, G.; Maróti, G.; Balogh, J.; Arvani, S.; Rákhely, G. Hydrogenases, Accessory Genes and the Regulation of [NiFe] Hydrogenase Biosynthesis in Thiocapsa Roseopersicina. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2002, 27, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogotov, I.N.; Zorin, N.A.; Serebriakova, L.T.; Kondratieva, E.N. The Properties of Hydrogenase from Thiocapsa Roseopersicina. BBA—Enzymol. 1978, 523, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagyinka, C.; Zorin, N.A.; Kovács, K.L. Unconsidered Factors Affecting Hydrogenase Activity Measurement. Anal. Biochem. 1984, 142, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, Á.T.; Rákhely, G.; Balogh, J.; Maróti, G.; Cournac, L.; Carrier, P.; Mészáros, L.S.; Peltier, G.; Kovàcs, K.L. Hydrogen Independent Expression of HupSL Genes in Thiocapsa Roseopersicina BBS. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 4807–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rákhely, G.; Kovács, Á.T.; Maróti, G.; Fodor, B.D.; Csanádi, G.; Latinovics, D.; Kovács, K.L. Cyanobacterial-Type, Heteropentameric, NAD+-Reducing NiFe Hydrogenase in the Purple Sulfur Photosynthetic Bacterium Thiocapsa Roseopersicina. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rákhely, G.; Laurinavichene, T.V.; Tsygankov, A.A.; Kovács, K.L. The Role of Hox Hydrogenase in the H2 Metabolism of Thiocapsa Roseopersicina. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2007, 1767, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Meuer, J.; Bartoschek, S.; Koch, J.; Künkel, A.; Hedderich, R. Purification and Catalytic Properties of Ech Hydrogenase from Methanosarcina Barkeri. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 265, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincturk, H.B.; Demir, V.; Aykanat, T. Bd Oxidase Homologue of Photosynthetic Purple Sulfur Bacterium Allochromatium Vinosum Is Co-Transcribed with a Nitrogen Fixation Related Gene. Antonie Leeuwenhoek Int. J. Gen. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 99, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madigan, M.T. Microbiology of nitrogen fixation by anoxygenic photosynthetic bacteria. In Anoxygenic Photosynthetic Bacteria. Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration; Blankenship, R.E., Madigan, M.T., Bauer, C.E., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, Germany, 1995; Volume 2, pp. 915–928. [Google Scholar]
- Dahl, C. Sulfur Metabolism in Phototrophic Bacteria. In Modern Topics in the Phototrophic Prokaryotes; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 27–66. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, J.A.; Denkmann, K.; Pereira, I.S.A.C.; Archer, M.; Dahl, C. Thiosulfate Dehydrogenase (TsdA) from Allochromatium Vinosum: Structural and Functional Insights into Thiosulfate Oxidation. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 9222–9238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brune, D.C. Isolation and Characterization of Sulfur Globule Proteins from Chromatium Vinosum and Thiocapsa Roseopersicina. Arch. Microbiol. 1995, 163, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prange, A.; Dahl, C.; Trüper, H.G.; Chauvistré, R.; Modrow, H.; Hormes, J. X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy of Bacterial Sulfur Globules: A Detailed Reply. Microbiology 2002, 148, 2268–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigaard, N.U.; Dahl, C. Sulfur metabolism in phototrophic sulfur bacteria. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2009, 54, 103–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stockdreher, Y.; Sturm, M.; Josten, M.; Sahl, H.G.; Dobler, N.; Zigann, R.; Dahl, C. New Proteins Involved in Sulfur Trafficking in the Cytoplasm of Allochromatium Vinosum. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 12390–12403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsygankov, A.A.; Zorin, N.A.; Starodubov, A.S.; Khasimov, M.K.; Melnikova, M.S.; Doronin, I.A.; Vasilov, R.G. A Simple Method for Oriented Immobilization of HydSL Hydrogenase of Thiocapsa Bogorovii on Carbon Electrodes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2023, 48, 39989–39999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsygankov, A.A.; Khusnutdinova, A.N. Hydrogen in Metabolism of Purple Bacteria and Prospects of Practical Application. Microbiology 2015, 84, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).