Study of the Interface between Wild Bird Populations and Poultry and Their Potential Role in the Spread of Avian Influenza
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
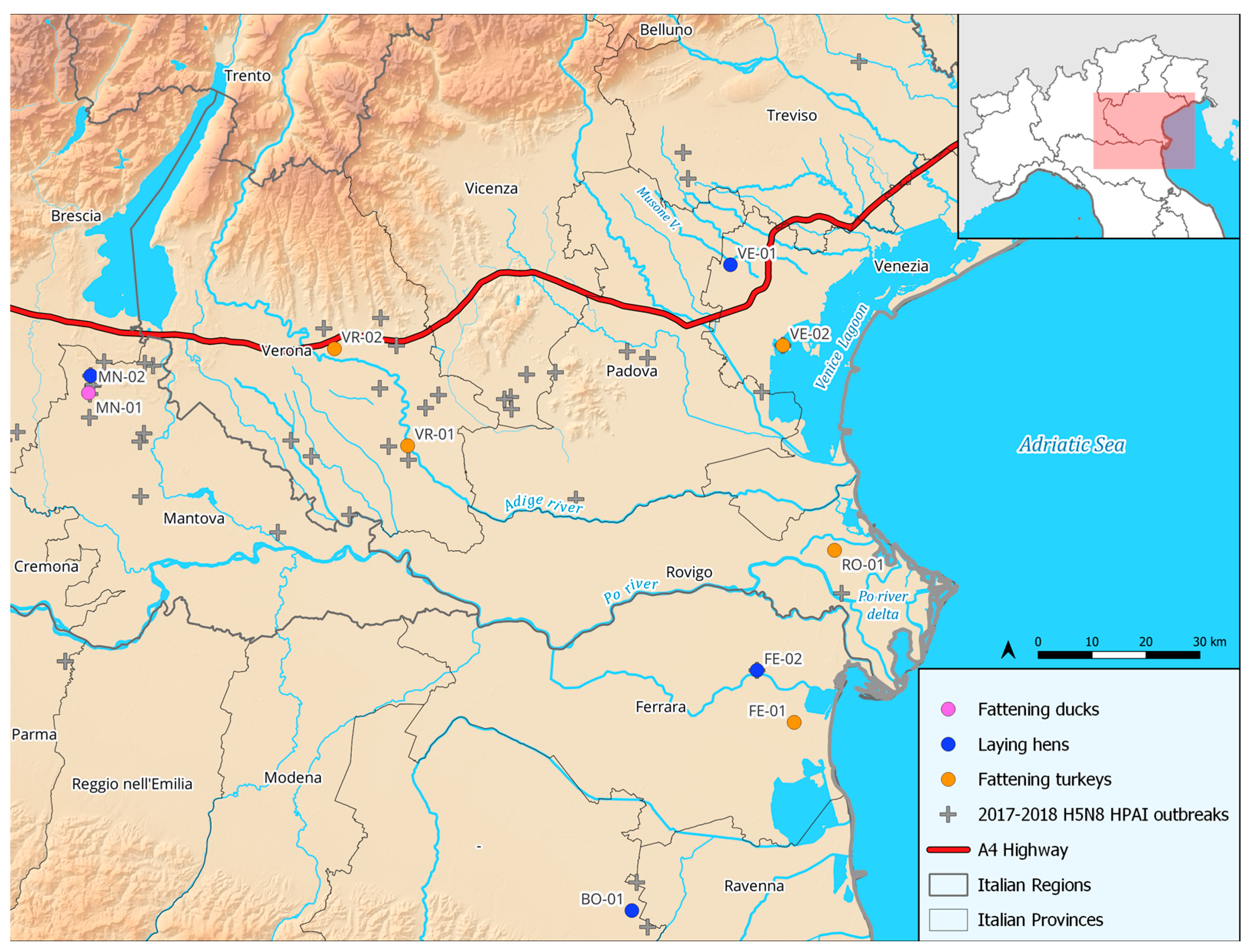
2.1. Definition of the Study Area
2.2. Ornithological Transects
2.3. Camera-Trapping Activities
2.4. Data Analysis
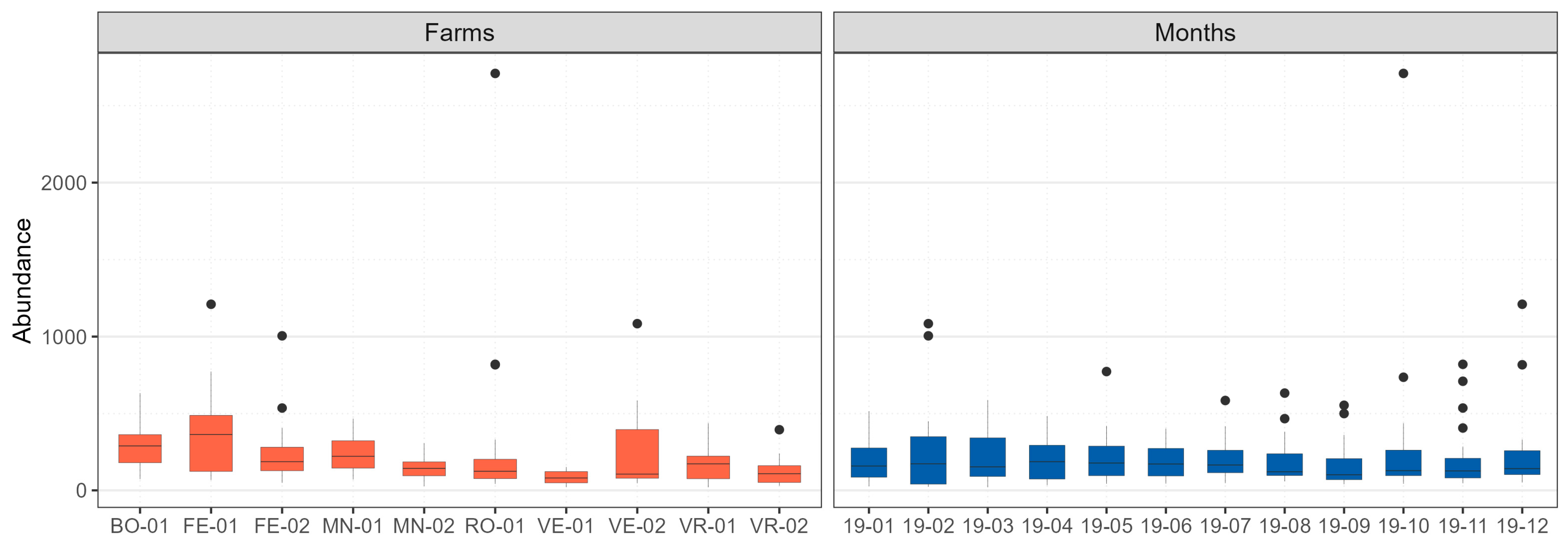
2.4.1. Descriptive Analysis of Transect Data
2.4.2. Multivariate Analysis
2.4.3. Biodiversity Measures
2.4.4. Descriptive Analysis of Camera-Trapping Data
2.4.5. Statistical Tests and Software
3. Results
3.1. Ornithological Transects
3.1.1. Correspondence Analysis
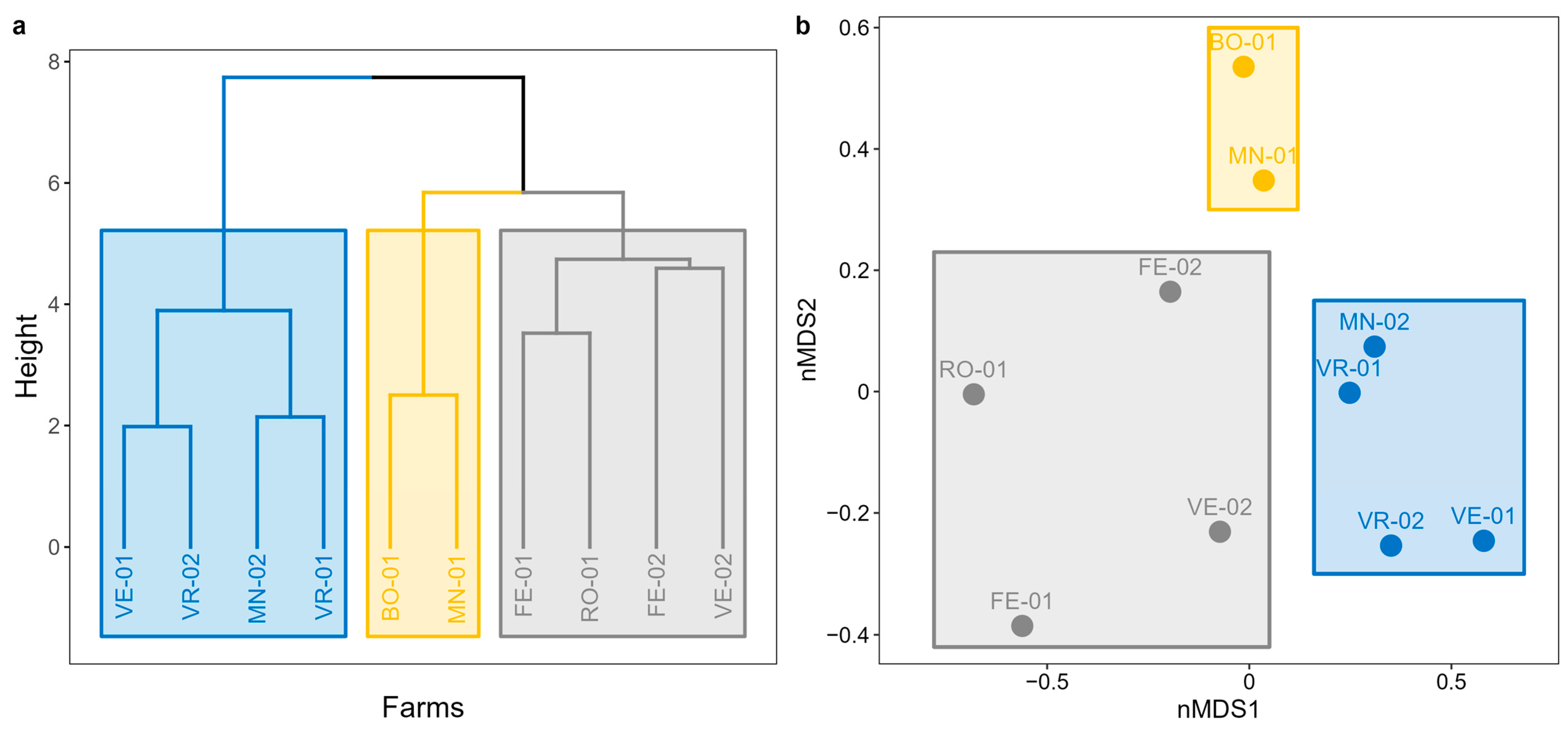
3.1.2. Non-Metric Multidimensional Scaling and Cluster Analysis
- Cluster 1: a group of 4 farms (FE-01, FE-02, RO-01, and VE-02) located in the eastern zone of the study area, near the coast, potentially influenced by the lagoon ecosystem.
- Cluster 2: a group consisting of 2 farms (BO-01 and MN-01) located over 100 km apart but sharing the exclusive presence of intensive crops and small inhabited centers nearby.
- Cluster 3: a third group of 4 farms (MN-02, VE-01, VR-01, and VR-02) distributed in the northern zone of the study area, encompassing the inland ecosystems.
3.1.3. Alfa Diversity
3.2. Camera Trapping
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mulatti, P.; Ferrè, N.; Marangon, S. Spatial Distribution of 2000-2007 Low Pathogenicity Avian Influenza Epidemics in Northern Italy. In Pandemic Influenza Virus; Majumdar, S.K., Brenner, F., Huffman, J., McLean, R., Panah, A., Pietrobon, P., Keeler, S., Shive, S., Eds.; Pennsylvania Academy of Science: East Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2010; pp. 232–247. [Google Scholar]
- Fornasiero, D.; Fusaro, A.; Zecchin, B.; Mazzucato, M.; Scolamacchia, F.; Manca, G.; Terregino, C.; Dorotea, T.; Mulatti, P. Integration of Epidemiological and Genomic Data to Investigate H5N1 HPAI Outbreaks in Northern Italy in 2021–2022. Pathogens 2023, 12, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulatti, P.; Fusaro, A.; Scolamacchia, F.; Zecchin, B.; Azzolini, A.; Zamperin, G.; Terregino, C.; Cunial, G.; Monne, I.; Marangon, S. Integration of genetic and epidemiological data to infer H5N8 HPAI virus transmission dynamics during the 2016–2017 epidemic in Italy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 18037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlhoch, C.; Fusaro, A.; Gonzales, J.L.; Kuiken, T.; Marangon, S.; Niqueux, E.; Staubach, C.; Terregino, C.; Guajardo, I.M.; Chuzhakina, K.; et al. Avian influenza overview June–September 2022. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlhoch, C.; Fusaro, A.; Gonzales, J.L.; Kuiken, T.; Marangon, S.; Mirinaviciute, G.; Niqueux, E.; Stahl, K.; Staubach, C.; Terregino, C.; et al. Avian influenza overview December 2022–March 2023. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e07917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sims, L.; Harder, T.C.; Brown, I.H.; Gaidet, N.; Belot, G.; Von Dobschuetz, S.; Lubroth, J. Highly Pathogenic H5 Avian Influenza in 2016 and 2017—Observations and Future Perspectives. 2016. Available online: http://www.fao.org/documents/card/en/c/d249523c-f898-4b3a-9c15-98890c9cbb33/ (accessed on 6 May 2023).
- Swayne, D.E.; Suarez, D.L.; Sims, L.D. Influenza. In Diseases of Poultry, 14th ed.; Swayne, G.Z.D.E., Boulianne, M., Logue, C.M., McDougald, L.R., Nair, V., Suarez, D.L., de Wit, S., Grimes, T., Johnson, D., Kromm, M., et al., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. AAAP: Ames, IA, USA, 2019; pp. 210–256. [Google Scholar]
- Verhagen, J.H.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; Lewis, N. Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Viruses at the Wild–Domestic Bird Interface in Europe: Future Directions for Research and Surveillance. Viruses 2021, 13, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stallknecht, D.E.; Brown, J.D. Wild bird infections and the ecology of avian influenza viruses. Anim. Influ. 2017, 153–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallknecht, D.E.; Shane, S.M. Host range of avian influenza virus in free-living birds. Veter Res. Commun. 1988, 12, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shriner, S.A.; Root, J.J. A Review of Avian Influenza A Virus Associations in Synanthropic Birds. Viruses 2020, 12, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, R.G.; Bean, W.J.; Gorman, O.T.; Chambers, T.M.; Kawaoka, Y. Evolution and ecology of influenza A viruses. Microbiol. Rev. 1992, 56, 152–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munster, V.J.; Baas, C.; Lexmond, P.; Waldenstrom, J.; Wallensten, A.; Fransson, T.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Beyer, W.E.; Schutten, M.; Olsen, B.; et al. Spatial, temporal, and species variation in prevalence of influenza A viruses in wild migratory birds. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stallknecht, D.E. Ecology and Epidemiology of Avian Influenza Viruses in Wild Bird Populations: Waterfowl, Shorebirds, Pelicans, Cormorants, Etc. Avian Dis. 1997, 47, 61–69. [Google Scholar]
- Caron, A.; Grosbois, V.; Etter, E.; Gaidet, N.; de Garine-Wichatitsky, M. Bridge hosts for avian influenza viruses at the wildlife/domestic interface: An eco-epidemiological framework implemented in southern Africa. Prev. Veter Med. 2014, 117, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siengsanan-Lamont, J.; Robertson, I.; Blacksell, S.; Ellis, T.; Fenwick, S.; Saengchoowong, S.; Suwanpukdee, S.; Yongyuttawichai, P.; Sariya, L.; Prompiram, P.; et al. Virological and molecular epidemiological investigations into the role of wild birds in the epidemiology of influenza A/H5N1 in central Thailand. Veter Microbiol. 2011, 148, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siengsanan, J.; Chaichoune, K.; Phonaknguen, R.; Sariya, L.; Prompiram, P.; Kocharin, W.; Tangsudjai, S.; Suwanpukdee, S.; Wiriyarat, W.; Pattanarangsan, R.; et al. Comparison of outbreaks of h5n1 highly pathogenic avian influenza in wild birds and poultry in thailand. J. Wildl. Dis. 2009, 45, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welfare EFSA Panel on Animal Health and Welfare (AHAW); More, S.; Bicout, D.; Bøtner, A.; Butterworth, A.; Calistri, P.; Depner, K.; Edwards, S.; Garin-Bastuji, B.; Good, M.; et al. Avian influenza. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaidet, N.; Cappelle, J.; Takekawa, J.Y.; Prosser, D.J.; Iverson, S.A.; Douglas, D.C.; Perry, W.M.; Mundkur, T.; Newman, S.H. Potential spread of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 by wildfowl: Dispersal ranges and rates determined from large-scale satellite telemetry. J. Appl. Ecol. 2010, 47, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reperant, L.A.; Fučkar, N.S.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; Dobson, A.P.; Kuiken, T. Spatial and Temporal Association of Outbreaks of H5N1 Influenza Virus Infection in Wild Birds with the 0 °C Isotherm. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zhan, D.; Li, L.; Lei, F.; Liu, B.; Liu, D.; Xiao, H.; Feng, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, B.; et al. H5N1 avian influenza re-emergence of Lake Qinghai: Phylogenetic and antigenic analyses of the newly isolated viruses and roles of migratory birds in virus circulation. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, A.V.; Pearce, J.M.; Flint, P.L.; Franson, J.C.; Ip, H.S. Genetic evidence of intercontinental movement of avian influenza in a migratory bird: The northern pintail (Anas acuta). Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 4754–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-I.; Park, S.-J.; Kwon, H.-I.; Kim, E.-H.; Si, Y.-J.; Jeong, J.-H.; Lee, I.-W.; Nguyen, H.D.; Kwon, J.-J.; Choi, W.S.; et al. Genetic and phylogenetic characterizations of a novel genotype of highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) H5N8 viruses in 2016/2017 in South Korea. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 53, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliendo, V.; Lewis, N.S.; Pohlmann, A.; Baillie, S.R.; Banyard, A.C.; Beer, M.; Brown, I.H.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; Hansen, R.D.E.; Lameris, T.K.; et al. Transatlantic spread of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 by wild birds from Europe to North America in 2021. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleyheeg, E.; van Dijk, J.G.B.; Tsopoglou-Gkina, D.; Woud, T.Y.; Boonstra, D.K.; Nolet, B.A.; Soons, M.B. Movement patterns of a keystone waterbird species are highly predictable from landscape configuration. Mov. Ecol. 2017, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- E Burns, T.; Ribble, C.; Stephen, C.; Kelton, D.; Toews, L.; Osterhold, J.; Wheeler, H. Use of observed wild bird activity on poultry farms and a literature review to target species as high priority for avian influenza testing in 2 regions of Canada. Can. Vet. J. 2012, 53, 158. [Google Scholar]
- Caron, A.; Cappelle, J.; Cumming, G.S.; de Garine-Wichatitsky, M.; Gaidet, N. Bridge hosts, a missing link for disease ecology in multi-host systems. Veter Res. 2015, 46, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamp, J.; Reinhard, A.; Frenzel, M.; Kämpfer, S.; Trappe, J.; Hölzel, N. Farmland bird responses to land abandonment in Western Siberia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 268, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voříšek, P.; Klvaňová, A.; Wotton, S.; Gregory, R.D. A Best Practice Guide for Wild Bird Monitoring Schemes. 2008, p. 150. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/350453083_Best_practice_guide_for_wild_bird_monitoring_schemes (accessed on 6 May 2023).
- Welbourne, D.J.; Paull, D.J.; Claridge, A.W.; Ford, F. A frontier in the use of camera traps: Surveying terrestrial squamate assemblages. Remote. Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2017, 3, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repubblica Italiana. Decreto Legislativo 10 agosto 2018, n. 101. Gazz. Uff. 2018, pp. 2–5. Available online: https://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/id/2018/09/04/18G00129/sg (accessed on 3 June 2023).
- Greenacre, M.; Primicerio, R. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data. 2013. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/259890313_Multivariate_Analysis_of_Ecological_Data (accessed on 7 May 2023).
- Scardi, M. Tecniche di Analisi dei dati in Ecologia. 2009. Available online: http://www.michele.scardi.name/corsi/metodi.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Dexter, E.; Rollwagen-Bollens, G.; Bollens, S.M. The trouble with stress: A flexible method for the evaluation of nonmetric multidimensional scaling. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2018, 16, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, R.H. Dominance and Diversity in Land Plant Communities. Science 1965, 147, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, R.H. Whittaker 1960.pdf. Ecol. Monogr. 1960, 30, 279–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routledge, R.D. On Whittaker’ s Components of Diversity. Ecology 1977, 58, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magurran, A.E. Measuring Biological Diversity; Wiley-Blackwell by John Wiley & Sons: Carlton Victoria, Australia, 2004; ISBN 978-632-05633-0. [Google Scholar]
- Jost, L. Entropy and diversity. Oikos 2006, 113, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, A.J.; Baetens, J.M.; De Baets, B. Ecological Diversity: Measuring the Unmeasurable. Mathematics 2018, 6, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, A.C. Descriptive and Inferential Statistics. Compr. Clin. Psychol. 1998, 3, 243–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosner, B.; Glynn, R.J.; Lee, M.-L.T. The Wilcoxon signed rank test for paired comparisons of clustered data. Biometrics 2005, 62, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R: The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 13 September 2023).
- Posit Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; Posit Software: Boston, MA, USA, 2023; Available online: http://www.posit.co/ (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- Finotello, F.; Mastrorilli, E.; Di Camillo, B. Measuring the diversity of the human microbiota with targeted next-generation sequencing. Brief. Bioinform. 2016, 19, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; O’hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.; Wagner, H. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.4-6. 2018. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 27 April 2018).
- Nenadic, O.; Greenacre, M. Correspondence Analysis in R, with two- and three-dimensional graphics: The ca package. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kassambara, A.; Mundt, F. Factoextra: Extract and Visualize the Results of Multivariate Data Analyses. R Package Version 1.0.6. 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=factoextra (accessed on 29 September 2021).
- Wickham, H. Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, E.B. Exploring contingency tables with correspondence analysis. Bioinformatics 1989, 5, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brichetti, P.; Fracasso, G. Check-list of Italian Birds, updated to the end of 2014. Riv. Ital. di Ornitol. 2015, 85, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbers, A.R.W.; Gonzales, J.L. Quantification of visits of wild fauna to a commercial free-range layer farm in the Netherlands located in an avian influenza hot-spot area assessed by video-camera monitoring. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 67, 661–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veen, J.; Brouwer, J.; Atkinson, P.; Bilgin, C.; Blew, J.; Eksioglu, M.; Hoffmann, M.; Nardelli, R.; Spina, F.; Tendi, C.; et al. Ornithological Data Relevant to the Spread of Avian Influenza in Europe (phase2): Further Identification and First Field Assessment of Higher Risk Species. 2007, p. 60. Available online: https://www.wetlands.org/download/2860/ (accessed on 2 May 2023).
- Jourdain, E.; Gunnarsson, G.; Wahlgren, J.; Latorre-Margalef, N.; Bröjer, C.; Sahlin, S.; Svensson, L.; Waldenström, J.; Lundkvist, A.; Olsen, B. Influenza virus in a natural host, the mallard: Experimental infection data. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnal, A.; Vittecoq, M.; Pearce-Duvet, J.; Gauthier-Clerc, M.; Boulinier, T.; Jourdain, E. Laridae: A neglected reservoir that could play a major role in avian influenza virus epidemiological dynamics. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 41, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, K.Y.; Joh, S.J.; Kim, M.C.; Kang, M.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Kwon, J.H.; Kim, J.H. The susceptibility of magpies to a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus subtype H5N1. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89, 1156–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.-K.; Joh, S.-J.; Kim, M.-C.; Lee, Y.-J.; Choi, J.-G.; Lee, E.-K.; Wee, S.-H.; Sung, H.-W.; Kwon, J.-H.; Kang, M.-I.; et al. Highly pathogenic avian influenza in Magpies (Pica pica sericea) in South Korea. J. Wildl. Dis. 2005, 41, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, A.; Gonzales, J.; Huneau, A.; Mulatti, P.; Kuiken, T.; Staubach, C.; Stegeman, A.; Antoniou, S.-E.; Baldinelli, F.; Van Der Stede, Y.; et al. Annual Report on surveillance for avian influenza in poultry and wild birds in Member States of the European Union in 2018. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldinelli, F.; Papanikolaou, A.; Stoicescu, A.; Van der Stede, Y.; Aznar, I. Annual Report on surveillance for Avian Influenza in poultry and wild birds in Member States of the European Union in 2019. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar, I.; Baldinelli, F.; Papanikolaou, A.; Stoicescu, A.; Van der Stede, Y. Annual Report on surveillance for avian influenza in poultry and wild birds in Member States of the European Union in 2020. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aznar, I.; Baldinelli, F.; Stoicescu, A.; Kohnle, L. Annual report on surveillance for avian influenza in poultry and wild birds in Member States of the European Union in 2021. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) in Italy. Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale delle Venezie. Available online: https://www.izsvenezie.com/reference-laboratories/avian-influenza-newcastle-disease/italy-update/ (accessed on 16 October 2023).
- Root, J.J.; Bosco-Lauth, A.M.; Marlenee, N.L.; Bowen, R.A. Viral shedding of clade 2.3.4.4 H5 highly pathogenic avian influenza A viruses by American robins. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1823–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolnik, C. A current review of avian influenza in pigeons and doves (Columbidae). Veter Microbiol. 2014, 170, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, B.M.; El-shazly, M.M.; El-sanousi, A.A.; Youssef, Y.I. Isolation of H5 Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus from Cattle Egret (Bubulcus ibis) near Affected Broiler Chicken Flocks in Egypt. J. Virol. Sci. 2017, 2, 62–70. [Google Scholar]
- Phuong, D.Q.; Dung, N.T.; Jørgensen, P.H.; Van, D.T.; Tung, D.D.; Christensen, J.P. Virulence of h5n1 influenza virus in cattle egrets (Bubulcus ibis). J. Wildl. Dis. 2011, 47, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- De Marco, M.A.; Campitelli, L.; Delogu, M.; Raffini, E.; Foni, E.; di Trani, L.; Scaffidi, M.; Donatelli, I. Serological evidences showing the involvement of free-living pheasants in the influenza ecology. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 4, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Hjulsager, C.K.; Seekings, A.H.; Warren, C.J.; Lean, F.Z.; Núñez, A.; James, J.; Thomas, S.S.; Banyard, A.C.; Slomka, M.J.; et al. Pathogenesis and infection dynamics of high pathogenicity avian influenza virus (HPAIV) H5N6 (clade 2.3.4.4b) in pheasants and onward transmission to chickens. Virology 2022, 577, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, A.; De Garine-Wichatitsky, M.; Gaidet, N.; Chiweshe, N.; Cumming, G.S. Research, part of a Special Feature on Risk mapping for avian influenza: A social-ecological problem Estimating Dynamic Risk Factors for Pathogen Transmission Using Community-Level Bird Census Data at the Wildlife/Domestic Interface. Ecol. Soc. 2010, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

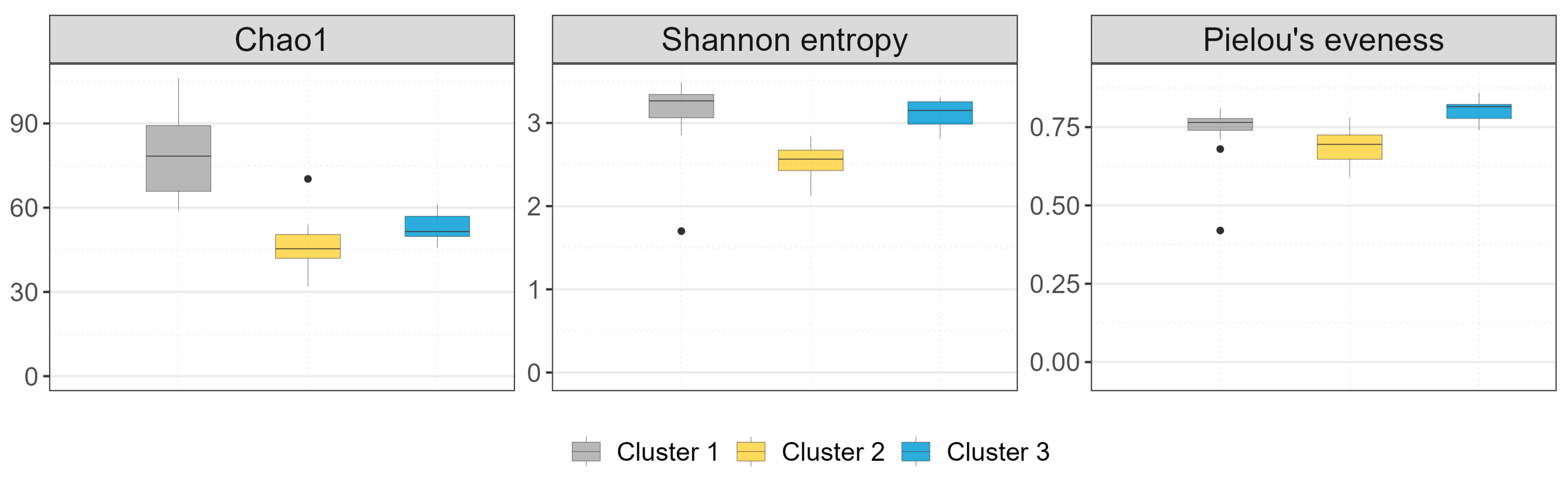
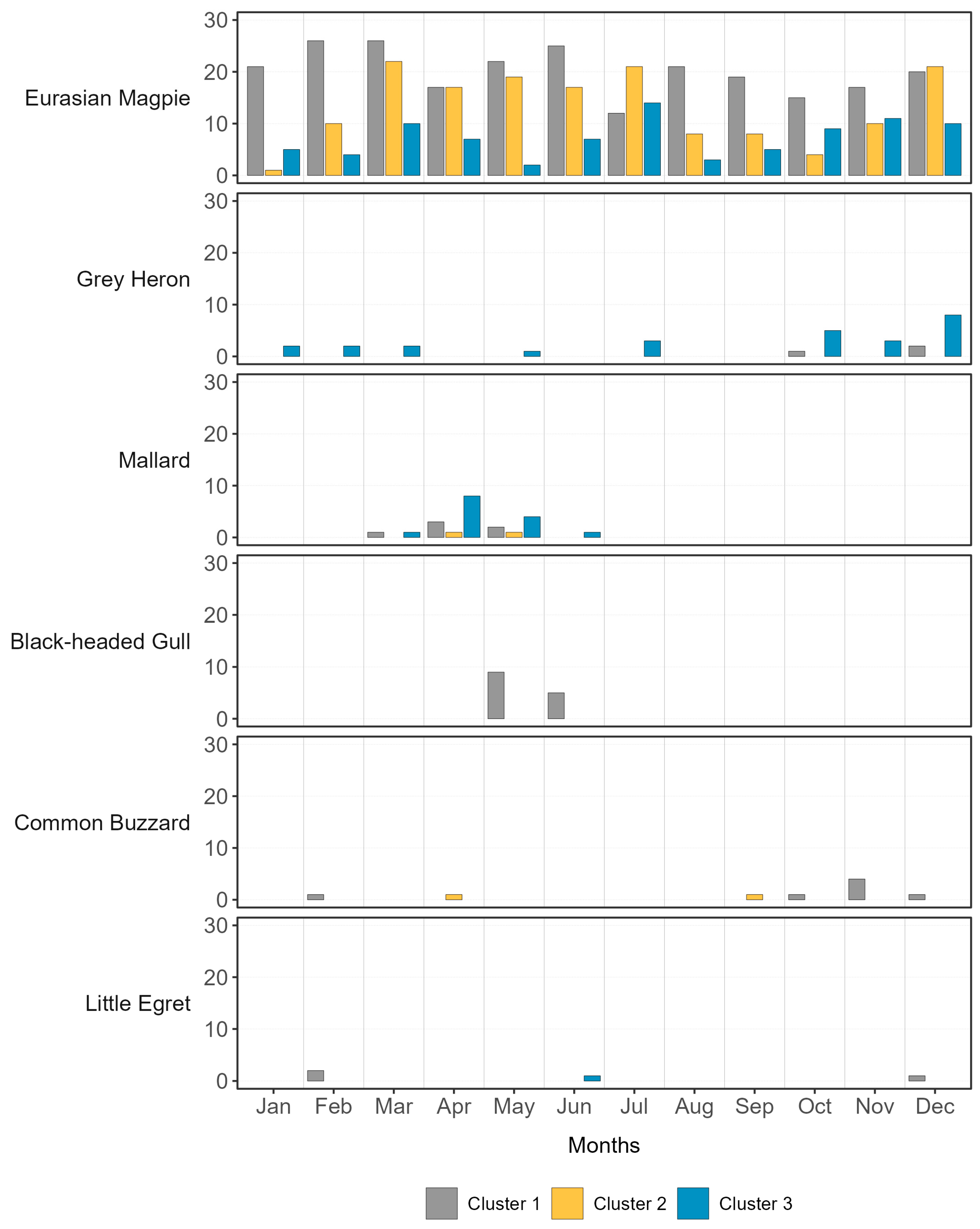

| Index | Description | Numerical Range [min; max] |
|---|---|---|
| Species richness (Sobs) | The number of observed species | [0; +∞] |
| Chao1 | A non-parametric index that estimates the expected number of species in an area. The observed species richness is corrected for the number of undetected species, which is estimated based on the distribution of rare species [38]. | [0; +∞] |
| Shannon entropy | It quantifies both biodiversity and species dominance [39]. | [0; ln(Sobs)] |
| Pielou’s evenness | It indicates how evenly each species is represented within the population under study [40]. | [0; 1] |
| Common Name (Scientific Name) | BO-01 | FE-01 | FE-02 | MN-01 | MN-02 | RO-01 | VE-01 | VE-02 | VR-01 | VR-02 | No. Farms | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eurasian Collared Dove (Streptopelia decaocto) | 3 | 142 | 3 | 9 | 26 | 4 | 1 | 15 | 21 | 55 | 10 | |
| Common Wood Pigeon (Columba palumbus) | 2 | 57 | 5 | 13 | 28 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 9 | ||
| Eurasian Magpie (Pica pica) | * | 106 | 4 | 3 | 78 | 65 | 180 | 104 | 19 | 8 | 9 | |
| Common Blackbird (Turdus merula) | 13 | 38 | 1 | 26 | 2 | 7 | 1 | 5 | 160 | 9 | ||
| Cattle Egret (Bubulcus ibis) | 17 | 13 | 25 | 38 | 6 | 4 | 6 | |||||
| Hooded Crow (Corvus cornix) | 19 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 6 | |||||
| Common Pheasant (Phasianus colchicus) | 3 | 28 | 26 | 14 | 2 | 5 | ||||||
| Eurasian Jay (Garrulus glandarius) | 1 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 22 | 5 | ||||||
| Mallard (Anas platyrhynchos) | * | 2 | 2 | 4 | 14 | 4 | ||||||
| Rock Pigeon (Columba livia) | 5 | 7 | 1 | 121 | 4 | |||||||
| Common Starling (Sturnus vulgaris) | 2 | 24 | 12 | 25 | 4 | |||||||
| Little Owl (Athene noctua) | 4 | 1 | 7 | 21 | 4 | |||||||
| Common Chaffinch (Fringilla coelebs) | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||||||
| Yellow-legged Gull (Larus michahellis) | 14 | 9 | 2 | 3 | ||||||||
| Eurasian Tree Sparrow (Passer montanus) | 4 | 10 | 1 | 3 | ||||||||
| Common Buzzard (Buteo buteo) | * | 2 | 6 | 1 | 3 | |||||||
| Grey Heron (Ardea cinerea) | * | 2 | 1 | 26 | 3 | |||||||
| Little Egret (Egretta garzetta) | * | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | |||||||
| European Robin (Erithacus rubecula) | 3 | 1 | 12 | 3 | ||||||||
| European Turtle Dove (Streptopelia turtur) | 1 | 1 | 7 | 3 | ||||||||
| European Green Woodpecker (Picus viridis) | 1 | 2 | 7 | 3 | ||||||||
| Common Kestrel (Falco tinnunculus) | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | ||||||||
| Barn Swallow (Hirundo rustica) | 3 | 1 | 2 | |||||||||
| Common Redstart (Phoenicurus phoenicurus) | 2 | 1 | 2 | |||||||||
| Common Chiffchaff (Phylloscopus collybita) | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||||||
| Italian Sparrow (Passer italiae) | 15 | 1 | 2 | |||||||||
| European Goldfinch (Carduelis carduelis) | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||||||
| White Wagtail (Motacilla alba) | 9 | 9 | 2 | |||||||||
| Black-headed Gull (Chroicocephalus ridibundus) | * | 12 | 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| Peregrine Falcon (Falco peregrinus) | * | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Common Stonechat (Saxicola torquatus) | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Eurasian Jackdaw (Corvus monedula) | 5 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Eurasian Hoopoe (Upupa epops) | 10 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Eurasian Blue Tit (Cyanistes caeruleus) | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Black-winged Stilt (Himantopus himantopus) | 7 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Mediterranean Gull (Ichthyaetus melanocephalus) | 6 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Great Egret (Ardea alba) | * | 2 | 1 | |||||||||
| Common Swift (Apus apus) | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Purple Heron (Ardea purpurea) | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Common Moorhen (Gallinula chloropus) | 2 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Richness | 18 | 18 | 8 | 8 | 15 | 16 | 6 | 16 | 7 | 18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martelli, L.; Fornasiero, D.; Scarton, F.; Spada, A.; Scolamacchia, F.; Manca, G.; Mulatti, P. Study of the Interface between Wild Bird Populations and Poultry and Their Potential Role in the Spread of Avian Influenza. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102601
Martelli L, Fornasiero D, Scarton F, Spada A, Scolamacchia F, Manca G, Mulatti P. Study of the Interface between Wild Bird Populations and Poultry and Their Potential Role in the Spread of Avian Influenza. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(10):2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102601
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartelli, Luca, Diletta Fornasiero, Francesco Scarton, Arianna Spada, Francesca Scolamacchia, Grazia Manca, and Paolo Mulatti. 2023. "Study of the Interface between Wild Bird Populations and Poultry and Their Potential Role in the Spread of Avian Influenza" Microorganisms 11, no. 10: 2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102601
APA StyleMartelli, L., Fornasiero, D., Scarton, F., Spada, A., Scolamacchia, F., Manca, G., & Mulatti, P. (2023). Study of the Interface between Wild Bird Populations and Poultry and Their Potential Role in the Spread of Avian Influenza. Microorganisms, 11(10), 2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102601