Position Control of Pneumatic Actuators Using Three-Mode Discrete-Valued Model Predictive Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. System Design and Modeling
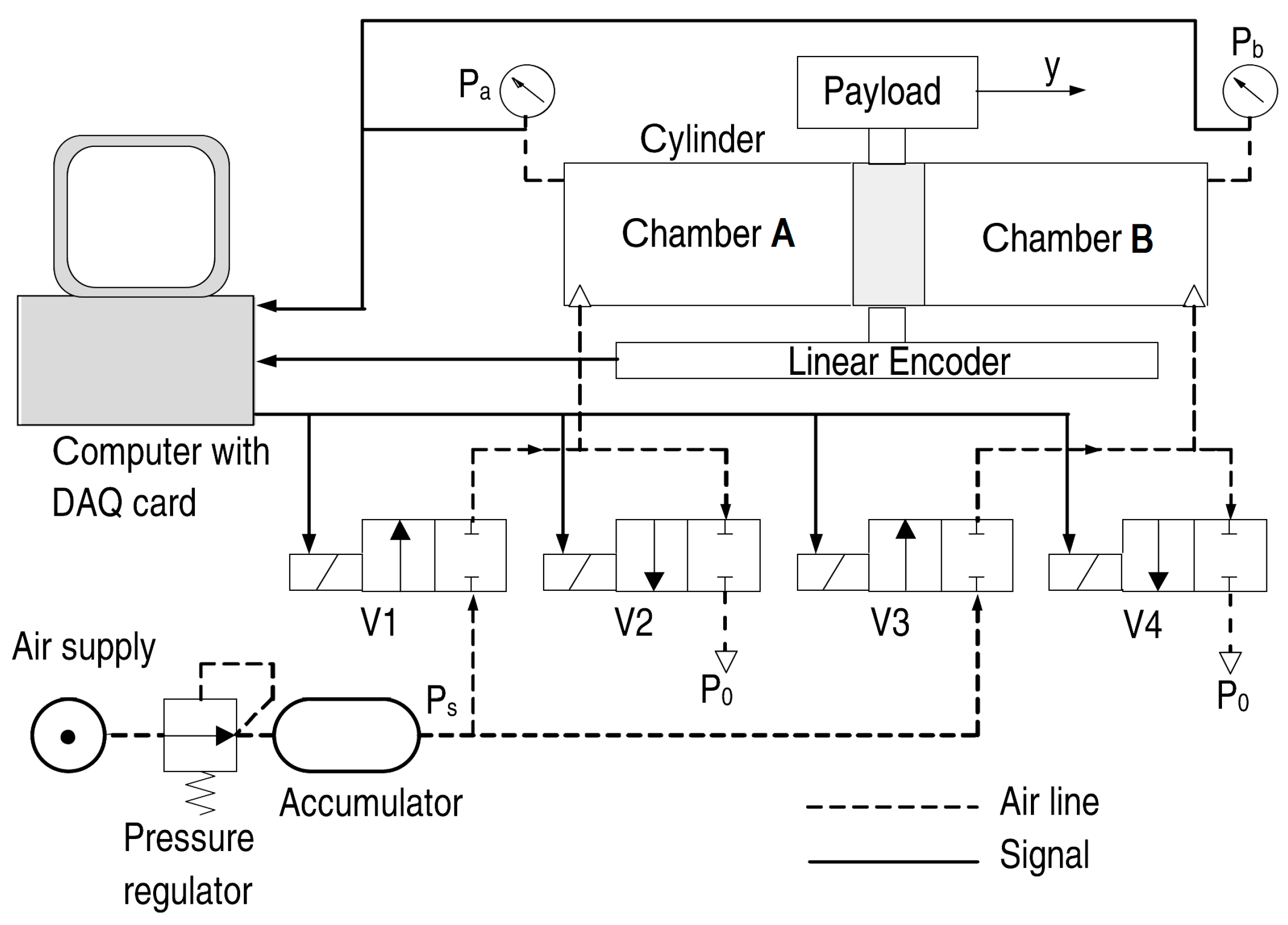
2.1. System Design
2.2. System Model
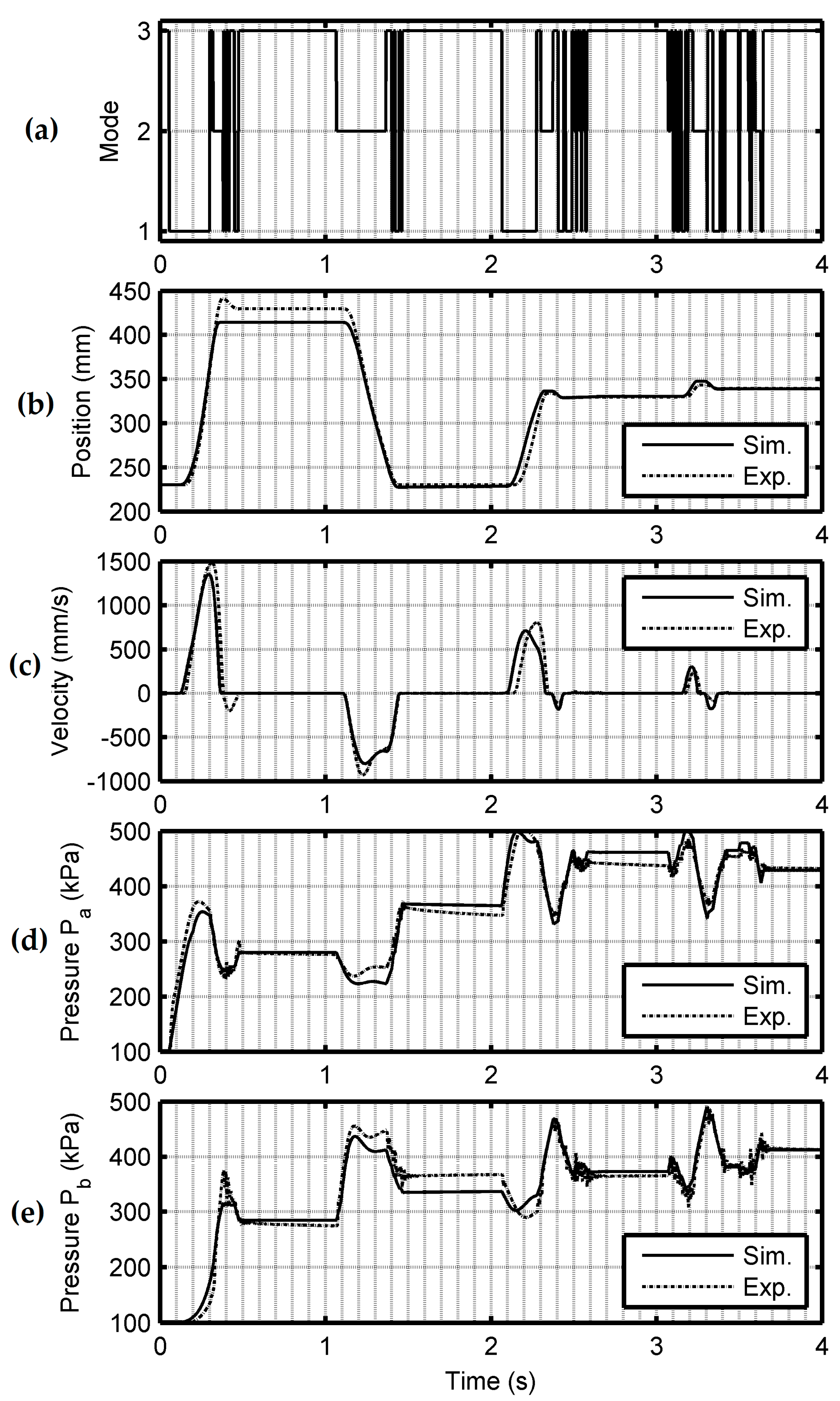
2.3. Model Fitting and Validation
3. Control Algorithms
3.1. SMC3
3.2. DVMPC1
| Algorithm 1: Prediction algorithm for DVMPC1 | |
| 1 | Set , , , and . |
| 2 | Compute |
| 3 | If , then use: , , and |
| 4 | Compute the predicted mass flow rates using: and |
| 5 | Compute the predicted pressure derivatives using: and |
| 6 | Compute the predicted pneumatic force using: |
| 7 | Substitute , and into (19) to obtain the predicted friction force, |
| 8 | Compute the predicted acceleration, , using (18), , , and |
| 9 | Set |
| 10 | If , then go to Step 2 |
| 11 | Stop |
3.3. DVMPC2
4. Controller Parameter Optimization
5. Experimental Verification
5.1. Testbed
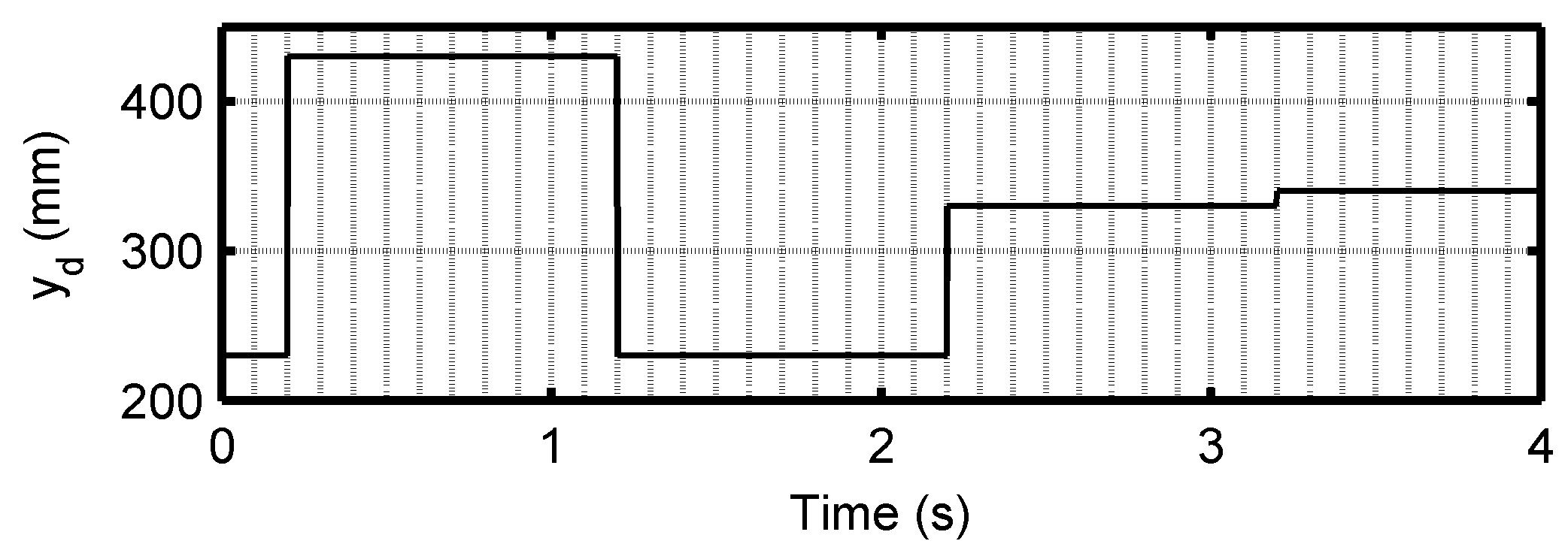
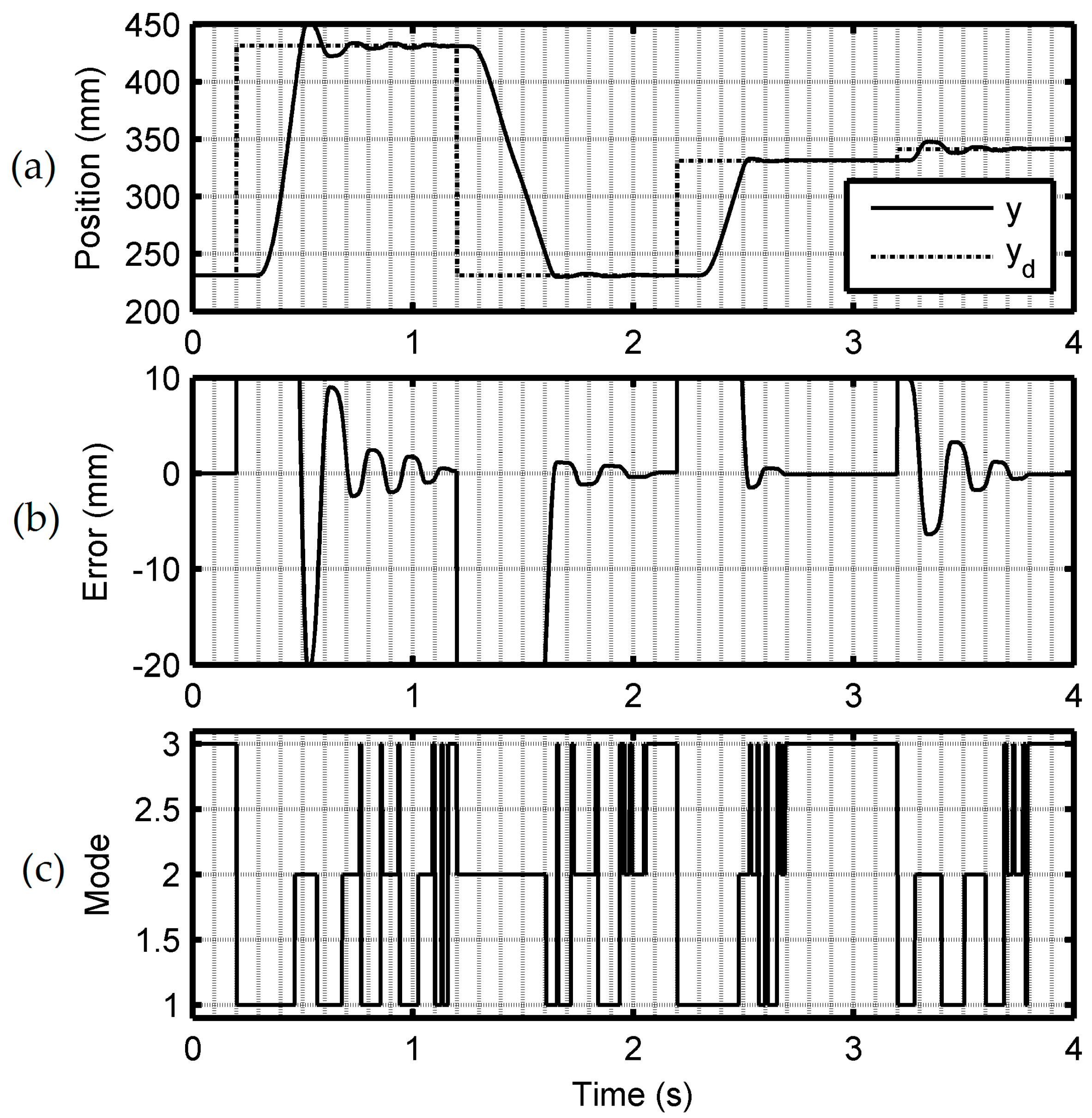
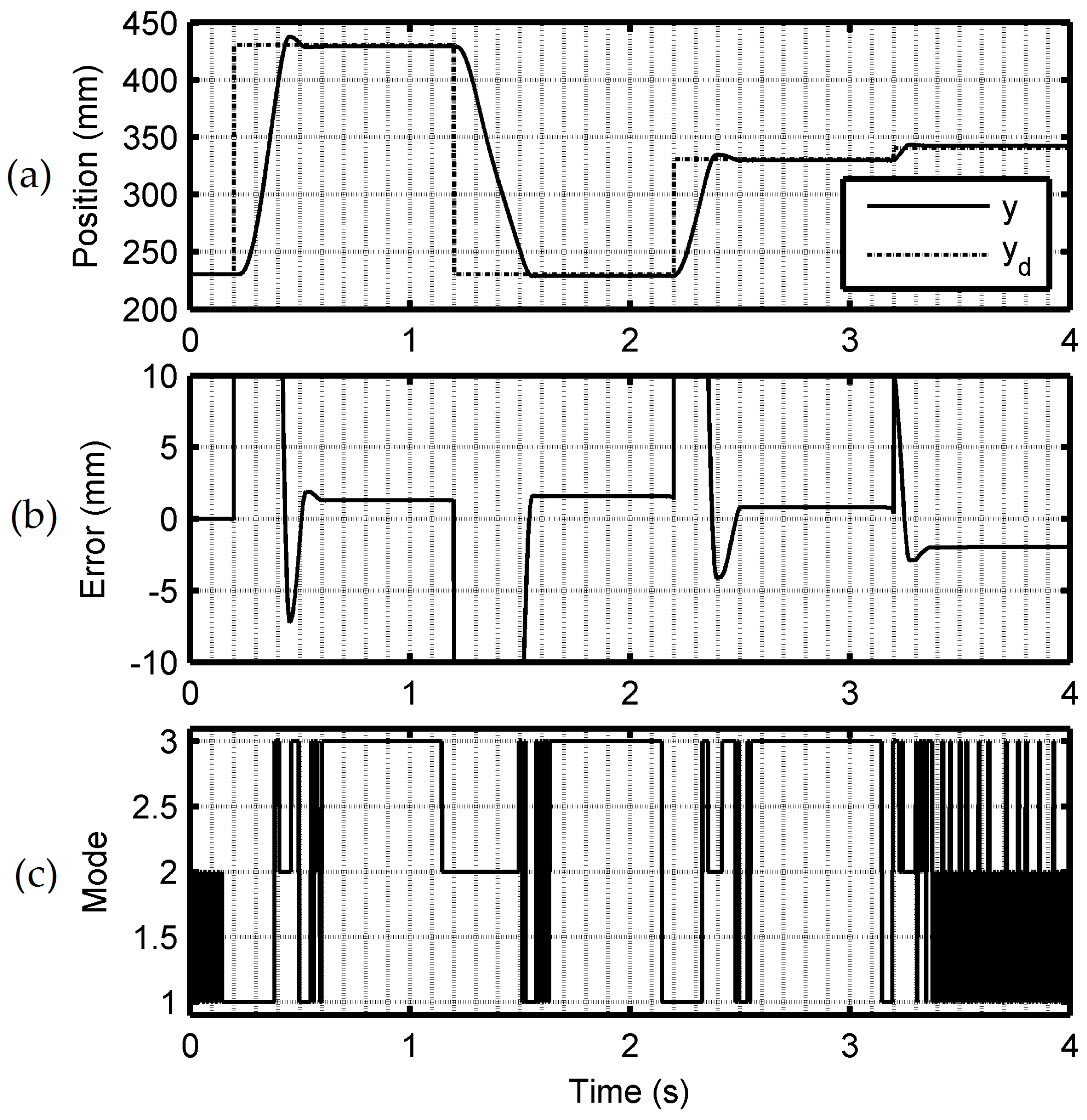
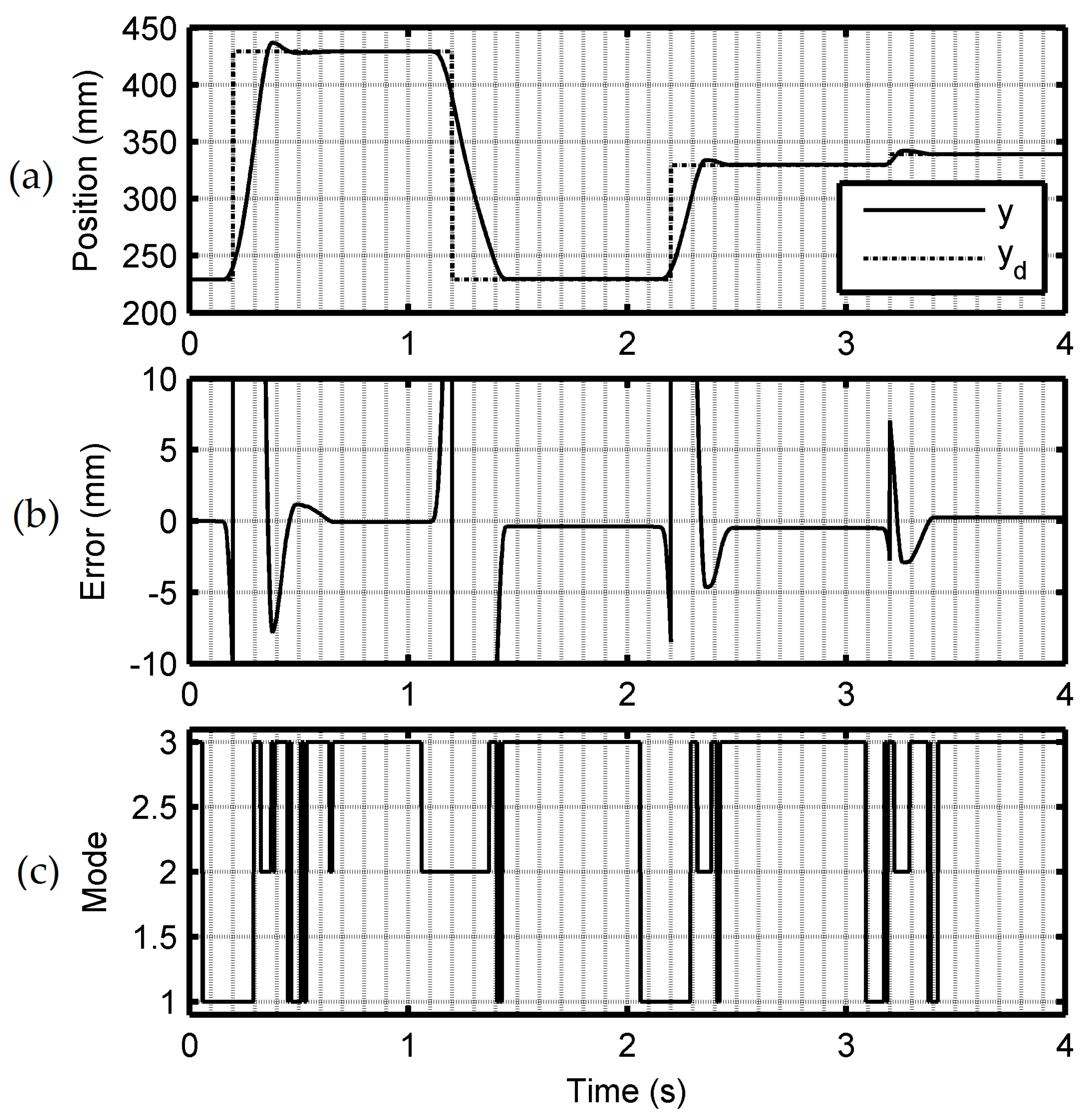
5.2. Experimental Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Varseveld, R.B.; Bone, G.M. Accurate position control of a pneumatic actuator using on/off solenoid valves. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 1997, 2, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Zhang, J.; Barth, E.J.; Goldfarb, M. Nonlinear model-based control of pulse width modulated pneumatic servo systems. ASME J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2006, 128, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, S.; Tavakoli, M.; Pham, M.T.; Leleve, A. Nonlinear discontinuous dynamics averaging and PWM-based sliding mode control of solenoid-valve pneumatic actuators. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazare, M.; Taghizadeh, M.; Kazemi, M.G. Optimal hybrid scheme of dynamic neural network and PID controller based on harmony search algorithm to control a PWM-driven pneumatic actuator position. J. Vib. Control 2018, 24, 3538–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.K.; Mishra, J.K.; Radke, M.G. Reduced order sliding mode control for pneumatic actuator. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 1994, 2, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, E.J.; Goldfarb, M. A control design method for switching systems with application to pneumatic servo systems. In Proceedings of the ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 17–22 November 2002; pp. 463–469. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.; Leavitt, J.; Jabbari, F.; Bobrow, J.E. Accurate sliding-mode control of pneumatic systems using low-cost solenoid valves. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2007, 12, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, S.; Le, M.Q.; Tavakoli, M.; Pham, M.T. Improved tracking and switching performance of an electro-pneumatic positioning system. Mechatronics 2012, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Abdelwahed, S. Discrete-input receding horizon control applied to pneumatic hopping robot energy regulation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Montréal, QC, Canada, 7–10 October 2007; pp. 1567–1572. [Google Scholar]
- Grancharova, A.; Johansen, T.A. Design and comparison of explicit model predictive controllers for an electropneumatic clutch actuator using On/Off valves. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2011, 16, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bone, G.M.; Chen, X. Position control of hybrid pneumatic-electric actuators. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference, Montréal, QC, Canada, 27–29 June 2012; pp. 1793–1799. [Google Scholar]
- Bone, G.M.; Xue, M.T.; Flett, J. Position control of hybrid pneumatic–electric actuators using discrete-valued model-predictive control. Mechatronics 2015, 25, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jünger, M.; Liebling, T.; Naddef, D.; Nemhauser, G.; Pulleyblank, W.; Reinelt, G. (Eds.) 50 Years of Integer Programming 1958–2008: From the Early Years to the State-of-the-Art; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nouri, B.M.Y.; Al-Bender, F.; Swevers, J.; Vanherck, P.; Van Brussel, H. Modelling a pneumatic servo positioning system with friction. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 28–30 June 2000; pp. 1067–1071. [Google Scholar]
- Andrighetto, P.L.; Valdiero, A.C.; Carlotto, L. Study of the friction behavior in industrial pneumatic actuators. In Proceedings of the ABCM Symposium Series in Mechatronics, Ouro Preto, Brazil, 6–11 November 2005; pp. 369–376. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, Z.; Bone, G.M. Nonlinear modeling and control of servo pneumatic actuators. IEEE Trans. Control Syst Technol. 2008, 16, 562–569. [Google Scholar]
- Cagienard, R.; Grieder, P.; Kerrigan, E.C.; Morari, M. Move blocking strategies in receding horizon control. J. Proc. Control 2007, 17, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audet, C.; Dennis, J.E. Mesh adaptive direct search algorithms for constrained optimization. SIAM J. Optim. 2006, 17, 188–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Digabel, S. Algorithm 909: NOMAD: Nonlinear optimization with the MADS algorithm. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 2011, 37, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0.001 s | Sampling period | |
| 4.91 × 10−4 m2 | Chamber A cross-sectional area | |
| 4.91 × 10−4 m2 | Chamber B cross-sectional area | |
| 293 K | Air temperature | |
| 0.6 m | Cylinder stroke | |
| 6.0 × 105 Pa | Supply pressure (absolute) | |
| 1.0 × 105 Pa | Atmospheric pressure (absolute) | |
| 2.14 kg | Nominal total mass | |
| 0.004 s | Valve energizing delay time | |
| 0.001 s | Valve de-energizing delay time | |
| 1.7 × 10−6 (m·kg) 0.5 | Chamber filling coefficient | |
| 6.1 × 10−9 m·s | Chamber discharging coefficient | |
| 2.65 × 10−8 m·s | Choked mass flow rate coefficient | |
| 54 N | Static friction force in the positive direction | |
| 48 N | Static friction force in the negative direction | |
| 81 N | Coulomb friction force in the positive direction | |
| 78 N | Coulomb friction force in the negative direction | |
| 7.9 N·s·m−1 | Viscous friction coefficient in the positive direction | |
| 23 N·s·m−1 | Viscous friction coefficient in the negative direction | |
| 0.37 m·s−1 | Stribeck velocity in the positive direction | |
| 0.36 m·s−1 | Stribeck velocity in the negative direction |
| Controller Type | Total mass (kg) | SPS (s−1) | RMSE (mm) | ITAE (smm) | SSE (mm) | OS (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMC3 | 2.14 | 7.75 | 64.7 | 15.81 | 0.876 | 8.02 |
| DVMPC1 | 2.14 | 22.08 | 51.3 | 7.98 | 1.145 | 4.16 |
| DVMPC2 | 2.14 | 5.70 | 32.2 | 2.95 | 0.578 | 3.78 |
| SMC3 | 3.36 | 7.80 | 63.3 | 16.99 | 1.637 | 12.56 |
| DVMPC1 | 3.36 | 25.43 | 51.0 | 9.07 | 1.778 | 8.71 |
| DVMPC2 | 3.36 | 7.25 | 32.3 | 3.81 | 1.172 | 8.11 |
| SMC3 | 0.95 | 7.20 | 60.9 | 11.71 | 0.326 | 1.92 |
| DVMPC1 | 0.95 | 36.23 | 48.5 | 6.78 | 0.968 | 0.67 |
| DVMPC2 | 0.95 | 5.15 | 26.7 | 2.34 | 0.782 | 1.03 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, H.; Bone, G.M.; Zhang, Y. Position Control of Pneumatic Actuators Using Three-Mode Discrete-Valued Model Predictive Control. Actuators 2019, 8, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/act8030056
Qi H, Bone GM, Zhang Y. Position Control of Pneumatic Actuators Using Three-Mode Discrete-Valued Model Predictive Control. Actuators. 2019; 8(3):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/act8030056
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Haitao, Gary M. Bone, and Yile Zhang. 2019. "Position Control of Pneumatic Actuators Using Three-Mode Discrete-Valued Model Predictive Control" Actuators 8, no. 3: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/act8030056
APA StyleQi, H., Bone, G. M., & Zhang, Y. (2019). Position Control of Pneumatic Actuators Using Three-Mode Discrete-Valued Model Predictive Control. Actuators, 8(3), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/act8030056





