Performance and Applications of L1B2 Ultrasonic Motors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
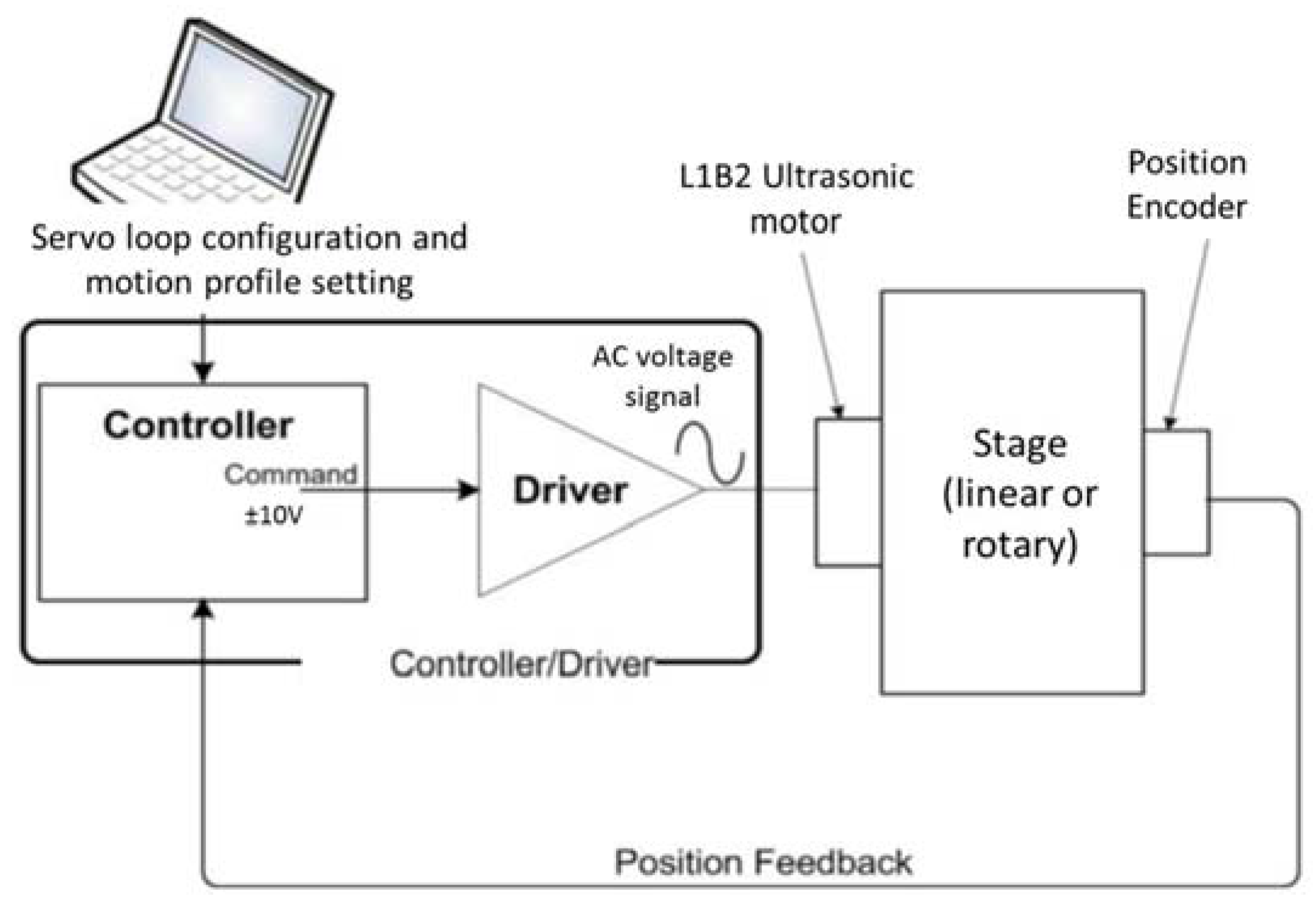
2. General Design of a Motion Solution
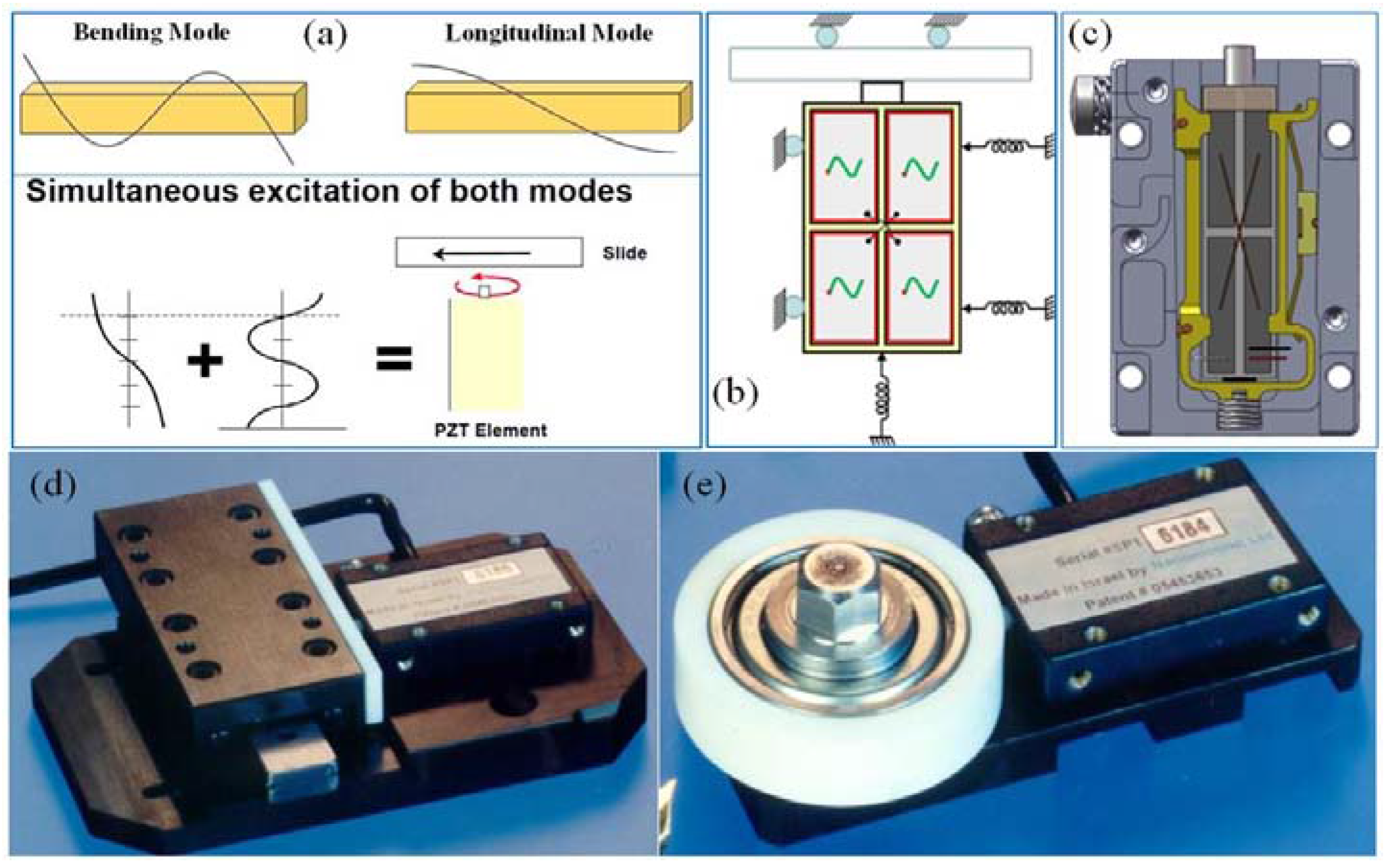
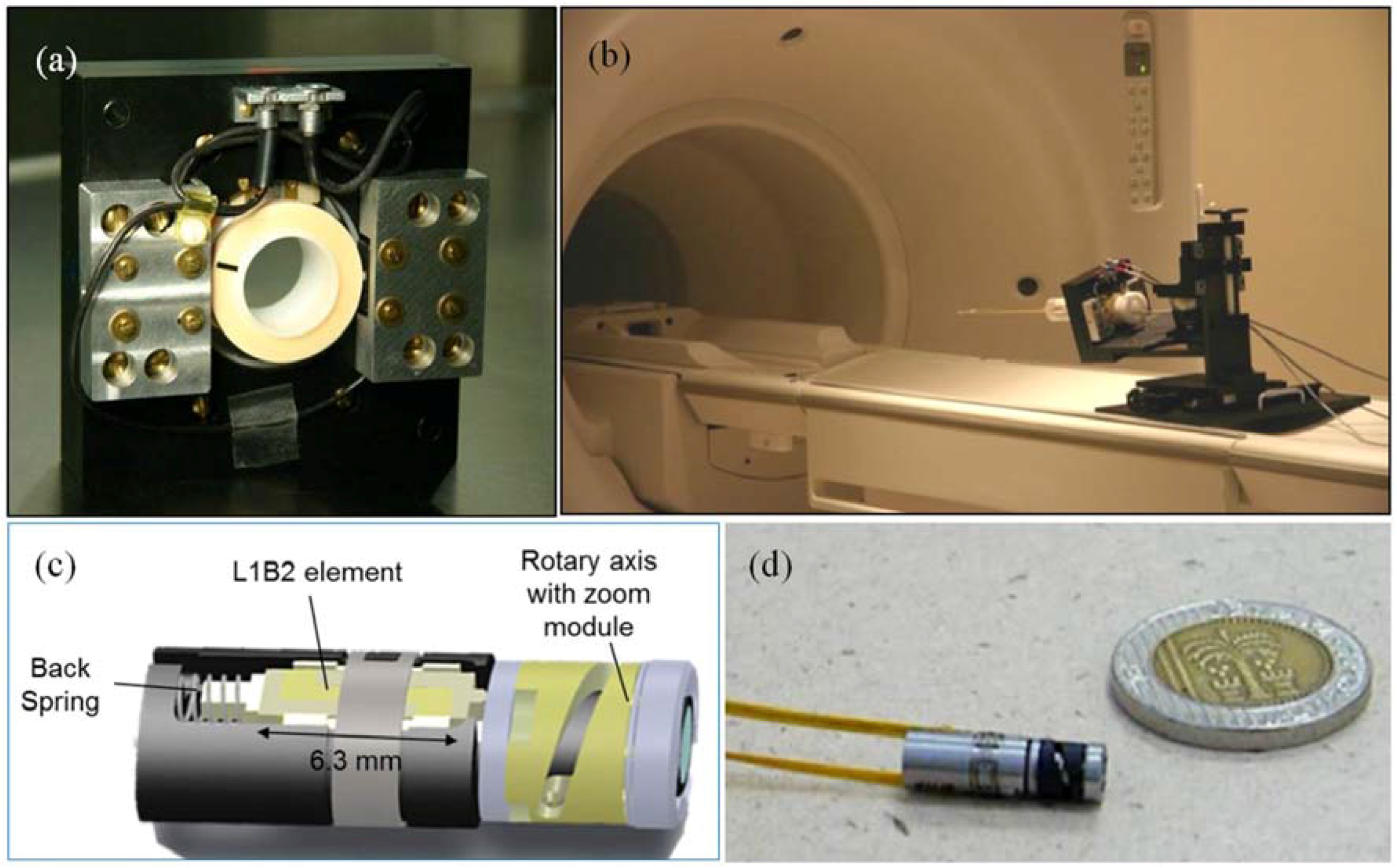
2.1. The L1B2 Motor
2.2. Motor Drive
2.3. Motion Control
3. Operational Conditions
3.1. Temperature Range
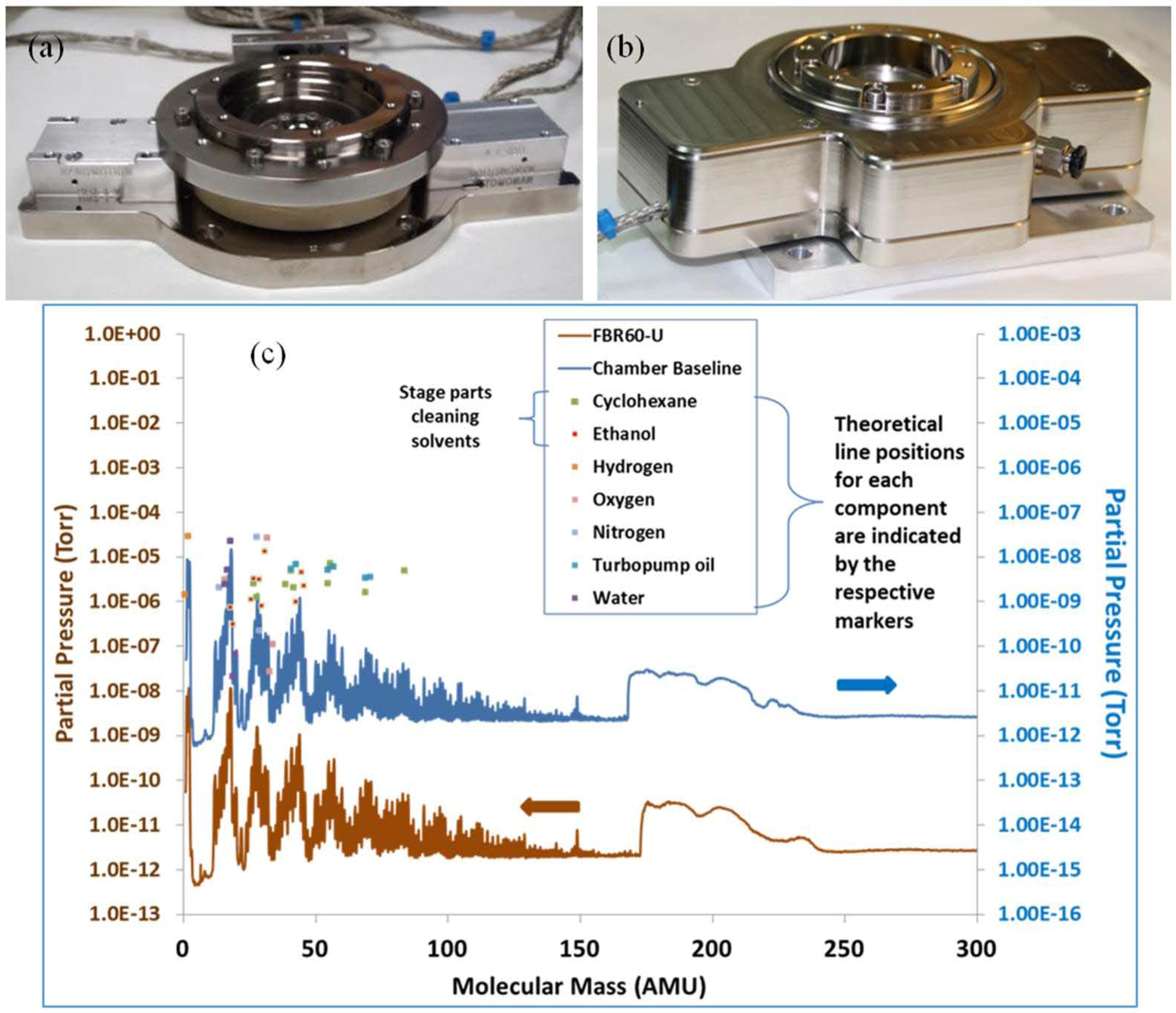
3.2. Vacuum Operation
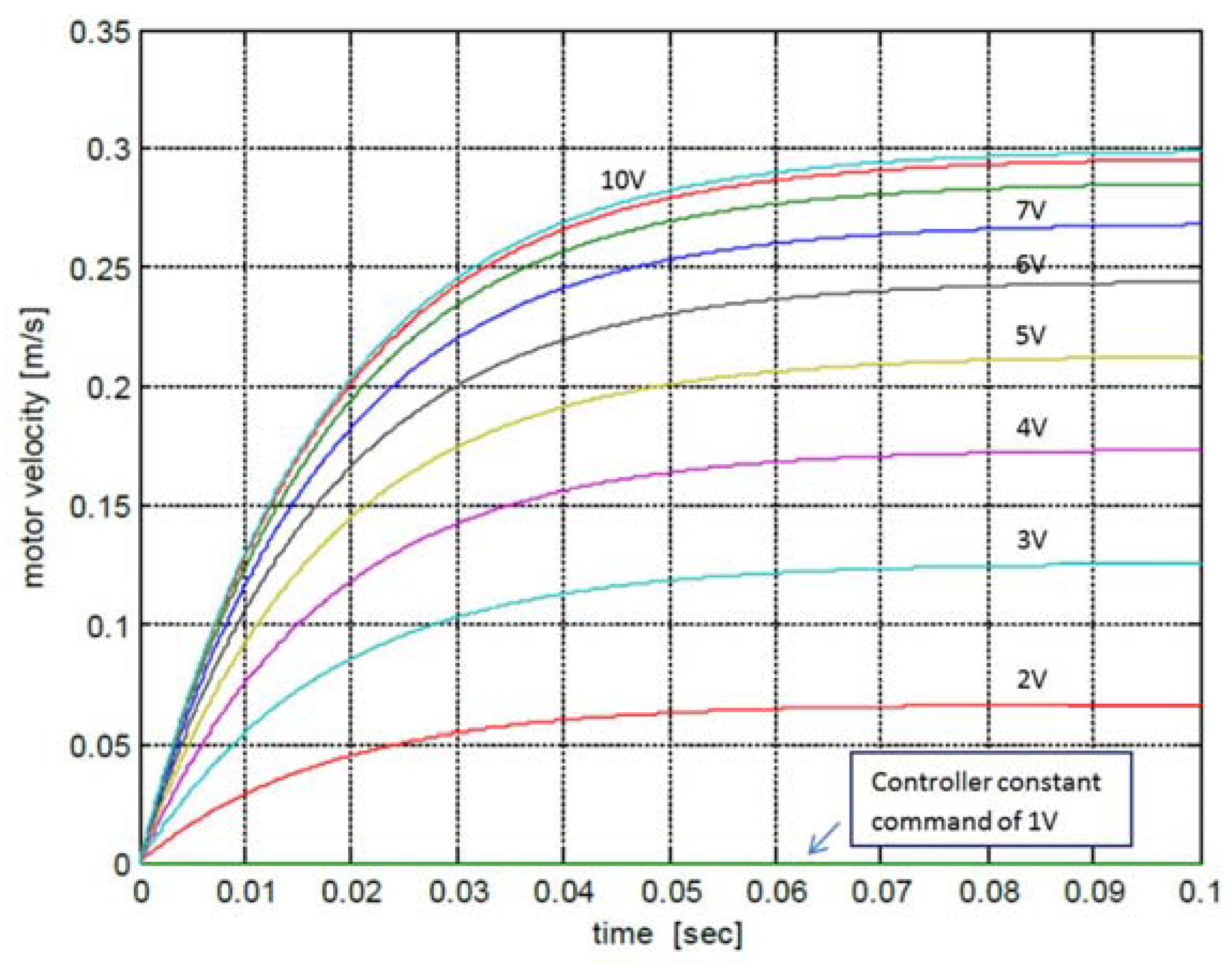
3.3. Envelope of Performance
3.4. Friction and Wear Considerations
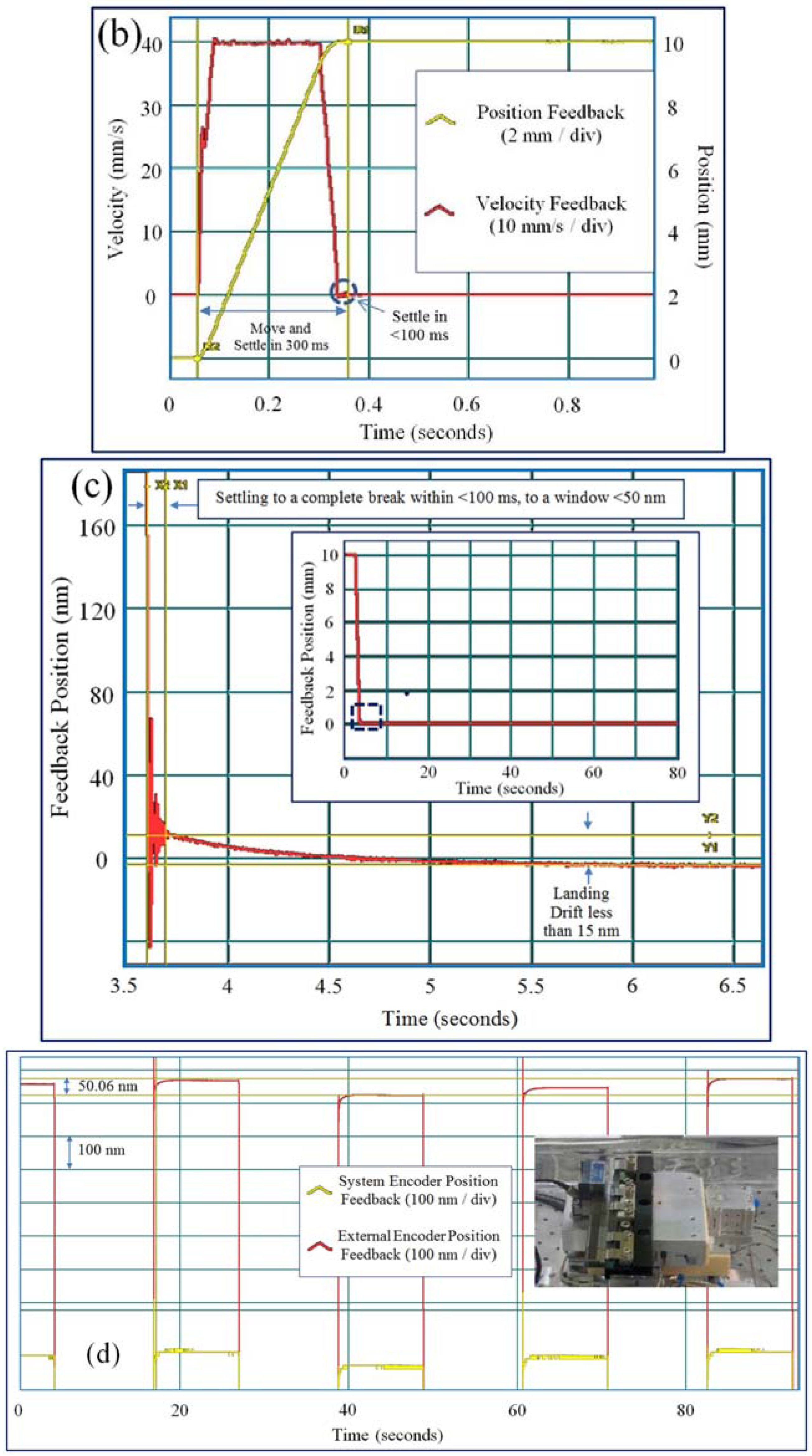
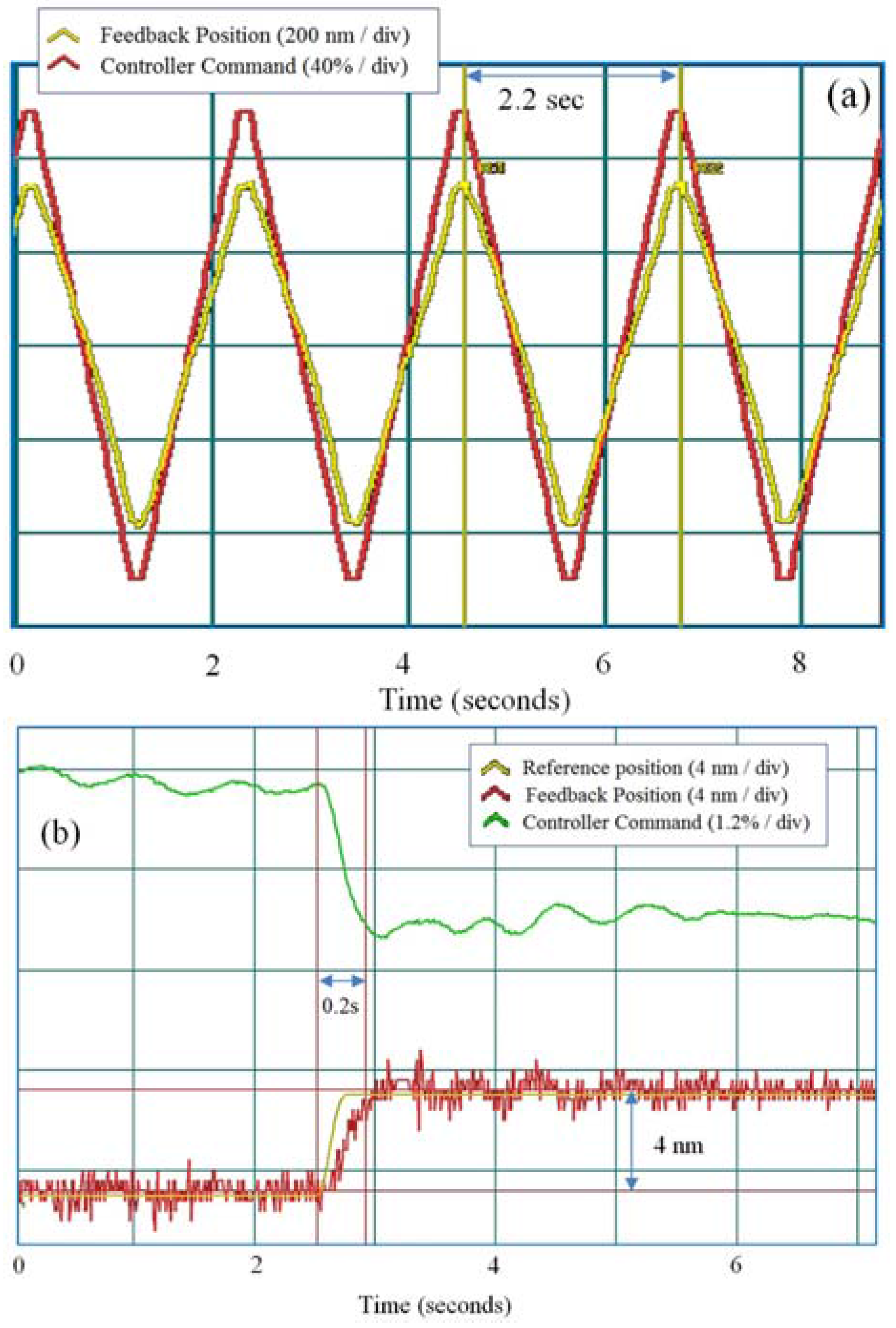
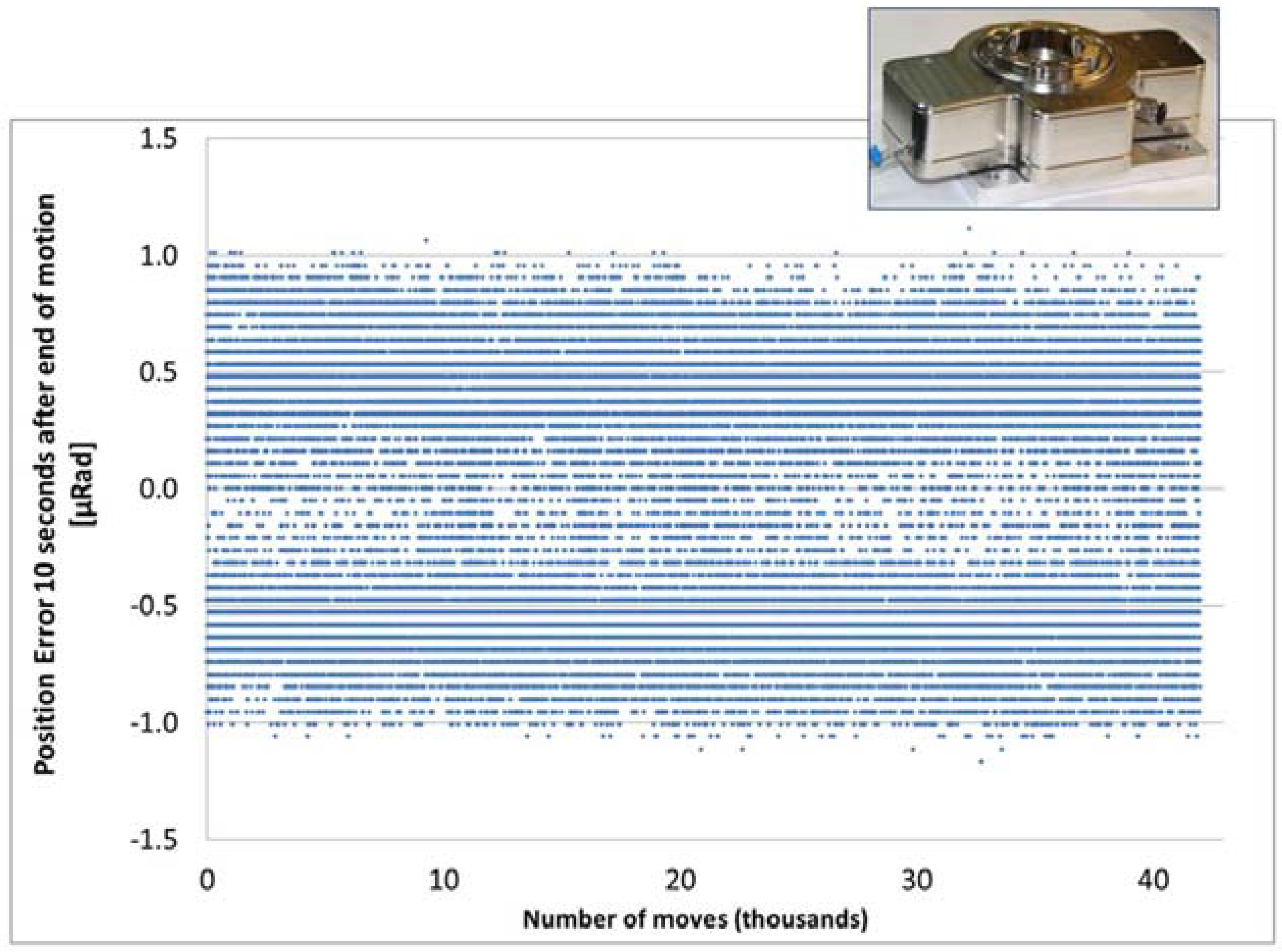
4. Positioning Accuracy
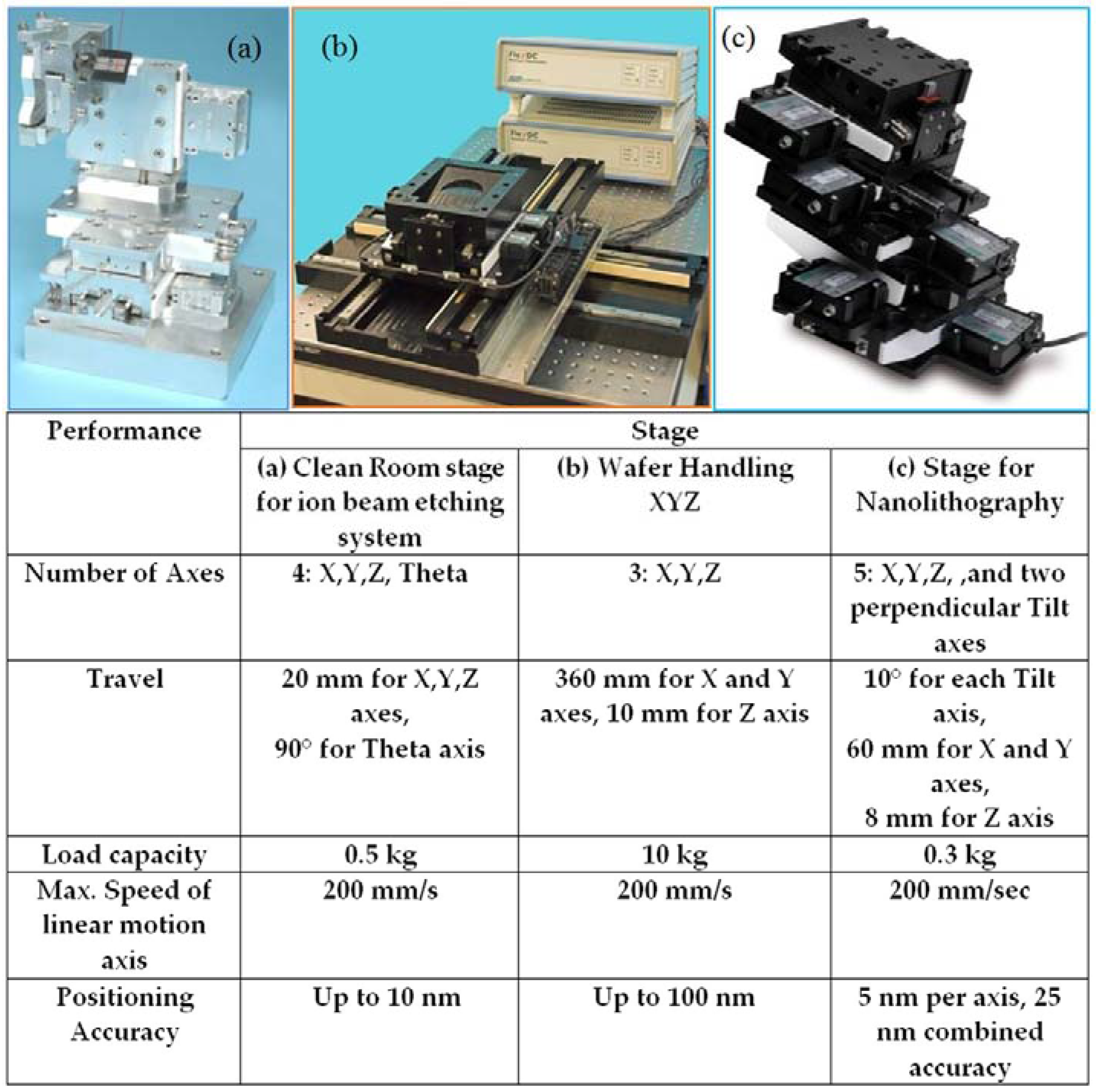
5. Examples of Motion Solutions
5.1. Vacuum Stages for Space Applications
5.2. Semiconductor Market
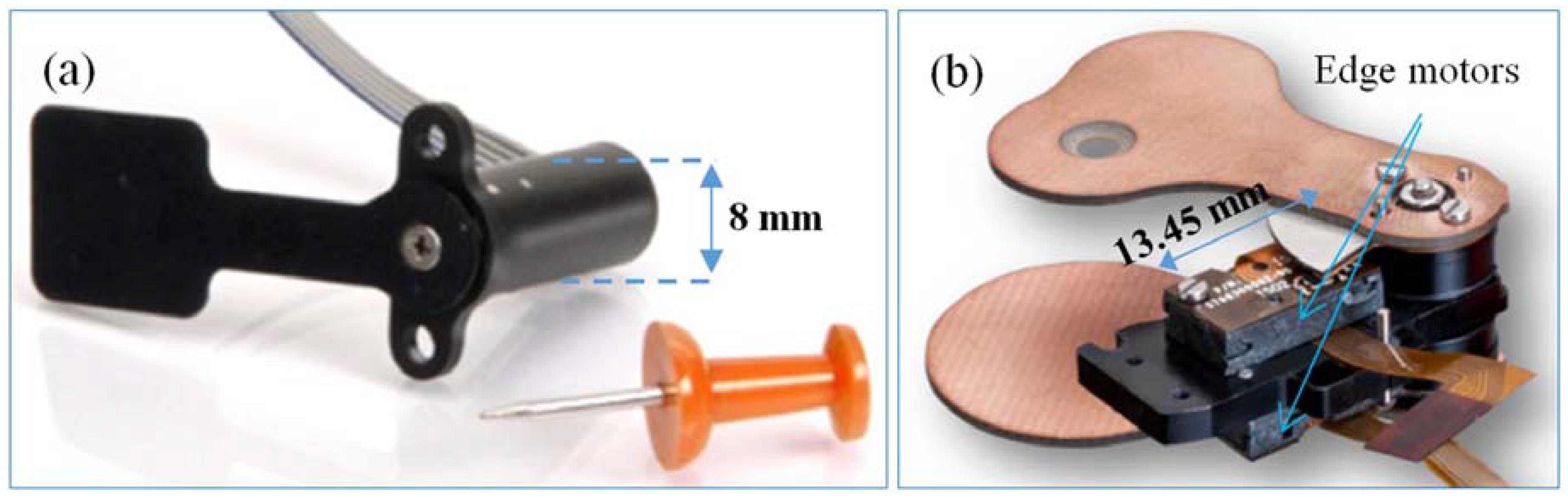
5.3. Biomedical Applications
5.4. Electro-Optics Modules
6. Summary
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uchino, K. Piezoelectric ultrasonic motor: Overview. Smart Mater. Struct. 1998, 7, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sashida, T.; Kenjo, T. An Introduction to Ultrasonic Motors; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Nanomotion Ltd. Motion Systems. Available online: http://www.nanomotion.com/product-type/motion-systems/ (accessed on 11 April 2016).
- Wiwattananon, P.; Bryant, R.G. Performance Comparisons and Down Selection of Small Motors for Two-Blade Heliogyro Solar Sail 6U CubeSat. NASA Technical Report NASA/TM–2015-218784. 2015. Available online: http://ntrs.nasa.gov/search.jsp?R=20150017043 (accessed on 11 April 2016). [Google Scholar]
- Uchino, K. Introduction to Piezoelectric Actuators and Transducers. Defense Technical Information Center Document ADA429659. 2003. Available online: http://www.dtic.mil/cgi-bin/GetTRDoc?AD=ADA429659 (accessed on 11 April 2016).
- Hemsel, T.; Mracek, M.; Twiefel, J.; Vasiljev, P. Piezoelectric linear motor concepts based on coupling of longitudinal vibrations. Ultrasonics 2006, 44, e591–e596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyagi, M.; Tomikawa, Y. Ultrasonic motor based on coupled longitudinal-bending vibrations of a diagonally symmetric piezoelectric ceramic plate. Electron. Commun. Jpn. 1996, 79, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.S.; Lee, C.H.; Hwang, S.H. Dynamic modeling and analysis of a bimodal ultrasonic motor. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2003, 50, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zumeris, J. Ceramic Motor. U.S. Patent No. 5,453,653, 26 September 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Ganor, Z.; Shiv, L.; Karasikov, N.; Avital, A. Piezoelectric Motors and Motor Driving Configurations. U.S. Patent No. 6,979,936 B1, 27 December 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tomikawa, Y.; Takano, T.; Umeda, H. Thin rotary and linear ultrasonic motors using a double-mode piezoelectric vibrator of the first longitudinal and second bending modes. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1992, 31, 3073–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Dong, S.; Ren, B.; Luo, H. A double-mode piezoelectric single-crystal ultrasonic micro-actuator. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2010, 57, 2596–2600. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Dong, S. A high-temperature double-mode piezoelectric ultrasonic linear motor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 072902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganor, Z.; Rafaeli, I.; Shiv, L.; Karasikov, N. Multilayer Piezoelectric Motor. U.S. Patent No. 7,075,211 B1, 11 July 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Nanomotion Ltd. AB1A Driver User Manual. Available online: http://www.nanomotion.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/AB1A458000-00-User-Manual-AB1A1.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2016).
- Nanomotion Ltd. AB5 and AB51 Drivers User Manual. Available online: http://www.nanomotion.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/AB05458200-02-User-Manual.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2016).
- Nanomotion Ltd. User Manual HR Motors. Available online: http://www.nanomotion.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/HR00458000-00-HR-Motor-User-Manual.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2016).
- Nanomotion Ltd. XCD Software Version 1.4.0.7. Available online: http://www.nanomotion.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/05/XCD-software-version-1-4-0-7.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2016).
- Outgassing Data for Selecting Spacecraft Materials Online. Available online: https://outgassing.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 11 April 2016).
- Ganor, Z. High Resolution Piezoelectric Motor. U.S. Patent No. 7,061,158 B2, 13 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- User Guide XCD-HR Controller/Drivers. Available online: http://www.nanomotion.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/XCDH458002-00-XCD-HR-Contr-Driver-UM_.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2016).
- Nanomotion Ltd. Edge Motor. Available online: http://www.nanomotion.com/motion-product/edge-motor/ (accessed on 11 April 2016).






| Material/Part | Weight Percent of the Motor |
|---|---|
| Low outgassing metals | 49.57 |
| Plastic | 2.71 |
| Wiring (insulation + copper strands) | 18.14 |
| Adhesive | 0.06 |
| Elastomer | 0.08 |
| Ceramics | 29.44 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peled, G.; Yasinov, R.; Karasikov, N. Performance and Applications of L1B2 Ultrasonic Motors. Actuators 2016, 5, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/act5020015
Peled G, Yasinov R, Karasikov N. Performance and Applications of L1B2 Ultrasonic Motors. Actuators. 2016; 5(2):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/act5020015
Chicago/Turabian StylePeled, Gal, Roman Yasinov, and Nir Karasikov. 2016. "Performance and Applications of L1B2 Ultrasonic Motors" Actuators 5, no. 2: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/act5020015
APA StylePeled, G., Yasinov, R., & Karasikov, N. (2016). Performance and Applications of L1B2 Ultrasonic Motors. Actuators, 5(2), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/act5020015






