Modeling of a Dielectric Elastomer Bender Actuator
Abstract
:1. Introduction
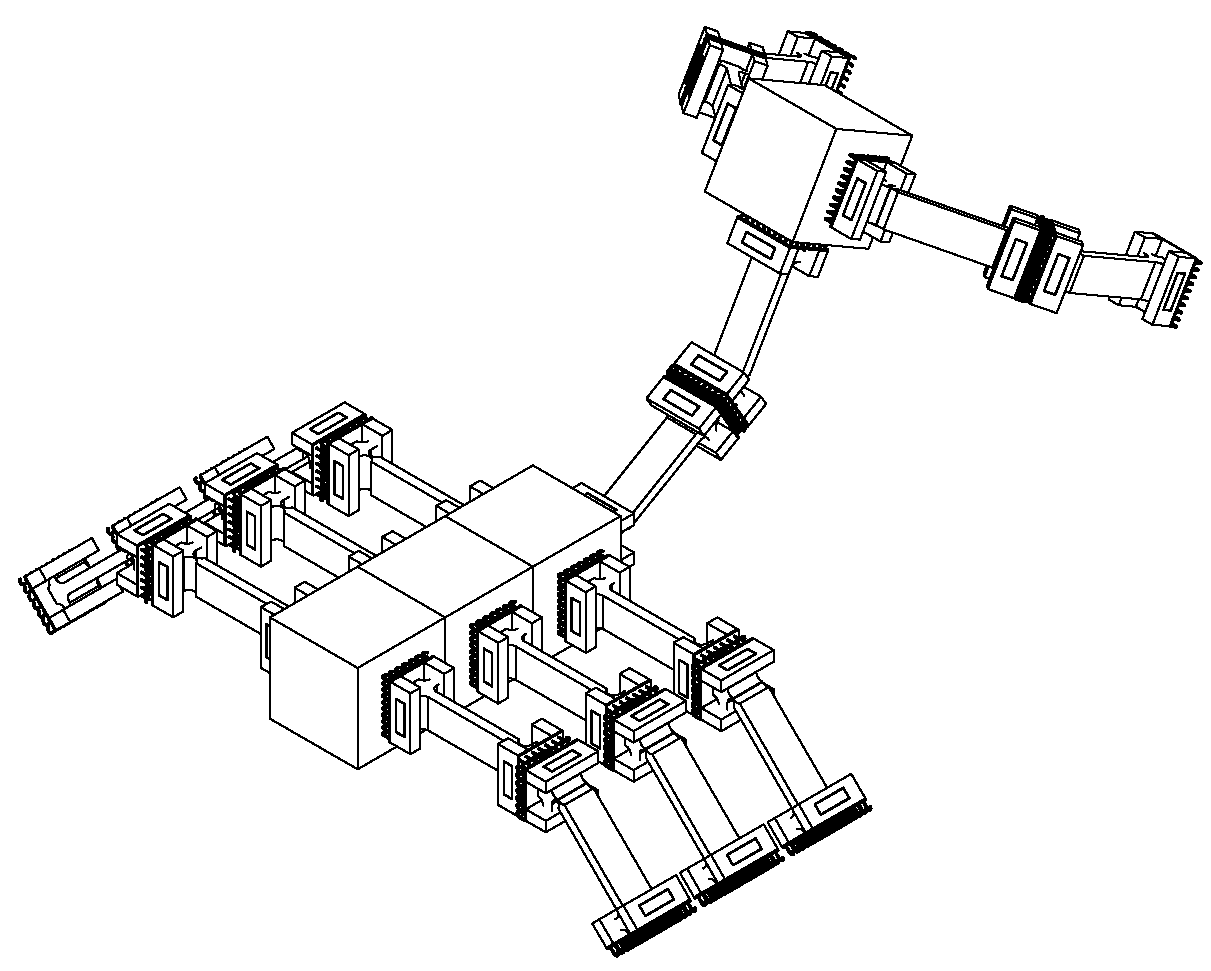
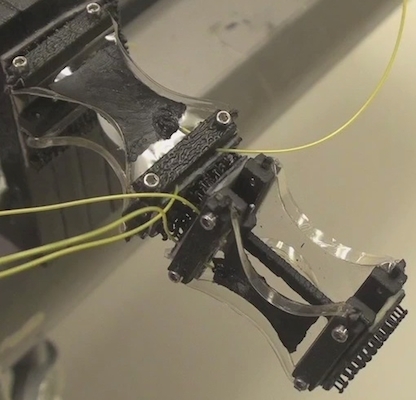
2. Miniaturization Study
2.1. Module Performance Metrics
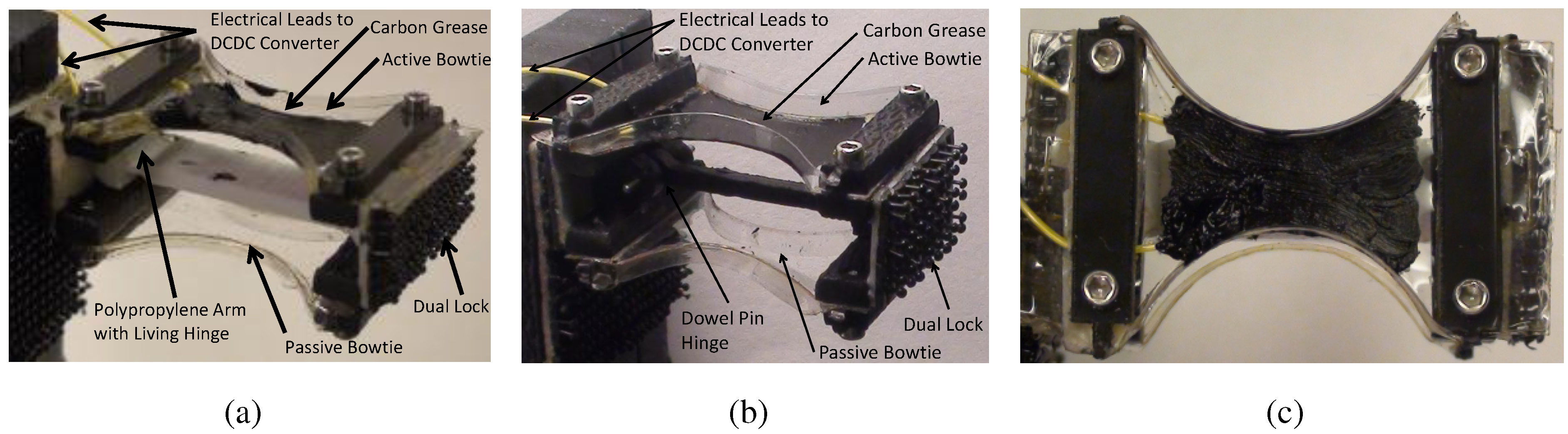
2.2. Actuator Comparison
| Max Strain | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Actuator | Ref. | (Nm/kg) | (%) |
| Shape Memory Alloy | [23] | 780 | 8 |
| Dielectric Elastomer (Acrylic) | [17,24] | 3,300 | 215 |
| Dielectric Elastomer (Silicone) | [17,24] | 320 | 63 |
| Relaxor Ferroelectric Polymer | [25] | 720 | 7 |
| Piezoelectric Stack (PZT) | [26,27] | 5 | 0.2 |
| Piezoelectric Bender (PZT) | [28] | 3.5 | 0.2 |
| Brushless DC Motor | [29] | 0.1 | ∞ |
2.3. Dielectric Elastomer Actuator
2.4. Agonist-Antagonist Benders
2.5. Modeling
3. Module: Materials and Methods
3.1. DEA Linear Actuator
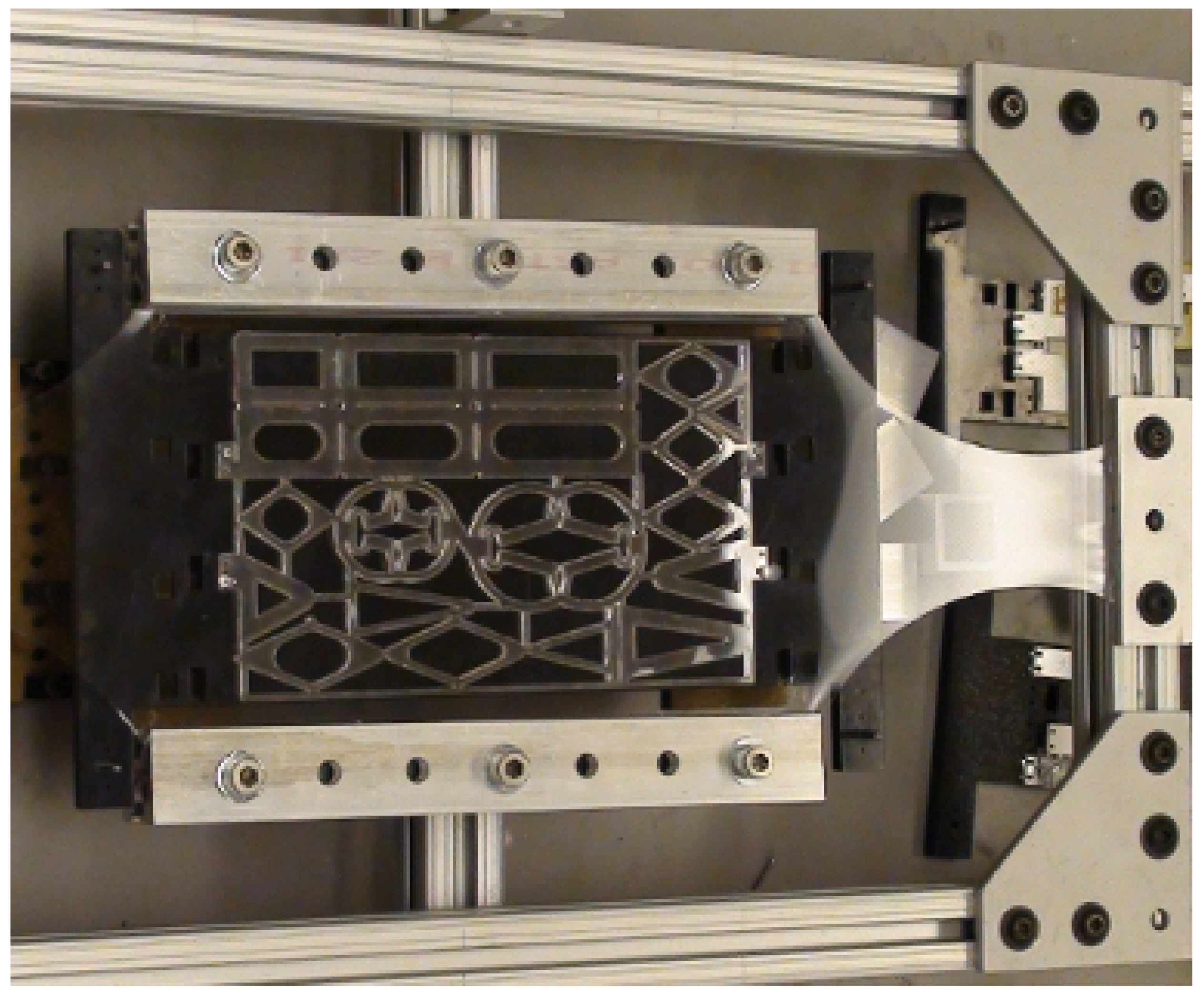
3.2. Structure
3.3. Batch Fabrication
| Force to | Specific | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | s | γ | Weight | Work | |||
| Figure | (mm) | (mm) | (%) | (g) | (m) | (J/kg) | |
| 5(a) | 12 | 6 | 50 | 3.0 | 0.06 | 50 | 2.9 |
| 5(b) | 11 | 6 | 55 | 11.8 | 0.13 | 91 | 5.3 |
| 5(c) | 15 | 5 | 33 | 26.1 | 0.12 | 218 | 10.7 |
| 6(a) | 3 | 1 | 33 | 0.36 | 0.005 | 72 | 0.7 |
| 6(c) | 3 | 1 | 33 | 4.3 | 0.02 | 215 | 2.1 |
4. Experimental Results
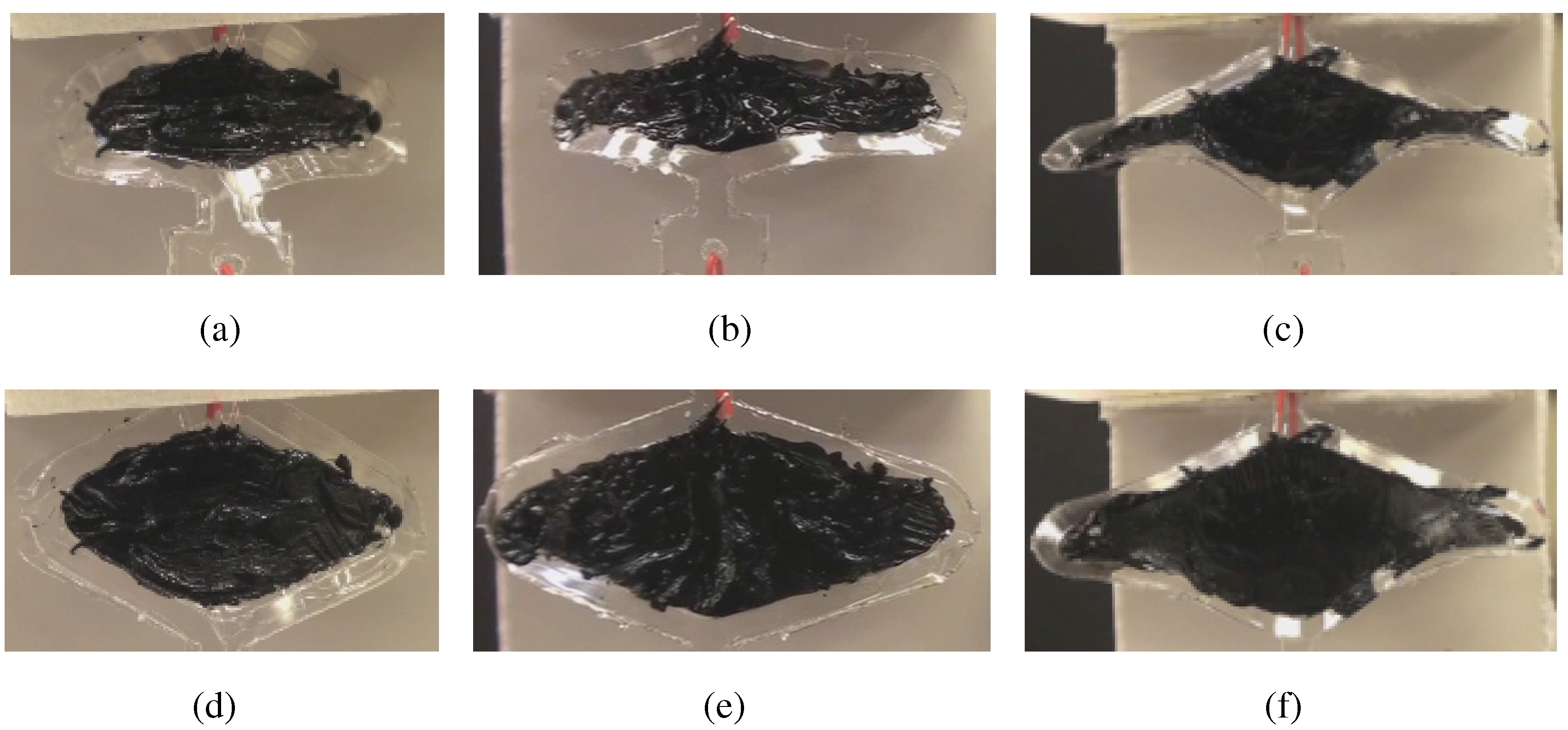
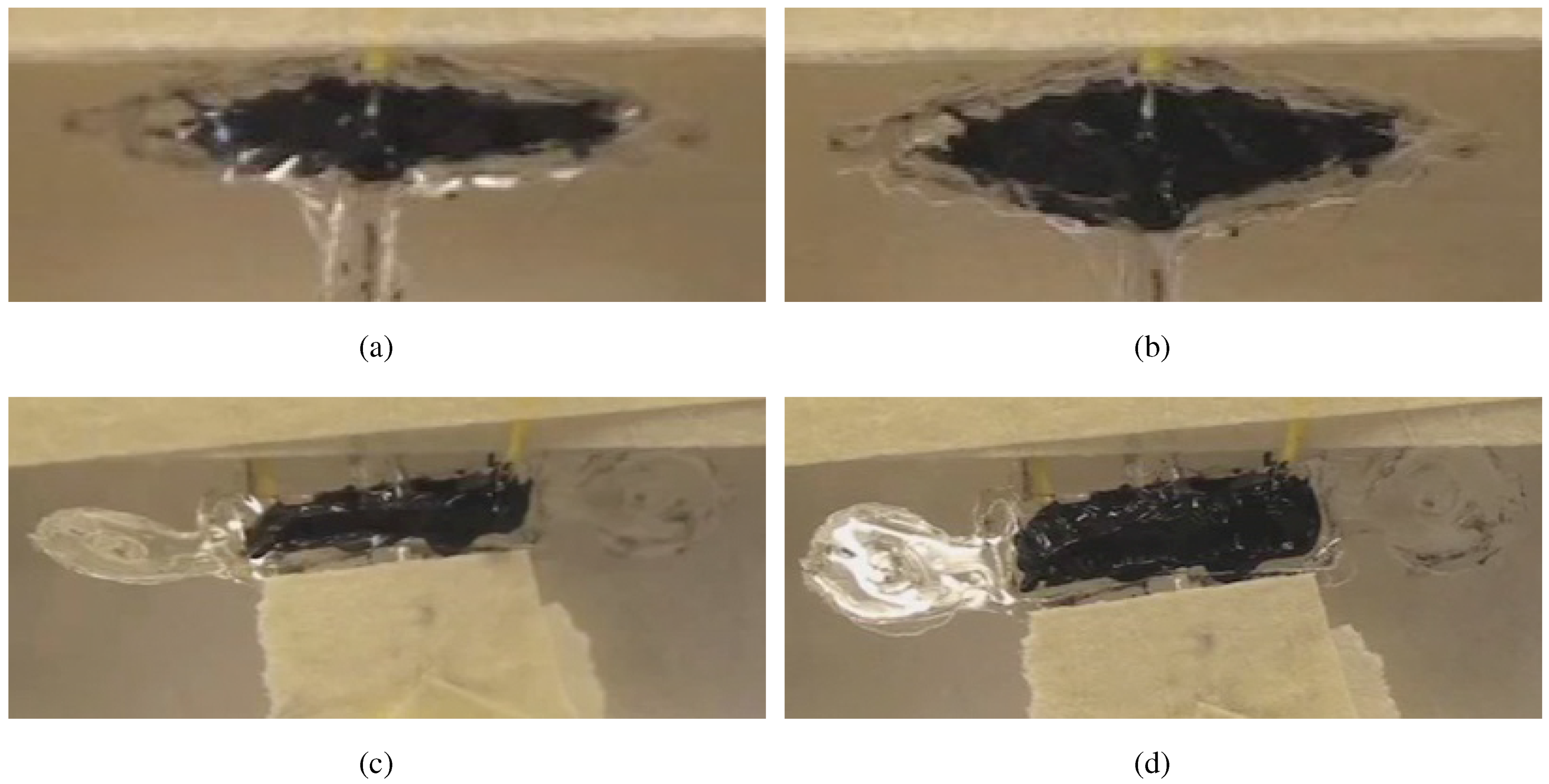
4.1. Agonist-Antagonist Bender

4.2. Demonstrations

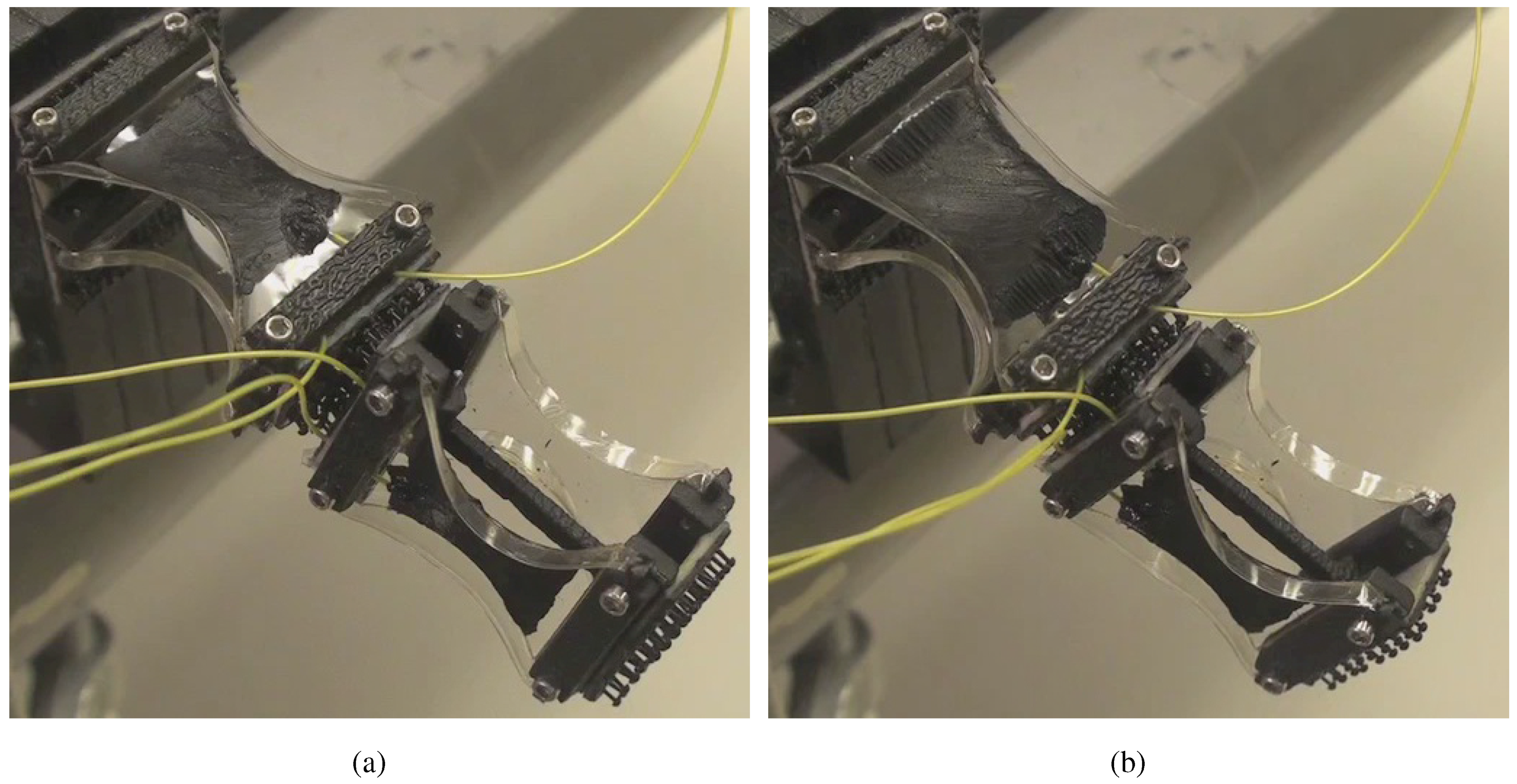
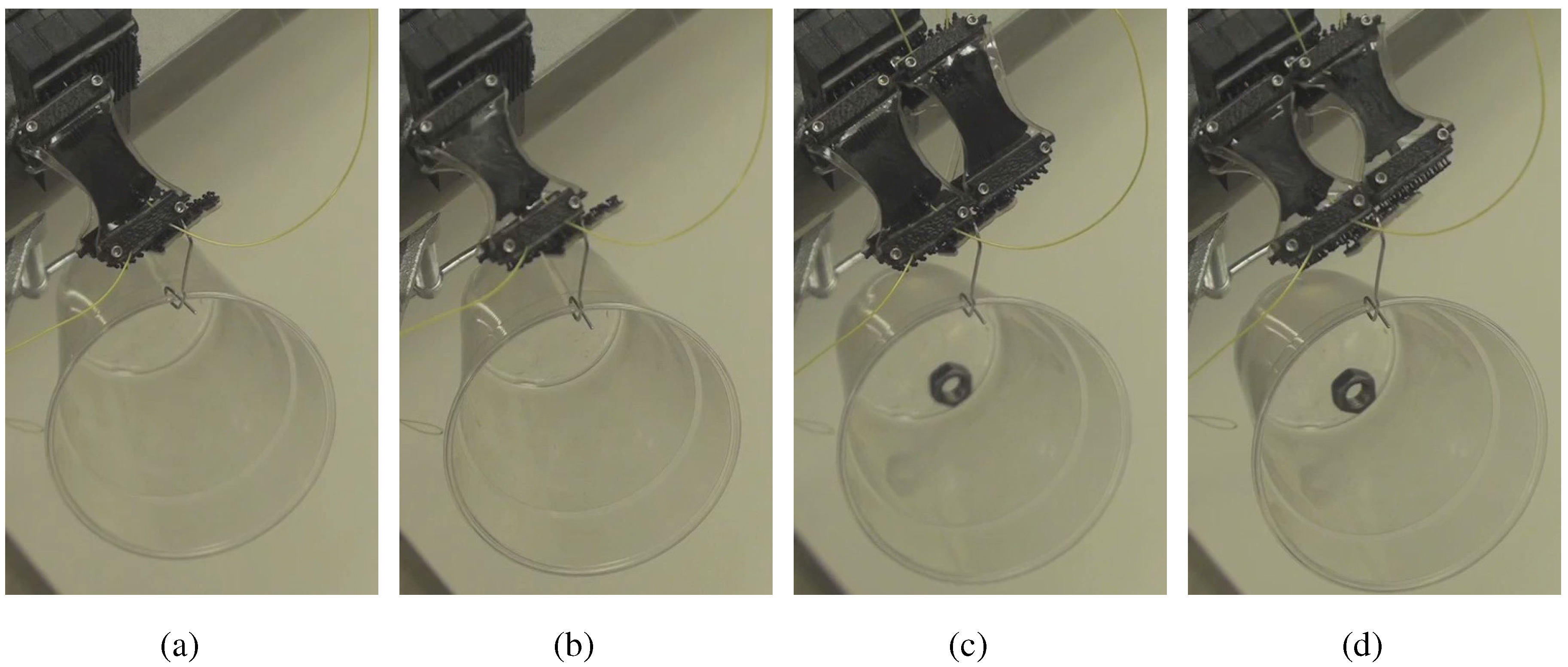
4.3. Observations
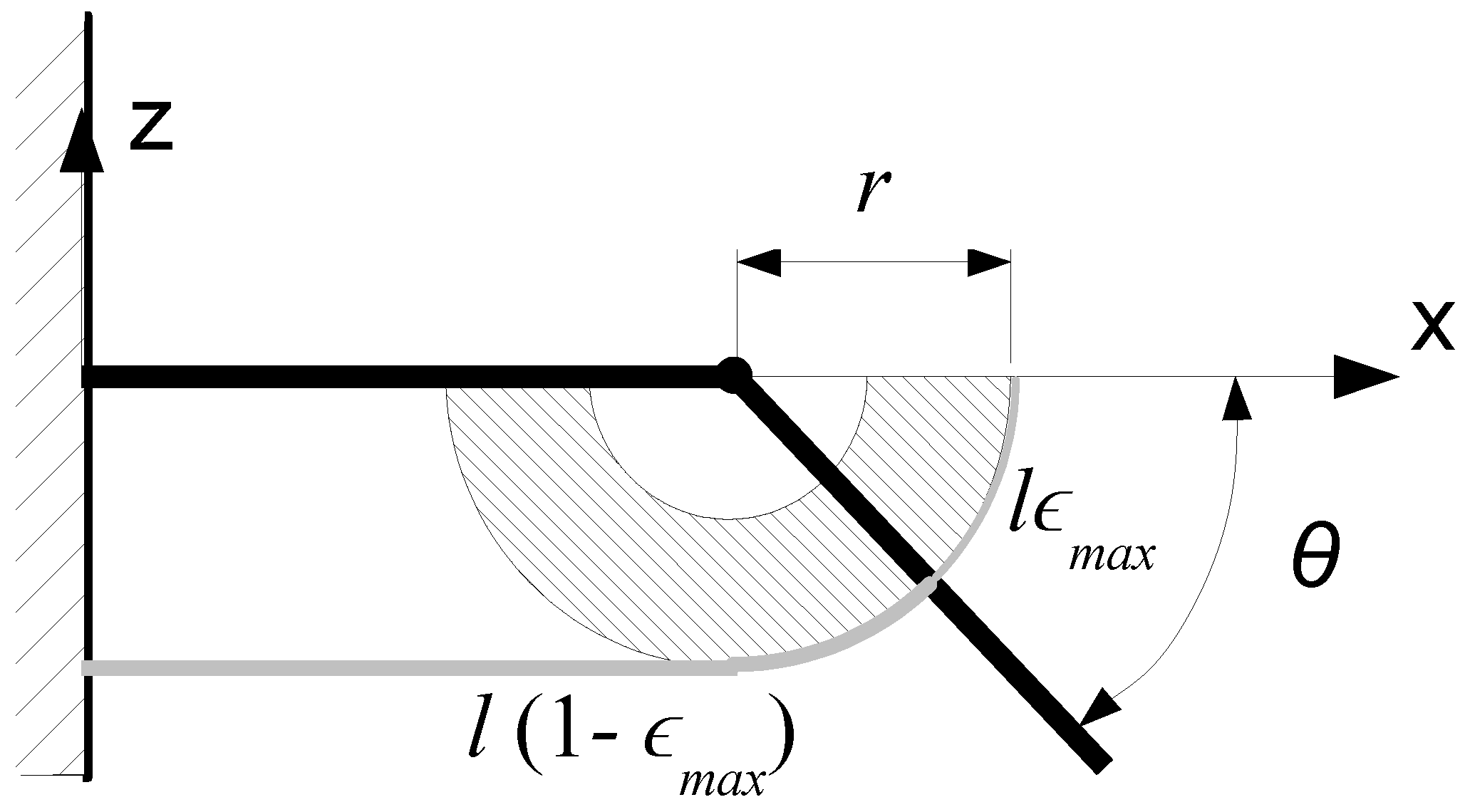
5. Model
5.1. Model Review

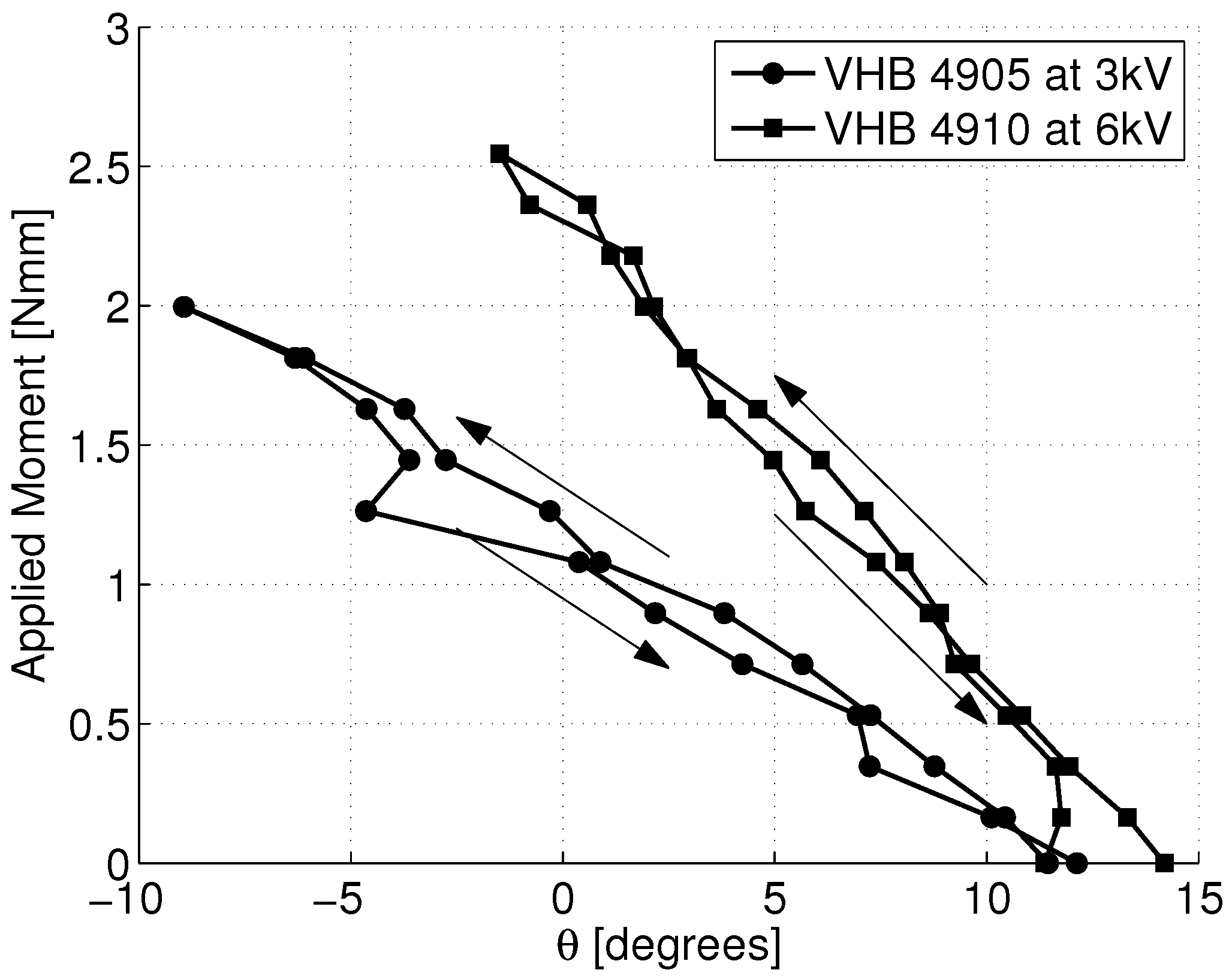
5.2. Model Refinement
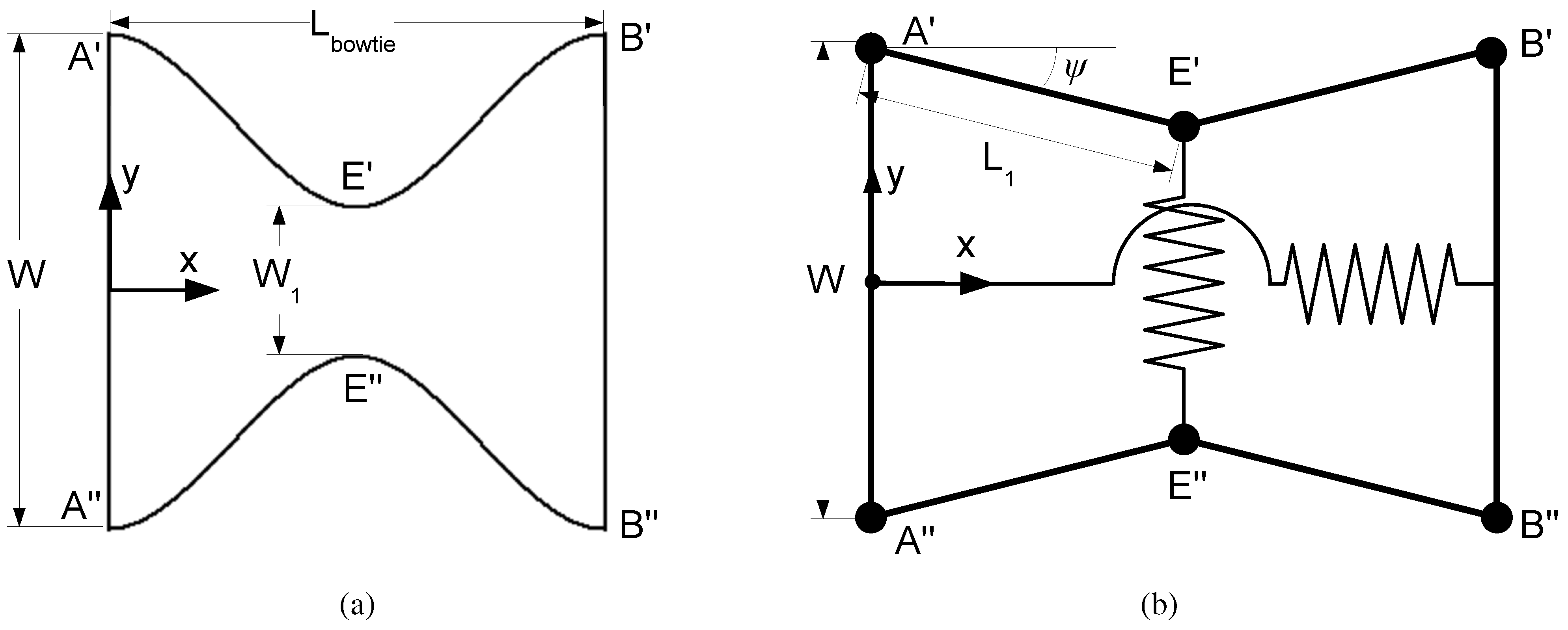

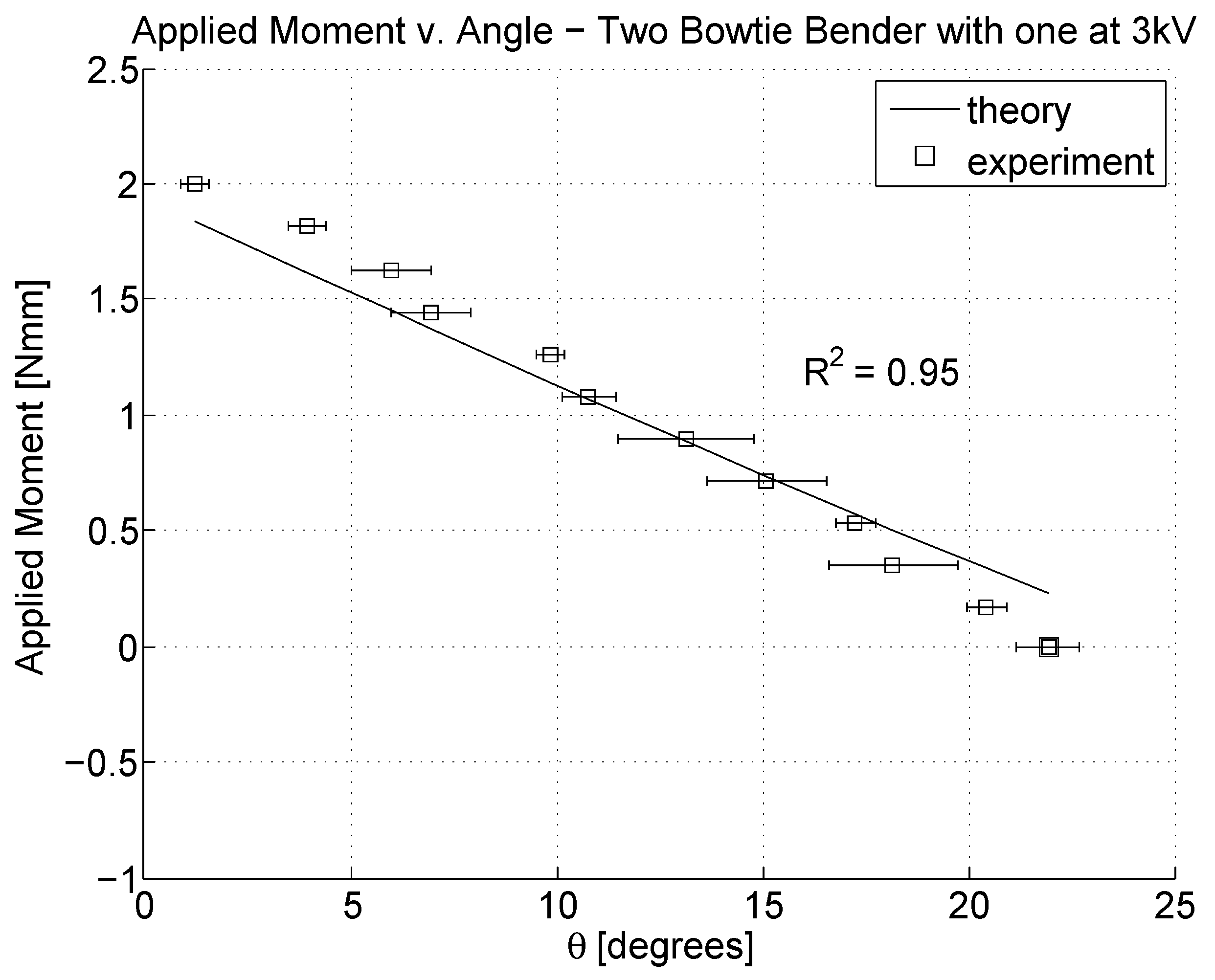
5.3. Model Fit to Data
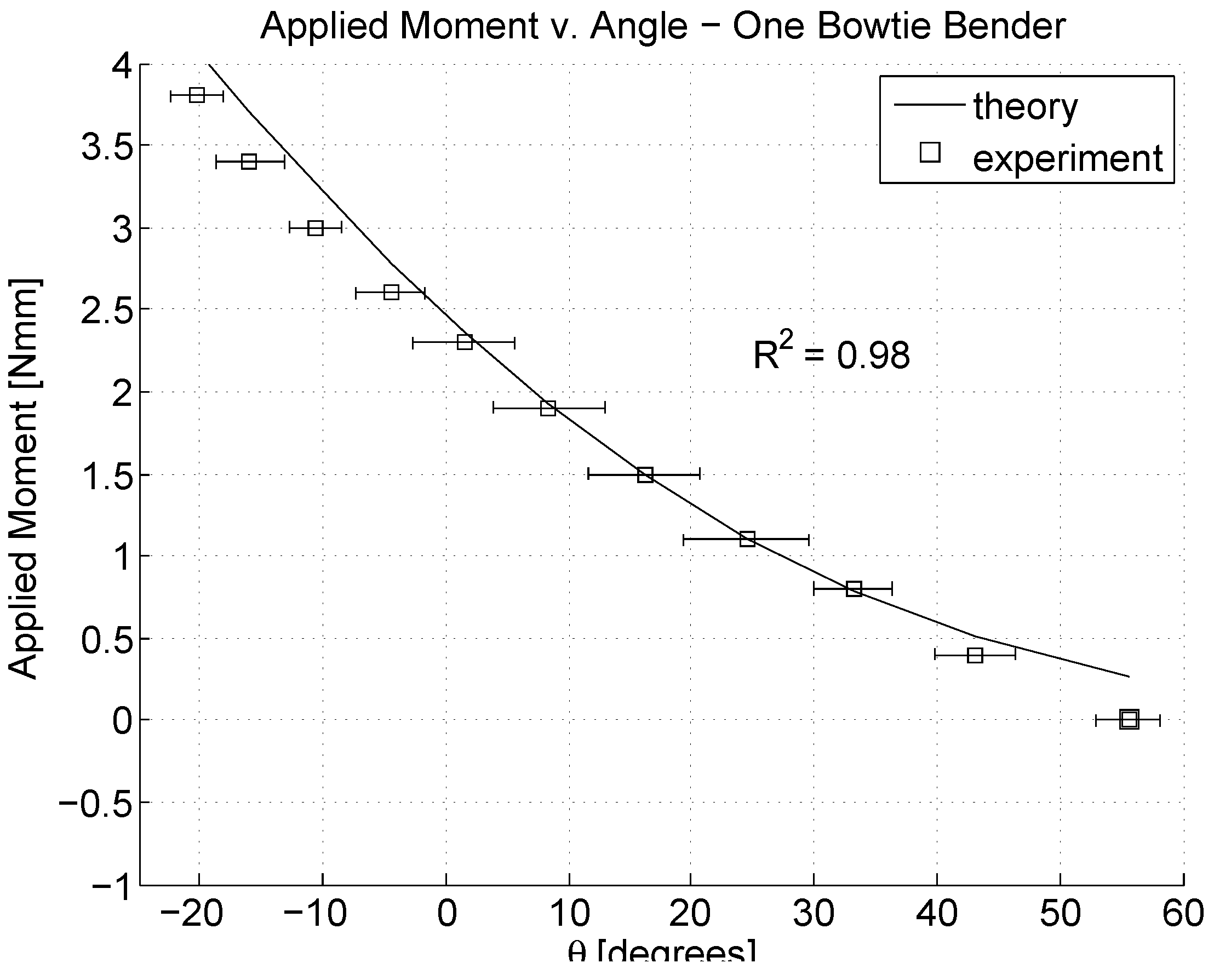
6. Conclusions
References
- White, P.J.; Latscha, S.; Schlaefer, S.; Yim, M. Dielectric elastomer bender actuator applied to modular robotics. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–30 September 2011; pp. 408–413.
- Campbell, J.; Pillai, P. Collective actuation. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2008, 27, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, M.; Tolley, M.; Lipson, H.; Erickson, D. Hydrodynamically Tunable Affinities for Fluidic Assembly. Langmuir 2009, 25, 3769–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neubert, J.; Cantwell, A.; Constantin, S.; Kalontarov, M.; Erickson, D.; Lipson, H. A Robotic Module for Stochastic Fluidic Assembly of 3D Self-Reconfiguring Structures. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–7 May 2010; pp. 2479–2484.
- Gilpin, K.; Knaian, A.; Rus, D. Robot Pebbles: One Centimeter Modules for Programmable Matter through Self-Disassembly. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–7 May 2010.
- Donald, B.R.; Levey, C.G.; Paprotny, I. Planar Microassembly by Parallel Actuation of MEMS Microrobots. J. Microelectromechanical Syst. 2008, 17, 789–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawashe, C.; Floyd, S.; Sitti, M. Assembly and Disassembly of Magnetic Mobile Micro-Robots towards 2-D Reconfigurable Micro-Systems. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Robotics Research, Lucerne, Switzerland, 31 August–3 September 2009.
- White, P.J.; Posner, M.L.; Yim, M. Strength Analysis of Miniature Folded Right Angle Tetrahedron Chain Programmable Matter. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–7 May 2010; pp. 2785–2790.
- Yoshida, E.; Murata, S.; Kokaji, S.; Kamimura, A.; Tomita, K.; Kurokawa, H. Get Back in Shape! A hardware prototype self-reconfigurable modular microrobot that uses shape memory alloy. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2002, 9, 54–61. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes, E.; An, B.; Benbernou, N.; Tanaka, H.; Kim, S.; Demaine, E.; Rus, D.; Wood, R. Programmable matter by folding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagozler, M.E.; Goldstein, S.C.; Reid, J.R. Stress-Driven MEMS Assembly + Electrostatic Forces = 1 mm Diameter Robot. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Louis, MO, USA, 11–15 October 2009.
- Nagy, Z.; Flückiger, M.; Oung, R.; Kaliakatsos, I.; Hawkes, E.; Nelson, B.; Harada, K.; Susilo, E.; Menciassi, A.; Dario, P.; et al. Assembling reconfigurable endoluminal surgical systems: opportunities and challenges. Int. J. Biomechatronics Biomed. Robot. 2009, 1, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, R.; Bongard, J.; Grand, S. How the Body Shapes the Way We Think: A New View of Intelligence; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- OHalloran, A.; OMalley, F.; McHugh, P. A review on dielectric elastomer actuators, technology, applications, and challenges. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 071101–071101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, F.; De Rossi, D.; Kornbluh, R.; Pelrine, R.; Sommer-Larsen, P. Dielectric Elastomers as Electromechanical Transducers; Elsevier Amsterdam: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pelrine, R.; Kornbluh, R.; Joseph, J.; Heydt, R.; Pei, Q.; Chiba, S. High-field deformation of elastomeric dielectrics for actuators. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2000, 11, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelrine, R.; Kornbluh, R.; Pei, Q.; Joseph, J. High-speed electrically actuated elastomers with strain greater than 100%. Science 2000, 287, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lochmatter, P.; Kovacs, G. Design and characterization of an active hinge segment based on soft dielectric EAPs. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 141, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.J.; Yim, M. Scalable Modular Self-reconfigurable Robots Using External Actuation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, San Diego, CA, USA, 29 October–2 November 2007; pp. 2773–2778.
- Støy, K.; Brandt, D.; Christensen, D.J. Self-Reconfigurable Robots—An Introduction; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Murata, S.; Yoshida, E.; Tomita, K.; Kurokawa, H.; Kamimura, A.; Kokaji, S. Hardware design of modular robotic system. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Takamatsu, Japan, 31 October–5 November 2000; Volume 3, pp. 2210–2217.
- Yim, M. Locomotion with a Unit Modular Reconfigurable Robot. PhD Thesis, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Components, N.D. Nitinol SM495 Wire, 2011. Available online: http://www.nitinol.com/media/files/material-properties-pdfs/sm495_wire_data[Converted]_v2.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2014).
- Kornbluh, R.; Pelrine, R.; Joseph, J.; Pei, Q.; Chiba, S. Ultra-high strain response of elastomeric polymer dielectrics. In Proceedings of the Materials Research Society Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 27 November–1 December 2000; Volume 600, pp. 119–130.
- Bar-Cohen, Y. Electroactive Polymer (EAP) Actuators as Artificial Muscles: Reality, Potential, and Challenges; SPIE Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Cross, L.; Ma, W. Recent Progress in High Strain Electroactive Actuator Materials. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Adaptive Structures and Technologies, Potsdam, Berlin, Germany, 7–9 October 2003; p. 3.
- Instrumente, P. Miniature Multilayer Piezo Stack Actuators, 2011. Available online: http://www.physikinstrumente.com/en/pdf/PL022_Datasheet.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2014).
- Wood, R.; Steltz, E.; Fearing, R. Optimal energy density piezoelectric bending actuators. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2005, 119, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulhaber. Brushless DC-Micromotors Series 0206, 2011. Available online: http://www.micromo.com/uploadpk/0206_B_DFF.pdf (accessed on 28 March 2011).
- Plante, J.; Dubowsky, S. Large-scale failure modes of dielectric elastomer actuators. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2006, 43, 7727–7751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoldi, K.; Gei, M. Instabilities in multilayered soft dielectrics. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2011, 59, 18–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudykh, S.; Bhattacharya, K.; deBotton, G. Multiscale instabilities in soft heterogeneous dielectric elastomers. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2014, 470, 20130618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudykh, S.; Bhattacharya, K.; deBotton, G. Snap-through actuation of thick-wall electroactive balloons. Int. J. Linear Mech. 2012, 47, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornbluh, R.; Pelrine, R. High-performance acrylic and silicone elastomers. In Dielectric Elastomers as Electromechanical Transducers: Fundamentals, Materials, Devices, Models and Applications of an Emerging Electroactive Polymer Technology; Publisher: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, Q.; Rosenthal, M.; Stanford, S.; Prahlad, H.; Pelrine, R. Multiple-degrees-of-freedom electroelastomer roll actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2004, 13, N86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, D.; Campbell, J.; Støy, K. Anatomy-based organization of morphology and control in self-reconfigurable modular robots. Neural Comput. Appl. 2010, 19, 787–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordi, C.; Michel, S.; Kovacs, G.; Ermanni, P. Scaling of planar dielectric elastomer actuators in an agonist-antagonist configuration. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2010, 161, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, E.M.; Boyce, M.C. A three-dimensional constitutive model for the large stretch behavior of rubber elastic materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1993, 41, 389–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, J.; Boyce, M. Constitutive modeling of the large strain time-dependent behavior of elastomers. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1998, 46, 931–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouinard, P.; Plante, J. Bistable antagonistic dielectric elastomer actuators for binary robotics and mechatronics. Mechatron. IEEE ASME Trans. 2012, 17, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Keplinger, C.; Baumgartner, R.; Bauer, S.; Yang, W.; Suo, Z. Giant voltage-induced deformation in dielectric elastomers near the verge of snap-through instability. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2013, 61, 611–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gei, M.; Springhetti, R.; Bortot, E. Performance of soft dielectric laminated composites. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 104014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toupin, R.A. The elastic dielectric. J. Ration. Mech. Anal. 1956, 5, 849–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorfmann, A.; Ogden, R. Nonlinear electroelasticity. Acta Mech. 2005, 174, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, R.; Dorfmann, A.; Ogden, R. Nonlinear electroelastostatics: A variational framework. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 2009, 60, 154–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henann, D.L.; Chester, S.A.; Bertoldi, K. Modeling of dielectric elastomers: Design of actuators and energy harvesting devices. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2013, 61, 2047–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofod, G.; Sommer-Larsen, P. Silicone dielectric elastomer actuators: Finite-elasticity model of actuation. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2005, 122, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissler, M. Modeling Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. PhD Thesis, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Zurich, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Suo, Z. Method to analyze programmable deformation of dielectric elastomer layers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 251902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Hong, W.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Suo, Z. Propagation of instability in dielectric elastomers. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2008, 45, 3739–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, B.; Calius, E.; Xie, S.; Anderson, I. An experimentally validated model of a dielectric elastomer bending actuator. In Proceedings of the 15th International Symposium on: Smart Structures and Materials & Nondestructive Evaluation and Health Monitoring, International Society for Optics and Photonics, San Diego, CA, USA, 9 March 2008; pp. 69270T–69270T.
- O’Brien, B.; McKay, T.; Calius, E.; Xie, S.; Anderson, I. Finite element modelling of dielectric elastomer minimum energy structures. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2009, 94, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Kunz, A.; Lochmatter, P.; Kovacs, G. Dielectric Elastomer Spring Roll Actuators for a Portable Force Feedback Device. In Proceedings of the 14th Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems, Alexandria, VA, USA, 25–26 March 2006; pp. 347–353.
- Kofod, G.; Paajanen, M.; Bauer, S. New design concept for dielectric elastomer actuators. Proc. SPIE 2006, 6168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plante, J. Dielectric Elastomer Actuators for Binary Robotics and Mechatronics. PhD Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Howell, L. Compliant Mechanisms; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Suo, Z. Theory of dielectric elastomers. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 2010, 23, 549–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollosche, M.; Zhu, J.; Suo, Z.; Kofod, G. Complex interplay of nonlinear processes in dielectric elastomers. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 85, 051801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gent, A. A new constitutive relation for rubber. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1996, 69, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Huang, J.; Jordi, C.; Kovacs, G.; Huang, R.; Clarke, D.R.; Suo, Z. Dielectric elastomer actuators under equal-biaxial forces, uniaxial forces, and uniaxial constraint of stiff fibers. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 6167–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, B.T.; Jensen, B.D.; Howell, L.L. A pseudo-rigid-body model for initially-curved pinned-pinned segments used in compliant mechanisms. J. Mech. Des. 2001, 123, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacour, S.P.; Prahlad, H.; Pelrine, R.; Wagner, S. Mechatronic system of dielectric elastomer actuators addressed by thin film photoconductors on plastic. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2004, 111, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, F.; Salaris, C.; De Rossi, D. Folded dielectric elastomer actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, S300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, F.; Migliore, A.; Serra, G.; De Rossi, D. Helical dielectric elastomer actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2005, 14, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Brochu, P.; Zhang, H.; Jan, A.; Pei, Q. Long lifetime dielectric elastomer actuators under continuous high strain actuation. In Proceedings of the 16th International Symposium on: Smart Structures and Materials & Nondestructive Evaluation and Health Monitoring, International Society for Optics and Photonics, San Diego, CA, USA, 8 March 2009; pp. 72870O–72870O.
- Schlaak, H.; Jungmann, M.; Matysek, M.; Lotz, P. Novel multilayer electrostatic solid state actuators with elastic dielectric (Invited Paper). Proc. SPIE 2005, 5759, 121. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
White, P.; Latscha, S.; Yim, M. Modeling of a Dielectric Elastomer Bender Actuator. Actuators 2014, 3, 245-269. https://doi.org/10.3390/act3030245
White P, Latscha S, Yim M. Modeling of a Dielectric Elastomer Bender Actuator. Actuators. 2014; 3(3):245-269. https://doi.org/10.3390/act3030245
Chicago/Turabian StyleWhite, Paul, Stella Latscha, and Mark Yim. 2014. "Modeling of a Dielectric Elastomer Bender Actuator" Actuators 3, no. 3: 245-269. https://doi.org/10.3390/act3030245
APA StyleWhite, P., Latscha, S., & Yim, M. (2014). Modeling of a Dielectric Elastomer Bender Actuator. Actuators, 3(3), 245-269. https://doi.org/10.3390/act3030245