Abstract
A cellulose-based triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) with fiber–wave–arch structure was prepared through a multi-fluid electrospinning process for air filtration and wind sensing. The TENG is composed of a cellulose nanocrystals (CNC)/zein membrane and a cyanoethyl cellulose (CEC)/polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane. The results show that the addition of CEC improves the output performance and filterability of TENG. At the same time, the reduced diameter and high roughness of CEC/PVDF nanofibers improve the output performance of the TENG. The TENG with a 6 wt% CEC/PVDF solution concentration has the highest output performance with a short-circuit current of 3.30 μA and an open-circuit voltage of 10.01 V. The particle filtration of 12 wt% CEC/PVDF TENG is the best, showing an efficiency of 98.84% and a pressure drop of 50 Pa. The TENG also has a good formaldehyde filtration capability with an efficiency of 92% at 0.25 mg/m3. The TENG shows great potential in self-powered sensor applications.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of science and nanomaterial preparation technology, wearable electronic devices have attracted significant attention [1]. To adapt to various application conditions, the functionalization of wearable electronic devices has become an inevitable trend. However, technological progress and industrial production have brought about increasingly serious environmental pollution, so the development of wearable electronic devices that can be used for human respiratory protection has become an urgent need. At present, shortness of breath and respiratory failure or even cessation have been caused by severe diseases endangering human health. Pollutants in the air mainly include harmful chemical gases and particulate pollutants [2]. People should not only protect themselves against the hazards of outdoor air but also spend more time protecting against harmful air substances in relatively closed spaces or buildings, such as flying dust in the working environment and volatilization of formaldehyde gas from indoor furniture [3,4]. As the concentration of pollutants in indoor air is two to five times higher than that in outdoor air [5], wearable electronic protective equipment is very necessary. The main function of these electronic devices is to remove particulate matter (PM) and harmful chemical gases in the air to alleviate related respiratory health problems [6,7]. Moreover, the unique surface morphology and physical properties of wearable electronic devices can be used in many situations to achieve multi-functional applications. For some patients with long-term chronic respiratory diseases, the resulting shortness of breath or even respiratory arrest from particulate matter can seriously threaten human life and health. Fortunately, real-time detection of these respiratory diseases can be achieved through wearable electronic devices. Therefore, the development of a new type of flexible wearable electronic device is of practical significance for physical protection and respiratory disease monitoring. As a kind of wearable electronic device, the new type of triboelectric device has great application potential in energy harvesting, medical monitoring, and artificial intelligence [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17].
In recent years, the triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) has attracted widespread attentions in the world, as it can convert mechanical energy into electrical energy based on the principles of contact charging and electrostatic induction. Due to its simple and flexible structural design [18,19] and diversity of raw materials, the TENG exhibits unique merits of high voltage, easy processability, environmental friendliness, and low fabrication cost. Various TENGs have been demonstrated to harvest energy from a variety of sources [20], such as mechanical vibration [21], human activity [22,23], and water waves [24]. The performance of TENG is mainly determined by the selection of materials and the design of the structure. With the advancement of materials and micro/nanomanufacturing technology, TENG can realize the organic combination of mechanical flexibility, stretchability, and conductivity. Through reasonable structural design and material selection, a variety of wearable flexible electronic devices can be prepared for different application fields. The preparation of micro/nanostructures is an effective way to expand the friction area and increase the friction charge density. At present, micropatterns such as pillars, cubes and pyramids [25,26] have been fabricated to construct high-output triboelectric devices for energy collection.
A TENG can not only harvest energy but can also be used as a self-powered sensor for pressure detection, medical monitoring, and other sensors [25,27,28,29,30]. As a self-powered electronic sensor, a TENG can achieve multiple sensing functions, including pressure, position, strain, and sliding [31]. It is urgently essential to explore new strategies and fabricate unique structures to construct a TENG with high output performance and multifunctional application. At present, a few studies about TENGs based on electrospun fibers have been reported; however, there has been limited systematic study on the mechanism to clarify the effect of fiber morphology on TENG output performance.
Herein, we propose a novel multi-fluid mixing electrospinning strategy to prepare a multi-level (fiber–wave–arch tertiary) structured TENG using cyanoethyl cellulose (CEC)/polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) to efficiently harvest energy and sense wind force. The designed TENG also filters air particles and harmful chemical gases to protect human health. One of its dielectrics is an electrospun cellulose nanocrystals (CNC)/zein membrane with rich hydroxyl and amino functional groups, which are beneficial for filtration of harmful formaldehyde gases. A CEC/PVDF membrane with high electronegativity and filtering performance was prepared as another dielectric of the TENG. It was proved that the addition of CEC could effectively increase the roughness of CEC/PVDF nanofibers, and rough surfaces can significantly improve its filtration performance and electrical performance. Our study provides a promising approach for the development of multi-functional wearable electronic devices.
1.1. Materials
CNC and CEC were supplied by Beijing North Century Cellulose Technology Development Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). Zein and acetone were purchased from Shanghai Aladdin Chemical Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). N, N-dimethylformamide (DMF) and n-butanol were obtained from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). PVDF was received from Arkema (Shanghai) Chemical Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
1.2. Fabrication of TENG Dielectric Membranes
CNC/zein precursor solutions with a concentration of 24 wt% was configured, in which the addition amount of CNC was 3 wt% of the total mass of the solute. The solvents used were DMF and n-butanol with a volume ratio of 3/1. The precursor liquid was ultrasonically dispersed. The electrospinning (SS, Beijing Yong Kang Le Ye Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) was carried out with a feeding rate of 0.05 mm/min. High voltage (12–13 kV) was applied between the needle tip and the drum collector device covered with aluminum foil, and the distance between them was set as 18 cm. The relative humidity and temperature of the spinning environment were maintained at 25–30% and 25 °C, respectively. The prepared fibers were named as 24 wt% CNC/zein. For the preparation of CEC/PVDF nanofibrous membrane, the concentrations of CEC/PVDF solutions were 6 wt%, 9 wt%, and 12 wt%. The mass of CEC was 8 wt% of the total solute mass. The solvents were acetone and DMF. PVDF solutions were prepared as a contrast sample. During the electrospinning process, the feeding rate was adjusted to 1 mL/h, and the spinning voltage was set as 14–16 kV. The spinning environment humidity was maintained at 40–50%, and the spinning temperature was 25 °C. The distance between the needle tip and the receiving device was 18 cm. The prepared fibrous membranes were named as 6 wt%, 9 wt%, and 12 wt% CEC/PVDF, and 12 wt% PVDF.
1.3. Preparation of TENG with a Multi-Level Structure
CEC/PVDF solutions with concentrations of 12 wt% and 9 wt% were prepared. The syringes containing the two precursor solutions were arranged in parallel during electrospinning, and the carbon fibrous felt was used as the receiving matrix. Detailed process parameters are the same as described in Section 2.2. The obtained fibrous membrane was named as 9 + 12 wt% CEC/PVDF. The 24 wt% CNC/zein nanofibrous membrane was also synthesized.
1.4. Characterizations
The microscopic morphology of the nanofibrous membrane was examined by Scanning electron microscopy (SEM, JSM-7500 F, JEOL, Tokyo, Japan). The water contact angle was measured by a contact angle measuring system (OCA 40, Dataphysics Co., Ltd., Stuttgart, Germany). Fourier transform infrared (FTIR, NICOLET 6700, Thermo Fisher Co., Ltd., Agawam, MA, USA) analysis was used to explain the changes in molecular structure and internal functional groups during the conversion of polymer materials into nanocomposite. The open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current of this TENG were measured via an electrochemical workstation (CHI600E, Chenhua Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). A filter material tester (LZC-H, Hangzhou Bai Ming Instrument Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China) was used to characterize the filtration performance of the nanofibrous membrane, and the formaldehyde filtration was tested by an indoor air quality analyzer (des-F, Deersi Environmental Testing and Governance Co., Ltd., Wuxi, China). The formula for filtration efficiency and more experimental details have been provided in the Supplementary Materials.
2. Results
2.1. Design Principles
The selection of materials and the design of the structure are the two most important factors that affect the performance of a TENG. Therefore, the construction of a multi-level structure is one of the necessary means to realize the high output performance and multi-functional application of a TENG. In our research, PVDF was selected as the polymer matrix of composites because of its excellent spinnability and remarkable electronegativity for constructing TENGs [32]. Moreover, PVDF is an electret material with excellent filtering effect [33] and many advantages such as flexibility and high chemical stability [34]. CEC is a material with high dielectric properties, and the introduction of dielectric material has proved to be an effective strategy to increase TENG charge density. The electrospinning method used in our experiment is different from the traditional electrospinning process, which has been widely used to fabricate aligned or random nanofiber [35,36]. We utilized the different volatilization rates of mixed solvents and the coagulation rates of polymers to control the micro/nanostructures of prepared nanofibers, and electrospun CEC/PVDF nanofibers with high roughness were successfully prepared. In theory, the roughness can imbue a TENG with good output and filtering performance. CNC/zein nanofibers with a large number of reactive functional groups were selected to achieve the function of the TENG adsorbing formaldehyde.
The schematic of the electrospinning process to fabricate CEC/PVDF nanofibers is illustrated in Figure S1. The polymer jet was elongated by a strong electric field, and rapidly shrunk and solidified with the evaporation of solvents. Therefore, we took advantage of the characteristics of the shrinkage force and degree of solidification of nanofibers with different concentrations of polymer fluid during the drying process to prepare a multi-level structured CEC/PVDF membrane. A new strategy of multi-fluid mixing electrospinning technology was employed to prepare 9 wt% and 12 wt% CEC/PVDF membranes, as shown in Figure 1. The precursor solutions were arranged in parallel to electrospinning, and the prepared TENG had a fiber–wave–arch multi-level structure. A TENG prepared by multi-fluid hybrid electrospinning technology has good advantages in the fields of energy harvesting and self-powered sensing due to its unique structure; it is therefore expected to be assembled into masks to collect human breathing energy and protect human respiratory health.
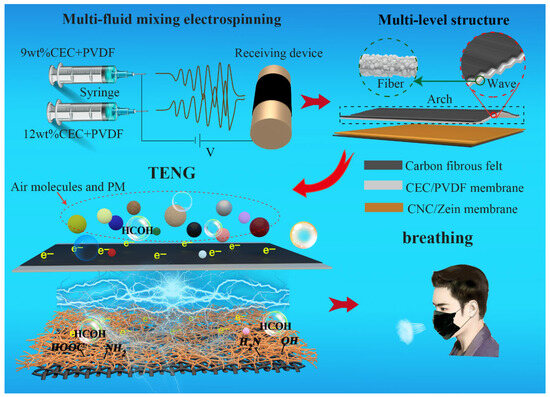
Figure 1.
Schematic for the preparation of cellulose-based TENG with a multi-level structure.
2.2. Morphology and Structure of Cellulose-Based TENG Dielectric Membranes
Figure 2 shows SEM images of electrospun CEC/PVDF nanofibers with different solution concentrations. In the electrospinning process, a high concentration of 12 wt% PVDF solution was sprayed and stretched uniformly, and quickly solidified to form polymer nanofiber (Figure 2g), which was in accordance with most electrospun structures in the literature [32]. When CEC was added to the precursor solution, compared with 12 wt% PVDF nanofibers, 12 wt% CEC/PVDF nanofibers not only had a larger diameter but also possessed a large number of tiny spherical particles on the surfaces of nanofibers, as shown in Figure 2a,d. Therefore, the addition of CEC greatly increased the roughness of CEC/PVDF nanofibers. Theoretically, the increase in surface roughness of triboelectric devices is one of important methods to improve the output performance of a TENG.
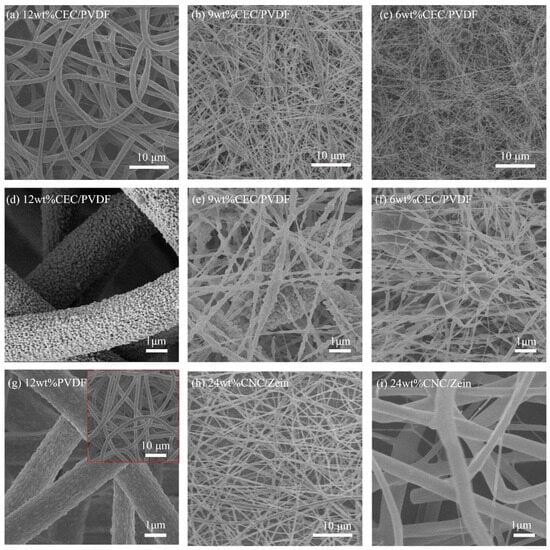
Figure 2.
SEM images of CEC/PVDF nanofibers with different solution concentrations (a–f), 12 wt% PVDF nanofibers, the illustration is an enlarged image (g), and 24 wt% CNC/zein nanofibers (h,i).
As the concentration of precursor solution continued to decrease, the surface tension of the solution decreased rapidly, so it was difficult for the solution jet to keep stable and it tended to shrink into a sphere. The uniformly distributed liquid droplets finally solidified to hierarchical micro/nanostructures, as shown in Figure 2b,c,e,f. It was observed from Figure 2b,e that compared with 12 wt% CEC/PVDF nanofibers, the diameter of 9 wt% CEC/PVDF nanofibers was reduced due to the decrease in the concentration of the precursor solution. Most of the 9 wt% CEC/PVDF nanofibers were composed of spindles and thin fibers with nano-spherical particles on the spindle surface. When the concentration of the CEC/PVDF solution further decreased to 6 wt%, the nanofiber diameter (Figure 2c,f) was further reduced, and its thickness was relatively uneven with some larger smooth spheres existing on the surfaces of the nanofibers.
A protein-functionalized microfiber/protein nanofiber bi-layered air filter with synergistically enhanced filtration performance by a viable method, CNC/zein was selected as another dielectric of the TENG. Figure 2h,i are the SEM images of 24 wt% CNC/zein nanofibers. It was clearly illustrated that the morphology of 24 wt% CNC/zein nanofiber was basically the same as traditional electrospun nanofibers. The fibers had a smooth surface, uniform diameter, and regular shape. Compared with 12 wt% CEC/PVDF nanofibers, the diameter of 24 wt% CNC/zein nanofibers was smaller and the surface was smoother. In addition, it could be found that there was no chemical functional group change in CEC/PVDF and CNC/zein nanofibrous membranes, as shown in Figures S2 and S3. We also measured the contact angle of the membranes, and the results showed that CEC/PVDF nanofibers had excellent hydrophobic properties, as demonstrated in Figure S4.
2.3. Output Performance of Cellulose-Based TENG with Different CEC/PVDF Membranes
The effects of nanofibrous morphology on the electrical output performance of TENG is shown in Figure 3. The aluminum (Al) collector in electrospinning was directly used as the electrode, and different concentrations of CEC/PVDF nanofibers and 24 wt% CNC/zein nanofibers were performed as the two dielectrics to form the TENG. Its working model was a vertical contact separation mode to collect energy [37,38], and its structure is shown in Figure 3a(I). The electricity generation process of the TENG is depicted in Figure 3a(II–V). When the membranes were pressed, the top membrane and bottom membrane contacted and rubbed against each other. According to the triboelectric series, CEC/PVDF is much more triboelectrically negative than CNC/zein. When another CNC/zein dielectric was in contact with its surface, charges would transfer from the CNC/zein to the CEC/PVDF, which would make the CEC/PVDF negatively charged, and the CNC/zein had the same amount of positive charges (Figure 3a(II)). When the TENG was separated, the opposite and equal charges were generated on the respective aluminum electrodes due to electrostatic induction, and the top Al electrode possessed a lower electric potential than the bottom Al electrode, generating an electric pulse which drove the electrons flow to flow through an external load from the top Al electrode to the bottom Al electrode (Figure 3a(III)). When the membranes were moved close to each other again, the redistributed charge would form a reverse electrical pulse, driving the charge to flow in the opposite direction (Figure 3a(V)). Therefore, when a new equilibrium was reached, an alternating electron would be observed with cycles of contacting and separating process. According to the working principle of the TENG (Figure 3a), an instantaneous current and voltage of positive and negative was measured when the TENG was driven by a cyclic reciprocating motion of the linear motor.
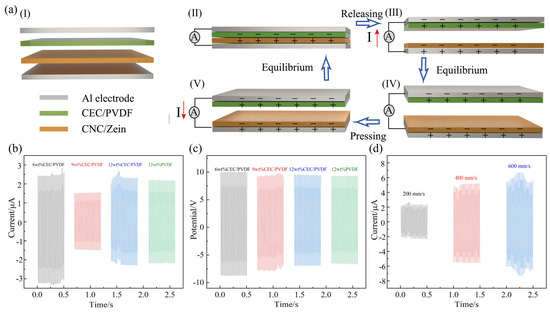
Figure 3.
The working mechanism of cellulose-based TENG (a); characterization of the output performance of the cellulose-based TENG with different precursor solution concentrations under motor speeds of 200 mm/s (b,c); cellulose-based TENG with 12 wt% CEC/PVDF output performance under different motor speeds of 200–600 mm/s (d).
Figure 3b shows the short-circuit current of TENG with different CEC/PVDF nanofibrous membranes when the motor speed was 200 mm/s. It was found that the short-circuit currents of the TENG with 6 wt%, 9 wt%, 12 wt% CEC/PVDF, and 12 wt% PVDF were 3.30 μA, 1.53 μA, 2.67 μA, and 2.193 μA, respectively. The addition of CEC improved the output performance of the TENG, which was attributed to the increase in fibrous roughness and the dielectric properties. Furthermore, as the spinning concentration increased, the diameter of the nanofibers gradually increased. From the chart, we could see that the thinner nanofibers had a higher short-circuit current. Therefore, the diameter reductions in the CEC/PVDF nanofibers remarkably increased the short-circuit current of the TENG. This is because of the fact that smaller fibers allowed more fibers to be distributed in the dielectric film per unit area, and the increase in fiber density caused more triboelectric charges to be generated per unit area, thereby improving the output performance of the TENG. The short-circuit current of 12 wt% CEC/PVDF nanofibers was higher than the 9 wt% CEC/PVDF nanofibers due to the increase in fiber surface roughness, and the large number of small balls on the surface of the 12 wt% CEC/PVDF nanofibers greatly improved its roughness. The open-circuit voltages of the TENG with 6 wt%, 9 wt%, 12 wt% CEC/PVDF, and 12% PVDF were 10.01 V, 9.81 V, 9.52 V, and 9.32 V, respectively, as shown in Figure 3c. The open-circuit voltage of the TENG with different fiber diameters and morphologies only had slight changes, and its changing trend was to gradually decrease as the increase in fiber diameter, which was the same as the short-circuit current change trend. In summary, the decrease in the diameter and the increase in roughness of the electrospun nanofibers can improve the output performance of a TENG. The frequency of a TENG’s friction is one of the important factors affecting its output performance. We have also tested the influence of the motor speed on the TENG’s output performance during the contact and separation. In the contact separation type TENG, the stepper motor speed determines the frequency of the TENG collision. When the motor speeds were 200 mm/s, 400 mm/s, and 600 mm/s, the short-circuit currents of TENG of 12 wt% CEC/PVDF were 2.67 μA, 5.55 μA, and 7.28 μA, respectively, as shown in Figure 3d. The results showed that the collision frequency had a positive effect on improvement of the electrical output performance of the TENG.
2.4. Particle Filtration of Cellulose-Based TENG Dielectric Membranes
Electrospun nanofibrous membranes possess broad application prospects in the field of air filtration due to the fascinating features that accompany the controllable fibers morphology and a high specific surface area [39,40]. Furthermore, materials with excellent properties can be mixed into the spinning solution to effectively adjust the fiber diameter, surface morphology, and specific surface area [41]. This strategy greatly improves the adsorption and filtration effects of materials. The main filtration mechanism of the nanofibrous membrane is as follows: When the gas containing particles contacts the fibers, it passes through the filter medium under the action of pressure, and the small molecule dust particles are intercepted by the fibrous layer, so as to separate the tiny particles from the air. The filtration mechanism of nanofibers is often the result of multiple filtering effects, mainly the following effects: gravity effect, inertial effect, interception effect, diffusion effect, and electrostatic effect, as demonstrated in Figure 4a. The strongly polar and electronegative functional groups (-CN and -F) exposed by CEC/PVDF nanofiber interact strongly with various pollutants. The filtration efficiency of 6 wt%, 9 wt%, 12 wt% CEC/PVDF and 24 wt% CNC/zein nanofibrous membranes were 96.24%, 96.75%, 98.84%, 84.83%, respectively. The pressure drops were 62 Pa, 65 Pa, 50 Pa, 53 Pa in sequence, as shown in Figure 4b. It could be observed that the 12 wt% CEC/PVDF nanofibers had the highest filtration efficiency and the lowest pressure drop, which can be attributed to the change in fibrous morphology and the increase in specific surface area. Figure 1 clearly showed that there were nano-scale spherical protrusions and holes on the surface of 12 wt% CEC/PVDF nanofibers, making the surface rough. This morphology could increase the effective contact area and probability between pollutant particles and related fibers, improving the inertia effect, interception effect, and diffusion effect of nanofibers to further increase its air filtration performance. On the other hand, the low bulk density of 12 wt% CEC/PVDF nanofibrous membrane reduced its pressure drop. The low concentration nanofibers had defects in spatial distribution due to uneven morphology. In addition, thin fibers might break during airflow, resulting in low filtration efficiency. The significant pressure drop was due to dense fiber distribution.
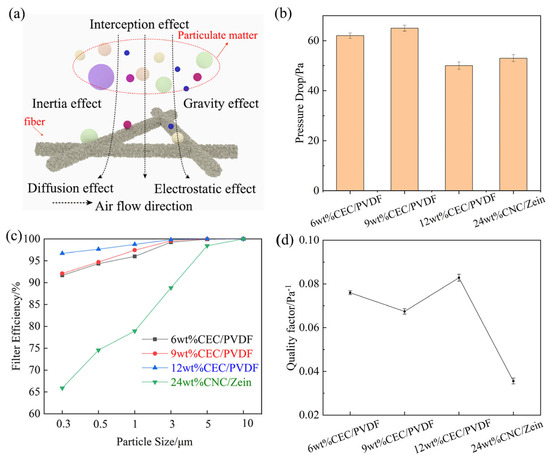
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of nanofiber filtration (a); pressure drop of CEC/PVDF nanofibrous membranes with different concentrations and 24 wt% CNC/zein nanofibrous membrane (b); filtration efficiency of particles at different sizes (c); QF of CEC/PVDF nanofibrous membranes with different concentrations and 24 wt% CNC/zein nanofibrous membrane (d).
In addition, among air pollutants, solid particulate matter (PM) with a diameter less than 2.5 μm is more difficult to remove and is more harmful to the human body because it cannot be intercepted by the fluff in the nose. Therefore, it is of great significance to develop intelligent materials to capture small-sized particles. Comparing with other concentrations of CEC/PVDF membranes and 24 wt% CNC/zein membrane, 12 wt% CEC/PVDF nanofibers were excellent candidate for filtering small-sized (<3 μm) PM (Figure 4c). Generally, the capture of small-size particles is more dependent on diffusion and interception effects. The existence of rough structures (nano-scale holes and protrusions) and a high specific surface area of 12 wt% CEC/PVDF nanofiber provided more sites for gas adsorption, and therefore enhanced the nonslip behavior and stagnation of PM (<3 μm). High-performance filter materials must not only have higher filtration efficiency but also require lower pressure drop to reduce energy consumption. In order to measure the contribution of filtration efficiency and pressure drop to filtration performance, it can be balanced by introducing a quality factor (QF) [42]. The increase in the QF needs to improve the filtration efficiency of the filter material or reduce the pressure drop of the filter material. The larger the QF values, the better the comprehensive filtration performance of the nanofiber membranes. It can be observed from Figure 4d that the QF of 6 wt%, 9 wt%, 12 wt% CEC/PVDF and 24 wt% CNC/zein nanofibrous membranes are 0.0537, 0.0527, 0.0891, and 0.0355, respectively. Among them, the unique structure of 12 wt% CEC/PVDF nanofibers made it have the highest QF. Therefore, creating a large number of holes and protrusions on the surface of nanofibers is a very beneficial method to improve filtration efficiency.
2.5. Formaldehyde Filtration of Cellulose-Based TENG Dielectric Membranes
Formaldehyde (HCHO) is a very common and harmful chemical gas that exists in various places of human activities. It combines with proteins in the human body and endanger human health. Therefore, removal of HCHO is a very necessary function for filters to protect human health. As a protein extracted from corn, zein is an effective material for removing HCHO. Its numerous functional groups can provide protein–gas chemical interactions, as shown in Figure 5a. The addition of CNC can greatly enrich the functional groups of zein molecules. CNC/zein nanofibers possess various functional groups (such as carboxyl, amino, and hydroxyl charged groups, and many polar/non-polar functional groups). These functional groups can be used as active sites to produce a variety of interactions among chemical pollutants, including hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, charge–charge interactions, and so on [43,44]. HCHO has high reactivity and can undergo nucleophilic addition reactions with CNC/zein nanofiber with −OH, −SH, and −NH2 groups. When HCHO passed through the filter medium of CNC/zein nanofibers, it was removed through chemical reactions. The volatilization of the HCHO solution was used to simulate the indoor HCHO environment, and the experimental detection device is shown in Figure 5b. By adjusting the concentration of the HCHO solution, we prepared three different HCHO gas concentrations at 0.25 mg/m3, 0.59 mg/m3, and 0.98 mg/m3, which was higher than the safe concentration of 0.08 mg/m3, to test the HCHO efficiency. After the CNC/zein nanofiber filtered the HCHO in the air, their removal rates were 92%, 67%, and 35%, respectively, as shown in Figure 5c. Figure 5c illustrates the color change diagram after the reaction of HCHO gas with the detection solution before and after filtration at an HCHO concentration of 0.25 mg/m3; it can be seen that the color of the reaction solution after filtration is basically the same as that of the standard solution. When HCHO gas passed through the CNC/zein filter, the concentration of HCHO was reduced from 0.98 to 0.25 mg/m3, and the capture efficiency was increased from 35% to 92%, higher than other formaldehyde filtration materials like keratin powder (90.63%) and keratin/PVP-based composite materials (90.39%) [45].
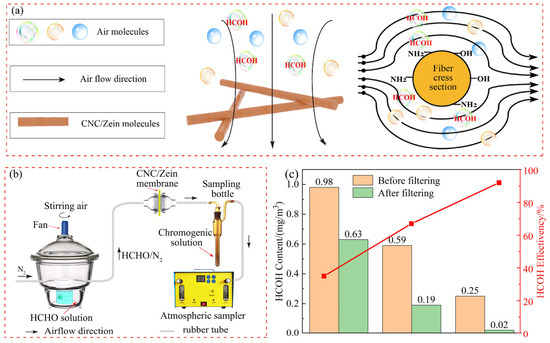
Figure 5.
Formaldehyde filtration mechanism (a); diagram of formaldehyde filter detection devices (b); formaldehyde filtration efficiency and HCOH content before and after filtration (c).
When the content of formaldehyde gas in the air was low, the HCHO molecules had enough time and reaction sites to react with the functional groups presenting in the CNC/zein nanofibers while the mixed air was passing through the filter medium. With the increase in HCHO content in the air, some of the formaldehyde molecules were squeezed out by other gas molecules, and there was not enough time to contact the functional groups. The molecules quickly passed through the surface of the nanofibrous filter medium, which reduced the efficiency of CNC/zein nanofibers. Therefore, CNC/zein had a positive protective effect on indoor formaldehyde gas, and the filtering effect was more obvious at low and medium concentrations.
2.6. Structure and Sensing of Cellulose-Based TENG with Multi-Level Structure
On the basis of the previous research, we found that CEC/PVDF nanofibrous membranes and CNC/zein nanofibrous membrane had excellent filtering effects while generating electricity. In this work, porous carbon fibrous felt was used as an electrode. A new strategy of multi-fluid mixing electrospinning technology was used to prepare a TENG. After the solvent in the CEC/PVDF precursor solution evaporated and dried, a unique structure appeared in the CEC/PVDF nanofibrous membrane. As shown in Figure 6a, there was a large area of shrinkage on the film, and a number of grooves were formed in the middle area of the film. Therefore, a regular parallel wave was formed in the middle of the 9 + 12 wt% CEC/PVDF nanofibrous membrane, and the two sides of the film were irregular grooves perpendicular to the middle wave. This regular wave shape made the membrane shrink inward spontaneously to form an arch, as shown in Figure 6a. Therefore, CEC/PVDF membranes presented micro/nanofibers on the microscopic level and wave and arch on the macroscopic level, so it had a tertiary structure of fiber–wave–arch shapes with different scales. The unique structure was elastic and returned to the prototype after pressing during the power generation process, and the CEC/PVDF dielectric did not need to provide additional force required for separation. Thus, it could be used to collect the mechanical energy of the human body when people are speaking and breathing. We used SEM to monitor structures of CEC/PVDF nanofibers to explore the reasons for its formation (Figure 6b and Figure S5). According to the previous experimental results, we knew that the 9 wt% CEC/PVDF nanofibers were composed of a thick spindles and fine fibers, and the diameter of 12 wt% CEC/PVDF nanofibers was larger. In Figure 6b, we found these two kinds of fibers are randomly mixed together, the 12 wt% CEC/PVDF nanofibers maintained its original shape, and some of the 9 wt% CEC/PVDF nanofibers adhered to the 12 wt% CEC/PVDF nanofibers to form a fibrous bundle skeleton. The 9 wt% CEC/PVDF nanofibers between these skeletons mechanically broke at the weaker fine fibers. This phenomenon might be caused by the shrinkage of fibers during the drying process. The formation of the fibrous bundle skeleton made the mechanical properties of the thick fibrous stronger, while the thin fibers broke under the pulling of the thick fibrous bundle. It was the special distribution of fibers inside the 9 + 12 wt% CEC/PVDF membrane that made it have a unique multilayer structure.
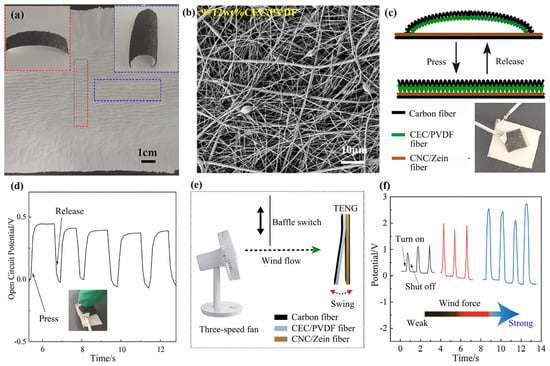
Figure 6.
Optical image (a) and SEM image (b) of 9 + 12 wt% CEC/PVDF nanofibers; pressure self-powered sensor structure (c) and open-circuit voltage of 9 + 12 wt% CEC/PVDF TENG (d); wind detection device (e) and its open-circuit voltage of cellulose-based TENG (f).
This unique multi-level structure can not only harvest energy but also act as a pressure self-powered sensor. The CEC/PVDF membrane was cut into 1 × 1 cm2 to detect finger pressure, as shown in Figure 6d. An electrochemical workstation was used to detect the change in the open-circuit voltage of the TENG with the pressure of the finger. The sensing principle of the TENG is shown in Figure 6c. When the TENG was not pressed, it did not generate electrical signals. When the finger pressed down, the arched CEC/PVDF dielectric was transformed into a flat shape; if the pressure was large enough, the wavy shape would also be stretched out, deforming the size of the friction contact area of the TENG and thereby generating electrical signals until the open-circuit voltage reached the highest value. When the finger was released, the contact surface between the two dielectrics was quickly separated, which reduced the charge generated by friction. With the repeated pressing and release, the peak of the open-circuit voltage appeared repeatedly. From Figure 6d we can see that the waveform and peaks of each wave were basically the same; this indicated that the self-powered sensor had better reproducibility for the same pressure detection. In addition, the TENG exhibited good filtering performance and unique structure, which was expected to be constructed into a sensor the size of a breathing valve on a mask to detect the breathing state. We assembled the TENG into a 3 × 3 cm2 area as a wind detector. A three-speed fan was used as a power, and the baffle that it could move up and down were regarded as a wind switch. The change in the TENG electrical signals under different wind force were detected by adjusting the wind speed of the fan (Figure 6e). Figure 6f is the open-circuit voltage change diagram of the TENG under different wind force levels. As the wind force increased, the open-circuit voltage also continued to increased. This was mainly because the increase in wind force caused the increase in contact area between the dielectrics, so more charges were generated on the surface of the dielectric. In summary, the TENG can detect the magnitude of the wind, and it is expected to be used for breathing detection with further research.
3. Conclusions
A multi-level structural TENG with excellent filtration efficiency was prepared, which was applied to mechanical energy harvesting and self-powered sensing. The three-level (fiber–wave–arch) structures were fabricated by a multi-fluid mixing electrospinning method. It was found that the concentration of the precursor solution played an important role in the morphology of the electrospun nanofibers. As the concentration of CEC/PVDF solution decreased, the diameter of the CEC/PVDF nanofiber gradually decreased and its shape gradually converted from fiber to a spindle and a sphere. The addition of CEC effectively improved the surface roughness of the CEC/PVDF nanofibers, and a large number of beads and holes appeared on the surface of CEC/PVDF nanofiber. Reducing the diameter and increasing the roughness of the electrospun nanofibers effectively improved the output performance of the TENG. The electrical output performance of the TENG with a spinning solution concentration of 6 wt% was the highest. In addition, the increased surface roughness of the CEC/PVDF nanofibers improved the filtration efficiency of the TENG. The protrusions and depressions on the fibers were beneficial for the capture of small particulate matter (<3 μm). The particle filtration performance of the 12 wt% CEC/PVDF TENG was the best. CNC/zein nanofiber, which was rich in hydroxyl and amino groups, had a good filter effect on the adsorption of HCOH in the air. On the basis of the above-mentioned results, different concentrations of CEC/PVDF solutions were used to assemble a TENG with a fiber–wave–arch structure by a multi-fluid mixing electrospinning technology. As a self-powered sensor, the 9 + 12 wt% CEC/PVDF TENG successfully detected finger pressing and wind force, demonstrating its applicability to power electronic sensing device. Thanks to excellent filtering performance, high adsorption of harmful gases, and the ability to harvest energy sources, the synthesized TENG will have wide potential applications in self-powered electronics and human protection wearable devices.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/act13050178/s1, Figure S1: The schematic of electrospinning process to prepare CEC/PVDF nanofibers; Figure S2: FTIR spectrum of CEC, PVDF and CEC/PVDF nanofibers; Figure S3: FTIR spectrum of CNC, zein and CNC/Zein nanofibers; Figure S4: The water contact angle of CEC/PVDF, PVDF and CNC/Zein nanofibrous membranes; Figure S5: The SEM image of 9 + 12 wt% CEC/PVDF fibrous membrane.
Author Contributions
J.H. and H.Y. contributed equally to this work. J.H.: Methodology, Investigation, Software, Writing—Original Draft. H.Y.: Supervision, Formal Analysis, Software, Conceptualization. Y.Z.: Formal Analysis, Writing—Review. G.H.: Guidance, Writing—Review and Editing. W.C.: Conceptualization, Guidance, Writing—Review and Editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Special Project for Double First-Class—Cultivation of Innovative Talents (000/41113102).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Rogers, J.A.; Huang, Y. A Curvy, Stretchy future for electronics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 10875–10876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elieveld, J.L.; Evans, J.S.; Fnais, M.; Giannadaki, D.; Pozzer, A. The contribution of outdoor air pollution sources to premature mortality on a global scale. Nature 2015, 525, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, R.; Ye, M.; Zhao, Y.; Kang, J.; Ma, P.; Li, J.; Yang, X. Acute formaldehyde exposure induced early Alzheimer-like changes in mouse brain. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2018, 28, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checkoway, H.; Dell, L.D.; Boffetta, P.; Gallagher, A.E.; Crawford, L.; Lees, P.S.; Mundt, K.A. Formaldehyde exposure and mortality risks from acute myeloid leukemia and other Lymphohematopoietic Malignancies in the US National Cancer Institute cohort study of workers in Formaldehyde Industries. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2015, 57, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedel, T. Air filtration: Evaluating filtration efficiency. Filtr. Sep. 2012, 49, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulejko, P.; Adamec, V.; Skeřil, R.; Schüllerová, B.; Bencko, V. Levels and health risk assessment of PM10 aerosol in Brno. Cent. Eur. J. Public Health 2017, 25, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Miri, M.; Aval, H.E.; Ehrampoush, M.H.; Mohammadi, A.; Toolabi, A.; Nikonahad, A.; Derakhshan, Z.; Abdollahnejad, A. Human health impact assessment of exposure to particulate matter: An AirQ software modeling. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 16513–16519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.H.; Shi, Z.Q.; Hu, G.H.; Xiong, C.X.; Isogai, A.; Yang, Q.L. Recent advances in cellulose-based piezoelectric and triboelectric nanogenerators for energy harvesting: A review. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 1910–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Duan, L.; Zhang, L.M.; Wang, L.D.; Dong, G.F.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible organic tribotronic transistor memory for a visible and wearable touch monitoring system. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.; Tian, L.; Zhao, X.Y.; Xiang, S.X.; Tang, Y.J.; Liang, E.; Mao, Y.C. Washable textile-structured single-electrode triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered wearable electronics. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 19143–19150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paria, S.; Si, S.K.; Karan, S.K.; Das, A.K.; Maitra, A.; Bera, R.; Halder, L.; Bera, A.; De, A.; Khatua, B.B. A strategy to develop highly efficient TENGs through the dielectric constant, internal resistance optimization, and surface modification. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 3979–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Peng, W.; Xiao, T.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical study of sliding-electrification-gated tribotronic transistors and logic device. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2018, 4, 1700337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. On Maxwell’s displacement current for energy and sensors: The origin of nanogenerators. Mater. Today 2017, 20, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Lee, C.; Kim, S.H.; Park, M.U.; Yang, J.; Yi, Y.; Yoo, K.-H. Tribodiffusion-driven triboelectric nanogenerators based on MoS2. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 10316–10325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wong, M.C.; Hao, J. Strategies and progress on improving robustness and reliability of triboelectric nanogenerators-ScienceDirect. Nano Energy 2019, 55, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Rahman, Z.U.; Wang, D.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Paper-based triboelectric nanogenerators and their application in self-powered anticorrosion and antifouling. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2016, 4, 18022–18030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wong, M.C.; Guo, Q.Y.; Jia, T.Z.; Hao, J.H. Healable and shape-memory dual functional polymers for reliable and multipurpose mechanical energy harvesting devices. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 16267–16276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Huang, L.B.; Wong, M.C.; Chen, L.; Bai, G.; Hao, J. Self-Powered Sensors: Environmentally Friendly Hydrogel-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Versatile Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Sensors. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1601529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Pan, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Dai, G.; Zou, H.; Dong, K.; Wang, Z.L. An Ultra-Low-Friction Triboelectric-Electromagnetic Hybrid Nanogenerator for Rotation Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Wind Speed Sensor. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 9433–9440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Gao, R.; Wang, Y.-C.; Zhang, X.; Zou, J.-J.; Wang, Z.L. Liquid-FEP-based U-tube triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting water-wave energy. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4062–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liu, R.; Wang, J.; Zi, Y.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. A spring-based resonance coupling for hugely enhancing the performance of triboelectric nanogenerators for harvesting low-frequency vibration energy. Nano Energy 2016, 32, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, S.; Yi, F.; Zi, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Sustainably powering wearable electronics solely by biomechanical energy. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Q.; Sun, J.; Liu, H.; Bao, R.; Yu, R.; Zhai, J.; Pan, C.; Wang, Z.L. Skin-inspired highly stretchable and conformable matrix networks for multifunctional sensing. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Kong, D.S.; Choi, M.; Kim, H.B.; Lee, J.H.; Murillo, G.; Lee, M.; Kim, S.S.; Jung, J.H. Floating buoy-based triboelectric nanogenerator for an effective vibrational energy harvesting from irregular and random water waves in wild sea. Nano Energy 2018, 45, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.-R.; Lin, L.; Zhu, G.; Wu, W.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.L. Transparent Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Self-Powered Pressure Sensors Based on Micropatterned Plastic Films. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3109–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.; Joe, D.J.; Yoon, J.H.J.B.; Lee, K.J. Performance-enhanced triboelectric nanogenerator enabled by wafer-scale nanogenerates of multistep pattern downscaling. Nano Energy 2017, 35, 415–423. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Xie, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, W.; Niu, S.; Wen, X.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric active sensor array for self-powered static and dynamic pressure detection and tactile imaging. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 8266–8274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Yang, W.Q.; Zhang, T.; Jing, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.S.; Bai, P.; Wang, Z.L. Self-powered, ultrasensitive, flexible tactile sensors based on contact electrification. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 3208–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.; Zhu, G.; Jing, Q.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Su, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.L. Membrane-based self-powered triboelectric sensors for pressure change detection and its uses in security surveillance and healthcare monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 5807–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lin, Z.-H.; Zhou, Y.S.; Jing, Q.; Su, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.L. Human skin based triboelectric nanogenerators for harvesting biomechanical energy and as self-powered active tactile sensor system. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 9213–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Lin, L.; Chen, J. Triboelectric nanogenerator. Green. Energy Environ. 2018, 21, 88–97. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Xiong, J.; Parida, K.; Guo, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Shao, J.; Lee, P.S. Transparent and stretchable bimodal triboelectric nanogenerators with hierarchical micro-nanostructures for mechanical and water energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2019, 64, 103904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, C.; Huang, X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Min, M.; Wang, L.; Huang, H.; Hsiao, B.S. Anionic Surfactant Triggered Steiner Geometrical Poly (vinylidene fluoride) Nano-Fiber/Nets Air Filter for Efficient Particulate Matter Removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 42891–42904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.F.; Parida, K.; Cheng, X.; Lee, P.S. Flexible Superamphiphobic Film for Water Energy Harvesting. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 2, 1600186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Bu, N.; Duan, Y.; Pan, Y.; Liu, H.; Yin, Z.; Xiong, Y. Electrohydrodynamic direct-writing. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 12007–12017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Luo, H.; Gao, D.; Zhou, X.; Cui, P.; Thangavel, G.; Parida, K.; Lee, P.S. Self-restoring, waterproof, tunable microstructural shape memory triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered water temperature sensor. Nano Energy 2019, 61, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, W.; Bai, P.; Su, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Broadband vibrational energy harvesting based on a triboelectric nanogenerator. Adv. Energy. Mater. 2014, 4, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Bai, P.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Ultrathin, rollable, paper-based triboelectric nanogenerator for acoustic energy harvesting and self-powered sound recording. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4236–4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; He, H.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X.; Li, J.; Chen, F.; Yuan, D.; Ning, X. Efficient synthesis of PVDF/PI side-by-side bicomponent nanofiber membrane with enhanced mechanical strength and good thermal stability. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.S.; Yan, X.; Yan, F.F.; Chen, F.X.; Hao, L.Y.; Chen, S.J.; Lou, T.; Ning, X.; Long, Y.Z. In situ electrospinning iodine-based fibrous meshes for antibacterial wound dressing. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Attabi, R.; Morsi, Y.; Schu, J.A.; Dume, L.F. Electrospun Membranes for Airborne Contaminants Capture, Handbook of Nanofiber; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 3, pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Cheng, C.S.; Chan, C.K.; Chao, Z. The aerosol penetration through an electret fibrous filter. Chin. Phys. 2006, 8, 1864–1870. [Google Scholar]
- Souzandeh, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, W.H. “Green” nano-filters: Fine nanofiber of natural protein for high efficiency filtration of particulate pollutants and toxic gases. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 105948–105956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souzandeh, H.; Johnson, K.S.; Wang, Y.; Bhamidipaty, K.; Zhong, W.H. Soy-proteinbased nanofabrics for highly efficient and multifunctional air filtration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 20023–20031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, R.; Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Lu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Huang, C.; Ke, Q.; Zhao, Y. Zeolite imidazole framework-8(ZIF-8) decorated keratin-based air filters with formaldehyde removal and photocatalytic disinfection performance. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 23, 100689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).