The Composition and Function of Intestinal Microbiota Were Altered in Farmed Bullfrog Tadpoles (Aquarana catesbeiana) during Metamorphosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Morphology Measurements
2.3. Intestinal Histological Processing
2.4. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Parameters
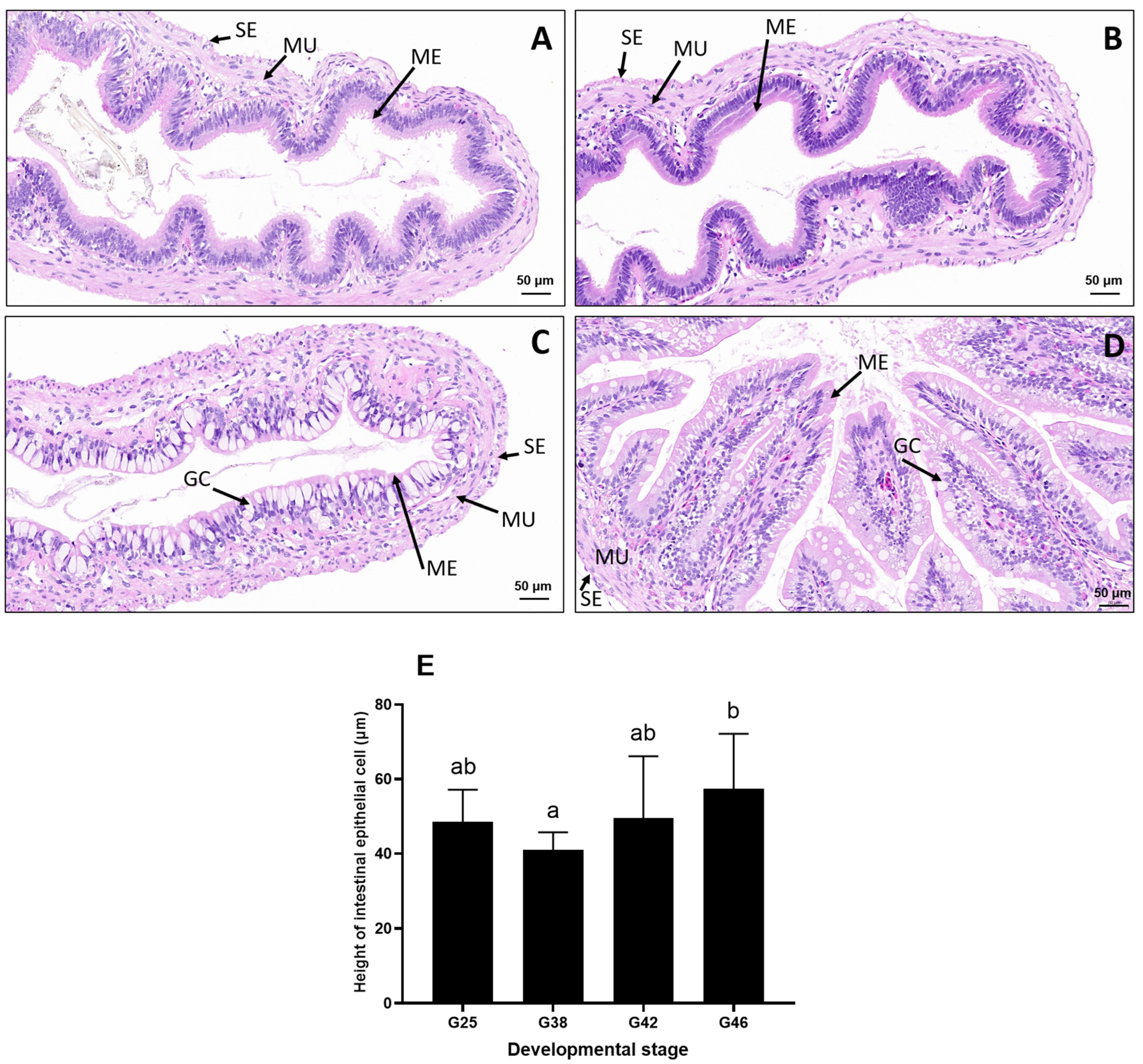
3.2. Intestine Histology
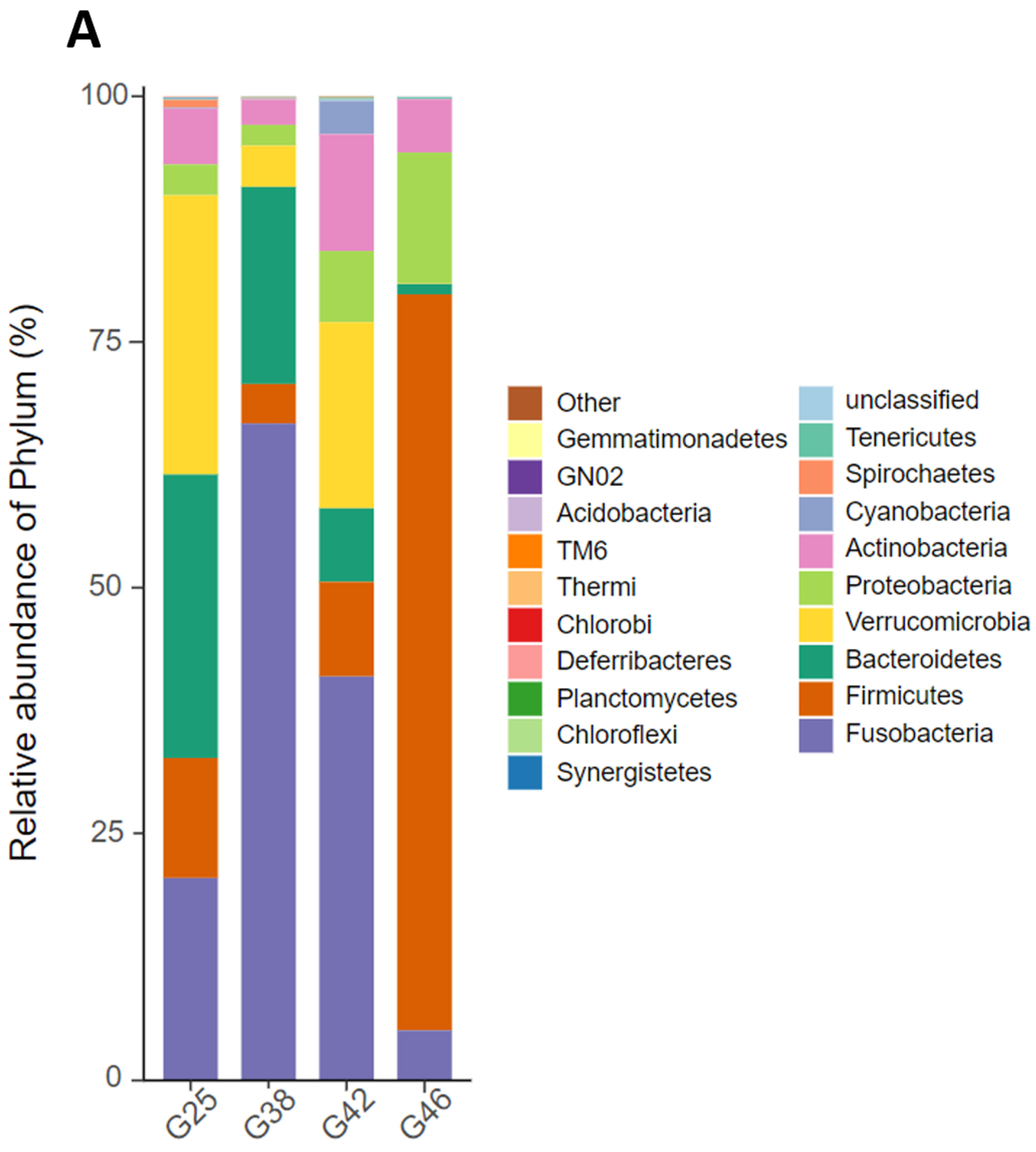
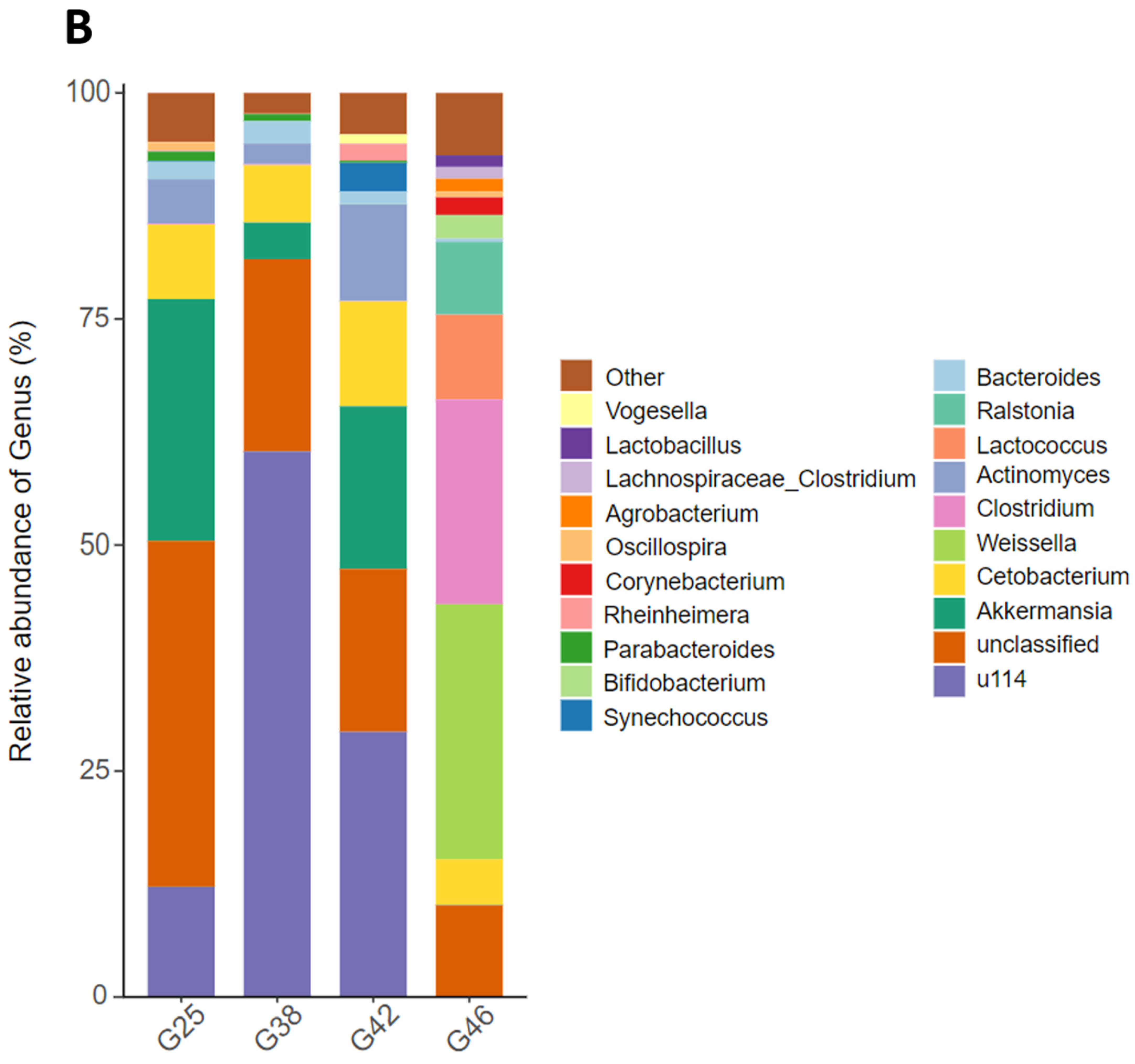
3.3. Changes in the Intestinal Microbial Composition at the Phylum Level and the Genus Level
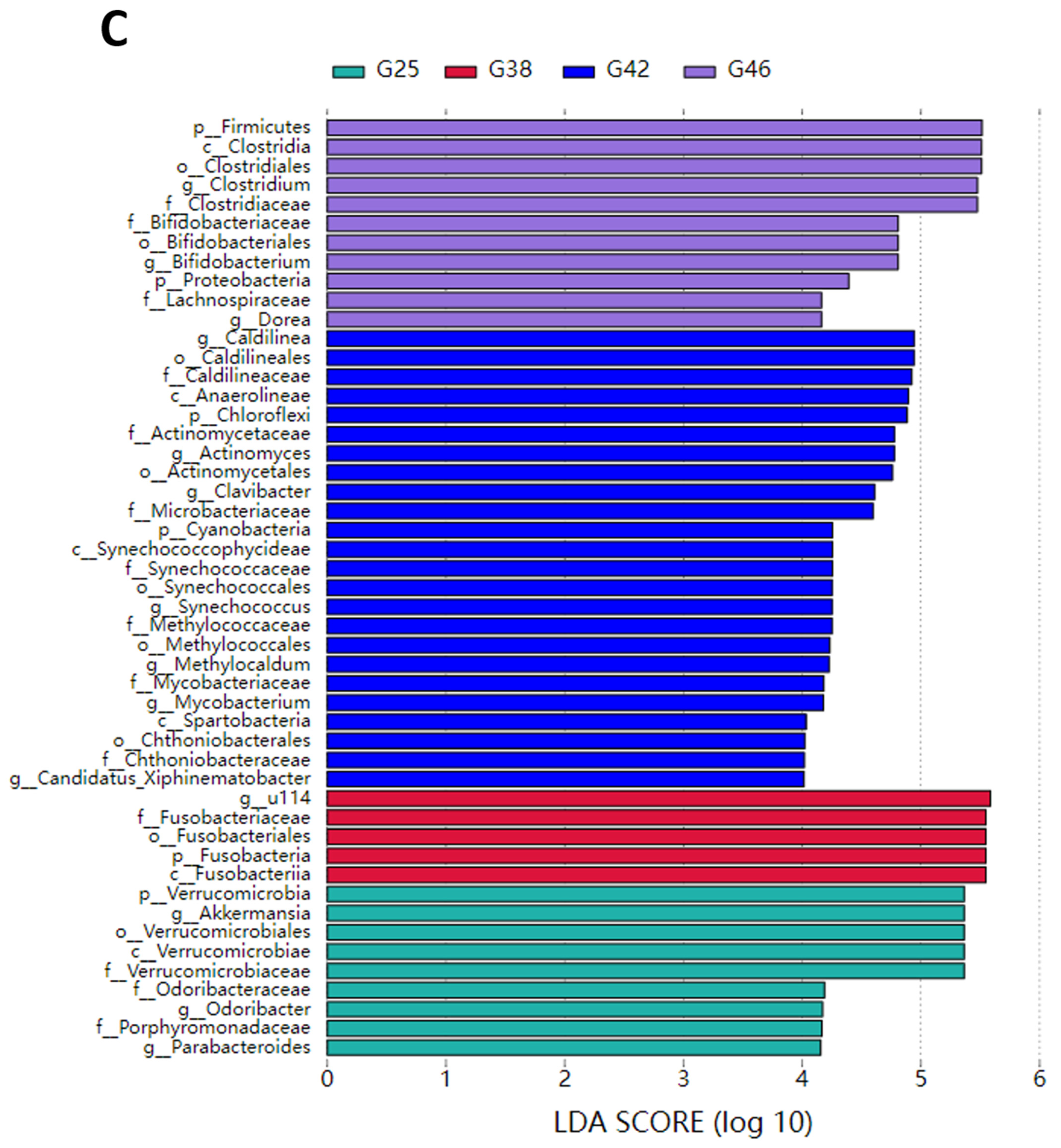
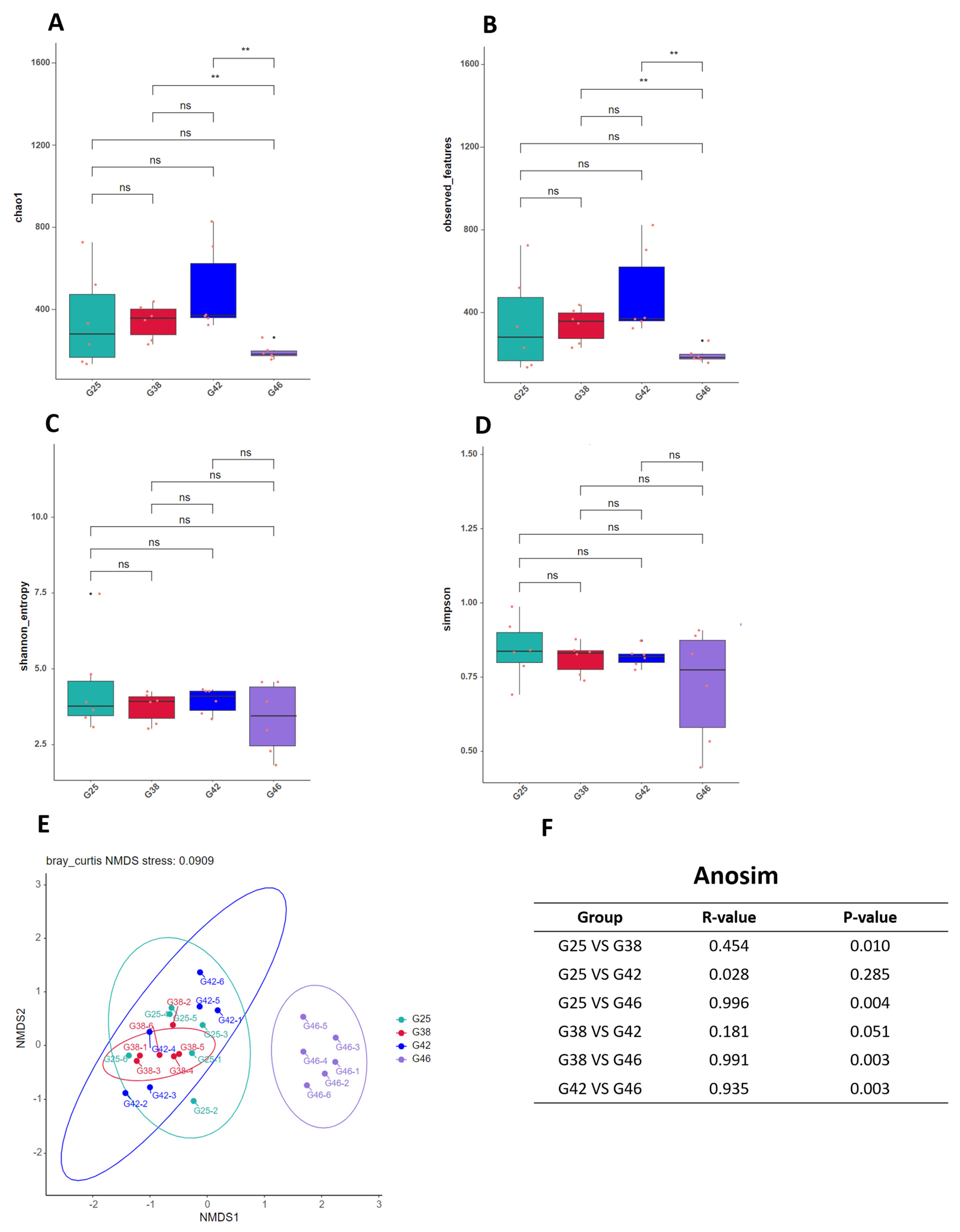
3.4. Diversity Analysis of the Intestinal Microbiota
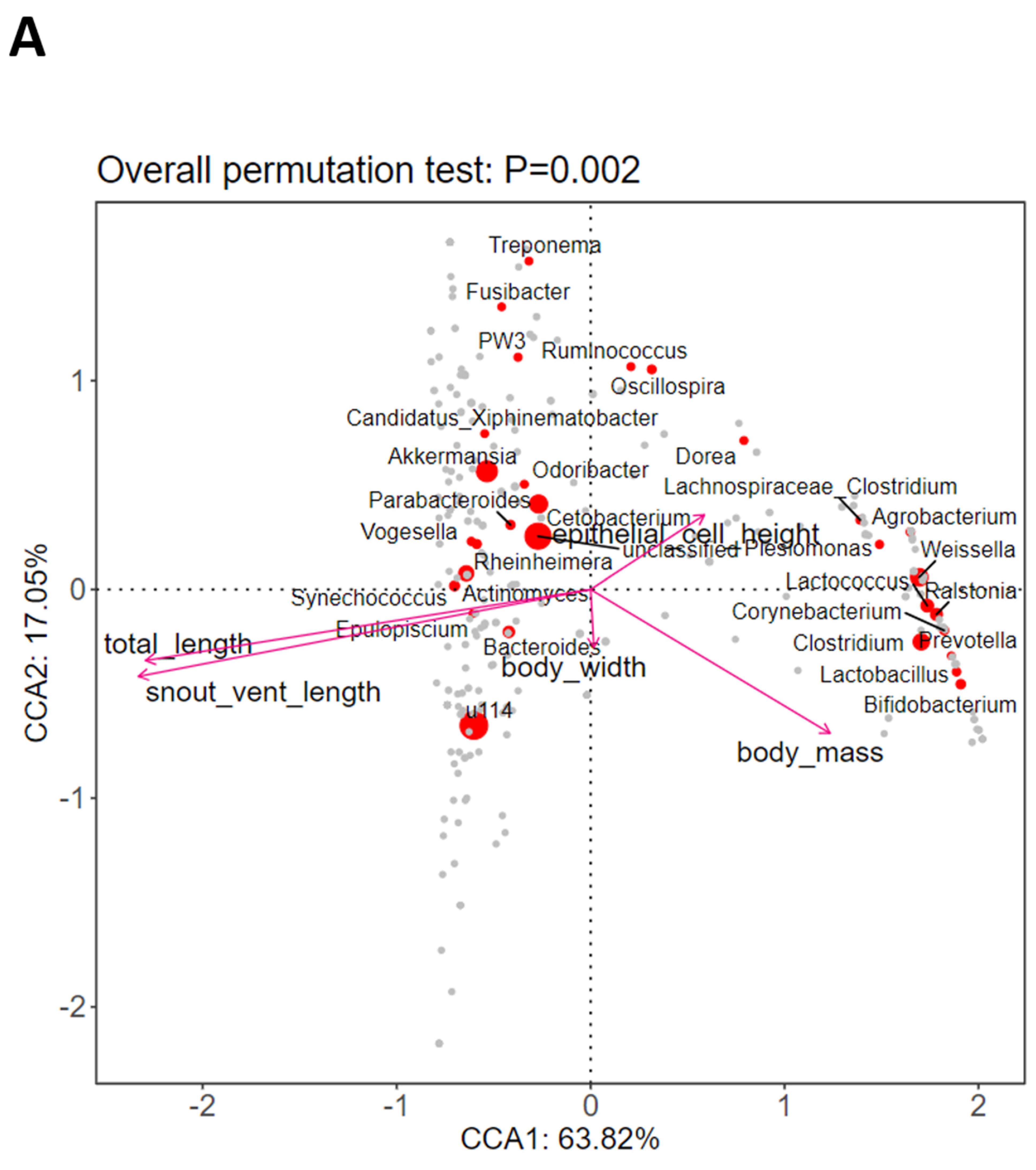
3.5. Correlations of the Morphological Changes with the Intestinal Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.; Wang, H.-N.; Fekede Regassa, J.; Wang, X.-L. Independent Origin of Chytrid Fungus In China. Russ. J. Herpetol. 2018, 25, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zeng, G.; Yu, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, K.; Qin, Z.; Jiang, B.; Li, W.; Su, Y.; Lin, L.; et al. Acute septicemia and diagnostic evaluation of Aeromonas veronii infection in American bullfrogs (Aquarana catesbeiana). Aquaculture 2024, 580, 740349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosner, K.L. A simplified table for staging anuran embryos and larvae with notes on identification. Herpetologica 1960, 16, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Lalremsanga, H.T.; Sailo, S.; Hooroo, R.N.K. External morphology, oral structure and feeding behaviour of Kaloula pulchra tadpoles Gray, 1831 (Amphibia: Anura: Microhylidae). Sci. Technol. J. 2017, 5, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanan, D.; Pratama, A.; Zhu, Y.; Venezia, O.; Sassone-Corsi, M.; Chowdhary, K.; Galván-Peña, S.; Sefik, E.; Brown, C.; Gélineau, A.; et al. Regulatory T cells in the face of the intestinal microbiota. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Liwinski, T.; Elinav, E. Interaction between microbiota and immunity in health and disease. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, L.; Hu, S.; Ye, C.; Huang, Y. Fauna Sinica. Amphibia. Volume 2. Anura; Chinese Academy of Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Pirrung, M.; Gonzalez, A.; Knight, R. EMPeror: A tool for visualizing high-throughput microbial community data. Gigascience 2013, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohart, F.; Gautier, B.; Singh, A.; Lê Cao, K.-A. mixOmics: An R package for ‘omics feature selection and multiple data integration. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Mcglinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Package “vegan” title community ecology package version 2.5-7. CRAN Repos. 2020, 2, 1–286. [Google Scholar]
- Langille, M.G.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Beiko, R.G. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Liu, R.; Meng, J.; Wang, H. Changes in intestinal microbial community of Rana chensinensis tadpoles during metamorphosis. Aquaculture 2020, 516, 734606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, L.W.; Artis, D. Intestinal epithelial cells: Regulators of barrier function and immune homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovira, J.; Villaro, A.C.; Bodegas, M.E.; Valverde, E.; Sesma, P. Metamorphic changes in the stomach of the frog Rana temporaria tadpoles. Tissue Cell 1995, 27, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, K.D.; Cary, T.L.; Karasov, W.H.; Dearing, M.D. Restructuring of the amphibian gut microbiota through metamorphosis. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warne, R.W.; Kirschman, L.; Zeglin, L. Manipulation of gut microbiota during critical developmental windows affects host physiological performance and disease susceptibility across ontogeny. J. Anim. Ecol. 2019, 88, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, A.M.; Mohammed, H.H.; Arias, C.R. Characterization of the gut microbiota of three commercially valuable warmwater fish species. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 116, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, T.M.; Rogers, T.L.; Brown, M.V. The gut bacterial community of mammals from marine and terrestrial habitats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Long, M.; Gatesoupe, F.J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, A.; Gong, X. Comparative analysis of the intestinal bacterial communities in different species of carp by pyrosequencing. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 69, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, H.; Kato, Y.; Chikaraishi, T.; Moritani, M.; Ban-Tokuda, T.; Wakita, M. Microbial diversity in ostrich ceca as revealed by 16S ribosomal RNA gene clone library and detection of novel Fibrobacter species. Anaerobe 2010, 16, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middelbos, I.S.; Vester Boler, B.M.; Qu, A.; White, B.A.; Swanson, K.S.; Fahey, G.C., Jr. Phylogenetic characterization of fecal microbial communities of dogs fed diets with or without supplemental dietary fiber using 454 pyrosequencing. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R.; Kaser, A. Obesity and the microbiota. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 1476–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Kong, L.; Johnston, L.J.; Lu, L.; Ma, X. Dietary nutrients shape gut microbes and intestinal mucosa via epigenetic modifications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, X.; Chen, Q.; Liang, X.; Kumar, V.; Loor, A.; Dong, H.; Liu, C.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J. The Composition and Function of Intestinal Microbiota Were Altered in Farmed Bullfrog Tadpoles (Aquarana catesbeiana) during Metamorphosis. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12102020
Zheng X, Chen Q, Liang X, Kumar V, Loor A, Dong H, Liu C, Yang J, Zhang J. The Composition and Function of Intestinal Microbiota Were Altered in Farmed Bullfrog Tadpoles (Aquarana catesbeiana) during Metamorphosis. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(10):2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12102020
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Xiaoting, Qiuyu Chen, Xueying Liang, Vikash Kumar, Alfredo Loor, Hongbiao Dong, Chang Liu, Jinlong Yang, and Jiasong Zhang. 2024. "The Composition and Function of Intestinal Microbiota Were Altered in Farmed Bullfrog Tadpoles (Aquarana catesbeiana) during Metamorphosis" Microorganisms 12, no. 10: 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12102020
APA StyleZheng, X., Chen, Q., Liang, X., Kumar, V., Loor, A., Dong, H., Liu, C., Yang, J., & Zhang, J. (2024). The Composition and Function of Intestinal Microbiota Were Altered in Farmed Bullfrog Tadpoles (Aquarana catesbeiana) during Metamorphosis. Microorganisms, 12(10), 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12102020







