Two Sporadic Cases of Legionellosis Associated with the Use of Domestic Ultrasonic Humidifiers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Epidemiological and Environmental Study
2.2. Microbiological Characterisation of the Isolates
2.3. Isolation and Characterisation of Protozoa
3. Results
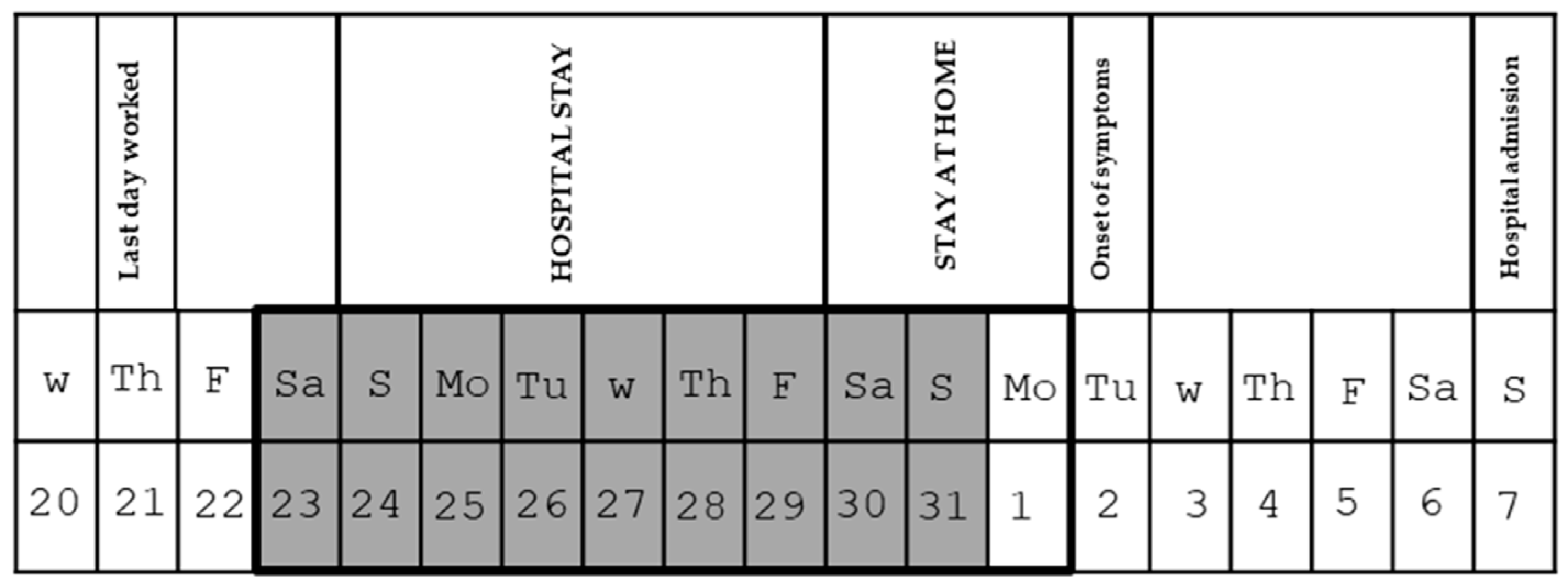
3.1. Case 1
3.2. Case 2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Orkis, L.T.; Harrison, L.H.; Mertz, K.J.; Brooks, M.M.; Bibby, K.J.; Stout, J.E. Environmental sources of community-acquired legionnaires’ disease: A review. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2018, 221, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.; Stevenson, D.; Bennett, A.; Walker, J. Occurrence of Legionella in UK household showers. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2017, 220, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Controlling Legionella in Cooling Towers. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/control-legionella/php/toolkit/cooling-towers-module.html (accessed on 22 September 2024).
- Helbig, J.H.; Bernander, S.; Castellani Pastoris, M.; Etienne, J.; Gaia, V.; Lauwers, S.; Lindsay, D.; Lück, P.C.; Marques, T.; Mentula, S.; et al. Pan-European study on culture-proven Legionnaires’ disease: Distribution of Legionella pneumophila serogroups and monoclonal subgroups. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 21, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legionnaires’ Disease—Annual Epidemiological Report for 2022; European Centre for Disease Prevencion and Control: Stockholm, Sweden, 2023.
- Dagan, A.; Epstein, D.; Mahagneh, A.; Nashashibi, J.; Geffen, Y.; Neuberger, A.; Miller, A. Community-acquired versus nosocomial Legionella pneumonia: Factors associated with Legionella-related mortality. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 40, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Miguel-Balsa, E.; Jaimez Navarro, E.; Cascajero, A.; González-Camacho, F.; González-Rubio, J.M. Fulminant septic shock due to community-acquired pneumonia caused by Legionella pneumophila SG1 Olda OLDA ST1. Case report. J. Infect. Public Health 2024, 17, 1047–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Rubio, J.M.; Cascajero, A.; Baladrón, B.; González-Camacho, F. Characterisation of Legionella Clinical Isolates in Spain from 2012 to 2022. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.V.; Joseph, C. Guidelines for investigating single cases of Legionnaires’ disease. Commun. Dis. Public Health 2002, 5, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- UNE-EN-ISO 11731; Water Quality—Enumeration of Legionella. Spanish Standardisation and Certification Association (AENOR: Asociación Española de Normalización y Certificación): Madrid, Spain, 2017.
- Axelsson-Olsson, D.; Olofsson, J.; Ellström, P.; Waldenström, J.; Olsen, B. A simple method for long-term storage of Acanthamoeba species. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 104, 935–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgcomb, V.P.; Kysela, D.T.; Teske, A.; de Vera Gomez, A.; Sogin, M.L. Benthic eukaryotic diversity in the Guaymas Basin hydrothermal vent environment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7658–7662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeChevallier, M.W.; Prosser, T.; Stevens, M. Opportunistic Pathogens in Drinking Water Distribution Systems—A Review. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, A.M.; Von Dwingelo, J.E.; Price, C.T.; Abu Kwaik, Y. Cellular microbiology and molecular ecology of Legionella-amoeba interaction. Virulence 2013, 4, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, C.T.D.; Hanford, H.E.; Al-Quadan, T.; Santic, M.; Shin, C.J.; Da’as, M.S.J.; Abu Kwaik, Y. Amoebae as training grounds for microbial pathogens. mBio 2024, 15, e0082724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hines, S.A.; Chappie, D.J.; Lordo, R.A.; Miller, B.D.; Janke, R.J.; Lindquist, H.A.; Fox, K.R.; Ernst, H.S.; Taft, S.C. Assessment of relative potential for Legionella species or surrogates inhalation exposure from common water uses. Water Res. 2014, 56, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, A.M.; Yao, W.; Gallagher, D.L. Exposure at the indoor water-air interface: Fill water constituents and the consequent air emissions from ultrasonic humidifiers: A systematic review. Indoor Air 2022, 32, e13129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, N.M.; Reens, A.L.; Robertson, C.E.; Stanish, L.F.; Harris, J.K.; Stevens, M.J.; Frank, D.N.; Kotter, C.; Pace, N.R. Molecular analysis of single room humidifier bacteriology. Water Res. 2015, 69, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyndall, R.L.; Lehman, E.S.; Bowman, E.K.; Milton, D.K.; Barbaree, J.M. Home Humidifiers as a Potential Source of Exposure to Microbial Pathogens, Endotoxins, and Allergens. Indoor Air 1995, 5, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Ahn, K.H.; Yu, I.J. Outbreak of bioaerosols with continuous use of humidifier in apartment room. Toxicol. Res. 2012, 28, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebecca Mitting, V.R.; Grossman, T.; Whittaker, E.; Chalker, V.; Lai, S.; Hoffman, P.; Atkin, S.; Qureshi, S.; Hatcher, J. Severe neonatal legionellosis associated with use of home humidifiers—A case report. Clin. Infect. Pract. 2020, 7–8, 100050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, P.T.; Brooks, E.F.; Costales, C.; Moreno, A.; Jensen, T.D.; Budvytiene, I.; Khan, A.; Pham, T.H.M.; Schwenk, H.T.; Bhatt, A.S.; et al. Near-fatal Legionella pneumonia in a neonate linked to home humidifier by metagenomic next generation sequencing. Med 2022, 3, 565–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonilla Escobar, B.A.; Montero Rubio, J.C.; Martínez Juárez, G. Legionella pneumophila pneumonia associated with the use of a home humidifier in an immunocompetent girl. Med. Clin. 2014, 142, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reinares Ortiz, J.; Pérez-Serrano, J.; González-Rubio, J.M.; González-Camacho, F. Two Sporadic Cases of Legionellosis Associated with the Use of Domestic Ultrasonic Humidifiers. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12112139
Reinares Ortiz J, Pérez-Serrano J, González-Rubio JM, González-Camacho F. Two Sporadic Cases of Legionellosis Associated with the Use of Domestic Ultrasonic Humidifiers. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(11):2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12112139
Chicago/Turabian StyleReinares Ortiz, Javier, Jorge Pérez-Serrano, Juana María González-Rubio, and Fernando González-Camacho. 2024. "Two Sporadic Cases of Legionellosis Associated with the Use of Domestic Ultrasonic Humidifiers" Microorganisms 12, no. 11: 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12112139
APA StyleReinares Ortiz, J., Pérez-Serrano, J., González-Rubio, J. M., & González-Camacho, F. (2024). Two Sporadic Cases of Legionellosis Associated with the Use of Domestic Ultrasonic Humidifiers. Microorganisms, 12(11), 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12112139







