Coronavirus Disease 2019-Associated Coagulopathy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
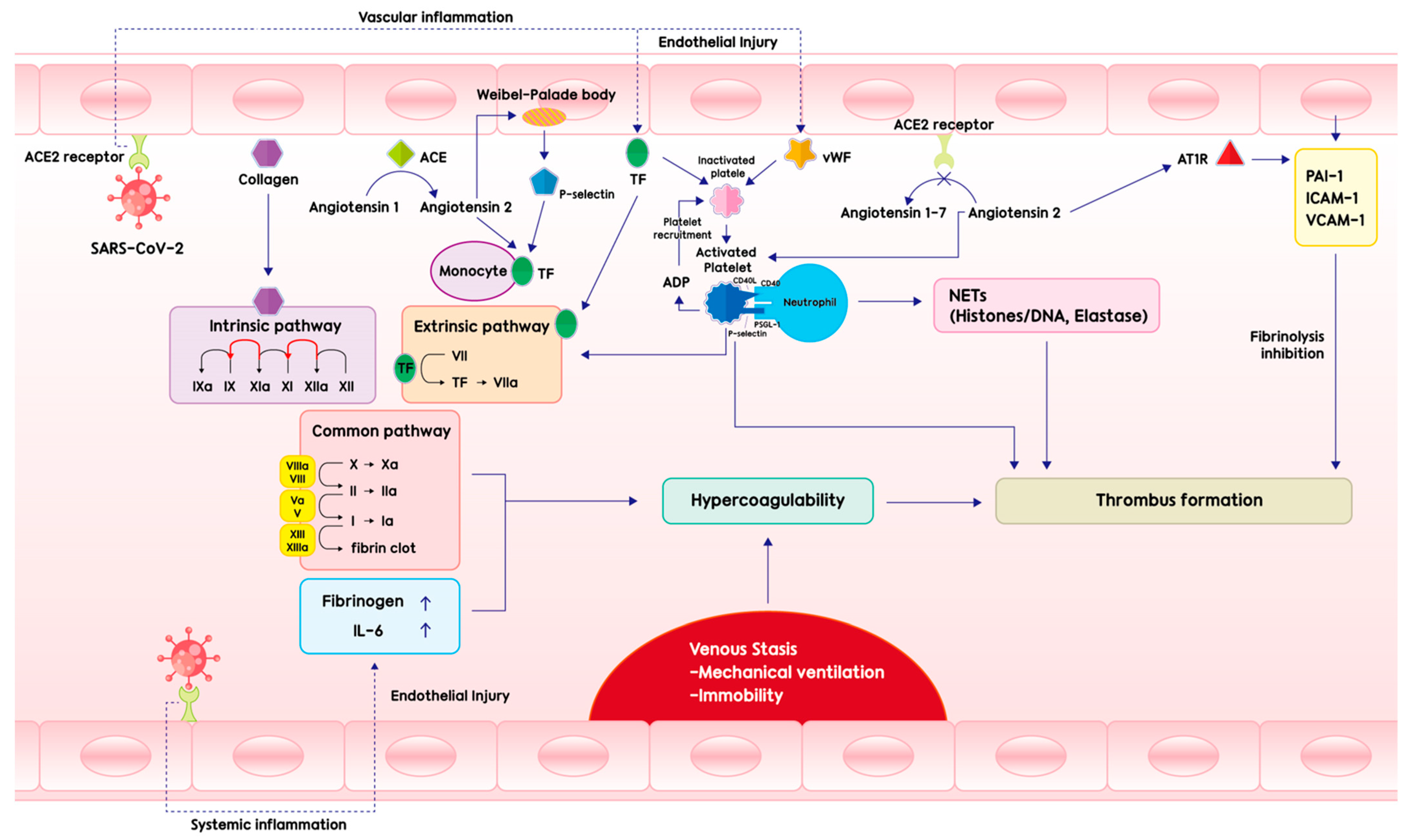
2. Pathogenesis
3. Clinical Manifestations
4. Diagnosis
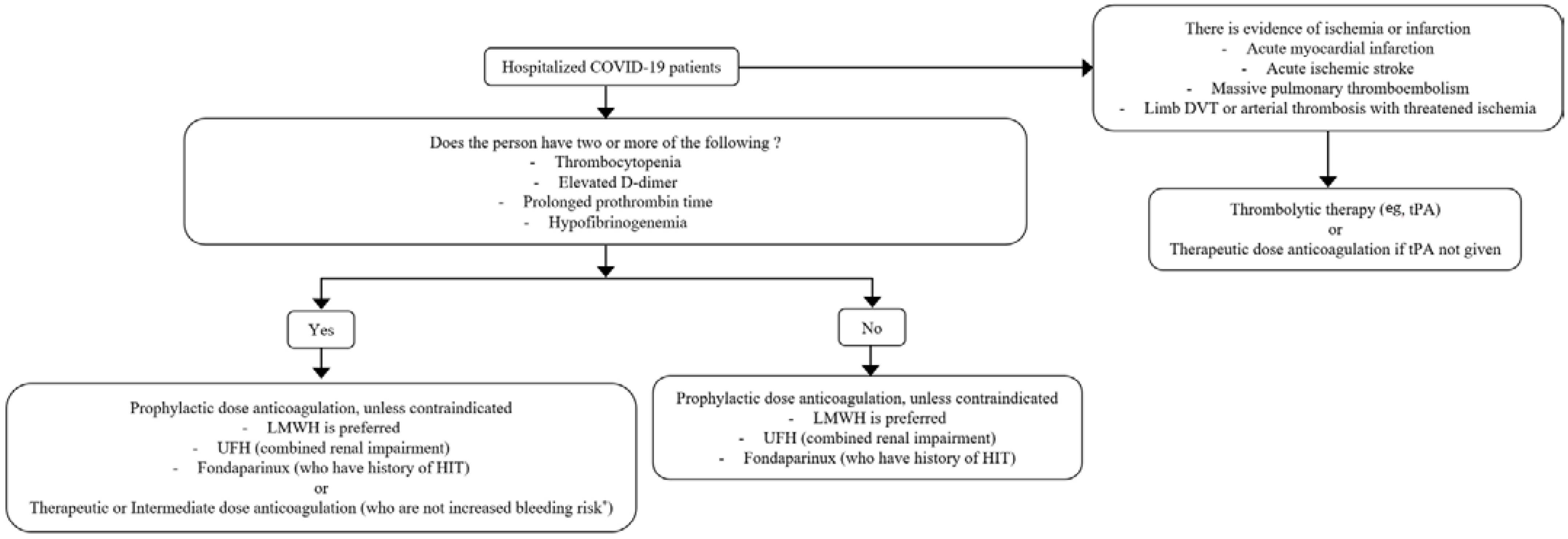
5. Treatment
6. Prevention
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, N.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z. Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bikdeli, B.; Madhavan, M.V.; Jimenez, D.; Chuich, T.; Dreyfus, I.; Driggin, E.; Nigoghossian, C.; Ageno, W.; Madjid, M.; Guo, Y.; et al. COVID-19 and Thrombotic or Thromboembolic Disease: Implications for Prevention, Antithrombotic Therapy, and Follow-Up: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 2950–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klok, F.A.; Kruip, M.; van der Meer, N.J.M.; Arbous, M.S.; Gommers, D.; Kant, K.M.; Kaptein, F.H.J.; van Paassen, J.; Stals, M.A.M.; Huisman, M.V.; et al. Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19. Thromb. Res. 2020, 191, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, S.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, F. Prevalence of venous thromboembolism in patients with severe novel coronavirus pneumonia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1421–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenner, W.J.; Gorog, D.A. Incidence of thrombotic complications in COVID-19: On behalf of ICODE: The International COVID-19 Thrombosis Biomarkers Colloquium. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 52, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middeldorp, S.; Coppens, M.; van Haaps, T.F.; Foppen, M.; Vlaar, A.P.; Müller, M.C.A.; Bouman, C.C.S.; Beenen, L.F.M.; Kootte, R.S.; Heijmans, J.; et al. Incidence of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1995–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llitjos, J.F.; Leclerc, M.; Chochois, C.; Monsallier, J.M.; Ramakers, M.; Auvray, M.; Merouani, K. High incidence of venous thromboembolic events in anticoagulated severe COVID-19 patients. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1743–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagot, C.N.; Arya, R. Virchow and his triad: A question of attribution. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 143, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gando, S.; Wada, T. Thromboplasminflammation in COVID-19 Coagulopathy: Three Viewpoints for Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 649122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowenstein, C.J.; Solomon, S.D. Severe COVID-19 Is a Microvascular Disease. Circulation 2020, 142, 1609–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P.; Lüscher, T. COVID-19 is, in the end, an endothelial disease. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 3038–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norooznezhad, A.H.; Mansouri, K. Endothelial cell dysfunction, coagulation, and angiogenesis in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Microvasc. Res. 2021, 137, 104188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magro, C.; Mulvey, J.J.; Berlin, D.; Nuovo, G.; Salvatore, S.; Harp, J.; Baxter-Stoltzfus, A.; Laurence, J. Complement associated microvascular injury and thrombosis in the pathogenesis of severe COVID-19 infection: A report of five cases. Transl. Res. 2020, 220, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yuan, X.; Chen, H.; Chaturvedi, S.; Braunstein, E.M.; Brodsky, R.A. Direct activation of the alternative complement pathway by SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins is blocked by factor D inhibition. Blood 2020, 136, 2080–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cugno, M.; Meroni, P.L.; Gualtierotti, R.; Griffini, S.; Grovetti, E.; Torri, A.; Lonati, P.; Grossi, C.; Borghi, M.O.; Novembrino, C.; et al. Complement activation and endothelial perturbation parallel COVID-19 severity and activity. J. Autoimmun. 2021, 116, 102560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranucci, M.; Ballotta, A.; Di Dedda, U.; Baryshnikova, E.; Dei Poli, M.; Resta, M.; Falco, M.; Albano, G.; Menicanti, L. The procoagulant pattern of patients with COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1747–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipolloni, L.; Sessa, F.; Bertozzi, G.; Baldari, B.; Cantatore, S.; Testi, R.; D’Errico, S.; Di Mizio, G.; Asmundo, A.; Castorina, S.; et al. Preliminary Post-Mortem COVID-19 Evidence of Endothelial Injury and Factor VIII Hyperexpression. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, C.L.; Truong, A.D.; Auld, S.C.; Polly, D.M.; Tanksley, C.L.; Duncan, A. COVID-19-associated hyperviscosity: A link between inflammation and thrombophilia? Lancet 2020, 395, 1758–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robba, C.; Battaglini, D.; Ball, L.; Valbusa, A.; Porto, I.; Della Bona, R.; La Malfa, G.; Patroniti, N.; Brunetti, I.; Loconte, M.; et al. Coagulative Disorders in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients with Acute Distress Respiratory Syndrome: A Critical Review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslamifar, Z.; Behzadifard, M.; Soleimani, M.; Behzadifard, S. Coagulation abnormalities in SARS-CoV-2 infection: Overexpression tissue factor. Thromb. J. 2020, 18, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzaroni, M.G.; Piantoni, S.; Masneri, S.; Garrafa, E.; Martini, G.; Tincani, A.; Andreoli, L.; Franceschini, F. Coagulation dysfunction in COVID-19: The interplay between inflammation, viral infection and the coagulation system. Blood Rev. 2021, 46, 100745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, H. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Clin. Chim. Acta 2004, 344, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panigada, M.; Bottino, N.; Tagliabue, P.; Grasselli, G.; Novembrino, C.; Chantarangkul, V.; Pesenti, A.; Peyvandi, F.; Tripodi, A. Hypercoagulability of COVID-19 patients in intensive care unit: A report of thromboelastography findings and other parameters of hemostasis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1738–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, F.L.; Vogler, T.O.; Moore, E.E.; Moore, H.B.; Wohlauer, M.V.; Urban, S.; Nydam, T.L.; Moore, P.K.; McIntyre, R.C., Jr. Fibrinolysis Shutdown Correlation with Thromboembolic Events in Severe COVID-19 Infection. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2020, 231, 193–203.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Plebani, M.; Henry, B.M. Thrombocytopenia is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infections: A meta-analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 506, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiery-Antier, N.; Binquet, C.; Vinault, S.; Meziani, F.; Boisramé-Helms, J.; Quenot, J.P. Is Thrombocytopenia an Early Prognostic Marker in Septic Shock? Crit. Care Med. 2016, 44, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godoy, L.C.; Goligher, E.C.; Lawler, P.R.; Slutsky, A.S.; Zarychanski, R. Anticipating and managing coagulopathy and thrombotic manifestations of severe COVID-19. Cmaj 2020, 192, E1156–E1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhou, F.; Sun, W.; Chen, L.; Lan, L.; Li, H.; Xiao, F.; Li, Y.; Kolachalama, V.B.; Li, Y.; et al. Relationship Between Serum Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Nucleic Acid and Organ Damage in Coronavirus 2019 Patients: A Cohort Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansory, E.M.; Srigunapalan, S.; Lazo-Langner, A. Venous Thromboembolism in Hospitalized Critical and Noncritical COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. TH Open 2021, 5, e286–e294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Liu, Y.; Cai, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Fu, C. Prevalence of Venous Thromboembolism in Critically Ill Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 603558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollias, A.; Kyriakoulis, K.G.; Lagou, S.; Kontopantelis, E.; Stergiou, G.S.; Syrigos, K. Venous thromboembolism in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Vasc. Med. 2021, 26, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, T.; Haslbauer, J.D.; Nienhold, R.; Savic, S.; Hopfer, H.; Deigendesch, N.; Frank, S.; Turek, D.; Willi, N.; Pargger, H.; et al. Postmortem examination of COVID-19 patients reveals diffuse alveolar damage with severe capillary congestion and variegated findings in lungs and other organs suggesting vascular dysfunction. Histopathology 2020, 77, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichmann, D.; Sperhake, J.P.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Steurer, S.; Edler, C.; Heinemann, A.; Heinrich, F.; Mushumba, H.; Kniep, I.; Schröder, A.S.; et al. Autopsy Findings and Venous Thromboembolism in Patients With COVID-19: A Prospective Cohort Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, M.; Verleden, S.E.; Kuehnel, M.; Haverich, A.; Welte, T.; Laenger, F.; Vanstapel, A.; Werlein, C.; Stark, H.; Tzankov, A.; et al. Pulmonary Vascular Endothelialitis, Thrombosis, and Angiogenesis in COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilaloglu, S.; Aphinyanaphongs, Y.; Jones, S.; Iturrate, E.; Hochman, J.; Berger, J.S. Thrombosis in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 in a New York City Health System. JAMA 2020, 324, 799–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, J.; Tacquard, C.; Severac, F.; Leonard-Lorant, I.; Ohana, M.; Delabranche, X.; Merdji, H.; Clere-Jehl, R.; Schenck, M.; Fagot Gandet, F.; et al. High risk of thrombosis in patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: A multicenter prospective cohort study. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patell, R.; Khan, A.M.; Bogue, T.; Merrill, M.; Koshy, A.; Bindal, P.; Joyce, R.; Aird, W.C.; Neuberg, D.; Bauer, K.A.; et al. Heparin induced thrombocytopenia antibodies in COVID-19. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, E295–E296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Beato, R.; Morales-Ortega, A.; Fernández, F.J.H.; Morón, A.I.P.; Ríos-Fernández, R.; Rubio, J.L.C.; Centeno, N.O. Immune thrombocytopenia and COVID-19: Case report and review of literature. Lupus 2021, 30, 1515–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kewan, T.; Gunaratne, T.N.; Mushtaq, K.; Alayan, D.; Daw, H.; Haddad, A. Outcomes and management of immune thrombocytopenia secondary to COVID-19: Cleveland clinic experience. Transfusion 2021, 61, 2014–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, A.; Suliman, A.M.; Abdallah, E.I.; Abakar, M.A.A.; Elbasheir, M.M.; Muddathir, A.M.; Aldakheel, F.M.; Bin Shaya, A.S.; Alfahed, A.; Alharthi, N.S.; et al. Influence of COVID-19 on lymphocyte and platelet parameters among patients admitted to intensive care unit and emergency. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 2579–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yan, X.; Fan, Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z. D-dimer levels on admission to predict in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1324–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escher, R.; Breakey, N.; Lämmle, B. Severe COVID-19 infection associated with endothelial activation. Thromb. Res. 2020, 190, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, S.; Moreno-Castaño, A.B.; Palomo, M.; Martinez-Sanchez, J.; Torramadé-Moix, S.; Téllez, A.; Ventosa, H.; Seguí, F.; Escolar, G.; Carreras, E.; et al. Distinctive Biomarker Features in the Endotheliopathy of COVID-19 and Septic Syndromes. Shock 2022, 57, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavord, S.; Scully, M.; Hunt, B.J.; Lester, W.; Bagot, C.; Craven, B.; Rampotas, A.; Ambler, G.; Makris, M. Clinical Features of Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia and Thrombosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1680–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goligher, E.C.; Bradbury, C.A.; McVerry, B.J.; Lawler, P.R.; Berger, J.S.; Gong, M.N.; Carrier, M.; Reynolds, H.R.; Kumar, A.; Turgeon, A.F.; et al. Therapeutic Anticoagulation with Heparin in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawler, P.R.; Goligher, E.C.; Berger, J.S.; Neal, M.D.; McVerry, B.J.; Nicolau, J.C.; Gong, M.N.; Carrier, M.; Rosenson, R.S.; Reynolds, H.R.; et al. Therapeutic Anticoagulation with Heparin in Noncritically Ill Patients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, R.D.; de Barros, E.S.P.G.M.; Furtado, R.H.M.; Macedo, A.V.S.; Bronhara, B.; Damiani, L.P.; Barbosa, L.M.; de Aveiro Morata, J.; Ramacciotti, E.; de Aquino Martins, P.; et al. Therapeutic versus prophylactic anticoagulation for patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 and elevated D-dimer concentration (ACTION): An open-label, multicentre, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 2253–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perepu, U.S.; Chambers, I.; Wahab, A.; Ten Eyck, P.; Wu, C.; Dayal, S.; Sutamtewagul, G.; Bailey, S.R.; Rosenstein, L.J.; Lentz, S.R. Standard prophylactic versus intermediate dose enoxaparin in adults with severe COVID-19: A multi-center, open-label, randomized controlled trial. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 2225–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholzberg, M.; Tang, G.H.; Rahhal, H.; AlHamzah, M.; Kreuziger, L.B.; Áinle, F.N.; Alomran, F.; Alayed, K.; Alsheef, M.; AlSumait, F.; et al. Effectiveness of therapeutic heparin versus prophylactic heparin on death, mechanical ventilation, or intensive care unit admission in moderately ill patients with COVID-19 admitted to hospital: RAPID randomised clinical trial. BMJ 2021, 375, n2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyropoulos, A.C.; Goldin, M.; Giannis, D.; Diab, W.; Wang, J.; Khanijo, S.; Mignatti, A.; Gianos, E.; Cohen, M.; Sharifova, G.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Therapeutic-Dose Heparin vs. Standard Prophylactic or Intermediate-Dose Heparins for Thromboprophylaxis in High-risk Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: The HEP-COVID Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2021, 181, 1612–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rentsch, C.T.; Beckman, J.A.; Tomlinson, L.; Gellad, W.F.; Alcorn, C.; Kidwai-Khan, F.; Skanderson, M.; Brittain, E.; King, J.T., Jr.; Ho, Y.L.; et al. Early initiation of prophylactic anticoagulation for prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 mortality in patients admitted to hospital in the United States: Cohort study. BMJ 2021, 372, n311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, G.D.; Burnett, A.; Allen, A.; Blumenstein, M.; Clark, N.P.; Cuker, A.; Dager, W.E.; Deitelzweig, S.B.; Ellsworth, S.; Garcia, D.; et al. Thromboembolism and anticoagulant therapy during the COVID-19 pandemic: Interim clinical guidance from the anticoagulation forum. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2020, 50, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hajizadeh, N.; Moore, E.E.; McIntyre, R.C.; Moore, P.K.; Veress, L.A.; Yaffe, M.B.; Moore, H.B.; Barrett, C.D. Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) treatment for COVID-19 associated acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): A case series. J. Thromb. Haemost 2020, 18, 1752–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, C.D.; Oren-Grinberg, A.; Chao, E.; Moraco, A.H.; Martin, M.J.; Reddy, S.H.; Ilg, A.M.; Jhunjhunwala, R.; Uribe, M.; Moore, H.B.; et al. Rescue therapy for severe COVID-19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome with tissue plasminogen activator: A case series. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2020, 89, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christie, D.B., 3rd; Nemec, H.M.; Scott, A.M.; Buchanan, J.T.; Franklin, C.M.; Ahmed, A.; Khan, M.S.; Callender, C.W.; James, E.A.; Christie, A.B.; et al. Early outcomes with utilization of tissue plasminogen activator in COVID-19-associated respiratory distress: A series of five cases. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2020, 89, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiNicolantonio, J.J.; Barroso-Aranda, J. Harnessing adenosine A2A receptors as a strategy for suppressing the lung inflammation and thrombotic complications of COVID-19: Potential of pentoxifylline and dipyridamole. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 143, 110051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, R.; Malhamé, I.; Teshler, L.; Acharya, G.; Hunt, B.J.; McLintock, C. A critical review of the pathophysiology of thrombotic complications and clinical practice recommendations for thromboprophylaxis in pregnant patients with COVID-19. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2020, 99, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. Available online: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov (accessed on 27 July 2022).
- Cuker, A.; Tseng, E.K.; Nieuwlaat, R.; Angchaisuksiri, P.; Blair, C.; Dane, K.; Davila, J.; DeSancho, M.T.; Diuguid, D.; Griffin, D.O.; et al. American Society of Hematology 2021 guidelines on the use of anticoagulation for thromboprophylaxis in patients with COVID-19. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 872–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iba, T.; Warkentin, T.E.; Thachil, J.; Levi, M.; Levy, J.H. Proposal of the Definition for COVID-19-Associated Coagulopathy. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivas, D.; Roldán, V.; Esteve-Pastor, M.A.; Roldán, I.; Tello-Montoliu, A.; Ruiz-Nodar, J.M.; Cosín-Sales, J.; Gámez, J.M.; Consuegra, L.; Ferreiro, J.L.; et al. Recommendations on antithrombotic treatment during the COVID-19 pandemic. Position statement of the Working Group on Cardiovascular Thrombosis of the Spanish Society of Cardiology. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2020, 73, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Samkari, H.; Karp Leaf, R.S.; Dzik, W.H.; Carlson, J.C.T.; Fogerty, A.E.; Waheed, A.; Goodarzi, K.; Bendapudi, P.K.; Bornikova, L.; Gupta, S.; et al. COVID-19 and coagulation: Bleeding and thrombotic manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Blood 2020, 136, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouhat, B.; Besutti, M.; Bouiller, K.; Grillet, F.; Monnin, C.; Ecarnot, F.; Behr, J.; Capellier, G.; Soumagne, T.; Pili-Floury, S.; et al. Elevated D-dimers and lack of anticoagulation predict PE in severe COVID-19 patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2001811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, G.; Weber, V.; Stegmayr, B. Therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE) as a plausible rescue therapy in severe vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2021, 60, 103174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Jeune, S.; Suhl, J.; Benainous, R.; Minvielle, F.; Purser, C.; Foudi, F.; Warzocha, U.; Dhote, R. High prevalence of early asymptomatic venous thromboembolism in anticoagulated COVID-19 patients hospitalized in general wards. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 51, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Nie, L.; Xiang, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Fu, X.; Ren, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Q. D-Dimer and Prothrombin Time Are the Significant Indicators of Severe COVID-19 and Poor Prognosis. Biomed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 6159720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyvandi, F.; Artoni, A.; Novembrino, C.; Aliberti, S.; Panigada, M.; Boscarino, M.; Gualtierotti, R.; Rossi, F.; Palla, R.; Martinelli, I.; et al. Hemostatic alterations in COVID-19. Haematologica 2021, 106, 1472–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, I.; Ciavarella, A.; Abbattista, M.; Aliberti, S.; De Zan, V.; Folli, C.; Panigada, M.; Gori, A.; Artoni, A.; Ierardi, A.M.; et al. Increasing dosages of low-molecular-weight heparin in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Intern. Emerg Med. 2021, 16, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paranjpe, I.; Fuster, V.; Lala, A.; Russak, A.J.; Glicksberg, B.S.; Levin, M.A.; Charney, A.W.; Narula, J.; Fayad, Z.A.; Bagiella, E.; et al. Association of Treatment Dose Anticoagulation with In-Hospital Survival Among Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 122–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Bai, H.; Chen, X.; Gong, J.; Li, D.; Sun, Z. Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients with coagulopathy. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1094–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramacciotti, E.; Barile Agati, L.; Calderaro, D.; Aguiar, V.C.R.; Spyropoulos, A.C.; de Oliveira, C.C.C.; Lins Dos Santos, J.; Volpiani, G.G.; Sobreira, M.L.; Joviliano, E.E.; et al. Rivaroxaban versus no anticoagulation for post-discharge thromboprophylaxis after hospitalisation for COVID-19 (MICHELLE): An open-label, multicentre, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 2022, 399, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, J.M.; Brooks, M.M.; Sciurba, F.C.; Krishnan, J.A.; Bledsoe, J.R.; Kindzelski, A.; Baucom, A.L.; Kirwan, B.A.; Eng, H.; Martin, D.; et al. Effect of Antithrombotic Therapy on Clinical Outcomes in Outpatients With Clinically Stable Symptomatic COVID-19: The ACTIV-4B Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 326, 1703–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| . | COVID-19-Associated Coagulopathy | Acute Decompensated Disseminated Intravascular Coagulopathy | Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia (VITT) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Major finding | Thrombosis | Bleeding | Thrombosis |
| Platelet | Normal/decreased | Decreased | Decreased |
| PT/aPTT | Normal/prolonged | Prolonged | Normal/slightly increased |
| D-dimer | Increased | Increased | Increased |
| Fibrinogen | Increased | Decreased | Decreased |
| Factor VIII | Increased | Decreased | Increased |
| Fibrin degradation product (FDP) | Increased | Increased | Increased |
| Study | Number of Participants | Mortality (%) | Venous Thromboembolism (%) | Organ Support Free Day | Major Bleeding (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Therapeutic | Prophylactic | Therapeutic | Prophylactic | Therapeutic | Prophylactic | Therapeutic | Prophylactic | Therapeutic | Prophylactic | |
| [46] | 534 | 564 | 37.3 | 35.5 | 6.4 | 10.4 | 1 | 4 | 3.8 | 2.3 |
| [48] | 311 | 304 | 11 | 8 | 7 | 10 | N/A | N/A | 3 | 1 |
| [50] | 228 | 237 | 1.8 | 7.6 | 0.9 | 2.5 | 25.8 | 24.1 | 0.9 | 1.7 |
| [51] | 129 | 124 | 19.4 | 25 | 10.9 | 29 | N/A | N/A | 4.7 | 1.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, J.-W.; Kim, D.-Y.; Yun, N.; Kim, D.-M. Coronavirus Disease 2019-Associated Coagulopathy. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10081556
Seo J-W, Kim D-Y, Yun N, Kim D-M. Coronavirus Disease 2019-Associated Coagulopathy. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(8):1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10081556
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, Jun-Won, Da-Young Kim, Nara Yun, and Dong-Min Kim. 2022. "Coronavirus Disease 2019-Associated Coagulopathy" Microorganisms 10, no. 8: 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10081556
APA StyleSeo, J.-W., Kim, D.-Y., Yun, N., & Kim, D.-M. (2022). Coronavirus Disease 2019-Associated Coagulopathy. Microorganisms, 10(8), 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10081556






