Potential Use of Deep-Sea Sediment Bacteria for Oil Spill Biodegradation: A Laboratory Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
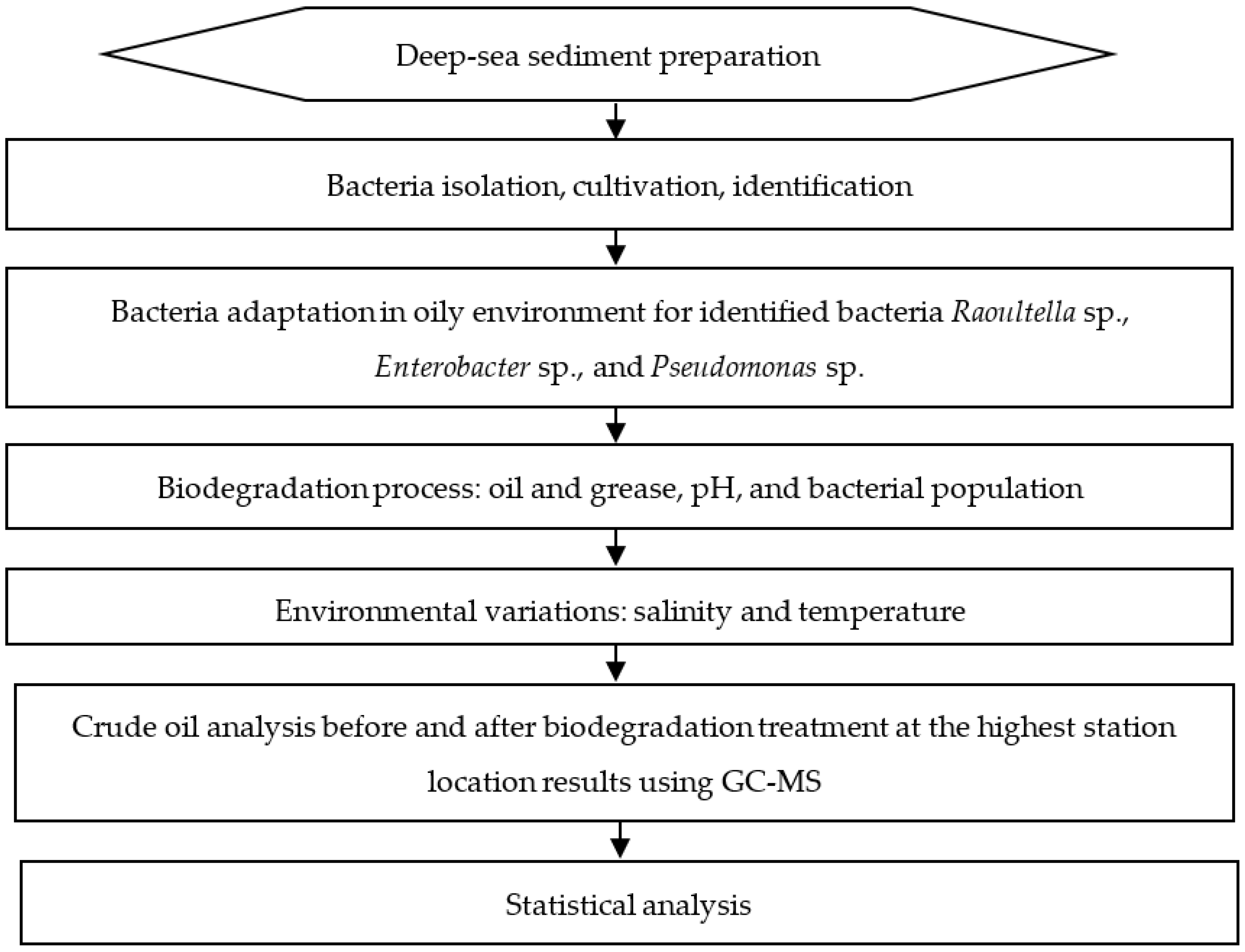
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Bacteria Isolation, Cultivation, and Identification
2.3. Biodegradation Process
2.3.1. Time-Series Biodegradation Experiment
2.3.2. pH and Bacterial Growth
2.3.3. Environmental Variations
2.4. Crude Oil Analysis
2.4.1. Oil Fractionation
2.4.2. GC-MS Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Crude Oil Biodegradation
3.2. GC-MS Analysis of the Crude Oil Components
3.2.1. Paraffin
3.2.2. Aromatics
3.3. Degradation Rate and Environmental Variations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fingas, M. The Basics of Oil Spill Cleanup, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; p. 286. [Google Scholar]
- US EPA. The Fate of Spilled Oil. In Understanding Oil Spills and Oil Spill Response; US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2018-01/documents/ospguide99.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Bostrom, A.; Walker, A.H.; Scott, T.; Pavia, R.; Leschine, T.M.; Starbird, K. Oil spill response risk judgments, decisions, and mental models: Findings from surveying U.S. stakeholders and coastal residents. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2015, 21, 581–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramseur, J.L. Deepwater Horizon oil spill: The fate of the oil. In Congressional Research Service Report for Congress; Congressional Research Service, Library of Congress: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; pp. 7–57. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Y.; Zhao, X.; Cai, Z.; O’Reilly, S.E.; Hao, X.; Zhao, D. A review of oil, dispersed oil and sediment interactions in the aquatic environment: Influence on the fate, transport and remediation of oil spills. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 79, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syakti, A.D.; Yani, M.; Hidayati, N.V.; Siregar, A.S.; Doumenq, P.; Sudiana, I.M. Bioremediation potential of hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria isolated from a mangrove contaminated by petroleum hydrocarbons on the Cilacap coast, Indonesia. Bioremediat. J. 2013, 17, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syakti, A.D.; Lestari, P.; Simamora, S.; Sari, L.K.; Lestari, F.; Idris, F.; Agustiadi, T.; Akhlus, S.; Hidayati, N.V. Culturable hydrocarbonoclastic marine bacterial isolates from Indonesian seawater in the Lombok Strait and Indian Ocean. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darmayati, Y.; Sanusi, H.S.; Prartono, T.; Santosa, D.W.; Nuchsin, R. The effect of biostimulation and biostimulation-bioaugmentation on biodegradation of oil-pollution on sandy beaches using mesocosms. Int. J. Mar. Sci. 2015, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dwinovantyo, A.; Susanti, S.; Prabowo, N.W.; Rahmaniar, R.; Prartono, T. Oil spill biodegradation by bacteria isolated from Jakarta Bay Marine Sediments. Ilmu Kelaut. 2016, 21, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazen, T.C.; Dubinsky, E.A.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Piceno, Y.M.; Singh, N.; Jansson, J.K.; Probst, A.; Borglin, S.E.; Fortney, J.L.; et al. Deep-sea oil plume enriches indigenous oil-degrading bacteria. Science 2010, 330, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwinovantyo, A.; Prartono, T.; Syafrizal, S.; Udiharto, U.; Effendi, H. Isolation of deep-sea sediment bacteria for oil spill biodegradation. ELBA Bioflux 2015, 7, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Wasify, R.S.; Hamed, S.R. Bacterial biodegradation of crude oil using local isolates. J. Microbiol. 2014, 2010, 863272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society and Testing Materials (ASTM). Standard test method for oil and grease (fluorocarbon extractable substances) by gravimetric determination. ASTM Water Environ. Technol. 2010, 11, 471–476. [Google Scholar]
- Razika, B.; Abbes, B.; Messaoud, C.; Soufi, K. Phenol and benzoic acid degradation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Water Res. Prot. 2010, 2, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Widdel, F. Theory and Measurement of Bacterial Growth; Universität Bremen: Bremen, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Atmadipoera, A.S.; Molcard, R.; Madec, G.; Wijffela, S.; Sprintasll, S.; Koch-Larrouy, A.; Jaya, I.; Supangat, A. Characteristic and variability of the Indonesian Throughflow water at the Outflow straits. Deep Sea Res. I 2009, 56, 1942–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, T.; Du, Y.; Strachan, J.; Meyers, G.; Slingo, J. Sea surface temperature and its variability in the Indonesian region. Oceanography 2005, 18, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prartono, T.; Wolff, G.A. Organic geochemistry of lacustrine sediments: A record of the changing trophic status of Rostherne Mere, UK. Org. Geochem. 1998, 28, 729–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, I.C.; Schwing, P.T.; Brooks, G.R.; Larson, R.A.; Hastings, D.W.; Ellis, G.; Goddard, E.A.; Hollander, D.J. Hydrocarbons in Deep-Sea Sediments following the 2010 Deepwater Horizon Blowout in the Northeast Gulf of Mexico. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanshahian, M.; Cappello, S. Crude oil biodegradation in marine environments. In Biodegradation—Engineering and Technology; Chamy, R., Rosenkranz, F., Eds.; InTech Open: London, UK, 2013; pp. 101–136. [Google Scholar]
- Santosa, D.A.; Listiyawati, L.; Irawathi, T.; Herdiyantoro, D.; Ananda, R.W.U.; Adiwibowo, S. Biotechnology for remediation of oil sludge and petroleum contaminated ecosystem using bacteria isolated from Indonesia’s region. Environ. Res. 2004, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Rio, L.D.; Hadwin, A.; Pinto, L.; MacKinnon, M.; Moore, M. Degradation of naphthenic acids by sediment microorganisms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Nugroho, A. Biodegradation of petroleum sludge in microcosm scale: A preliminary assessment simulation simple as bioremediation land treatment. Makara J. Tek. 2006, 10, 82–89. (In Indonesian) [Google Scholar]
- Venosa, A.D.; MacNaughton, S.J.; Stephen, J.R. Microbial population changes during bioremediation of an experimental oil spill. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 65, 3566–3574. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, D.F.; Sakata, S.K.; Comesseto, J.V.; Bicego, M.C.; Pellizari, V.H. Diversity of hydrocarbon-degrading Raoultella isolated from hydrocarbon-contaminated estuaries. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 106, 1304–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.J.; Smith, B.E.; Sutton, P.A.; McGenity, T.J.; Rowland, S.J.; Whitby, C. Microbial biodegradation of aromatic alkanoic naphthenic acids is affected by the degree of alkyl side chain branching. ISME J. 2011, 5, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.E.; Lewis, C.A.; Belt, S.T.; Whitby, C.; Rowland, S.J. Effects of alkyl chain branching on the biotransformation of naphthenic acids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 9323–9328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plohl, K.; Lescovsek, H.; Bricelj, M. Biological degradation of motor oil in water. Acta Chim. Slov. 2001, 49, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiao, N.; Cottrell, M.T.; Kirchman, D.L. Contribution of major bacterial groups to bacterial biomass production along a salinity gradient in the South China Sea. J. Aquat. Microb. 2006, 43, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandón, L.M.; Marín, M.A.; Quintero, M.; Jutinico-Shubach, L.M.; Montoya-Giraldo, M.; Santos-Acevedo, M.; Gómez-León, J. Diversity of cultivable bacteria from deep-sea sediments of the Colombian Caribbean and their potential in bioremediation. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2022, 115, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.W.; Alzubaidi, F.S.; Hamza, S.J. Biodegradation of crude oil in contaminated water by local isolates of Enterobacter cloacae. J. Sci. 2014, 55, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Dell’ Anno, F.; Rastelli, E.; Sansone, C.; Brunet, C.; Ianora, A.; Dell’ Anno, A. Bacteria, Fungi and Microalgae for the Bioremediation of Marine Sediments Contaminated by Petroleum Hydrocarbons in the Omics Era. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syafrizal, S.; Prastiko, R.B.; Prartono, T.; Kussuryani, Y. Effect of Dietanolamide (DEA) surfactant addition and deep-sea bacteria activities on the biodegradability of artificial oily wastewater in seawater media. Sci. Contrib. Oil Gas 2018, 41, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






 ), (b) bacteria population (
), (b) bacteria population ( ), and pH (
), and pH ( ) during experiment.
) during experiment.
 ), (b) bacteria population (
), (b) bacteria population ( ), and pH (
), and pH ( ) during experiment.
) during experiment.

| Parameter | Before Biodegradation | After Biodegradation |
|---|---|---|
| Pr/Ph | 2.25 | 2.25 |
| n-C17/Pr | 0.84 1 | 0.52 |
| n-C18/Ph | 1.54 1 | 1.04 |
| CPI C11–19 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| CPI C20–27 | 0.96 | 0.96 |
| Day | Bacteria Population (CFU mL−1) | Growth Rate, µ (day−1) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 8.3 × 107 | - |
| 1 | 8.5 × 107 | 0.02 |
| 2 | 9.2 × 107 | 0.08 |
| 3 | 1.0 × 108 | 0.10 |
| 4 | 1.1 × 108 | 0.08 |
| 7 | 1.2 × 108 | 0.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prartono, T.; Dwinovantyo, A.; Syafrizal, S.; Syakti, A.D. Potential Use of Deep-Sea Sediment Bacteria for Oil Spill Biodegradation: A Laboratory Simulation. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10081616
Prartono T, Dwinovantyo A, Syafrizal S, Syakti AD. Potential Use of Deep-Sea Sediment Bacteria for Oil Spill Biodegradation: A Laboratory Simulation. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(8):1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10081616
Chicago/Turabian StylePrartono, Tri, Angga Dwinovantyo, Syafrizal Syafrizal, and Agung Dhamar Syakti. 2022. "Potential Use of Deep-Sea Sediment Bacteria for Oil Spill Biodegradation: A Laboratory Simulation" Microorganisms 10, no. 8: 1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10081616
APA StylePrartono, T., Dwinovantyo, A., Syafrizal, S., & Syakti, A. D. (2022). Potential Use of Deep-Sea Sediment Bacteria for Oil Spill Biodegradation: A Laboratory Simulation. Microorganisms, 10(8), 1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10081616







