Functionalized Noble Metal Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Herpesvirus Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Standard Antiviral Treatment
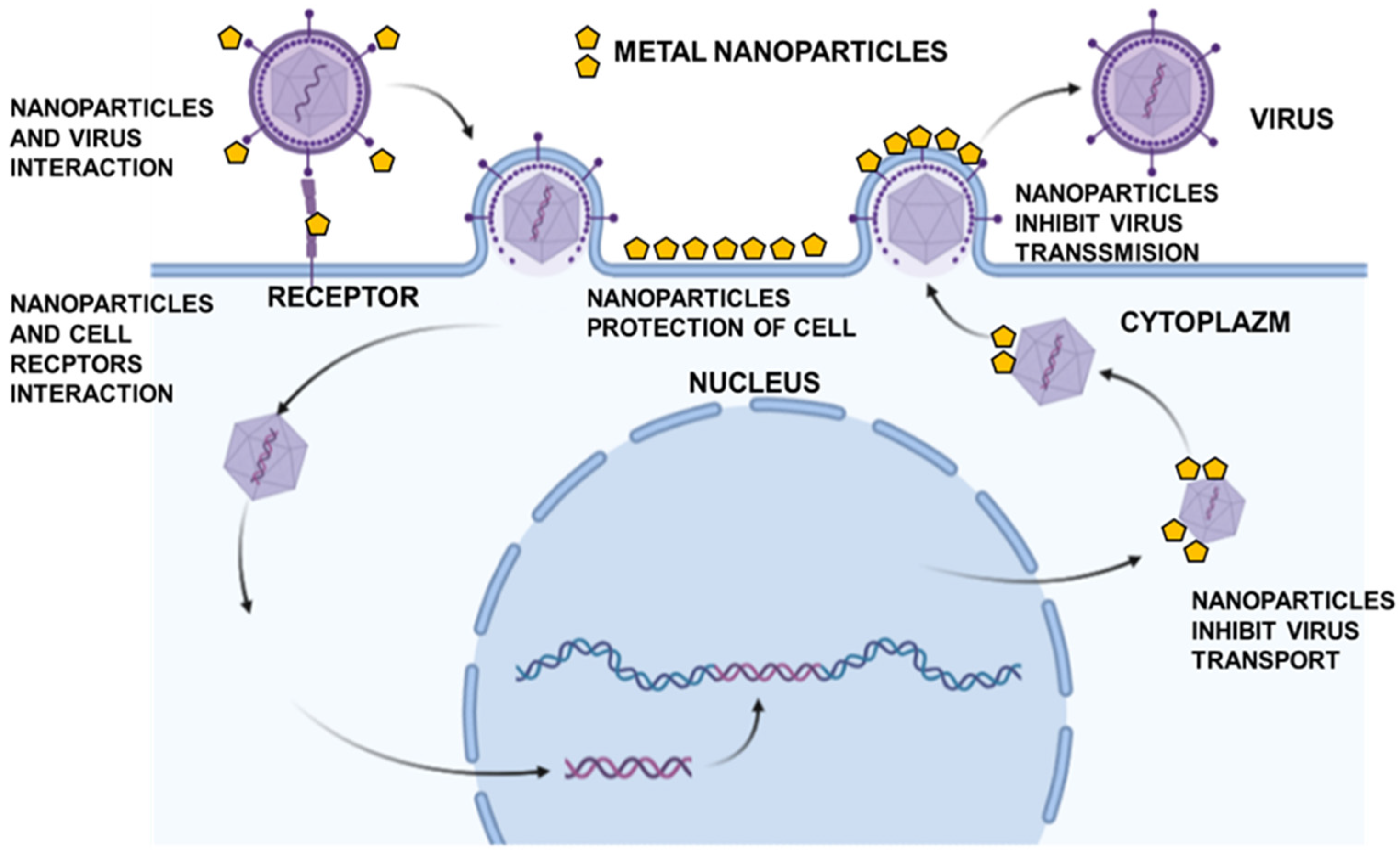
3. Noble Metal Nanoparticles as Antiviral Drugs
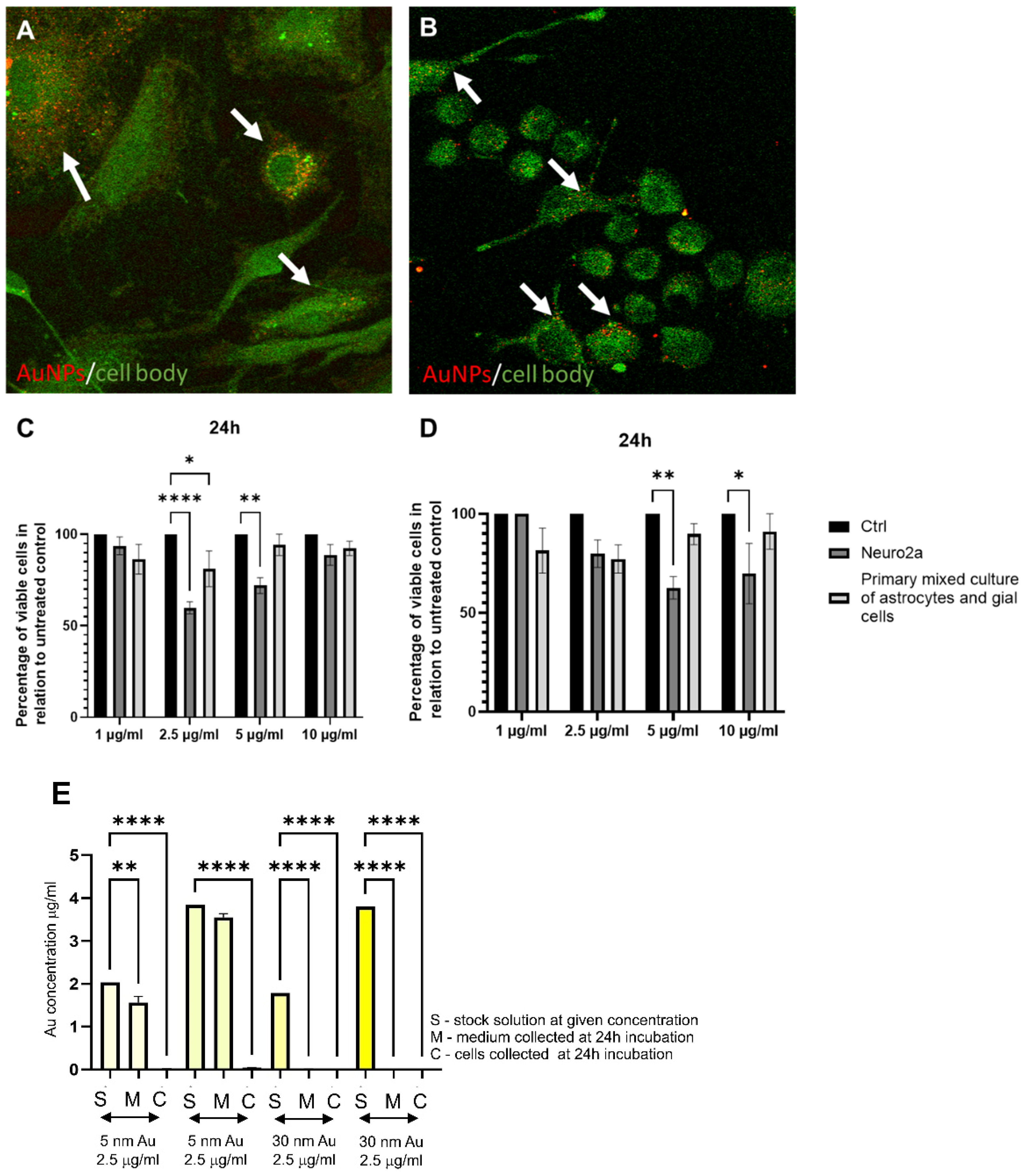
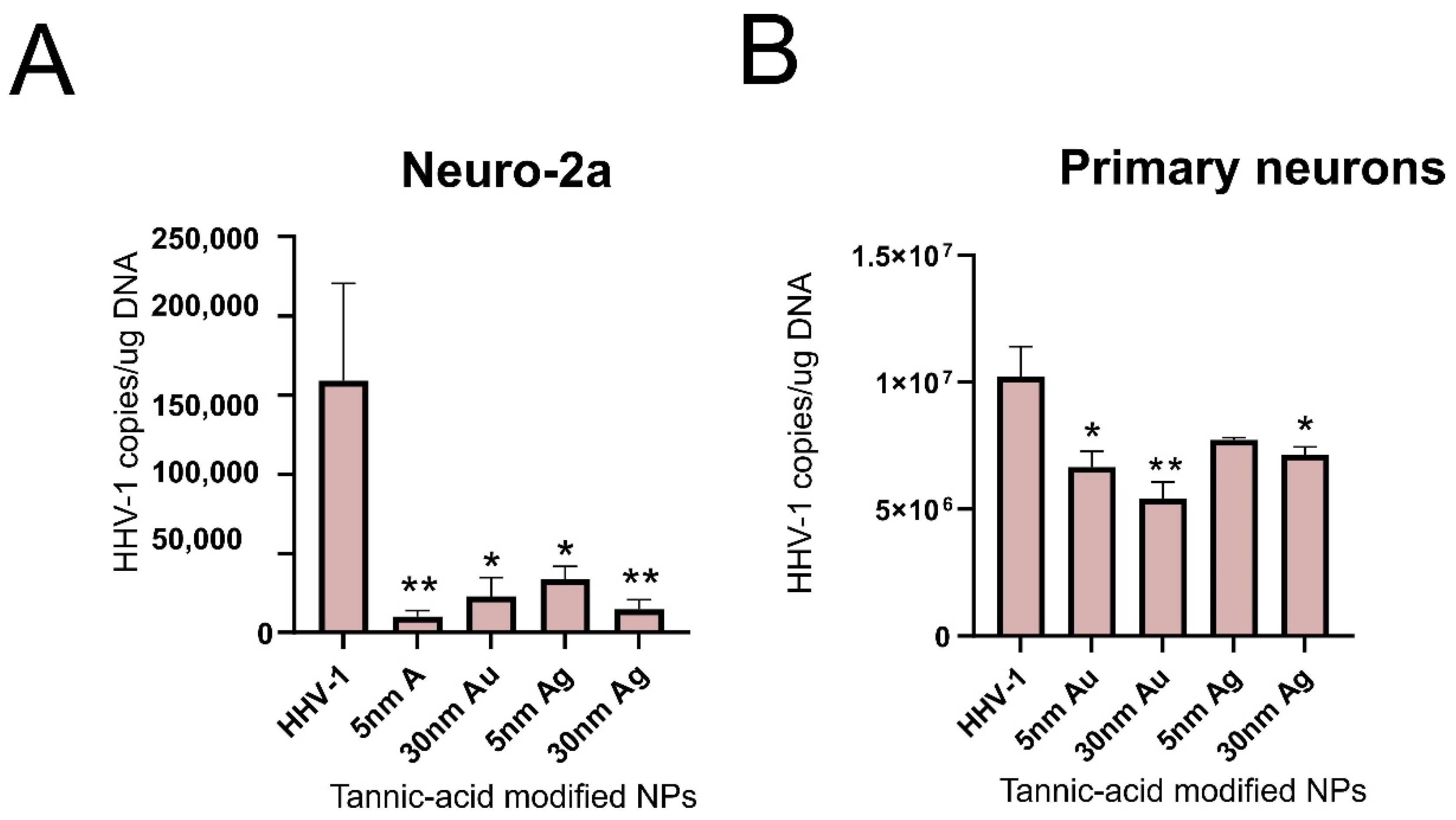
4. Gold Nanoparticles
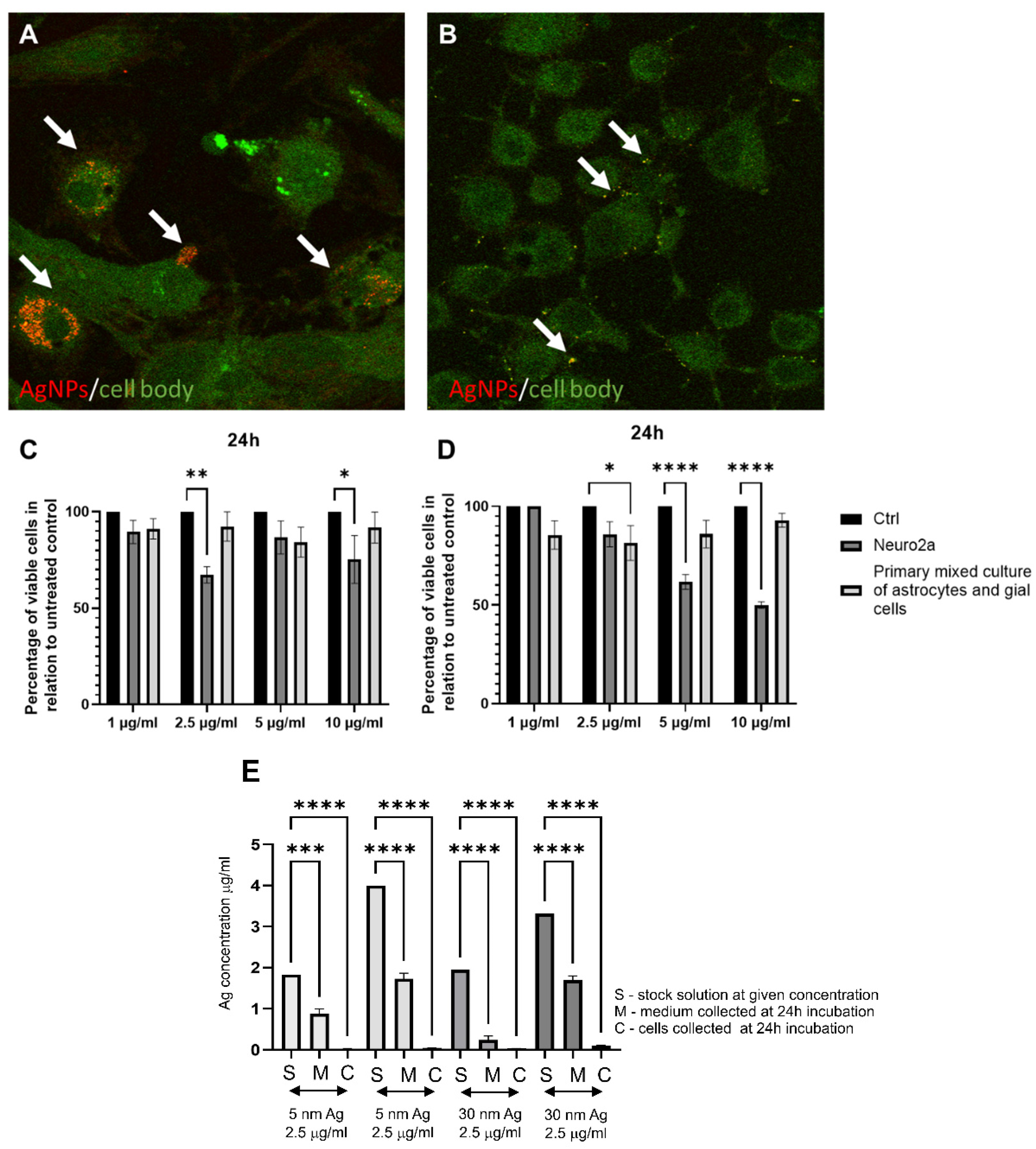
5. Silver Nanoparticles
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klapper, P.E.; Cleator, G.M. Herpes simplex virus. Intervirology 1997, 40, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, J.D.; Bednarik, D.P.; Raj, N.B.; Rosen, C.A.; Sodroski, J.G.; Haseltine, W.A.; Pitha, P.M. Activation of human immunodeficiency virus by herpesvirus infection: Identification of a region within the long terminal repeat that responds to a trans-acting factor encoded by herpes simplex virus 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 7408–7412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caserta, M.T.; Mock, D.J.; Dewhurst, S. Human herpesvirus 6. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilden, D.H.; Mahalingam, R.; Cohrs, R.J.; Tyler, K.L. Herpesvirus infections of the nervous system. Nat. Clin. Pract. Neurol. 2007, 3, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roizman, B.; Knipe, D.M. Herpes simplex viruses and their replication. In Fields Virology, 4th ed.; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Griffen, D.E., Eds.; Lippincott Williams: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Britton, P.; Jones, C. Central nervous system herpesvirus infections. Paediatr. Child Health 2014, 24, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, F.O.; Rabson, A.S.; Yee, C.L.; Tralka, T.S. Herpesvirus hominis: Isolation from human trigeminal ganglion. Science 1972, 178, 306–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, C.; Morrow, R.A.; Stanberry, L.R. Human Herpesviruses: Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 and 2; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 829–853. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, S.C. Viral infections of the mouth. Drugs Dis. 2016. Available online: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1079920-overview (accessed on 2 October 2022).
- Kumar, A.; Stavrakis, G.; Karaba, A.H. Herpesviruses and Inflammasomes: One Sensor Does Not Fit All. MBio 2022, 13, e01737-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmutzhard, E. Viral infections of the CNS with special emphasis on herpes simplex infections. J. Neurol. 2001, 248, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitley, R.J.; Gnann, J.W. Viral encephalitis: Familiar infections and emerging pathogens. Lancet 2002, 359, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcocci, M.E.; Napoletani, G.; Protto, V.; Kolesova, O.; Piacentini, R.; Puma, D.D.L.; De Chiara, G. Herpes simplex virus-1 in the brain: The dark side of a sneaky infection. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 808–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waltl, I.; Kalinke, U. Beneficial and detrimental functions of microglia during viral encephalitis. Trends Neurosci. 2021, 45, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protto, V.; Marcocci, M.E.; Miteva, M.T.; Piacentini, R.; Puma, D.D.L.; Grassi, C.; De Chiara, G. Role of HSV-1 in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis: A challenge for novel preventive/therapeutic strategies. COPHAR 2022, 63, 102200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, S.; Recuero, M.; Bullido, M.J.; Valdivieso, F.; Aldudo, J. Herpes simplex virus type I induces the accumulation of intracellular β-amyloid in autophagic compartments and the inhibition of the non-amyloidogenic pathway in human neuroblastoma cells. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 430.e19–430.e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, G.; Aldudo, J.; Alonso, M.; Santana, S.; Valdivieso, F. Herpes simplex virus type 1 in-duces nuclear accumulation of hyperphosphorylated tau in neuronal cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 2012, 90, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piacentini, R.; De Chiara, G.; Li Puma, D.D.; Ripoli, C.; Marcocci, M.E.; Garaci, E.; Grassi, C. HSV-1 and Alzheimer’s disease: More than a hypothesis. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danics, K.; Forrest, S.L.; Kapas, I.; Erber, I.; Schmid, S.; Törő, K.; Kovacs, G.G. Neurodegenerative proteinopathies associated with neuroinfections. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 2021, 128, 1551–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.H.; Goh, C.L. Viral infections affecting the skin in organ transplant recipients. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2006, 7, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, A.; Johnston, C. Treatment and prevention of herpes simplex virus type 1 in immunocompetent adolescents and adults. Retrieved Feb. 2021, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Sicurella, M.; Sguizzato, M.; Mariani, P.; Pepe, A.; Baldisserotto, A.; Buzzi, R.; Esposito, E. Natural Polyphenol-Containing Gels against HSV-1 Infection: A Comparative Study. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, A.; Adams, S.D.; Lee, L.H.; Murray, S.R.; Hsu, S.D.; Hammond, J.R.; Chu, T.C. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus type 1 with the modified green tea polyphenol palmitoyl-epigallocatechin gallate. FCT 2013, 52, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Toumy, S.A.; Salib, J.Y.; El-Kashak, W.A.; Marty, C.; Bedoux, G.; Bourgougnon, N. Antiviral effect of polyphenol rich plant extracts on herpes simplex virus type 1. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2018, 7, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churqui, M.P.; Lind, L.; Thörn, K.; Svensson, A.; Savolainen, O.; Aranda, K.T.; Eriksson, K. Extracts of Eq-uisetum gigan-teum L and Copaifera reticulate Ducke show strong antiviral activity against the sexually transmitted pathogen herpes simplex virus type 2. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 210, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; Shabaan, M.T.; Hassan, L.; Morsi, H.H. Antiviral activity of algae biosynthesized silver and gold nanoparticles against Herps Simplex (HSV-1) virus in vitro using cell-line culture technique. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2022, 32, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domènech, B.; Muñoz, M.; Muraviev, D.N.; Macanás, J. Polymer-silver nanocomposites as antibacterial materials. Formatex 2013, 630–640. [Google Scholar]
- Krzyzowska, M.; Chodkowski, M.; Janicka, M.; Dmowska, D.; Tomaszewska, E.; Ranoszek-Soliwoda, K.; Grobelny, J. Lactoferrin-Functionalized Noble Metal Nanoparticles as New Antivirals for HSV-2 Infection. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlowski, P.; Tomaszewska, E.; Ranoszek-Soliwoda, K.; Gniadek, M.; Labedz, O.; Malewski, T.; Nowakowska, J.; Chodaczek, G.; Celichowski, G.; Grobelny, J.; et al. Tannic acid-modified silver and gold nanoparticles as novel stimulators of dendritic cells activation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodnar, D.C.; Mitrea, L.; Călinoiu, L.F.; Szabo, K.; Ştefănescu, B.E. Removal of Bacteria, Viruses, and Other Microbial Entities by Means of Nanoparticles; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 465–491. [Google Scholar]
- Srijampa, S.; Buddhisa, S.; Ngernpimai, S.; Sangiamdee, D.; Chompoosor, A.; Tippayawat, P. Effects of gold nanoparticles with different surface charges on cellular internalization and cytokine responses in monocytes. Bio Nano Sci. 2019, 9, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, W.H.; Borm, P.J.A. Drug delivery and nanoparticles: Applications and hazards. Int. J. Nanomed. 2008, 3, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baram-Pinto, D.; Shukla, S.; Gedanken, A.; Sarid, R. Inhibition of HSV-1 attachment, entry, and cell-to-cell spread by functionalized multivalent gold nanoparticles. Small 2010, 6, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagno, V.; Andreozzi, P.; D’Alicarnasso, M.; Jacob Silva, P.; Mueller, M.; Galloux, M.; Stellacci, F. Broad-spectrum non-toxic antiviral nanoparticles with a virucidal inhibition mechanism. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagno, V.; Gasbarri, M.; Medaglia, C.; Gomes, D.; Clement, S.; Stellacci, F.; Tapparel, C. Sulfonated nanomaterials with broad-spectrum antiviral activity extending beyond heparan sulfate-dependent viruses. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, 02001-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehranfar, A.; Izadyar, M. Theoretical design of functionalized gold nanoparticles as antiviral agents against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 10284–10289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lysenko, V.; Lozovski, V.; Lokshyn, M.; Gomeniuk, Y.V.; Dorovskih, A.; Rusinchuk, N.; Bolbukh, Y. Nanoparticles as antiviral agents against adenoviruses. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 025021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Qiu, K.; He, Q.; Lei, Q.; Lu, W. Mechanisms of blood-brain barrier disruption in herpes simplex encephalitis. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019, 14, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Liu, H.; Huang, C.; Wang, R.; Luo, M.; Lu, W. Herpes Simplex Virus 1-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Damage Involves Apoptosis Associated with GM130-Mediated Golgi Stress. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asil, S.M.; Ahlawat, J.; Barroso, G.G.; Narayan, M. Nanomaterial based drug delivery systems for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 4109–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho-de-Souza, J.L.; Treger, J.S.; Dang, B.; Kent, S.B.H.; Pepperberg, D.R.; Bezanilla, F. Photosensitivity of neurons enabled by cell-targeted gold nanoparticles. Neuron 2015, 86, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paviolo, C.; Stoddart, P.R. Gold nanoparticles for modulating neuronal behavior. J. Nanomater. 2017, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, J.; Needham, K.; Brown, W.G.A.; Nayagam, B.A.; McArthur, S.L.; Yu, A.; Stoddart, P.R. Gold-nanorod-assisted near-infrared stimulation of primary auditory neurons. Adv. Health Mater. 2014, 3, 1862–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paviolo, C.; Haycock, J.W.; Cadusch, P.J.; McArthur, S.L.; Stoddart, P.R. Laser exposure of gold nanorods can induce intracellular calcium transients. J. Biophotonics 2014, 7, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Izquierdo, I.; Serramia, M.J.; Gomez, R.; De La Mata, F.J.; Bullido, M.J.; Muñoz-Fernández, M.A. Gold Nanoparticles Crossing Blood-Brain Barrier Prevent HSV-1 Infection and Reduce Herpes Associated Amyloid-βsecretion. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 155. [Google Scholar]
- Madhusudanan, P.; Jerard, C.; Katiyar, N.; Raju, G.; Shankarappa, S.A. Effect of gold nanoparticle treated dorsal root ganglion cells on peripheral neurite differentiation. Toxicol. In Vitro 2021, 74, 105175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, A.; Das, S.; Ojha, D.; Chattopadhyay, D.; Mukherjee, A. Highly monodispersed gold nanoparticles synthesis and inhibition of herpes simplex virus infections. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 89, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaiser, B.K.; Hirn, S.; Kermanizadeh, A.; Kanase, N.; Fytianos, K.; Wenk, A.; Stone, V. Effects of silver nanoparticles on the liver and hepatocytes in vitro. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 131, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.L.; Hsiao, I.L.; Lin, H.C.; Wang, C.F.; Huang, Y.J.; Chuang, C.Y. Silver nanoparticles affect on gene expression of inflammatory and neurodegenerative responses in mouse brain neural cells. Environ. Res. 2015, 136, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Muresanu, D.F.; Patnaik, R.; Sharma, H.S. Size-and age-dependent neurotoxicity of engineered metal nanoparticles in rats. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 48, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recordati, C.; De Maglie, M.; Cella, C.; Argentiere, S.; Paltrinieri, S.; Bianchessi, S.; Scanziani, E. Repeated oral administration of low doses of silver in mice: Tissue distribution and effects on central nervous system. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2021, 18, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.J.; Bae, E.; Yi, J.; Kim, Y.; Choi, K.; Lee, S.H.; Park, K. Kwangsik Par. Repeated-dose toxicity and inflammatory responses in mice by oral administration of silver nanoparticles. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 30, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowska-Bouta, B.; Zięba, M.; Orzelska-Górka, J.; Skalska, J.; Sulkowski, G.; Frontczak-Baniewicz, M.; Strużyńska, L. Influence of a low dose of silver nanoparticles on cerebral myelin and behavior of adult rats. Toxicology 2016, 363, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Dan, M.; Shao, A.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, C.; Yokel, R.A.; Watanabe, D. Silver nanoparticles induce tight junction disruption and astrocyte neurotoxicity in a rat blood–brain barrier primary triple coculture model. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 6105. [Google Scholar]
- Tyavambiza, C.; Elbagory, A.M.; Madiehe, A.M.; Meyer, M.; Meyer, S. The antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects of silver nanoparticles synthesised from Cotyledon orbiculata aqueous extract. Nanomater 2021, 11, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldovan, B.; David, L.; Vulcu, A.; Olenic, L.; Perde-Schrepler, M.; Fischer-Fodor, E.; Baldea, I.; Clichici, S.; Filip, G.A. In vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory properties of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using Viburnum opulus L. fruits extract. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 79, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Carter, D.A.; Leo, B.F.; Ruenraroengsak, P.; Chen, S.; Goode, A.E.; Theodorou, I.G.; Porter, A.E. Silver nanoparticles reduce brain inflammation and related neurotoxicity through induction of H2S-synthesizing enzymes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerzson, M.F.; Bona, N.P.; Soares, M.S.; Teixeira, F.C.; Rahmeier, F.L.; Carvalho, F.B.; Stefanello, F.M. Tannic Acid Ameliorates STZ-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease-Like Impairment of Memory, Neuroinflammation, Neuronal Death and Modulates Akt Expression. Neurotox. Res. 2020, 37, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Rezai-Zadeh, K.; Koyama, N.; Arendash, G.W.; Yamaguchi, H.; Kakuda, N.; Town, T. Tannic acid is a natural β-secretase inhibitor that prevents cognitive impairment and mitigates Alzheimer-like pathology in transgenic mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 6912–6927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, E.; Orłowski, P.; Winnicka, K.; Tomaszewska, E.; Bąska, P.; Celichowski, G.; Krzyżowska, M. Multifunctional tannic acid/silver nanoparticle-based mucoadhesive hydrogel for improved local treatment of HSV infection: In vitro and in vivo studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlowski, P.; Tomaszewska, E.; Gniadek, M.; Baska, P.; Nowakowska, J.; Sokolowska, J.; Nowak, Z.; Donten, M.; Celichowski, G.; Grobelny, J.; et al. Tannic acid modified silver nanoparticles show antiviral activity in herpes simplex virus type 2 infection. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orłowski, P.; Kowalczyk, A.; Tomaszewska, E.; Ranoszek-Soliwoda, K.; Węgrzyn, A.; Grzesiak, J.; Celichowski, G.; Grobelny, J.; Eriksson, K.; Krzyzowska, M. Antiviral Activity of Tannic Acid Modified Silver Nanoparticles: Potential to Activate Immune Response in Herpes Genitalis. Viruses 2018, 10, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Functional Group/Modification/Metal | Potential Antiviral Mechanism | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| MES (Au) 1 | inhibits viral attachment and cell-to-cell spreading | [33] |
| LT (Au/Ag) 2 | inhibits viral attachment and entry into the host cell | [28] |
| MUS (Au) 3 | mimics the heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPG) binding site on the cell surface | [34] |
| MUS-Ot(Au) 4 | prevents the virus from binding and/or entering the cell | [35] |
| Amin (Au) 5 | blocks receptor-binding domain | [36] |
| SiO2 (Au) 6 | blocks penetration of the virus into the cell due to a change in the membrane potential. | [37] |
| TA (Ag) 7 | blocks virus attachment, entry, and cell-to-cell spreading | [29] |
| CD(Au) 8 | prevents the virus from binding and/or entering the cell | [35] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Janicka, M.; Ranoszek-Soliwoda, K.; Chodaczek, G.; Antos-Bielska, M.; Brytan, M.; Tomaszewska, E.; Celichowski, G.; Grobelny, J.; Cymerys, J.; Krzyżowska, M.; et al. Functionalized Noble Metal Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Herpesvirus Infection. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2161. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10112161
Janicka M, Ranoszek-Soliwoda K, Chodaczek G, Antos-Bielska M, Brytan M, Tomaszewska E, Celichowski G, Grobelny J, Cymerys J, Krzyżowska M, et al. Functionalized Noble Metal Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Herpesvirus Infection. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(11):2161. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10112161
Chicago/Turabian StyleJanicka, Martyna, Katarzyna Ranoszek-Soliwoda, Grzegorz Chodaczek, Małgorzata Antos-Bielska, Marek Brytan, Emilia Tomaszewska, Grzegorz Celichowski, Jarosław Grobelny, Joanna Cymerys, Małgorzata Krzyżowska, and et al. 2022. "Functionalized Noble Metal Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Herpesvirus Infection" Microorganisms 10, no. 11: 2161. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10112161
APA StyleJanicka, M., Ranoszek-Soliwoda, K., Chodaczek, G., Antos-Bielska, M., Brytan, M., Tomaszewska, E., Celichowski, G., Grobelny, J., Cymerys, J., Krzyżowska, M., & Chodkowski, M. (2022). Functionalized Noble Metal Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Herpesvirus Infection. Microorganisms, 10(11), 2161. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10112161






