Relationship between the Cycle Threshold Value (Ct) of a Salmonella spp. qPCR Performed on Feces and Clinical Signs and Outcome in Horses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Sampling Procedures
2.3. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Assay
2.4. Statistical Analysis
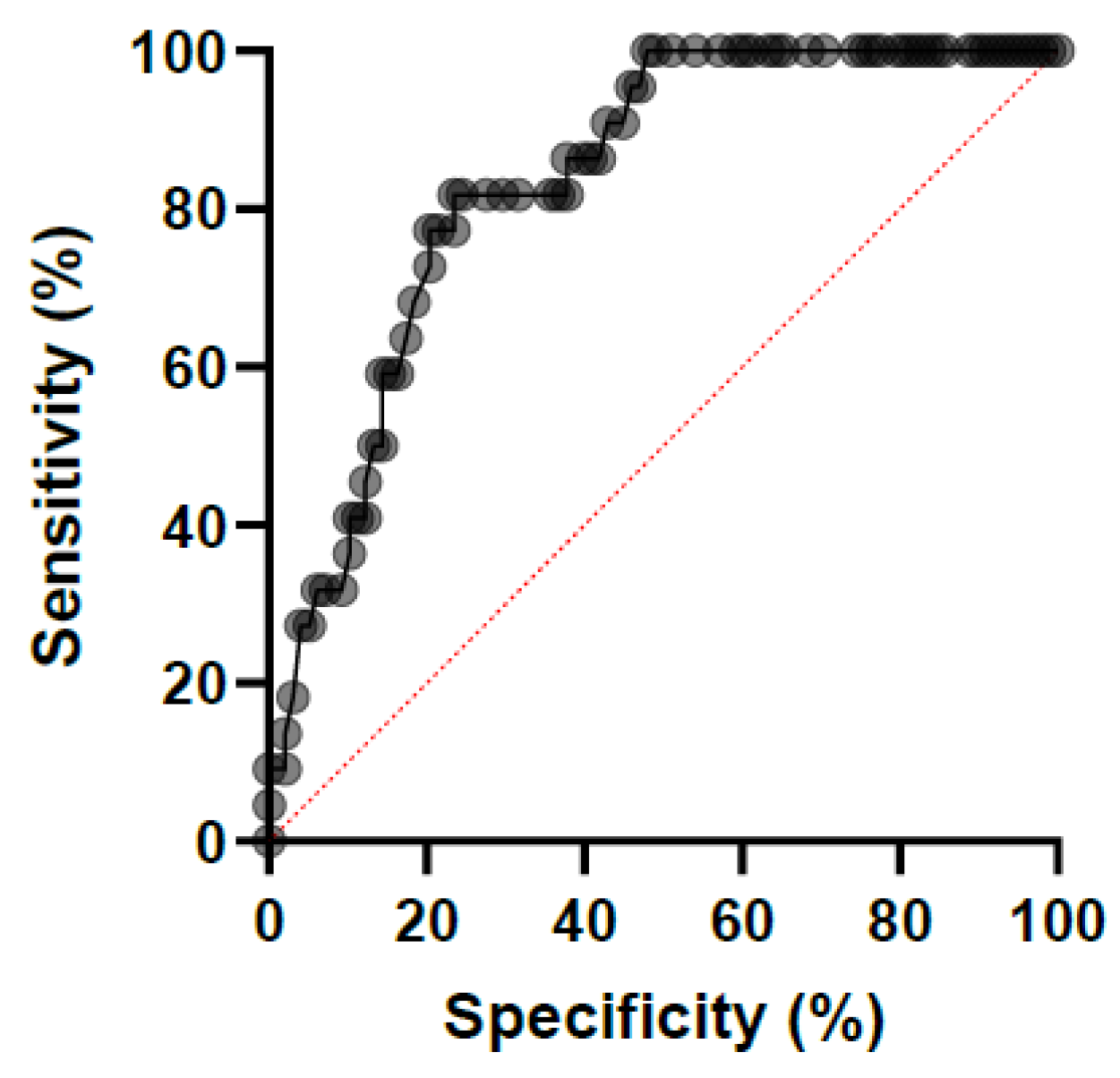
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaw, S.D.; Stämpfli, H. Diagnosis and Treatment of Undifferentiated and Infectious Acute Diarrhea in the Adult Horse. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2018, 34, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, G.L.; Popa, M.L. Salmonella spp. Infection—A continuous threat worldwide. Germs 2021, 11, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teklemariam, A.D.; Al-Hindi, R.R.; Albiheyri, R.S.; Alharbi, M.G.; Alghamdi, M.A.; Filimban, A.A.R.; Al Mutiri, A.S.; Al-Alyani, A.M.; Alseghayer, M.S.; Almaneea, A.M.; et al. Human Salmonellosis: A Continuous Global Threat in the Farm-to-Fork Food Safety Continuum. Foods 2023, 12, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besser, J.M. Salmonella epidemiology: A whirlwind of change. Food Microbiol. 2018, 71, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, J.A.; Long, M.T.; Traub-Dargatz, J.L.; Besser, T.E. Salmonellosis. In Equine Infectious Diseases, 2nd ed.; Sellon, D., Long, M.T., Eds.; Saunders Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2014; pp. 321–333. [Google Scholar]
- Kirk, M.D.; Pires, S.M.; Black, R.E.; Caipo, M.; Crump, J.A.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Doepfer, D.; Fazil, A.; Fischer-Walker, C.L.; Hald, T.; et al. World Health Organization estimates of the global and regional disease burden of 22 foodborne bacterial, protozoal, and viral diseases, 2010: A data synthesis. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001921. [Google Scholar]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Salmonellosis. In ECDC. Annual Epidemiological Report for 2021; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2022; Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/SALM_AER_2021.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2023).
- Arnold, M.; Piers Smith, R.; Tang, Y.; Guzinski, J.; Petrovska, L. Bayesian Source Attribution of Salmonella Typhimurium Isolates From Human Patients and Farm Animals in England and Wales. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 579888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espié, E.; De Valk, H.; Vaillant, V.; Quelquejeu, N.; Le Querrec, F.; Weill, F.X. An outbreak of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serotype Newport infections linked to the consumption of imported horse meat in France. Epidemiol. Infect. 2005, 133, 373–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, D.H.; Hancock, D.D.; Roozen, P.M.; Szymanski, M.H.; Scheenstra, B.C.; Cady, K.M.; Besser, T.E.; Paul A Chudek, P.A. Household contamination with Salmonella enterica. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, M.P.; Brady, T.H.; Couëtil, L.L.; Liljebjelke, K.; Maurer, J.J.; Wu, C.C. Investigation and control of an outbreak of salmonellosis caused by multidrug-resistant Salmonella typhimurium in a population of hospitalized horses. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 107, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steneroden, K.K.; Van Metre, D.C.; Jackson, C.; Morley, P.S. Detection and control of a nosocomial outbreak caused by Sal-monella Newport at a large animal hospital. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2010, 24, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, S.C.; Aceto, H.; Cassidy, J.; Holt, J.; Young, S.; Love, B.; Tewari, D.; Munro, D.S.; Benson, C.E. Molecular character ization of cephalosporin-resistant Salmonella enterica sero type Newport isolates from animals in Pennsylvania. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 4679–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dallap Schaer, B.L.; Aceto, H.; Rankin, S.C. Outbreak of salmonellosis caused by Salmonella enterica serovar Newport MDR-AmpC in a large animal veterinary teaching hospital. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2010, 24, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soza-Ossandón, P.; Rivera, D.; Tardone, R.; Riquelme-Neira, R.; García, P.; Hamilton-West, C.; Adell, A.D.; González-Rocha, G.; Moreno-Switt, A.I. Widespread Environmental Presence of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella in an Equine Veterinary Hospital That Received Local and International Horses. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, F.W.; Villar, R.G.; Angulo, F.J.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.; Swaminathan, B. Salmonella nomenclature. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 2465–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tindall, B.J.; Grimont, P.A.; Garrity, G.M.; Euzéby, J.P. Nomenclature and taxonomy of the genus Salmonella. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, K.; Baker, S.; Kim, C.C.; Detweiler, C.S.; Dougan, G.; Falkow, S. Genomic comparison of Salmonella enterica serovars and Salmonella bongori by use of an S. enterica serovar typhimurium DNA microarray. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union One Health 2018 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05926. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/zoonoses-EU-one-health-2018-report.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2023). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martelli, F.; Sue, K.; Lawes, J. Surveillance for Salmonella in horses in Great Britain. Vet. Rec. 2019, 184, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, I.M.; Lawhon, S.D.; Norman, K.N.; Threadgill, D.S.; Ohta, N.; Vinasco, J.; Scott, H.M. Serotype Diversity and Antimi-crobial Resistance among Salmonella enterica Isolates from Patients at an Equine Referral Hospital. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e02829-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uzal, F.A.; Arroyo, L.G.; Navarro, M.A.; Gomez, D.E.; Asín, J.; Henderson, E. Bacterial and viral enterocolitis in horses: A review. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2022, 34, 354–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Duijkeren, E.; Sloet van Oldruitenborgh-Oosterbaan, M.M.; Houwers, D.J.; van Leeuwen, W.J.; Kalsbeek, H.C. Equine salmonellosis in a Dutch veterinary teaching hospital. Vet. Rec. 1994, 13, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Duijkeren, E.; Flemming, C.; Sloet van Oldruitenborgh-Oosterbaan, M.M.; Kalsbeek, H.C.; van der Giessen, J.W. Diagnosing salmonellosis in horses. Culturing of multiple versus single faecal samples. Vet. Q. 1995, 17, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Duijkeren, E.; Wannet, W.J.; Heck, M.E.; van Pelt, W.; Sloet van Oldruitenborgh-Oosterbaan, M.M.; Smit, J.A. Houwers, D.J. Sero types, phage types and antibiotic susceptibilities of Salmonella strains isolated from horses in The Netherlands from 1993 to 2000. Vet. Microbiol. 2002, 86, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddox, T.W.; Clegg, P.D.; Williams, N.J.; Pinchbeck, G.L. Antimicrobial resistance in bacteria from horses: Epidemiology of antimicrobial resistance. Equine Vet. J. 2015, 47, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walther, B.; Tedin, K.; Lübke-Becker, A. Multidrug-resistant opportunistic pathogens challenging veterinary infection control. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 200, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelli, F.; Sue, K.; Lawes, J. Salmonella and salmonellosis in horses: An overview. Vet. Rec. 2018, 182, 659–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theelen, M.J.; Wilson, W.D.; Edman, J.M.; Magdesian, K.G.; Kass, P.H. Temporal trends in prevalence of bacteria isolated from foals with sepsis: 1979–2010. Equine Vet. J. 2014, 46, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, A.E.; Reid, S.W.; Maskell, D.J.; Parkhill, J.; Fookes, M.C.; Harris, S.R.; Brown, D.J.; Coia, J.E.; Mulvey, M.R.; Gilmour, M.W.; et al. Distinguishable epidemics of multidrug-resistant Salmonella Typhimurium DT104 in different hosts. Science 2013, 341, 1514–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Hello, S.; Bekhit, A.; Granier, S.A.; Barua, H.; Beutlich, J.; Zając, M.; Münch, S.; Sintchenko, V.; Bouchrif, B.; Fashae, K.; et al. The global establishment of a highly-fluoroquinolone resistant Salmonella enterica serotype Kentucky ST198 strain. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dargatz, D.A.; Traub-Dargatz, J.L. Multidrug-resistant Salmonella and nosocomial infections. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2004, 20, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallap Schaer, B.L.; Aceto, H.; Caruso, M.A.; Brace, M.A. Identification of predictors of Salmonella shedding in adult horses presented for acute colic. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2012, 26, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, B.A.; Bauknecht, K.; Slovis, N.M.; Morley, P.S. Factors associated with equine shedding of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica and its impact on health outcomes. Equine Vet. J. 2018, 50, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekiri, A.B.; MacKay, R.J.; Gaskin, J.M.; Freeman, D.E.; House, A.M.; Giguère, S.; Troedsson, M.R.; Schuman, C.D.; von Chamier, M.M.; Henry, K.M.; et al. Epidemiologic analysis of nosocomial Salmonella infections in hospitalized horses. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2009, 234, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, B.A.; Morley, P.S. Risk factors for shedding of Salmonella enterica among hospitalized large animals over a 10-year period in a veterinary teaching hospital. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 2239–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez, L.C. Disorders of the gastrointestinal system. In Equine Internal Medicine, 4th ed.; Reed, S.M., Warwick, B.W., Sellon, D., Eds.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2018; pp. 709–842. [Google Scholar]
- Pusterla, N.; Byrne, B.A.; Hodzic, E.; Mapes, S.; Jang, S.S.; Magdesian, K.G. Use of quantitative real-time PCR for the detection of Salmonella spp. in fecal samples from horses at a veterinary teaching hospital. Vet. J. 2010, 186, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekiri, A.B.; Long, M.T.; Hernandez, J.A. Diagnostic performance and application of a real-time PCR assay for the detection of Salmonella in fecal samples collected from hospitalized horses with or without signs of gastrointestinal tract disease. Vet. J. 2016, 208, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.P.; Alinovi, C.A.; Couëtil, L.L.; Wu, C.C. Evaluation of a PCR to detect Salmonella in fecal samples of horses admitted to a veterinary teaching hospital. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2005, 17, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, N.D.; Martin, L.J.; Simpson, R.B.; Wallis, D.E.; Neibergs, H.L. Comparison of polymerase chain reaction and micro-biological culture for detection of salmonellae in equine feces and environmental samples. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1996, 57, 780–786. [Google Scholar]
- Kurowski, P.B.; Traub-Dargatz, J.L.; Morley, P.S.; Gentry-Weeks, C.R. Detection of Salmonella spp. in fecal specimens by use of real-time polymerase chain reaction assay. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2002, 63, 1265–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.R.; Stensland, W.R.; Wang, C.H.; O’Connor, A.M.; Trampel, D.W.; Harmon, K.M.; Strait, E.L.; Frana, T.S. Detection of Salmonella enteritidis in pooled poultry environmental samples using a serotype-specific real-time-polymerase chain reaction assay. Avian Dis. 2013, 57, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brizuela, M.E.; Goñi, S.E.; Cardama, G.A.; Zinni, M.A.; Castello, A.A.; Sommese, L.M.; Farina, H.G. Correlation of SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load and Clinical Evolution of Pediatric Patients in a General Hospital From Buenos Aires, Argentina. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 883395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, M.F.; Kwong, J.; Lambert, S.; Massie, S.; Lockhart, S. Prognostic Value and Development of a Scoring System in Horses With Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2017, 31, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Southwood, L.L.; Lindborg, S.; Myers, M.; Aceto, H.W. Influence of Salmonella status on the long-term outcome of horses after colic surgery. Vet. Surg. 2017, 46, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, M.M.; Feist, M.D. Real-time PCR method for Salmonella spp. targeting the stn gene. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 516–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piorkowski, G.; Baronti, C.; de Lamballerie, X.; de Fabritus, L.; Bichaud, L.; Pastorino, B.A.; Bessaud, M. Development of generic Taqman PCR and RT-PCR assays for the detection of DNA and mRNA of β-Actin-encoding sequences in a wide range of animal species. J. Virol. Methods. 2014, 202, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hird, D.W.; Casebolt, D.B.; Carter, J.D.; Pappaioanou, M.; Hjerpe, C.A. Risk factors for salmonellosis in hospitalized horses. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1986, 188, 173–177. [Google Scholar]
- Traub-Dargatz, J.L.; Salman, M.D.; Jones, R.L. Epidemiologic study of salmonellae shedding in the feces of horses and potential risk factors for development of the infection in hospitalized horses. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1990, 196, 1617–1622. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, L.M.; Morley, P.S.; Traub-Dargatz, J.L.; Salman, M.D.; Gentry-Weeks, C. Factors associated with Salmonella shedding among equine colic patients at a veterinary teaching hospital. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2001, 218, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilcoyne, I.; Magdesian, K.G.; Guerra, M.; Dechant, J.E.; Spier, S.J.; Kass, P.H. Prevalence of and risk factors associated with Salmonella shedding among equids presented to a veterinary teaching hospital for colic (2013–2018). Equine Vet. J. 2022, 55, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alinovi, C.A.; Ward, M.P.; Couëtil, L.L.; Wu, C.C. Risk factors for fecal shedding of Salmonella from horses in a veterinary teaching hospital. Prev. Vet. Med. 2003, 12, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luethy, D.; Feldman, R.; Stefanovski, D.; Aitken, M.R. Risk factors for laminitis and nonsurvival in acute colitis: Retrospective study of 85 hospitalized horses (2011–2019). J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 2019–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopper, J.J.; Willette, J.A.; Kogan, C.J.; Seguin, A.; Bolin, S.R.; Schott, H.C., 2nd. Detection of pathogens in blood or feces of adult horses with enteric disease and association with outcome of colitis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 2465–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willette, J.A.; Kopper, J.J.; Kogan, C.J.; Seguin, M.A.; Schott, H.C. Effect of season and geographic location in the United States on detection of potential enteric pathogens or toxin genes in horses ≥6-mo-old. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2022, 34, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hensel, M.; Meason-Smith, C.; Plumlee, Q.D.; Myers, A.N.; Coleman, M.C.; Lawhon, S.; Rodrigues Hoffmann, A.; Rech, R.R. Retrospective Analysis of Aetiological Agents Associated with Pulmonary Mycosis Secondary to Enteric Salmonellosis in Six Horses by Panfungal Polymerase Chain Reaction. J. Comp. Pathol. 2020, 174, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinola, S.A.; Mwanza, M.; Ateba, C.N. Occurrence, Genetic Diversities And Antibiotic Resistance Profiles Of Salmonella Serovars Isolated From Chickens. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 3327–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murray, R.A.; Lee, C.A. Invasion genes are not required for Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium to breach the intestinal epithelium: Evidence that salmonella pathogenicity island 1 has alternative functions during infection. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 5050–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buehler, A.J.; Wiedmann, M.; Kassaify, Z.; Cheng, R.A. Evaluation of invA Diversity among Salmonella Species Suggests Why Some Commercially Available Rapid Detection Kits May Fail To Detect Multiple Salmonella Subspecies and Species. J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khatib, K.; Hadeer, R.A.; Saad, A.; Kalaydjian, A.; Fayad, E.; Mahfouz, Y.; Dougnon, V.; Daoud, Z.; Abdel-Massih, R.M. Determination of MIC, MPC, and MSW of Ilex paraguariensis against non-typhoidal Salmonella with identification of the mechanisms of resistance and pathogenicity factors. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 174, 105905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, S.; Kurazono, H.; Chongsanguam, M.; Hayashi, H.; Cheun, H.; Suzuki, S.; Shirahata, T. Establishment of the PCR system specific to Salmonella spp. and its application for the inspection of food and fecal samples. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1999, 61, 1245–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Cerro, A.; Soto, S.M.; Landeras, E.; Gonzalez-Hevia, M.A.; Guijarro, J.A.; Mendoza, M.C. PCR-based procedures in detection and DNA-fingerprinting of Salmonella from samples of animal origin. Food Microbiol. 2002, 19, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malorny, B.; Hoorfar, J.; Bunge, C.; Helmuth, R. Multicenter validation of the analytical accuracy of Salmonella PCR: Towards an international standard. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murugkar, H.V.; Rahman, H.; Dutta, P.K. Distribution of virulence genes in Salmonella serovars isolated from man & animals. Indian J. Med. Res. 2003, 117, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Ziemer, C.J.; Steadham, S.R. Evaluation of the specificity of Salmonella PCR primers using various intestinal bacterial species. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 37, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartnack, A.K.; Van Metre, D.C.; Morley, P.S. Salmonella enterica shedding in hospitalized horses and associations with diarrhea occurrence among their stablemates and gastrointestinal-related illness or death following discharge. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2012, 240, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainar-Jaime, R.C.; House, J.K.; Smith, B.P.; Kamiya, D.Y. Influence of fecal shedding of Salmonella organisms on mortality in hospitalized horses. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1998, 213, 1162–1166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Fu, B.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H. Quantification of viable but nonculturable bacterial pathogens in anaerobic di-gested sludge. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 6043–6050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, W.; Kelley, E.; Bowers, J.; Engelthaler, D. Normalization of SARS-CoV-2 viral load via RT-qPCR provides higher-resolution data for comparison across time and between patients. Virus Res. 2021, 306, 198604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amory, H.; Cesarini, C.; De Maré, L.; Loublier, C.; Moula, N.; Detilleux, J.; Saulmont, M.; Garigliany, M.-M.; Lecoq, L. Relationship between the Cycle Threshold Value (Ct) of a Salmonella spp. qPCR Performed on Feces and Clinical Signs and Outcome in Horses. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1950. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11081950
Amory H, Cesarini C, De Maré L, Loublier C, Moula N, Detilleux J, Saulmont M, Garigliany M-M, Lecoq L. Relationship between the Cycle Threshold Value (Ct) of a Salmonella spp. qPCR Performed on Feces and Clinical Signs and Outcome in Horses. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(8):1950. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11081950
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmory, Hélène, Carla Cesarini, Lorie De Maré, Clémence Loublier, Nassim Moula, Johann Detilleux, Marc Saulmont, Mutien-Marie Garigliany, and Laureline Lecoq. 2023. "Relationship between the Cycle Threshold Value (Ct) of a Salmonella spp. qPCR Performed on Feces and Clinical Signs and Outcome in Horses" Microorganisms 11, no. 8: 1950. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11081950
APA StyleAmory, H., Cesarini, C., De Maré, L., Loublier, C., Moula, N., Detilleux, J., Saulmont, M., Garigliany, M.-M., & Lecoq, L. (2023). Relationship between the Cycle Threshold Value (Ct) of a Salmonella spp. qPCR Performed on Feces and Clinical Signs and Outcome in Horses. Microorganisms, 11(8), 1950. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11081950






