Integral Reinforcement Learning-Based Stochastic Guaranteed Cost Control for Time-Varying Systems with Asymmetric Saturation Actuators
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1.
- This study develops an innovative DETC-based GCC approach for stochastic systems by using IRL algorithms with the MPCM. This approach can ensure that the system performance index is less than a certain upper bound.
- 2.
- By solving an improved HJI equation by designing a modified long-term performance cost function, the control inputs under ASAs can be obtained via an actor–critic–disturbance NN structure.
- 3.
- Through the introduction of dynamic parameters into triggering conditions in the DETC mechanism, the update rule for control inputs can be adjusted dynamically, which can reduce the computational complexity of sampling data.
2. Problem Statement
3. Stochastic Optimal GCC Design
4. Stochastic GCC Method Design via MPCM and IRL Algorithm
4.1. On-Policy GCC Design
| Algorithm 1 Model-based GCC algorithm for stochastic uncertain system (1). |
| Initialization Set initial admissible policies and . Step 1: A set of sampling points for the uncertain variable is selected on the basis of the MPCM ([40], Section II). Compute the value of at each sampling point: Step 2: Compute by computing the mean value of . Step 3: Update on the basis of solving the HJI equation: Step 4: Design the control pairs via Let s be updated as . If where is a small positive number and stops at step 4; Otherwise, please return to step 1. |
4.2. IRL-Based GCC Design with Asymmetric Constrained Inputs
| Algorithm 2 IRL-based GCC algorithm for system (1) with asymmetric constrained control. |
| Initialization Set the initial admissible policies and .
Step 1: Choose a set of sampling points for the uncertain variable based on MPCM ([40], Section II). For each sampling point, compute the value of Step 2: Compute by calculating the mean of . Step 3: Update , and through solving the HJI equation: Set s to . If , where is a chosen positive number, end at step 3; otherwise, return to step 1. |
5. Event-Triggered Construction of Optimal GCC
5.1. Event-Triggered GCC Design
5.2. NN-Based Control Design
5.3. Stability Analysis
6. Simulation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, M.; Shakoor, A.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, B. Optical manipulation of biological cells with a robot-tweezers system: A stochastic control approach. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2020, 67, 3232–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazmohammadi, N.; Tahsiri, A.; Anvari-Moghaddam, A.; Guerrero, J.M. Stochastic predictive control of multi-microgrid systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 5311–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Wu, C.; Wen, J. Vehicle longitudinal stochastic control for connected and automated vehicle platooning in highway systems. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 9563–9578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H.; Fu, M. Stochastic LQ optimal control with initial and terminal constraints. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2024, 69, 6261–6268. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.Y.; Mu, H.R.; Fu, S.J.; Han, H.G. Data-driven model predictive control for unknown nonlinear NCSs with stochastic sampling intervals and successive packet dropouts. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2025, 55, 2899–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xie, L.; Zhang, H. Solution to discrete-time linear FBSDEs with application to stochastic control problem. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2017, 62, 6602–6607. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Voos, H.; Darouach, M.; Hua, C. An application of linear algebra theory in networked control systems: Stochastic cyber-attacks detection approach. IMA J. Math. Control Inf. 2016, 33, 1081–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetinkaya, A.; Kishida, M. Instabilizability conditions for continuous-time stochastic systems under control input constraints. IEEE Control Syst. Lett. 2021, 6, 1430–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, D.; Hokayem, P.; Lygeros, J. Stochastic receding horizon control with bounded control inputs: A vector space approach. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2011, 56, 2704–2710. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, X.P.; Dang, X.K.; Do, V.D.; Corchado, J.M.; Truong, H.N. Robust adaptive fuzzy-free fault-tolerant path planning control for a semi-submersible platform dynamic positioning system with actuator constraints. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 12701–12715. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Xie, X.; Zhou, C. Locally expanded constraint-boundary-based adaptive composite control of a constrained nonlinear system with time-varying actuator fault. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2023, 31, 4121–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Diao, S.; Su, S.F.; Sun, Z.Y. Fixed-time adaptive neural network control for nonlinear systems with input saturation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 34, 1911–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Song, M.; Huang, B.; Huang, P. Adaptive tracking control for tethered aircraft systems with actuator nonlinearities and output constraints. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 3582–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, G. Adaptive fixed-time sliding mode control of vehicular platoons with asymmetric actuator saturation. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 8409–8423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Zhang, P. Asymptotic stabilization of USVs with actuator dead-zones and yaw constraints based on fixed-time disturbance observer. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 69, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Gao, N.; Liu, D.; Li, J.; Lewis, F.L. Recent progress in reinforcement learning and adaptive dynamic programming for advanced control applications. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2023, 11, 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Y. Value iteration-based distributed adaptive dynamic programming for multi-player differential game with incomplete information. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2025, 12, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Yang, Z.; Su, H.; Wang, L. Online adaptive dynamic programming for optimal self-learning control of VTOL aircraft systems with disturbances. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2022, 21, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Chen, W.; Tan, X.; Xiao, J.; Dong, Q. Observer-based optimal Backstepping security control for nonlinear systems using reinforcement learning strategy. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2024, 54, 7011–7023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Luo, Y. Neurodynamic programming and tracking control for nonlinear stochastic systems by PI algorithm. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 2892–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, M.; Lewis, F.L.; Zheng, M. Compensator-based self-learning: Optimal operational control for two-time-scale systems with input constraints. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 9465–9475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Gao, W.; Jiang, X.; Su, C.; Li, P. Two-dimensional model-free Q-learning-based output feedback fault-tolerant control for batch processes. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2024, 182, 108583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Jiang, Z.P. Reinforcement learning for adaptive optimal stationary control of linear stochastic systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2022, 68, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Peng, Y. Model-free tracking control for linear stochastic systems via integral reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2025, 22, 10835–10844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qu, Q.; Xiao, G.; Cui, Y. Optimal guaranteed cost sliding mode control for constrained-input nonlinear systems with matched and unmatched disturbances. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 29, 2112–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Jiang, Z.P. Event-based control of nonlinear systems with partial state and output feedback. Automatica 2015, 53, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Han, L.; Wei, Q.; Wang, X.; Dai, X.; Wang, F.Y. Event-triggered deep reinforcement learning using parallel control: A case study in autonomous driving. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2023, 8, 2821–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhu, Q. Event-triggered optimized control for nonlinear delayed stochastic systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2021, 68, 3808–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Liang, C.; Zhu, Q. Adaptive fuzzy event-triggered optimized consensus control for delayed unknown stochastic nonlinear multi-agent systems using simplified ADP. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2025, 22, 11780–11793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Zhang, W.; Luo, B.; Liu, D. Integral reinforcement learning-based dynamic event-triggered nonzero-sum games of USVs. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2025, 55, 1706–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, Z.g.; Zhang, H.; Tong, X.; Yan, Y. Mixed H2/H∞ control with dynamic event-triggered mechanism for partially unknown nonlinear stochastic systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2022, 20, 1934–1944. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, X.; Ma, D.; Wang, R.; Xie, X.; Zhang, H. Dynamic event-triggered-based integral reinforcement learning algorithm for frequency control of microgrid with stochastic uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2023, 69, 321–330. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.Y.; Li, Y.X.; Tong, S. Dynamic event-triggered reinforcement learning control of stochastic nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2023, 31, 2917–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wan, Y.; Lewis, F.L. Adaptive optimal decision in multi-agent random switching systems. IEEE Control Syst. Lett. 2019, 4, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Qin, Z.; Hong, Y.; Jiang, Z.P. Distributed optimization of nonlinear multiagent systems: A small-gain approach. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2021, 67, 676–691. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Ming, Z. Event-triggered guarantee cost control for partially unknown stochastic systems via explorized integral reinforcement learning strategy. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 35, 7830–7844. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, R.; Ma, J.; Su, P.; Dong, Y.; Cheng, J. Monte-Carlo integration models for multiple scattering based optical wireless communication. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2019, 68, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, X.; Cao, R.; Sun, Z. A multilevel Monte Carlo method for performing time-variant reliability analysis. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 31773–31781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Wan, Y.; Mills, K.; Filliben, J.J.; Lewis, F.L. A scalable sampling method to high-dimensional uncertainties for optimal and reinforcement learning-based controls. IEEE Control Syst. Lett. 2017, 1, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Wan, Y.; Roy, S.; Taylor, C.; Wanke, C.; Ramamurthy, D.; Xie, J. Multivariate probabilistic collocation method for effective uncertainty evaluation with application to air traffic flow management. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2014, 44, 1347–1363. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Wan, Y.; Lewis, F.L.; Lopez, V.G. Adaptive optimal control for stochastic multiplayer differential games using on-policy and off-policy reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 31, 5522–5533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z. Global asymptotic stability analysis for autonomous optimization. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2025, 70, 6953–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Li, H.; Qin, Z.; Wang, Z. Gradient-free cooperative source-seeking of quadrotor under disturbances and communication constraints. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 72, 1969–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Tang, Y.; Zhong, S.; Yin, C.; Huang, X.; Wang, W. Nonfragile asynchronous control for uncertain chaotic lurie network systems with bernoulli stochastic process. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2018, 28, 1693–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhang, H.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, H. Adaptive dynamic programming for H∞ tracking design of uncertain nonlinear systems with disturbances and input constraints. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2017, 31, 1567–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cui, X.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, H. Finite-horizon H∞ tracking control for unknown nonlinear systems with saturating actuators. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2017, 29, 1200–1212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, A.; Jagannathan, S. Stochastic optimal regulation of nonlinear networked control systems by using event-driven adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2016, 47, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasini, S.; Naghibi Sitani, M.B.; Kirampor, A. Reinforcement learning and neural networks for multi-agent nonzero-sum games of nonlinear constrained-input systems. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2016, 7, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


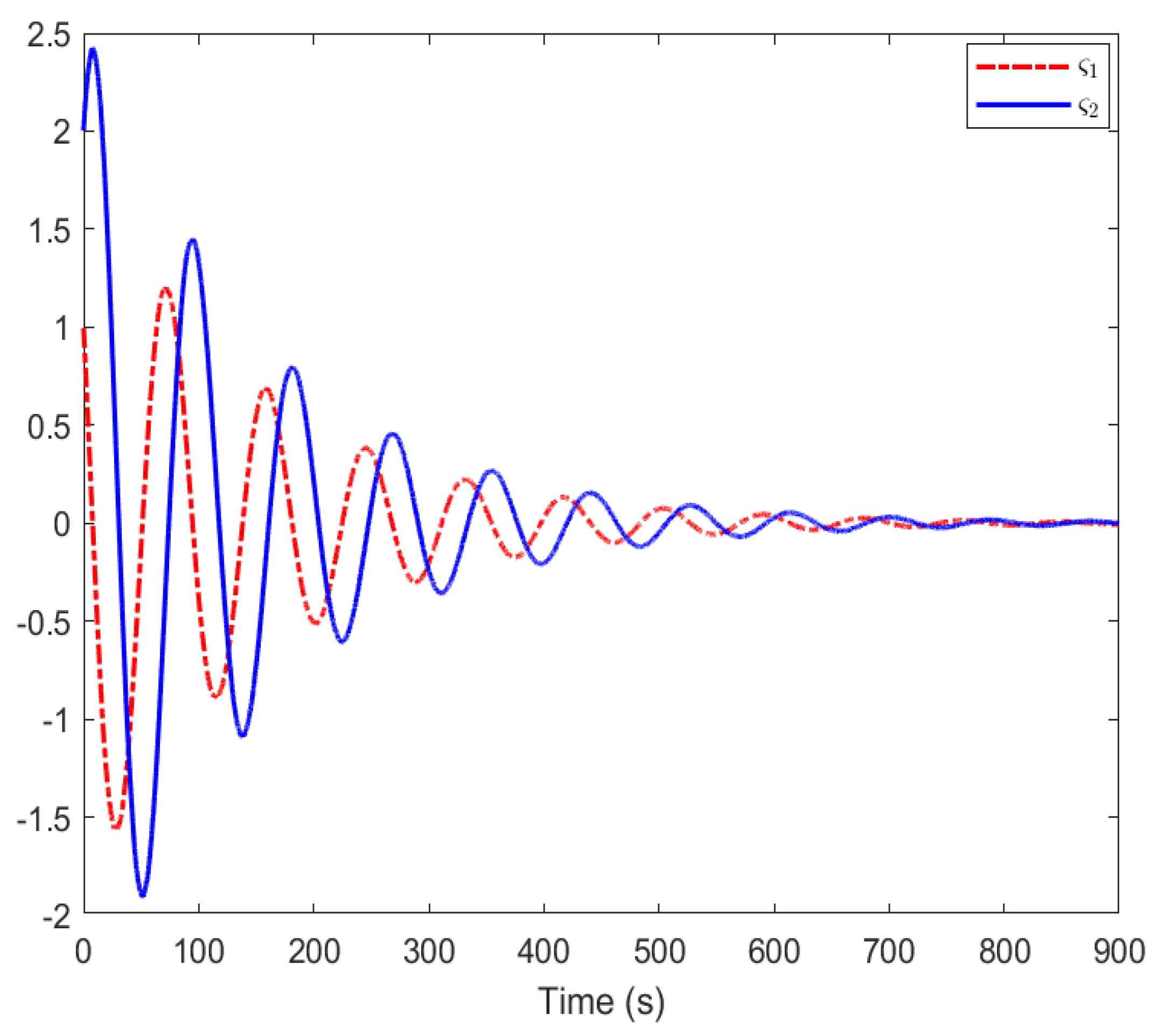




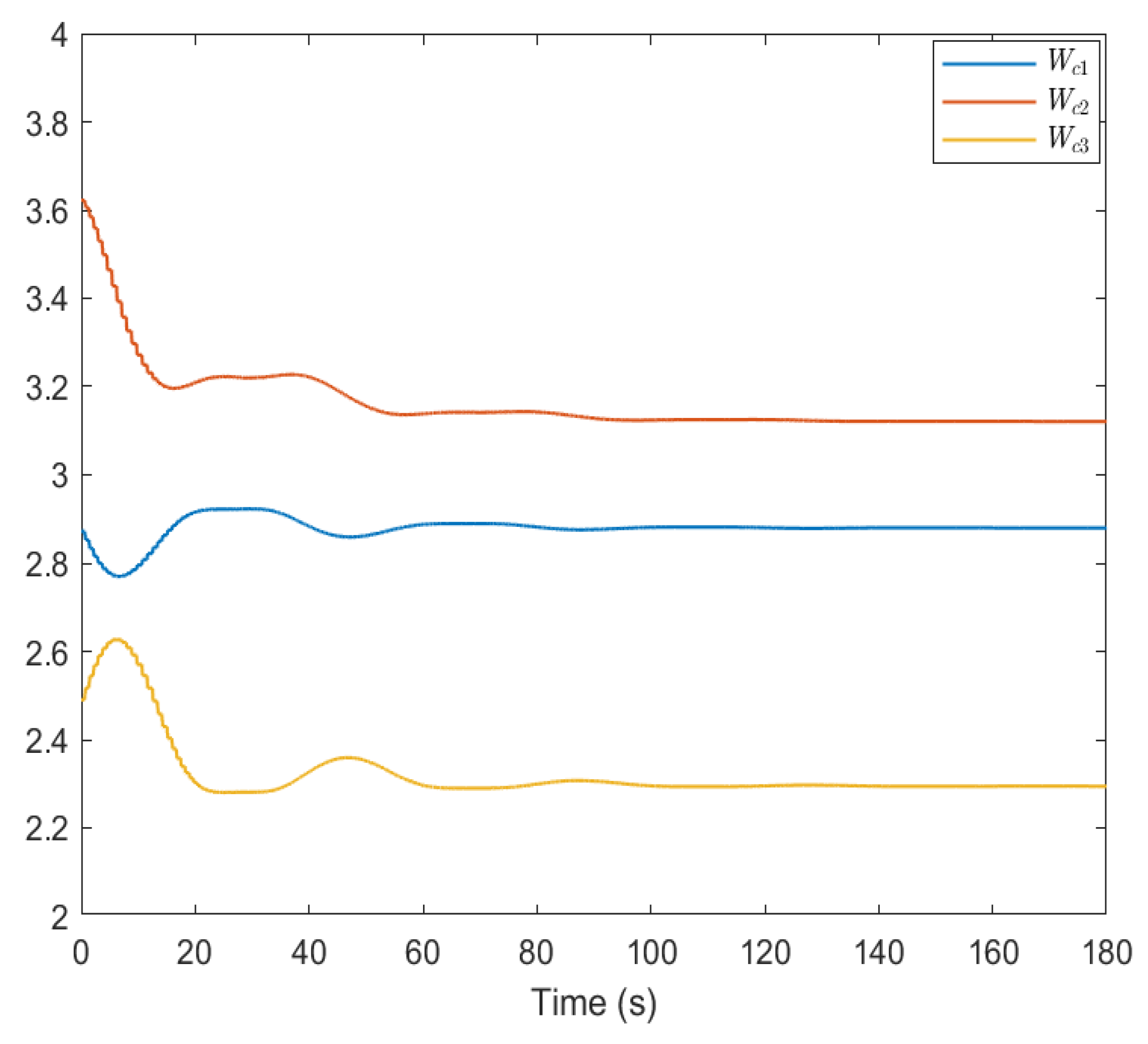



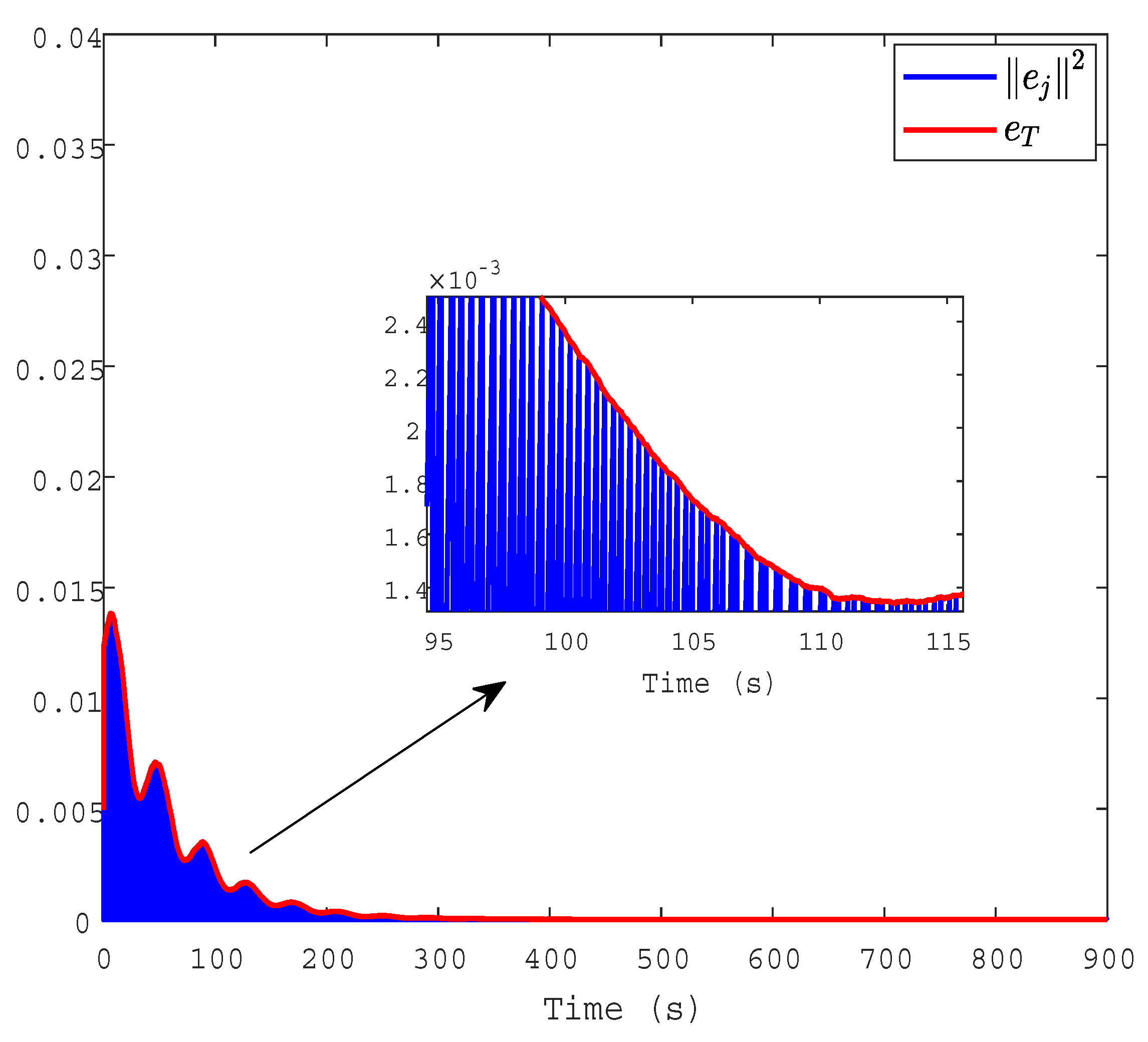
| Parameter | R | T | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| value | 1 | 0.005 | 5 | 0.5 | −0.8 | 1 | 0.5 | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Y.; Xie, M.; Zhang, J.; Ming, Z.; Gao, Z. Integral Reinforcement Learning-Based Stochastic Guaranteed Cost Control for Time-Varying Systems with Asymmetric Saturation Actuators. Actuators 2025, 14, 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14100506
Liang Y, Xie M, Zhang J, Ming Z, Gao Z. Integral Reinforcement Learning-Based Stochastic Guaranteed Cost Control for Time-Varying Systems with Asymmetric Saturation Actuators. Actuators. 2025; 14(10):506. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14100506
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Yuling, Mengjia Xie, Juan Zhang, Zhongyang Ming, and Zhiyun Gao. 2025. "Integral Reinforcement Learning-Based Stochastic Guaranteed Cost Control for Time-Varying Systems with Asymmetric Saturation Actuators" Actuators 14, no. 10: 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14100506
APA StyleLiang, Y., Xie, M., Zhang, J., Ming, Z., & Gao, Z. (2025). Integral Reinforcement Learning-Based Stochastic Guaranteed Cost Control for Time-Varying Systems with Asymmetric Saturation Actuators. Actuators, 14(10), 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14100506





