Integrating the Transcriptome and Proteome to Postulate That TpiA and Pyk Are Key Enzymes Regulating the Growth of Mycoplasma Bovis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Media
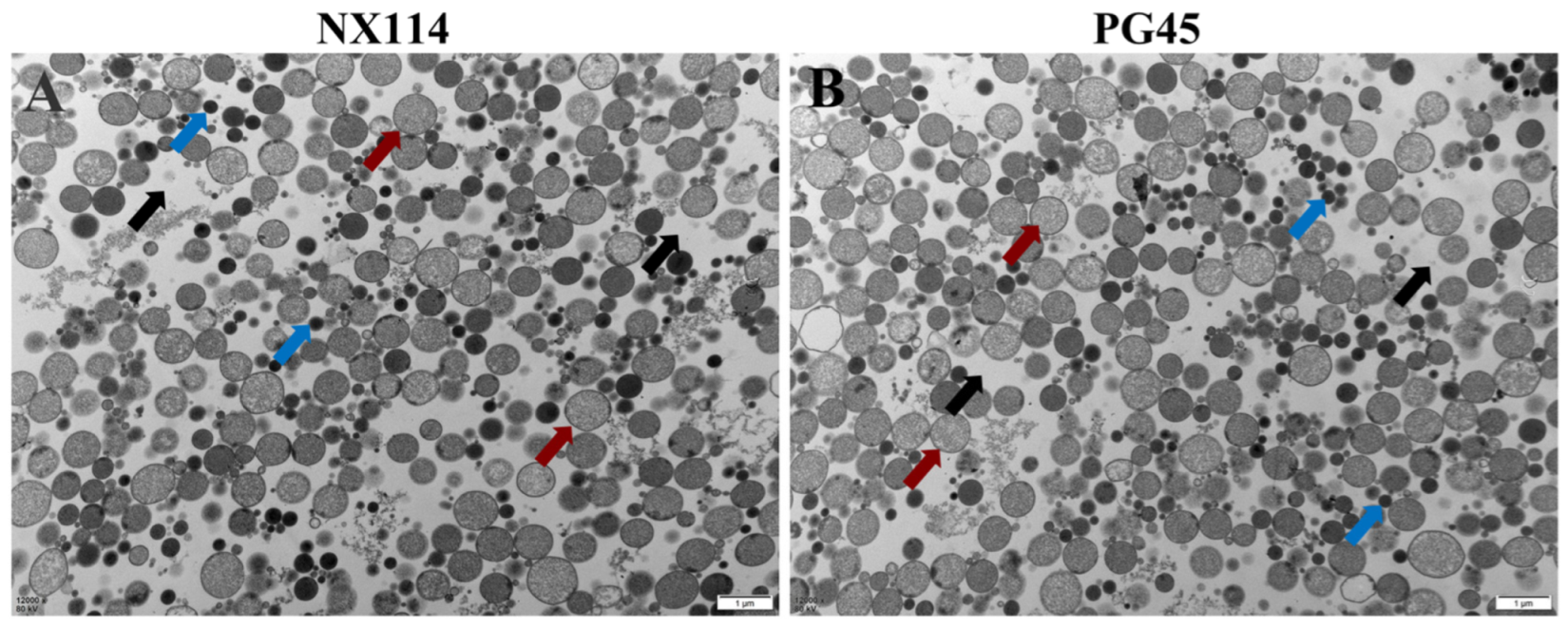
2.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.3. Transcriptomics Analysis of M. Bovis
2.4. Label-Free Quantitative Proteomics Analysis of M. Bovis
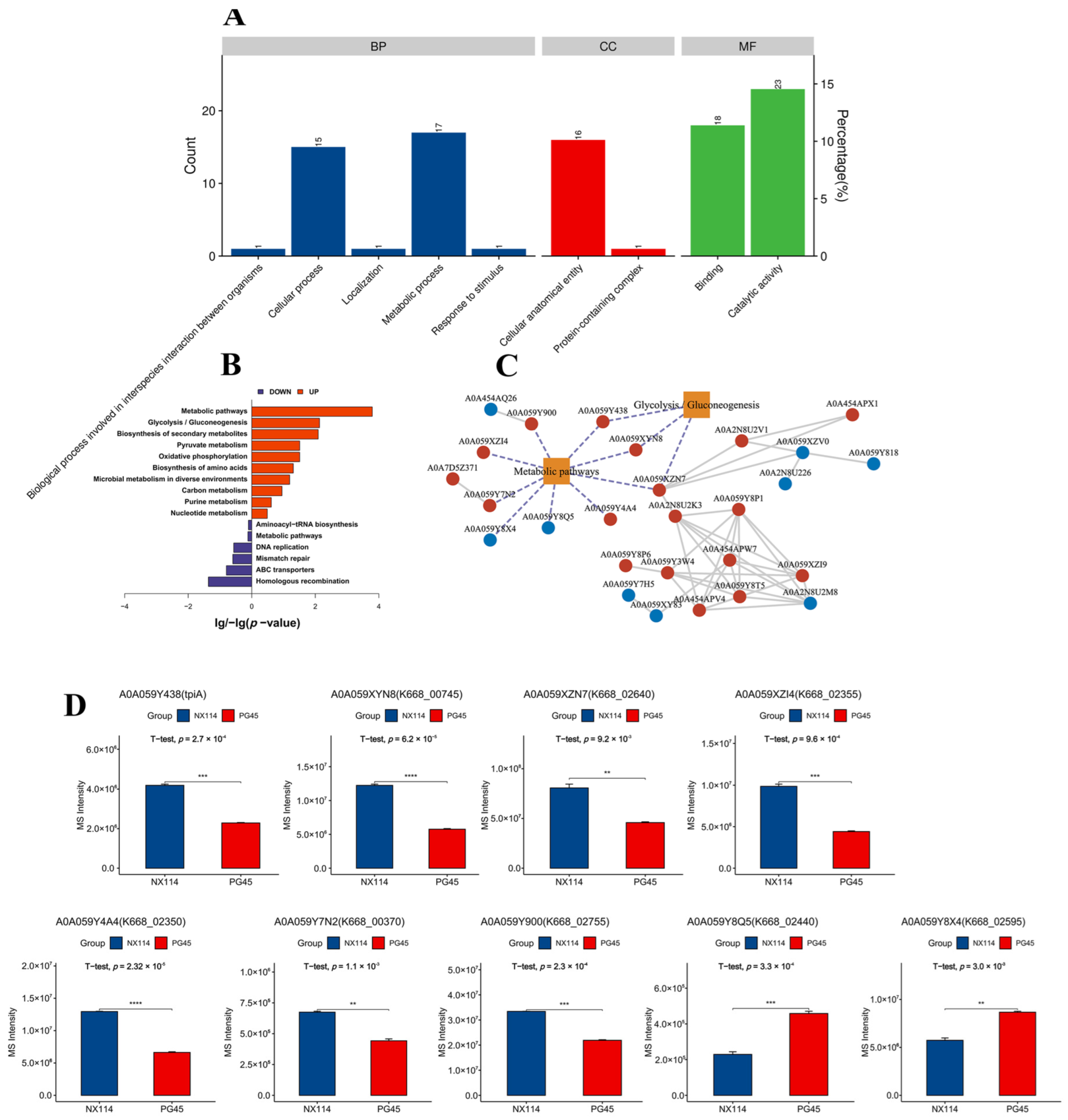
2.5. Bioinformatics Analysis
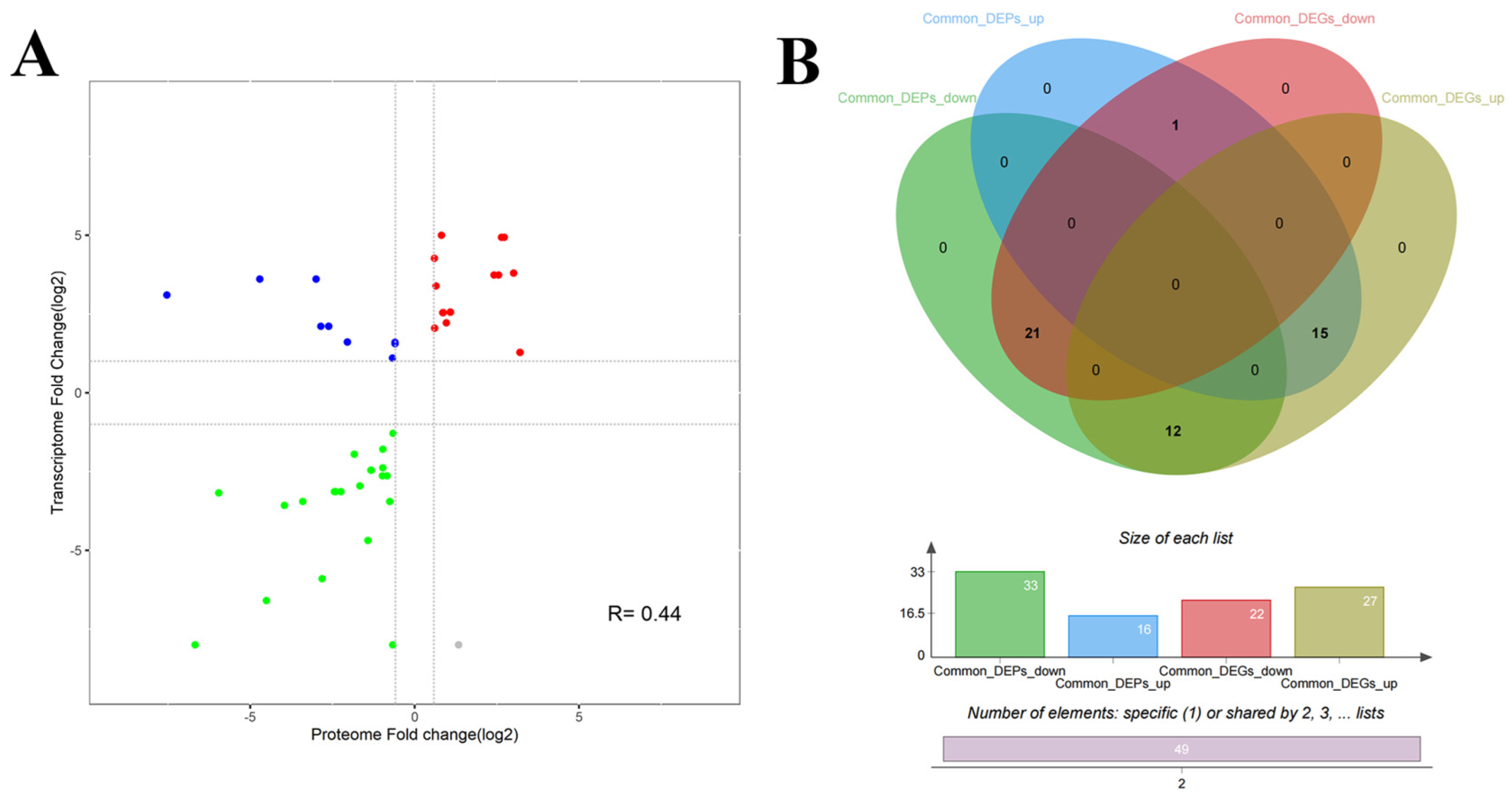
2.6. Combined Proteomic and Transcriptomic Analysis of M. Bovis
2.7. qRT-PCR Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Transmission Electron Microscopy of M. Bovis
3.2. Analysis of Prokaryotic Transcripts of M. Bovis
3.3. Four-Dimensional Label-Free Quantitative Proteomics Analysis of M. Bovis
3.4. Correlation Analysis of the Transcriptome and Proteome of M. Bovis
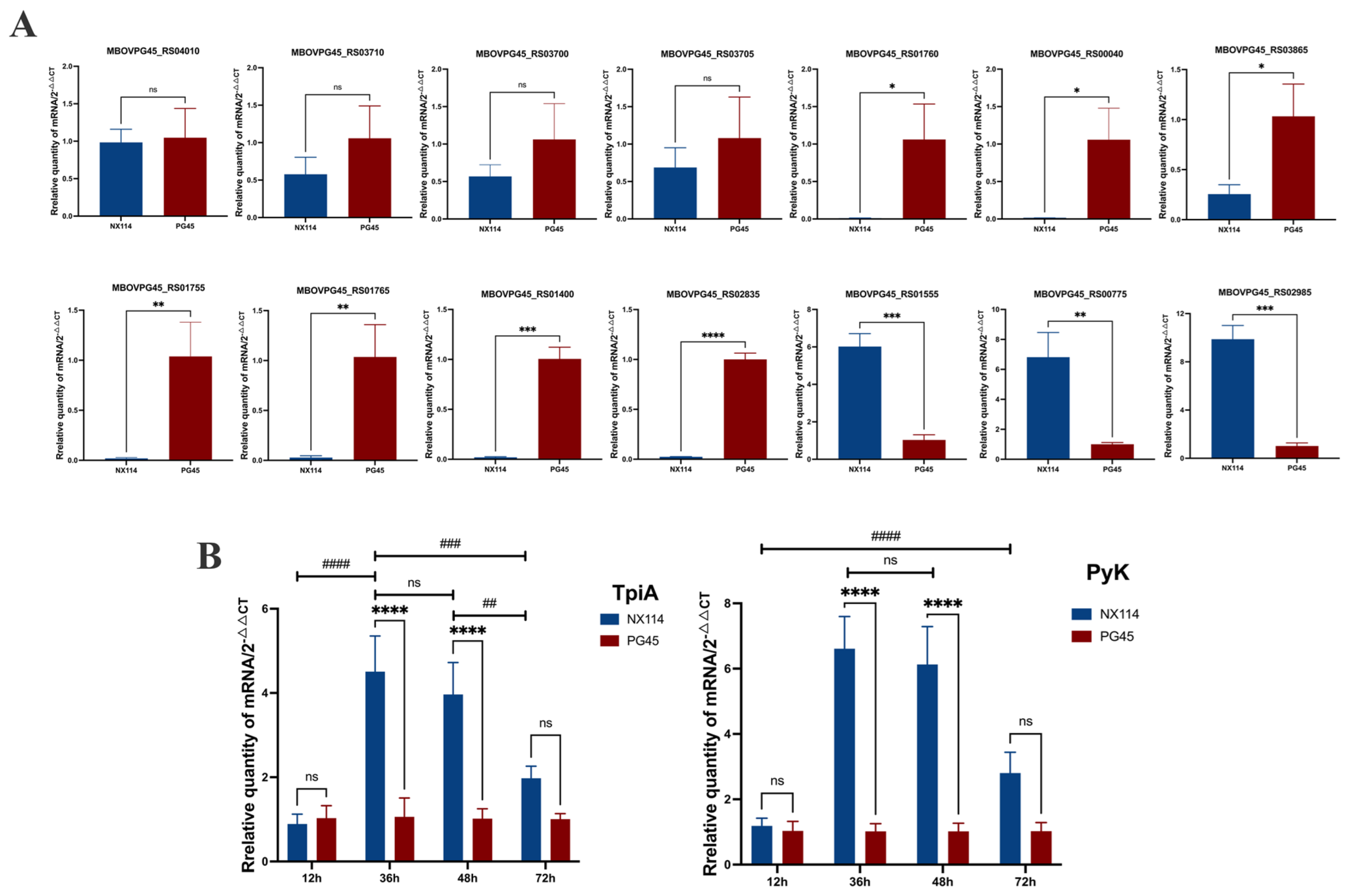
3.5. qRT-PCR Verification
4. Discussion
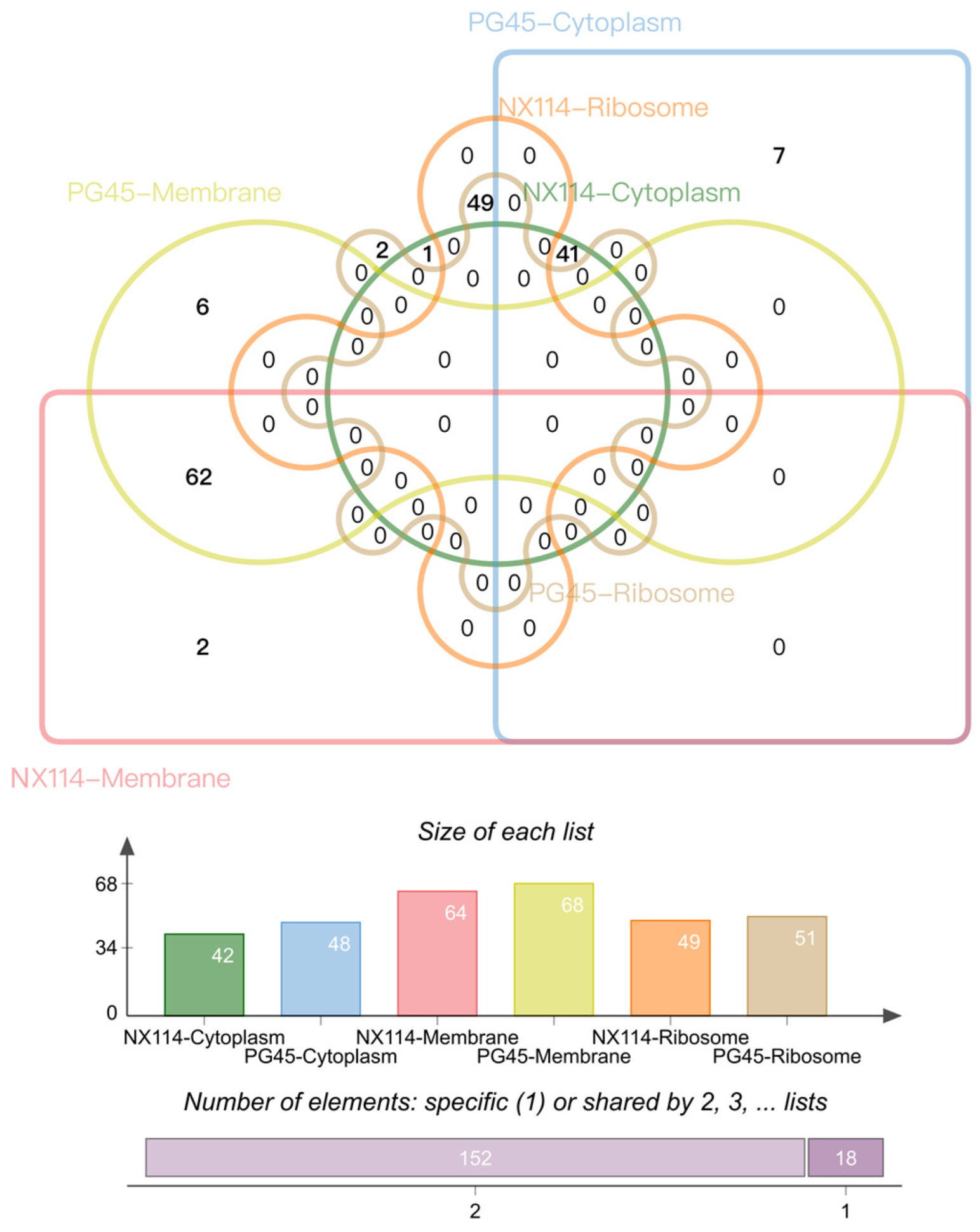
4.1. Important Components of Total Proteins of M. Bovis’ Clinical Strain
4.2. Analysis of M. Bovis Adhesion Protein
4.3. Potential Virulence-Related Proteins Overrepresented in M. Bovis NX114 Whole Cell Proteins
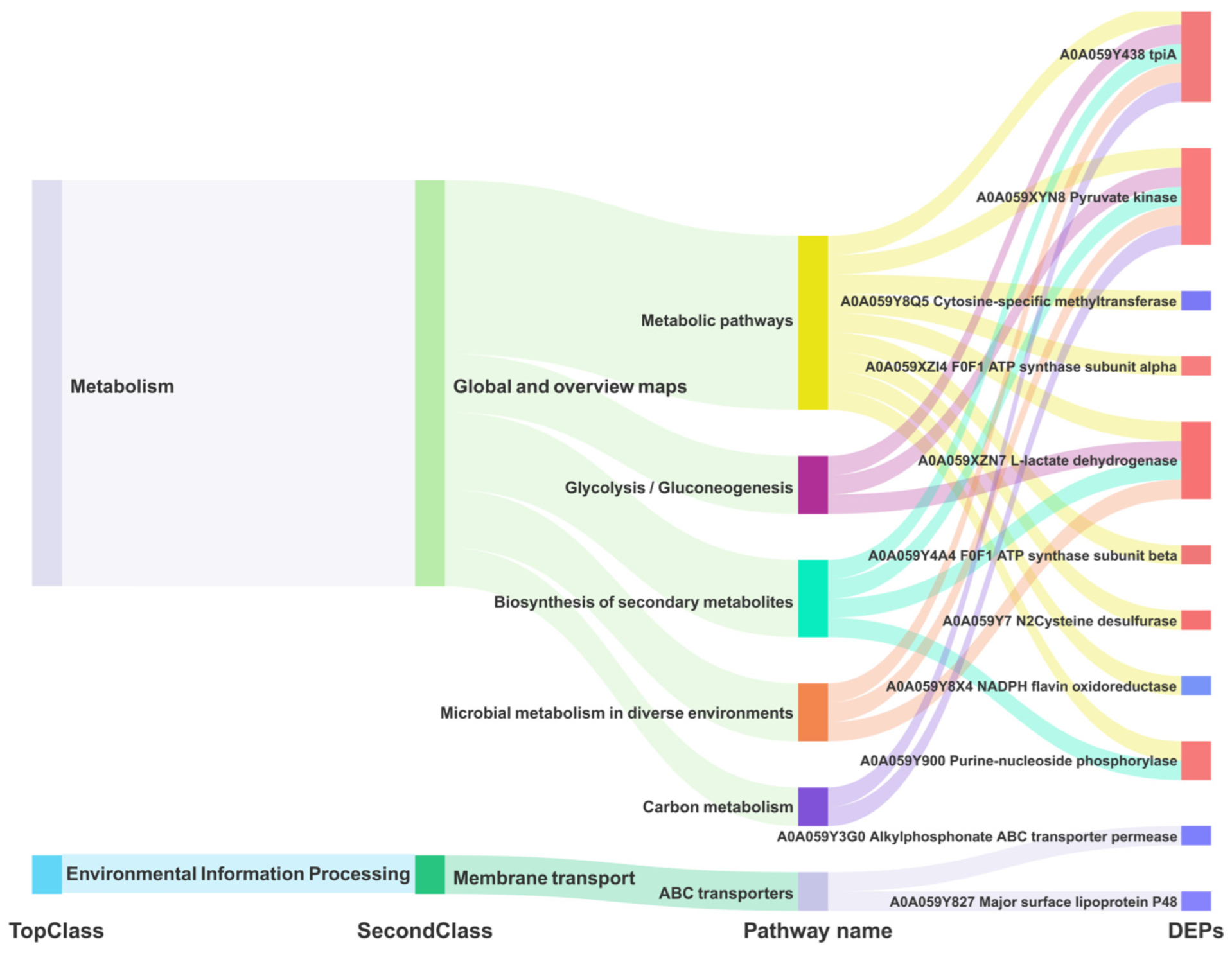
4.4. Trend in Common DGPs and DEGs, and Pathways at All Levels of M. Bovis
4.5. Key Enzymes Regulating Energy Metabolism and Growth in M. Bovis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suwanruengsri, M.; Uemura, R.; Kanda, T.; Fuke, N.; Nueangphuet, P.; Pornthummawat, A.; Yasuda, M.; Hirai, T.; Yamaguchi, R. Production of granulomas in Mycoplasma bovis infection associated with meningitis-meningoencephalitis, endocarditis, and pneumonia in cattle. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2022, 34, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelgie, A.E.; Desai, S.E.; Gelalcha, B.D.; Kerro Dego, O. Mycoplasma bovis mastitis in dairy cattle. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1322267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, C.A.M.; Ambroset, C.; Huleux, A.; Vialatte, A.; Colin, A.; Tricot, A.; Arcangioli, M.A.; Tardy, F. Monitoring Mycoplasma bovis Diversity and Antimicrobial Susceptibility in Calf Feedlots Undergoing a Respiratory Disease Outbreak. Pathogens 2020, 9, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okella, H.; Tonooka, K.; Okello, E. A Systematic Review of the Recent Techniques Commonly Used in the Diagnosis of Mycoplasma bovis in Dairy Cattle. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, A.M.; Abd El-Hamid, M.I.; Mohamed, Y.H.; Mohamed, H.M.; Al-Khalifah, D.H.M.; Hozzein, W.N.; Selim, S.; El-Neshwy, W.M.; El-Malt, R.M.S. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Bovine Mycoplasma Species in Egypt. Biology 2022, 11, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Merwe, J.; Prysliak, T.; Perez-Casal, J. Invasion of bovine peripheral blood mononuclear cells and erythrocytes by Mycoplasma bovis. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 4570–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, K.; Gondaira, S.; Fujiki, J.; Katagata, M.; Sawada, C.; Eguchi, A.; Iwasaki, T.; Iwano, H.; Higuchi, H. Invasion of Mycoplasma bovis into bovine synovial cells utilizing the clathrin-dependent endocytosis pathway. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 253, 108956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, M.; Wang, P.; Wu, W.; Peng, C. MBOVPG45_0375 Encodes an IgG-Binding Protein and MBOVPG45_0376 Encodes an IgG-Cleaving Protein in Mycoplasma bovis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 644224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebollo Couto, M.S.; Klein, C.S.; Voss-Rech, D.; Terenzi, H. Extracellular Proteins of Mycoplasma synoviae. ISRN Vet. Sci. 2012, 2012, 802308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paes, J.A.; Lorenzatto, K.R.; de Moraes, S.N.; Moura, H.; Barr, J.R.; Ferreira, H.B. Secretomes of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae and Mycoplasma flocculare reveal differences associated to pathogenesis. J. Proteom. 2017, 154, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Muhamed, S.A.; Khan, F.A.; Zhao, G.; Menghwar, H.; Faisal, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, X.; Rasheed, M.A.; Chen, Y.; et al. Identification of 60 secreted proteins for Mycoplasma bovis with secretome assay. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 143, 104135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Fang, L.; Liu, W.; Song, T.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, R.; Wang, D.; Xiao, S. Quantitative Proteomic Analyses of a Pathogenic Strain and Its Highly Passaged Attenuated Strain of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 4165735. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, D.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Hu, C.; Guo, A. MbovP0725, a secreted serine/threonine phosphatase, inhibits the host inflammatory response and affects metabolism in Mycoplasma bovis. mSystems 2024, 9, e0089123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, G.; Lu, D.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zubair, M.; Chen, Y.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; et al. Comparative Secretome Analyses of Mycoplasma bovis Virulent and Attenuated Strains Revealed MbovP0145 as a Promising Diagnostic Biomarker. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 666769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Han, X.; Chen, Y.; Mustafa, R.; Qi, J.; Chen, X.; Hu, C.; Chen, H.; Guo, A. Attenuated Mycoplasma bovis strains provide protection against virulent infection in calves. Vaccine 2014, 32, 3107–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiśniewski, J.R.; Zougman, A.; Nagaraj, N.; Mann, M. Universal sample preparation method for proteome analysis. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranakis, I.; Goniotakis, I.; Psaroulaki, A.; Sandalakis, V.; Tselentis, Y.; Gevaert, K.; Tsiotis, G. Proteome studies of bacterial antibiotic resistance mechanisms. J. Proteom. 2014, 97, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citti, C.; Dordet-Frisoni, E.; Nouvel, L.X.; Kuo, C.H.; Baranowski, E. Horizontal Gene Transfers in Mycoplasmas (Mollicutes). Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2018, 29, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürki, S.; Frey, J.; Pilo, P. Virulence, persistence and dissemination of Mycoplasma bovis. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 179, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.Y.; Pan, Q.; Wu, Q.; Xin, J.Q. Mycoplasma Bovis adhesins and their target proteins. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1016641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcutt, M.J.; Lysnyansky, I.; Sachse, K.; Fox, L.K.; Nicholas, R.A.J.; Ayling, R.D. Gap analysis of Mycoplasma bovis disease, diagnosis and control: An aid to identify future development requirements. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65 (Suppl. S1), 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Huang, J.; Zhu, H.; Guo, Y.; Khan, F.A.; Menghwar, H.; Zhao, G.; Guo, A. P27 (MBOV_RS03440) is a novel fibronectin binding adhesin of Mycoplasma bovis. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 308, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Dong, Y.; Baranowski, E.; Li, X.; Zhao, G.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Hu, C.; Chen, H.; et al. Mbov_0503 Encodes a Novel Cytoadhesin that Facilitates Mycoplasma bovis Interaction with Tight Junctions. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamu, J.Y.; Mitiku, F.; Hartley, C.A.; Sansom, F.M.; Marenda, M.S.; Markham, P.F.; Browning, G.F.; Tivendale, K.A. Mycoplasma bovis mbfN Encodes a Novel LRR Lipoprotein That Undergoes Proteolytic Processing and Binds Host Extracellular Matrix Components. J. Bacteriol. 2020, 203, e00154-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, S.; Long, C.; An, Z.; Xing, X.; Wen, F.; Bao, S. Mycoplasmas bovis P48 induces apoptosis in EBL cells via an endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent signaling pathway. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 255, 109013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Guo, A.; Cui, P.; Chen, Y.; Mustafa, R.; Ba, X.; Hu, C.; Bai, Z.; Chen, X.; Shi, L.; et al. Comparative geno-plasticity analysis of Mycoplasma bovis HB0801 (Chinese isolate). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowin, C.L.; Totten, P.A. The Unique Microbiology and Molecular Pathogenesis of Mycoplasma genitalium. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216 (Suppl. S2), S382–S388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masukagami, Y.; Nijagal, B.; Mahdizadeh, S.; Tseng, C.W.; Dayalan, S.; Tivendale, K.A.; Markham, P.F.; Browning, G.F.; Sansom, F.M. A combined metabolomic and bioinformatic approach to investigate the function of transport proteins of the important pathogen Mycoplasma bovis. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 234, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Yang, M.; Si, D.; Sun, J.; Liu, F.; Qi, Y.; He, S.; Guo, Y. UHPLC/MS-Based Untargeted Metabolomics Reveals Metabolic Characteristics of Clinical Strain of Mycoplasma bovis. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gründel, A.; Jacobs, E.; Dumke, R. Interactions of surface-displayed glycolytic enzymes of Mycoplasma pneumoniae with components of the human extracellular matrix. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 306, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Chen, D.; Yu, S.; Chen, H.; Tan, L.; Hu, M.; Qiu, X.; Song, C.; Ding, C. Characterization of triosephosphate isomerase from Mycoplasma gallisepticum. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, fnv140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mathur, D.; Malik, G.; Garg, L.C. Biochemical and functional characterization of triosephosphate isomerase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 263, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Qi, J.; Yu, S.; Yin, Y.; Tan, L.; Bao, S.; Qiu, X.; Wang, X.; Fei, R.; Ding, C. Expression and immunological characteristics of the surface-localized pyruvate kinase in Mycoplasma gallisepticum. Microb. Pathog. 2015, 89, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Tan, L.; Wang, S.; Tian, M.; Li, T.; Wang, X.; Ding, C.; et al. Characterization of Mycoplasma gallisepticum pyruvate dehydrogenase alpha and beta subunits and their roles in cytoadherence. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Query | Gene Symbol | Protein Name | FC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0A2N8U1Q4 | MBOVJF4278_00156 | Lipoprotein | 0.647776028116661 | Membrane |
| A0A2N8U289 | BBB47_01840 | Uncharacterized protein | 0.426185200746393 | |
| A0A2N8U2F7 | BBB47_00485 | DUF4064 domain-containing protein | 4.48373919443482 | |
| A0A2N8U2M4 | MBOVJF4278_00496 | Membrane-associated lipoprotein | 2.11617261459845 | |
| A0A454APD8 | MBOVPG45_0232 | Putative membrane protein (S41B peptidase family) | 0.0737862069159731 | |
| A0A454APP6 | MBOVPG45_0130 | Putative membrane protein | 1.81544954347197 | |
| A0A454APV4 | MBOVPG45_0381 | Putative membrane protein | 1.84465678217211 | |
| A0A454APW7 | atpD-1 | ATP synthase F1, beta subunit | 1.95182048388406 | |
| A0A4U0WAL6 | MBOVa_6030 | Uncharacterized protein | 2.3262641252808 | |
| A0A7D5Z8D8 | H0I36_00720 | Lipoprotein | 0.627424403333434 | |
| A0A2N8U2V1 | tpiA | Triosephosphate isomerase | 1.80897348893876 | Cytoplasm |
| A0A454APQ6 | polC | DNA polymerase III PolC-type | 0.56429428286765 | |
| A0A4U0WAK0 | lysS | Lysine-RNA ligase | 0.587245381151523 | |
| A0A7Z8HQJ6 | polC | DNA polymerase III PolC-type | 0.56429428286765 |
| Query | Protein Name | Gene Symbol | Subject_ID | Q.Log2FC | S.Log2FC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0A059XZ58 | Lipoprotein | K668_01635 | MBOVPG45_RS02835 | −2.997308862 | 3.609877228 |
| A0A059Y359 | Lipoprotein | K668_00750 | MBOVPG45_RS00780 | 0.964261054 | 2.221004141 |
| A0A059Y3S6 | Lipoprotein | K668_01310 | MBOVPG45_RS02855 | −0.597023412 | 1.601990172 |
| A0A059Y4D5 | Lipoprotein | K668_02500 | MBOVPG45_RS01755 | −1.317780028 | −2.456487243 |
| A0A059Y858 | Lipoprotein | K668_01325 | MBOVPG45_RS02835 | −4.70915507 | 3.609877228 |
| A0A059Y8R4 | Lipoprotein | K668_02490 | MBOVPG45_RS01765 | −1.664446972 | −2.954716109 |
| A0A059Y8V7 | Lipoprotein | K668_02495 | MBOVPG45_RS01760 | −1.420301578 | −4.687636632 |
| A0A059Y8Z2 | Lipoprotein | K668_02705 | MBOVPG45_RS01565 | 0.601695187 | 4.267861921 |
| A0A2N8U2D0 | Lipoprotein | MBOVJF4278_00420 | MBOVPG45_RS02150 | −2.813841488 | −5.901035411 |
| A0A2N8U3C5 | Lipoprotein | MBOVJF4278_00737 | MBOVPG45_RS03700 | −2.405070273 | −3.137107754 |
| A0A4U0WA90 | Lipoprotein | MBOVa_2490 | MBOVPG45_RS01755 | −1.33094428 | −2.456487243 |
| A0A4U0WBQ1 | Lipoprotein | MBOVa_0550 | MBOVPG45_RS03700 | −2.24311657 | −3.137107754 |
| A0A7D5Z8D8 | Lipoprotein | H0I36_00720 | MBOVPG45_RS00720 | −0.672486452 | 1.102694211 |
| A0A059Y3R1 | Lipoprotein_10 domain-containing protein | K668_01210 | MBOVPG45_RS02985 | 2.642605673 | 4.934087976 |
| A0A4V6WKP0 | Lipoprotein_10 domain-containing protein | MBOVa_4800 | MBOVPG45_RS02985 | 2.726388616 | 4.934087976 |
| A0A059Y4H6 | Membrane lipoprotein P81 | K668_02710 | MBOVPG45_RS01555 | −2.614465995 | 2.111194499 |
| A0A4U0WD17 | P80, predicted lipoprotein | MBOVa_2120 | MBOVPG45_RS01555 | −2.852551282 | 2.111194499 |
| A0A2N8U2T2 | Putative lipoprotein MPN_284 | MBOVJF4278_00566 | MBOVPG45_RS01555 | −2.614465995 | 2.111194499 |
| A0A7T5ZUY1 | Variable surface lipoprotein | HYD67_03760 | MBOVPG45_RS04915 | −3.959774718 | −3.572406784 |
| A0A454AQ79 | Variable surface lipoprotein, VspK | vspK | MBOVPG45_RS04010 | −3.402030599 | −3.450026003 |
| A0A059Y095 | Glycerol ABC transporter permease | K668_03520 | MBOVPG45_RS03710 | −5.958377462 | −3.175391715 |
| A0A059Y3S3 | ATPase | K668_02160 | MBOVPG45_RS02110 | −2.044928515 | 1.611376339 |
| A0A059Y3Y3 | ABC-2 type transporter ATP-binding protein | K668_02485 | MBOVPG45_RS01770 | −0.967247958 | −2.381064151 |
| A0A059Y4Z4 | Glycerol ABC transporter, permease component | K668_03515 | MBOVPG45_RS03705 | −4.508651244 | −6.594797599 |
| A0A059Y9E4 | Glycerol ABC transporter, glycerol binding protein | K668_03510 | MBOVPG45_RS03700 | −2.439239122 | −3.137107754 |
| A0A454APT2 | ATPase | MBOVPG45_0422 | MBOVPG45_RS02110 | −2.044928515 | 1.611376339 |
| A0A059Y511 | Ribosomal RNA small subunit methyltransferase I | rsmI | MBOVPG45_RS03865 | −1.83661242 | −1.948913065 |
| A0A059Y8H1 | Ribosomal RNA small subunit methyltransferase E | K668_01990 | MBOVPG45_RS02280 | 0.649478799 | 3.390515654 |
| A0A059Y438 | Triosephosphate isomerase | tpiA | MBOVPG45_RS01495 | 0.872625559 | 2.543542361 |
| A0A2N8U2V1 | Triosephosphate isomerase | tpiA | MBOVPG45_RS01495 | 0.855171265 | 2.543542361 |
| A0A059XYN8 | Pyruvate kinase | K668_00745 | MBOVPG45_RS00775 | 1.087484925 | 2.559921425 |
| A0A454APX1 | Pyruvate kinase | pyk | MBOVPG45_RS00775 | 1.087484925 | 2.559921425 |
| A0A4U0W9B9 | Pyruvate kinase | pyk | MBOVPG45_RS00775 | 1.087484925 | 2.559921425 |
| A0A059XZN7 | L-lactate dehydrogenase | K668_02640 | MBOVPG45_RS01630 | 0.816473286 | 4.999558053 |
| A0A059Y351 | Centromere protein F | K668_00230 | MBOVPG45_RS00230 | −0.967726122 | −1.790262413 |
| A0A059Y4B4 | DUF31 domain-containing protein | K668_02400 | MBOVPG45_RS01865 | 1.33879776 | −8 |
| A0A059Y4G0 | Permease | K668_02635 | MBOVPG45_RS01635 | 3.011818835 | 3.799031824 |
| A0A059Y7H5 | Trimethylamine dehydrogenase | K668_00045 | MBOVPG45_RS00040 | −0.838723456 | −2.634300196 |
| A0A059Y818 | ResIII domain-containing protein | K668_00795 | MBOVPG45_RS00815 | −0.656365875 | −1.285742333 |
| A0A059Y885 | Transposase | K668_01205 | MBOVPG45_RS03450 | 2.553808449 | 3.73816659 |
| A0A059Y8X4 | NADPH flavin oxidoreductase | K668_02595 | MBOVPG45_RS01660 | −0.59617792 | 1.562983938 |
| A0A059Y900 | Purine-nucleoside phosphorylase | K668_02755 | MBOVPG45_RS01510 | 0.609460858 | 2.051635587 |
| A0A2N8U339 | Transposase | H0I36_03435 | MBOVPG45_RS03450 | 2.415751165 | 3.73816659 |
| A0A2N8U3L0 | Variant surface antigen A | MBOVJF4278_00819 | MBOVPG45_RS04010 | −0.755880306 | −3.450026003 |
| A0A454AQ67 | Nucleotidyl transferase AbiEii/AbiGii toxin family protein | MBOVPG45_0815 | MBOVPG45_RS04055 | −0.664588662 | −8 |
| A0A4U0W9B3 | NADH dependent flavin oxidoreductase | MBOVa_7200 | MBOVPG45_RS00040 | −0.979012158 | −2.634300196 |
| A0A7Z8HPQ0 | Nitroreductase | BBB47_01090 | MBOVPG45_RS01660 | −0.59617792 | 1.562983938 |
| A0A8D4D676 | Abortive infection protein AbiGI | BC94_0718 | MBOVPG45_RS04050 | −6.67686922 | −8 |
| A0A8D4DA54 | HAD family hydrolase | BC94_0552 | MBOVPG45_RS01400 | −7.535743554 | 3.103338051 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, F.; Yang, M.; Liu, F.; Qi, Y.; Guo, Y.; He, S. Integrating the Transcriptome and Proteome to Postulate That TpiA and Pyk Are Key Enzymes Regulating the Growth of Mycoplasma Bovis. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2012. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12102012
Yang F, Yang M, Liu F, Qi Y, Guo Y, He S. Integrating the Transcriptome and Proteome to Postulate That TpiA and Pyk Are Key Enzymes Regulating the Growth of Mycoplasma Bovis. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(10):2012. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12102012
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Fei, Mengmeng Yang, Fan Liu, Yanrong Qi, Yanan Guo, and Shenghu He. 2024. "Integrating the Transcriptome and Proteome to Postulate That TpiA and Pyk Are Key Enzymes Regulating the Growth of Mycoplasma Bovis" Microorganisms 12, no. 10: 2012. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12102012
APA StyleYang, F., Yang, M., Liu, F., Qi, Y., Guo, Y., & He, S. (2024). Integrating the Transcriptome and Proteome to Postulate That TpiA and Pyk Are Key Enzymes Regulating the Growth of Mycoplasma Bovis. Microorganisms, 12(10), 2012. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12102012






