Dynamic Responses of Rhizosphere Microorganisms to Biogas Slurry Combined with Chemical Fertilizer Application during the Whole Life Cycle of Rice Growth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Crop Management
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Microbial Characteristics Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in Main Nutrients in Paddy Water during the Whole Growth of Rice
3.2. Changes in Microbial Diversity and Richness during the Whole Growth of Rice
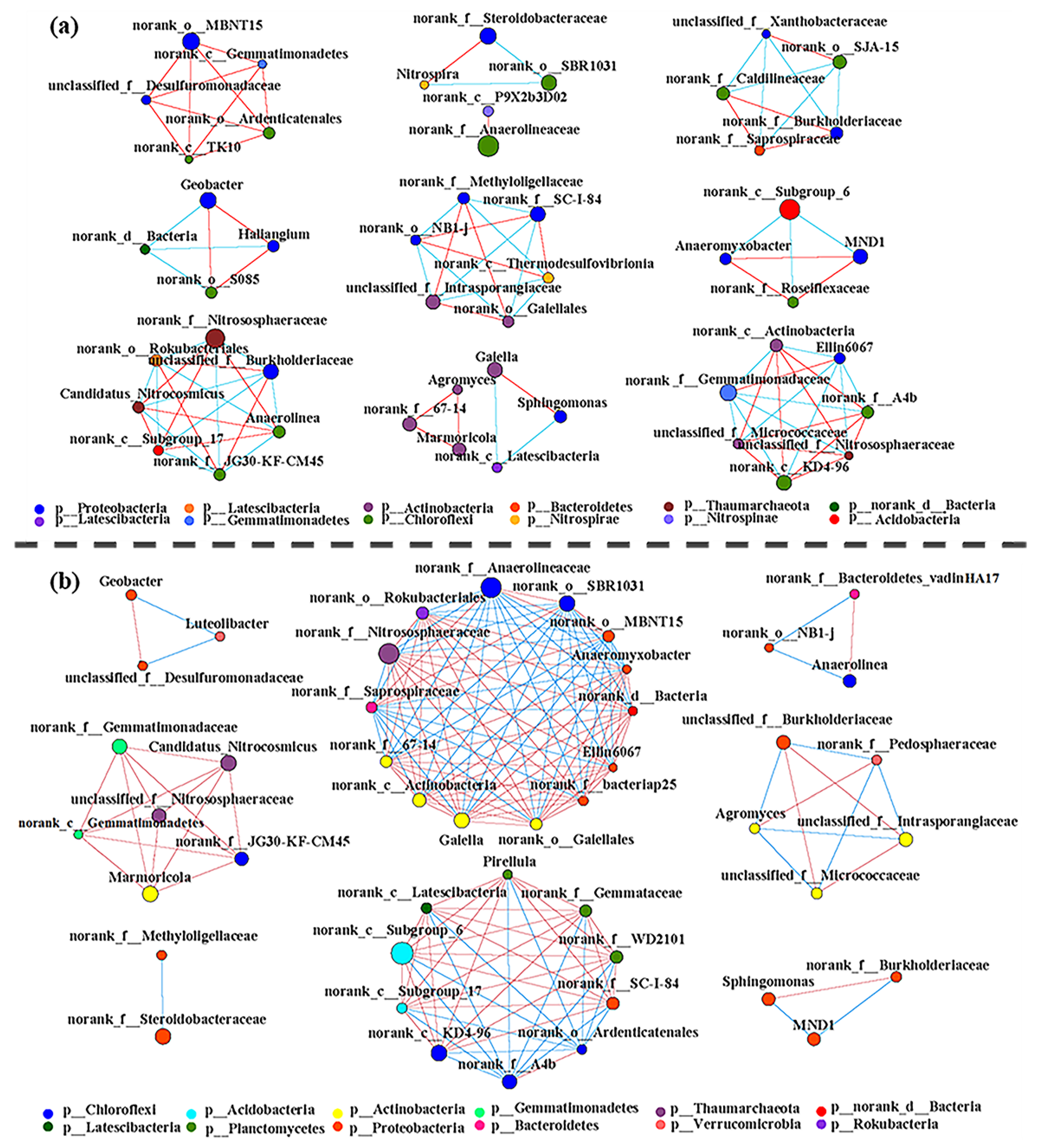
3.3. Changes in Bacterial Community Structure during the Whole Growth of Rice
3.4. Changes in Fungal Community Structure during the Whole Growth of Rice
3.5. Relationships between the Rhizosphere Microbial Communities and Environmental Factors
3.6. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, Y.; Wang, J.D.; Wu, H.S.; Yan, S.H.; Guo, D.J.; Wang, G.F.; Ma, Y. Soil chemical and microbial responses to biogas slurry amendment and its effect on Fusarium wilt suppression. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 107, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.T.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, R.; Song, N.H.; Liu, R.; Bu, Y.Q. Occurrence, Distribution, and Potential Role of Bacteria and Human Pathogens in Livestock Manure and Digestate: Insights from the Guangxi, China. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2021, 38, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubaker, J.; Risberg, K.; Pell, M. Biogas residues as fertilisers—Effects on wheat growth and soil microbial activities. Appl. Energy 2012, 99, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, M.Y.; Cao, Y.C.; Liang, P.; Wu, S.C.; Leung, A.O.W.; Christie, P. Replacement of mineral fertilizers with anaerobically digested pig slurry in paddy fields: Assessment of plant growth and grain quality. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 8916–8923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doreen, Z.; Andre, P.; Martin, K. Elemental composition of biogas residues: Variability and alteration during anaerobic digestion. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 67, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.L.; Li, S.X.; Zheng, X.Q.; Zhang, J.Q.; Bai, N.L.; Zhang, H.Y.; Lv, W.G. Effects of biogas slurry combined with chemical fertilizer on soil bacterial and fungal community composition in a paddy field. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 655515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Xian, Y.; Wu, J.; Gu, Y.F.; Yang, G.; Zhang, X.H.; Peng, H.; Yu, X.Y.; Xiao, Y.L.; Li, L. Effect of biogas slurry addition on soil properties, yields, and bacterial composition in the rice-rape rotation ecosystem over 3 years. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 2534–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.E.; Kent, A.D.; Brisson, V.L.; Gaudin, A.C.M. Agricultural management and plant selection interactively affect rhizosphere microbial community structure and nitrogen cycling. Microbiome 2019, 7, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Ali, S.; Shahid, M.A.; Mustafa, A.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Cura, J.A. Insights into the interactions among roots, rhizosphere, and rhizobacteria for improving plant growth and tolerance to abiotic stresses: A review. Cells 2021, 10, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.C.; Penton, C.R.; Xiong, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, R.F.; Liu, Z.Y.; Xu, X.; Li, R.; Shen, Q.R. Reshaping the rhizosphere microbiome by bio-organic amendment to enhance crop yield in a maize-cabbage rotation system. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 142, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Arafat, Y.; Din, R.U.; Yang, B.; Zhou, L.T.; Wang, J.Y.; Letuma, P.; Wu, H.M.; Qin, X.J.; Wu, L.K.; et al. Nitrogen Fertilizer Amendment Alter the Bacterial Community Structure in the Rhizosphere of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) and Improve Crop Yield. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.M.; Yuan, J.; Zhu, Y.H.; Yi, X.J.; Zhao, Q.; Fang, K.K.; Cao, L.K. Comparison of the Abundance and Community Structure of N-Cycling Bacteria in Paddy Rhizosphere Soil under Different Rice Cultivation Patterns. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.M.; Wang, Q.; Ma, J.W.; Chapman, S.; Zou, P.; Ye, J.; Yu, Q.G.; Sun, W.C.; Lin, H.; Jiang, L.N. Soil microbial activity and community composition as influenced by application of pig biogas slurry in paddy field in southeast China. Paddy Water Environ. 2020, 18, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.M.; Wang, Q.; Ma, J.W.; Zou, P.; Yu, Q.G.; Jiang, L.N. Fungal community composition change and heavy metal accumulation in response to the long-term application of anaerobically digested slurry in a paddy soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 196, 110453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Yin, J.Z.; Davy, A.J.; Pan, F.F.; Han, X.; Huang, S.N.; Wu, D.F. Biogas Slurry as an Alternative to Chemical Fertilizer: Changes in Soil Properties and Microbial Communities of Fluvo-AquicSoil in the North China Plain. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubar, A.A.; Huang, Q.; Kubar, K.A.; Khan, M.A.; Sajjad, M.; Gul, S.; Yang, C.; Wang, Q.Q.; Guo, G.M.; Kubar, G.M.; et al. Ammonium and Phosphate Recovery from Biogas Slurry: Multivariate Statistical Analysis Approach. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.Q.W.; Hu, J.H.; Xia, Q.M.; Zhang, S.L.; Li, X.; Pan, X.Y.; Zhao, R.P.; Wang, R.W.; Yan, W.M.; Shangguan, Z.P.; et al. Soil microbial mechanisms promoting ultrahigh rice yield. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 143, 107741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Gao, Y.; Jia, X.H.; Wang, M.M.; Ding, J.J.; Cheng, L.; Bao, F.; Wu, B. Network analysis reveals the strengthening of microbial interaction in biological soil crust development in the Mu Us Sandy Land, northwestern China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 144, 107782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.J.; Peng, J.J.; Liu, P.F.; Bei, Q.C.; Rensing, C.; Li, Y.; Yuan, H.M.; Liesack, W.; Zhang, F.S.; Cui, Z.L. Metagenomic insights into nitrogen and phosphorus cycling at the soil aggregate scale driven by organic material amendments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curlevski, N.J.A.; Xu, Z.H.; Anderson, I.C.; Cairney, J.W.G. Converting Australian tropical rainforest to native Araucariaceae plantations alters soil fungal communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clairmont, L.K.; Slawson, R.M. Contrasting Water Quality Treatments Result in Structural and Functional Changes to Wetland Plant-Associated Microbial Communities in Lab-Scale Mesocosms. Microb. Ecol. 2020, 79, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenk, S.; Hadar, Y.; Minz, D. Resilience of soil bacterial community to irrigation with water of different qualities under Mediterranean climate. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Xun, W.B.; Yan, H.; Ma, A.Y.; Xiong, W.; Shen, Q.R.; Zhang, R.F. Functional compensation dominates the assembly of plant rhizospheric bacterial community. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 150, 107968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.M.; Ji, G.D. Biotic factors drive distinct DNRA potential rates and contributions in typical Chinese shallow lake sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Suter, H.; He, J.Z.; Hu, H.W.; Chen, D.L. Nitrogen Addition Decreases Dissimilatory Nitrate Reduction to Ammonium in Rice Paddies. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e00870-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, H.K.; Lui, L.M.; Price, M.N.; Kazakov, A.E.; Carr, A.V.; Kuehl, J.V.; Owens, T.K.; Nielsen, T.; Arkin, A.P.; Deutschbauer, A.M. Selective carbon sources influence the end products of microbial nitrate respiration. Isme J. 2020, 14, 2034–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, B.; Tegetmeyer, H.E.; Sharma, R.; Klotz, M.G.; Ferdelman, T.G.; Hettich, R.L.; Geelhoed, J.S.; Strous, M. The environmental controls that govern the end product of bacterial nitrate respiration. Science 2014, 345, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, H.L.; An, S.S.; Bhople, P.; Davlatbekov, F. Geographic distance and soil microbial biomass carbon drive biogeographical distribution of fungal communities in Chinese Loess Plateau soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.M.M.; Estrada-Bonilla, G.A.; Lopes, C.M.; Matteoli, F.P.; Cotta, S.R.; Feiler, H.P.; Rodrigues, Y.F.; Cardoso, E. Does Organomineral Fertilizer Combined with Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria in Sugarcane Modulate Soil Microbial Community and Functions. Microb. Ecol. 2022, 84, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.P.; Yang, T.J.; Bao, Y.Z.; He, P.P.; Yang, K.M.; Mei, X.L.; Wei, Z.; Xu, Y.C.; Shen, Q.R.; Banerjee, S. Network analysis and subsequent culturing reveal keystone taxa involved in microbial litter decomposition dynamics. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 157, 108230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, B.K.; Zhao, B.S.; Ma, M.C.; Guan, D.W.; Li, J.; Chen, S.F.; Cao, F.M.; Shen, D.L.; et al. Thirty four years of nitrogen fertilization decreases fungal diversity and alters fungal community composition in black soil in northeast China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 95, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.F.; Luo, L.M.; Carswell, A.; Misselbrook, T.; Shen, J.H.; Han, J.G. Changes in soil organic carbon status and microbial community structure following biogas slurry application in a wheat-rice rotation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Zhao, G.H.; Zhang, H.M.; Shen, Y.Q.; Fei, H.B.; Cheng, W.D. Biogas slurry use as N fertilizer for two-season Zizania aquatica Turcz. in China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosys. 2017, 107, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.Q.; Ding, L.J.; Xue, K.; Yao, H.Y.; Quensen, J.; Bai, S.J.; Wei, W.X.; Wu, J.S.; Zhou, J.Z.; Tiedje, J.M.; et al. Long-term balanced fertilization increases the soil microbial functional diversity in a phosphorus-limited paddy soil. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
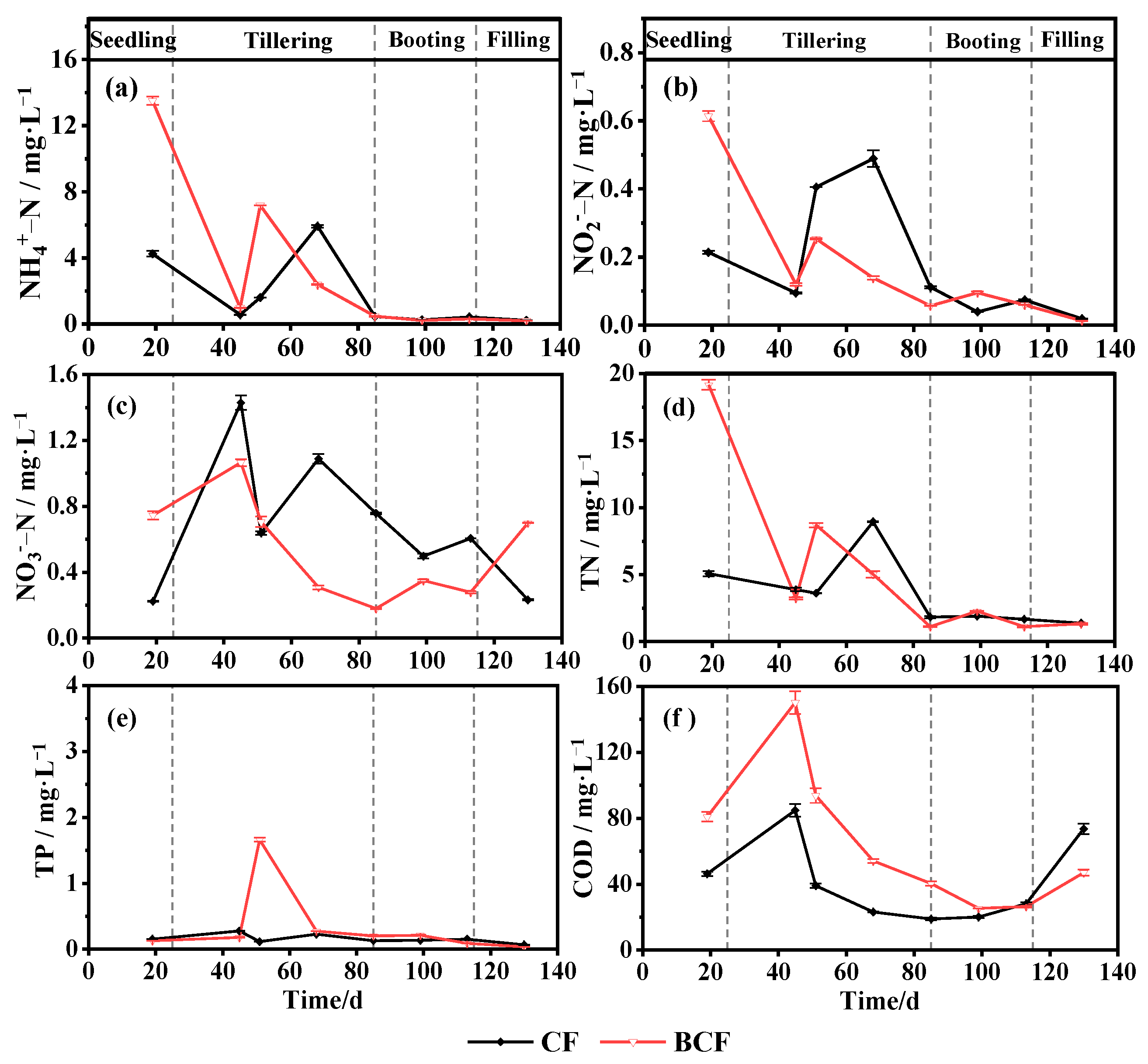
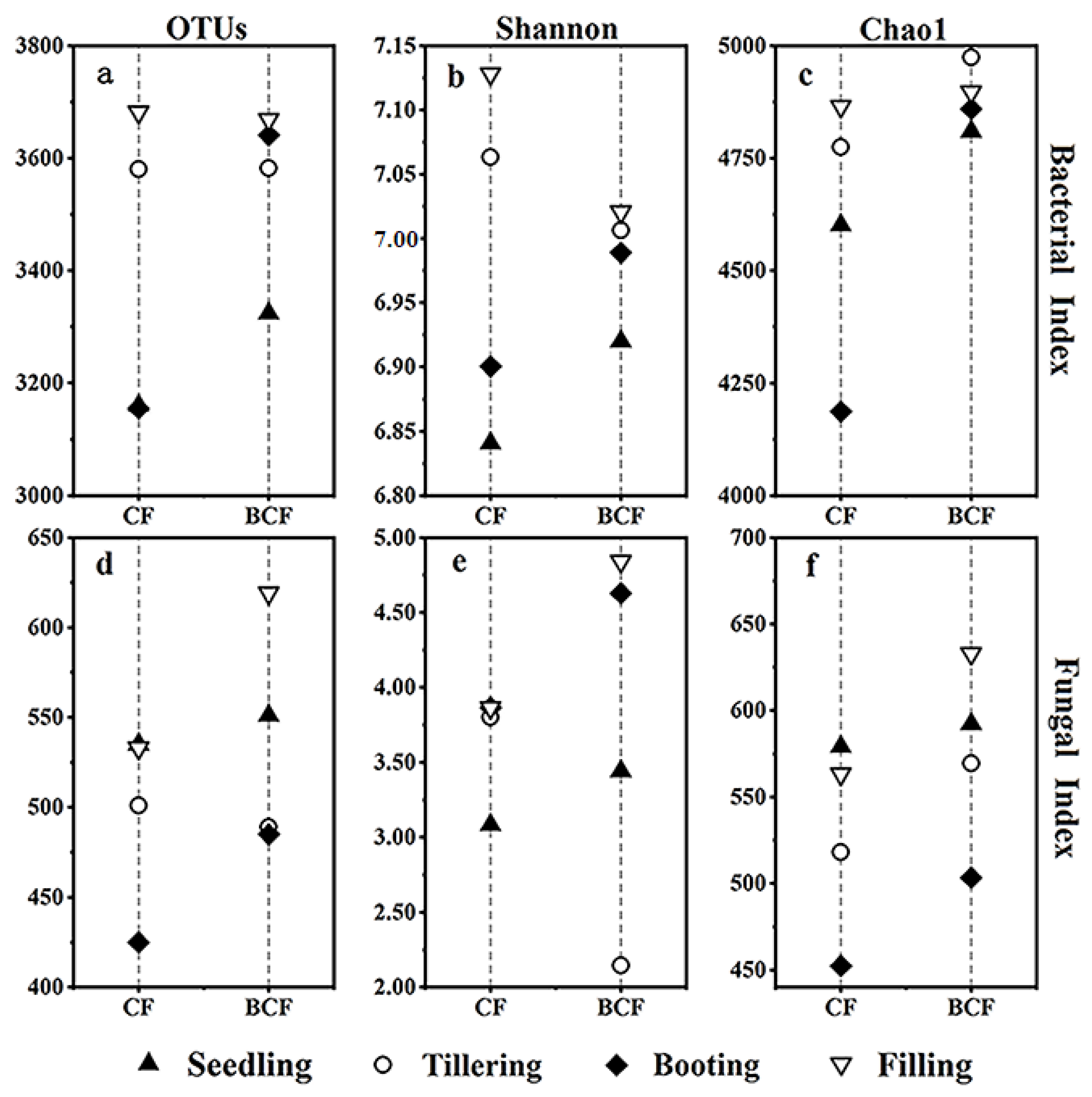
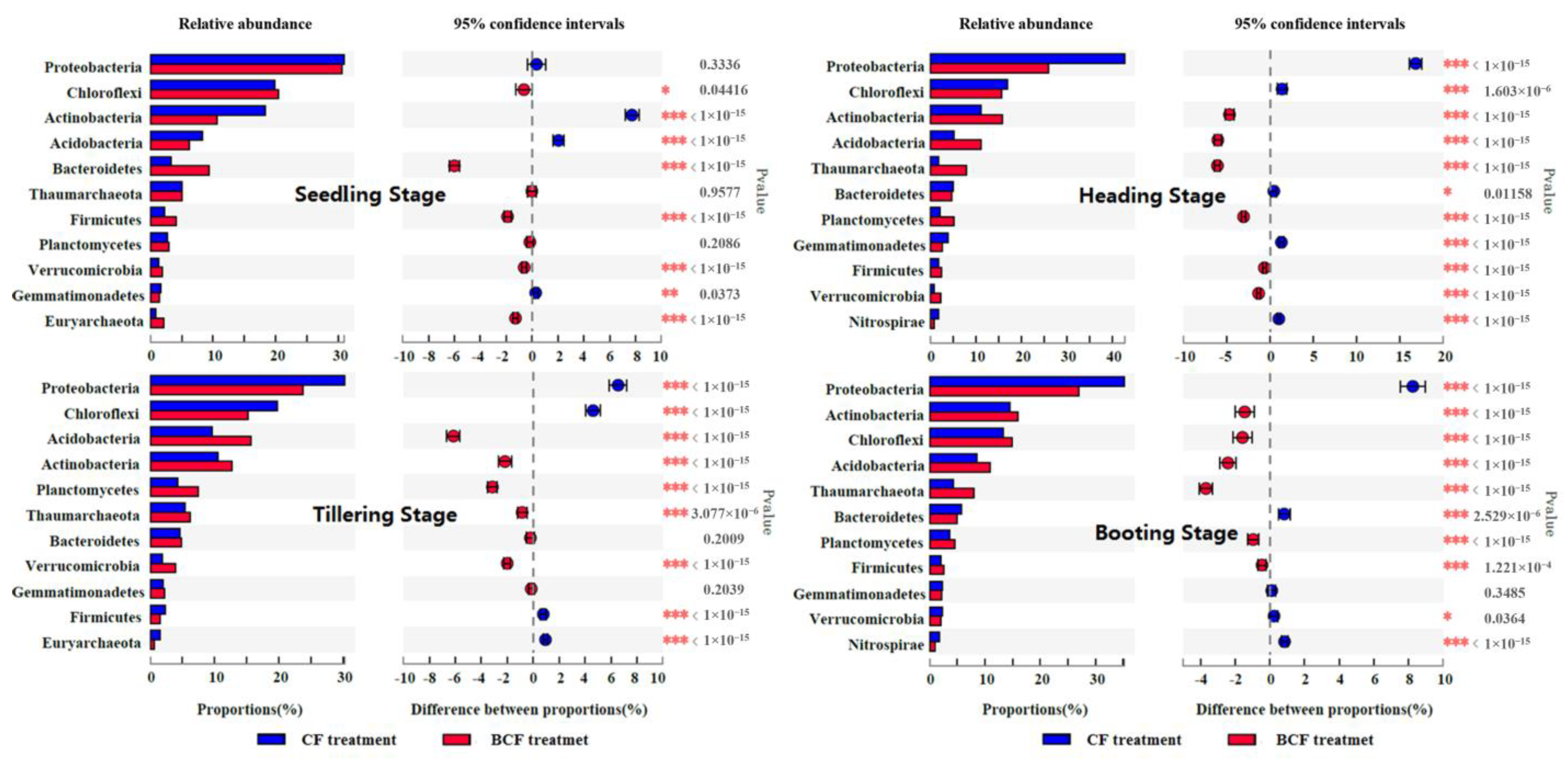


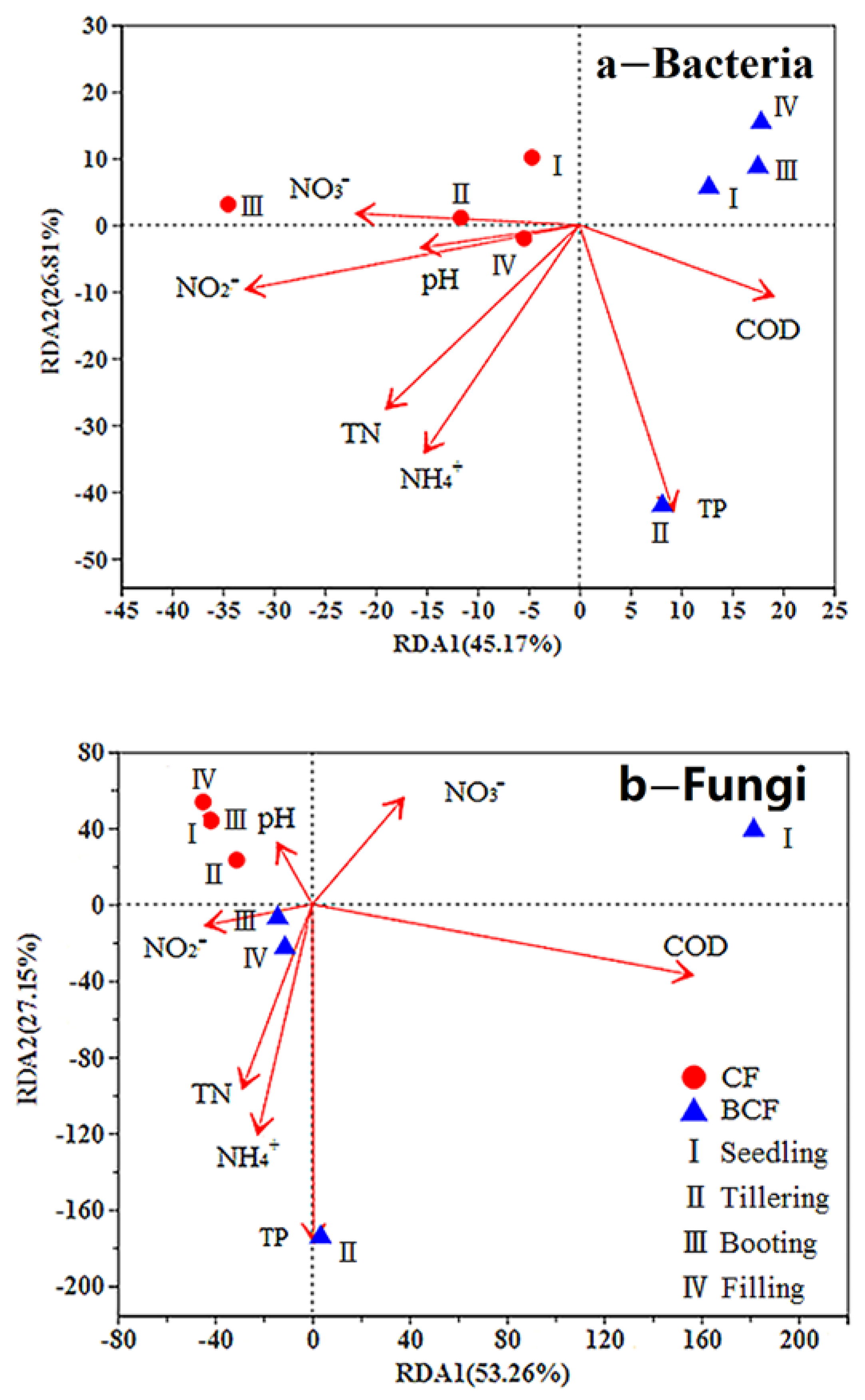
| Treatment | pH | TN (g kg−1) | TP (g kg−1) | TOC (g kg−1) | AN (mg kg−1) | AP (mg kg−1) | AK (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CF | 7.48 ± 0.04 a | 2.62 ± 0.10 a | 0.75 ± 0.03 a | 15.69 ± 3.20 a | 0.16 ± 0.08 a | 40.50 ± 5.25 a | 236.36 ± 6.43 a |
| BCF | 7.50 ± 0.05 a | 2.72 ± 0.20 a | 0.79 ± 0.05 a | 17.29 ± 2.91 a | 0.16 ± 0.04 a | 43.90 ± 6.11 a | 220.76 ± 10.55 a |
| Microbes | Genus/Family | CF | BCF | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seedling | Tillering | Booting | Filling | Seedling | Tillering | Booting | Filling | |||
| N-cycle- related microbes | AOB | Nitrosospira | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.06 |
| Nitrosomonas | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.04 | ||
| AOA | Nitrososphaeraceae | 3.99 | 4.26 | 1.51 | 3.48 | 4.04 | 5.05 | 6.09 | 6.43 | |
| Ca.Nitrocosmicus | 0.92 | 1.14 | 0.37 | 0.62 | 1.21 | 1.20 | 1.82 | 1.45 | ||
| NOB | Nitrospira | 0.32 | 0.42 | 0.63 | 0.78 | 0.25 | 0.36 | 0.61 | 0.50 | |
| Denitrifying bacteria | Steroidobacteraceae | 1.32 | 1.63 | 1.69 | 1.93 | 1.67 | 1.85 | 1.30 | 1.15 | |
| Thiobacillus | 0.76 | 0.49 | 0.50 | 0.09 | 1.23 | 0.17 | 0.12 | 0.04 | ||
| Pseudomonas | 0.78 | 0.30 | 0.23 | 0.27 | 1.00 | 0.22 | 0.10 | 0.11 | ||
| Rhodobacter | 0.07 | 0.1 | 0.11 | 0.39 | 0.45 | 0.31 | 0.13 | 0.05 | ||
| Steroidobacter | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.24 | 0.35 | ||
| Thauera | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.24 | 0.20 | 0.36 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.11 | ||
| DNRA bacteria | Geobacter | 1.39 | 1.70 | 1.87 | 1.29 | 0.71 | 0.42 | 0.43 | 0.92 | |
| Anaeromyxobacter | 0.62 | 0.56 | 1.32 | 0.58 | 0.34 | 0.38 | 0.51 | 0.72 | ||
| Ignavibacterium | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.31 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.11 | ||
| AnAOB | Ca.Brocadia | - | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.008 | 0.010 | 0.013 | |
| Ca.Anammoximicrobium | 0.013 | 0.003 | - | 0.005 | 0.051 | 0.022 | 0.01 | 0.013 | ||
| Phosphate- solubilizing- related microbes | PSB | Nitrososphaeraceae | 3.99 | 4.26 | 1.51 | 3.48 | 4.04 | 5.05 | 6.09 | 6.43 |
| Streptomyces | 0.47 | 0.20 | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.39 | 0.34 | 0.39 | 0.46 | ||
| Bacillus | 0.39 | 0.36 | 0.30 | 0.34 | 0.49 | 0.23 | 0.58 | 0.51 | ||
| Rhodococcus | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.24 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.14 | ||
| Fungi | Aspergillus | 10.30 | 5.14 | 0.22 | 0.96 | 0.70 | 0.04 | 0.33 | 0. 47 | |
| Mortierella | 1.06 | 2.17 | 4.62 | 2.38 | 0.70 | 0. 92 | 5.74 | 5.03 | ||
| Organic- matter- degrading- related microbes | Bacteria | Burkholderiaceae | 0.83 | 0.78 | 2.06 | 1.64 | 1.29 | 0.83 | 1.05 | 0.99 |
| Bacillus | 0.39 | 0.36 | 0.30 | 0.34 | 0.49 | 0.23 | 0.58 | 0.51 | ||
| Gaiella | 1.32 | 0.98 | 1.26 | 1.61 | 0.48 | 1.36 | 1.56 | 1.77 | ||
| Marmoricola | 1.31 | 0.86 | 0.88 | 1.02 | 1.10 | 1.20 | 1.83 | 1.57 | ||
| Anaerolinea | 1.09 | 1.11 | 0.46 | 0.60 | 1.51 | 0.79 | 0.57 | 0.84 | ||
| Fungi | Pyrenochaetopsis | 27.25 | 10.16 | 2.71 | 3.27 | 5.45 | 1.59 | 14.26 | 6.48 | |
| Mortierella | 1.06 | 2.17 | 4.62 | 2.38 | 0.70 | 0.92 | 5.74 | 5.03 | ||
| Penicillium | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.40 | 0.62 | ||
| Acremonium | 0. 576 | 0.244 | 0.003 | 0. 259 | 0.232 | 0.070 | 0.214 | 0.550 | ||
| Gibberella | 0. 27 | 0. 33 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.18 | 0. 53 | 3.88 | 2.57 | ||
| Hydnodontaceae | - | - | - | - | 0.006 | - | - | - | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Z.; Yang, Y.; Fan, Y.; He, Y.; Li, T. Dynamic Responses of Rhizosphere Microorganisms to Biogas Slurry Combined with Chemical Fertilizer Application during the Whole Life Cycle of Rice Growth. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11071755
Shi Z, Yang Y, Fan Y, He Y, Li T. Dynamic Responses of Rhizosphere Microorganisms to Biogas Slurry Combined with Chemical Fertilizer Application during the Whole Life Cycle of Rice Growth. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(7):1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11071755
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Zhenbao, Yanmei Yang, Yehong Fan, Yan He, and Tian Li. 2023. "Dynamic Responses of Rhizosphere Microorganisms to Biogas Slurry Combined with Chemical Fertilizer Application during the Whole Life Cycle of Rice Growth" Microorganisms 11, no. 7: 1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11071755
APA StyleShi, Z., Yang, Y., Fan, Y., He, Y., & Li, T. (2023). Dynamic Responses of Rhizosphere Microorganisms to Biogas Slurry Combined with Chemical Fertilizer Application during the Whole Life Cycle of Rice Growth. Microorganisms, 11(7), 1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11071755





