Genomic Features and Phylogenetic Analysis of Antimicrobial-Resistant Salmonella Mbandaka ST413 Strains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS)
2.3. Downstream Bioinformatic Analyses
2.4. Data Availability and Accession Numbers
3. Results
3.1. Genome Assembly, Genome Annotation, and MLST
3.2. Antimicrobial Resistance Determinants
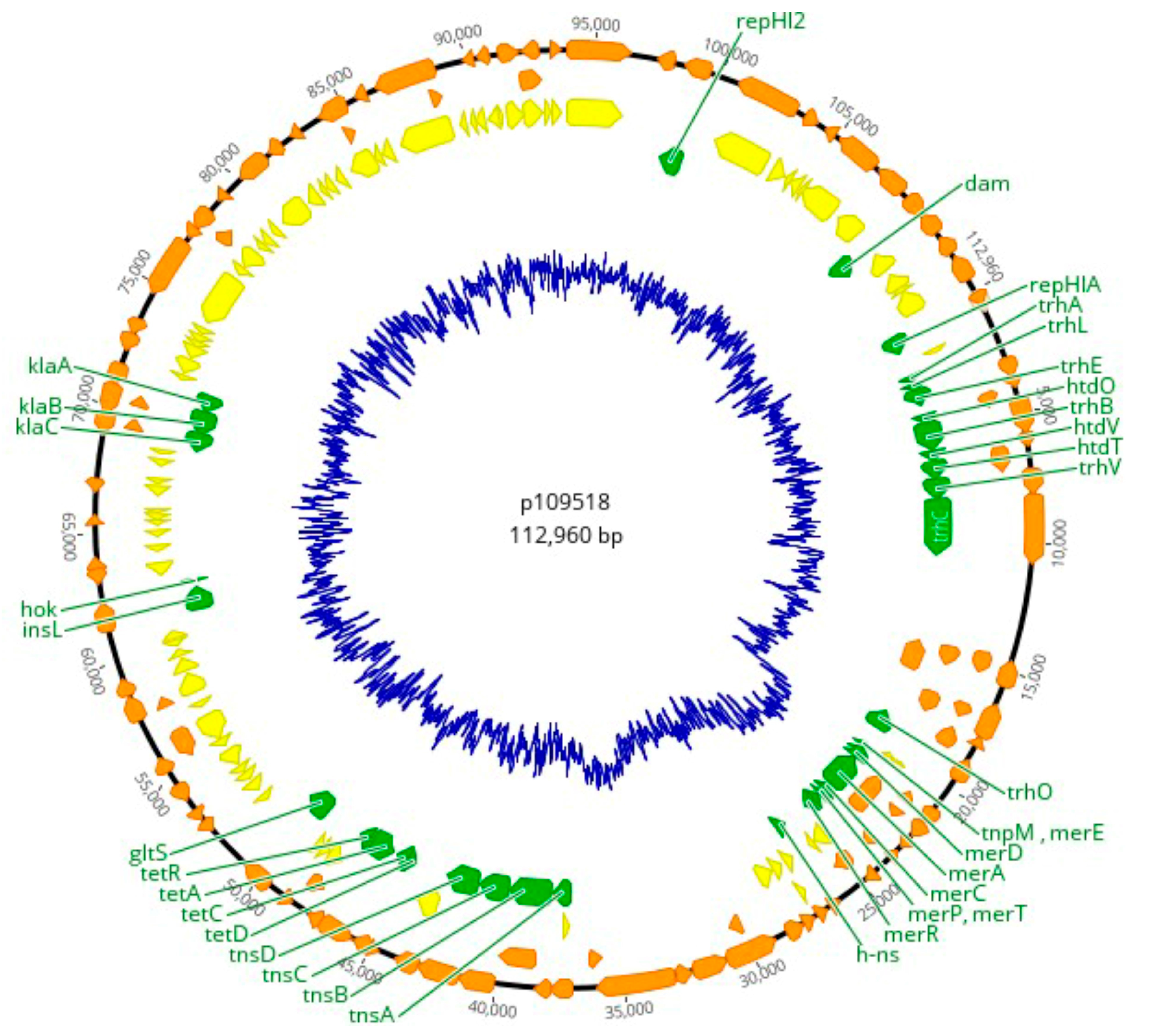
3.3. Plasmid Replicons and Homology to Published Plasmid Sequences
3.4. Analysis of SPIs and Virulence Determinants
3.5. Prophage Regions in Genomes of S. Mbandaka
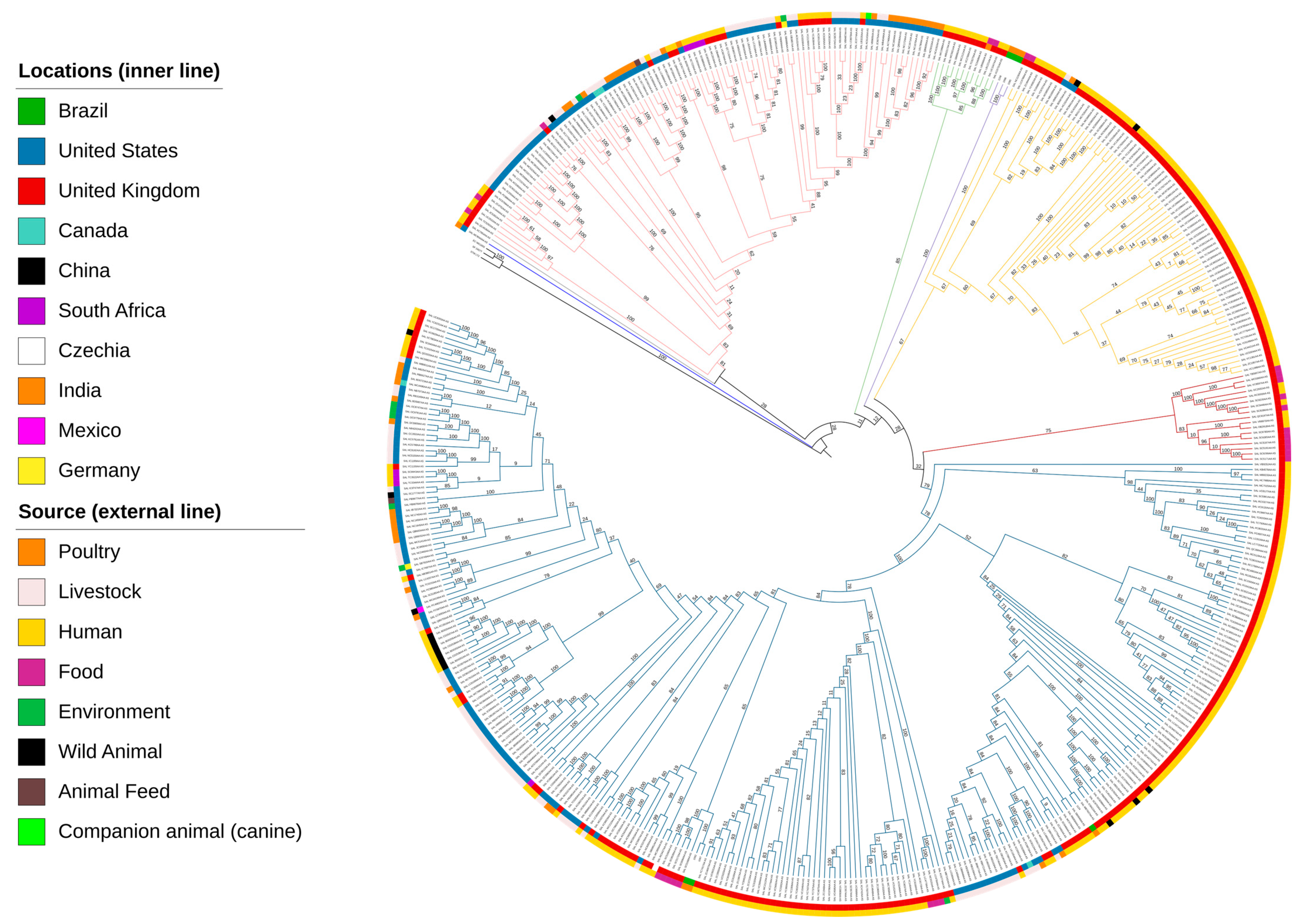
3.6. Phylogenetic Insights into S. Mbandaka
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fouladkhah, A.C.; Thompson, B.; Camp, J.S. Safety of Food and Water Supplies in the Landscape of Changing Climate. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Plain Language Summary on The European Union One Health 2022 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2023, 21, 211202. [Google Scholar]
- Issenhuth-Jeanjean, S.; Roggentin, P.; Mikoleit, M.; Guibourdenche, M.; De Pinna, E.; Nair, S.; Fields, P.I.; Weill, F.X. Supplement 2008-2010 (n. 48) to the White-Kauffann-Le Minor scheme. Res. Microbiol. 2014, 165, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, R.G.; Rosario, D.K.A.; Cunha-Neto, A.; Mano, S.B.; Figueiredo, E.E.S.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Worldwide Epidemiology of Salmonella Serovars in Animal Based Foods: A Meta-analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e00591-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zancan, F.T.; Berchieri Junior, A.; Fernandes, S.A.; Gama, N.M.S.Q. Salmonella spp. investigation in transport boxes of day-old birds. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2000, 31, 230–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanaway, J.D.; Parisi, A.; Sarkar, K.; Blacker, B.F.; Reiner, R.C.; Hay, S.I.; Nixon, M.R.; Dolecek, C.; James, S.L.; Mokdad, A.H.; et al. The global burden of non-typhoidal Salmonella invasive disease: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1312–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). European Food Safety Authority. Multi-Country Outbreak of Salmonella Mbandaka ST413, Possibly Linked to Consumption of Chicken Meat in the EU/EEA, Israel and the UK. 2022. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/multi-country-outbreak-Salmonella-mbandaka-st413-possibly-linked-consumption (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Berchieri Junior, A.; Paulillo, A.C.; Fernandes, A.S.; Irino, K.; Pessoa, G.V.A. Sensibilidade a antimicrobianos por Salmonella isolados de farinhas de origem animal utilizados no preparo de rações. Rev. Microbiol. 1985, 16, 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Keaton, A.A.; Schwensohn, C.A.; Brandenburg, J.M.; Pereira, E.; Adcock, B.; Tecle, S.; Hinnenkamp, R.; Havens, J.; Bailey, K.; Applegate, B.; et al. Multistate outbreak of Salmonella Mbandaka infections linked to sweetened puffed wheat cereal—United States, 2018. Epidemiol. Infect. 2022, 150, e135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoszowski, A.; Zając, M.; Lalak, A.; Przemyk, P.; Wasyl, D. Fifteen years of successful spread of Salmonella enterica serovar Mbandaka clone ST413 in Poland and its public health consequences. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2016, 23, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, H.; Zheng, S.; Wang, Z.; Sheng, H.; Shi, C.; Shi, X.; Niu, Q.; Yang, B. Prevalence, serotype, antibiotic susceptibility, and genotype of Salmonella in eggs from poultry farms and marketplaces in Yangling, Shaanxi Province, China. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, L.; Fenske, G.; Kaushik, S.R.; Nagaraja, T.G.; Thomas, M.; Scaria, J. Population structure of Salmonella enterica serotype Mbandaka reveals similar virulence potential irrespective of source and phylogenomic stratification. F1000Research 2020, 16, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benevides, V.P.; Rubio, M.S.; Rodrigues Alves, L.B.; Barbosa, F.O.; Souza, A.I.S.; Almeida, A.M.; Casas, M.R.T.; Guastalli, E.A.L.; Soares, N.M.; Berchieri Junior, A. Anti-microbial resistance in Salmonella serovars isolated from an egg-producing region in Brazil. Braz. J. Poult. Sci. 2020, 22, 001–010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High throughput Sequence Data. 2010. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Melhor, A.A.; DeJongh, H.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Vidro, E.M.; Kubal, H.; et al. The RAST server: Rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Yin, Y.; Jones, M.B.; Zhang, Z.; Kaiser, B.L.D.; Dinsmore, B.A.; Fitzgerald, C.; Fields, P.I.; Deng, X. Salmonella serotype determination utilizing high-throughput genome sequencing data. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, M.; Cosentino, S.; Rasmussen, S.; Rundsten, C.; Hasman, H.; Marvig, R.; Jelsbak, L.; Sicheritz-Pontén, T.; Ussery, D.; Aarestrup, F.; et al. Multilocus Sequence Typing of Total-Genome-Sequenced Bacteria. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achtman, M.; Wain, J.; Weill, F.X.; Nair, S.; Zhou, Z.; Sangal, V.; Krauland, M.G.; Hale, J.L.; Harbottle, H.; Uesbeck, A.; et al. Multilocus sequence typing as a replacement for serotyping in Salmonella enterica. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 16, e1009040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roer, L.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Lukjancenko, O.; Kaas, R.S.; Hasman, H.; Aarestrup, F.M. Is the Evolution of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica linked to restriction-modification systems? mSystems 2016, 1, e00009-16. [Google Scholar]
- Alikhan, N.F.; Petty, N.K.; Zakour, N.L.B.; Beatson, S.A. BLAST ring image generator (BRIG): Simple prokaryote genome comparisons. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkau, A.; Stuart-Edwards, M.; Stothard, P.; van Domselaar, G. Interactive microbial genome visualization with GView. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 3125–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouy, M.; Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. SeaView Version 4: A multiplatform graphical user interface for sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree building. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geneious Prime® (2023.1.2). 2023. Available online: https://www.geneious.com (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Chen, L.H.; Yang, J.; Yu, J.; Yao, Z.J.; Sun, L.L.; Shen, Y.; Jin, Q. VFDB: A reference database for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D325–D328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zankari, E.; Hasman, H.; Cosentino, S.; Vestergaard, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Larsen, M.V. Identification of acquired antimicrobial resistance genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; Garcia-Fernandez, A.; Larsen, M.V. In silico detection and typing of Plasmids using PlasmidFinder and Plasmid Multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 02412–02414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndt, D.; Grant, J.; Marcu, A.; Sajed, T.; Pon, A.; Liang, Y.; Wishart, D.S. PHASTER: A better, faster version of the PHAST phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W16–W21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Liang, Y.; Lynch, K.H.; Dennis, J.J.; Wishart, D.S. PHAST: A fast phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W347–W352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, A.C.; Mau, B.; Blattner, F.R.; Perna, N.T. Mauve: Multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikhan, N.F.; Zhou, Z.; Sergeant, M.J.; Achtman, M. A genomic overview of the population structure of Salmonella. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achtman, M.; Zhou, Z.; Alikhan, N.F.; Tyne, W.; Parkhill, J.; Cormican, M.; Chiou, C.S.; Torpdahl, M.; Litrup, E.; Prendergast, D.M.; et al. Genomic diversity of Salmonella enterica—The UoWUCC 10K genomes project. Wellcome Open Res. 2020, 5, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.G.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid Large-Scale Prokaryote Pan Genome Analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the Ultrafast Bootstrap Approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods. 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza Violante, M.; Michel, V.; Romero, K.; Bonifait, L.; Baugé, L.; Perrin-Guyomard, A.; Feurer, C.; Radomski, N.; Mallet, L.; Mistou, M.Y.; et al. Tell me if you prefer bovine or poultry sectors and I’ll tell you who you are: Characterization of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Mbandaka France. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1130891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Melo, A.N.F.; Monte, D.F.M.; de Souza Pedrosa, G.T.; Balkey, M.; Jin, Q.; Brown, E.; Allard, M.; de Oliveira, T.C.R.M.; Cao, G.; Magnani, M.; et al. Genomic investigation of antimicrobial resistance determinants and virulence factors in Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from contaminated food and human stool samples in Brazil. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 343, 109091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.A. Salmonella infections in immunocompromised adults. J. Infect. 2008, 56, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickter, J.K.; Cai, L.; Snyder, D.S. Endocarditis following Consumption of Cereal Associated with Salmonella enterica Subtype Mbandaka Outbreak. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2019, 27, 5464230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Qazi, I.H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, G.; Han, H. Salmonella virulence and immune escape. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rychlik, I.; Karasova, D.; Sebkova, A.; Volf, J.; Sisak, F.; Havlickova, H.; Kummer, V. Virulence potential of five major pathogenicity islands (SPI-1 to SPI-5) of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis for chickens. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraiva, M.M.S.; Benevides, V.P.; da Silva, N.M.V.; Varani, A.M.; de Freitas Neto, O.C.; Berchieri Junior, A.; Delgado-Suárez, E.J.; Rocha, A.D.L.; Eguale, T.; Munyalo, J.A.; et al. Genomic and Evolutionary Analysis of Salmonella enterica Serovar Kentucky Sequence Type 198 Isolated from Livestock in East Africa. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 772829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.; Mylona, E.; Frankel, G. Typhoidal Salmonella: Distinctive virulence factors and pathogenesis. Cell. Microbiol. 2018, 20, e12939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hensel, M.; Shea, J.E.; Waterman, S.R.; Mundy, R.; Nikolaus, T.; Banks, G.; Vazquez-Torres, A.; Gleeson, C.; Fang, F.C.; Holden, D.W. Genes encoding putative effector proteins of the type III secretion system of Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 are required for bacterial virulence and proliferation in macrophages. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 30, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Albert, J.; Mundy, R.; Yu, X.; Beuzón, C.R.; Holden, D.W. SseA is a chaperone for the SseB and SseD translocon components of the Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 encoded type III secretion system. Microbiology 2003, 149, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanc-Potard, A.B.; Solomon, F.; Kayser, J.; Groisman, E.A. The SPI-3 pathogenicity island of Salmonella enterica. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, M.N.; Yaghi, J.; El Khoury, A.; Felten, A.; Mistou, M.Y.; Atoui, A.; Radomski, N. Prediction of Salmonella serovars isolated from clinical and food matrices in Lebanon and genomic-based investigation focusing on Enteritidis serovar. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 333, 108831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaux, M.L.; D’Alessandro, B.; Vignoli, R.; Fraga, M. Phenotypic and genotypic survey of antibiotic resistance in Salmonella enterica isolates from dairy farms in Uruguay. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1055432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 33rd ed.; CLSI Supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pavelquesi, S.L.S.; de Oliveira Ferreira, A.C.A.; Rodrigues, A.R.M.; de Souza Silva, C.M.; Orsi, D.C.; da Silva, I.C.R. Presence of tetracycline and sulfonamide resistance genes in Salmonella spp.: Literature review. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMillan, E.A.; Jackson, C.R.; Frye, J.G. Transferable Plasmids of Salmonella enterica Associated with Antibiotic Resistance Genes. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 8, 562181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEwen, S.A.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J. Antimicrobial Use and Resistance in Animals. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, S93–S106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, N.T.; Fisher, J.F. Acquired Class D β-Lactamases. Antibiotics 2014, 3, 398–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, J.; Guerra, B.; Rodicio, M.R. Resistance to carbapenems in non-typhoidal Salmonella enterica serovars from humans, animals and food. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabry, M.A.; Abdel-Moein, K.A.; Abdel-Kader, F.; Hamza, E. Extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Salmonella serovars among healthy and diseased chickens and their public health implication. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 22, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Zwe, Y.H.; Chin, S.F.; Kohli, G.S.; Drautz-Moses, D.I.; Givskov, M.; Schlundt, J.; Schuster, S.C.; Yuk, H.; Yang, L. Characterization of a novel multidrug resistance plasmid pSGB23 isolated from Salmonella enterica subspecies enterica serovar Saintpaul. Gut Pathog. 2018, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrovat, K.; Zupančič, J.Č.; Seme, K.; Avguštin, J.A. QAC Resistance Genes in ESBL-Producing E. coli Isolated from Patients with Lower Respiratory Tract Infections in the Central Slovenia Region-A 21-Year Survey. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, R.; Thakare, R.; Amrin, N.; Prasad, K.N.; Chopra, S.; Tapan, N.D. Antimicrobial susceptibility pattern and sequence analysis of DNA gyrase and DNA topoisomerase IV in Salmonella enterica serovars Typhi and Paratyphi A isolates with decreased susceptibility to ciprofloxacin. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 110, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaves, D.J.; Randall, L.; Gray, D.T.; Buckley, A.; Woodward, M.J.; White, A.P.; Pid-dock, L.J.V. Prevalence of Mutations within the Quinolone Resistance-Determining Region of gyrA, gyrB, parC, and parE and Association with Antibiotic Resistance in Quinolone-Resistant Salmonella enterica. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 4012–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Fernandez, A.; Fortini, D.; Veldman, K.; Mevius, D.; Carattoli, A. Characterization of plasmids harbouring qnrS1, qnrB2 and qnrB19 genes in Salmonella. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 63, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, D.A.; Peters, G.A.; Ng, L.; Mulvey, M.R. Partial characterization of a genomic island associated with the multidrug resistance region of Salmonella enterica Typhymurium DT104. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2000, 189, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Doublet, B.; Boyd, D.; Mulvey, M.R.; Cloeckaert, A. The Salmonella genomic island 1 is an integrative mobilizable element. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 1911–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khemtong, S.; Chuanchuen, R. Class 1 integrons and Salmonella genomic island 1 among Salmonella enterica isolated from poultry and swine. Microb. Drug Resist. 2008, 14, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummins, M.L.; Hamidian, M.; Djordjevic, S.P. Salmonella Genomic Island 1 is Broadly Disseminated within Gammaproteobacteriaceae. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Fang, T.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, D.; Shi, X.; Shi, C. IncHI2 Plasmids Are Predominant in Antibiotic-Resistant Salmonella Isolates. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 219820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makalatia, K.; Kakabadze, E.; Bakuradze, N.; Grdzelishvili, N.; Stamp, B.; Herman, E.; Tapinos, A.; Coffey, A.; Lee, D.; Papadopoulos, N.G.; et al. Investigation of Salmonella Phage-Bacteria Infection Profiles: Network Structure Reveals a Gradient of Target-Range from Generalist to Specialist Phage Clones in Nested Subsets. Viruses 2021, 113, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mmolawa, P.T.; Schmieger, H.; Heuzenroeder, M.W. Bacteriophage ST64B, a genetic mosaic of genes from diverse sources isolated from Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium DT 64. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 6481–6485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, S.; Ullah, I.; Khanum, S.; Bailie, M.; Shamsi, B.; Ahmed, I.; Shah, S.T.A.; Javed, S.; Ghafoor, A.; Pervaiz, A.; et al. Phenotypic characterization and genome analysis of a novel Salmonella Typhimurium phage having unique tail fiber genes. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakhria, R.; Duck, D.; Lior, H. Extended phage-typing scheme for Escherichia coli O157:H7. Epidemiol. Infect. 1990, 105, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, P.S.; Griffin, P.M. Escherichia coli O157:H7. Lancet 1998, 10, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Sample ID | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assembly Attributes | 1092/18 | 1095/18 | 1096/18 | 1097/18 | 1124/18 | 1158/18 |
| Strain ID | SAMN37152295 | SAMN37152292 | SAMN37152296 | SAMN37152297 | SAMN37152298 | SAMN37152299 |
| Genome size (bp) | 4,854,182 | 4,929,569 | 4,929,238 | 4,738,760 | 4,934,713 | 4,916,385 |
| Contigs number | 41 | 36 | 37 | 28 | 51 | 52 |
| % GC | 52.2 | 51.9 | 51.9 | 52.2 | 51.9 | 51.8 |
| L50 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| N50 (bp) | 322,596 | 296,604 | 277,541 | 286,548 | 187,348 | 160,426 |
| Average depth of coverage | 108 | 75 | 45 | 27 | 52 | 36 |
| CDSs | 4956 | 4936 | 4977 | 4753 | 5010 | 4993 |
| rRNA | 11 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 8 |
| tRNA | 80 | 78 | 77 | 75 | 79 | 76 |
| Sample ID | AMR Phenotypes * | Resistance Gene | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aac(6′)-Iaa | aadA1/dfrA21 | sul1 | dfrA25 | tet(A) | tet(B) | blaOXA-129 | qacE | ||
| 1092/18 | StrSulSxtTetOxiCip | + | − | + | + | + | − | − | + |
| 1095/18 | StrSulSxtTetOxiAmoAmpAmcCip | + | + | + | − | − | + | + | + |
| 1096/18 | StrSulSxtTetOxiAmoAmpAmcCip | + | + | + | − | − | + | + | + |
| 1097/18 | StrSulCip | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 1124/18 | StrSulSxtTetOxiAmoAmpAmc | + | + | + | − | − | + | + | + |
| 1158/18 | StrSulSxtTetOxiAmoAmpAmc | + | + | + | − | − | + | + | + |
| Total | 6 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
| % | 100 | 66.7 | 83.3 | 16.7 | 16.7 | 66.7 | 66.7 | 83.3 | |
| Sample ID | Incompatibility Group | Size (bp) | ORFs | NCBI Accession | Homologous Plasmid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1095/18, 1096/18, 1097/18, 1124/18, and 1158/18 | IncHI2A | 274,762 | 295 | BX664015 | R478 |
| 1092/18 | IncN | 50,969 | 64 | AY046276 | R46 |
| Genome | Region Length a | Total Proteins | Contig | Region Position b | Phage Identity | Access Number | % GC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1092/18 | 46.4 Kb | 45 | 11 | 3–46,484 | Escherichia phage phiV10 | NC_007804 | 49.99 |
| 26.7 Kb | 34 | 15 | 66,909–93,641 | Enterobacteria phage Fels-2 | NC_010463 | 49.10 | |
| 24.7 Kb | 31 | 24 | 2–24,741 | Enterobacteria phage HK542 | NC_019769 | 53.23 | |
| 1095/18 | 36.3 Kb | 45 | 1 | 399,882–43,6265 | Salmonella phage SW9 | NC_049459 | 52.82 |
| 1096/18 | 36.4 Kb | 45 | 2 | 185,676–222,104 | Salmonella phage SW9 | NC_049459 | 52.83 |
| 1097/18 | 47.7 Kb | 54 | 9 | 152,566–200,279 | Enterobacteria phage ST64T | NC_004348 | 48.57 |
| 46.4 Kb | 45 | 13 | 3–46484 | Escherichia phage phiV10 | NC_007804 | 49.99 | |
| 38 Kb | 46 | 18 | 42,660–80,693 | Enterobacteria phage Fels-2 | NC_010463 | 50.29 | |
| 1124/18 | 36.3 Kb | 45 | 2 | 455,491–491,874 | Salmonella phage SW9 | NC_049459 | 52.82 |
| 1158/18 | 36.4 Kb | 45 | 1 | 138,261–174,689 | Salmonella phage SW9 | NC_049459 | 52.82% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benevides, V.P.; Saraiva, M.M.S.; Nascimento, C.F.; Delgado-Suárez, E.J.; Oliveira, C.J.B.; Silva, S.R.; Miranda, V.F.O.; Christensen, H.; Olsen, J.E.; Berchieri Junior, A. Genomic Features and Phylogenetic Analysis of Antimicrobial-Resistant Salmonella Mbandaka ST413 Strains. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12020312
Benevides VP, Saraiva MMS, Nascimento CF, Delgado-Suárez EJ, Oliveira CJB, Silva SR, Miranda VFO, Christensen H, Olsen JE, Berchieri Junior A. Genomic Features and Phylogenetic Analysis of Antimicrobial-Resistant Salmonella Mbandaka ST413 Strains. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(2):312. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12020312
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenevides, Valdinete P., Mauro M. S. Saraiva, Camila F. Nascimento, Enrique J. Delgado-Suárez, Celso J. B. Oliveira, Saura R. Silva, Vitor F. O. Miranda, Henrik Christensen, John E. Olsen, and Angelo Berchieri Junior. 2024. "Genomic Features and Phylogenetic Analysis of Antimicrobial-Resistant Salmonella Mbandaka ST413 Strains" Microorganisms 12, no. 2: 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12020312
APA StyleBenevides, V. P., Saraiva, M. M. S., Nascimento, C. F., Delgado-Suárez, E. J., Oliveira, C. J. B., Silva, S. R., Miranda, V. F. O., Christensen, H., Olsen, J. E., & Berchieri Junior, A. (2024). Genomic Features and Phylogenetic Analysis of Antimicrobial-Resistant Salmonella Mbandaka ST413 Strains. Microorganisms, 12(2), 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12020312









