Time-Stepping FEM-Based Multi-Level Coupling of Magnetic Field–Electric Circuit and Mechanical Structural Deformation Models Dedicated to the Analysis of Electromagnetic Actuators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
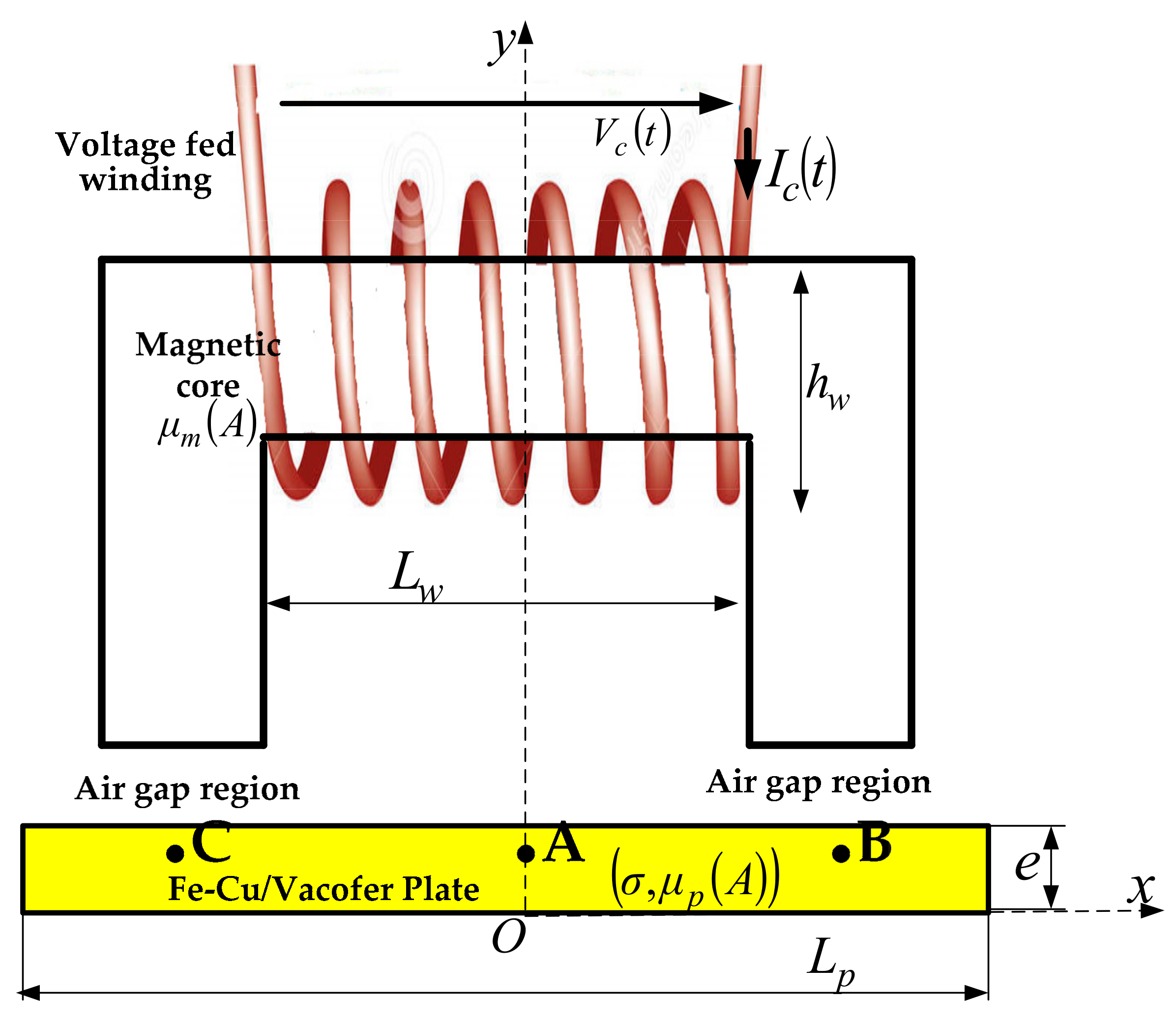
2. Presentation of the Basic Electromagnetic Actuator
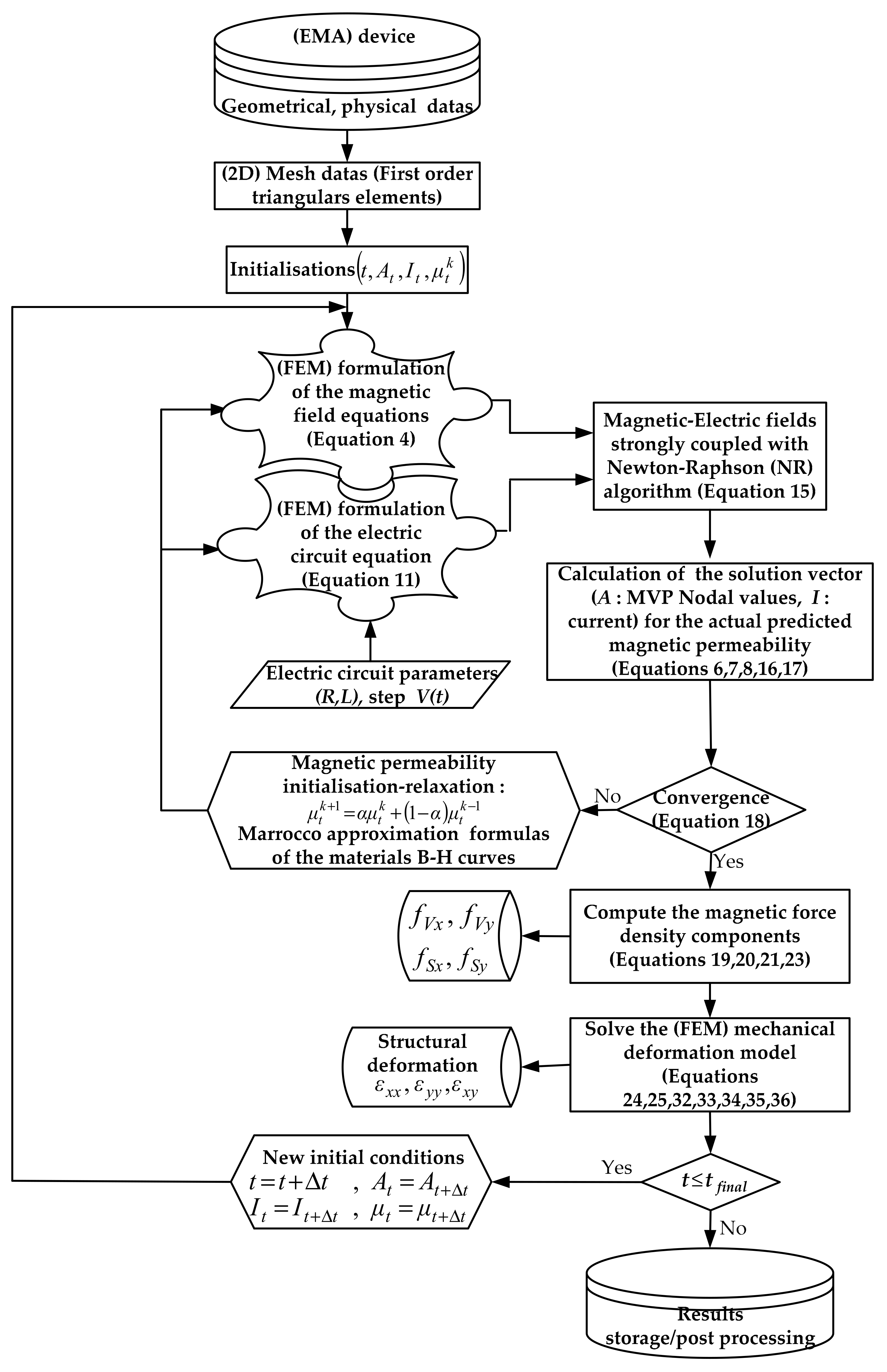
3. Strongly Coupled Magnetic Field–Circuit Formulation
3.1. Magnetic Field FEM Formulation
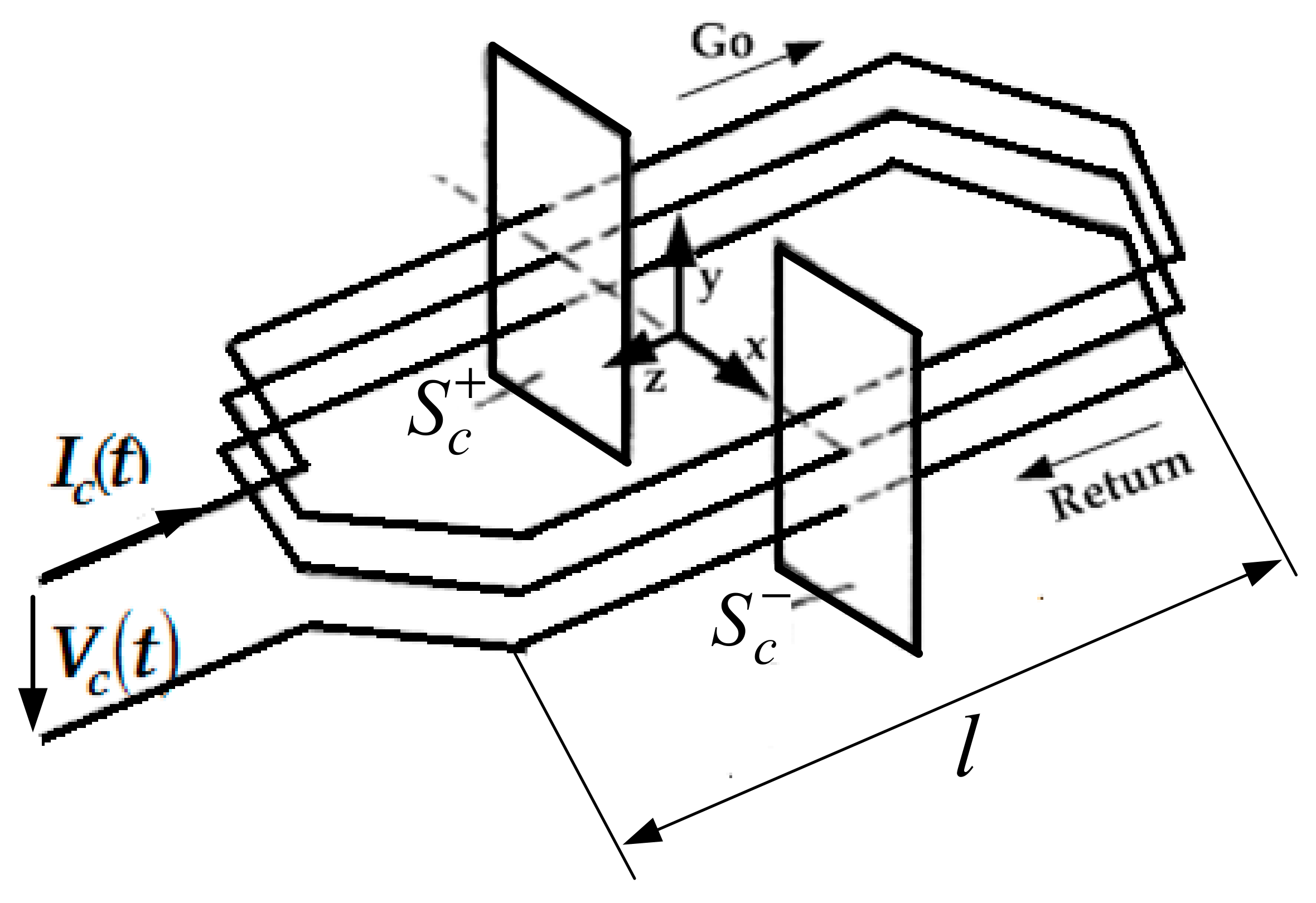
3.2. Electric Circuit (FEM) Formulation
3.3. Non-Linear Time-Stepping Magnetic Field–Circuit Coupled Model
4. Magnetic Eddy Current Force Calculation
5. Mechanical Deformation FEM Formulation Model
5.1. Equilibrium Equations
5.2. Constitution Equation (Stress–Strain)
5.3. Compatibility Equation (Strain–Displacement)
5.4. Finite Element Formulations
6. Application, Results, and Discussion
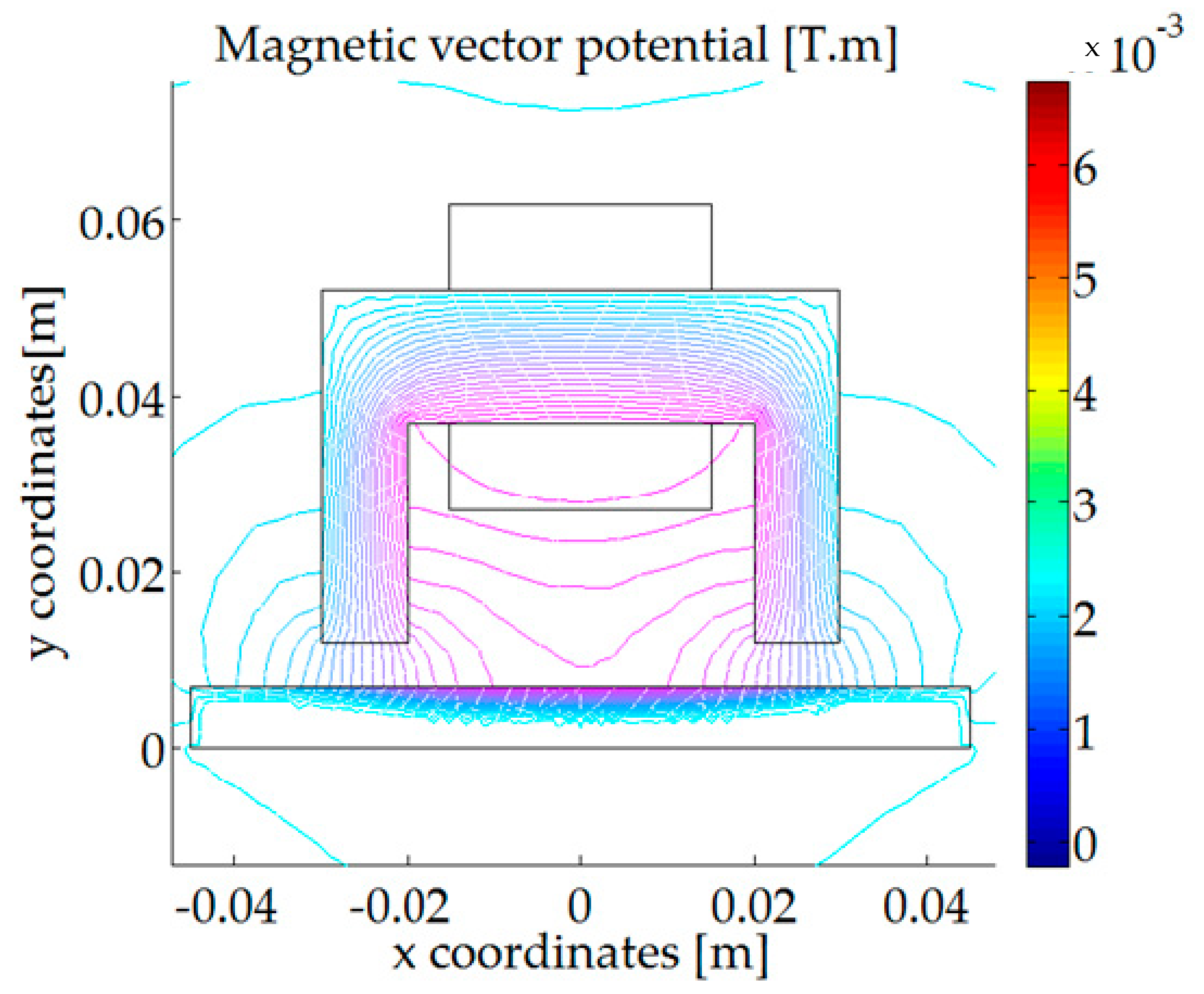
6.1. The Results of the Electromagnetic Simulations (FEM)
6.2. FEM Analyses for Structural–Mechanical Field
6.3. Analysis Parameters
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Symbol | Description |
| z-direction component of the magnetic vector potential | |
| Young’s modulus | |
| Surface magnetic force density components | |
| Volume magnetic force density components | |
| Magnetic force density vector of the mechanical problem | |
| Induced eddy current density | |
| Magnetic field | |
| Tangential and normal magnetic field, respectively | |
| Coil current | |
| Self-inductance of the coil | |
| Number of turns and the device symmetries, respectively | |
| Number of nodes and triangular finite element of the plate | |
| Resistance of the coil | |
| Global displacement vector | |
| , v | Displacement components in x- and y-directions, respectively |
| Voltage of the coil | |
| , | Mechanical stress tensor and strain tensor |
| , | Stresses along x- and y-directions, respectively |
| , | Stresses along xy- and yx-directions, respectively |
| , , | Deformation strain along x-, y-, and xy-directions, respectively |
| Weighting and shape functions of the FEM formulation | |
| Ω, | EMA studied domain and its surrounding boundary |
| Ωcoil, Ωcore,, Ωair | Load plate, coil, core, and air regions, respectively |
| Ωload | Boundary of the mechanical domain |
| , | Time step and relaxation factor |
| Electric conductivity | |
| Non-linear magnetic material permeability | |
| Magnetic permeability of air and the plate, respectively. | |
| Poisson’s ratio |
References
- Nguyen, M.K. Predicting Electromagnetic Noise in Induction Motors. Master’s Thesis, Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, F.; Zuo, S.; Deng, W.; Wu, S. Modeling and analysis of electromagnetic force, vibration, and noise in permanent-magnet synchronous motor considering current harmonics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 7455–7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Lee, S.H. Evaluation of mechanical deformation and distributive magnetic loads with different mechanical constraints in two parallel conducting bars. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2017, 71, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, P.; Delinchant, B.; Coulomb, J.L.; Du Peloux, B. Semi-Analytical Magneto-Mechanic Coupling with Contact Analysis for MEMS/NEMS. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 922–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Han, Q.; Chu, F. Review of electromagnetic vibration in electrical machines. Energies 2018, 11, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Xie, X.; Zhou, S. Design of a normal stress electromagnetic fast linear actuator. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagler, O.; Trost, M.; Hillerich, B.; Kozlowski, F. Efficient design and optimization of MEMS by integrating commercial simulation tools. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1998, 66, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, J.P.A.; Sadowski, N. Electromagnetic Modeling by Finite Element Methods; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003; ISBN 0-8247-4269-9. [Google Scholar]
- Hameyer, K.; Driesen, J.; De Gersem, H.; Belmans, R. The classification of coupled field problems. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1999, 35, 1618–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbhar, G.B.; Kulkarni, S.V.; Escarela-Perez, R.; Campero Littlewood, E. Applications of coupled field formulations to electrical machinery. COMPEL 2007, 26, 489–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.M.; Oh, Y.H.; Kim, J.K.; Song, J.S.; Hahn, S.C. Experimental verification and finite element analysis of short-circuit electromagnetic force for dry-type transformer. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Du, Y.; Xu, Z. Optimization Design of Electromagnetic Actuator Applied as Fast Tool Servo. Actuators 2017, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belahcen, A. Magneto Elasticity Magnetic Forces and Magnetostriction in Electrical Machines. Ph.D. Thesis, Helsinki University of Technolology, Espoo, Finland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Pantelyat, M.G.; Shulzhenko, N.G.; Matyukhin, Y.I.; Gontarowsky, P.P.; Dolezel, I.; Ulrych, B. Numerical simulation of electrical engineering devices: Magneto-thermo-mechanical coupling. COMPEL 2011, 30, 1189–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belahcen, A. Magneto-elastic coupling in rotating electrical machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 1624–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulomb, J.L. A Methodology for the Determination of Global Electromechanical Quantities from a Finite Element Analysis and its Application to the Evaluation of Magnetic Forces, Torques and Stiffness. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1983, 19, 2514–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobbio, S.; Alotto, P.; Delfino, F.; Girdinio, P.; Molfino, P. Equivalent Source Methods for 3-D Force Calculation with Nodal and Mixed FEM in Magnetostatic Problems. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2001, 37, 3137–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, T.W.; Reece, A.B.J.; Sangha, P.S. Induction Motor Analysis by Time-Stepping Techniques. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1988, 24, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William Gear, C. Numerical Initial Value Problems in Ordinary Differential Equations; Printice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1971; ISBN 0136266061. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, T.J.R.; Liu, W.K. Implicit-explicit finite elements in transient analysis: Stability theory. J. Appl. Mech. 1978, 45, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, J.R.; Ruehl, J.J.; Hirtenfelder, F. Coupled nonlinear electromagnetic and structural finite element analysis of an actuator excited by an electric circuit. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1995, 31, 1861–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, M.V.K.; Silvester, P. Finite-element analysis of magnetically saturated DC machines. IEEE Trans. Power App. Syst. 1971, PAS-90, 2362–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrocco, A. «Analyse numérique de problèmes d’électrotechnique». Ann. Sci. Math. 1977, 01, 271–296. [Google Scholar]
- Tandon, S.C.; Armor, A.F.; Chari, M.V.K. Nonlinear transient finite element field computation for electrical machines and devices. IEEE Trans. Power App. Syst. 1983, PAS-102, 1089–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; He, X.; Kim, D.K.; Elborai, S.; Choi, H.S.; Park, I.H.; Zahn, M. Evaluation of the mechanical deformation in incompressible linear and nonlinear magnetic material using various electromagnetic force density methods. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 97, 10E108-1–10E108-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, H.; Gao, Y.; Dozono, H.; Muramatsu, K. Coupled Magneto-Mechanical Analysis in Isotropic Materials under Multi-Axial Stress. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, H.; Gao, Y.; Kameari, A.; Dozono, H.; Muramatsu, K. Coupled Magneto-Mechanical Analysis Considering Permeability Variation by Stress Due to Both Magnetostriction and Electromagnetism. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbeler, R.C. Structural Analysis; Printice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 2012; ISBN 9780132570534. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Ionescu, B.; Besbes, M.; Razek, A. Calculation of mechanical deformation of magnetic materials in electromagnetic devices. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1995, 31, 1873–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benali, B. Contribution à la Modélisation des Systèmes Électrotechnique à l’aide des Formulations en Potentiels: Application à la Machine Asynchrone. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Sciences and Technology of Lille, Lille, France, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kou, B.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H. Characteristic Analysis and Control of a Hybrid Excitation Linear Eddy Current Brake. Energies 2015, 8, 7441–7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galopin, N.; Azoum, K.; Besbes, M.; Bouillault, F.; Daniel, L.; Hubert, O.; Alves, F. Caracterisation et modélisation des déformations induites par les forces magnétiques et par la magnetostriction. Revue Internationale du Génie Électrique-RS RIGE 2006, 9, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

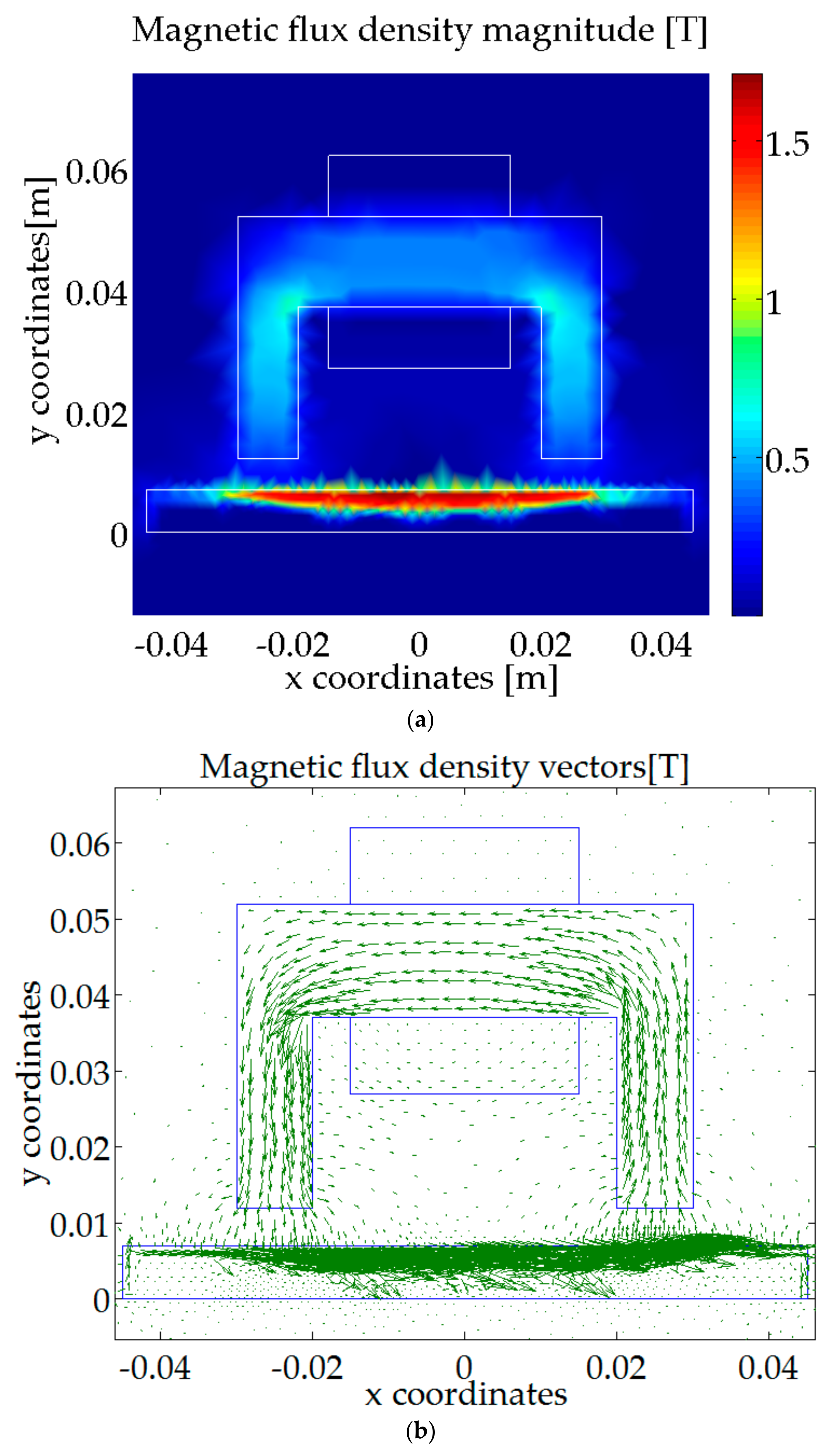
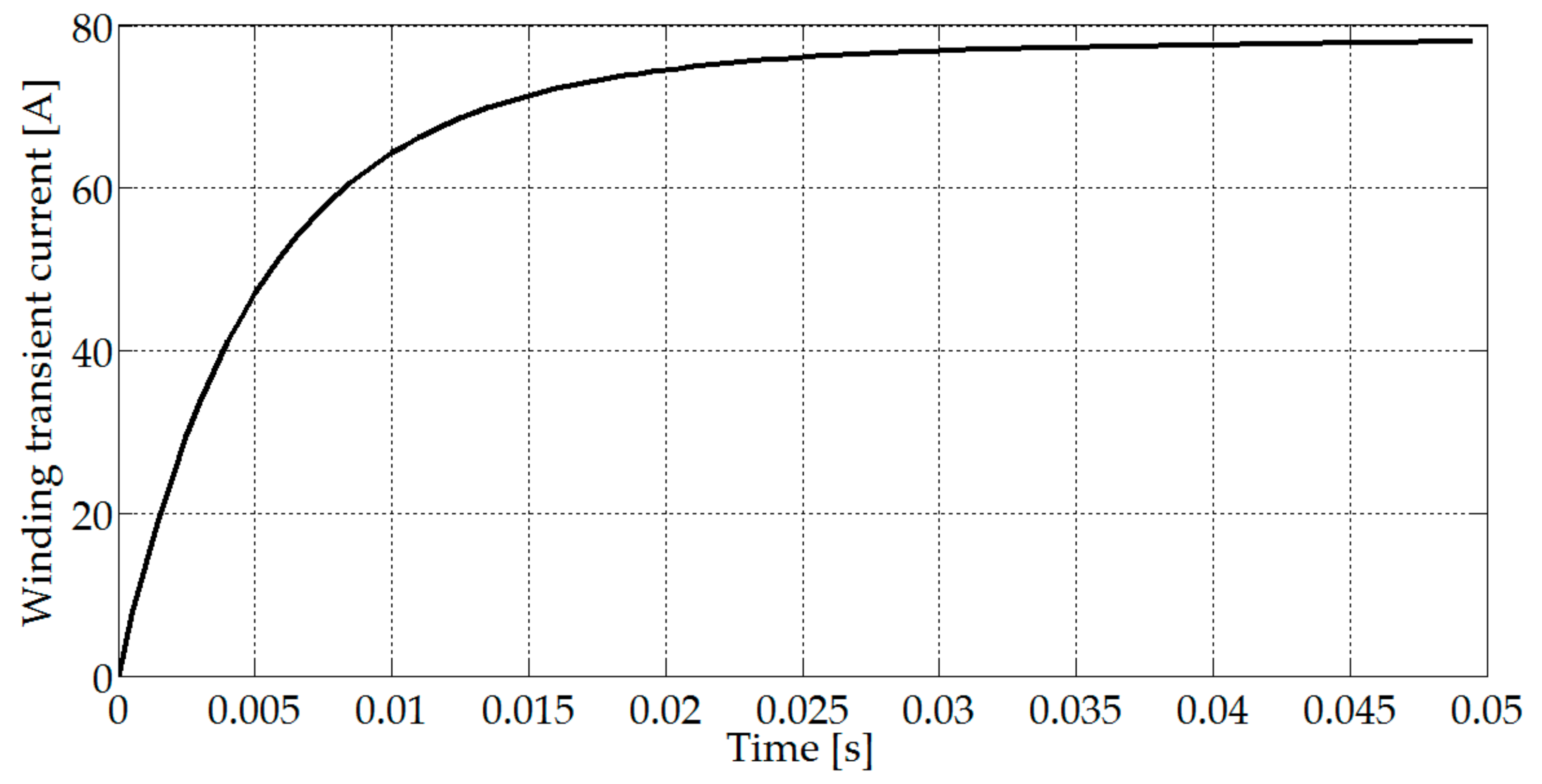
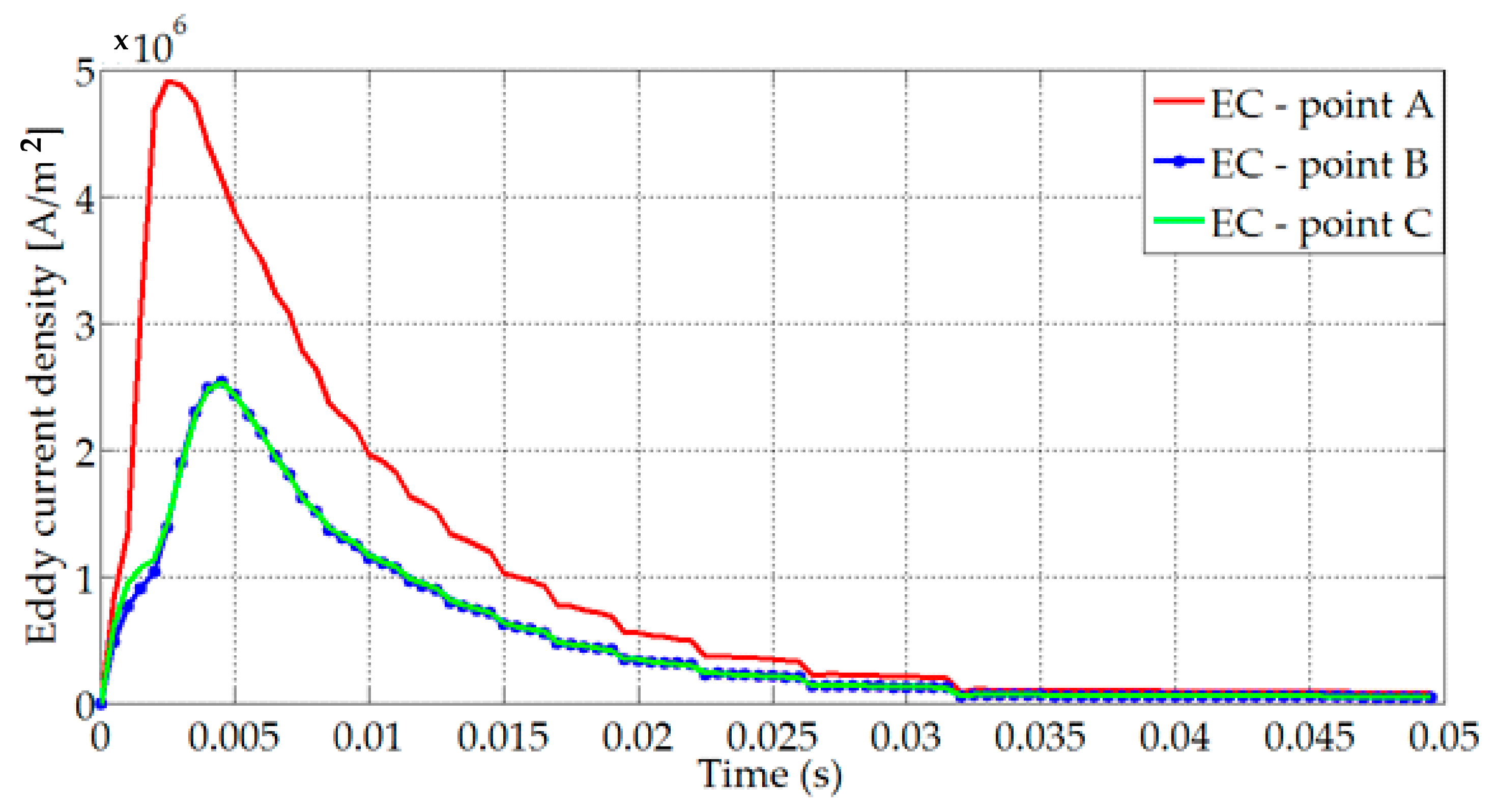
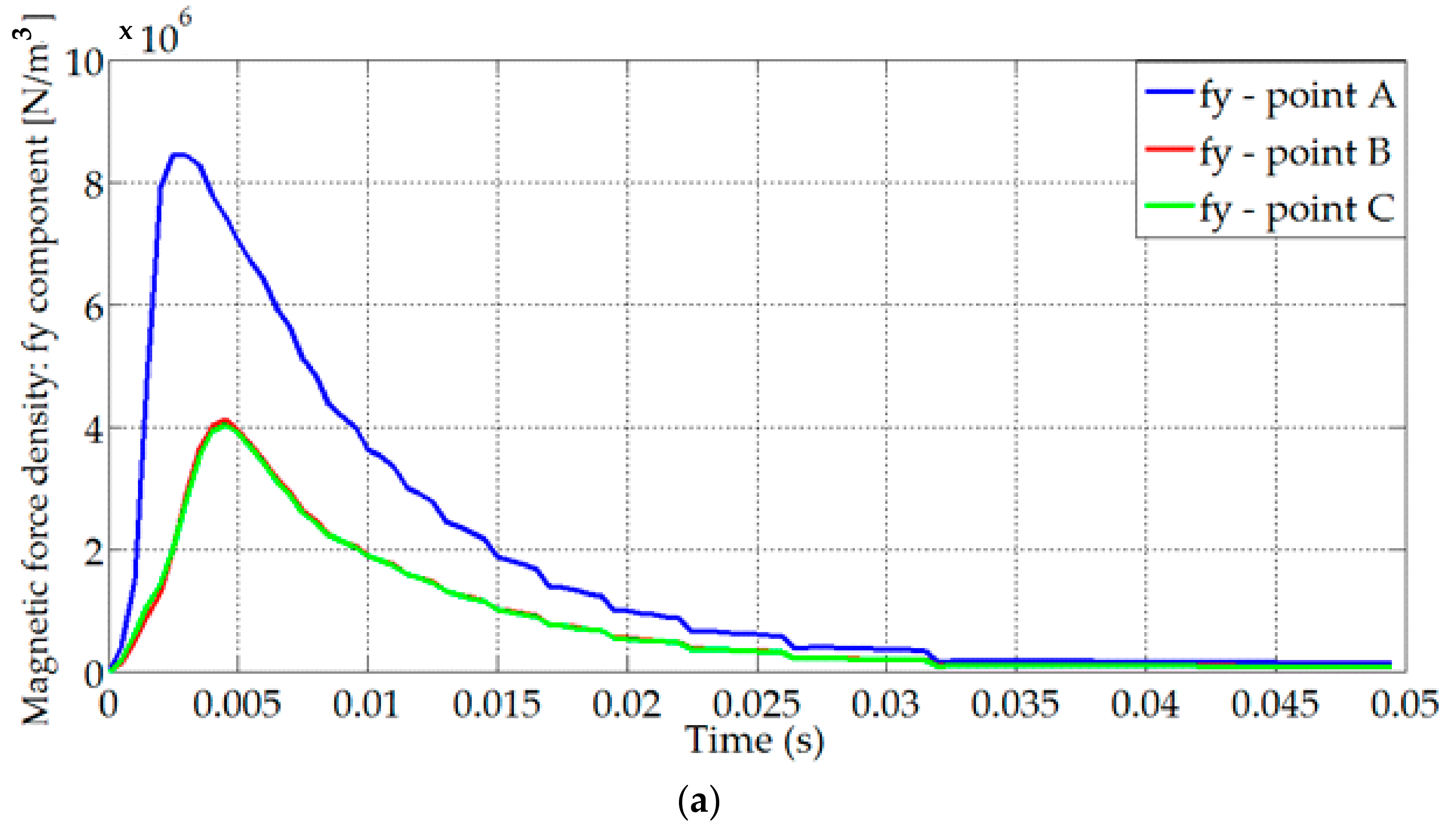
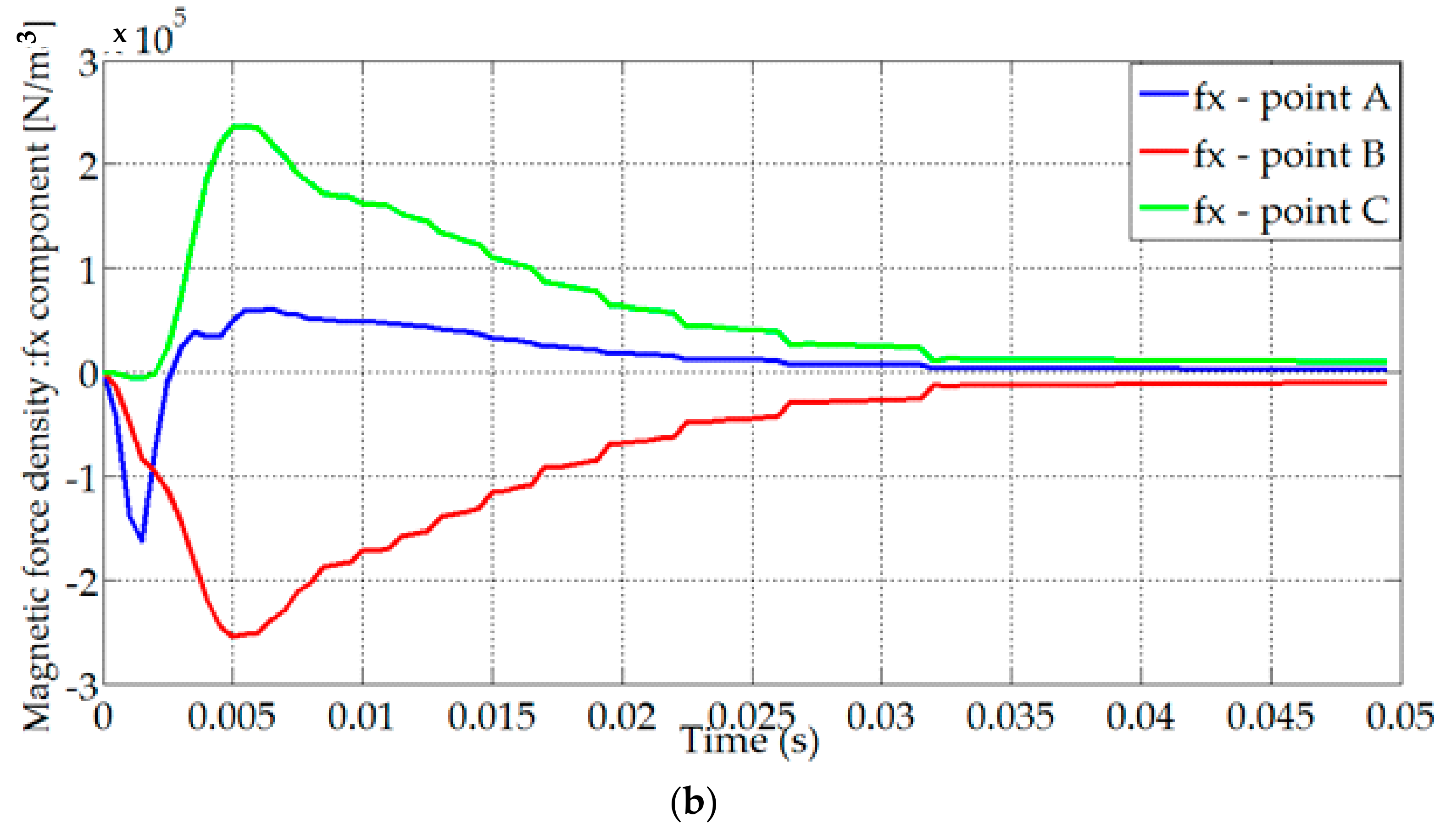
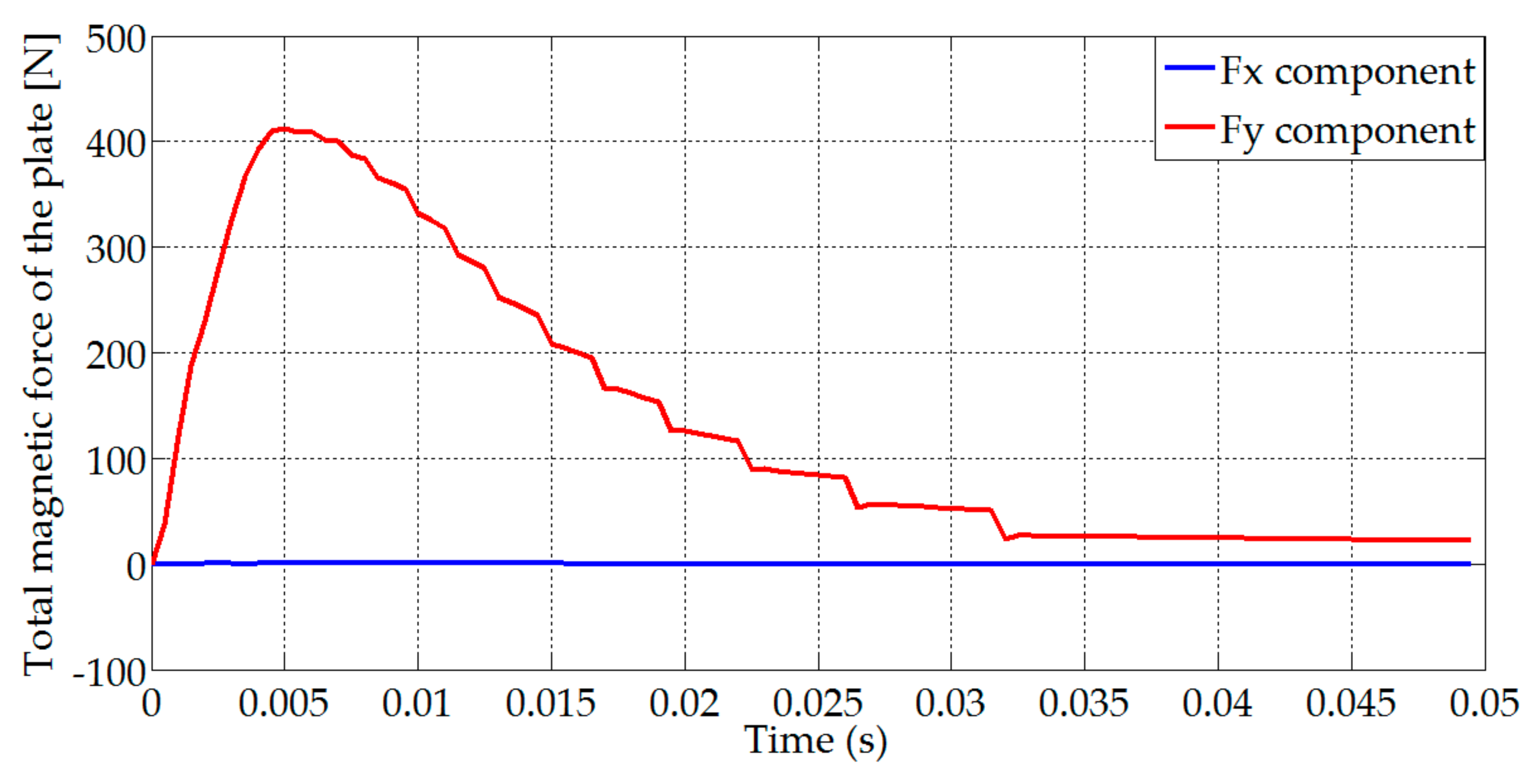
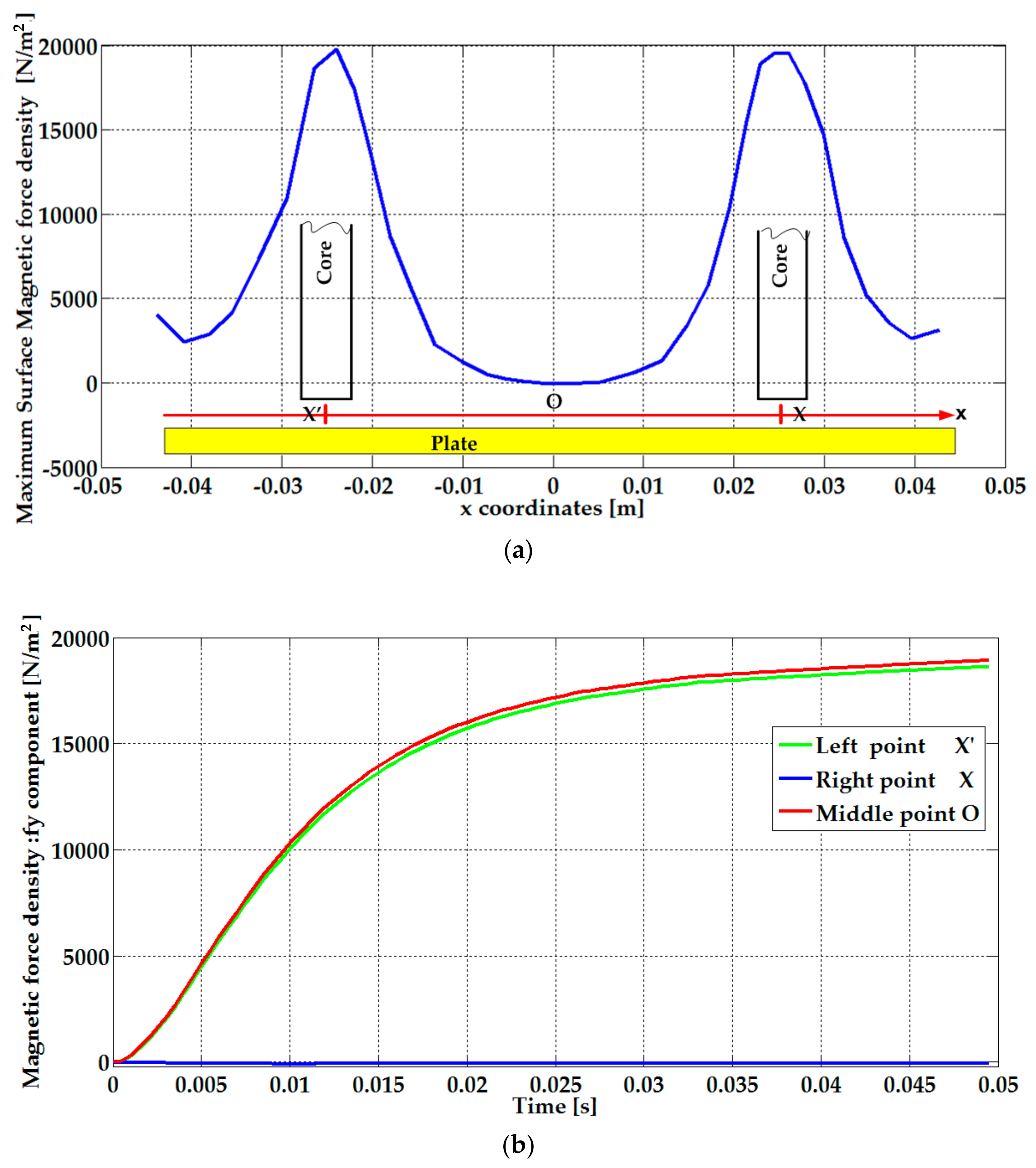
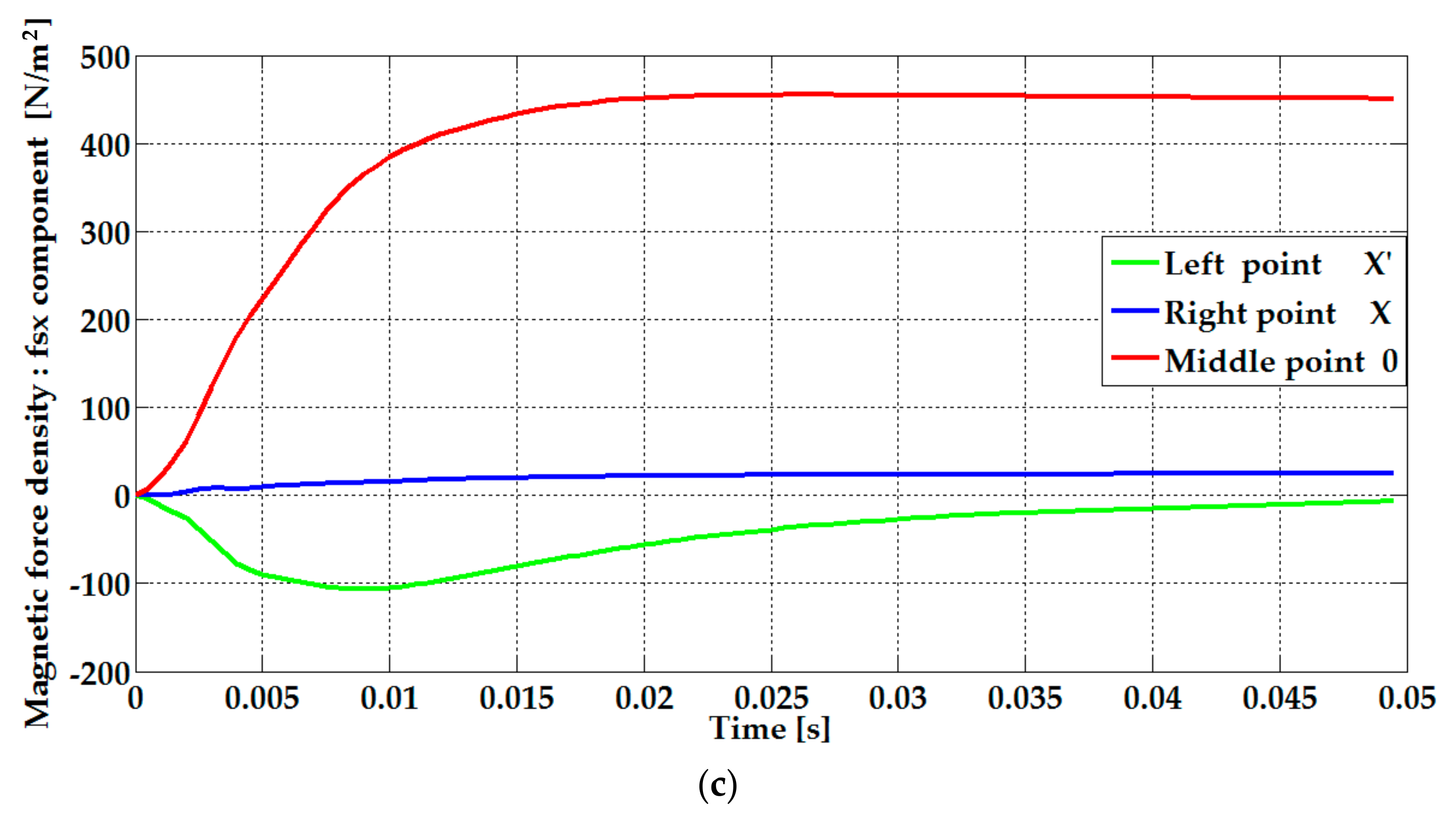
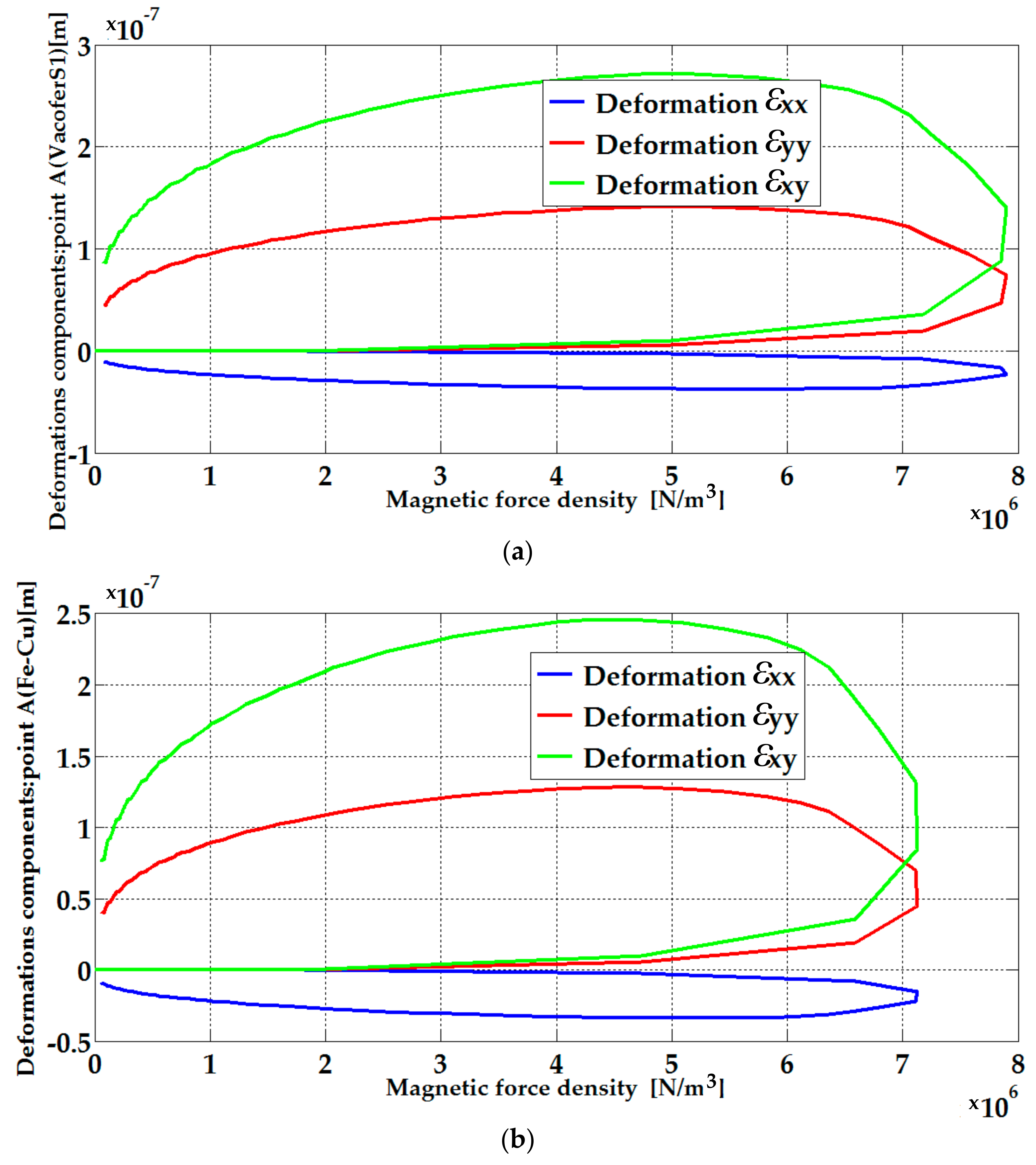
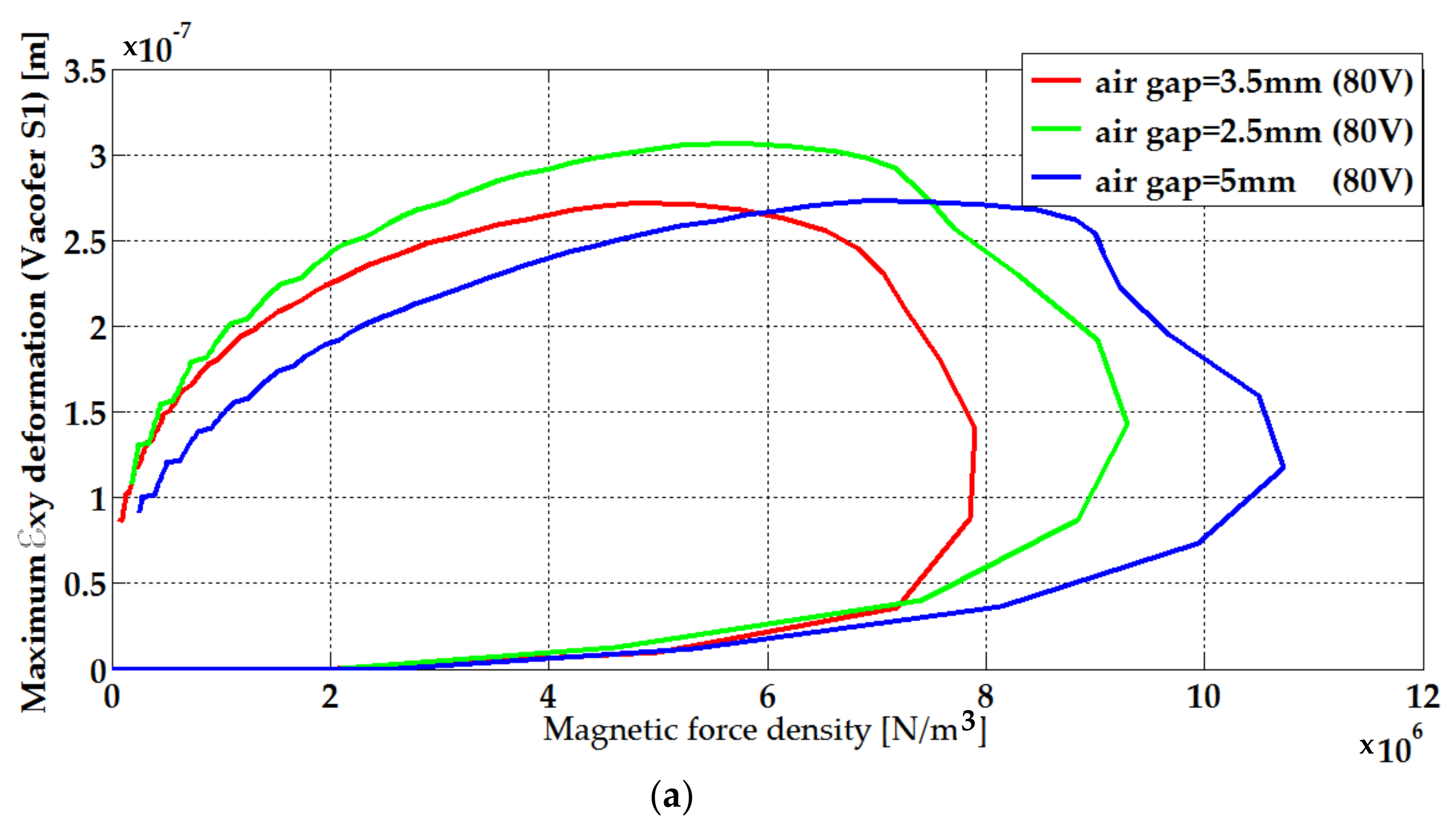
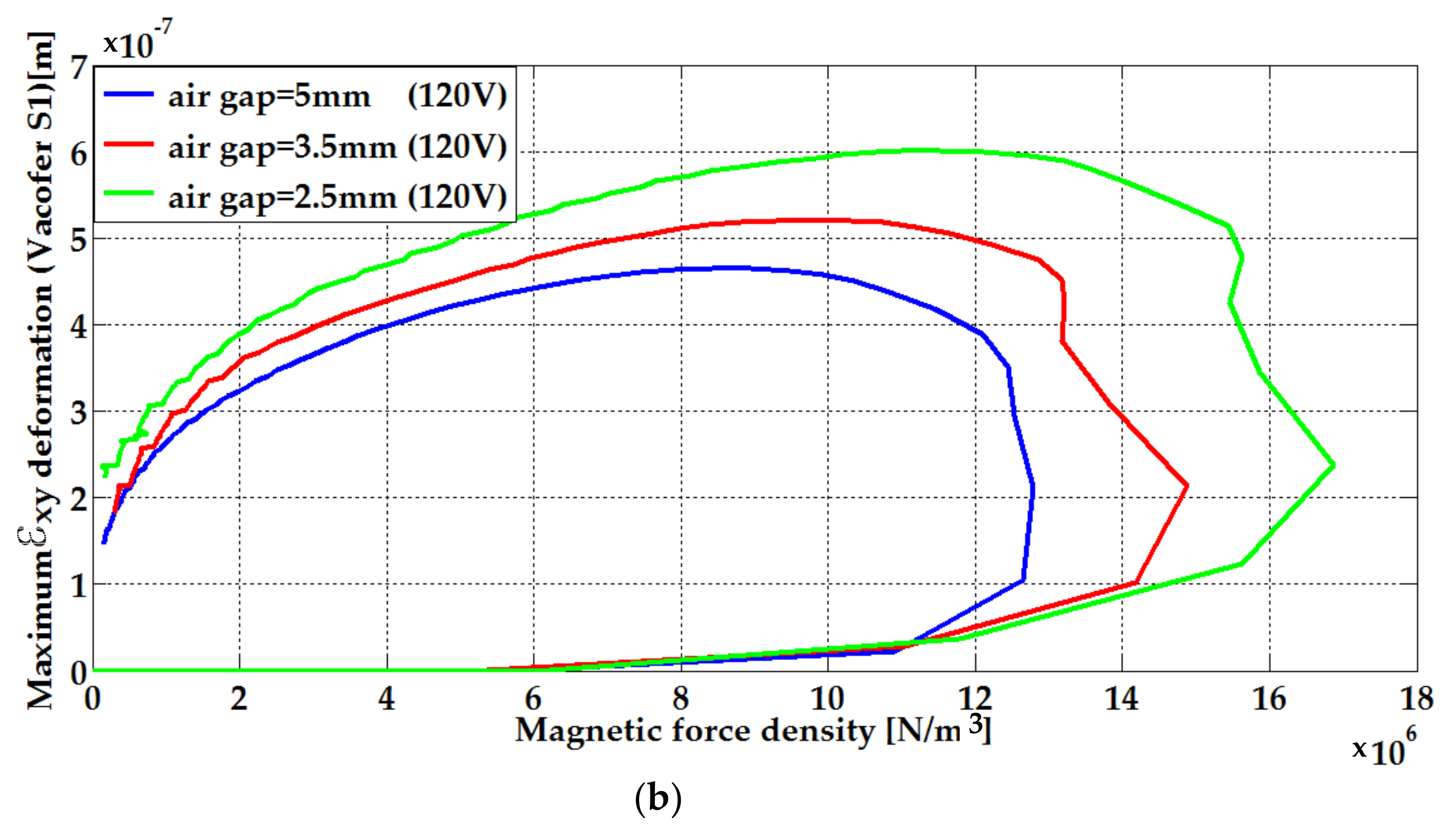
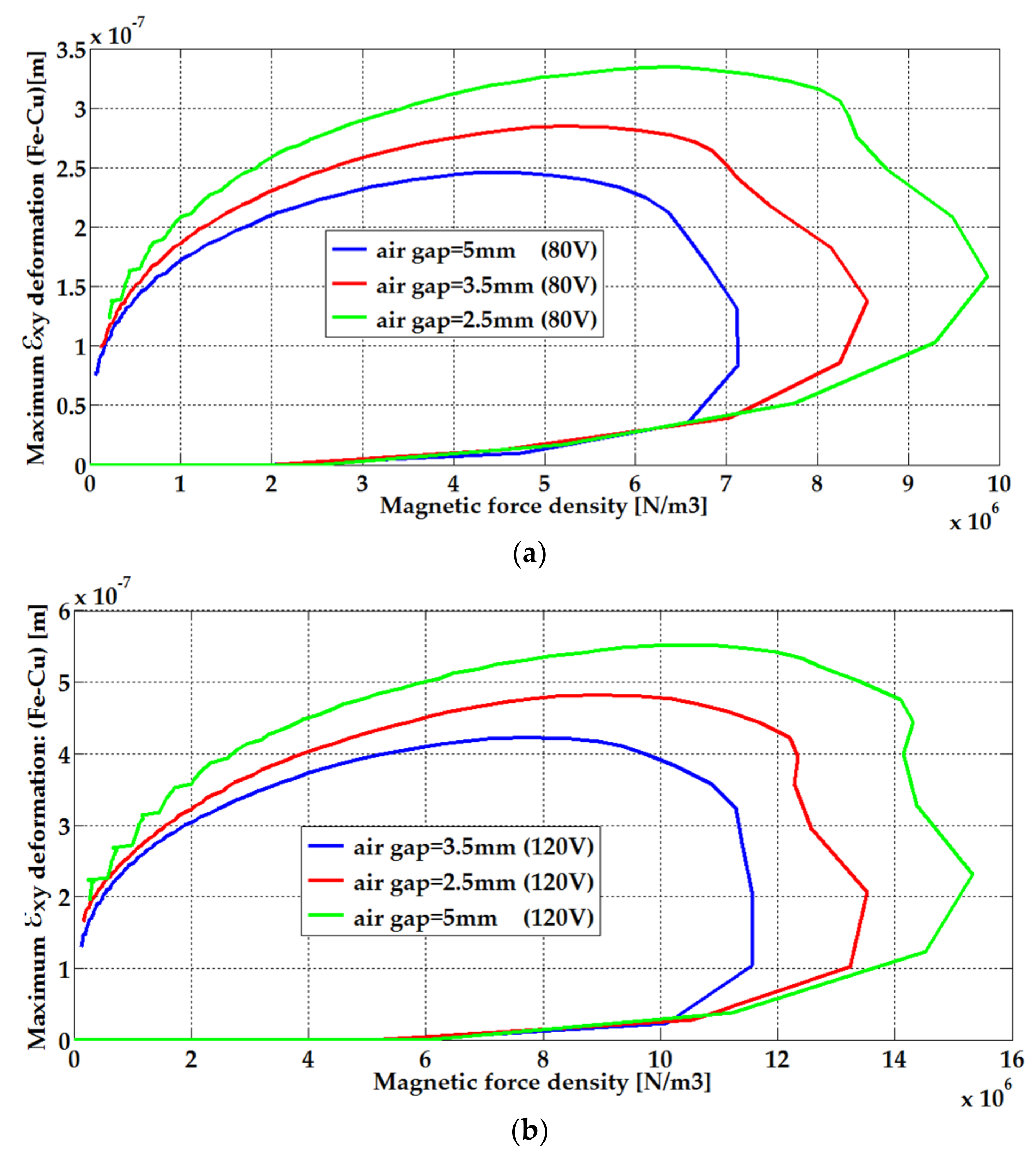
| Parameters | Plate Length (Lp) | Winding Width (Hw) | Winding Length (Lw) | Plate Thickness (e) | Air-Gap Thickness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value (mm) | 90 | 5 | 15 | 7 | 1–5 |
| Parameters | Young’s Modulus (E) | Poisson Ratio (υ) | Winding Resistance (Rc) | Winding Inductance (Lend) | Plate Electrical Conductivity (unit MS/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 200 kN/mm2 | 0.24 (Fe–Cu alloy) 0.33 (Vacofer S1) | 1 Ω | 5 mH | 9.1 (Fe–Cu alloy) 10.21 (Vacofer S1) |
| Air-Gap Thickness | Step Voltages | εxy Deformation (Peak Values) [µm] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| VacoferS1 | Fe-Cu Alloy | ||
| 5 mm | 80 V | 0.272 | 0.246 |
| 120 V | 0.465 | 0.423 | |
| 3.5 mm | 80 V | 0.307 | 0.285 |
| 120 V | 0.521 | 0.482 | |
| 2.5 mm | 80 V | 0.363 | 0.334 |
| 120 V | 0.602 | 0.552 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abba, F.; Rachek, M. Time-Stepping FEM-Based Multi-Level Coupling of Magnetic Field–Electric Circuit and Mechanical Structural Deformation Models Dedicated to the Analysis of Electromagnetic Actuators. Actuators 2019, 8, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/act8010022
Abba F, Rachek M. Time-Stepping FEM-Based Multi-Level Coupling of Magnetic Field–Electric Circuit and Mechanical Structural Deformation Models Dedicated to the Analysis of Electromagnetic Actuators. Actuators. 2019; 8(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/act8010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbba, Faiza, and M’hemed Rachek. 2019. "Time-Stepping FEM-Based Multi-Level Coupling of Magnetic Field–Electric Circuit and Mechanical Structural Deformation Models Dedicated to the Analysis of Electromagnetic Actuators" Actuators 8, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/act8010022
APA StyleAbba, F., & Rachek, M. (2019). Time-Stepping FEM-Based Multi-Level Coupling of Magnetic Field–Electric Circuit and Mechanical Structural Deformation Models Dedicated to the Analysis of Electromagnetic Actuators. Actuators, 8(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/act8010022




