Abstract
This paper proposes a mixed-mode (combining shear and squeeze working modes) vibration isolator using magnetorheological elastomer (MRE), which enables the isolator to have a larger working area and better isolation performance by combining the working modes of the MRE. Firstly, based on the magnetorheological effect working principle of the MRE, the material selection and dimensional parameters of each component are determined through structural design and magnetic circuit calculation. On this basis, magnetic field simulation is conducted using Maxwell 16.0 software to analyze the distribution of magnetic field lines and magnetic induction in the working area. Simultaneously, equivalent stiffness and equivalent damping models are established to explore the variation of vibration response with external current and excitation frequency conditions. Finally, a vibration isolation experimental platform is built to test the mixed-mode MRE isolator. The experimental results are basically consistent with the simulation modeling results. The experimental results showed that when the external excitation is in the frequency range of 16 Hz, effective semi-active vibration isolation control could be achieved by applying different current inputs. The isolation effect of the system is difficult to effectively control using current input when the external excitation is at high frequency. These results validate the rationality and feasibility of the mixed-mode MRE isolator structure, which provides a good reference for the design of MRE isolators.
1. Introduction
Magnetorheological elastomer (MRE) is a type of magnetorheological material, which is a mixture of high polymer (such as silicone rubber) and micrometer sized magnetic particles (such as carbonyl iron powder). The magnetic particles of the MRE form ordered aggregation structures by applying an external magnetic field, thereby exhibiting the loading force of magnetorheological effect. During this process, the elasticity and shear capacity of the material undergo changes, resulting in controllable stiffness and damping at the macroscopic level [1,2,3]. MRE is the solid state of magnetorheological fluids, which retain the controllable characteristics of fast response and good reversibility. MRE overcomes the problems of easy deposition, poor sealing and stability of magnetorheological fluids, and it is an ideal choice for various vibration applications [4,5].
The MRE isolator is a semi-active control device that can achieve sustainable adjustment of isolation performance by adjusting its own input voltage and current. It has the advantages of simple construction, strong adaptability, and wide adjustable range. The working principle of the MRE isolator can be expressed as follows: an external magnetic field is formed by power supply, and the magnetic particles inside the MRE are magnetized to generate reverse torque, thereby improving the MRE’s isolation ability to resist deformation. That is, as the stiffness of the MRE increases, the response of the isolated device to the vibration source is reduced [6,7].
Compared to squeeze MRE, shear mode MRE can exhibit more significant magnetorheological effects and the corresponding devices also have larger working displacements. In the early design of MRE isolators, the MRE typically operated in the shear mode. Liao et al. designed a shear-type MRE isolator, in which three coils supply magnetic fields to the MRE through the control of the supply current, and the isolator provides effective isolation performance under ON-OFF control [8]. Du et al. designed the semi-active/passive integrated isolator based on MRE and a spring. The coil of the MRE is wound around the upper and lower magnetic conductors to generate a magnetic field, and its dynamic performance was tested under single frequency and sweep frequency vibration excitation [9]. Zhu et al. explored the response time of a vibration isolation system based on an MRE isolator working in shear mode, and analysis results show that the response time of MRE isolators mainly depends on the changes in transient current amplitude, but is not highly correlated with shear strain [10]. Jalali et al. developed a novel bi-directional shear mode MRE isolator to enhance the dynamic response and identification capabilities of these intelligent mechanical devices and characterize the response behavior of the MRE isolator under vertical and horizontal shear modes [11]. In order to isolate torsional vibration in drilling systems, Syam et al. proposed an MRE semi-active isolator composed of silicone rubber and iron particles. Drilling prototype test results showed that the continuous rotational vibration amplitude of the prototype was attenuated by more than 40% [12].
The drawbacks of shear mode have also been revealed with the deepening of research on MRE isolators, which mainly include low magnetic circuit utilization, severe leakage phenomenon, and limited load-bearing capacity. Therefore, the squeeze-type MRE isolator has been further studied. The MRE isolator based on squeeze mode overcomes the above shortcomings and has good dynamic damping performance [13,14,15]. Du and Li et al. developed an MRE isolator for vehicle seats and achieved semi-active variable stiffness vibration control of the vehicle seat suspension. Experimental tests have shown that the device has high stiffness and large damping in the squeeze condition [16,17]. Yang et al. designed a compression MRE isolator and the mechanical tests were conducted by Instron. The effectiveness of the MRE isolator for vibration control was evaluated by the inertial measurement unit (IMU) isolation system [18]. To improve the low-frequency isolation bandwidth of quasi-zero stiffness isolators under amplitude excitation, Fu et al. proposed an adaptive bidirectional controllable MRE isolator. The resonance frequency can be reduced by a stiffness bidirectional-controllable isolator [19]. Rustighi et al. proposed a physical-based model to describe and predict the performance of an axially compressed MRE isolator. The result shows that the model is capable of predicting the tunability of the isolator [20]. The magnetic stiffness range of the squeeze MRE isolator will be reduced due to the gravity of the isolated device, and it is generally suitable for devices with a small working stroke [21].
Although the MRE technology holds great promise, several limitations must be overcome to realize its full potential. These include the need for improved material stability, dynamic modeling performance, and efficient frequency response characteristics [22,23]. The MRE isolator under a single working mode cannot maximize its isolation effect, so it is necessary to conduct dynamic and experimental analysis on the MRE isolator under a combined working mode. In order to overcome the shortcomings of the shear mode or compression mode, this paper designs a mixed-mode MRE isolator that integrates the shear and compression modes. The contributions of this paper are as follows: (1) The dimensions and magnetic circuit parameters of each component of the MRE isolator are provided, and the rationality of the structural design of the MRE isolator is analyzed and verified through magnetic field simulation. (2) Dynamic simulation and experiments are conducted to analyze the vibration response characteristics of the MRE isolator at different currents and frequencies.
The paper is organized as follows: Firstly, the material selection and dimensional parameters of each component of the MRE isolator are determined through structural design and magnetic circuit calculation. On this basis, magnetic field simulation is conducted to analyze the distribution of the magnetic field in the working area, and dynamic model simulation is conducted to analyze the vibration response of the MRE isolator. Finally, a vibration isolation experimental platform is built to test the frequency response characteristics of the mixed-mode MRE isolator.
2. The Structural Design of the Mixed-Mode MRE Isolator
2.1. Structure Design
Compared to the single working mode of traditional MRE isolators, the mixed-mode MRE isolator combines the working modes to provide a larger working area under a certain volume. The schematic diagram of the mixed-mode MRE isolator structure is shown in Figure 1, and its structural parameters are shown in Table 1. It consists of the dynamic magnetic conductor, outer sleeve, squeeze MRE, shear MRE, excitation coil, winding tube, inner gasket, upper cover, and bottom base. The MRE produced by the research group is composed of 70% carbonyl iron powder, 15% silicone rubber, and 15% silicone oil. There are two air gaps in the MRE isolator, where the air gap near the shear MRE provides actuation space for the shear MRE, and the air gap near the squeeze MRE prevents frictional interference between the magnetic conductor and winding tube. The working principle of the mixed-mode MRE isolator is as follows: an external magnetic field is formed by inputting an external current, and the MRE produces magnetorheological effects under the action of the external magnetic field. The elastic modulus increases with the increase of the magnetic field, that is, the stiffness of the isolator increases. The squeeze MRE absorbs the vertical vibration energy when stimulated by external factors, and the shear MRE weakens the lateral shaking, thereby reducing the response of the isolated device to the vibration source. The device is mainly used in vibration isolation and buffering scenarios such as vehicle seats and vibration bases.
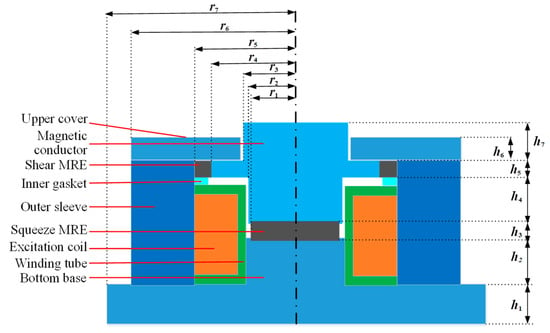
Figure 1.
The structure of the mixed-mode MRE isolator.

Table 1.
The structural parameters of the mixed-mode MRE isolator.
Comprehensive considerations should be given to high magnetic permeability, low hysteresis and cost-effectiveness when selecting magnetic materials for the MRE isolator. In order to improve the utilization efficiency of the magnetic field, selecting materials with high magnetic permeability can ensure that the magnetic field intensity generated by the excitation coil is optimized to the maximum extent possible [24,25]. Low-carbon steel is a common magnetic material, which has good magnetic permeability and mechanical strength, as well as low cost and easy processing. Taking into account all factors, we select the low-carbon steel as the magnetic material for the designed mixed-mode MRE isolator. The function of non-magnetic materials is to change the direction of magnetic field lines, thereby improving the utilization efficiency of magnetic fields. From the perspective of reducing magnetic leakage, non-magnetic materials with lower magnetic permeability should be selected. Strength, stiffness, and good processing performance should also be considered. Taking all factors into account, the austenitic stainless steel is selected as the non-magnetic material for the designed mixed-mode MRE isolator. Finally, the material selection for each component is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
The material selection for each component of the mixed-mode MRE isolator.
2.2. Magnetic Circuit Design
The excitation coil provides a controllable magnetic field for MRE devices, and it is necessary to design an efficient magnetic circuit to ensure superior magnetorheological effects. In an ideal situation, magnetic field lines should pass perpendicular to the MRE, which can fully utilize the magnetorheological effect. The most efficient magnetic circuit is a C-shaped magnetic circuit with a well-closed loop. In order to obtain a strong and uniform magnetic field, the gap between the two poles of the C-shaped magnetic circuit must be kept as small as possible [26].
Figure 2 shows two commonly used configurations for the magnetic circuit design of MRE devices. In Figure 2a, the MRE is tightly placed at the top and bottom of the coil. In order to fully utilize the magnetic field, the MRE is usually attached to the surface of the coil. In Figure 2b, the MRE is placed inside the excitation coil and serves as the magnetic core for the magnetic circuit. Compared with the weak diverging magnetic field outside the coil, the magnetic field inside the coil is strong and uniform, which provides a strong magnetic field and a large active area. Combining these two configurations, the magnetic circuit of the mixed-mode MRE isolator is shown in Figure 3. The shear MRE is tightly placed at the top of the coil, and the compression MRE is placed inside the excitation coil.
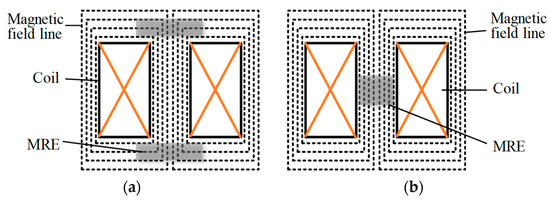
Figure 2.
Two commonly used magnetic circuits of the MRE devices. (a) Outside the coil; (b) Inside the coil.
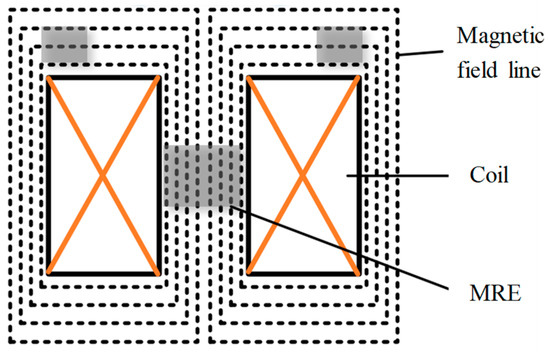
Figure 3.
The magnetic circuit of the mixed-mode MRE isolator.
Due to the fact that the magnetic permeability of magnetic materials far exceeds that of non-magnetic materials, the magnetic circuit is mainly composed of magnetic materials with high permeability, and the magnetic leakage effect is ignored. Therefore, the closed-loop magnetic circuit of the mixed-mode isolator mainly consists of the magnetic conductor, squeeze MRE, shear MRE, bottom base, and outer sleeve. The excitation coil generates a circular magnetic field after it is energized, and the magnetic field lines pass through various parts of highly permeable materials and MRE to form a closed loop. The magnetic flux passing through each component in this closed loop is the same. According to the magnetic circuit structure and Ohm’s law, the magnetic circuit of the MRE isolator can be simplified into an equivalent magnetic circuit as shown in Figure 4. The magnetic reluctance calculation of each part is as follows:
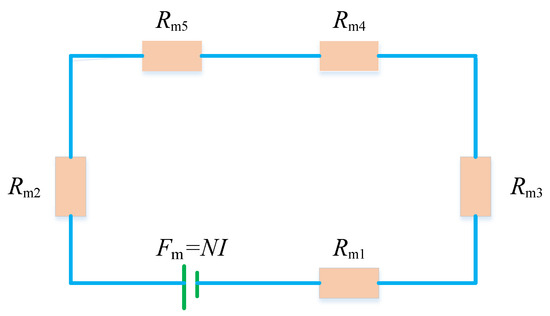
Figure 4.
The equivalent magnetic circuit.
The magnetic reluctance of each part is respectively obtained as:
where Rm1, Rm2, Rm3, Rm4 and Rm5 are the magnetic reluctance of the bottom base, squeeze MRE, outer sleeve, shear MRE, and magnetic conductor, respectively; μ1 is the magnetic permeability of low-carbon steel, μ1 = 4π × 10−4 H/m; μ2 is the magnetic permeability of the MRE, μ2 = 1.4π × 10−6 H/m [27].
The magnetic reluctance of each part of the magnetic circuit can be calculated by combining the structural parameters of the isolator. In order to exhibit strong magnetorheological effects, the MRE should first reach the magnetic saturation state under the same magnetic flux. According to Equations (1)–(5), the magnetic reluctance Rm2 of the squeeze MRE and the magnetic reluctance Rm4 of the shear MRE are the largest in the magnetic circuit, indicating that the magnetic circuit of the isolator meets the design requirements.
According to Ohm’s law for magnetic circuits, it can be obtained as:
where Fm is magneto-motive force; N is the number of coil turns; I is the input current; Rm is the total magnetic reluctance in the magnetic circuit; B is the magnetic induction of the MRE, and it is set to 0.6 T; and S is the cross-sectional area of MRE. To ensure the vibration operation of the isolator, a 2 A constant current source is selected for power supply. According to Equation (6), and considering actual machining errors and the magnetic leakage effect, the ideal number of coil turns is set to 700 turns.
3. The Simulation Analysis of the Mixed-Mode MRE Isolator
3.1. Magnetic Field Simulation Analysis
In order to verify the feasibility of the design scheme of the mixed-mode MRE isolator, Ansys Maxwell 16.0 software is used to perform finite element simulation on the working magnetic circuit of the isolator. The direction of magnetic field lines and magnetic induction in the magnetic circuit is obtained by simulating the working state of the isolator. Due to the symmetrical structure of the designed isolator, half of its cross-section is taken as the simulation object for simplified calculation. A 2D model of the isolator is established based on the structural parameters given in Table 1, and then different material properties are defined for each component according to Table 2.
Under Dirichlet boundary conditions, the magnetic vector potential on the boundary of the solution domain is set to 0, and the electric potential set to 0 as the reference point, indicating that the outer boundary of the solution domain is a non-magnetic area. Then, the cross-section of the excitation coil is selected and steady-state current source excitation is applied, and the value set as the magnetomotive force of the closed magnetic circuit of the isolator. Figure 5 shows the magnetic field distribution in the magnetic circuit of the mixed-mode MRE isolator.
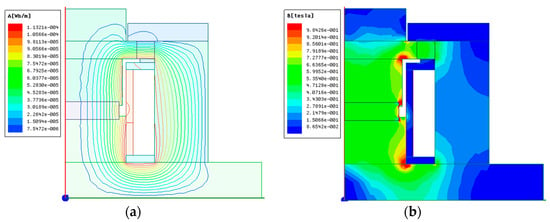
Figure 5.
The magnetic field simulation results of the mixed-mode MRE isolator. (a) Magnetic field line; (b) Magnetic induction.
As shown in Figure 5a, when the excitation coil is loaded with current input, the magnetic field lines pass vertically through the squeeze MRE and the shear MRE, and then return to the bottom base along the magnetic sleeve to form a closed loop. During this process, the excitation magnetic field can be fully utilized, which verifies the design rationality of the mixed-mode MRE isolator. In addition, the magnetic vector potential of the magnetic field lines in the simulation model of the isolator is larger at positions closer to the center of the coil, and their magnetic field lines are relatively dense. From Figure 5b, it can be seen that the magnetic field lines are almost entirely distributed in the designed magnetic circuit. The maximum magnetic induction occurs at the corner between the winding tube and bottom base, which is close to the saturation magnetic induction of low-carbon steel. The magnetic induction distribution is relatively uniform at the squeeze MRE and the shear MRE. After applying a current of 2.0 A to the excitation coil, the average magnetic induction of the squeeze MRE is 0.646 T, reaching the magnetic saturation state of the squeeze MRE prepared in this paper. The average magnetic induction of the shear MRE is 0.567 T, which almost reaches the magnetic saturation state of the shear MRE. Therefore, the mixed-mode MRE isolators not only have a more compact structure, but can also fully utilize the magnetorheological effect of the MRE.
The variation law of the average magnetic induction of the MRE with current can be obtained by controlling the input current. Figure 6 shows the average magnetic induction curve of the MRE under different currents. The magnetic induction values of shear MRE and squeeze MRE are very close and maintain the same change trend. The average magnetic induction of the MRE increases almost linearly when the loading current is in the range of 0–1.0 A. The growth rate of magnetic induction gradually slows down and eventually stabilizes when the loading current is greater than 1.0 A.
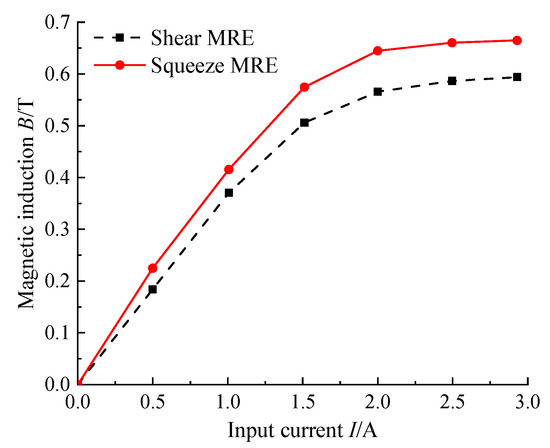
Figure 6.
The average magnetic induction of the MRE under different currents.
3.2. Dynamics Simulation Analysis
Based on the Kelvin model for viscoelastic materials, the dynamic model of the mixed-mode MRE can be equivalent to a parallel structure of springs and dampers, assuming that the isolator undergoes the same displacement changes in shear MRE and compression MRE during the vibration motion [28]. The isolation system model of the MRE isolator is shown in Figure 7.
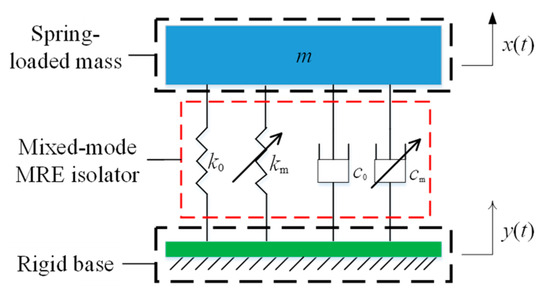
Figure 7.
The isolation system model of the MRE isolator.
The motion equation of the mixed-mode MRE isolator can be expressed as:
where m is the spring-loaded mass; c0 and cm are zero-field damping and magnetic damping; k0 and km are zero-field stiffness and magnetic stiffness; x(t) is the response displacement; and y(t) is the excitation displacement.
The equivalent stiffness and equivalent damping of the isolator can be expressed as:
Based on Figure 6, the numerical relationship between magnetic induction and input current can be obtained by fitting as:
where B1 and B2 represent the magnetic induction of shear MRE and compression MRE, respectively.
The dynamic shear and compression performance of the MRE is tested using a rotational rheometer (MCR302, Anton Paar), as shown in Figure 8. Cut the MRE sample into circular thin sheets with a diameter of 20 mm and a thickness of 1 mm, and preset a normal stress to prevent the MRE from slipping. The relationship between the magnetic-induced modulus and the loss factor of the MRE sample with magnetic induction variation is shown in Figure 9, and their relationship can be expressed through data fitting as follows:
where Gs and Gc are the shear and squeeze modulus, respectively; and η is the loss factor. Referring to [19], the shear stiffness and squeeze stiffness of the MRE can be calculated as:
where ks and kc are the shear stiffness and squeeze stiffness of the MRE, respectively; As and Ac are the shear area and squeeze area of the MRE, respectively; l is the length of the MRE; and h is the thickness of the MRE.

Figure 8.
Rotational rheometer.
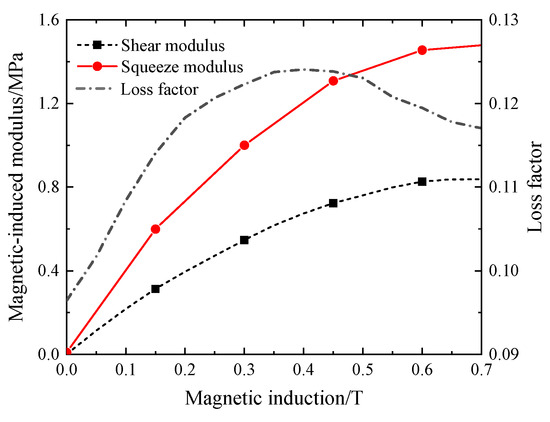
Figure 9.
The magnetic-induced modulus and loss factor of the MRE.
The equivalent stiffness of the mixed-mode MRE isolator is the sum of shear stiffness and squeeze stiffness. Combined with Equations (9)–(13), the relationship between equivalent stiffness and input current can be obtained as:
Referring to [19], the equivalent damping can be expressed as:
where ζ is the damping ratio. Characterizing the loss factor of the MRE allows the relationship between the damping ratio and input current to be obtained as:
The vibration characteristics of a mixed-mode MRE isolator are simulated under different currents and excitation frequencies. Figure 10 and Figure 11 respectively show the displacement and acceleration responses of the spring-loaded mass when the excitation frequency is 4–24 Hz and the excitation amplitude is 1 mm. The applied currents are 0 A, 0.5 A, 1.0 A, 1.5 A, and 2.0 A, respectively. In the frequency range of 4–16 Hz, the displacement amplitude and peak acceleration of the spring-loaded mass gradually decrease with the continuous increase of applied current. The relative decrease of the response amplitude changes very little and tends to stabilize when the applied current increases to a certain extent; this is because the MRE has reached magnetic saturation at this time.
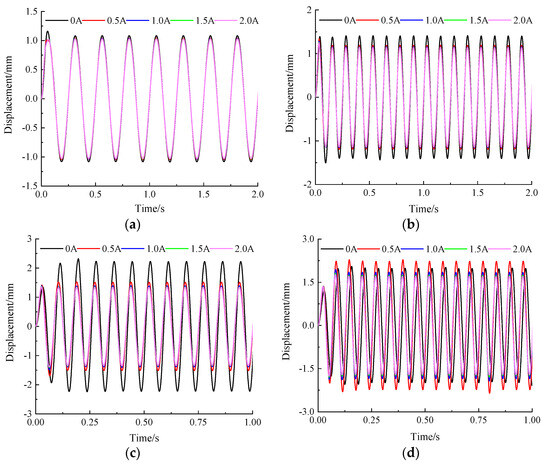
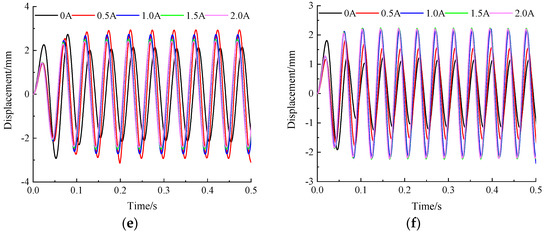
Figure 10.
The displacement response of spring-loaded mass under different currents. (a) 4 Hz; (b) 8 Hz; (c) 12 Hz; (d) 16 Hz; (e) 20 Hz; (f) 24 Hz.
Figure 11.
The acceleration response of spring-loaded mass under different currents. (a) 4 Hz; (b) 8 Hz; (c) 12 Hz; (d) 16 Hz; (e) 20 Hz; (f) 24 Hz.
According to the principle of vibration isolation, when the ratio of the external excitation frequency to the natural frequency of the system exceeds the threshold, increasing the stiffness and damping will result in a poor vibration isolation effect [29]. The vibration response under various external currents is significantly increased compared to that without current input when the external excitation frequency exceeds 16 Hz. When f = 20 Hz and applied I = 0 A, the displacement amplitude of the spring-loaded mass is 2.07 mm, and the peak acceleration is 0.29 m/s2. At this time, the isolation effect of the system is optimal. The displacement amplitude is 2.82 mm and the peak acceleration is 0.40 m/s2 when I = 0.5 A, indicating the worst isolation effect of the system. When f = 24 Hz and applied I = 0 A, the displacement amplitude of the spring-loaded mass is 1.29 mm, and the peak acceleration is 0.30 m/s2, indicating the best isolation effect of the system. At this response, the system isolation effect is the worst when I = 1.5 A.
4. The Experimental Analysis of the Mixed-Mode MRE Isolator
4.1. Experimental System
Through simulation analysis, the effectiveness of the vibration isolation performance of the mixed-mode MRE isolator has been preliminarily demonstrated. In order to further verify the accuracy of the simulation analysis, a prototype of the mixed-mode MRE isolator was fabricated based on the structural design in Section 2. The components and physical assembly of the mixed-mode MRE isolator are shown in Figure 12.
Figure 12.
The prototype of the mixed-mode MRE isolator. (a) Components; (b) Prototype.
The MRE isolator testing platform constructed is shown in Figure 13. The experimental platform mainly consists of excitation, isolation, control, and the acquisition system. In the experimental system, the type of the acquisition system is PCI-6221 produced by National Instruments (Austin, TX, USA), and the models of exciter and acceleration sensor are JZK-40 and CA-YD-181 produced by Sinocera Piezotronics Inc. (Yangzhou, China), respectively. The excitation system generates different excitation frequencies through the exciter. The vibration isolation system reduces the acceleration response by changing the stiffness and damping of the mixed-mode MRE isolator. The acquisition system measures the vibration acceleration amplitude and collects measurement data. The control system controls the current value connected to the excitation coil through a DC stabilized power supply. During the experiment, due to the magnetic field interference caused by the power supply, a magnetic isolation aluminum plate is installed to prevent it from being magnetized. The upper end of the magnetic isolation aluminum plate is connected to the base of the mixed-mode MRE isolator, and its magnetic conductor can be bolted to a spring-loaded mass weighing approximately 25 kg. Acceleration sensors are installed on the magnetic isolation aluminum plate and spring-loaded mass respectively for real-time measurement of response signals. The LabVIEW 18.0 program is used to obtain and analyze the analog signals, the data sampling frequency during the experiment is 1 kHz, and the DAQ data acquisition card is used to generate and obtain the signals required by the system.
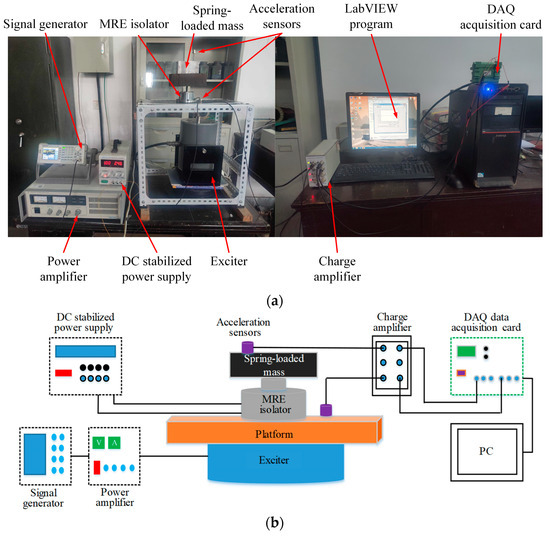
Figure 13.
The MRE isolator testing platform. (a) Experimental device; (b) Experimental principle.
4.2. The Comparison of Experimental and Simulation Results
In order to clearly reflect the comparison of the vibration isolation performance for the mixed-mode MRE isolator, the mean value of the acceleration response of simulation and experimental results is calculated. The acceleration comparison between experiment and simulation at each frequency is shown in Figure 14. The applied current remains constant, and the excitation frequency range is 4–24 Hz. Due to the neglect of the stiffness of the magnetic isolation aluminum plate and the weight of the isolator in the ideal simulation, the simulated acceleration amplitude is slightly greater than the experimental value. The simulation and experimental values are generally consistent and maintain a consistent change trend. The relative error between the experimental and simulation results is the largest and exceeds 10% when the excitation frequency is 12 Hz. In most other cases, the errors in experiments and simulations remain within a small range. These results validate the effectiveness of the theoretical analysis of the mixed-mode MRE isolator.
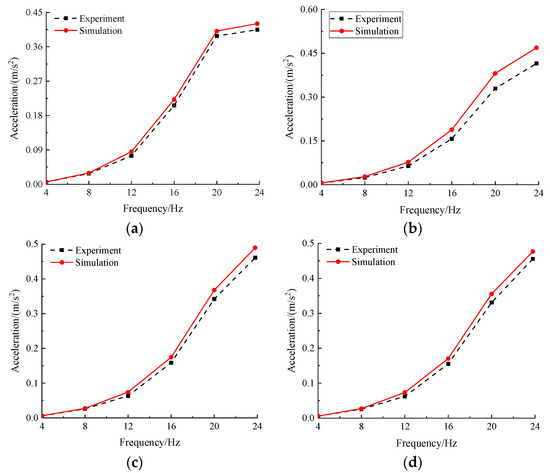
Figure 14.
Comparison of test and simulation results. (a) 0.5 A; (b) 1 A; (c) 1.5 A; (d) 2 A.
4.3. Experimental Result
The loading excitation used in this experiment is a sine wave with an excitation frequency of 4–24 Hz. The acceleration response signal of the vibration platform before isolation is collected through an acceleration sensor. As shown in Figure 15, the acceleration response of the vibration platform at different excitation frequencies before vibration isolation is applied. As shown in the figure, the acceleration amplitude of the vibration platform also increases continuously with the increase of excitation frequency, from 0.0075 m/s2 at 4 Hz to 0.6048 m/s2 at 24 Hz. The acceleration response without the MRE isolator at different frequencies is significantly higher than that with the MRE isolator. The experimental system needs to apply MRE isolators for the process of further isolation to suppress the vibration of the working platform.
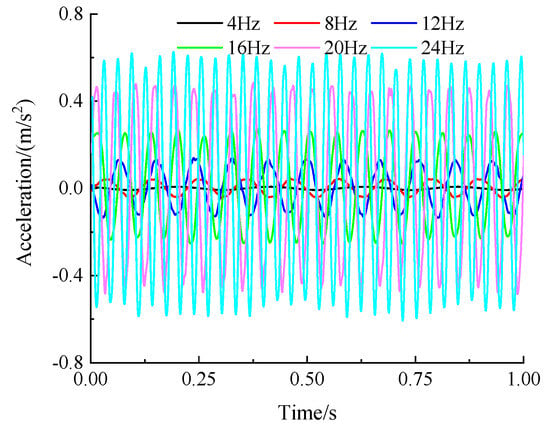
Figure 15.
The acceleration response before vibration isolation is applied.
The spring-loaded mass acceleration response of the MRE isolator under different currents is shown in Figure 16, where the spring-loaded mass is set to 25 kg, and the excitation frequency is set to 4 Hz to 24 Hz. The excitation currents are 0 A, 0.5 A, 1.0 A, 1.5 A, and 2.0 A, respectively. At a frequency of 4 Hz, there is almost no change in the acceleration response due to the small external frequency applied to the vibration system. In the frequency range of 4–16 Hz, the peak acceleration of the spring-loaded mass gradually decreases with the continuous increase of the applied current. The relative decrease of the response amplitude changes very little when the applied current increases to a certain extent. The amplitude of vibration acceleration under various external currents significantly increases when the external excitation frequency exceeds 16 Hz. The system with I = 0 A has the best isolation effect and the system with I = 0.5 A has the worst isolation effect when f = 20 Hz. The system with I = 0 A also demonstrated the best isolation effect and the system with I = 2.0 A has the worst isolation effect when f = 24 Hz. These experimental results are highly consistent with the simulation results.
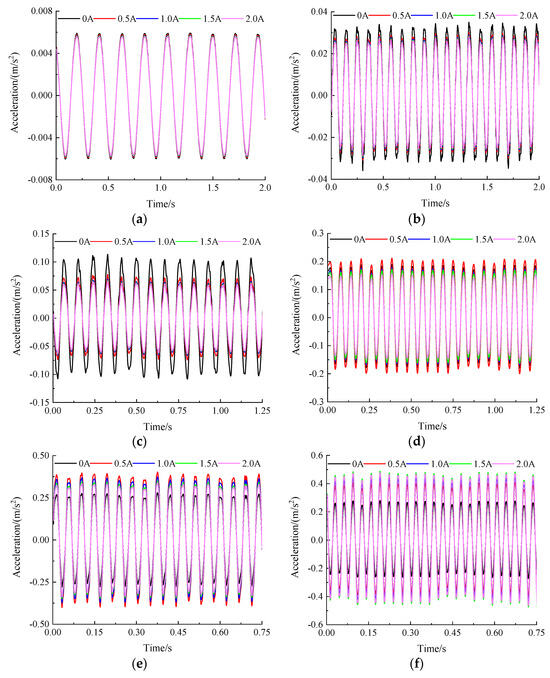
Figure 16.
The experimental acceleration response of spring-loaded mass under different currents. (a) 4 Hz; (b) 8 Hz; (c) 12 Hz; (d) 16 Hz; (e) 20 Hz; (f) 24 Hz.
According to Figure 16, the vibration attenuation rate curve of the system under different currents is shown in Figure 17. The vibration attenuation rate gradually increases under passive control with the current at 0 A, while the vibration attenuation rate of the system shows a trend of first increasing and then decreasing above 0.5 A. It is evident that within the frequency range of 20 Hz above 0.5 A, as the applied current continues to increase, the vibration attenuation rate of the system also increases, indicating that the isolation effect is constantly being optimized. Increasing the maximum input current to 2 A has only a minimal effect on the vibration attenuation rate of the system compared to that of the previous input current of 1.5 A. This is because the magnetic induction has reached saturation at the maximum input current. Meanwhile, the maximum attenuation rate occurs at a frequency of 12 Hz. This operating frequency range may avoid the resonance region and result in the vibration attenuation rate of 59.46% at I = 2 A. The deterioration of the vibration attenuation rate occurred at 20 Hz, and the worst attenuation rate is 14.08% at a current of 0.5 A. The vibration attenuation rate significantly decreases when external excitation frequency exceeds 16 Hz, and the isolation effect of the system varies randomly, making it impossible to achieve stable isolation performance.
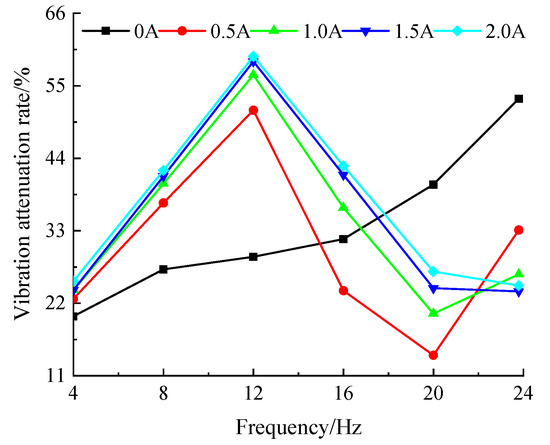
Figure 17.
The vibration attenuation rate under different currents.
5. Conclusions
Based on the principles of shear and extrusion working modes of MRE, this paper designs a mixed-mode MRE isolator to achieve a larger working area under a certain volume. The material selection and dimensional parameters of each component are determined based on the magnetic circuit calculation and structural design. Furthermore, the magnetic and non-magnetic materials in the assembly structure are arranged for improving the magnetic field utilization efficiency, and the various parameters of the isolator can be obtained through structural verification. On this basis, Maxwell 16.0 software is used to simulate the electromagnetic field and analyze the dynamic performance of the mixed-mode MRE isolator. The rationality of the structural design and the effectiveness of the simulation model are preliminarily verified. The simulation results show that the squeeze MRE and shear MRE have basically reached the designed magnetic saturation state.
Based on theoretical calculations and simulation analysis, the processed MRE isolator prototype was installed on the test platform for the isolation performance experiment. The test results showed that the acceleration response and vibration attenuation rate variation of the experiment and the simulation are basically consistent. In the frequency range of 4–16 Hz, as the applied current continues to increase, the isolation performance of the system is improved. The isolation performance of the system tends to stabilize when the applied current increases to a certain extent. The isolation effect of the MRE isolator without current input is generally optimal when the external excitation frequency exceeds 16 Hz, and the isolation effect of the system is difficult to effectively control using current input.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, Q.L.; conceptualization, Z.G.; methodology, L.Y.; validation, W.L.; formal analysis, S.J.; writing—review and editing, G.L.; project administration, G.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 52405104 and 52165004), Key R&D project of Jiangxi Province of China (No. 20212BBE51009), Natural Science Foundation Project of Jiangxi Province (20232BAB204041), Key Program for International S&T Cooperation Project of Jiangxi Province of China (20232BBH80010), and Double Height Project of Jiangxi Province Human Resources and Social Security Department in 2022.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Wei Liu was employed by the Jiangling Motor Corporation Limited Company. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Bastola, A.K.; Paudel, M.; Li, L.; Li, W.H. Recent progress of magnetorheological elastomers: A review. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 123002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Y.S.; Shen, H.C.; Sun, M.; Chai, H.; Wu, H.P.; Jiang, S.F. Experimental study of orthogonal bistable laminated composite shell driven by magnetorheological elastomer. Compos. Struct. 2021, 271, 114119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.J.; Chen, W.; Hu, H.S.; Hu, G.L.; Zhu, Q.Y. Effect of magnetorheological damper parameters on dynamic responses of a full-vehicle suspension system. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2020, 63, 483–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.D.; Sun, S.S.; Yang, J.; Deng, L.; Du, H.P.; Li, W.H. A hybrid MRE isolation system integrated with ball-screw inerter for vibration control. Smart Mater. Struct. 2021, 31, 025009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erenchun, A.; Kari, L.; Blanco, B.; Wang, B.C.; Irazu, L.; Gil-Negrete, N. Modeling and design of magnetorheological elastomer isolator system for an active control solution to reduce the vibration transmission in elevator context. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2024, 35, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.Q.; Dong, X.M.; Qi, S.; Wang, T.; Liang, Y.X. Development of a magnetorheological isolator with variable damping and variable stiffness for broadband vibration suppression. Smart Mater. Struct. 2021, 30, 025023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Wereley, N.M. Vibration isolation performance of an adaptive magnetorheological elastomer-based dynamic vibration absorber. Actuators 2022, 11, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.J.; Gong, X.L.; Xuan, S.H.; Kang, C.J.; Zong, L.H. Development of a real-time tunable stiffness and damping vibration isolator based on magnetorheological elastomer. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2012, 23, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.L.; Huang, X.G.; Li, Y.C.; Ouyang, Q.; Wang, J. Performance of a semi-active/passive integrated isolator based on a magnetorheological elastomer and spring. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 095024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Qi, S.; Xie, Y.P.; Fu, J.; Yu, M. Transient responses of magnetorheological elastomer and isolator under shear mode. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 044002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, A.; Dianati, H.; Norouzi, M.; Vatandoost, H.; Ghatee, M. A novel bi-directional shear mode magneto-rheological elastomer vibration isolator. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2020, 31, 2002–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syam, T.M.I.; Muthalif, A.G.A. Magnetorheological elastomer based torsional vibration isolator for application in a prototype drilling shaft. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 2022, 41, 676–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Li, J.C.; Li, W.H.; Du, H.P. A state-of-the-art review on magnetorheological elastomer devices. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 123001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Li, P.D.; Liao, G.Y.; Lai, J.J.; Yu, M. Development and dynamic characterization of a mixed mode magnetorheological elastomer isolator. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 2800104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatandoost, H.; Sedaghati, R.; Rakheja, S.; Hemmatian, M. Effect of pre-strain on compression mode properties of magnetorheological elastomers. Polym. Test. 2021, 93, 106888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.P.; Li, W.H.; Zhang, N. Semi-active variable stiffness vibration control of vehicle seat suspension using an MR elastomer isolator. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 105003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.H.; Zhang, X.Z.; Du, H.P. Development and simulation evaluation of a magnetorheological elastomer isolator for seat vibration control. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2012, 23, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.F.; Tao, Y. Magnetorheological elastomer isolator in compression mode for IMU vibration isolation. J. Mech. Mater. Struct. 2020, 15, 565–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Huang, Z.; Li, W.; Wang, W.; Zhong, C.; Qi, S.; Yu, M. A bidirectional-controllable magnetorheological elastomer-based quasi-zero-stiffness isolator. Smart Mater. Struct. 2024, 33, 085009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustighi, E.; Ledezma-Ramirez, D.F.; Tapia-Gonzalez, P.E.; Ferguson, N.; Zakaria, A. Modelling and experimental characterisation of a compressional adaptive magnetorheological elastomer isolator. J. Vib. Control 2022, 28, 3093–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.G.; Dong, X.F.; Xiong, X.Y.; Ren, J.Q.; Niu, L.K.; Li, C.M.; Zhang, D.G.; Guo, J.B. Development of an electrorheological elastomer isolator working in shear-squeeze mixed mode. Smart Mater. Struct. 2023, 32, 065004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Lu, J.Y.; Han, W.H.; Chen, G.L.; Wang, X.Z. Improving the performance of magnetorheological elastomer-based adaptive isolator through integrated compression-torsion structure. Smart Mater. Struct. 2024, 33, 075022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, A.; Sedaghati, R. The modeling of magnetorheological elastomers: A state-of-the-art review. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2300182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.J.; Xia, L.L.; Sun, L.Z. Multiscale magneto-mechanical coupling of magnetorheological elastomer isolators. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2023, 224, 104003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.L.; Zhou, F.; Yang, X.; Wang, N.B.; Yu, L.F.; Li, G. Analysis of pressure drop and response characteristics of an enhanced radial magnetorheological valve based on magneto-fluidic coupling. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2024, 589, 171589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Hu, G.L.; Qian, C.; Zhu, W.C. Analysis of braking performance and heat dissipation characteristics of multi-disc magnetorheological brake with an inner water-cooling mechanism. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2024, 604, 172313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Rui, X.T.; Yang, F.F. Investigation of the impacts on magnetic permeability of MREs. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 477, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, D.X.; Xiao, H.Y.; Sun, L.; Liu, G.J.; Wang, X.J.; Sun, L.Y. Study on a magnetorheological elastomer-base device for offshore platform vibration control. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2019, 30, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, G.D.; Hou, S.; Zhang, X.F.; Shan, X.B.; Hou, C.W.; Song, H.A.; Hou, W.J.; Li, J.M. A bio-inspired spider-like structure isolator for low-frequency vibration. Appl. Math. Mech. 2023, 44, 1263–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).