Effect of Environmental Heterogeneity and Trophic Status in Sampling Strategy on Estimation of Small-Scale Regional Biodiversity of Microorganisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
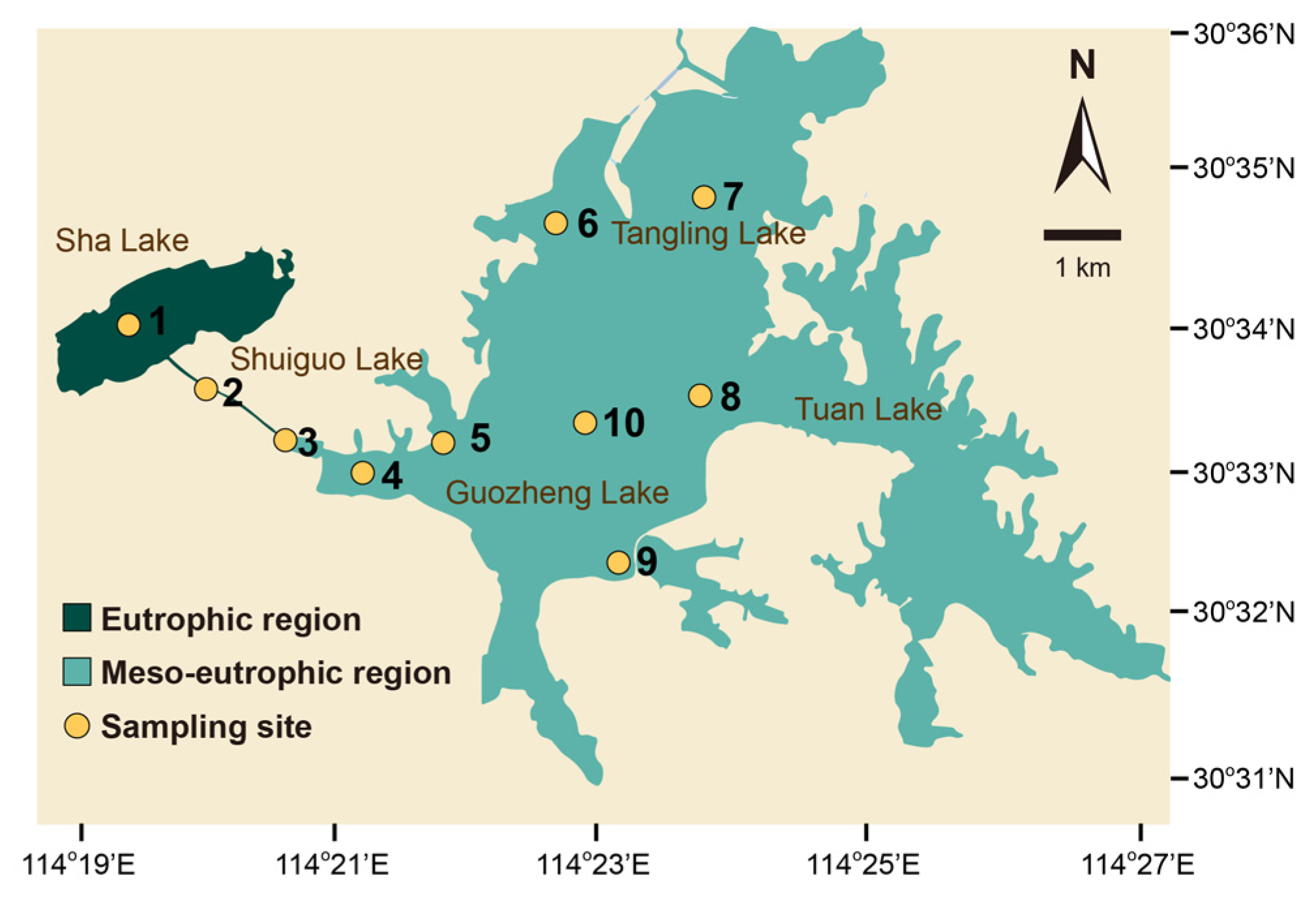
2.1. Sampling and Environmental Information
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR, and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.3. Sequence Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Microbial Diversities in Eutrophic and Meso-Eutrophic Regions
3.2. Rarefaction Curves and Relative Abundance of Taxonomic Groups in Samples
3.3. The Differences of Species Richness Overlap and Factors Related with Species Richness Overlap
3.4. The Relationship between Microbial Community and Environmental Factors
3.5. Spearman’s Rank Correlation and Threshold Indicator Taxa with Changing of Environmental Factors
3.6. The NCM Explains Different Community Variation between Samples from Regions with Different Trophic Status
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moss, B. Biodiversity in fresh waters-an issue of species preservation or system functioning? Environ. Conserv. 2000, 27, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.E. A trophic state index for lakes1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trolle, D.; Hamilton, D.P.; Pilditch, C.A.; Duggan, I.C.; Jeppesen, E. Predicting the effects of climate change on trophic status of three morphologically varying lakes: Implications for lake restoration and management. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2011, 26, 354–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefranc, M.; Thenot, A.; Lepere, C.; Debroas, D. Genetic diversity of small eukaryotes in lakes differing by their trophic status. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5935–5942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, H.; Hou, J.; Cao, X.; Song, C.; Zhou, Y. Sediment-water interaction in phosphorus cycling as affected by trophic states in a Chinese shallow lake (Lake Donghu). Hydrobiologia 2016, 776, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.; Whitfield, M.; Biggs, J.; Bray, S.; Fox, G.; Nicolet, P.; Sear, D. Comparative biodiversity of rivers, streams, ditches and ponds in an agricultural landscape in Southern England. Biol. Conserv. 2004, 115, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Hu, X.; Warren, A. Free-Living Ciliates in the Bohai and Yellow Seas, China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Lin, X.; Song, W. Ciliate Atlas: Species Found in the South China Sea; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rathour, R.; Gupta, J.; Mishra, A.; Rajeev, A.C.; Dupont, C.L.; Thakur, I.S. A comparative metagenomic study reveals microbial diversity and their role in the biogeochemical cycling of Pangong lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiersztyn, B.; Chróst, R.; Kaliński, T.; Siuda, W.; Bukowska, A.; Kowalczyk, G.; Grabowska, K. Structural and functional microbial diversity along a eutrophication gradient of interconnected lakes undergoing anthropopressure. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, W.; Huang, L. Microbial diversity in extreme environments. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Bass, D.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Song, W.; Yi, Z. Environmental parameters and substrate type drive microeukaryotic community structure during short-term experimental colonization in subtropical eutrophic freshwaters. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhao, Q.; McMinn, A.; Yang, E.J.; Jiang, Y. Planktonic microbial eukaryotes in polar surface waters: Recent advances in high-throughput sequencing. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2021, 3, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, C.; Rodríguez-Gallego, L.; Meerhoff, M.; Quintans, F.; Lacerot, G.; Mazzeo, N.; Scasso, F.; Paggi, J.C.; Peeters, E.T.; Marten, S. Determinants of biodiversity in subtropical shallow lakes (Atlantic coast, Uruguay). Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 2628–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, J.; Tonkin, J.D.; Shen, J.; Xiao, N.; Wang, J. The effects of abiotic and biotic factors on taxonomic and phylogenetic diversity of stream epilithic bacteria around Qiandao Lake. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 82, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, L.P.; Braghin, L.D.S.M.; Pinheiro, T.S.A.; Melo, P.A.M.D.C.; Bonecker, C.C.; Melo Júnior, M.D. Environmental filter drives the taxonomic and functional β-diversity of zooplankton in tropical shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 2021, 848, 1881–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda-Mendoza, R.M.; Briones-Roblero, C.I.; Gonzalez-Escobedo, R.; Rivera-Orduña, F.N.; Martínez-Jerónimo, F.; Zúñiga, G. Seasonal changes in the bacterial community structure of three eutrophicated urban lakes in Mexico city, with emphasis on Microcystis spp. Toxicon 2020, 179, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, B.O.; Hamer, M.P.; Collier, K.J.; Lake, M.D.; Surrey, G.M.; McArthur, K.; Nicholson, C.; Perrie, A.; Dale, M. A standardised sampling protocol for robust assessment of reach-scale fish community diversity in wadeable New Zealand streams. N. Z J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2010, 44, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Feng, W.; Shen, Y. Growth and production of free-living heterotrophic nanoflagellates in a eutrophic lake-Lake Donghu, Wuhan, China. Hydrobiologia 2003, 498, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, A.; Hu, Z.; Wang, J.; Shi, Z.; Tam, F. Structure of the phytoplankton community and its relationship to water quality in Donghu Lake, Wuhan, China. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2005, 47, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomisto, H.; Ruokolainen, K.; Yli-Halla, M. Dispersal, environment, and floristic variation of western Amazonian forests. Science 2003, 299, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, B.; Lechowicz, M.J. Neutrality, niches, and dispersal in a temperate forest understory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 7651–7656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; El-Serehy, H.A.; Al-Farraj, S.A.; Ma, H.; Thorsten, S.; Yi, Z. High salinity gradients and intermediate spatial scales shaped similar biogeographical and co-occurrence patterns of microeukaryotes in a tropical freshwater-saltwater ecosystem. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 4778–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, R.; Li, Z.; Wu, J.; Wei, X.; Wei, W.; Fang, J.; Cao, J.; Wei, Y.; et al. Community structure and activity potentials of archaeal communities in hadal sediments of the Mariana and Mussau trenches. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2022, 4, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Alain, K.; Shao, Z. Microorganisms from deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2021, 3, 204–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Shin, M.K.; Yi, Z.; Tan, Y. Progress in studies on the diversity and distribution of planktonic ciliates (Protista, Ciliophora) in the South China Sea. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2021, 3, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, D.J. Energy and large-scale patterns of animal- and plant-species richness. Am. Nat. 1991, 137, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svenning, J.C. On the role of microenvironmental heterogeneity in the ecology and diversification of neotropical Rain-Forest Palms (Arecaceae). Bot. Rev. 2001, 67, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tews, J.; Brose, U.; Grimm, V.; Tielbörger, K.; Jeltsch, F. Animal species diversity driven by habitat heterogeneity/diversity: The importance of keystone structures. J. Biogeogr. 2010, 31, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotaling, S.; Foley, M.E.; Zeglin, L.H.; Finn, D.S.; Tronstad, L.M.; Giersch, J.J.; Muhlfeld, C.C.; Weisrock, D.W. Microbial assemblages reflect environmental heterogeneity in alpine streams. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 2576–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, M.D. Periphytic community response to chronic nutrient enrichment by a reservoir discharge. Ecology 1980, 61, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, C.M. Nutrient spatial heterogeneity: Effects on community structure, physiognomy, and diversity of stream algae. Ecology 1990, 71, 905–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.C.; De Oliveira, P.; Gibeau, G. Epilithic diatom community response to years of PO4 fertilization: Kuparuk River, Alaska (68 oN Lat.). Hydrobiologia 1992, 240, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, Q. Spatial distribution and morphologic diversity of virioplankton in Lake Donghu, China. Acta Oecol. 2006, 29, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cheng, Z.; Li, J.; Miao, L. Community composition of NirS-type denitrifier in a shallow eutrophic lake. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 66, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Huang, J.; Filker, S.; Stoeck, T.; Bi, Y.; Yu, Y.; Song, W. Spatio-temporal patterns of zooplankton in a main-stem dam affected tributary: A case study in the Xiangxi River of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci. China Life Sci. 2019, 62, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.; Jardillier, L.; Deschamps, P.; Moreira, D.; Restoux, G.; Bertolino, P.; Lopezgarcia, P. Complex communities of small protists and unexpected occurrence of typical marine lineages in shallow freshwater systems. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 3610–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yu, Y.; Li, C.; Yan, Q. Comparative study on the gut microbiotas of four economically important Asian carp species. Sci. China Life Sci. 2018, 61, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanja, M.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 22 August 2022).
- Vegan: Community Ecology Package Version 2.0-10. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 22 August 2022).
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L.F. Numerical Ecology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Manly, B.F. Randomization, Bootstrap and Monte Carlo Methods in Biology; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kent, M. Vegetation Description and Data Analysis: A Practical Approach; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. UniFrac: A new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral. Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Somerfield, P.J.; Gorley, R.N. Testing of null hypotheses in exploratory community analyses: Similarity profiles and biota-environment linkage. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 366, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, P.M. Misidentification of the Bray-Curtis similarity index. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 368, 309–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehan, E.A. A generalized Wilcoxon Test for comparing arbitrarily singly-censored samples. Biometrika 1965, 52, 203–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spearman, C. The proof and measurement of association between two things. Am. J. Psychol. 1987, 100, 441–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.E.; King, R.S. A new method for detecting and interpreting biodiversity and ecological community thresholds. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2010, 1, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, W.T.; Lunn, M.; Woodcock, S.; Head, I.M.; Nee, S.; Curtis, T.P. Quantifying the roles of immigration and chance in shaping prokaryote community structure. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Chen, X.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, B. Characterization of sediment bacterial communities in plain lakes with different trophic statuses. Open Microbiol. 2017, 6, e00503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaver, J.R.; Crisman, T.L. The trophic response of ciliated protozoans in freshwater lakes1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1982, 27, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norian, A.; Amini, F.; Sakhaei, N.; Archangi, B.; Mokhtarpour, A. Evaluation of biodiversity of phytoplankton and determination of biological health quality of Arvand River (south west of Iran) using Trophic Diatom Index (TDI). Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2022, 21, 1047–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallimanis, A.S.; Bergmeier, E.; Panitsa, M.; Georghiou, K.; De Lipetrou, P.; Dimopoulos, P. Biogeographical determinants for total and endemic species richness in a continental archipelago. Biodivers. Conserv. 2010, 19, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjeldså, J.; Bowie, R.C.; Rahbek, C. The role of mountain ranges in the diversification of birds. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 43, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Meng, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X. Microbial assembly, interaction, functioning, activity and diversification: A review derived from community compositional data. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2019, 1, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloufi, S.; Catherine, A.; Mouillot, D.; Louvard, C.; Couté, A.; Bernard, C.; Troussellier, M. Environmental heterogeneity among lakes promotes hyper β-diversity across phytoplankton communities. Freshw. Biol. 2016, 61, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M. Ecology of Shallow Lakes; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Declerck, S.; Vandekerkhove, J.; Johansson, L.; Muylaert, K.; Conde-Porcuna, J.; Van Der Gucht, K.; Perez-Martinez, C.; Lauridsen, T.; Schwenk, K.; Zwart, G. Multi-group biodiversity in shallow lakes along gradients of phosphorus and water plant cover. Ecology 2005, 86, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declerck, S.; Vanderstukken, M.; Pals, A.; Muylaert, K.; Meester, L.D. Plankton biodiversity along a gradient of productivity and its mediation by macrophytes. Ecology 2007, 88, 2199–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianuca, A.T.; Declerck, S.; Lemmens, P.; Meester, L.D. Effects of dispersal and environmental heterogeneity on the replacement and nestedness components of β-diversity. Ecology 2017, 98, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, Q.; Yu, Y.; Dai, L. Spatiotemporal pattern of bacterioplankton in Donghu Lake. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2014, 32, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Bi, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, J.; Yu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Fang, T.; Cao, X.; He, Z.; Philippe, J.; et al. The impact of anthropogenic disturbance on bacterioplankton communities during the construction of Donghu Tunnel (Wuhan, China). Microb. Ecol. 2018, 77, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Dai, S. Effects of nitrite and toxic Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806 on the growth of freshwater rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 86, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.L.; Westerhoff, P.; Baker, L.; Hu, Q.; Esparza-Soto, M.; Sommerfeld, M. Characteristics and reactivity of algae-produced dissolved organic carbon. J. Environ. Eng. 2005, 131, 1574–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample | Richness | Shannon-Wiener Index | Chao 1 | Pielou’s Evenness | Sample | Richness | Shannon-Wiener Index | Chao 1 | Pielou’s Evenness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 480 | 3.224 | 795.431 | 0.522 | E1 | 81 | 2.289 | 102 | 0.521 |
| P2 | 492 | 3.464 | 822.694 | 0.559 | E2 | 95 | 2.380 | 127.5 | 0.523 |
| P3 | 522 | 3.694 | 781.110 | 0.590 | E3 | 137 | 2.539 | 159.8 | 0.516 |
| P4 | 537 | 3.638 | 931.631 | 0.579 | E4 | 139 | 2.737 | 168.063 | 0.555 |
| P5 | 994 | 4.251 | 1702.298 | 0.616 | E5 | 151 | 2.606 | 176.143 | 0.519 |
| P6 | 771 | 4.346 | 1296.606 | 0.654 | E6 | 137 | 2.599 | 178.938 | 0.528 |
| P7 | 1130 | 4.358 | 1814.052 | 0.620 | E7 | 161 | 2.770 | 198.143 | 0.545 |
| P8 | 896 | 4.374 | 1488.617 | 0.643 | E8 | 178 | 3.007 | 209.059 | 0.580 |
| P9 | 1227 | 4.502 | 1830.124 | 0.633 | E9 | 161 | 2.849 | 185 | 0.561 |
| P10 | 554 | 3.874 | 965.680 | 0.555 | E10 | 146 | 2.804 | 186.4 | 0.563 |
| Category | ID | Phylum | Genus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prokaryote | OTU1886 | Actinobacteria | Unclassified Microbacteriaceae |
| OTU456 | Actinobacteria | Unclassified Sporichthyaceae | |
| OTU484 | Actinobacteria | Alpinimonas | |
| OTU63 | Actinobacteria | Rhodoluna | |
| OTU1826 | Bacteroidetes | Sediminibacterium | |
| OTU2226 | Bacteroidetes | Flavobacterium | |
| OTU2898 | Bacteroidetes | Flavobacterium | |
| OTU1872 | Parcubacteria | Unclassified Azambacteria | |
| OTU1641 | Proteobacteria | Unclassified Rickettsiales | |
| OTU216 | Proteobacteria | Methylotenera | |
| OTU25 | Proteobacteria | Unclassified Comamonadaceae | |
| OTU2896 | Proteobacteria | Dechloromonas | |
| OTU580 | Proteobacteria | Unclassified Methylophilaceae | |
| Eukaryote | OTU163 | Cercozoa | Protaspa |
| OTU125 | Chlorophyta | Spermatozopsis | |
| OTU198 | Ciliophora | Tintinnidium | |
| OTU232 | Ciliophora | Tintinnidium | |
| OTU234 | Ciliophora | Unclassified Strobilidiidae | |
| OTU43 | Ciliophora | Unclassified Vorticellidae | |
| OTU71 | Ciliophora | Tintinnopsis | |
| OTU119 | Cryptophyta | Teleaulax | |
| OTU3 | Cryptophyta | Cryptomonas | |
| OTU73 | Cryptophyta | Plagioselmis | |
| OTU153 | Dinophyta | Unclassified Suessiales | |
| OTU151 | Fungi | Unclassfied Chytridiomycetes | |
| OTU166 | Metazoa | Parapharyngiella | |
| OTU41 | Metazoa | Parapharyngiella | |
| OTU17 | Ochrophyta | Unclassified Chrysophyceae | |
| OTU246 | Ochrophyta | Mallomonas | |
| OTU254 | Ochrophyta | Unclassfied Pedinellales | |
| OTU34 | Ochrophyta | Unclassified Mediophyceae | |
| OTU47 | Ochrophyta | Chrysosaccus | |
| OTU262 | Unclassified Eukaryota |
| Factor | Prokaryote | Eukaryote | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r2 | P | r2 | P | |
| DO | 0.850 * | 0.011 | 0.906 ** | 0.008 |
| NO3-N | 0.380 | 0.175 | 0.408 | 0.142 |
| NO2-N | 0.675 * | 0.018 | 0.773 * | 0.013 |
| AN | 0.335 | 0.218 | 0.449 | 0.117 |
| PO4 | 0.256 | 0.438 | 0.775 | 0.069 |
| Category | Factor | ID | Phylum | Genus | Env.cp | Purity | Reliability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | DO | OTU1900 | Actinobacteria | Gordonia | 9.660 | 0.998 | 0.972 |
| OTU1864 | Cyanobacteria | Cyanobacteria Subsection III | 10.5550 | 0.996 | 0.956 | ||
| OTU604 | Proteobacteria | Unclassified Proteobacteria | 10.5550 | 1 | 0.992 | ||
| OTU725 | Proteobacteria | Unclassified Proteobacteria | 9.660 | 1 | 0.968 | ||
| OTU2025 | Unclassified Bacteria | 9.660 | 0.998 | 0.956 | |||
| NO2-N | OTU1749 | Actinobacteria | Aeromicrobium | 0.0120 | 1 | 0.960 | |
| OTU1115 | Cyanobacteria | Unclassified Cyanobacteria | 0.0110 | 1 | 0.956 | ||
| OTU1127 | Cyanobacteria | Unclassified Cyanobacteria | 0.0120 | 1 | 0.964 | ||
| OTU114 | Cyanobacteria | Unclassified Cyanobacteria | 0.0120 | 0.998 | 0.984 | ||
| OTU1864 | Cyanobacteria | Cyanobacteria Subsection III | 0.0110 | 1 | 0.988 | ||
| OTU2287 | Cyanobacteria | Cyanobacteria Subsection IV | 0.0120 | 1 | 0.976 | ||
| OTU2328 | Cyanobacteria | Baikalospongia | 0.0120 | 0.996 | 0.972 | ||
| OTU409 | Cyanobacteria | Unclassified Cyanobacteria | 0.0120 | 0.998 | 0.966 | ||
| OTU2169 | Firmicutes | Romboutsia | 0.0120 | 1 | 0.972 | ||
| OTU1270 | Planctomycetes | Unclassified Planctomycetaceae | 0.0120 | 0.996 | 0.956 | ||
| OTU2570 | Planctomycetes | Unclassified Planctomycetaceae | 0.0120 | 0.998 | 0.950 | ||
| OTU1105 | Proteobacteria | Unclassified Proteobacteria | 0.0120 | 1 | 0.958 | ||
| OTU2066 | Proteobacteria | Unclassified Alphaproteobacteria | 0.0135 | 1 | 0.956 | ||
| OTU2197 | Proteobacteria | Unclassified Proteobacteria | 0.0120 | 1 | 0.966 | ||
| OTU753 | Proteobacteria | Unclassified Comamonadaceae | 0.0110 | 0.996 | 0.952 | ||
| OTU1346 | Thaumarchaeota | Nitrosoarchaeum | 0.0120 | 0.994 | 0.952 | ||
| OTU2025 | Unclassified Bacteria | 0.0135 | 0.998 | 0.954 | |||
| OTU2272 | Unclassified Bacteria | 0.0120 | 1 | 0.978 | |||
| E | DO | OTU139 | Ciliophora | Unclassified Prostomatea | 9.660 | 0.994 | 0.952 |
| OTU7 | Ciliophora | Unclassified Prostomatea | 10.5550 | 1 | 0.982 | ||
| OTU134 | Katablepharidophyta | Unclassified Katablepharidales | 9.660 | 0.998 | 0.970 | ||
| OTU231 | Ochrophyta | Unclassified Chrysophyceae | 9.660 | 0.990 | 0.950 | ||
| OTU273 | Ochrophyta | Mallomonas | 10.5550 | 0.996 | 0.990 | ||
| OTU137 | Perkinsea | Unclassified Perkinsida | 9.660 | 0.996 | 0.986 | ||
| NO2-N | OTU1 | Cercozoa | Cercozoa Novel clade 2 | 0.0135 | 0.998 | 0.950 | |
| OTU219 | Cercozoa | Peregrinia | 0.0135 | 0.996 | 0.954 | ||
| OTU131 | Ciliophora | Unclassified Mesodiniidae | 0.0135 | 0.996 | 0.958 | ||
| OTU217 | Ciliophora | Tintinnidium | 0.0135 | 1 | 0.986 | ||
| OTU274 | Ciliophora | Unclassified Prostomatea | 0.0135 | 1 | 0.962 | ||
| OTU177 | Cryptophyta | Cryptomonas | 0.0110 | 1 | 0.986 | ||
| OTU180 | Cryptophyta | Cryptomonas | 0.0110 | 0.994 | 0.956 | ||
| OTU3 | Cryptophyta | Cryptomonas | 0.0135 | 0.998 | 0.980 | ||
| OTU235 | Dinophyta | Prorocentrum | 0.0135 | 1 | 0.974 | ||
| OTU37 | Dinophyta | Prorocentrum | 0.0135 | 0.998 | 0.980 | ||
| OTU134 | Katablepharidophyta | Unclassified Katablepharidales | 0.0120 | 1 | 0.982 | ||
| OTU231 | Ochrophyta | Unclassified Chrysophyceae | 0.0135 | 1 | 0.978 | ||
| OTU238 | Ochrophyta | Pseudopedinella | 0.0135 | 1 | 0.960 | ||
| OTU137 | Perkinsea | Unclassified Perkinsida | 0.0135 | 0.998 | 0.974 | ||
| OTU285 | Stramenopiles_X | Unclassified Pseudodendromonadales | 0.0135 | 0.992 | 0.956 | ||
| OTU262 | Unclassified Eukaryota | 0.0135 | 1 | 0.960 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, C.; Langlois, G.A.; Zhao, Y. Effect of Environmental Heterogeneity and Trophic Status in Sampling Strategy on Estimation of Small-Scale Regional Biodiversity of Microorganisms. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10112119
Zhu C, Langlois GA, Zhao Y. Effect of Environmental Heterogeneity and Trophic Status in Sampling Strategy on Estimation of Small-Scale Regional Biodiversity of Microorganisms. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(11):2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10112119
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Changyu, Gaytha A. Langlois, and Yan Zhao. 2022. "Effect of Environmental Heterogeneity and Trophic Status in Sampling Strategy on Estimation of Small-Scale Regional Biodiversity of Microorganisms" Microorganisms 10, no. 11: 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10112119
APA StyleZhu, C., Langlois, G. A., & Zhao, Y. (2022). Effect of Environmental Heterogeneity and Trophic Status in Sampling Strategy on Estimation of Small-Scale Regional Biodiversity of Microorganisms. Microorganisms, 10(11), 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10112119





