Insertion Sequences within Oxacillinases Genes as Molecular Determinants of Acinetobacter baumannii Resistance to Carbapenems—A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolates Origin and Their Selection Criteria
2.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. PCR Analysis
2.4.1. blaOXA Gene Detection and High-Resolution Melting Analysis
2.4.2. ISAba1-blaOXA-23 Gene Detection
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bacterial Strains Origin
3.2. Bacterial Strains Antimicrobial Susceptibility
3.3. Presence of blaOXA Genes among Meropenem-Susceptible A. baumannii Isolates
3.4. Presence of ISAba1-blaOXA-23 among Carbapenem-Resistant A. baumannii Isolates (n = 53)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, M.F.; Lan, C.Y. Antimicrobial resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: From bench to bedside. World J. Clin. Cases 2014, 2, 787–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijkshoorn, L.; Nemec, A.; Seifert, H. An Increasing Threat in Hospitals: Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peleg, A.Y.; Seifert, H.; Paterson, D.L. Acinetobacter baumannii: Emergence of a Successful Pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 538–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protic, D.; Pejovic, A.; Andjelkovic, D.; Djukanovic, N.; Savic, D.; Piperac, P.; Markovic Denic, L.; Zdravkovic, M.; Todorovic, Z. Nosocomial Infections Caused by Acinetobacter baumannii: Are We Losing the Battle? Surg. Infect. 2016, 17, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, L.C.S.; Visca, P.; Towner, K.J. Acinetobacter baumannii: Evolution of a Global Pathogen. Pathog. Dis. 2014, 71, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, M.; Park, K.S.; Bae, I.K.; Kim, Y.B.; Cha, C.-J.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Biology of Acinetobacter baumannii: Pathogenesis, Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms, and Prospective Treatment Options. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Hu, R. Risk Factors for Pneumonia Caused by Antimicrobial Drug-Resistant or Drug-Sensitive Acinetobacter baumannii Infections. Medicine 2020, 99, e21051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballouz, T.; Aridi, J.; Afif, C.; Irani, J.; Lakis, C.; Nasreddine, R.; Azar, E. Risk Factors, Clinical Presentation, and Outcome of Acinetobacter baumannii Bacteremia. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depka, D.; Bogiel, T.; Rzepka, M.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E. The Prevalence of Virulence Factor Genes among Carbapenem-Non-Susceptible Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Strains and Their Usefulness as Potential Molecular Biomarkers of Infection. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wu, L.; Mei, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, R.; Jia, X. Distribution of Virulence-Associated Genes and Antimicrobial Susceptibility in Clinical Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 21663–21673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, F.C.; Dexter, C.; Kostoulias, X.; Uddin, M.I.; Peleg, A.Y. The Mechanisms of Disease Caused by Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, I.; Cerqueira, G.M.; Bhuiyan, S.; Peleg, A.Y. Carbapenem Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: Laboratory Challenges, Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Strategies. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2013, 11, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, L.B. Federal funding for the study of antimicrobial resistance in nosocomial pathogens: No ESKAPE. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 1079–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Custovic, A.; Smajlovic, J.; Tihic, N.; Hadzic, S.; Ahmetagic, S.; Hadzagic, H. Epidemiological Monitoring of Nosocomial Infections Caused by Acinetobacter baumannii. Med. Arch. 2014, 68, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakidis, I.; Vasileiou, E.; Pana, Z.D.; Tragiannidis, A. Acinetobacter baumannii Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms. Pathogens 2021, 10, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisold, A.J.; Luxner, J.; Bedenić, B.; Diab-Elschahawi, M.; Berktold, M.; Wechsler-Fördös, A.; Zarfel, G.E. Diversity of Oxacillinases and Sequence Types in Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii from Austria. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Naas, T.; Nordmann, P. Diversity, Epidemiology, and Genetics of Class D β-Lactamases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turton, J.F.; Ward, M.E.; Woodford, N.; Kaufmann, M.E.; Pike, R.; Livermore, D.M.; Pitt, T.L. The Role of ISAba1 in Expression of OXA Carbapenemase Genes in Acinetobacter baumannii. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 258, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słoczyńska, A.; Wand, M.E.; Tyski, S.; Laudy, A.E. Analysis of BlaCHDL Genes and Insertion Sequences Related to Carbapenem Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Strains Isolated in Warsaw, Poland. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.T.; Pham, S.C.; Ly, A.K.; Nguyen, C.V.V.; Vu, T.T.; Ha, T.M. Overexpression of BlaOXA-58 Gene Driven by ISAba3 Is Associated with Imipenem Resistance in a Clinical Acinetobacter baumannii Isolate from Vietnam. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 7213429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, M.; Martins, A.F.; Barth, A.L. Mobile genetic elements related to carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eucast: Clinical Breakpoints and Dosing of Antibiotics. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints (accessed on 25 August 2023).
- Woodford, N.; Ellington, M.J.; Coelho, J.M.; Turton, J.F.; Ward, M.E.; Brown, S.; Amyes, S.G.B.; Livermore, D.M. Multiplex PCR for Genes Encoding Prevalent OXA Carbapenemases in Acinetobacter spp. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2006, 27, 351–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Exner, M.; Bhattacharya, S.; Christiansen, B.; Gebel, J.; Goroncy-Bermes, P.; Hartemann, P.; Heeg, P.; Ilschner, C.; Kramer, A.; Larson, E.; et al. Antibiotic Resistance: What Is so Special about Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria? GMS Hyg. Infect. Control 2017, 12, Doc05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassetti, M.; Peghin, M.; Vena, A.; Giacobbe, D.R. Treatment of Infections Due to MDR Gram-Negative Bacteria. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmal, S.; Athar Hashmi, F.; Imran, I. Recent Progress in Development and Applications of Biomaterials. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llor, C.; Bjerrum, L. Antimicrobial Resistance: Risk Associated with Antibiotic Overuse and Initiatives to Reduce the Problem. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2014, 5, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagas, M.E.; Bliziotis, I.A.; Kasiakou, S.K.; Samonis, G.; Athanassopoulou, P.; Michalopoulos, A. Outcome of Infections Due to Pandrug-Resistant (PDR) Gram-Negative Bacteria. BMC Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Publishes List of Bacteria for Which New Antibiotics Are Urgently Needed. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/27-02-2017-who-publishes-list-of-bacteria-for-which-new-antibiotics-are-urgently-needed (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Bandić-Pavlović, D.; Zah-Bogović, T.; Žižek, M.; Bielen, L.; Bratić, V.; Hrabač, P.; Slačanac, D.; Mihaljević, S.; Bedenić, B. Gram-negative bacteria as causative agents of ventilator-associated pneumonia and their respective resistance mechanisms. J. Chemother. 2020, 32, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, F.; Khan, Z.; Sohail, M.; Tahir, A.; Tipu, I.; Saleem, H.G.M. Antibiotic Resistance Pattern of Acinetobacter baumannii Isolated From Bacteremia Patients In Pakistan. J. Ayub Med. Coll. Abbottabad 2022, 34, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lob, S.H.; Hoban, D.J.; Sahm, D.F.; Badal, R.E. Regional differences and trends in antimicrobial susceptibility of Acinetobacter baumannii. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 47, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elham, B.; Fawzia, A. Colistin Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii Isolated from Critically Ill Patients: Clinical Characteristics, Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Outcome. Afr. Health Sci. 2019, 19, 2400–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, M.M. Synergistic activities of colistin combined with other antimicrobial agents against colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, B.A.; Amyes, S.G.B. OXA β-Lactamases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 241–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turton, J.F.; Woodford, N.; Glover, J.; Yarde, S.; Kaufmann, M.E.; Pitt, T.L. Identification of Acinetobacter baumannii by detection of the blaOXA-51-like carbapenemase gene intrinsic to this species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2974–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahador, A.; Raoofian, R.; Pourakbari, B.; Taheri, M.; Hashemizadeh, Z.; Hashemi, F.B. Genotypic and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: Analysis of ISAba Elements and BlaOXA-23-like Genes Including a New Variant. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wei, Y.; Jian, C.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Z. Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: A challenge in the intensive care unit. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1045206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalanuria, A.A.; Ziai, W.; Mirski, M. Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in the ICU. Crit. Care 2014, 18, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konca, C.; Tekin, M.; Geyik, M. Susceptibility Patterns of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Indian J. Pediatr. 2021, 88, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

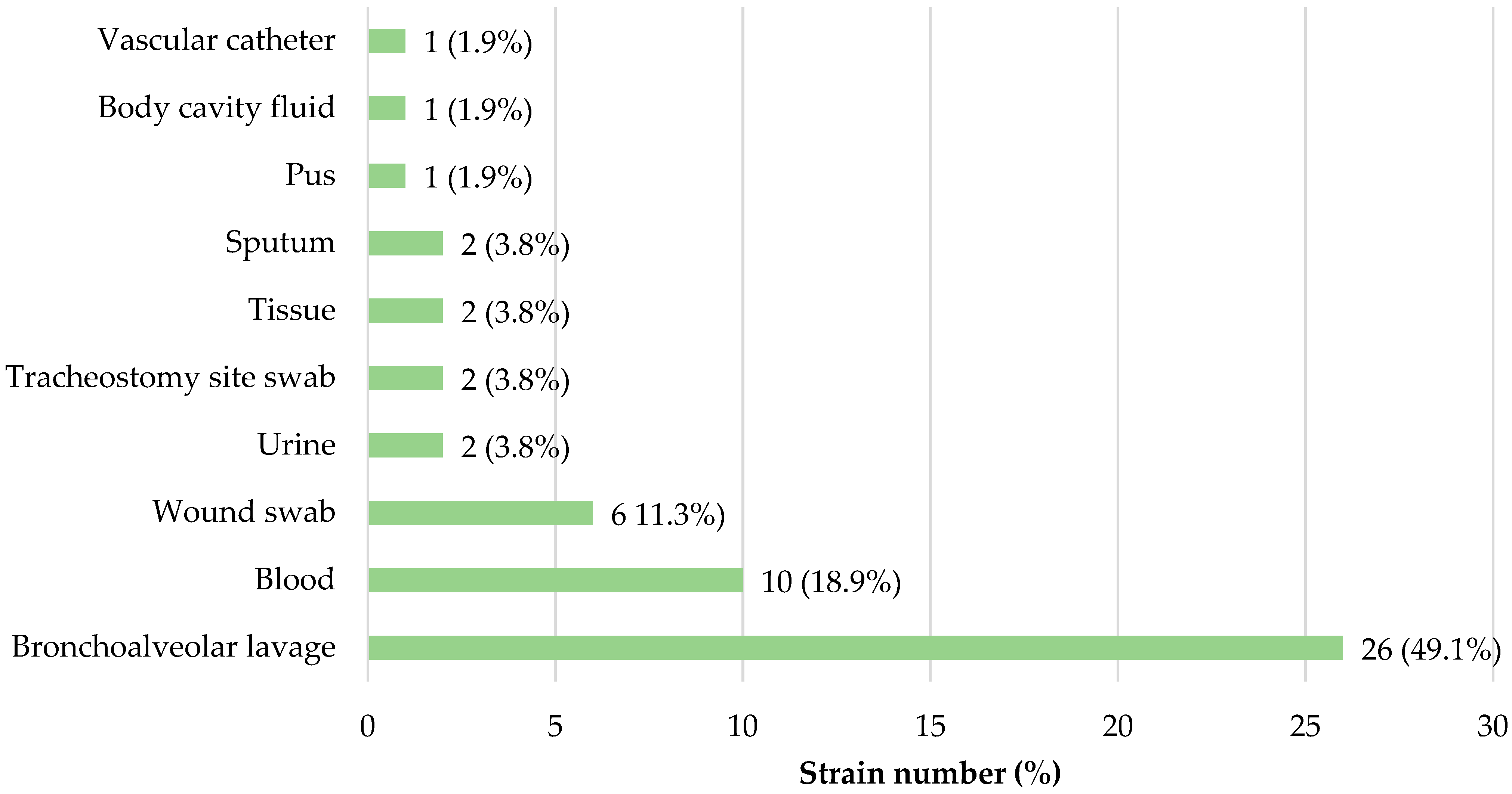
| Gene Detected | Primer Sequences 5′→3′ | Tm (°C) | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Product Length (bp) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| blaOXA-40 | F: GGTTAGTTGGCCCCCTTAA | 51.8 | 58 | 246 | [23] |
| R: AGTTGAGCGAAAAGGGGATT | 49.7 | ||||
| blaOXA-23 | F: GATCGGATTGGAGAACCAGA | 50.3 | 58 | 501 | [23] |
| R: ATTTCTGACCGCATTTCCAT | 47.7 | ||||
| blaOXA-51 | F: TAATGCTTTGATCGGCCTTG | 49.7 | 58 | 353 | [23] |
| R: TGGATTGCACTTCATCTTGG | 49.7 | ||||
| ISAba1-blaOXA-23 | F: AATCACAAGCATGATGAGCG | 49.7 | 54 | 962 | [19] |
| R: CATTTCTGACCGCATTTCCAT | 50.5 |
| Clinic/Department | Strain Number (%) |
|---|---|
| Department of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care | 8 (22.8%) |
| Clinical Unit of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care with Cardiac Anesthesiology Division | 7 (20.0%) |
| Department of Cardiology | 3 (8.6%) |
| Department of Neurology | 3 (8.6%) |
| Department of General, Oncologic and Pediatric Urology | 2 (5.7%) |
| Department of Liver and General Surgery | 2 (5.7%) |
| Department of Nephrology, Hypertension and Internal Medicine | 2 (5.7%) |
| Department of Otolaryngology and Laryngological Oncology with Audiology and Phoniatrics Unit | 2 (5.7%) |
| Department of Dermatology, Sexually Transmitted Diseases and Immunodermatology | 1 (2.9%) |
| Department of Emergency Medicine | 1 (2.9%) |
| Department of Endocrinology and Diabetology | 1 (2.9%) |
| Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology | 1 (2.9%) |
| Department of Transplantation and General Surgery | 1 (2.9%) |
| Chronic Wound Care | 1 (2.9%) |
| Clinic/Department | Strain Number (%) |
|---|---|
| Department of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care | 42 (79.2%) |
| Department of Endocrinology and Diabetology | 3 (5.7%) |
| Department of Cardiology | 2 (3.8%) |
| Department of Geriatrics | 2 (3.8%) |
| Department of Liver and General Surgery | 2 (3.8%) |
| Department of Cardiac Surgery | 1 (1.9%) |
| Department of Rehabilitation | 1 (1.9%) |
| Number (%) of Strains | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Antimicrobial | Susceptible | Susceptible, Increased Exposure | Resistant |
| IMP | 30 (85.7) | 2 (5.7) | 3 (8.6) |
| MEM | 35 (100) | 0 | 0 |
| TOB | 25 (71.4) | 0 | 10 (28.6) |
| AMK | 28 (80.0) | 1 (2.9) | 6 (17.1) |
| CIP | 7 (20.0) | 16 (45.7) | 12 (34.3) |
| LEV | 23 (65.7) | 0 | 12 (34.3) |
| SXT | 22 (62.9) | 0 | 13 (37.1) |
| COL | 33 (94.3) | 0 | 2 (5.7) |
| Number (%) of Strains | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Antimicrobial | Susceptible | Susceptible, Increased Exposure | Resistant |
| IMP | 0 | 0 | 53 (100) |
| MEM | 0 | 0 | 53 (100) |
| TOB | 5 (9.4) | 0 | 48 (90.6) |
| AMK | 1 (1.9) | 0 | 52 (98.1) |
| CIP | 0 | 0 | 53 (100) |
| LEV | 0 | 0 | 53 (100) |
| SXT | 0 | 2 (3.7) | 51 (96.2) |
| COL | 42 (79.2) | 0 | 11 (20.8) |
| Specimen Origin | Unit | Gene Detected | ISAba1 | IMP | MEM | TOB | AMK | CIP | LEV | SXT | COL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bronchoalveolar lavage | ICU | blaOXA-23 | + | R | S | R | S | R | R | R | S |
| Wound swab | ICU | blaOXA-23 | + | S | S | R | S | R | R | R | S |
| Pus | ICU | blaOXA-40 | n/a | R | S | S | S | R | R | R | R |
| Urine | ICU | blaOXA-40 | n/a | S | S | S | S | I | S | S | S |
| Vascular catheter | NEU | blaOXA-40 | n/a | R | S | R | S | R | R | R | S |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Depka, D.; Bogiel, T.; Rzepka, M.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E. Insertion Sequences within Oxacillinases Genes as Molecular Determinants of Acinetobacter baumannii Resistance to Carbapenems—A Pilot Study. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2057. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12102057
Depka D, Bogiel T, Rzepka M, Gospodarek-Komkowska E. Insertion Sequences within Oxacillinases Genes as Molecular Determinants of Acinetobacter baumannii Resistance to Carbapenems—A Pilot Study. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(10):2057. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12102057
Chicago/Turabian StyleDepka, Dagmara, Tomasz Bogiel, Mateusz Rzepka, and Eugenia Gospodarek-Komkowska. 2024. "Insertion Sequences within Oxacillinases Genes as Molecular Determinants of Acinetobacter baumannii Resistance to Carbapenems—A Pilot Study" Microorganisms 12, no. 10: 2057. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12102057
APA StyleDepka, D., Bogiel, T., Rzepka, M., & Gospodarek-Komkowska, E. (2024). Insertion Sequences within Oxacillinases Genes as Molecular Determinants of Acinetobacter baumannii Resistance to Carbapenems—A Pilot Study. Microorganisms, 12(10), 2057. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12102057





