Pathogenic Leptospira Species Are Widely Disseminated among Wild Rodents in Urban Areas of Guangzhou, Southern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
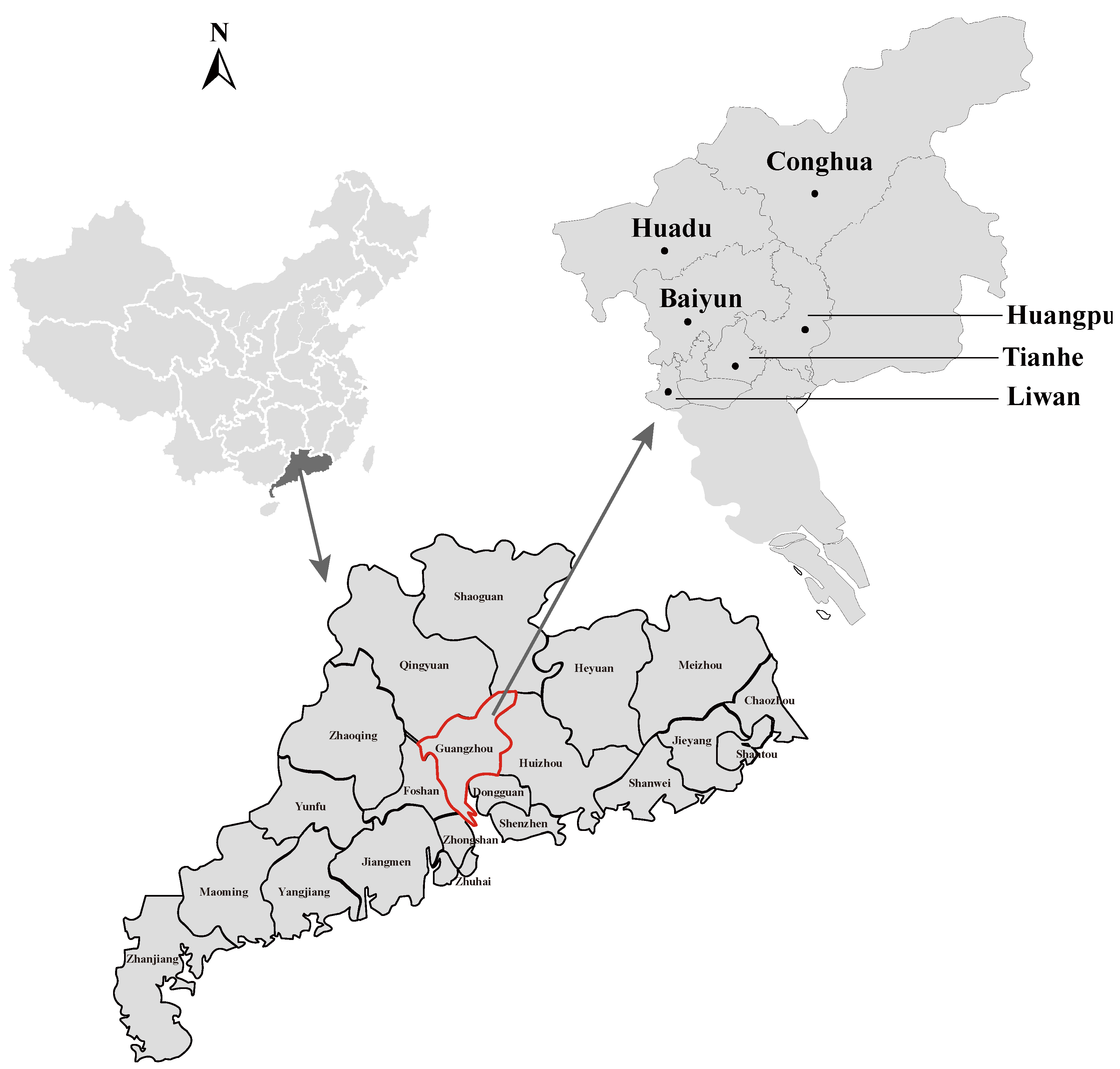
2.1. Rodents Trapping and Samples Processing
2.2. Detection and Molecular Characterization of Pathogenic Leptospira
2.3. Sequence Comparison and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4. Statistical Data Analysis
2.5. Ethics Statement
3. Results
3.1. Detection of Pathogenic Leptospira
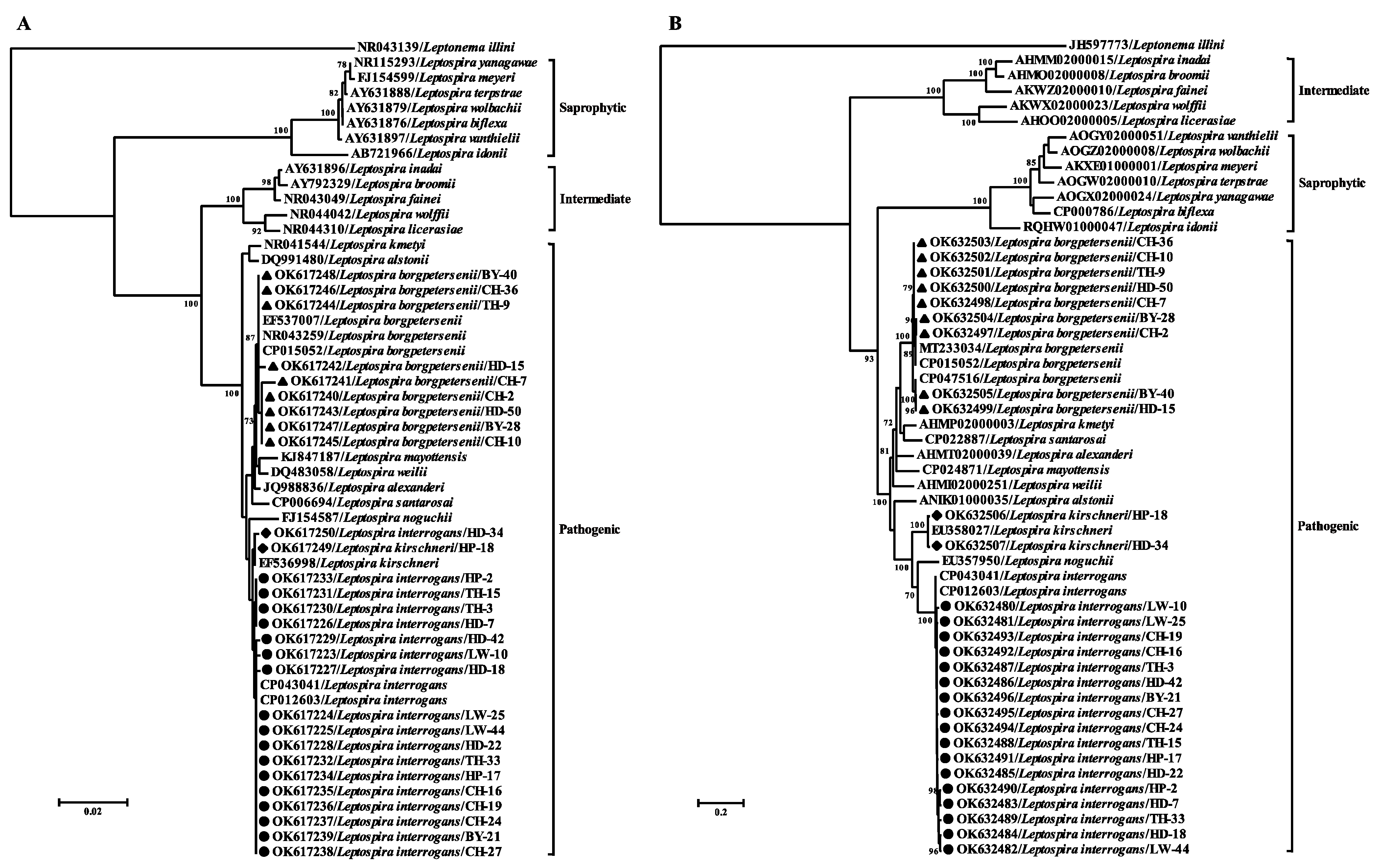
3.2. Molecular Characterization of Pathogenic Leptospira
3.3. Distribution of Pathogenic Leptospira in Rodents
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levett, P.N. Leptospirosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 14, 296–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bharti, A.R.; Nally, J.E.; Ricaldi, J.N.; Matthias, M.A.; Diaz, M.M.; Lovett, M.A.; Levett, P.N.; Gilman, R.H.; Willig, M.R.; Gotuzzo, E.; et al. Leptospirosis: A zoonotic disease of global importance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2003, 3, 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.; Hagan, J.E.; Calcagno, J.; Kane, M.; Torgerson, P.; Martinez-Silveira, M.S.; Stein, C.; Abela-Ridder, B.; Ko, A.I. Global morbidity and mortality of Leptospirosis: A systematic review. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hartskeerl, R.A.; Collares-Pereira, M.; Ellis, W.A. Emergence, control and re-emerging leptospirosis: Dynamics of infection in the changing world. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricaldi, J.N.; Swancutt, M.A.; Matthias, M.A. Current trends in translational research in leptospirosis. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 26, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, H.M.; Hertz, J.T.; Munishi, O.M.; Galloway, R.L.; Marks, F.; Saganda, W.; Maro, V.P.; Crump, J.A. Estimating leptospirosis incidence using hospital-based surveillance and a population-based health care utilization survey in Tanzania. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dupouey, J.; Faucher, B.; Edouard, S.; Richet, H.; Kodjo, A.; Drancourt, M.; Davoust, B. Human leptospirosis: An emerging risk in Europe? Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 37, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, M.; Agnello, S.; Chetta, M.; Amato, B.; Vitale, G.; Bella, C.D.; Vicari, D.; Presti, V. Human leptospirosis cases in Palermo Italy. The role of rodents and climate. J. Infect. Public Health 2018, 11, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picardeau, M. Virulence of the zoonotic agent of leptospirosis: Still terra incognita? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaipadungpanit, J.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Chierakul, W.; Smythe, L.D.; Petkanchanapong, W.; Limpaiboon, R.; Apiwatanaporn, A.; Slack, A.T.; Suputtamongkol, Y.; White, N.J.; et al. A dominant clone of Leptospira interrogans associated with an outbreak of human leptospirosis in Thailand. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2007, 1, e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Lin, X.; Yan, J. Leptospira and leptospirosis in China. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 27, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Yan, J. Leptospirosis prevalence in Chinese populations in the last two decades. Microbes Infect. 2012, 14, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhewantara, P.W.; Mamun, A.A.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Yin, W.-W.; Ding, F.; Guo, D.; Hu, W.; Costa, F.; Ko, A.I.; Soares Magalhães, R.J. Epidemiological shift and geographical heterogeneity in the burden of leptospirosis in China. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2018, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Mehmood, K.; Liu, J.; McDonough, S.P.; Tang, Z.; Chang, Y.F. Leptospirosis trends in China, 2007–2018: A retrospective observational study. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, W.A. Animal leptospirosis. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 387, 99–137. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.J.; Gong, X.Q.; Xiao, X.; Liu, J.W.; Han, H.J.; Qin, X.R.; Lei, S.C.; Gu, X.L.; Yu, H.; Yu, X.J. Detection of Leptospira interrogans in Hedgehogs from central China. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2020, 20, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerburg, B.G.; Singleton, G.R.; Kijlstra, A. Rodent-borne diseases and their risks for public health. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 35, 221–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.P.; Lin, X.D.; Wang, W.; Tian, J.H.; Cong, M.L.; Zhang, H.L.; Wang, M.R.; Zhou, R.H.; Wang, J.B.; Li, M.H.; et al. Phylogeny and origins of hantaviruses harbored by bats, insectivores, and rodents. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djadid, N.D.; Ganji, Z.F.; Gouya, M.M.; Rezvani, M.; Zakeri, S. A simple and rapid nested polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism technique for differentiation of pathogenic and nonpathogenic Leptospira spp. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 63, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourhy, P.; Herrmann Storck, C.; Theodose, R.; Olive, C.; Nicolas, M.; Hochedez, P.; Lamaury, I.; Zinini, F.; Brémont, S.; Landier, A.; et al. Serovar diversity of pathogenic Leptospira circulating in the French West Indies. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guernier, V.; Richard, V.; Nhan, T.; Rouault, E.; Tessier, A.; Musso, D. Leptospira diversity in animals and humans in Tahiti, French Polynesia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burland, T.G. DNASTAR’s Lasergene sequence analysis software. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 132, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Posada, D. jModelTest: Phylogenetic model averaging. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshghi, A.; Cullen, P.A.; Cowen, L.; Zuerner, R.L.; Cameron, C.E. Global proteome analysis of Leptospira interrogans. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 4564–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bulach, D.M.; Zuerner, R.L.; Wilson, P.; Seemann, T.; McGrath, A.; Cullen, P.A.; Davis, J.; Johnson, M.; Kuczek, E.; Alt, D.P.; et al. Genome reduction in Leptospira borgpetersenii reflects limited transmission potential. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14560–14565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, T.; Qiu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, E.; Li, S.; Chang, Y.F.; Guo, X.; Jiang, X.; et al. Genetic characteristics of pathogenic Leptospira in wild small animals and livestock in Jiangxi Province, China, 2002-2015. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Huang, C.; Han, S.; Yuan, G.; Zhang, Q.; He, H. Epidemiology and genetic diversity of zoonotic pathogens in urban rats (Rattus spp.) from a subtropical city, Guangzhou, southern China. Zoonoses Public Health 2020, 67, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, H.; Li, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zeng, L.; Xu, J.; Xu, Y.; Chang, Y.F.; Guo, X.; et al. Molecular typing of pathogenic Leptospira serogroup icterohaemorrhagiae strains circulating in China during the past 50 years. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maiden, M.C.; Bygraves, J.A.; Feil, E.; Morelli, G.; Russell, J.E.; Urwin, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zurth, K.; Caugant, D.A.; et al. Multilocus sequence typing: A portable approach to the identification of clones within populations of pathogenic microorganisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3140–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tucunduva de Faria, M.; Athanazio, D.A.; Gonçalves Ramos, E.A.; Silva, E.F.; Reis, M.G.; Ko, A.I. Morphological alterations in the kidney of rats with natural and experimental Leptospira infection. J. Comp. Pathol. 2007, 137, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koizumi, N.; Miura, K.; Sanai, Y.; Takemura, T.; Ung, T.T.H.; Le, T.T.; Hirayama, K.; Hasebe, F.; Nguyen, H.L.K.; Hoang, P.V.M.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of Leptospira interrogans in Rattus norvegicus in Hanoi, Vietnam. Acta Trop. 2019, 194, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa, J.P.; Bucarey, S.A.; Cattan, P.E.; Landaeta-Aqueveque, C.; Ramírez-Estrada, J. Renal carriage of Leptospira species in rodents from Mediterranean Chile: The Norway rat (Rattus norvegicus) as a relevant host in agricultural lands. Acta Trop. 2017, 176, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boey, K.; Shiokawa, K.; Rajeev, S. Leptospira infection in rats: A literature review of global prevalence and distribution. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifah, I.; Abdul Halim, A.; Rahmat, M.S.; Nadia, M.F.; Ubil, Z.E.; Asmah, H.; Shafariatul Akmar, I.; Picardeau, M.; Siti Haslina, O.; Nasir, M.A. Isolation by culture and PCR identification of LipL32 gene of pathogenic Leptospira spp. in wild rats of Kuala Lumpur. Malays. J. Pathol. 2017, 39, 161–166. [Google Scholar]
- Himsworth, C.G.; Bidulka, J.; Parsons, K.L.; Feng, A.Y.T.; Tang, P.; Jardine, C.M.; Kerr, T.; Mak, S.; Robinson, J.; Patrick, D.M. Ecology of Leptospira interrogans in Norway rats (Rattus norvegicus) in an inner-city neighborhood of Vancouver, Canada. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himsworth, C.G.; Parsons, K.L.; Jardine, C.; Patrick, D.M. Rats, cities, people, and pathogens: A systematic review and narrative synthesis of literature regarding the ecology of rat-associated zoonoses in urban centers. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2013, 13, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minter, A.; Himsworth, C.G.; Byers, K.A.; Childs, J.E.; Ko, A.I.; Costa, F. Tails of two cities: Age and wounding are associated with carriage of Leptospira interrogans by Norway rats (Rattus norvegicus) in ecologically distinct urban environments. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Qin, P.; Lu, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, S.; Li, M.; Yang, Z. Meteorological factors and risk of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in Guangzhou, southern China, 2006–2015. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Primers | Sequences (5′ → 3′) | Amplicon (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rrs | nest-1F | GGCGGCGCGTCTTAAACATG | 525 | [19] |
| nest-1R | GTCCGCCTACGCACCCTTTACG | [19] | ||
| nest-2F | CAAGTCAAGCGGAGTAGCAA | 289 | [19] | |
| nest-2R | CTTAACCTGCTGCCTCCCGTA | [19] | ||
| nest-1F | GGCGGCGCGTCTTAAACATG | 1300 | [19] | |
| rrs-1R | GTACAAGGTCCGGGAACGTA | This study | ||
| nest-2F | CAAGTCAAGCGGAGTAGCAA | 1100 | [19] | |
| rrs-2R | GCGAGTTGGCTACCCTTTGT | This study | ||
| secY | secY-1F | GAAGGWCTTCTCGGAATGGTGG | 1200 | This study |
| secY-1R | CCKTCCCTTAATTTTAGACTTCTTC | This study | ||
| secY-2F | GCKCTYGGRATYATGCCTTA | 1100 | This study | |
| secY-2R | TTCATRAAGCCTTCRTAATTTCTCA | This study |
| Species | Location | Total (%,CI) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liwan | Huadu | Tianhe | Huangpu | Baiyun | Conghua | ||
| R. norvegicus | 3/46 | 7/50 | 4/50 | 2/48 | 3/46 | 3/10 | 22/250 8.8, 5.9−13.0) |
| R. losea | − | − | − | − | − | 5/40 | 5/40 (12.5, 5.5−26.1) |
| R. tanezumi | 0/2 | − | − | − | − | − | 0/2 (0) |
| Mus musculus | 0/2 | − | − | 1/2 | − | − | 1/4 (25.0, 4.6−69.9) |
| Total (%,CI) | 3/50 (6.0, 2.1−16.2) | 7/50 (14.0, 7.0−26.2) | 4/50 (8.0, 3.2−18.8) | 3/50 (6.0, 2.1−16.2) | 3/46 (6.5, 2.2−17.5) | 8/50 (16.0, 8.3−28.5) | 28/296 (9.5, 6.6−13.3) |
| Species | No. of Individuals | No. per Species (Positive Rate per Species, %, CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L. interrogans | L. borgpetersenii | L. kirschneri | ||
| R. norvegicus | 250 | 12 (4.8, 2.8−8.2) | 8 (3.2, 1.6−6.2) | 2 (0.8, 0.2−2.9) |
| R. losea | 40 | 4 (10.0, 4.0−23.0) | 1 (2.5, 0.4−12.9) | − |
| R. tanezumi | 2 | − | − | − |
| Mus musculus | 4 | 1 (25.0, 4.6−69.9) | − | − |
| Total (%, CI) | 296 | 17 (5.7, 3.6−9.0) | 9 (3.0, 1.6−5.7) | 2 (0.7, 0.2−2.4) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, J.-W.; Wei, Y.-H.; Yao, X.-Y.; Chen, H.-Y.; Liu, H.; Sun, J.; Chen, S.-Y. Pathogenic Leptospira Species Are Widely Disseminated among Wild Rodents in Urban Areas of Guangzhou, Southern China. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10050873
Shao J-W, Wei Y-H, Yao X-Y, Chen H-Y, Liu H, Sun J, Chen S-Y. Pathogenic Leptospira Species Are Widely Disseminated among Wild Rodents in Urban Areas of Guangzhou, Southern China. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(5):873. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10050873
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Jian-Wei, Yue-Hong Wei, Xin-Yan Yao, Hai-Yan Chen, Hong Liu, Jing Sun, and Shou-Yi Chen. 2022. "Pathogenic Leptospira Species Are Widely Disseminated among Wild Rodents in Urban Areas of Guangzhou, Southern China" Microorganisms 10, no. 5: 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10050873
APA StyleShao, J.-W., Wei, Y.-H., Yao, X.-Y., Chen, H.-Y., Liu, H., Sun, J., & Chen, S.-Y. (2022). Pathogenic Leptospira Species Are Widely Disseminated among Wild Rodents in Urban Areas of Guangzhou, Southern China. Microorganisms, 10(5), 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10050873






