Dietary Beta-Hydroxy-Beta-Methyl Butyrate Supplementation Inhibits Hepatic Fat Deposition via Regulating Gut Microbiota in Broiler Chickens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Protocol
2.2. Determination of Serum and Hepatic Lipid Profile as Well as Serum Metabolic Hormones
2.3. Measurements of Liver Fatty Acid Composition
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.5. Cecal Microbiome Analysis by 16S rRNA Sequencing
2.6. Cecal SCFAs Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
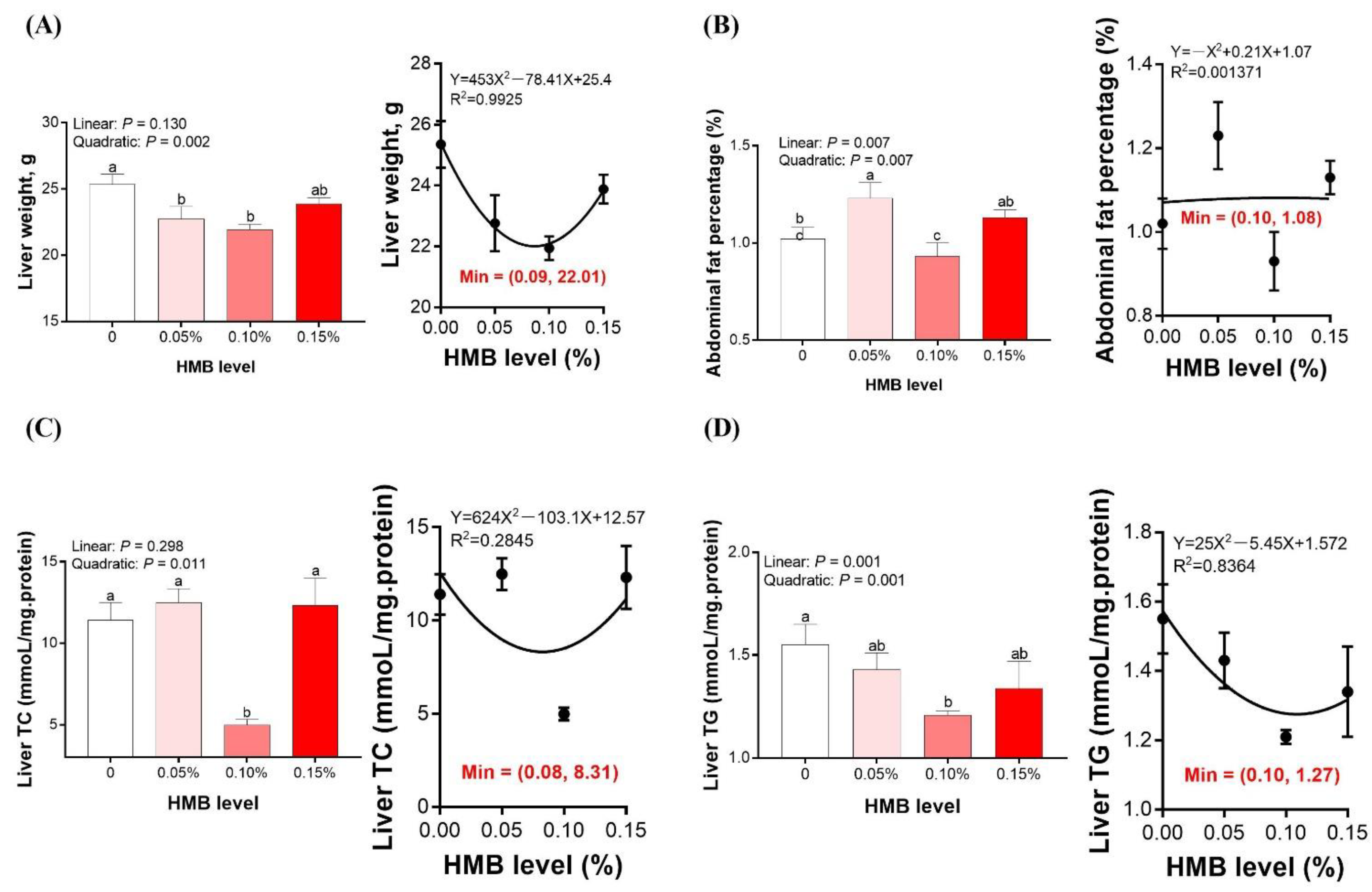
3.1. Liver Weight and Abdominal Fat Percentage
3.2. Serum Lipid Profile
3.3. Fatty Acid Composition in the Liver Tissue
3.4. Lipid Metabolism-Related Genes Expression in the Liver
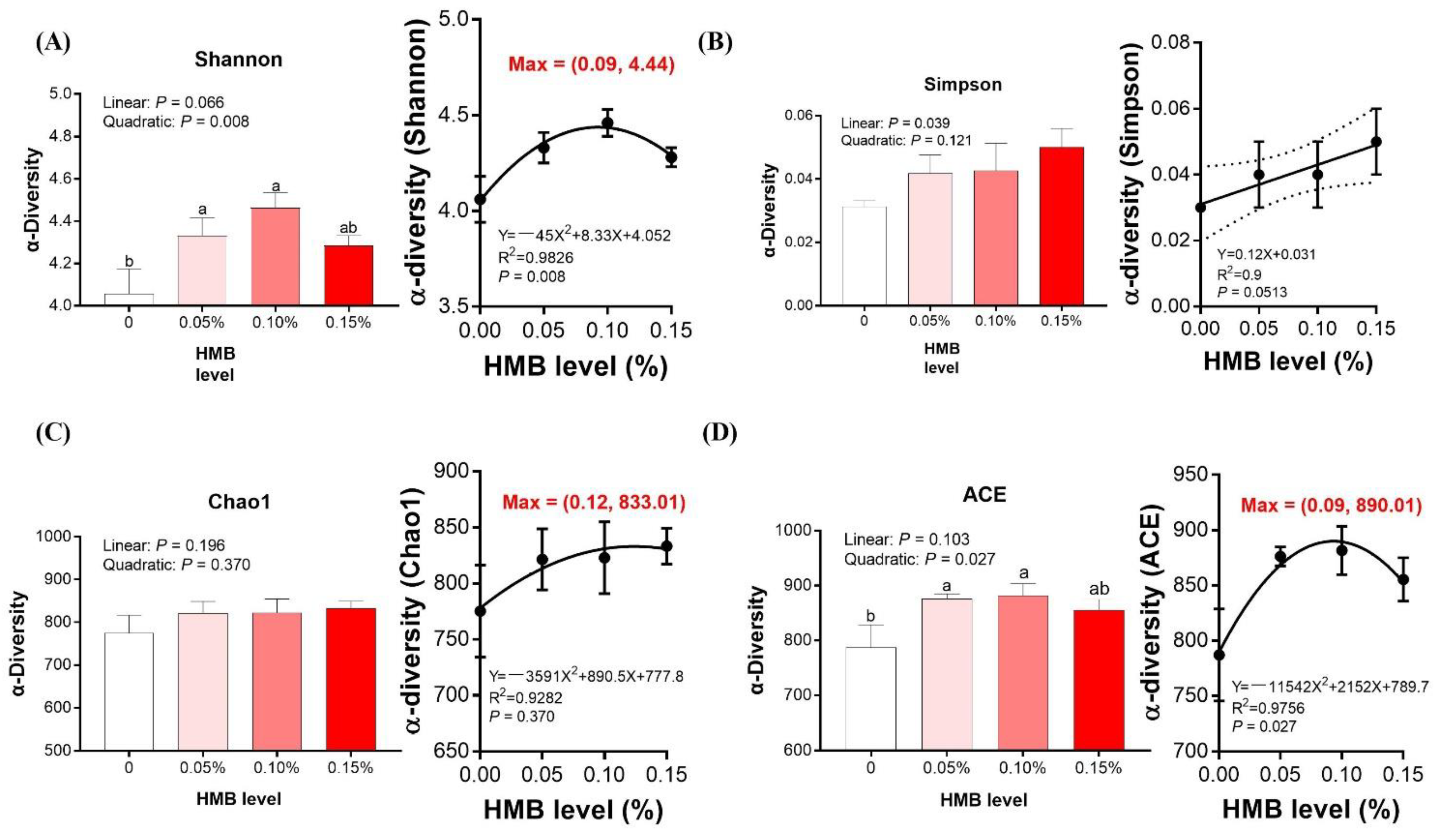
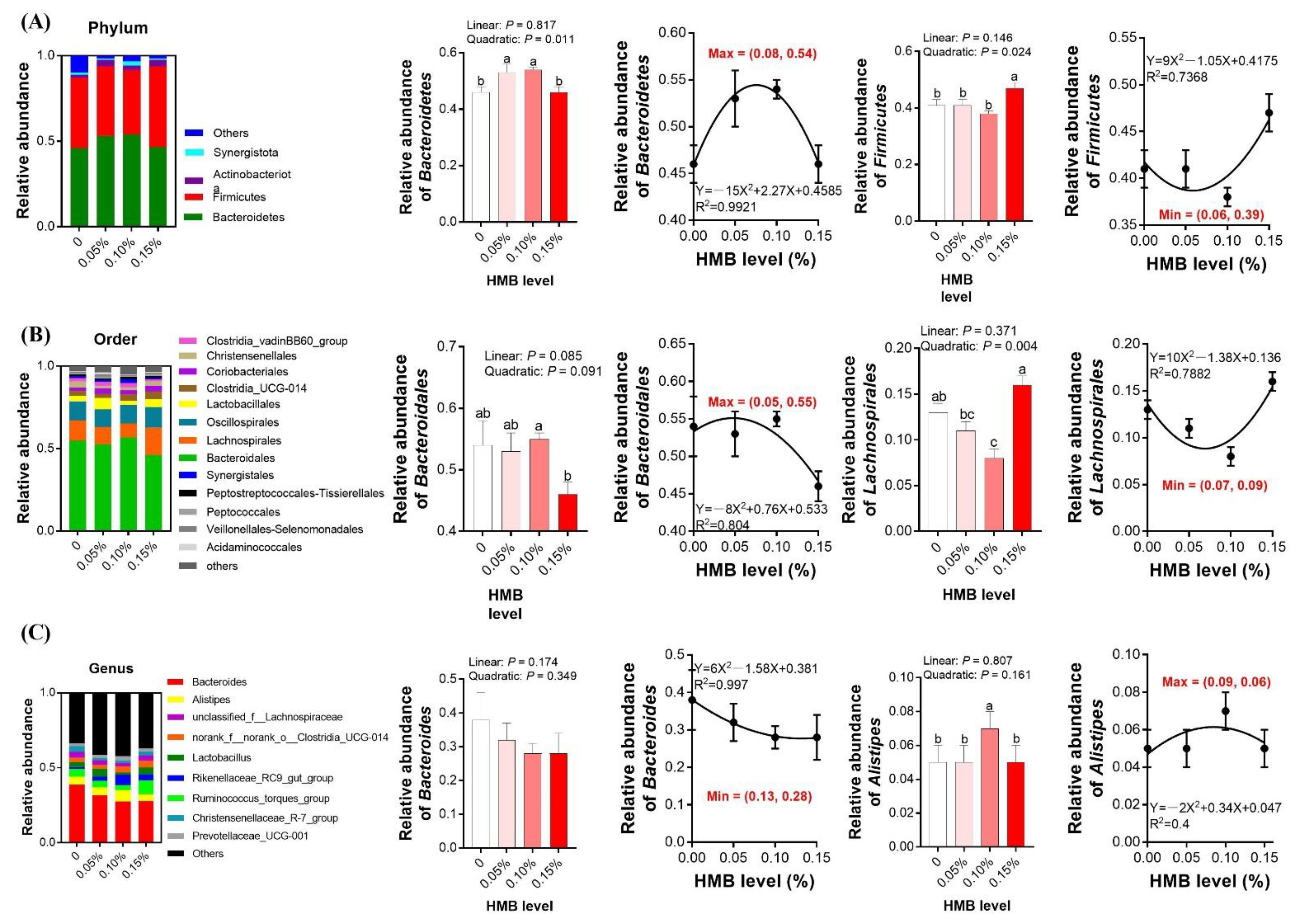
3.5. Cecal Microbiota
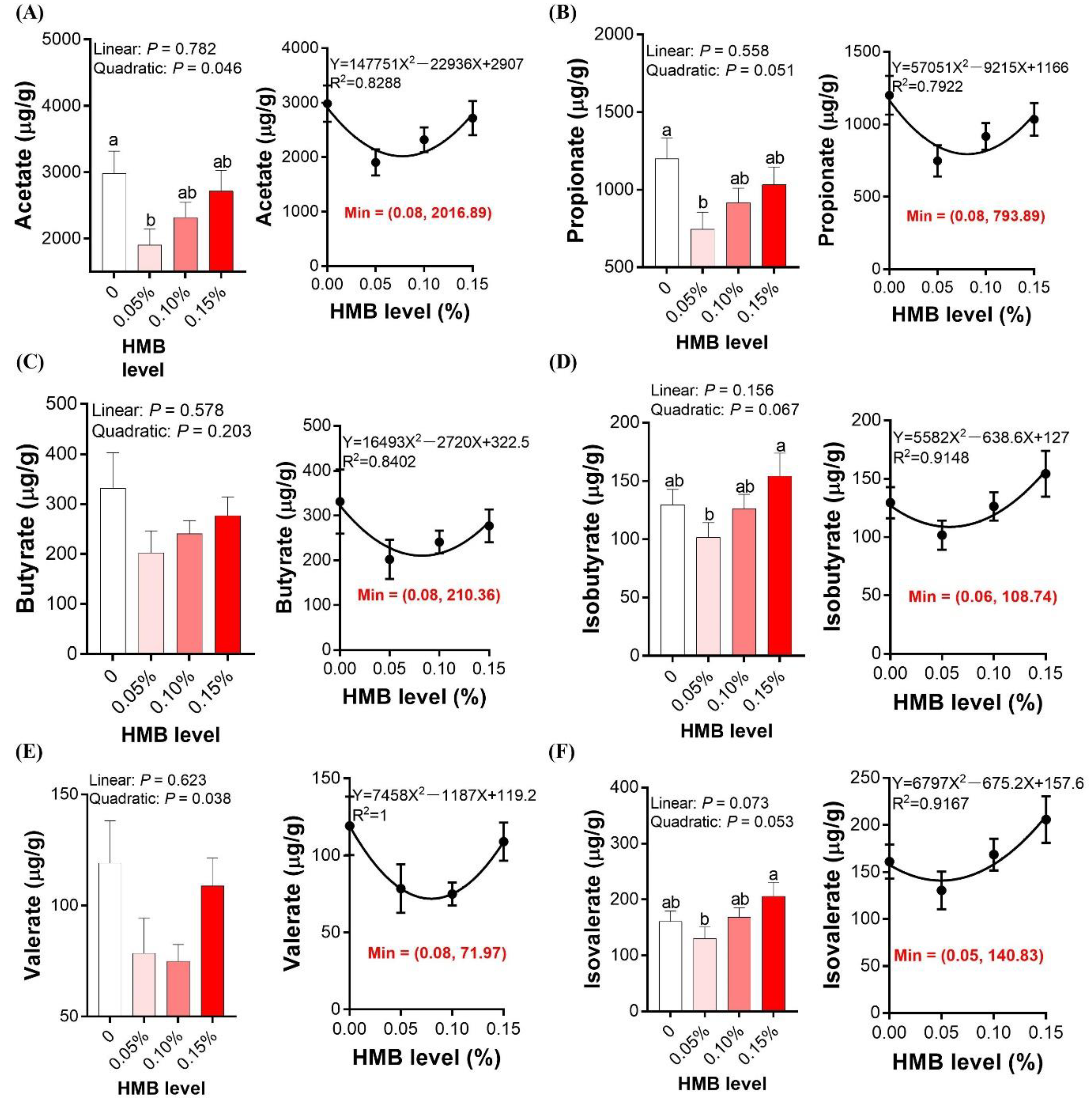
3.6. Cecal SCFAs Concentrations
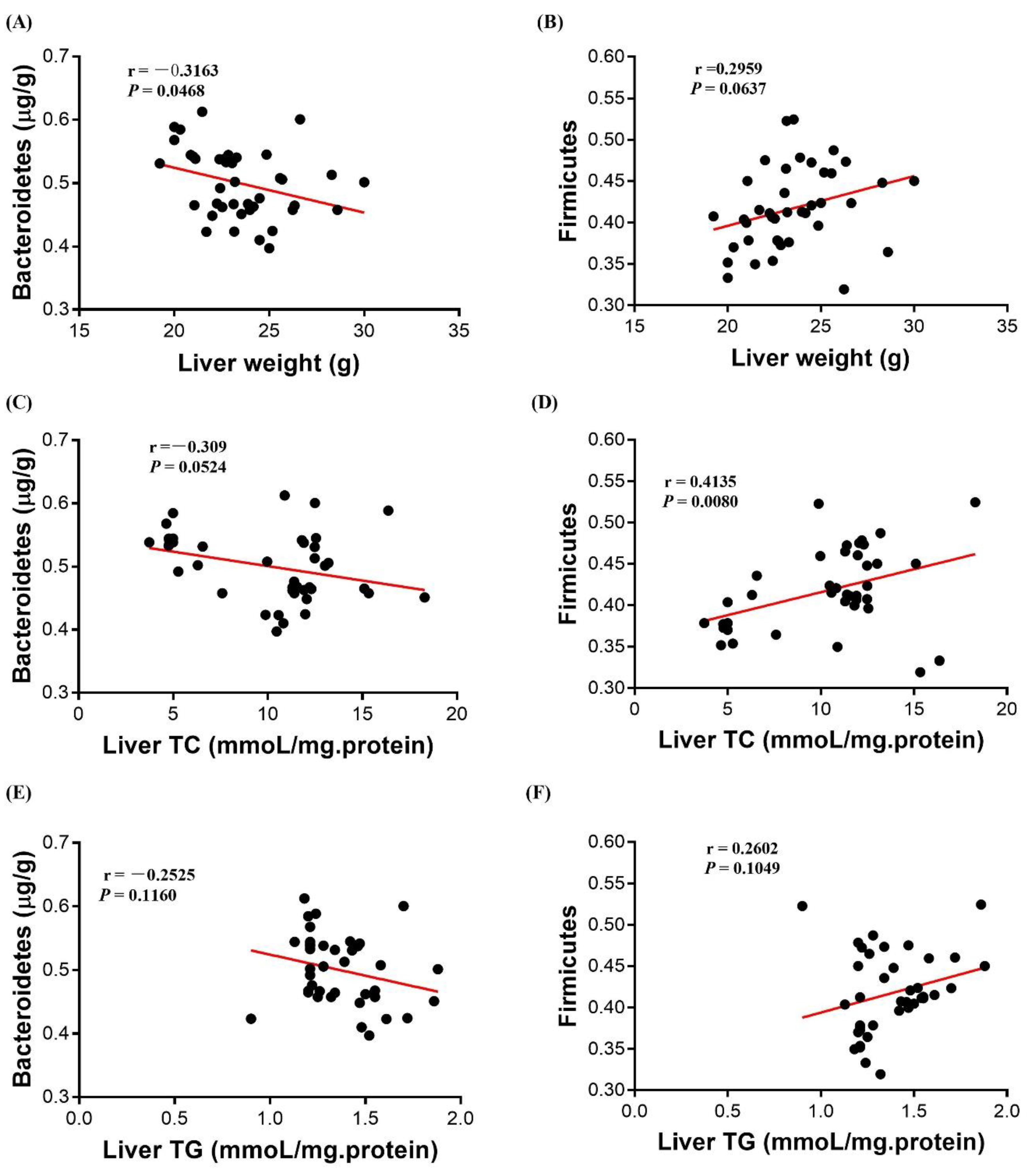
3.7. Correlation Analysis
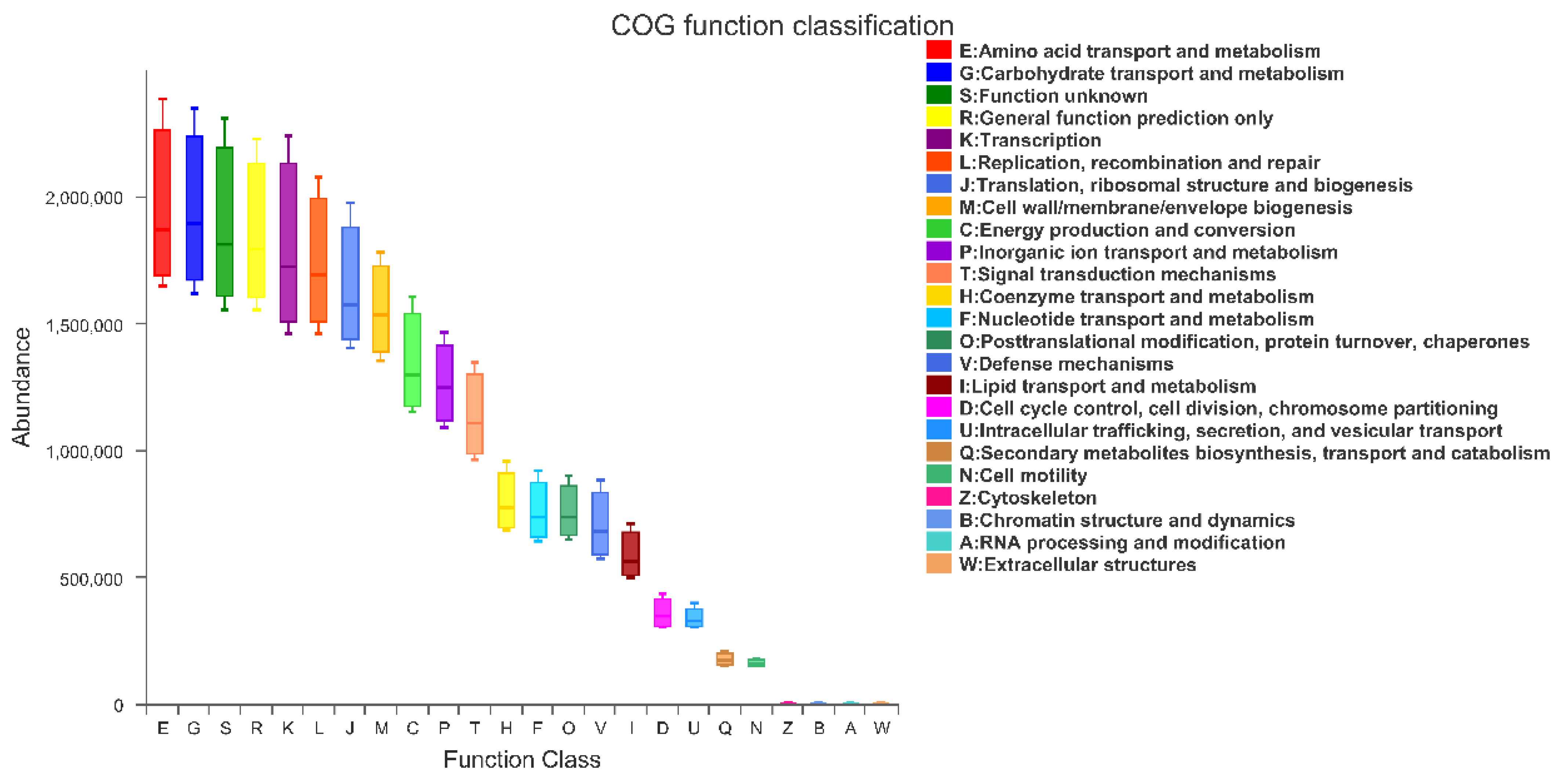
3.8. PICRUSt Functional Prediction Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kearney, J. Food consumption trends and drivers. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2010, 365, 2793–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Yan, W.; Sun, C.; Ji, C.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, J.; Yang, N. The gut microbiota is largely independent of host genetics in regulating fat deposition in chickens. ISME J. 2019, 13, 1422–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, P.B. Evolution of the Modern Broiler and Feed Efficiency. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2014, 2, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, L.; Romsos, D.R.; Leveille, G.A. In vivo estimation of fatty acid synthesis in the chicken (Gallus domesticus) utilizing 3H2O. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Comp. Biochem. 1976, 54, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Song, Z.; Wang, X.; Jiao, H.; Lin, H. Dexamethasone-induced hepatic lipogenesis is insulin dependent in chickens (Gallus gallus domesticus). Stress 2011, 14, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Fan, W.L.; Xing, S.Y.; Wang, J.; Li, P.; Liu, R.R.; Li, Q.H.; Zheng, M.Q.; Cui, H.X.; Wen, J.; et al. Effects of balanced selection for intramuscular fat and abdominal fat percentage and estimates of genetic parameters. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Lin, Q.; Yang, Y.; Hang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wu, C.; Xie, Z. Nuciferine reduced fat deposition by controlling triglyceride and cholesterol concentration in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 7101–7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Lin, H. Propionate inhibits fat deposition via affecting feed intake and modulating gut microbiota in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2020, 100, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Aquila, T.; Hung, Y.; Carreiro, A.; Buhman, K.K. Recent discoveries on absorption of dietary fat: Presence, synthesis, and metabolism of cytoplasmic lipid droplets within enterocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2016, 1861, 730–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeckman, A.; Towle, H.C. The Role of SREBP-1c in Nutritional Regulation of Lipogenic Enzyme Gene Expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 27029–27035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ma, S.; Huang, X.; Huang, Y. Effect of Chinese herbal medicine treatment on plasma lipid profile and hepatic lipid metabolism in Hetian broiler. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 1918–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Shen, G.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C. Curcumin supplementation regulates lipid metabolism in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Zhang, H.J.; Wu, S.G.; Yue, H.Y.; Zuo, J.J.; Feng, D.Y.; Qi, G.H. Effect of beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate calcium on growth, blood parameters, and carcass qualities of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.Y.; Song, B.; Zheng, C.B.; Zheng, J.; Yin, Y.L.; Chen, J.S. Dietary beta-hydroxy-beta-methyl butyrate supplementation affects growth, carcass characteristics, meat quality, and serum metabolomics profile in broiler chickens. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 633964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.H.; Zhong, Y.Z.; Xiao, H.; Zheng, C.B.; Song, B.; Wang, W.; Guo, Q.P.; Li, Y.Y.; Han, H.; Gao, J.; et al. Gut microbiota mediates the protective effects of dietary β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate (HMB) against obesity induced by high-fat diets. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 10019–10033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, F.; Guo, Q.; Long, C.; Yin, Y.; Kong, X.; Peng, M.; Wang, W. beta-Hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate modulates lipid metabolism in adipose tissues of growing pigs. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4836–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Duan, Y.; Li, Y.; Tang, Y.; Geng, M.; Oladele, O.A.; Kim, S.W.; Yin, Y. Effects of dietary n-6:n-3 PUFA ratio on fatty acid composition, free amino acid profile and gene expression of transporters in finishing pigs. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Song, B.; Guo, Q.; Zheng, J.; Li, F.; Duan, Y.; Peng, C. Alterations of the Muscular Fatty Acid Composition and Serum Metabolome in Bama Xiang Mini-Pigs Exposed to Dietary Beta-Hydroxy Beta-Methyl Butyrate. Animals 2021, 11, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczesniak, K.A.; Ostaszewski, P.; Fuller, J.C., Jr.; Ciecierska, A.; Sadkowski, T. Dietary supplementation of beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate in animals—A review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2015, 99, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suad, K.A.; Al-Shamire, J.S.H.; Dhyaa, A.A. Histological and biochemical evaluation of supplementing broiler diet with β-hydroxy-methyl butyrate calcium (β-HMB-Ca). Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 19, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaoyue, W.; Fengna, L.; Yehui, D.; Qiuping, G.; Wenlong, W.; Lingyu, Z.; Jianzhong, L.; Shanping, H.; Wen, C.; Yulong, Y. Dietary taurine regulates free amino acid profiles and taurine metabolism in piglets with diquat-induced oxidative stress. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 62, 103569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarthy, M.V.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. The metabolic basis of onalcoholic steatohepatitis. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2020, 3, e00112. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Rajagopal, G. The significance of plasma high density lipoprotein cholesterol (hdlc). Nepal Med. Coll. J. 2007, 9, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Horrocks, L.A.; Yeo, Y.K. Health benefits of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Pharmacol. Res. 1999, 40, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, T.; Mapiye, C.; Aalhus, J.; Beaulieu, A.; Patience, J.; Zijlstra, R.; Dugan, M. Flaxseed fed pork: N−3 fatty acid enrichment and contribution to dietary recommendations. Meat Sci. 2014, 96, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bláha, V.; Solichová, D.; Černohorský, D.; Brátová, M.; Vyroubal, P.; Zadák, Z. Bioanalysis of PUFA metabolism and lipid peroxidation in coronary atherosclerosis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2000, 22, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, H.D.; Guo, K.; Windsor, D.; Butterwith, S.C. Adipose Tissue Lipogenesis and Fat Deposition in Leaner Broiler Chickens. J. Nutr. 1992, 122, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theil, P.K.; Lauridsen, C. Interactions between dietary fatty acids and hepatic gene expression in livers of pigs during the weaning period. Livest. Sci. 2007, 108, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhuang, J.; Rao, K.; Li, X.; Zhao, R. Effect of early feed restriction on hepatic lipid metabolism and expression of lipogenic genes in broiler chickens. Res. Vet. Sci. 2010, 89, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Martin, M.; Li, Z.; Shyy, J.Y. Endothelial dysfunction: The role of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-induced NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing protein 3 inflammasome in atherosclerosis. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2014, 25, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecomte, V.; Meugnier, E.; Euthine, V.; Durand, C.; Freyssenet, D.; Nemoz, G.; Rome, S.; Vidal, H.; Lefai, E. A New Role for Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Protein 1 Transcription Factors in the Regulation of Muscle Mass and Muscle Cell Differentiation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 1182–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Koo, S.-H. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Molecular mechanisms for the hepatic steatosis. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2013, 19, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Tian, M.; Sun, R.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, L.; Jin, L.; Chen, L.; Zhou, W.; Duan, K.; Chen, Y.; et al. SIRT 5 inhibits peroxisomal ACOX 1 to prevent oxidative damage and is downregulated in liver cancer. EMBO Rep. 2018, 19, e45124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-M.; Sun, Y.-S.; Zhao, L.-Q.; Chen, T.-T.; Fan, M.-N.; Jiao, H.-C.; Zhao, J.-P.; Wang, X.-J.; Li, F.-C.; Li, H.-F.; et al. SCFAs-Induced GLP-1 Secretion Links the Regulation of Gut Microbiome on Hepatic Lipogenesis in Chickens. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ma, N.; Song, P.; He, T.; Levesque, C.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, A.; Ma, X. Grape Seed Proanthocyanidin Affects Lipid Metabolism via Changing Gut Microflora and Enhancing Propionate Production in Weaned Pigs. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wexler, H.M. Bacteroides: The good, the bad, and the nitty-gritty. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 593–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Bäckhed, F.; Turnbaugh, P.; Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R.D.; Gordon, J.I. Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11070–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnell, J.A.; Reimer, R.A. Prebiotic fibres dose-dependently increase satiety hormones and alter Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes in lean and obese JCR:LA-cp rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 107, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, A.; Zhang, C.; Cao, Y.B.; Cao, Q.Q.; Liu, F.; Yang, Y.R.; Tong, Z.X.; Rehman, M.U.; Wang, X.B.; Huang, S.C. The fungicide thiram perturbs gut microbiota community and causes lipid metabolism disorder in chickens. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Bonder, M.J.; Cenit, M.C.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Maatman, A.; Dekens, J.A.M.; Brandsma, E.; Marczynska, J.; Imhann, F.; Weersma, R.K.; et al. The Gut Microbiome Contributes to a Substantial Proportion of the Variation in Blood Lipids. Circ. Res. 2015, 117, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Sharma, R.K.; Malhotra, S.; Pothuraju, R.; Shandilya, U.K. Lactobacillus rhamnosus NCDC17 ameliorates type-2 diabetes by improving gut function, oxidative stress and inflammation in high-fat-diet fed and streptozotocin-treated rats. Benef. Microbes 2017, 8, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, D.; Denman, S.; Hughes, R.J.; Geier, M.S.; Crowley, T.; Chen, H.; Haring, V.; Moore, R. Intestinal microbiota associated with differential feed conversion efficiency in chickens. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, D.; Geier, M.S.; Denman, S.; Haring, V.; Crowley, T.; Hughes, R.J.; Moore, R. Identification of chicken intestinal microbiota correlated with the efficiency of energy extraction from feed. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meimandipour, A.; Shuhaimi, M.; Hair-Bejo, M.; Azhar, K.; Kabeir, B.M.; Rasti, B.; Yazid, A.M. In vitro fermentation of broiler cecal content: The role of Lactobacilli and pH value on the composition of microbiota and end products fermentation. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 49, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Genes 1 | Primers | Sequences (5′-3′) | Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | Forward | GCTGGGTTGAGCGACTAATG | 173 |
| Reverse | GGGAAACTGGCAAAGGACTG | ||
| LPL | Forward | TCATTGTTGTGGACTGGC | 139 |
| Reverse | TGGACATTGTTGAGAGGGT | ||
| SREBP-1c | Forward | CCTGGAAGAAGCATCATGGC | 181 |
| Reverse | AGAGCACAGAGGATTCGGAG | ||
| PPARα | Forward | TGTGGAGATCGTCCTGGTCT | 103 |
| Reverse | CGTCAGGATGGTTGGTTTGC | ||
| ACOX1 | Forward | ATGTCACGTTCACCCCATCC | 133 |
| Reverse | AGGTAGGAGACCATGCCAGT | ||
| CPT-1 | Forward | GAAGACGGACACTGCAAAGG | 223 |
| Reverse | GGGCAAGTTGAATGAAGGCA | ||
| β-actin | Forward | GTGTGATGGTTGGTATGGGC | 225 |
| Reverse | CTCTGTTGGCTTTGGGGTTC |
| Items 1 | Dietary Levels of HMB, % | SEM | p-Value 1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.15 | ANOVA | Linear | Quadratic | ||
| TG, mmol/L | 0.45 a | 0.45 ab | 0.38 c | 0.41 bc | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.006 | 0.018 |
| TC, mmol/L | 3.02 | 3.20 | 3.00 | 2.96 | 0.19 | 0.413 | 0.422 | 0.428 |
| LDL-C, mmol/L | 0.72 | 0.66 | 0.65 | 0.70 | 0.16 | 0.884 | 0.806 | 0.718 |
| HDL-C, mmol/L | 2.07 b | 2.24 ab | 2.33 a | 2.14 ab | 0.15 | 0.050 | 0.367 | 0.024 |
| Items | Dietary Levels of HMB, % | SEM | p-Value 1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.15 | ANOVA | Linear | Quadratic | ||
| C10:0 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.08 | 0.84 | 0.37 | 0.66 |
| C12:0 | 0.16 a | 0.15 ab | 0.14 b | 0.13 b | 0.05 | 0.04 | <0.01 | 0.02 |
| C14:0 | 0.14 b | 0.12 b | 0.19 a | 0.16 ab | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.12 | 0.24 |
| C16:0 | 16.70 | 16.17 | 17.09 | 16.04 | 0.42 | 0.44 | 0.65 | 0.80 |
| C16:1 | 0.35 c | 0.61 b | 1.01 a | 0.74 b | 0.17 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| C17:0 | 0.17 ab | 0.16 b | 0.19 a | 0.17 ab | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.24 | 0.49 |
| C18:0 | 24.67 | 24.69 | 22.88 | 22.85 | 0.47 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.06 |
| C18:1 n9t | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.08 |
| C18:1 n9c | 5.32 b | 6.00 b | 6.20 b | 7.54 a | 0.38 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| C18:2 n6c | 21.42 ab | 22.44 a | 20.88 b | 20.81 b | 0.39 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.15 |
| C18:3 n6 | 0.13 c | 0.17 a | 0.17 ab | 0.15 b | 0.05 | <0.01 | 0.16 | <0.01 |
| C20:1 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.06 | 0.18 | 0.23 | 0.29 |
| C18:3 n3 | 0.27 b | 0.47 a | 0.58 a | 0.43 a | 0.14 | <0.01 | 0.05 | <0.01 |
| C20:2 | 0.70 ab | 0.62 b | 0.75 a | 0.74 a | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 0.14 |
| C22:0 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.07 | 0.69 | 0.26 | 0.48 |
| C20:3 n6 | 1.21 | 1.39 | 1.36 | 1.33 | 0.18 | 0.55 | 0.43 | 0.38 |
| C20:4 n6 | 19.29 | 19.63 | 18.17 | 20.30 | 0.71 | 0.76 | 0.81 | 0.79 |
| C24:0 | 0.64 b | 0.93 a | 0.80 ab | 0.75 ab | 0.16 | 0.06 | 0.56 | 0.08 |
| C22:6 n3 | 4.34 ab | 4.00 b | 4.75 a | 4.64 a | 0.25 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.14 |
| SFA 2 | 42.95 | 42.70 | 41.76 | 40.59 | 0.52 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.07 |
| MUFA3 | 5.98 c | 6.88 bc | 7.50 ab | 8.54 a | 0.40 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| PUFA 4 | 47.35 | 48.71 | 48.57 | 48.39 | 0.71 | 0.90 | 0.87 | 0.98 |
| ∑PUFA:SFA | 1.11 | 1.14 | 1.17 | 1.19 | 0.12 | 0.60 | 0.22 | 0.41 |
| ∑n6 PUFA 5 | 42.04 | 43.63 | 40.57 | 42.59 | 0.68 | 0.44 | 0.81 | 0.96 |
| ∑n3 PUFA 6 | 4.61 bc | 4.47 c | 5.32 a | 5.07 ab | 0.25 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| ∑n6:n3 PUFA | 9.12 ab | 9.80 a | 7.67 c | 8.53 bc | 0.33 | <0.01 | 0.03 | 0.10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Tang, Z.; Zheng, C.; Zhong, Y.; Zheng, J.; Duan, G.; Yin, Y.; Duan, Y.; Song, Z. Dietary Beta-Hydroxy-Beta-Methyl Butyrate Supplementation Inhibits Hepatic Fat Deposition via Regulating Gut Microbiota in Broiler Chickens. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10010169
Zhang S, Tang Z, Zheng C, Zhong Y, Zheng J, Duan G, Yin Y, Duan Y, Song Z. Dietary Beta-Hydroxy-Beta-Methyl Butyrate Supplementation Inhibits Hepatic Fat Deposition via Regulating Gut Microbiota in Broiler Chickens. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(1):169. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10010169
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shiyu, Zhiyi Tang, Changbing Zheng, Yinzhao Zhong, Jie Zheng, Geyan Duan, Yulong Yin, Yehui Duan, and Zehe Song. 2022. "Dietary Beta-Hydroxy-Beta-Methyl Butyrate Supplementation Inhibits Hepatic Fat Deposition via Regulating Gut Microbiota in Broiler Chickens" Microorganisms 10, no. 1: 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10010169
APA StyleZhang, S., Tang, Z., Zheng, C., Zhong, Y., Zheng, J., Duan, G., Yin, Y., Duan, Y., & Song, Z. (2022). Dietary Beta-Hydroxy-Beta-Methyl Butyrate Supplementation Inhibits Hepatic Fat Deposition via Regulating Gut Microbiota in Broiler Chickens. Microorganisms, 10(1), 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10010169






