Research on Multi-Mode Variable Parameter Intelligent Shift Control Method of Loader Based on RBF Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Loader Operation Process
2.1. Loader Operation Process Analysis
2.2. Loader Vehicle Parameters
3. Loader Multi-Mode Variable Parameter Shift Law Design
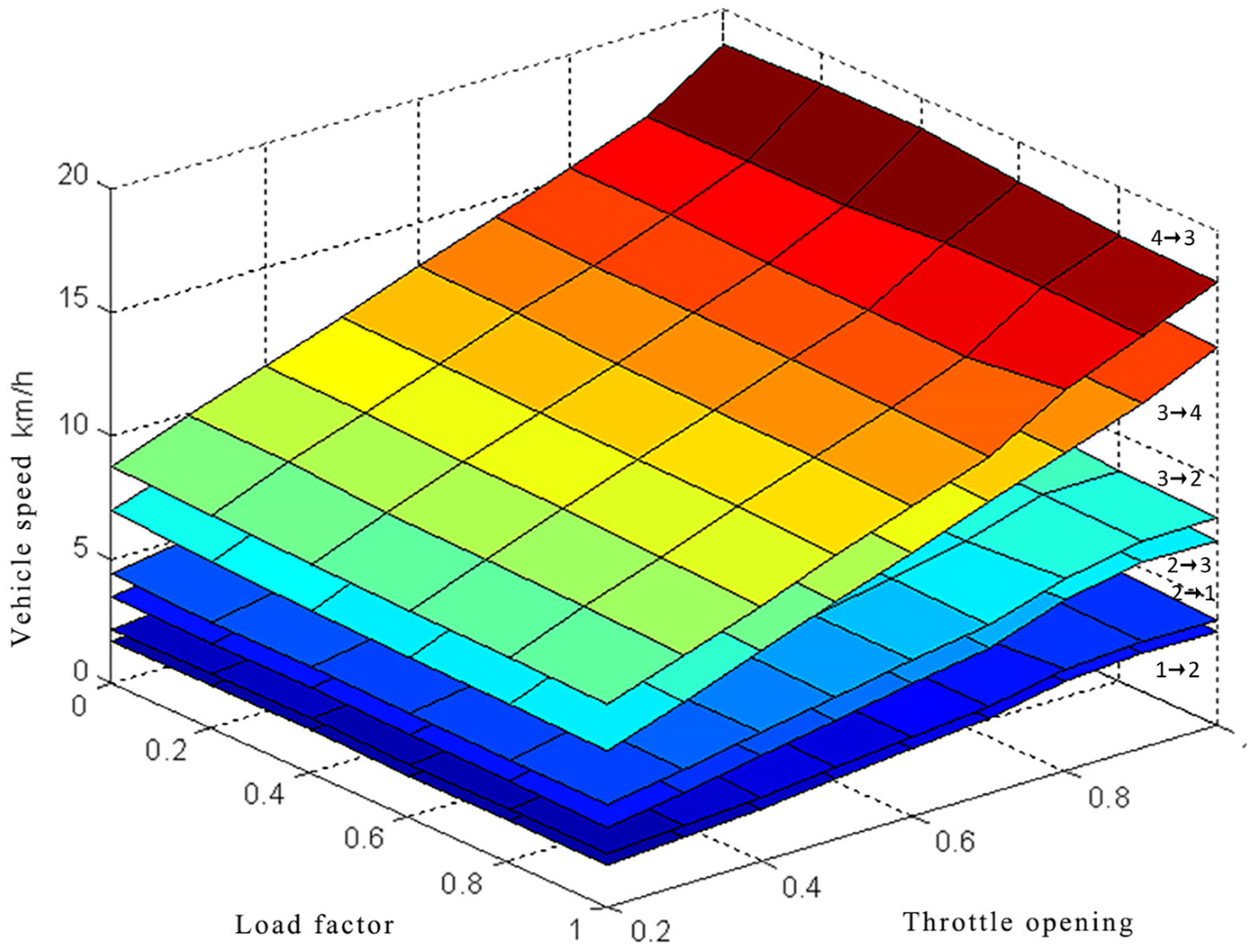
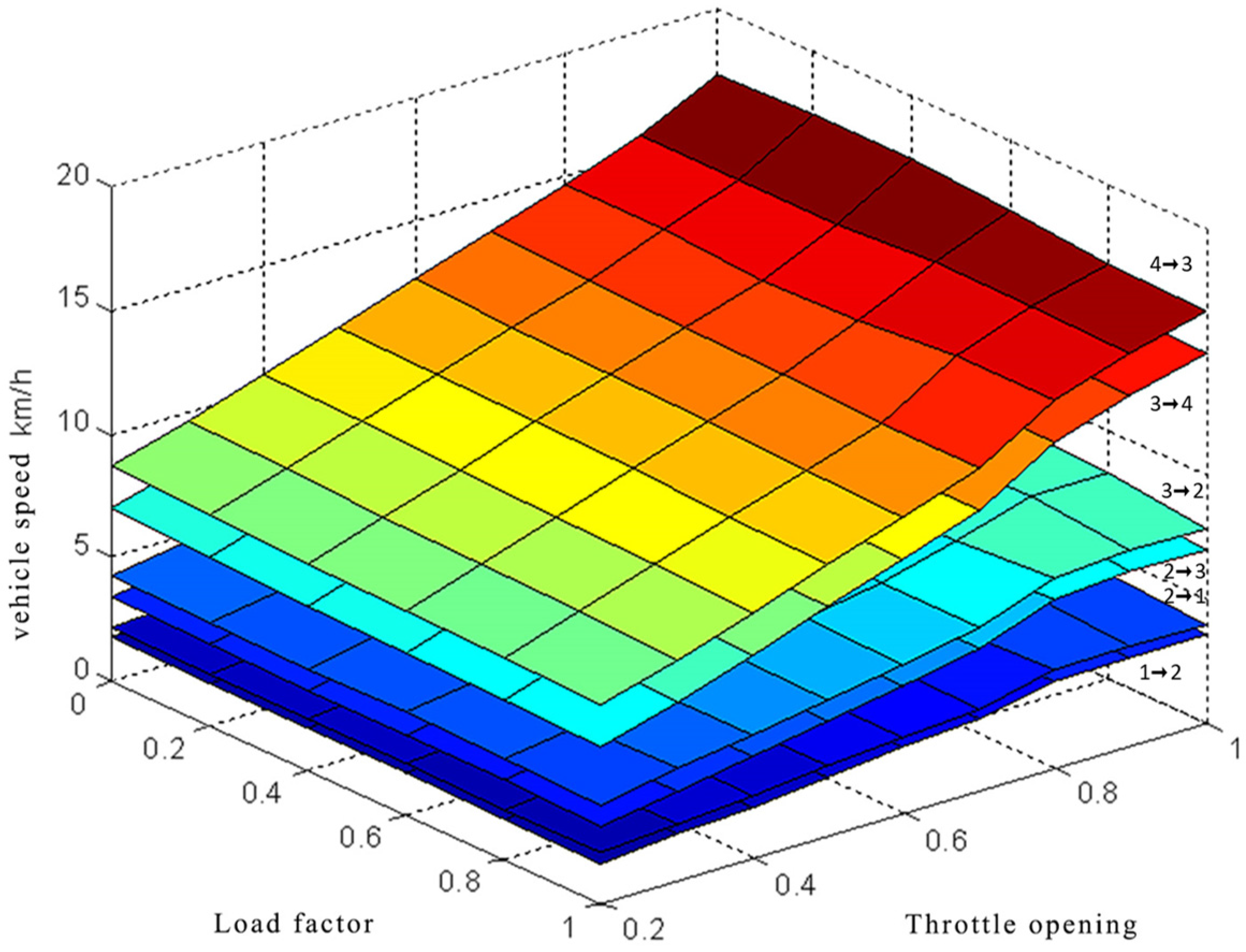
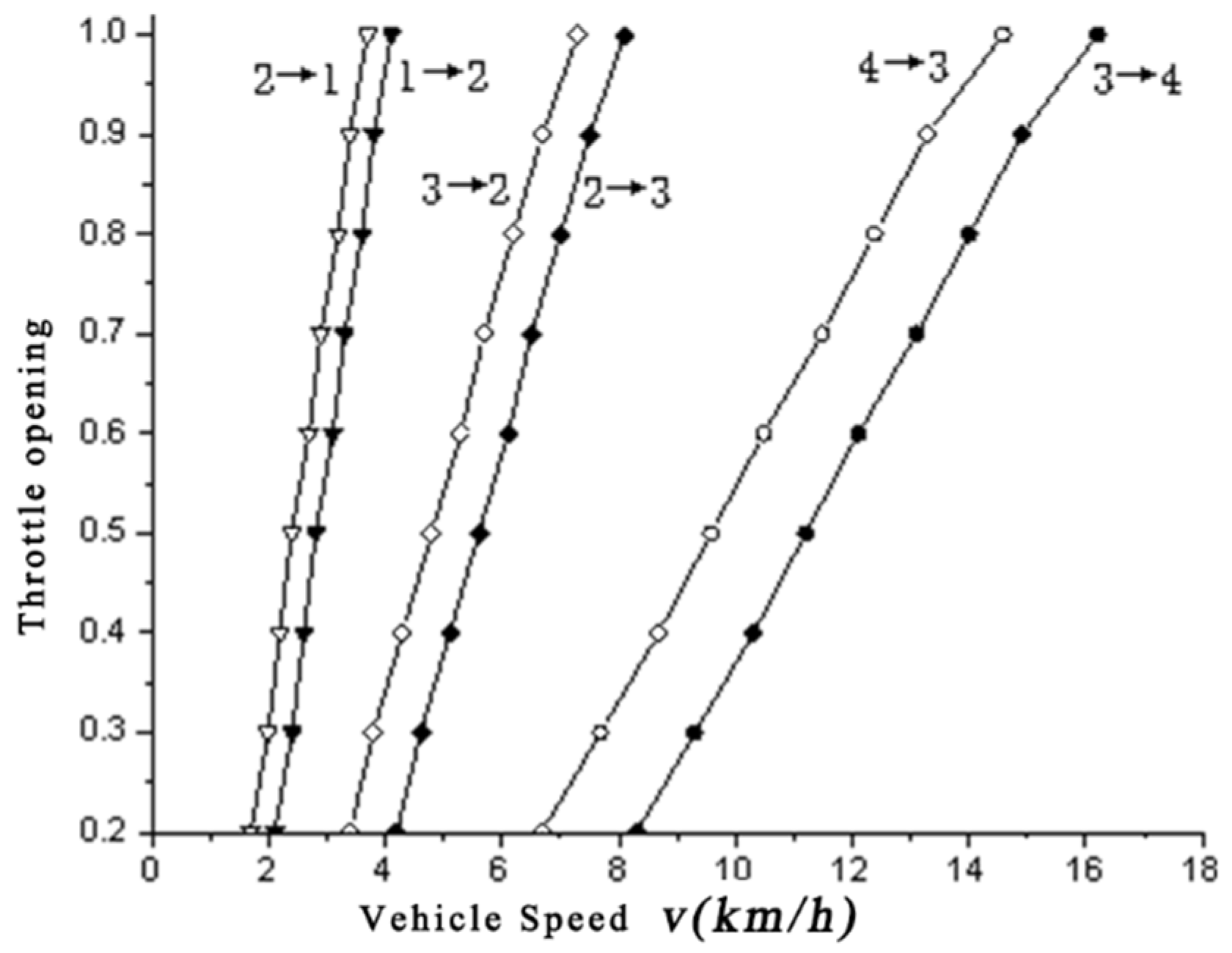
3.1. Power Mode Shift Law Design
3.2. Standard Mode Shift Law Design
3.3. Economic Mode Shift Law Design
4. Intelligent Gear Shift Control Method for Loader Based on RBF Networks
4.1. RBF Network Learning Algorithm
- (1)
- Initialization: given the initial center (0) of each node.
- ①
- Determination of center . The k-means cluster analysis technique was used to determine ;
- ②
- Determination of the radius . The size of the radius determines the range of the RBF unit’s response to the input vector and affects the final classification accuracy of the network;
- ③
- Regulating weight w. Here, the regulating weights w are the connection weights between the output layer and the implicit layer of the network, which can be realized by the following two methods to regulate the weights of the network, respectively;
- ④
- Linear least squares method. The network output of this method is: ;
- ⑤
- Gradient method. The iterative formula is as follows: .
4.2. Creation of RBF Neural Network Function Newrb
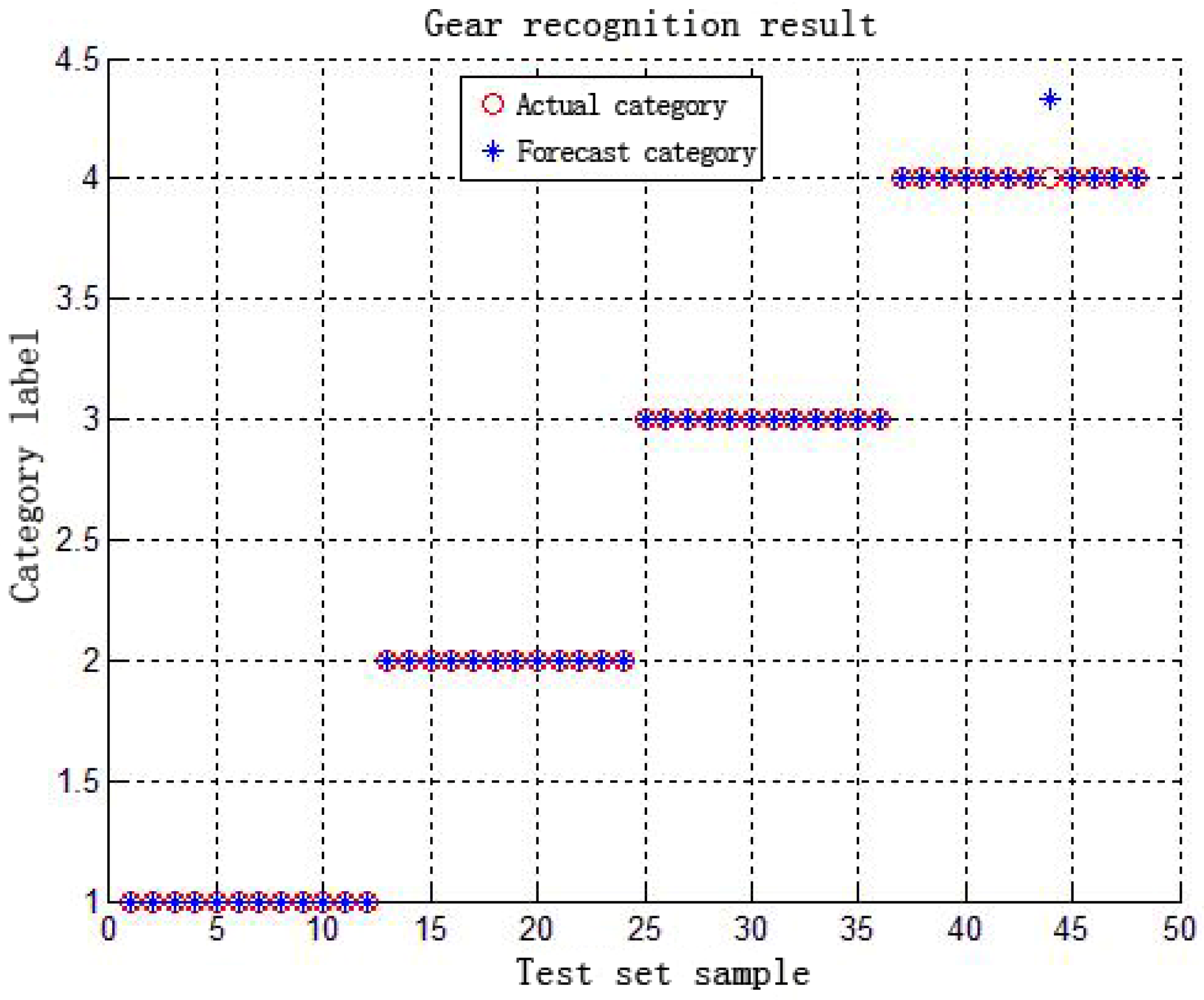
4.3. RBF Neural Network Loader Intelligent Shift Control Simulation Experiments
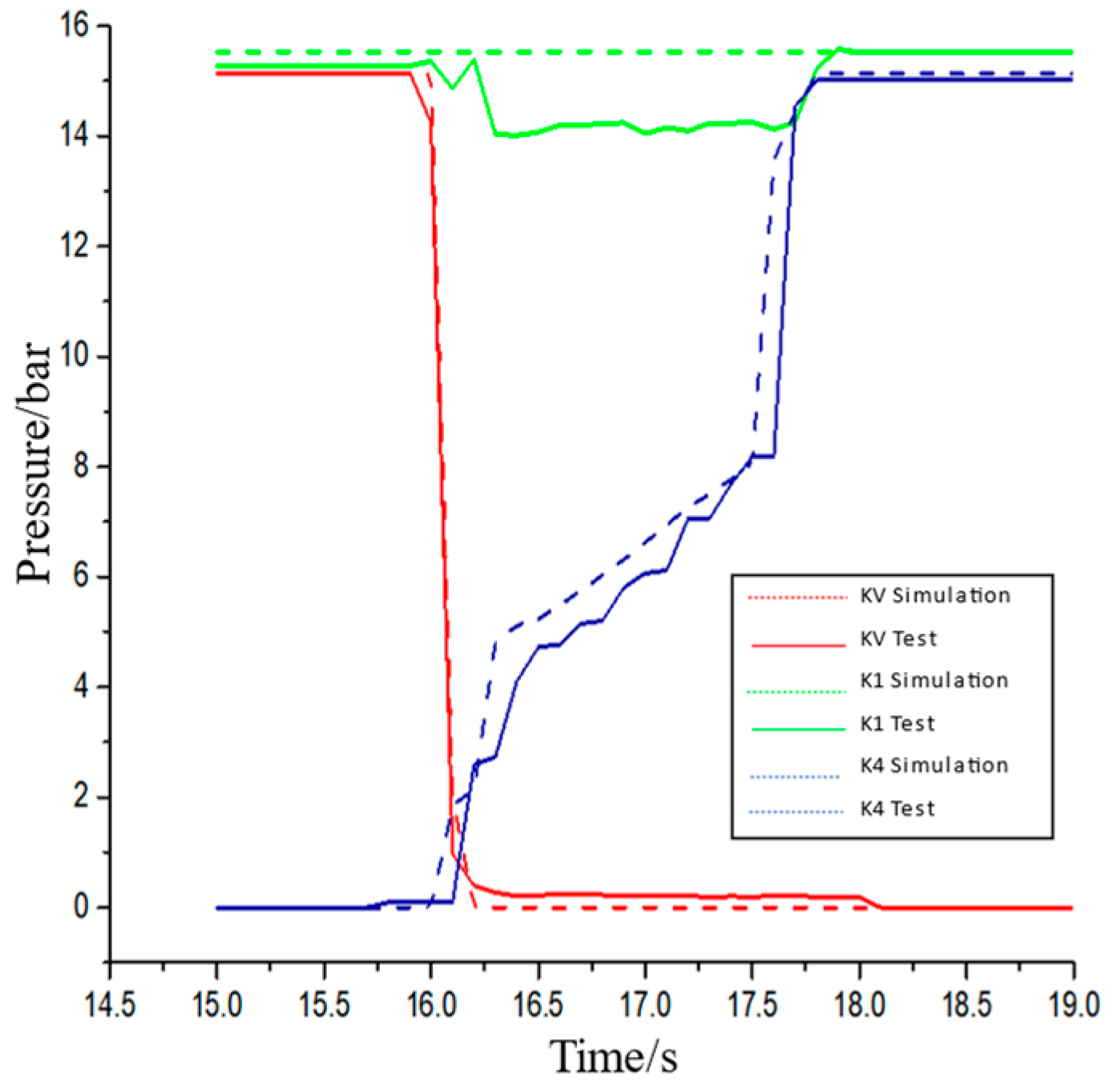
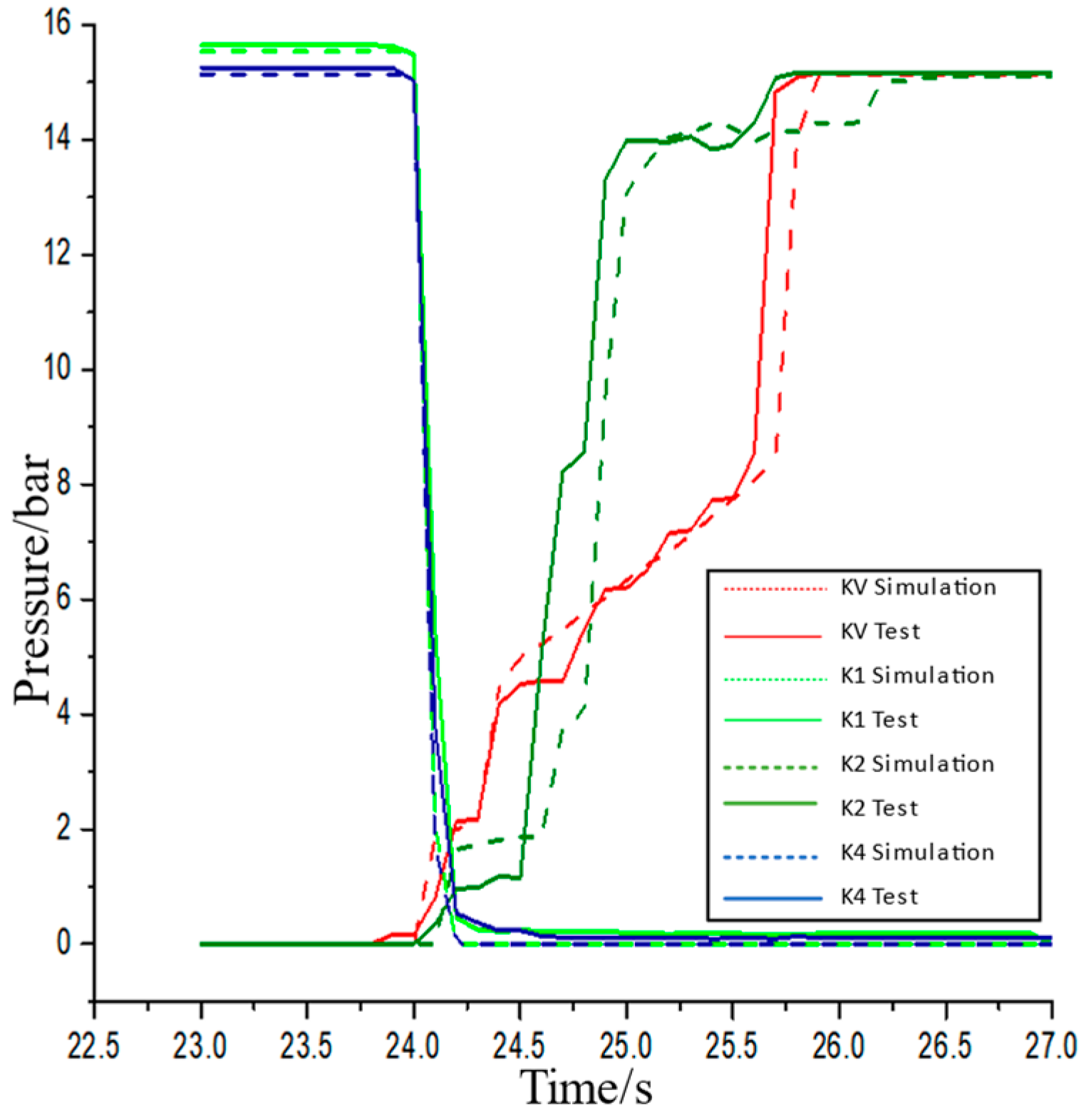
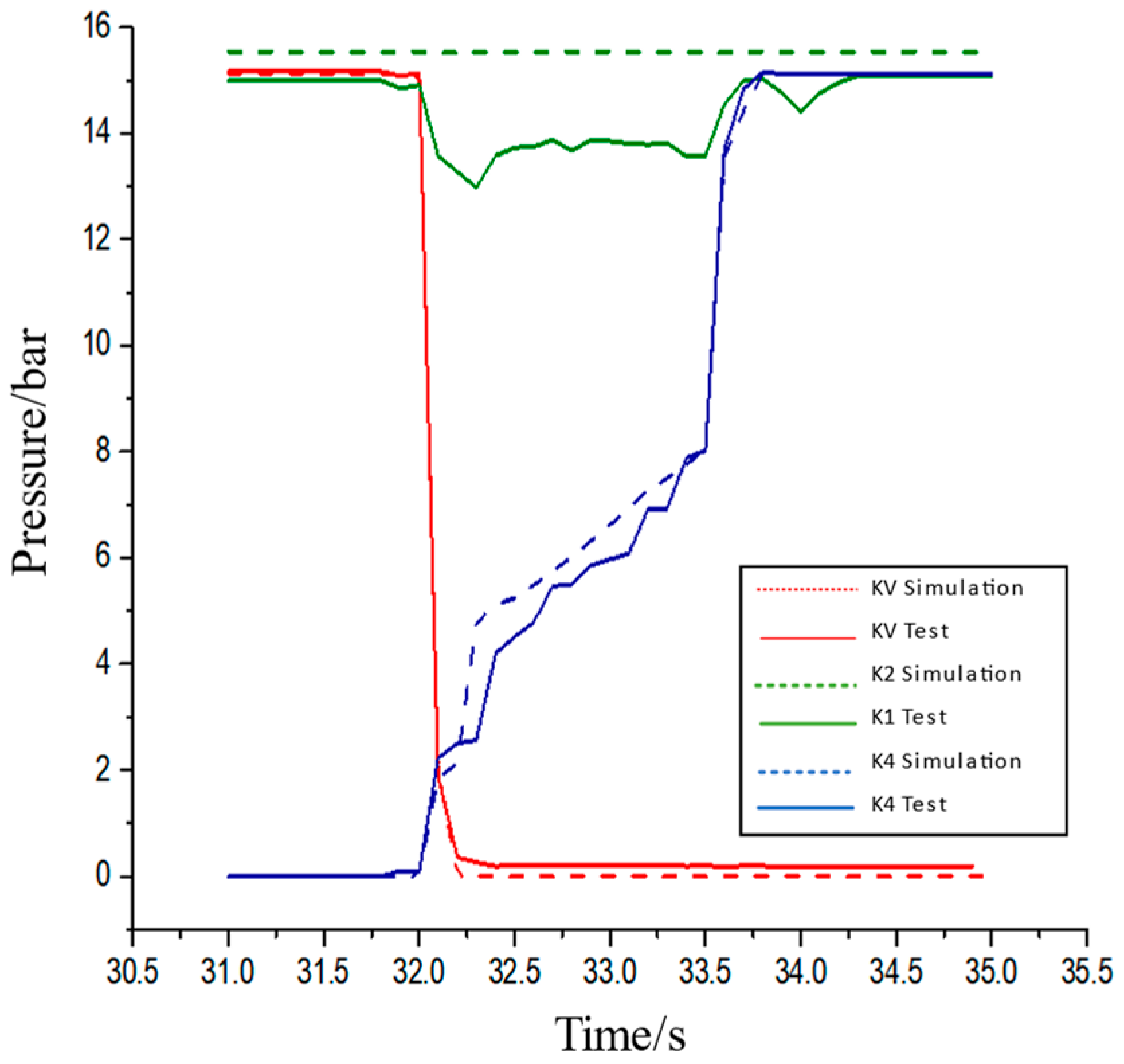
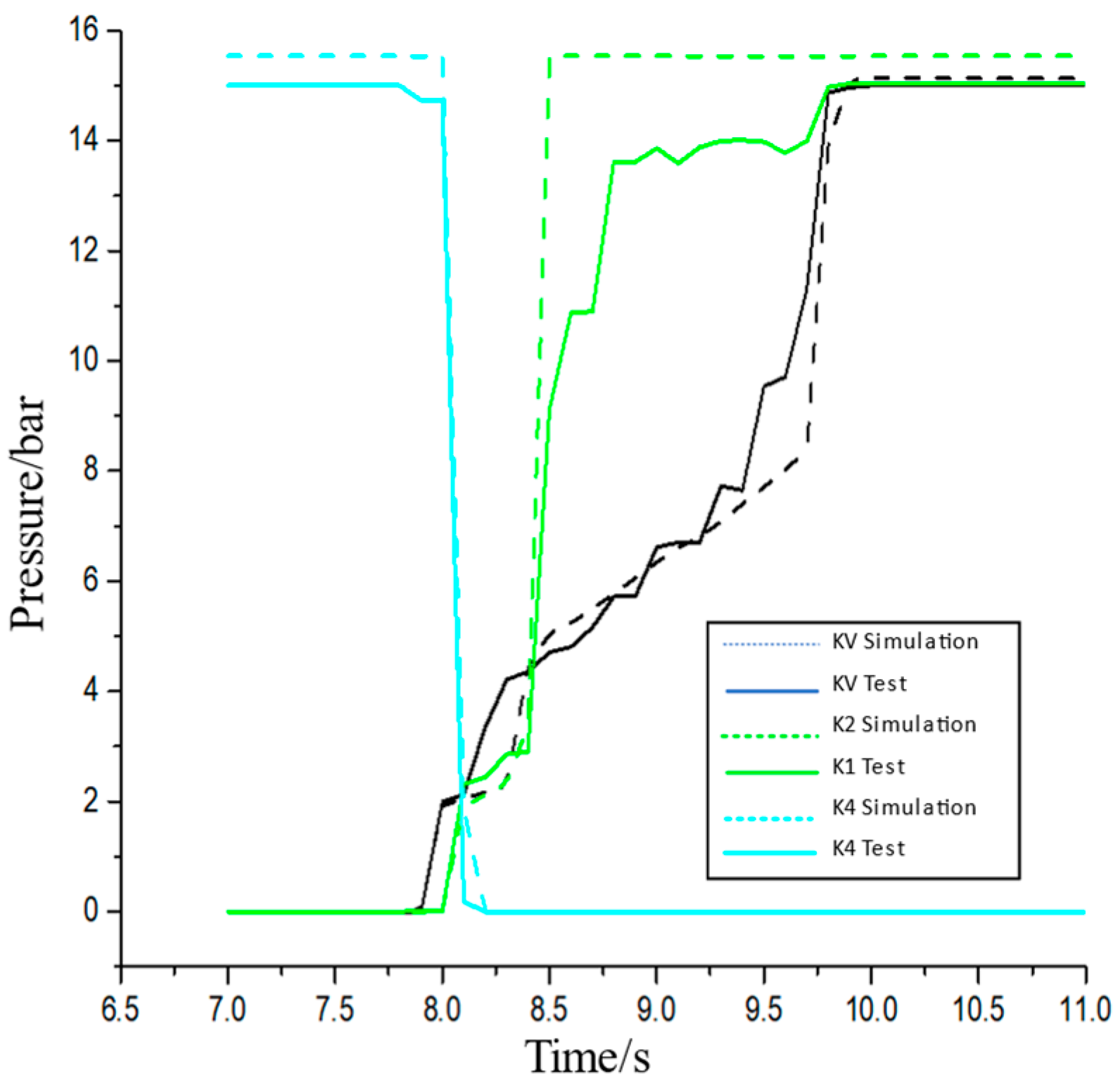
5. RBF Network-Based Loader Multi-Mode Variable Parameter Intelligent Shift Law Test
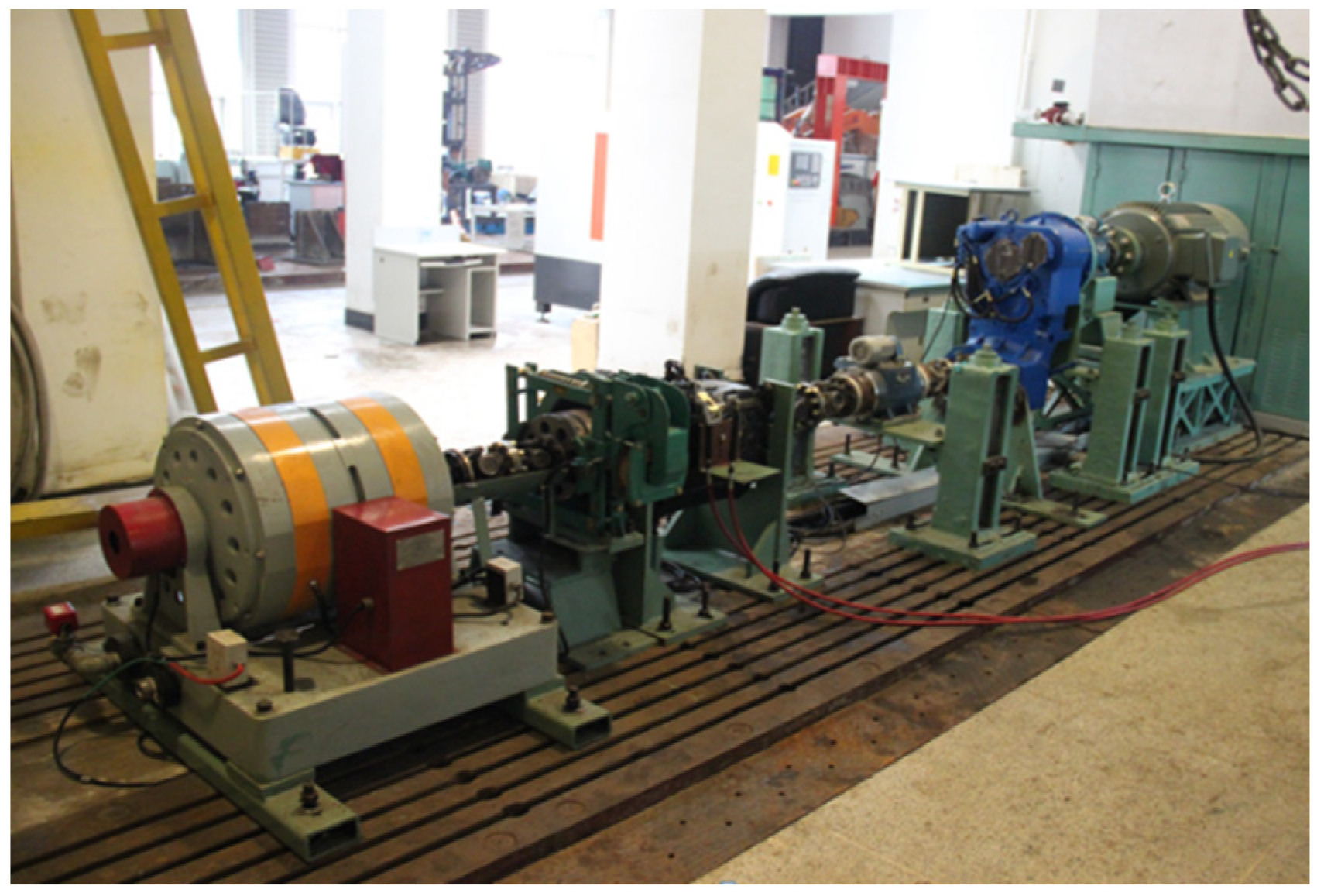
5.1. Shift Law Test System
5.2. Intelligent Shift Law Test Experiment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chou, C.; Ma, W. Hydraulic and Fluid Power Transmission System of Construction Machinery: Hydraulic Volume; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P. Power Matching Analysis of Wheel Loader Based on Typical Working Condition Test. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D. Basic principle of automatic speed adjustment of construction vehicles. Constr. Mach. Equip. 2006, 37, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G. CLG8128H wheel loader. Constr. Mach. Maint. 2016, 4, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Hui, J.; Zhang, H.; Geng, L.; Bu, Z.F. Research on primary and secondary operating conditions power matching method of engine and torque converter. J. Mech. Eng. 2023, 59, 300–314. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Q. Optimized Design and Experimental Research on Power Matching of Loader Transmission. Ph.D. Thesis, Shandong University, Jinan, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P.; Zhang, J.C.; Ding, H.F.; Chen, Z.M.; Zhao, Y.Q. Kinematics and dynamics analysis of a new loader working device[J/OL]. J. Mech. Eng. 2024, 60, 1–13. Available online: http://kns-cnki-net.vpn.jlenu.edu.cn/kcms/detail/11.2187.TH.20240401.1059.024.html (accessed on 28 April 2024).
- Guan, D. Research on Three-Parameter Automatic Gear Shift Law and Electronic Control System of Loader. Ph.D. Thesis, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J. Research on Three-Parameter Integrated Shift Strategy of Engineering Vehicles. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G. Research on Dynamic Gearshift Law of Engineering Vehicles Based on New Three-Parameter. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Shao, S.; Li, X.; Meng, G.L. Automatic gear shift strategy of loader based on intelligent control. J. Mech. Eng. 2009, 45, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Wu, G.; Li, Y.; Li, Y. Research on intelligent control system of loader. Constr. Mach. 2009, 40, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Sun, S.; Rui, H.; Wang, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, W.W.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H.; Chen, H.Y.; Liu, J. Overview of academic research on road construction machinery in China-2018. China J. Highw. 2018, 31, 1–164. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L. Intelligent shifting law of loader based on real-time working conditions. J. Agric. Eng. 2009, 25, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T. Research on automatic gear shift of loader based on fuzzy control. Constr. Mach. 2017, 48, 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, D.; Li, T.; Zhang, M. Control strategy of hybrid loader based on automatic transmission. J. Northeast. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2015, 36, 532–536. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, K.; Yun, S.; Ko, K.; Ha, S.; Kim, P.; Seo, J.; Yi, K. Gear ratio and shift schedule optimisation of wheel loader transmission for performance and energy efficiency. Autom. Constr. 2016, 69, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-X.; Gong, D.; Zhang, Y.-S.; Deng, J.; Shen, Y. Modeling and genetic algorithm optimization of wheel loader driveline using three-parameter auto shift strategy. J. Jilin Univ. (Eng. Ed.) 2011, 41, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, G.; Sha, L.; Li, F.; Hao, Y.; Zhou, L. Fatigue reliability of loader arm based on radial basis function neural network response surface method. J. Jilin Univ. (Eng. Ed.) 2009, 39, 1516–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Research on Energy Saving of Hydraulic Transmission System of Wheel Loader. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Reno, F. Quantifying Operability of Working Machines. Ph.D. Thesis, Linking University, Linköping, Sweden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J. Research on Driving Trajectory Planning and Trajectory Tracking Control of Wheel Loader Based on Driving Data. Ph.D. Thesis, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L. Research on Control Strategy of Loader Hydrostatic Transmission (HST) System. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y. Research on Torque Converter Pump Wheel Clutch and Its Application on Loader. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. Research on Multiple Mode Automatic Transmission Shifting Law of Loader. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Ma, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, S. IOT and cloud computing based parallel implementation of optimized RBF neural network for loader automatic shift control. Comput. Commun. 2020, 158, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Ma, W.; You, L. Research on Intelligent Shift Control Strategy of The Loader Based on Radial Basis Function Neural Network. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1550, 062003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L. Simulation and Experimental Research on Loader Hydraulic Transmission Shift Quality. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X. Simulation and Experimental Research on Power Shift Impact of 816G Transmission. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Ma, W.; Liu, C. Analysis and Experimental Research on Shifting Impact of Loader Transmission. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1550, 042031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Serial Number | Parameter Name | Parameter Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Loader quality | 24,500 kg |
| 2 | Rated carrying capacity | 7 t |
| 3 | Bucket volume | 4.2 m3 |
| 4 | Maximum lifting height | 3200 mm |
| 5 | Three items and total time | 11.42 s |
| 6 | Maximum lifting force | 218 kN |
| 7 | Frontal area | 7.5 m2 |
| 8 | Wheelbase | 3450 mm |
| 9 | Minimum turning radius | 7260 mm |
| 10 | Gears and ratios | See Table 2 and Table 3 |
| 11 | Drive axle | Four-wheel drive, ratio: 23.334 |
| 12 | Tire diameter | 1.59 m |
| Parameter | Forward 1st Gear | Forward 2nd Gear | Forward 3rd Gear | Forward 4th Gear |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gear ratio i | 3.972 | 2.207 | 0.970 | 0.608 |
| Transmission efficiency η | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.92 |
| Parameter | Forward 1st Gear | Forward 2nd Gear | Forward 3rd Gear | Forward 4th Gear |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gear ratio i | 93.382 | 51.887 | 22.805 | 14.294 |
| Transmission efficiency η | 0.828 | 0.828 | 0.828 | 0.828 |
| Torque Converter Speed Ratio i | Engine Speed nT r/min | Engine Torque TT N·m | Output Power PT kW | Efficiency η |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1659.34 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.1 | 169.2 | 1510.35 | 26.76 | 0.27 |
| 0.2 | 336.4 | 1342.02 | 47.27 | 0.47 |
| 0.3 | 504 | 1177.88 | 62.16 | 0.62 |
| 0.4 | 674.8 | 1011.50 | 71.47 | 0.71 |
| 0.5 | 853 | 857.19 | 76.56 | 0.77 |
| 0.6 | 1044 | 726.99 | 79.47 | 0.81 |
| 0.7 | 1250.2 | 593.67 | 77.72 | 0.81 |
| 0.8 | 1480.8 | 444.42 | 68.91 | 0.77 |
| 0.9 | 1763.1 | 280.53 | 51.79 | 0.71 |
| 0.95 | 1969.35 | 165.50 | 34.13 | 0.63 |
| 1 | 2134 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| First Gear | Second Gear | ||||
| Vehicle Speed v m/s | Traction Force Fk kN | Power P kW | Vehicle Speed v m/s | Traction Force Fk kN | Power P kW |
| 0 | 155.93 | 0 | 0 | 86.64 | 0 |
| 0.150 | 141.93 | 21.41 | 0.272 | 78.86 | 21.41 |
| 0.300 | 126.11 | 37.82 | 0.539 | 70.07 | 37.82 |
| 0.450 | 110.68 | 49.73 | 0.808 | 61.50 | 49.73 |
| 0.602 | 95.05 | 57.18 | 1.083 | 52.81 | 57.18 |
| 0.761 | 80.55 | 61.26 | 1.369 | 44.76 | 61.26 |
| 0.931 | 68.31 | 63.59 | 1.675 | 37.96 | 63.59 |
| 1.114 | 55.79 | 62.18 | 2.006 | 31.00 | 62.18 |
| 1.319 | 41.76 | 55.13 | 2.375 | 23.20 | 55.13 |
| 1.572 | 26.36 | 41.44 | 2.828 | 14.65 | 41.44 |
| 1.756 | 15.55 | 27.31 | 3.161 | 8.64 | 27.31 |
| 1.903 | 0 | 0 | 3.425 | 0 | 0 |
| Third Gear | Fourth Gear | ||||
| Vehicle Speed v m/s | Traction Force Fk kN | Power P kW | Vehicle Speed v m/s | Traction Force Fk kN | Power P kW |
| 0 | 38.08 | 0 | 0 | 24.54 | 0 |
| 0.617 | 34.66 | 21.41 | 0.958 | 22.33 | 21.41 |
| 1.228 | 30.80 | 37.82 | 1.906 | 19.84 | 37.82 |
| 1.839 | 27.03 | 49.73 | 2.856 | 17.42 | 49.73 |
| 2.464 | 23.21 | 57.18 | 3.822 | 14.96 | 57.18 |
| 3.114 | 19.67 | 61.26 | 4.833 | 12.67 | 61.26 |
| 3.811 | 16.68 | 63.59 | 5.914 | 10.75 | 63.59 |
| 4.564 | 13.62 | 62.18 | 7.083 | 8.78 | 62.18 |
| 5.406 | 10.20 | 55.13 | 8.389 | 6.57 | 55.13 |
| 6.436 | 6.44 | 41.44 | 9.989 | 4.15 | 41.44 |
| 7.189 | 3.80 | 27.31 | 11.158 | 2.45 | 27.31 |
| 7.792 | 0 | 0 | 12.092 | 0 | 0 |
| Throttle Opening | 1–2 Shift Points m/s | 2–3 Shift Points m/s | 3–4 Shift Points m/s |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 0.583 | 1.139 | 2.250 |
| 0.3 | 0.639 | 1.278 | 2.556 |
| 0.4 | 0.722 | 1.444 | 2.861 |
| 0.5 | 0.806 | 1.583 | 3.167 |
| 0.6 | 0.889 | 1.750 | 3.472 |
| 0.7 | 0.972 | 1.889 | 3.778 |
| 0.8 | 1.139 | 2.167 | 4.278 |
| 0.9 | 1.194 | 2.333 | 4.639 |
| 1 | 1.194 | 2.333 | 4.972 |
| Throttle Opening | 1–2 Shift Points m/s | 2–3 Shift Points m/ss | 3–4 Shift Points m/s |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 0.583 | 1.167 | 2.306 |
| 0.3 | 0.667 | 1.278 | 2.583 |
| 0.4 | 0.722 | 1.417 | 2.861 |
| 0.5 | 0.778 | 1.556 | 3.111 |
| 0.6 | 0.861 | 1.694 | 3.361 |
| 0.7 | 0.917 | 1.806 | 3.639 |
| 0.8 | 1 | 1.944 | 3.889 |
| 0.9 | 1.055 | 2.083 | 4.139 |
| 1 | 1.139 | 2.25 | 4.5 |
| Part Name | Specification | Main Parameters and Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Motor | BPV355M-4 | Rating: 160 kW |
| Rated Torque: 1500 N·m | ||
| Hydraulic Transmission | -- | 6 forward, 3 reverse gears |
| Eddy Current Dynamometer | DW250 | Rating: 250 kW |
| Rated Speed: 5000 r/min | ||
| Booster Box | -- | Gear Ratio: 0.25 |
| Speed and Torque Sensors | JC2C | Rated Torque: 2000 N·m |
| Rated Speed: 4000 r/min | ||
| Accuracy Class: ±0.2% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, G.; Jin, T.; Wang, J. Research on Multi-Mode Variable Parameter Intelligent Shift Control Method of Loader Based on RBF Network. Actuators 2024, 13, 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13070234
Wu G, Jin T, Wang J. Research on Multi-Mode Variable Parameter Intelligent Shift Control Method of Loader Based on RBF Network. Actuators. 2024; 13(7):234. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13070234
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Guanghua, Tianyu Jin, and Junnian Wang. 2024. "Research on Multi-Mode Variable Parameter Intelligent Shift Control Method of Loader Based on RBF Network" Actuators 13, no. 7: 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13070234
APA StyleWu, G., Jin, T., & Wang, J. (2024). Research on Multi-Mode Variable Parameter Intelligent Shift Control Method of Loader Based on RBF Network. Actuators, 13(7), 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13070234







