Campylobacter jejuni in Poultry: Pathogenesis and Control Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Campylobacter jejuni Cellular Structure and Morphology
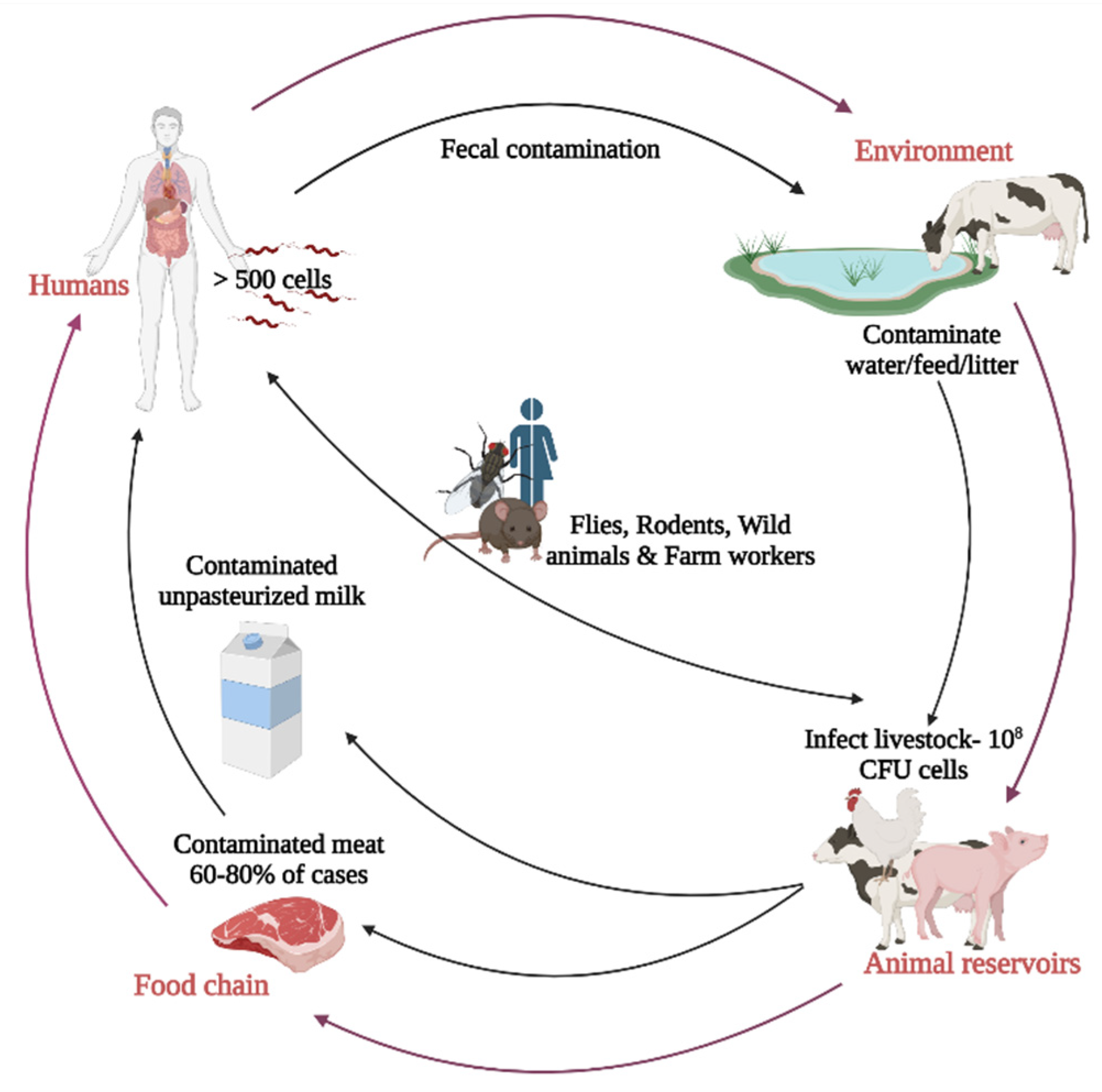
3. Source and Transmission of Campylobacter jejuni in Poultry
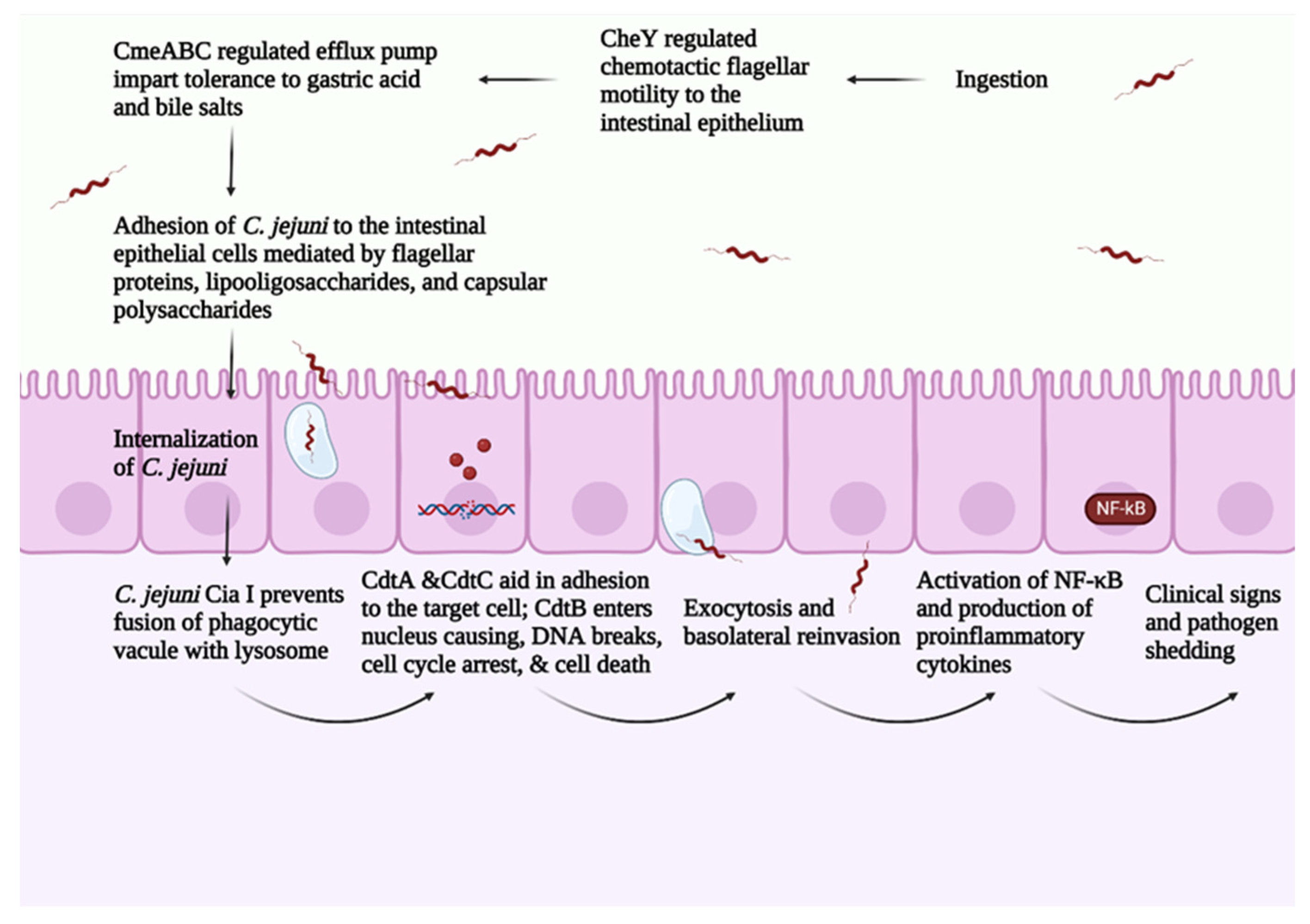
4. Pathogenesis of C. jejuni in Broilers
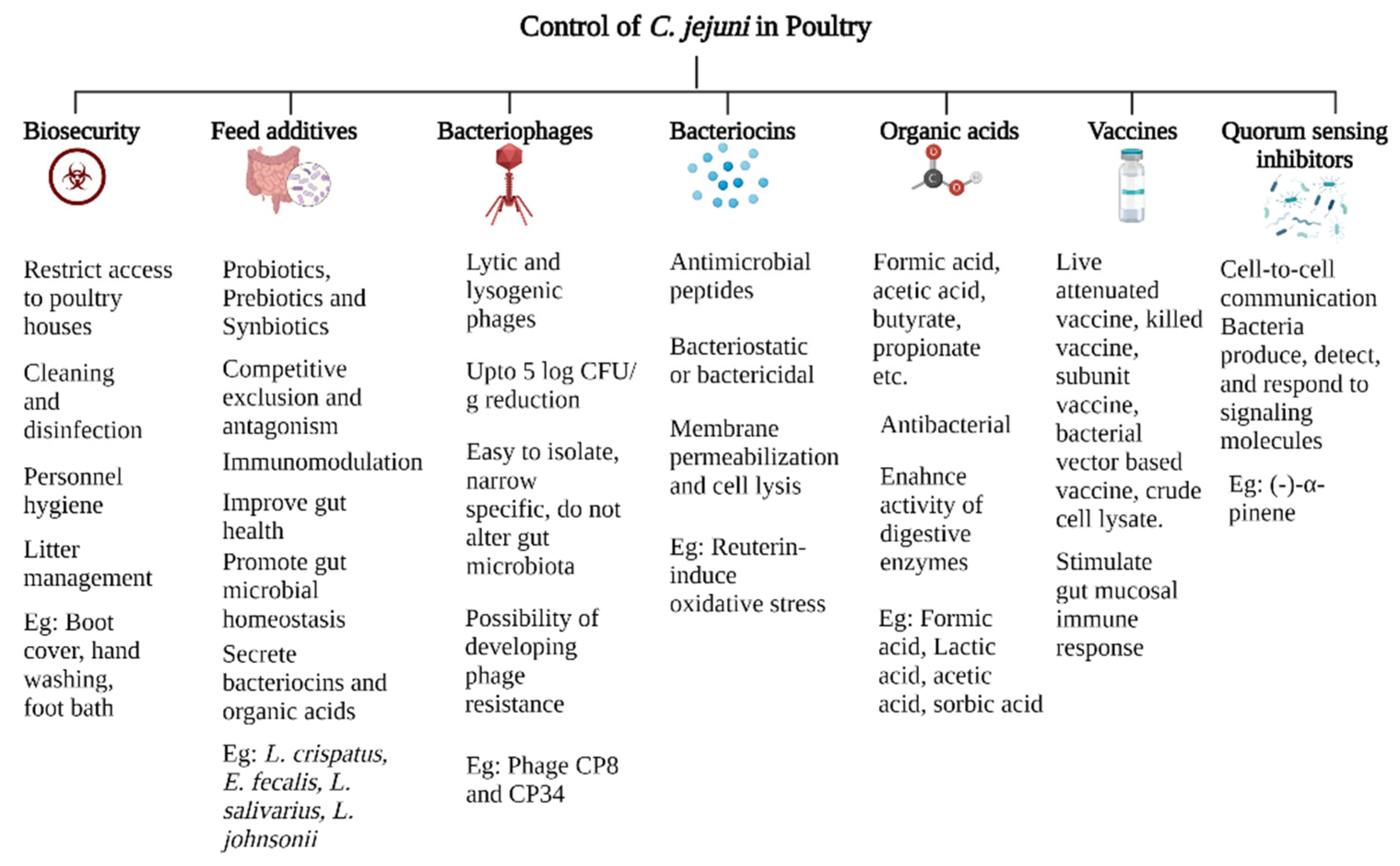
5. Control of C. jejuni in Broilers: (Preharvest)
5.1. Biosecurity
5.2. Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotic
5.3. Organic Acids
5.4. Bacteriophages
5.5. Bacteriocins
5.6. Vaccines
5.6.1. Whole Cell Vaccine and Live Attenuated Vaccine
5.6.2. Crude Cell Lysate
5.6.3. Subunit Vaccine
5.6.4. Bacterial Vector-Based Vaccine
5.7. Quorum Sensing Inhibitors
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Escherich, T. Beitrage zur Kenntniss der Darmbacterien. III. Ueber das Vorkommen von Vibrionen im Darmcanal und den Stuhlgangen der Sauglinge (Articles adding to the knowledge of intestinal bacteria. III. On the existence of vibrios in the intestines and feces of babies). Münchener Med. Wochenschrift 1886, 33, 815–817. [Google Scholar]
- McFadyean, J.; Stockman, S. Report of the Deparmental Committee Appointed by the Board of Agriculture and Fisheries Toenquire into Epizootic Abortion, Part III 1–64; Hermajesty’s Stationary office: London, UK, 1913. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, T. Spirilla associated with disease of the fetal membranes in cattle (infectious abortion). J. Exp. Med. 1918, 28, 701–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stegenga, T.; Terpstra, J. Over Vibrio fetus infecties bij het rund en enzootishe steriliteit. Tijdschr. Diergeneeskd. 1949, 74, 293–296. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, L. A vibrio associated with swine dysentery. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1944, 5, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Vinzent; Dumas; Picard; Lemierre. Septicemie Grave au Cours de la Grossesse, Due a un Vibrion-Avortement Consecutif. In Proceedings of the Semaine des Hopitaux, Paris, France, June 1947; p. 709. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, A. A gastro-enteritis outbreak probably due to a bovine strain of vibrio. Yale J. Biol. Med. 1946, 18, 243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dekeyser, P.; Gossuin-Detrain, M.; Butzler, J.-P.; Sternon, J. Acute enteritis due to related vibrio: First positive stool cultures. J. Infect. Dis. 1972, 125, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butzler, J.P. Campylobacter, from obscurity to celebrity. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2004, 10, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epps, S.V.; Harvey, R.B.; Hume, M.E.; Phillips, T.D.; Anderson, R.C.; Nisbet, D.J. Foodborne Campylobacter: Infections, metabolism, pathogenesis and reservoirs. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 6292–6304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skarp, C.P.A.; Hänninen, M.L.; Rautelin, H.I.K. Campylobacteriosis: The role of poultry meat. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pielsticker, C.; Glünder, G.; Rautenschlein, S. Colonization properties of Campylobacter jejuni in chickens. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 2, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozu Clarke, A.; Ajlouni, S. Recommended Practices to Eliminate Campylobacter from Live Birds and Chicken Meat in Japan. Food Saf. 2021, 9, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Palacios, G.M. The Health Burden of Campylobacter Infection and the Impact of Antimicrobial Resistance: Playing Chicken. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 701–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathima, S.; Shanmugasundaram, R.; Adams, D.; Selvaraj, R. Gastrointestinal Microbiota and Their Manipulation for Improved Growth and Performance in Chickens. Foods 2022, 11, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, E.J.; Nakane, D.; Kabata, Y.; Hendrixson, D.R.; Nishizaka, T.; Beeby, M. Campylobacter jejuni motility integrates specialized cell shape, flagellar filament, and motor, to coordinate action of its opposed flagella. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frirdich, E.; Biboy, J.; Adams, C.; Lee, J.; Ellermeier, J.; Gielda, L.D.; Dirita, V.J.; Girardin, S.E.; Vollmer, W.; Gaynor, E.C. Peptidoglycan-modifying enzyme Pgp1 is required for helical cell shape and pathogenicity traits in Campylobacter jejuni. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maue, A.C.; Mohawk, K.L.; Giles, D.K.; Poly, F.; Ewing, C.P.; Jiao, Y.; Lee, G.; Ma, Z.; Monteiro, M.A.; Hill, C.L.; et al. The polysaccharide capsule of Campylobacter jejuni modulates the host immune response. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, B.L.; Guerry, P.; Poly, F. Global Distribution of Campylobacter jejuni Penner Serotypes: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, P.M.; Hendrixson, D.R. Campylobacter jejuni: Collective components promoting a successful enteric lifestyle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houliston, R.S.; Vinogradov, E.; Dzieciatkowska, M.; Li, J.; St Michael, F.; Karwaski, M.F.; Brochu, D.; Jarrell, H.C.; Parker, C.T.; Yuki, N.; et al. Lipooligosaccharide of Campylobacter jejuni: Similarity with multiple types of mammalian glycans beyond gangliosides. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 12361–12370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-C.; Oh, E.; Hwang, S.; Ryu, S.; Jeon, B. Non-selective regulation of peroxide and superoxide resistance genes by PerR in Campylobacter jejuni. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, E.; McMullen, L.; Jeon, B. Impact of oxidative stress defense on bacterial survival and morphological change in Campylobacter jejuni under aerobic conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, O.; Morishita, T.Y.; Zhang, Q. Campylobacter colonization in poultry: Sources of infection and modes of transmission. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2002, 3, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanker, S.; Lee, A.; Sorrell, T. Horizontal transmission of Campylobacter jejuni amongst broiler chicks: Experimental studies. Epidemiol. Infect. 1990, 104, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlan, A.J.; Coward, C.; Grant, A.J.; Maskell, D.J.; Gog, J.R. Campylobacter jejuni colonization and transmission in broiler chickens: A modelling perspective. J. R. Soc. Interface 2007, 4, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, M.P. Association of Campylobacter jejuni with laying hens and eggs. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1984, 47, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, K.; DaMassa, A.; Morishita, T.; Shivaprasad, H.L.; Bickford, A. Pathogenicity of Campylobacter jejuni for turkeys and chickens. Avian Dis. 1992, 36, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, B.B.; Beletti, M.E.; Melo, R.T.d.; Mendonça, E.P.; Coelho, L.R.; Nalevaiko, P.C.; Rossi, D.A. Campylobacter jejuni in commercial eggs. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2014, 45, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neill, S.; Campbell, J.; O’brien, J. Egg penetration by Campylobacter jejuni. Avian Pathol. 1985, 14, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prachantasena, S.; Charununtakorn, P.; Muangnoicharoen, S.; Hankla, L.; Techawal, N.; Chaveerach, P.; Tuitemwong, P.; Chokesajjawatee, N.; Williams, N.; Humphrey, T.; et al. Distribution and Genetic Profiles of Campylobacter in Commercial Broiler Production from Breeder to Slaughter in Thailand. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonaidi-Jafari, N.; Khamesipour, F.; Ranjbar, R.; Kheiri, R. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter species isolated from the avian eggs. Food Control 2016, 70, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, N.H.; Abdel-Moein, K.A.-A.; Barakat, A.M.A.K.; Hegazi, A.G.; Abd El-Razik, K.A.E.-H.; Sadek, S.A.S. Isolation and molecular characterization of Campylobacter jejuni from chicken and human stool samples in Egypt. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelier, J.M.; Minet, J.; Magras, C.; Colwell, R.R.; Federighi, M. Recovery in embryonated eggs of viable but nonculturable Campylobacter jejuni cells and maintenance of ability to adhere to HeLa cells after resuscitation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 5154–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibanda, N.; McKenna, A.; Richmond, A.; Ricke, S.C.; Callaway, T.; Stratakos, A.C.; Gundogdu, O.; Corcionivoschi, N. A Review of the Effect of Management Practices on Campylobacter Prevalence in Poultry Farms. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazeleger, W.C.; Wouters, J.A.; Rombouts, F.M.; Abee, T. Physiological activity of Campylobacter jejuni far below the minimal growth temperature. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 3917–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, L.; Heyndrickx, M.; Grijspeerdt, K.; Vandekerchove, D.; Rollier, I.; De Zutter, L. Routes for Campylobacter contamination of poultry meat: Epidemiological study from hatchery to slaughterhouse. Epidemiol. Infect. 2003, 131, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, D.G.; Elvers, K.T.; Dopfer, D.; Hansson, I.; Jones, P.; James, S.; Gittins, J.; Stern, N.J.; Davies, R.; Connerton, I.; et al. Biosecurity-based interventions and strategies to reduce Campylobacter spp. on poultry farms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 8605–8614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, E. The isolation of Campylobacter jejuni from flies. Epidemiol. Infect. 1983, 91, 223–226. [Google Scholar]
- Royden, A.; Wedley, A.; Merga, J.Y.; Rushton, S.; Hald, B.; Humphrey, T.; Williams, N.J. A role for flies (Diptera) in the transmission of Campylobacter to broilers? Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 3326–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hald, B.; Skovgård, H.; Bang, D.D.; Pedersen, K.; Dybdahl, J.; Jespersen, J.B.; Madsen, M. Flies and Campylobacter infection of broiler flocks. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 1490–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, A.; Marshall, J.C.; Biggs, P.J.; Midwinter, A.C.; French, N.P. Seasonality of Campylobacter jejuni isolates associated with human campylobacteriosis in the Manawatu region, New Zealand. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkkola, S.; Rossi, M.; Jaakkonen, A.; Simola, M.; Tikkanen, J.; Hakkinen, M.; Tuominen, P.; Huitu, O.; Niemimaa, J.; Henttonen, H.; et al. Host-Dependent Clustering of Campylobacter Strains From Small Mammals in Finland. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 621490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Guk, J.-H.; Mun, S.-H.; An, J.-U.; Kim, W.; Lee, S.; Song, H.; Seong, J.K.; Suh, J.G.; Cho, S. The Wild Mouse (Micromys minutus): Reservoir of a Novel Campylobacter jejuni Strain. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, K.D.; Meece, J.K.; Henkel, J.S.; Shukla, S.K. Birds, migration and emerging zoonoses: West Nile virus, Lyme disease, influenza A and enteropathogens. Clin. Med. Res. 2003, 1, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, R.J.; Razgour, O. Emerging zoonotic diseases originating in mammals: A systematic review of effects of anthropogenic land-use change. Mammal Rev. 2020, 50, 336–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keatts, L.O.; Robards, M.; Olson, S.H.; Hueffer, K.; Insley, S.J.; Joly, D.O.; Kutz, S.; Lee, D.S.; Chetkiewicz, C.-L.B.; Lair, S.; et al. Implications of Zoonoses From Hunting and Use of Wildlife in North American Arctic and Boreal Biomes: Pandemic Potential, Monitoring, and Mitigation. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 627654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysok, B.; Sołtysiuk, M.; Stenzel, T. Wildlife Waterfowl as a Source of Pathogenic Campylobacter Strains. Pathogens 2022, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldenström, J.; Axelsson-Olsson, D.; Olsen, B.; Hasselquist, D.; Griekspoor, P.; Jansson, L.; Teneberg, S.; Svensson, L.; Ellström, P. Campylobacter jejuni colonization in wild birds: Results from an infection experiment. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutschall, S.K.; Hetman, B.M.; Bondo, K.J.; Gannon, V.P.J.; Jardine, C.M.; Taboada, E.N. Campylobacter jejuni Strain Dynamics in a Raccoon (Procyon lotor) Population in Southern Ontario, Canada: High Prevalence and Rapid Subtype Turnover. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indykiewicz, P.; Andrzejewska, M.; Minias, P.; Śpica, D.; Kowalski, J. Prevalence and Antibiotic Resistance of Campylobacter spp. in Urban and Rural Black-Headed Gulls Chroicocephalus ridibundus. EcoHealth 2021, 18, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchi, F.; Fabbri, M.C.; Tinacci, L.; Nuvoloni, R.; Marotta, F.; Di Marcantonio, L.; Cilia, G.; Macchioni, F.; Armani, A.; Fratini, F.; et al. Genetic resistance to Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni in wild boar (Sus scrofa L.). Rendiconti Lincei Scienze Fisiche Naturali 2022, 33, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, S.; Sato, S.; Maruyama, S.; Miyagawa, A.; Nakamura, K.; Nakamura, M.; Asakura, H.; Sugiyama, H.; Takai, S.; Maeda, K.; et al. Prevalence and whole-genome sequence analysis of Campylobacter spp. strains isolated from wild deer and boar in Japan. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 82, 101766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hald, B.; Skov, M.N.; Nielsen, E.M.; Rahbek, C.; Madsen, J.J.; Wainø, M.; Chriél, M.; Nordentoft, S.; Baggesen, D.L.; Madsen, M. Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in wild birds on Danish livestock farms. Acta Vet. Scand. 2016, 58, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramabu, S.; Boxall, N.; Madie, P.; Fenwick, S. Some potential sources for transmission of Campylobacter jejuni to broiler chickens. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 39, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ondrašovičová, S.; Pipová, M.; Dvořák, P.; Hričínová, M.; Hromada, R.; Kremeň, J. Passive and active immunity of broiler chickens against Campylobacter jejuni and ways of disease transmission. Acta Vet. Brno 2012, 81, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cawthraw, S.A.; Wassenaar, T.M.; Ayling, R.; Newell, D.G. Increased colonization potential of Campylobacter jejuni strain 81116 after passage through chickens and its implication on the rate of transmission within flocks. Epidemiol. Infect. 1996, 117, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, S.; Bakhshi, B.; Najar-Peerayeh, S. Significant contribution of the CmeABC Efflux pump in high-level resistance to ciprofloxacin and tetracycline in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli clinical isolates. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2021, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alav, I.; Kobylka, J.; Kuth, M.S.; Pos, K.M.; Picard, M.; Blair, J.M.; Bavro, V.N. Structure, assembly, and function of tripartite efflux and type 1 secretion systems in gram-negative bacteria. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 5479–5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Cagliero, C.; Guo, B.; Barton, Y.W.; Maurel, M.C.; Payot, S.; Zhang, Q. Bile salts modulate expression of the CmeABC multidrug efflux pump in Campylobacter jejuni. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 7417–7424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Wang, Y.; Shi, F.; Barton, Y.W.; Plummer, P.; Reynolds, D.L.; Nettleton, D.; Grinnage-Pulley, T.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Q. CmeR functions as a pleiotropic regulator and is required for optimal colonization of Campylobacter jejuni in vivo. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 1879–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chandrashekhar, K.; Kassem, I.I.; Rajashekara, G. Campylobacter jejuni transducer like proteins: Chemotaxis and beyond. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tram, G.; Klare, W.P.; Cain, J.A.; Mourad, B.; Cordwell, S.J.; Day, C.J.; Korolik, V. Assigning a role for chemosensory signal transduction in Campylobacter jejuni biofilms using a combined omics approach. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerry, P. Campylobacter flagella: Not just for motility. Trends Microbiol. 2007, 15, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermans, D.; Van Deun, K.; Martel, A.; Van Immerseel, F.; Messens, W.; Heyndrickx, M.; Haesebrouck, F.; Pasmans, F. Colonization factors of Campylobacter jejuni in the chicken gut. Vet. Res. 2011, 42, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.A.; Marston, K.L.; Woodall, C.A.; Maskell, D.J.; Linton, D.; Karlyshev, A.V.; Dorrell, N.; Wren, B.W.; Barrow, P.A. Adaptation of Campylobacter jejuni NCTC11168 to high-level colonization of the avian gastrointestinal tract. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 3769–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, U.; Biswas, D.; Allan, B.; Willson, P.; Potter, A.A. Influence of Campylobacter jejuni fliA, rpoN and flgK genes on colonization of the chicken gut. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 118, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, C.M.; Clyne, M.; Bourke, B. Campylobacter jejuni adhere to and invade chicken intestinal epithelial cells in vitro. Microbiology 2007, 153, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, D.A.; Williams, L.K.; Kanamarlapudi, V.; Humphrey, T.J.; Wilkinson, T.S. The bacterial species Campylobacter jejuni induce diverse innate immune responses in human and avian intestinal epithelial cells. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemka, A.; Whelan, S.; Gough, R.; Clyne, M.; Gallagher, M.E.; Carrington, S.D.; Bourke, B. Purified chicken intestinal mucin attenuates Campylobacter jejuni pathogenicity in vitro. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Deun, K.; Pasmans, F.; Ducatelle, R.; Flahou, B.; Vissenberg, K.; Martel, A.; Van den Broeck, W.; Van Immerseel, F.; Haesebrouck, F. Colonization strategy of Campylobacter jejuni results in persistent infection of the chicken gut. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 130, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.-J.; Xiao, D.; Zhao, F.; Gu, Y.-X.; Meng, F.-L.; He, L.-H.; Ma, G.-Y.; Zhang, J.-Z. Comparative proteomic analysis of Campylobacter jejuni cultured at 37 °C and 42 °C. Jpn J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 62, 356–361. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, M.G.d.; Rizzi, C.; Galli, V.; Lopes, G.V.; Haubert, L.; Dellagostin, O.A.; Silva, W.P.D. Presence of genes associated with adhesion, invasion, and toxin production in Campylobacter jejuni isolates and effect of temperature on their expression. Can. J. Microbiol. 2019, 65, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duangnumsawang, Y.; Zentek, J.; Goodarzi Boroojeni, F. Development and Functional Properties of Intestinal Mucus Layer in Poultry. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 745849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struwe, W.B.; Gough, R.; Gallagher, M.E.; Kenny, D.T.; Carrington, S.D.; Karlsson, N.G.; Rudd, P.M. Identification of O-glycan Structures from Chicken Intestinal Mucins Provides Insight into Campylobactor jejuni Pathogenicity. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2015, 14, 1464–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortada, M.; Cosby, D.E.; Akerele, G.; Ramadan, N.; Oxford, J.; Shanmugasundaram, R.; Ng, T.T.; Selvaraj, R.K. Characterizing the immune response of chickens to Campylobacter jejuni (Strain A74C). PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, M.A.; Bourassa, D.V.; Krehling, J.T.; Munoz, L.; Chasteen, K.S.; Escobar, C.; Macklin, K.S. Effects of Common Litter Management Practices on the Prevalence of Campylobacter jejuni in Broilers. Animals 2022, 12, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.; Messam, L.L.; Meade, J.; Gibbons, J.; McGill, K.; Bolton, D.; Whyte, P. The impact of biosecurity and partial depopulation on Campylobacter prevalence in Irish broiler flocks with differing levels of hygiene and economic performance. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2016, 6, 31454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, F.; Ellis-Iversen, J.; Rushton, S.; Bull, S.A.; Harris, S.A.; Bryan, S.J.; Gonzalez, A.; Humphrey, T.J. Influence of season and geography on Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli subtypes in housed broiler flocks reared in Great Britain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3741–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekdahl, K.; Normann, B.; Andersson, Y. Could flies explain the elusive epidemiology of campylobacteriosis? BMC Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, A.A.; Yalçın, S.; Latorre, J.D.; Basiouni, S.; Attia, Y.A.; Abd El-Wahab, A.; Visscher, C.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Huber, C.; Hafez, H.M. Probiotics, prebiotics, and phytogenic substances for optimizing gut health in poultry. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Cyr, M.J.; Guyard-Nicodème, M.; Messaoudi, S.; Chemaly, M.; Cappelier, J.M.; Dousset, X.; Haddad, N. Recent Advances in Screening of Anti-Campylobacter Activity in Probiotics for Use in Poultry. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortada, M.; Cosby, D.E.; Shanmugasundaram, R.; Selvaraj, R.K. In vivo and in vitro assessment of commercial probiotic and organic acid feed additives in broilers challenged with Campylobacter coli. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2020, 29, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghareeb, K.; Awad, W.A.; Mohnl, M.; Porta, R.; Biarnés, M.; Böhm, J.; Schatzmayr, G. Evaluating the efficacy of an avian-specific probiotic to reduce the colonization of Campylobacter jejuni in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 1825–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal-McKinney, J.M.; Lu, X.; Duong, T.; Larson, C.L.; Call, D.R.; Shah, D.H.; Konkel, M.E. Production of Organic Acids by Probiotic Lactobacilli Can Be Used to Reduce Pathogen Load in Poultry. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robyn, J.; Rasschaert, G.; Messens, W.; Pasmans, F.; Heyndrickx, M. Screening for lactic acid bacteria capable of inhibiting Campylobacter jejuni in in vitro simulations of the broiler chicken caecal environment. Benef. Microbes 2012, 3, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mundi, A.; Delcenserie, V.; Amiri-Jami, M.; Moorhead, S.; Griffiths, M.W. Cell-free preparations of Lactobacillus acidophilus strain La-5 and Bifidobacterium longum strain NCC2705 affect virulence gene expression in Campylobacter jejuni. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 1740–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, V. The role of probiotics in the inhibition of Campylobacter jejuni colonization and virulence attenuation. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 1503–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha-Abdelaziz, K.; Astill, J.; Kulkarni, R.R.; Read, L.R.; Najarian, A.; Farber, J.M.; Sharif, S. In vitro assessment of immunomodulatory and anti-Campylobacter activities of probiotic lactobacilli. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śmiałek, M.; Kowalczyk, J.; Koncicki, A. The Use of Probiotics in the Reduction of Campylobacter spp. Prevalence in Poultry. Animals 2021, 11, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, F.; Jin, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Screening of adhesive lactobacilli with antagonistic activity against Campylobacter jejuni. Food Control 2014, 44, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ştef, L.; Dumitrescu, G.; Simiz, E.; Cean, A.; Julean, C.; Ştef, D.; Pet, E.; Peţ, I.; Gherasim, V.; Corcionivoschi, N. The Effect of Probiotics on Broiler Growth and Intestinal Morphology when Used to Prevent Campylobacter jejuni Colonization. Sci. Pap. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 48, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Helmy, Y.A.; Kassem, I.I.; Kumar, A.; Rajashekara, G. In vitro evaluation of the impact of the probiotic E. coli Nissle 1917 on Campylobacter jejuni’s invasion and intracellular survival in human colonic cells. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyard-Nicodème, M.; Keita, A.; Quesne, S.; Amelot, M.; Poezevara, T.; Le Berre, B.; Sánchez, J.; Vesseur, P.; Martín, Á.; Medel, P.; et al. Efficacy of feed additives against Campylobacter in live broilers during the entire rearing period. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguiar, V.F.; Donoghue, A.M.; Arsi, K.; Reyes-Herrera, I.; Metcalf, J.H.; de los Santos, F.S.; Blore, P.J.; Donoghue, D.J. Targeting motility properties of bacteria in the development of probiotic cultures against Campylobacter jejuni in broiler chickens. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baffoni, L.; Gaggìa, F.; Di Gioia, D.; Santini, C.; Mogna, L.; Biavati, B. A Bifidobacterium-based synbiotic product to reduce the transmission of C. jejuni along the poultry food chain. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 157, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saint-Cyr, M.J.; Haddad, N.; Taminiau, B.; Poezevara, T.; Quesne, S.; Amelot, M.; Daube, G.; Chemaly, M.; Dousset, X.; Guyard-Nicodème, M. Use of the potential probiotic strain Lactobacillus salivarius SMXD51 to control Campylobacter jejuni in broilers. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 247, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indikova, I.; Humphrey, T.J.; Hilbert, F. Survival with a Helping Hand: Campylobacter and Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittoe, D.K.; Ricke, S.C.; Kiess, A.S. Organic Acids and Potential for Modifying the Avian Gastrointestinal Tract and Reducing Pathogens and Disease. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skånseng, B.; Kaldhusdal, M.; Moen, B.; Gjevre, A.G.; Johannessen, G.; Sekelja, M.; Trosvik, P.; Rudi, K. Prevention of intestinal Campylobacter jejuni colonization in broilers by combinations of in-feed organic acids. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Deun, K.; Haesebrouck, F.; Van Immerseel, F.; Ducatelle, R.; Pasmans, F. Short-chain fatty acids and l-lactate as feed additives to control Campylobacter jejuni infections in broilers. Avian Pathol. 2008, 37, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heres, L.; Engel, B.; Urlings, H.A.; Wagenaar, J.A.; van Knapen, F. Effect of acidified feed on susceptibility of broiler chickens to intestinal infection by Campylobacter and Salmonella. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 99, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, M.; Butcher, J.; Stintzi, A. Nutrient acquisition and metabolism by Campylobacter jejuni. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, P.; Young, P.; Holtrop, G.; Flint, H.J. Diversity of human colonic butyrate-producing bacteria revealed by analysis of the butyryl-CoA: Acetate CoA-transferase gene. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushanov, L.; Lasareishvili, B.; Janashia, I.; Zautner, A.E. Application of Campylobacter jejuni Phages: Challenges and Perspectives. Animals 2020, 10, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keen, E.C. A century of phage research: Bacteriophages and the shaping of modern biology. Bioessays 2015, 37, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernicki, A.; Nowaczek, A.; Urban-Chmiel, R. Bacteriophage therapy to combat bacterial infections in poultry. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachrach, G.; Leizerovici-Zigmond, M.; Zlotkin, A.; Naor, R.; Steinberg, D. Bacteriophage isolation from human saliva. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 36, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhya, I.; Segal, J.P.; Carding, S.R.; Hart, A.L.; Hold, G.L. The gut virome: The ‘missing link’ between gut bacteria and host immunity? Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2019, 12, 1756284819836620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Sugimura, N.; Burgermeister, E.; Ebert, M.P.; Zuo, T.; Lan, P. The gut virome: A new microbiome component in health and disease. eBioMedicine 2022, 81, 104113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannathan, B.V.; Dakoske, M.; Vijayakumar, P.P. Bacteriophage-mediated control of pre-and post-harvest produce quality and safety. LWT 2022, 169, 113912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, C.L.; Atterbury, R.J.; El-Shibiny, A.; Connerton, P.L.; Dillon, E.; Scott, A.; Connerton, I.F. Bacteriophage Therapy To Reduce Campylobacter jejuni Colonization of Broiler Chickens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 6554–6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C.M.; Gannon, B.W.; Halfhide, D.E.; Santos, S.B.; Hayes, C.M.; Roe, J.M.; Azeredo, J. The in vivo efficacy of two administration routes of a phage cocktail to reduce numbers of Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni in chickens. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.; Kittler, S.; Klein, G.; Glünder, G. Impact of a Single Phage and a Phage Cocktail Application in Broilers on Reduction of Campylobacter jejuni and Development of Resistance. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darbandi, A.; Asadi, A.; Mahdizade Ari, M.; Ohadi, E.; Talebi, M.; Halaj Zadeh, M.; Darb Emamie, A.; Ghanavati, R.; Kakanj, M. Bacteriocins: Properties and potential use as antimicrobials. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.; Li, P.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, T.; Shan, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Lü, X. Current status and potentiality of class II bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria: Structure, mode of action and applications in the food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 120, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, N.J.; Eruslanov, B.V.; Pokhilenko, V.D.; Kovalev, Y.N.; Volodina, L.L.; Perelygin, V.V.; Mitsevich, E.V.; Mitsevich, I.P.; Borzenkov, V.N.; Levchuk, V.P.; et al. Bacteriocins reduce Campylobacter jejuni colonization while bacteria producing bacteriocins are ineffective. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2008, 20, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, N.J.; Svetoch, E.A.; Eruslanov, B.V.; Perelygin, V.V.; Mitsevich, E.V.; Mitsevich, I.P.; Pokhilenko, V.D.; Levchuk, V.P.; Svetoch, O.E.; Seal, B.S. Isolation of a Lactobacillus salivarius strain and purification of its bacteriocin, which is inhibitory to Campylobacter jejuni in the chicken gastrointestinal system. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 3111–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelsson, L.; Chung, T.; Dobrogosz, W.; Lindgren, S. Production of a broad spectrum antimicrobial substance by Lactobacillus reuteri. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 1989, 2, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer, L.; Auchtung, T.A.; Hermans, K.E.; Whitehead, D.; Borhan, B.; Britton, R.A. The antimicrobial compound reuterin (3-hydroxypropionaldehyde) induces oxidative stress via interaction with thiol groups. Microbiology 2010, 156, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouts, D.E.; Mongodin, E.F.; Mandrell, R.E.; Miller, W.G.; Rasko, D.A.; Ravel, J.; Brinkac, L.M.; DeBoy, R.T.; Parker, C.T.; Daugherty, S.C. Major structural differences and novel potential virulence mechanisms from the genomes of multiple Campylobacter species. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asare, P.T.; Zurfluh, K.; Greppi, A.; Lynch, D.; Schwab, C.; Stephan, R.; Lacroix, C. Reuterin demonstrates potent antimicrobial activity against a broad panel of human and poultry meat Campylobacter spp. isolates. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo-Villanueva, K.Y.; Akerele, G.O.; Al Hakeem, W.G.; Renu, S.; Shanmugasundaram, R.; Selvaraj, R.K. A Novel Approach against Salmonella: A Review of Polymeric Nanoparticle Vaccines for Broilers and Layers. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, M.; Tominaga, A.; Ueda, M.; Ohshima, R.; Kobayashi, M.; Tsukada, M.; Yokoyama, E.; Takehara, K.; Deguchi, K.; Honda, T.; et al. Irrelevance between the induction of anti-Campylobacter humoral response by a bacterin and the lack of protection against homologous challenge in Japanese Jidori chickens. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2012, 74, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, B.E.; Rollins, D.M.; Mallinson, E.T.; Carr, L.; Joseph, S.W. Campylobacter jejuni in broiler chickens: Colonization and humoral immunity following oral vaccination and experimental infection. Vaccine 1997, 15, 1922–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, B.; Saisom, T.; Sasipreeyajan, J.; Luangtongkum, T. Live-Attenuated Oral Vaccines to Reduce Campylobacter Colonization in Poultry. Vaccines 2022, 10, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, T.; Pina-Mimbela, R.; Kumar, A.; Binjawadagi, B.; Liu, Z.; Renukaradhya, G.J.; Rajashekara, G. Evaluation of nanoparticle-encapsulated outer membrane proteins for the control of Campylobacter jejuni colonization in chickens. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 2201–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha-Abdelaziz, K.; Hodgins, D.C.; Alkie, T.N.; Quinteiro-Filho, W.; Yitbarek, A.; Astill, J.; Sharif, S. Oral administration of PLGA-encapsulated CpG ODN and Campylobacter jejuni lysate reduces cecal colonization by Campylobacter jejuni in chickens. Vaccine 2018, 36, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulthurst, S. The Type VI secretion system: A versatile bacterial weapon. Microbiology 2019, 165, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, Y.-W.; Lai, E.-M. Type VI secretion effectors: Methodologies and biology. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Nisaa, K.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Mallick, A.I. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of mucosal delivery of recombinant hcp of Campylobacter jejuni Type VI secretion system (T6SS) in chickens. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 111, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziprin, R.L.; Young, C.R.; Stanker, L.H.; Hume, M.E.; Konkel, M.E. The absence of cecal colonization of chicks by a mutant of Campylobacter jejuni not expressing bacterial fibronectin-binding protein. Avian Dis. 1999, 43, 586–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyszyńska, A.; Raczko, A.; Lis, M.; Jagusztyn-Krynicka, E.K. Oral immunization of chickens with avirulent Salmonella vaccine strain carrying C. jejuni 72Dz/92 cjaA gene elicits specific humoral immune response associated with protection against challenge with wild-type Campylobacter. Vaccine 2004, 22, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beery, J.; Hugdahl, M.; Doyle, M. Colonization of gastrointestinal tracts of chicks by Campylobacter jejuni. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1988, 54, 2365–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, P. LuxS and quorum-sensing in Campylobacter. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engebrecht, J.; Silverman, M. Identification of genes and gene products necessary for bacterial bioluminescence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 4154–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassler, B.L. How bacteria talk to each other: Regulation of gene expression by quorum sensing. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 1999, 2, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvers, K.T.; Park, S.F. Quorum sensing in Campylobacter jejuni: Detection of a luxS encoded signalling molecule. Microbiology 2002, 148, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñones, B.; Miller, W.G.; Bates, A.H.; Mandrell, R.E. Autoinducer-2 Production in Campylobacter jejuni Contributes to Chicken Colonization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, P.; Sahin, O.; Burrough, E.; Sippy, R.; Mou, K.; Rabenold, J.; Yaeger, M.; Zhang, Q. Critical Role of LuxS in the Virulence of Campylobacter jejuni in a Guinea Pig Model of Abortion. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligowska, M.; Cohn, M.T.; Stabler, R.A.; Wren, B.W.; Brøndsted, L. Effect of chicken meat environment on gene expression of Campylobacter jejuni and its relevance to survival in food. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 145 (Suppl. 1), S111–S115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shagieva, E.; Teren, M.; Michova, H.; Strakova, N.; Karpiskova, R.; Demnerova, K. Adhesion, Biofilm Formation, and luxS Sequencing of Campylobacter jejuni Isolated From Water in the Czech Republic. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 596613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimunović, K.; Sahin, O.; Kovač, J.; Shen, Z.; Klančnik, A.; Zhang, Q.; Smole Možina, S. (-)-α-Pinene reduces quorum sensing and Campylobacter jejuni colonization in broiler chickens. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, S.; Heredia, N.; Arechiga-Carvajal, E.; García, S. Citrus Extracts as Inhibitors of Quorum Sensing, Biofilm Formation and Motility of Campylobacter jejuni. Food Biotechnol. 2014, 28, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimunović, K.; Ramić, D.; Xu, C.; Smole Možina, S. Modulation of Campylobacter jejuni Motility, Adhesion to Polystyrene Surfaces, and Invasion of INT407 Cells by Quorum-Sensing Inhibition. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Hakeem, W.G.; Fathima, S.; Shanmugasundaram, R.; Selvaraj, R.K. Campylobacter jejuni in Poultry: Pathogenesis and Control Strategies. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2134. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10112134
Al Hakeem WG, Fathima S, Shanmugasundaram R, Selvaraj RK. Campylobacter jejuni in Poultry: Pathogenesis and Control Strategies. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(11):2134. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10112134
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Hakeem, Walid Ghazi, Shahna Fathima, Revathi Shanmugasundaram, and Ramesh K. Selvaraj. 2022. "Campylobacter jejuni in Poultry: Pathogenesis and Control Strategies" Microorganisms 10, no. 11: 2134. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10112134
APA StyleAl Hakeem, W. G., Fathima, S., Shanmugasundaram, R., & Selvaraj, R. K. (2022). Campylobacter jejuni in Poultry: Pathogenesis and Control Strategies. Microorganisms, 10(11), 2134. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10112134






