Adaptive Piezoelectric Absorber for Active Vibration Control
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Adaptive Absorbers and Neutralizers
3. Design of the Adaptive Piezoelectric Absorber
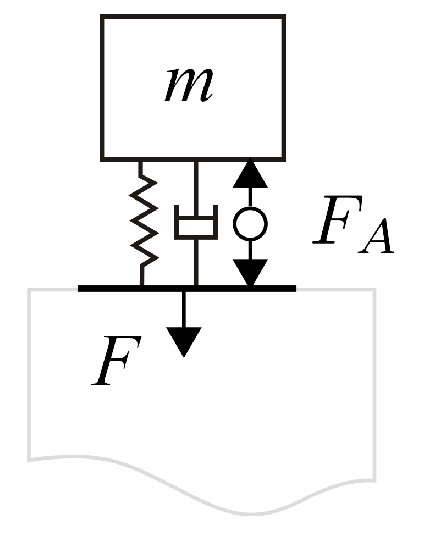
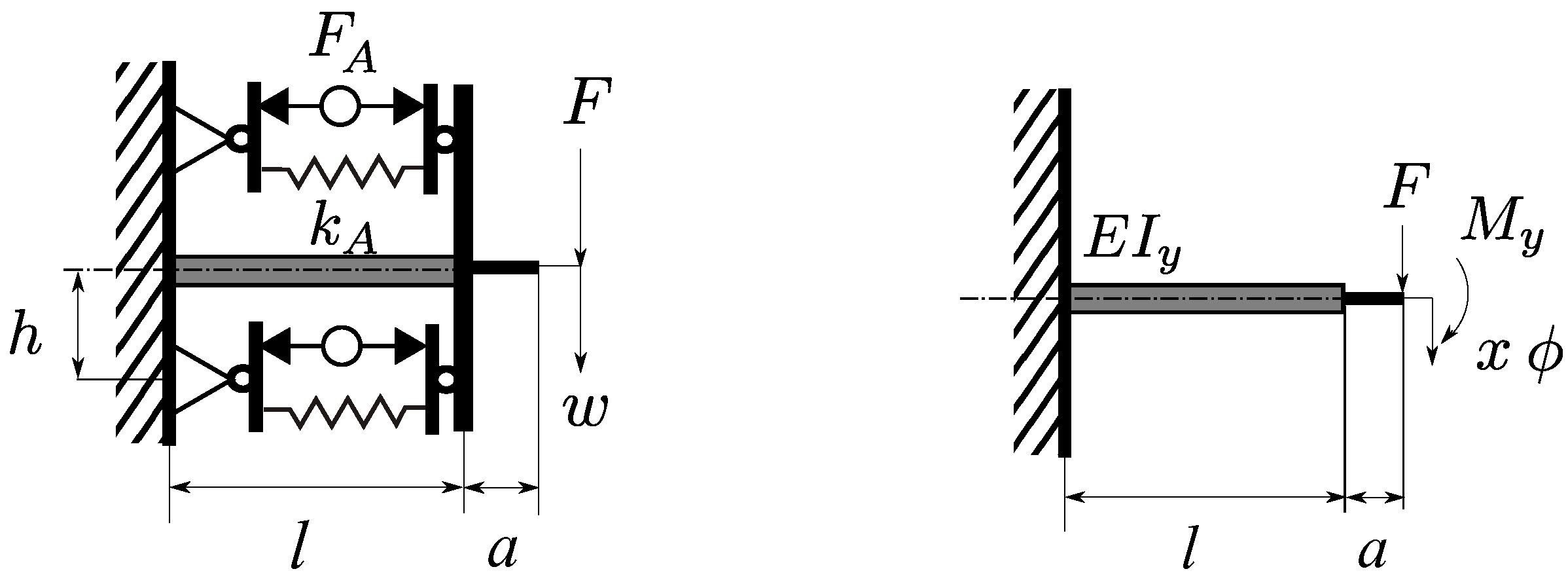
3.1. Basic Equations
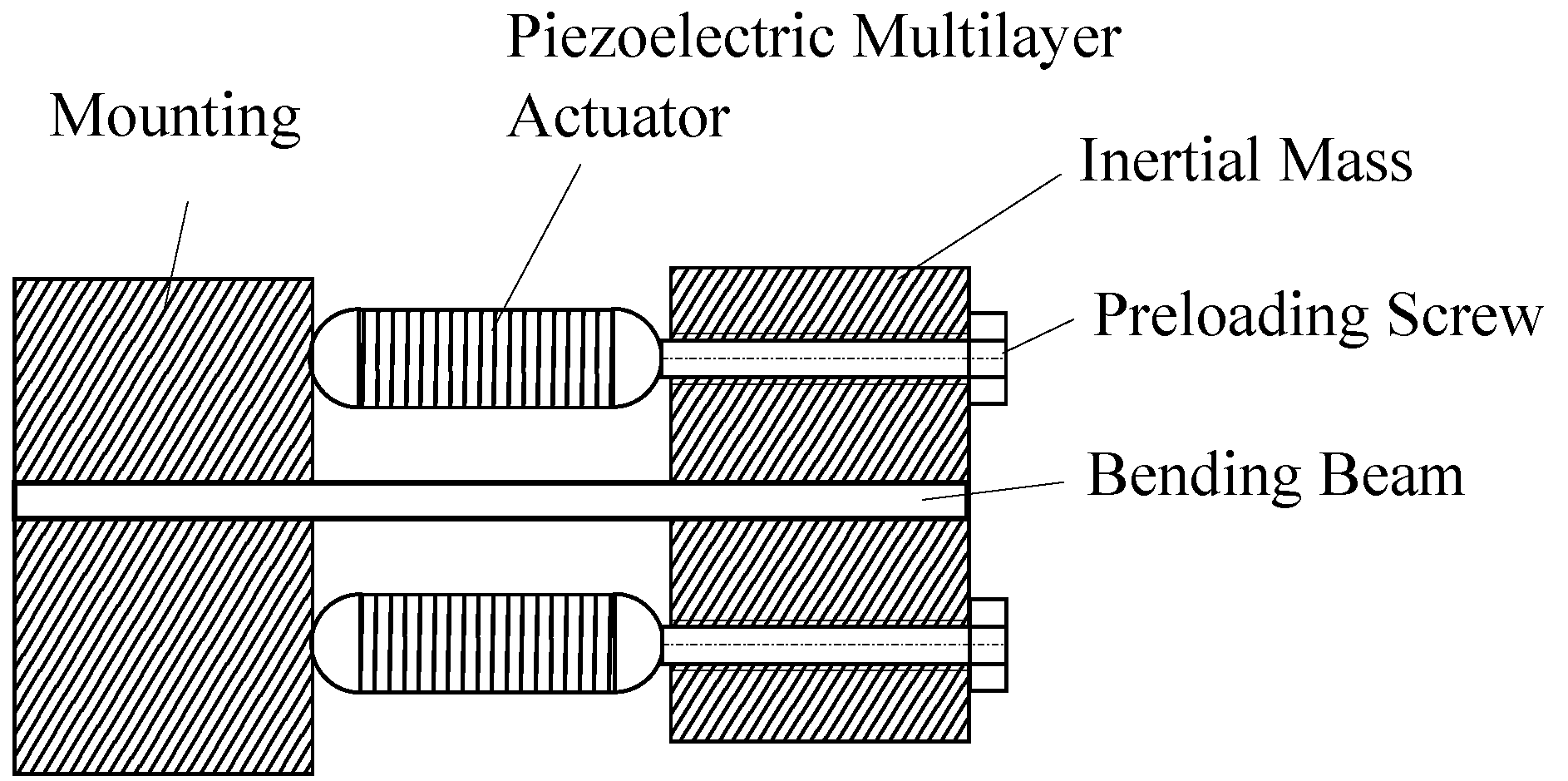
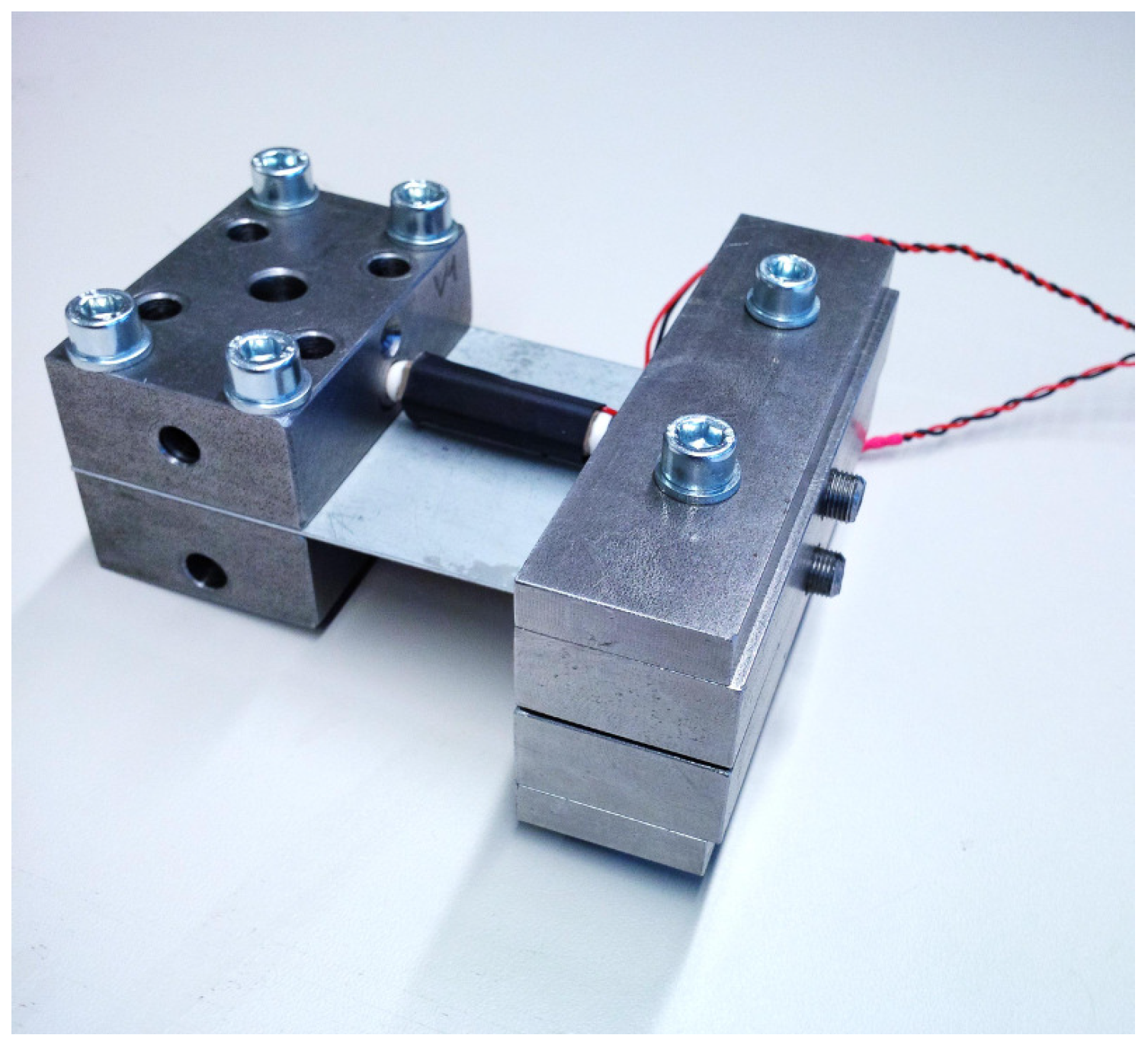
3.2. Mechanical Design of the Adaptive Absorber
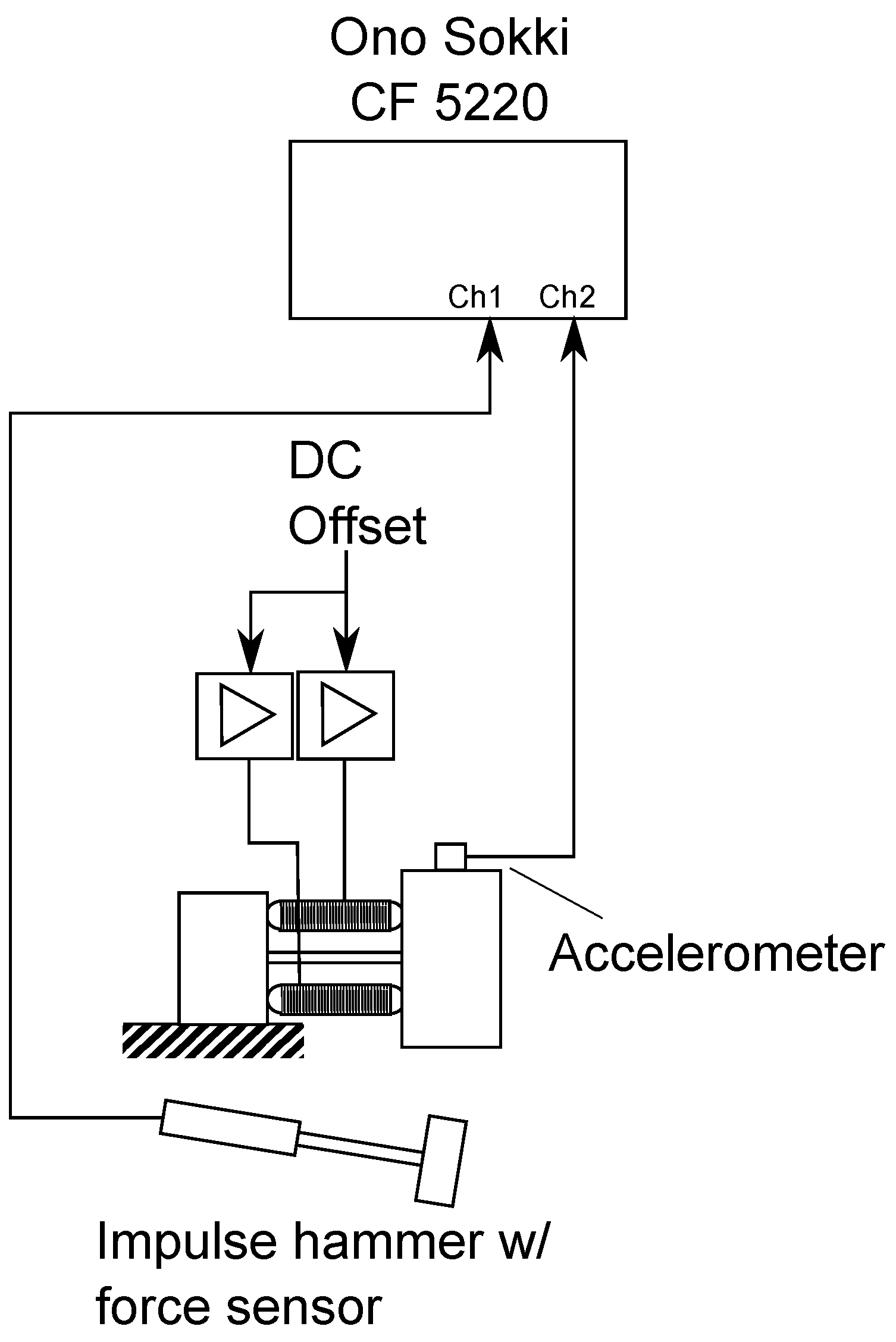
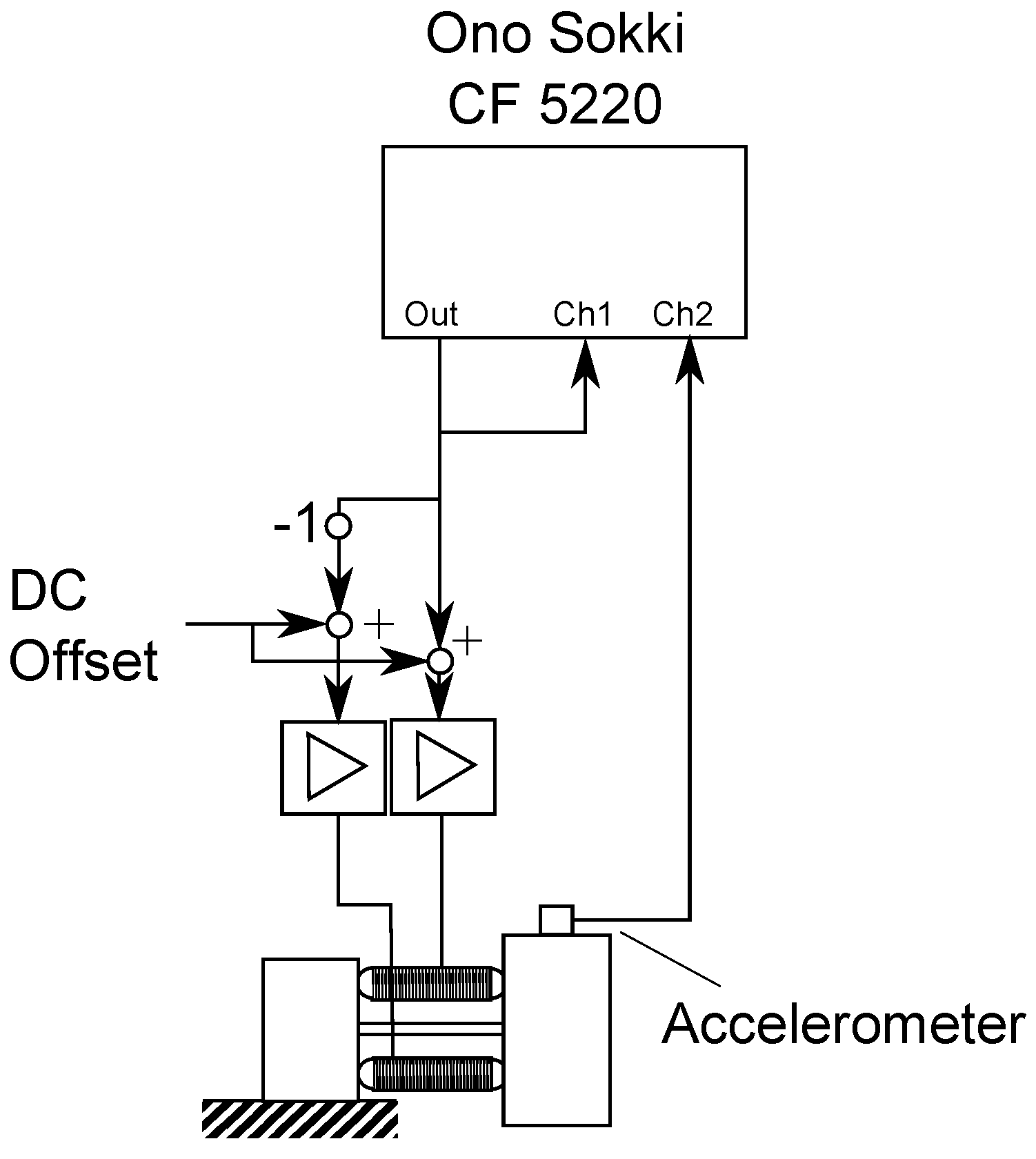
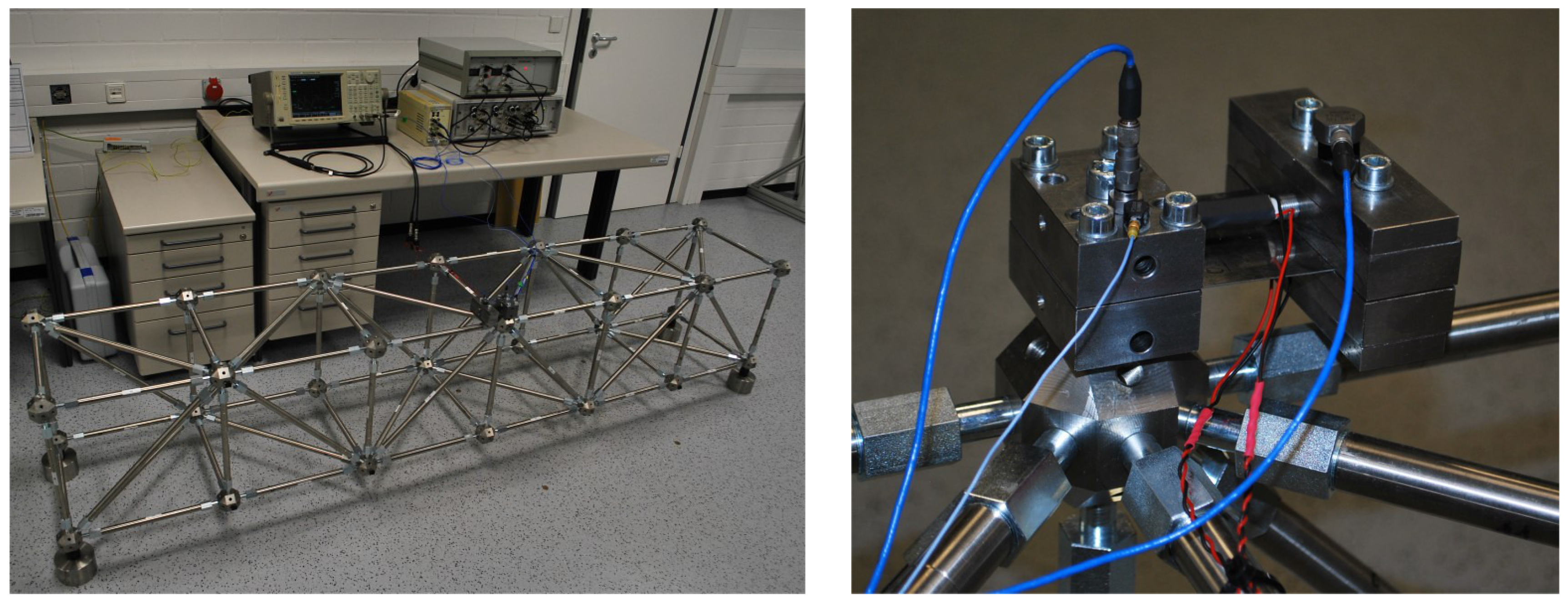
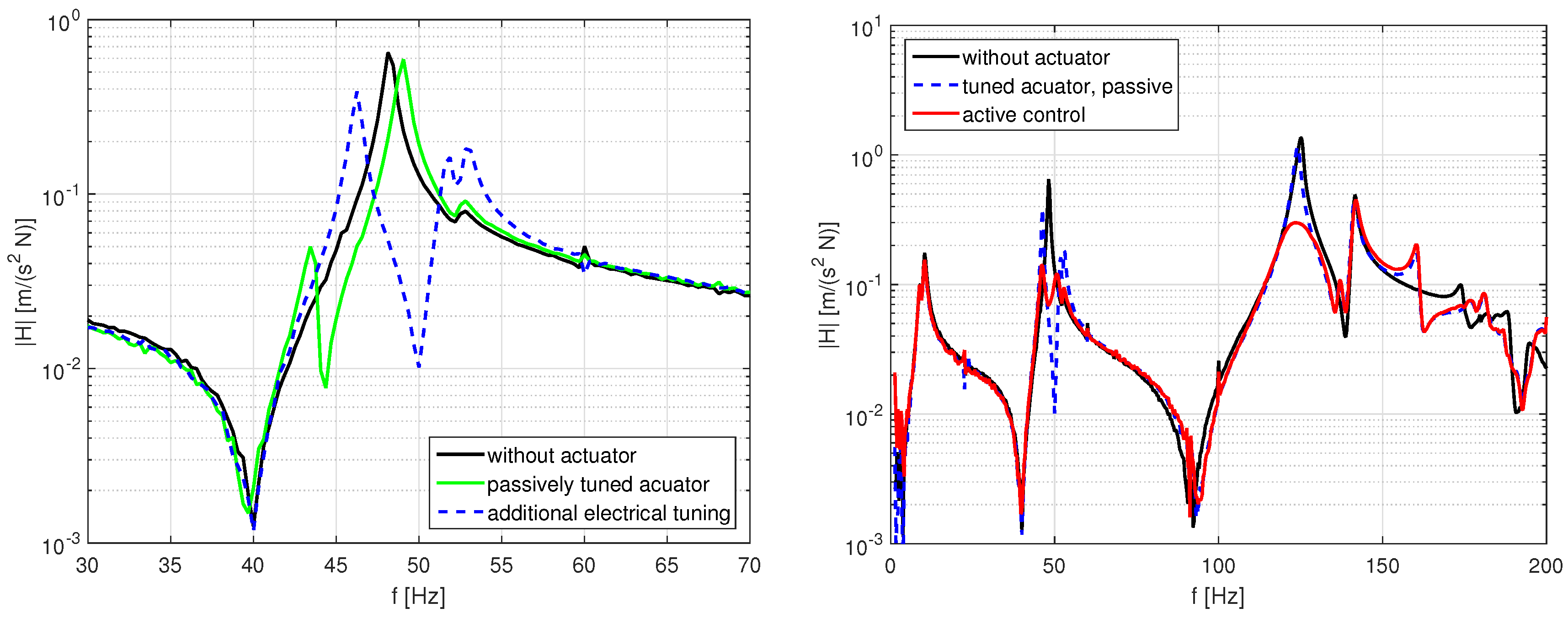
4. Experimental Validation
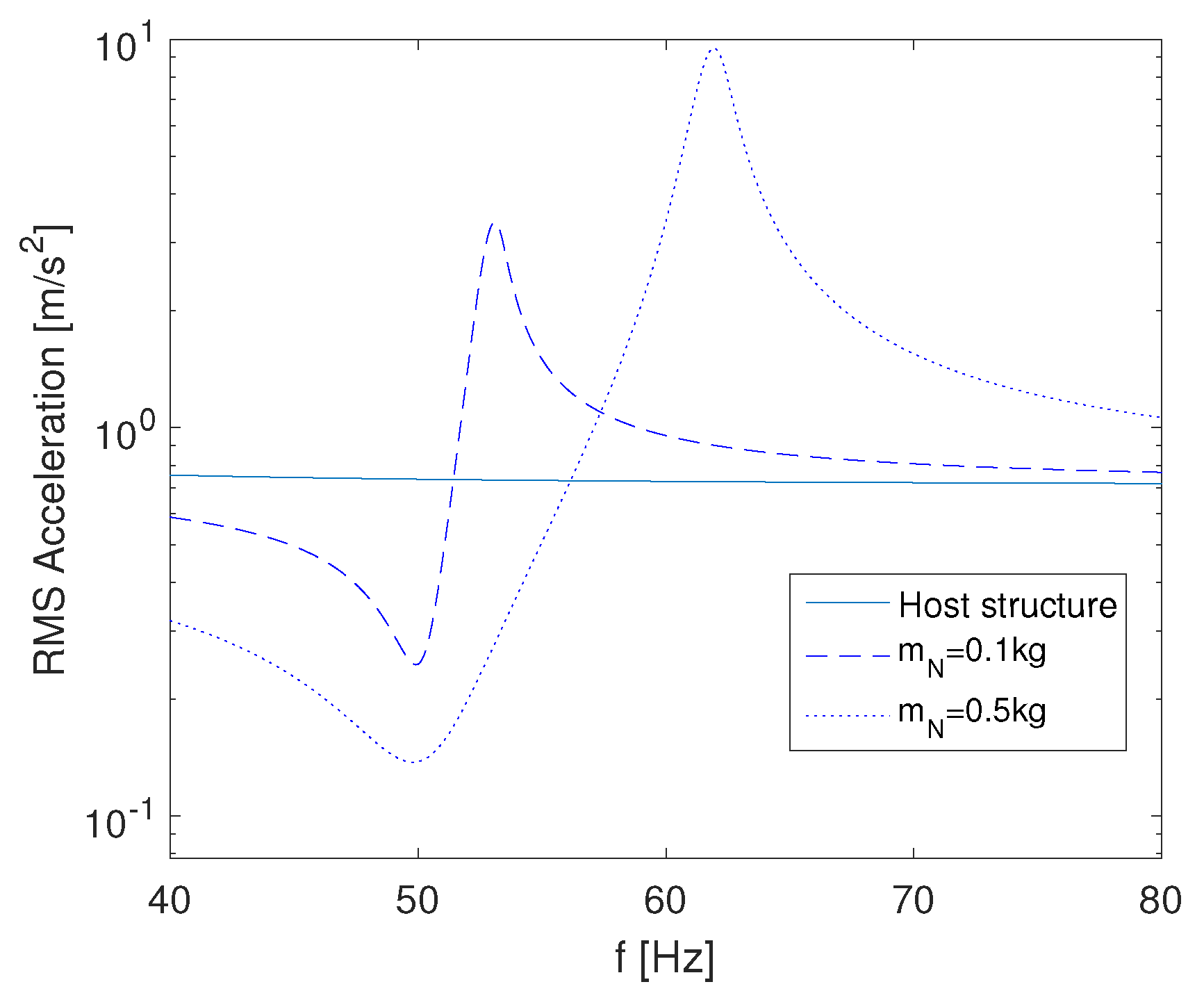
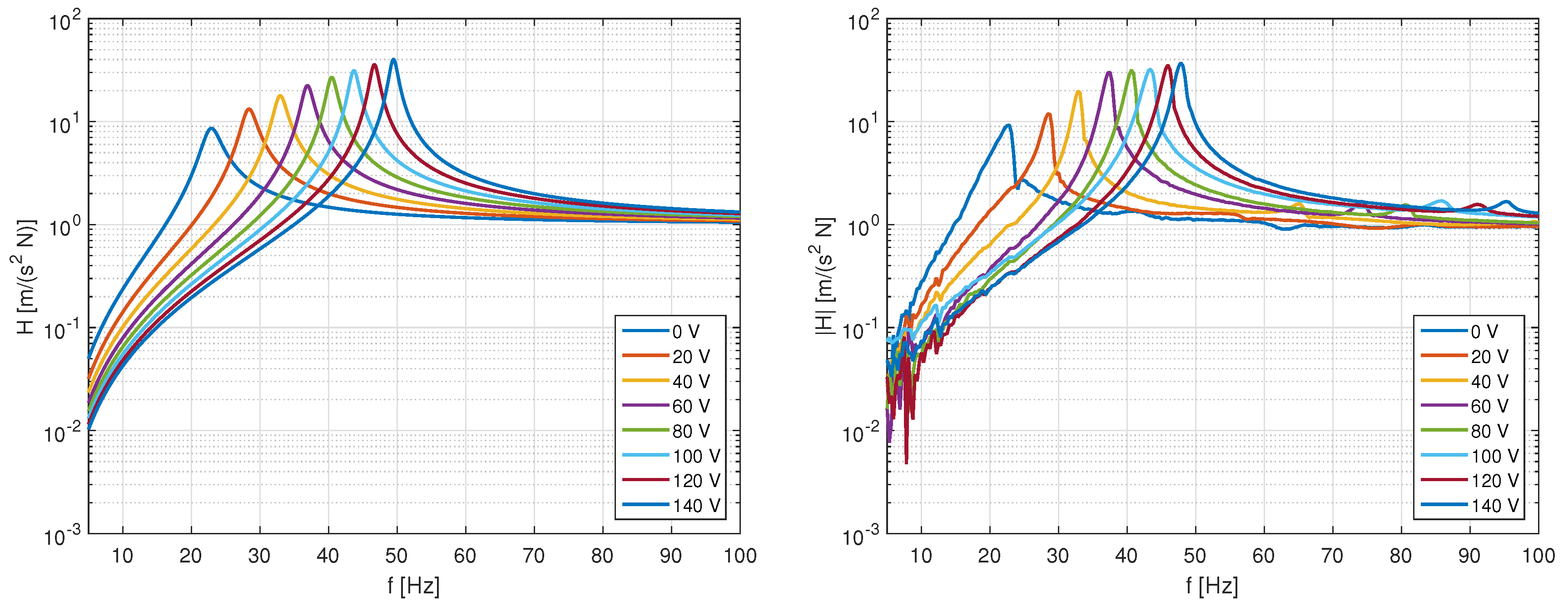
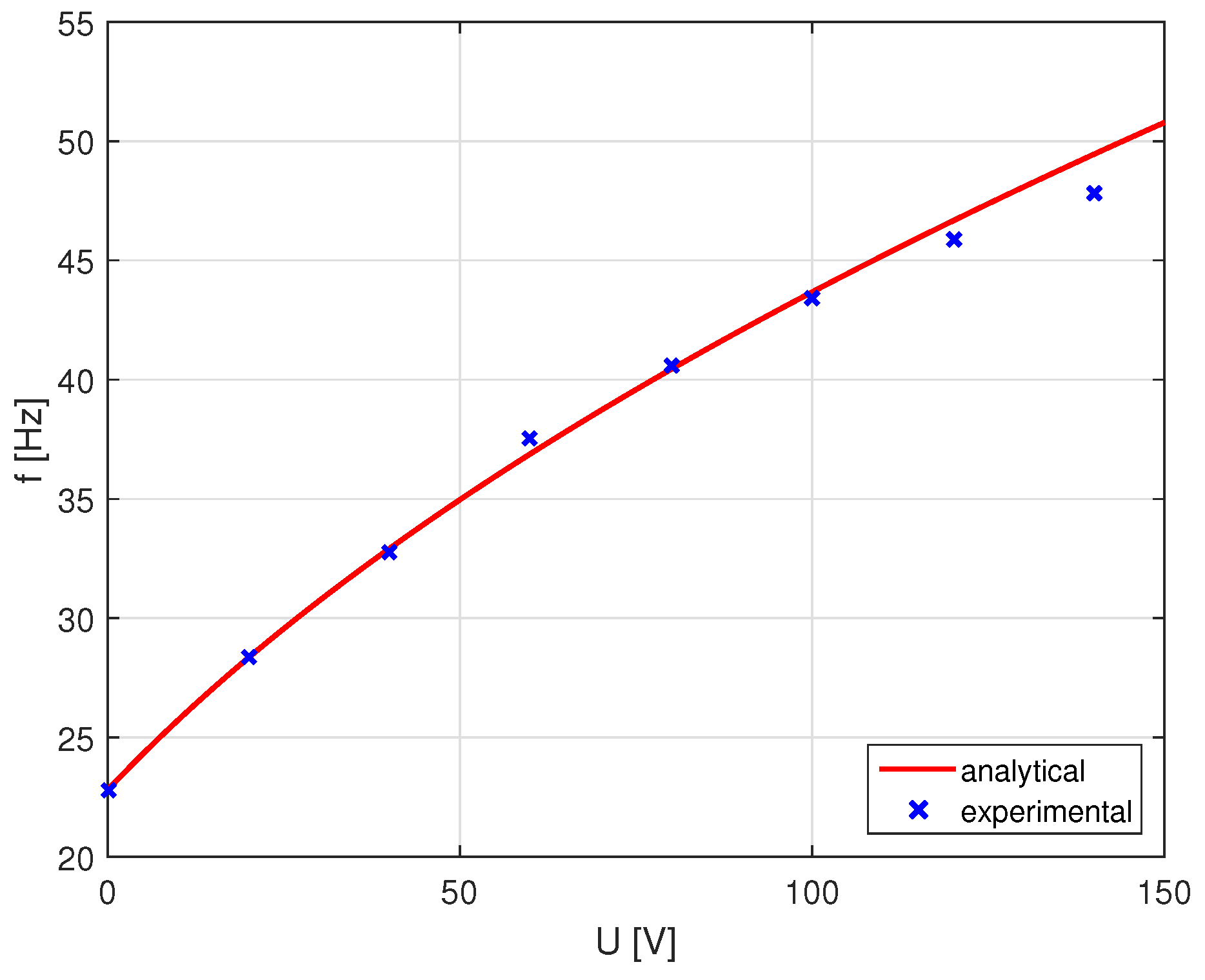
4.1. Analysis of the Adaptive Absorber Characteristics
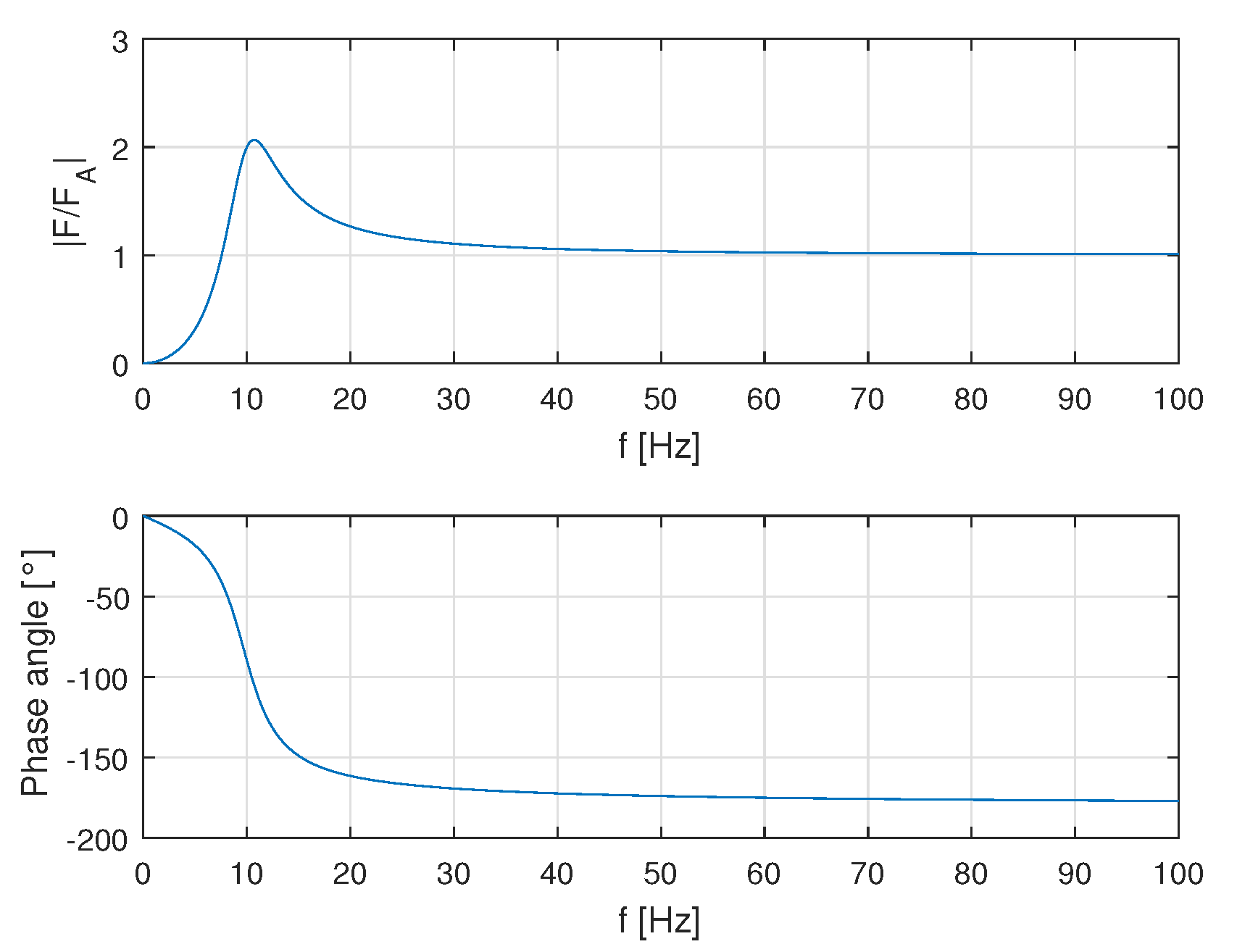
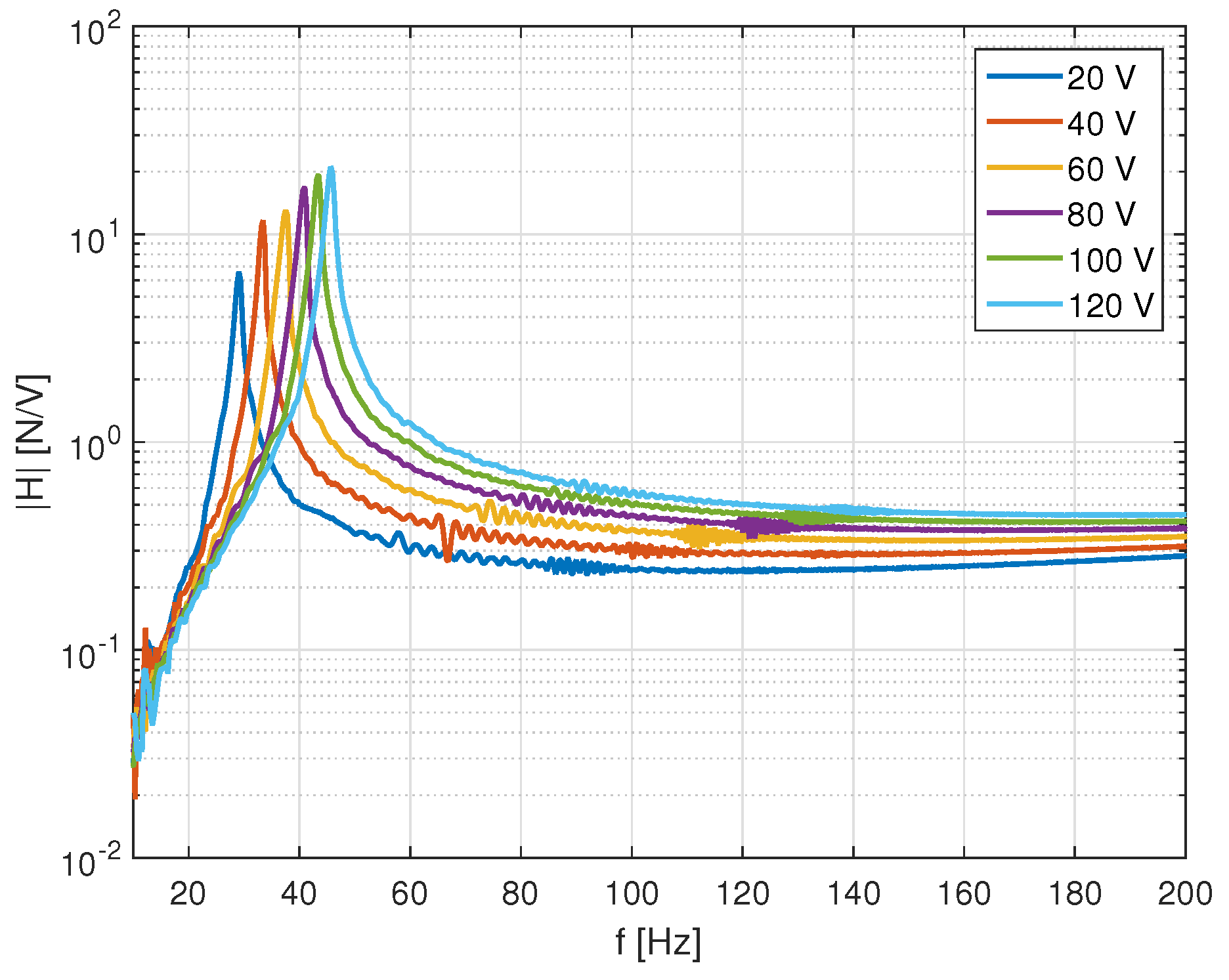
4.2. Inertial Mass Actuator Performance
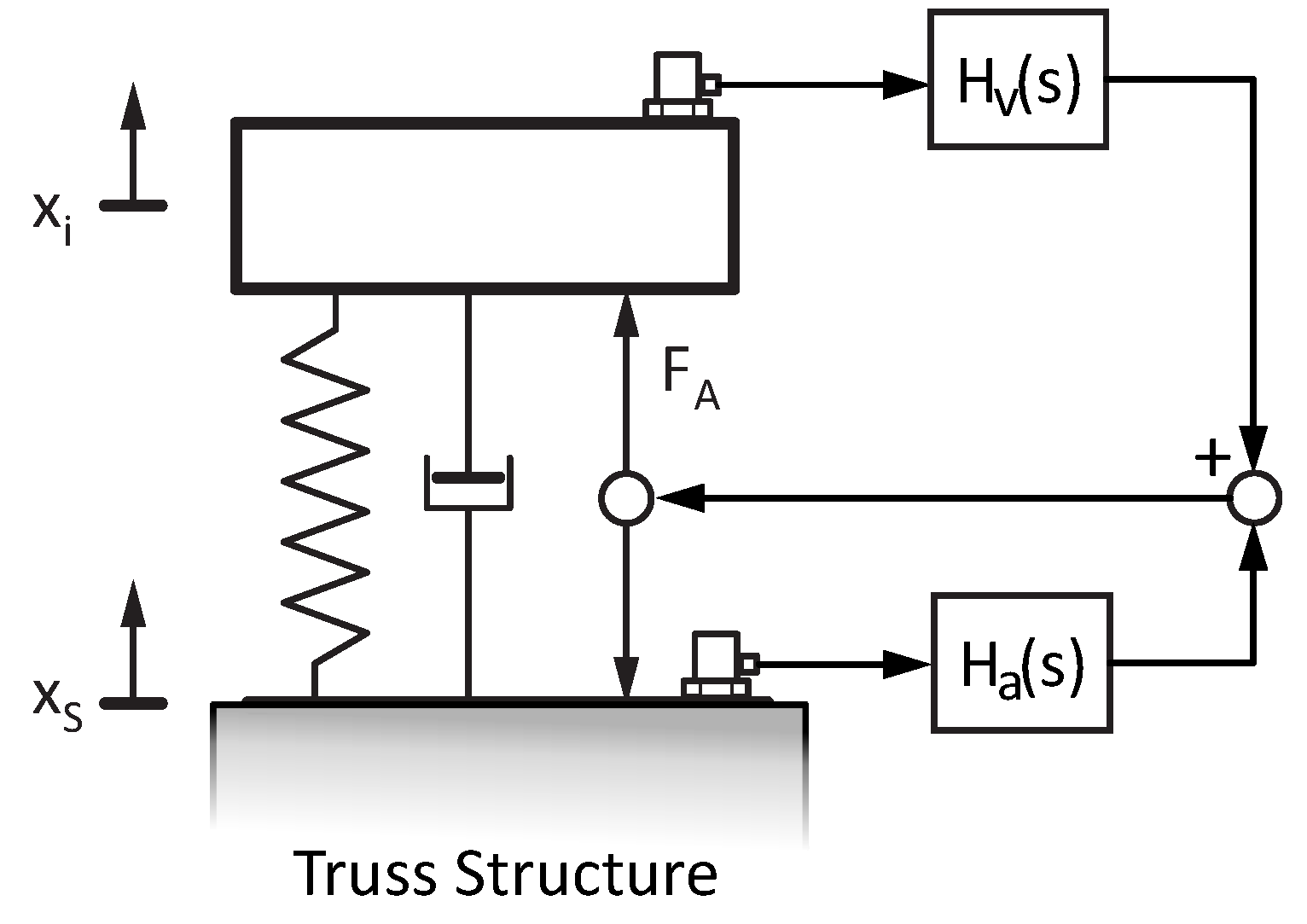
5. Application to an Active Vibration Control System
6. Results and Discussion
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frahm, H. Device for damping vibrations of bodies. US Patent 989,958, 18 April 1911. [Google Scholar]
- Brennan, M.J. Some Recent Developments in Adaptive Tuned Vibration Absorbers/Neutralisers. Shock Vib. 2006, 13, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.I.; Kidner, M.R.F. Vibration Absorbers: A Review of Applications in Interior Noise Control of Propeller Aircraft. J. Vib. Control 2004, 10, 1221–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonello, P. Adaptive Tuned Vibration Absorbers: Design Principles, Concepts and Physical Implementation. In Vibration Analysis and Control - New Trends and Developments; Beltran-Carbajal, F., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, D.; Pfeiffer, T.; Vrbata, J.; Melz, T. Adaptive-passive vibration control systems for industrial applications. Proc. SPIE 2015, 9433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winberg, M.; Johansson, S.; Claesson, I. Inertial mass actuators, understanding and tuning. In Proceedings of the ICSV 11, St. Petersburg, Russia, 5–8 July 2004.
- Konstanzer, P.; Grünewald, M.; Jänker, P.; Storm, S. Piezo Tuneable Vibration Absorber System for Aircraft Interior Noise Reduction. In Proceedings of the Euronoise 2006, Tampere, Finland, 30 May–1 June 2006.
- Herold, S.; Mayer, D.; Melz, T.; Röglin, T. Design and Test of a Piezoelectric Inertial Mass Actuator for Active Vibration Control. In Vibration Engineering and Technology of Machinery; Sinha, J., Ed.; Mechanisms and Machine Science, Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 23, pp. 587–597. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, D.; Kauba, M.; Herold, S.; Koch, T. Approaches for distributed active and passive vibration compensation. In Proceedings of the ISMA 2010, 24th International Conference on Noise and Vibration Engineering, Leuven, Belgium, 20–22 September 2010; p. 13.
- Hagood, N.W.; Crawley, E.F. Experimental investigation into passive damping enhancement for space structures. J. Guidance Control Dyn. 1991, 14, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preumont, A. Vibration Control of Active Structures; Springer: Dordrecht, Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Crawley, E.F.; Luis, J.D. Use of piezoelectric actuators as elements of intelligent structures. AIAA J. 1987, 25, 1373–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjeddou, A. Advances in piezoelectric finite element modeling of adaptive structural elements: A survey. Comput. Struct. 2000, 76, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruschmeyer, K. Piezokeramik: Grundlagen, Werkstoffe, Applikationen; Expert-Verl.: Renningen-Malmsheim, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Herold, S.; Mayer, D.; Hanselka, H. Transient Simulation of Adaptive Structures. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2004, 15, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, S.; Atzrodt, H.; Mayer, D.; Thomaier, M. Modeling approaches for active systems. Proc. SPIE 2006, 6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, S. Signal Processing for Active Control; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]

| Concept | Static Pre-Stress | Variable Geometry | Dynamic Forces |
|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |
| Actuator type | Static, high force | Static, high stroke | Dynamic force |
| Examples | Piezoelectric | Motor, shape memory alloys | Piezoelectric, electrodynamic |
| Energy Supply | Continuously | During adaptation | Continuously |
| Quantity | Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| beam | |||
| length | l | ||
| width | b | 60 | |
| thickness | d | ||
| Young’s modulus | E | ||
| mass | |||
| mass | m | ||
| actuator | |||
| stiffness | |||
| max. block force | 2000 | ||
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herold, S.; Mayer, D. Adaptive Piezoelectric Absorber for Active Vibration Control. Actuators 2016, 5, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/act5010007
Herold S, Mayer D. Adaptive Piezoelectric Absorber for Active Vibration Control. Actuators. 2016; 5(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/act5010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerold, Sven, and Dirk Mayer. 2016. "Adaptive Piezoelectric Absorber for Active Vibration Control" Actuators 5, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/act5010007
APA StyleHerold, S., & Mayer, D. (2016). Adaptive Piezoelectric Absorber for Active Vibration Control. Actuators, 5(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/act5010007





