Abstract
Soft fiber-reinforced actuators have demonstrated significant potential across various robotics applications. However, the actuation motion in these actuators is typically limited to a single type of motion behavior, such as bending, extending, and twisting. Additionally, a combination of bending with twisting and extending with twisting can occur in fiber-reinforced actuators. This paper presents two novel hybrid actuators in which shape memory alloy (SMA) wires are used as reinforcement for pneumatic actuation, and upon electrical activation, they create a twisting motion. As a result, the hybrid soft SMA-reinforced actuators can select between twisting and bending, as well as twisting and extending. In pneumatic mode, a bending angle of 40° and a longitudinal strain of 20% were achieved for the bending/twisting and extending/twisting actuators, respectively. When the SMA wires are electrically activated by the Joule effect, the actuators achieved more than 90% of the maximum twisting angle (24°) in almost 2 s. Passive recovery, facilitated by the elastic response of the soft chamber, took approximately 10 s. The double-helical reinforcement by SMA wires not only enables twisting in both directions but also serves as an active recovery mechanism to more rapidly return the finger to the initial position (within 2 s). The resulting pneumatic–electric-driven soft actuators enhance dexterity and versatility, making them suitable for applications in walking robots, in-pipe crawling robots, and in-hand manipulation.
1. Introduction
The demand for versatile soft robots, those capable of performing a broader range of tasks, is driving the necessity for a new category of multi-functional actuators. For instance, beyond their fundamental role of picking up and putting down objects [1,2], soft grippers and bionic hands are expected to be involved in in-hand manipulations [3]. Moreover, walking and crawling robots [4,5] are expected to adjust their locomotion direction [6]. Therefore, actuators that are capable of performing multiple actions are needed, such as those that combine bending, extending, and twisting in a selective and controlled manner. Fiber-reinforced pneumatic actuators have been widely used in grippers and exploration robots [7,8,9,10,11]. However, achieving multifunctionality in a single fiber-reinforced actuator has not yet been thoroughly explored. Nevertheless, multifunctionality has been presented by segmentally patterning different reinforcements [12,13]. Furthermore, there are very few works demonstrating pure twisting, without significant longitudinal or bending deformation, in fiber-reinforced pneumatic actuators, with this becoming possible by varying the fiber angles [14].
Two widely recognized categories of soft fluidic actuators include fiber-reinforced actuators and pneumatic network (PneuNet) actuators [15]. Nevertheless, the geometry of fiber-reinforced actuators is more anthropomorphic, resembling human fingers, making them a preferable choice for applications in soft robotic hands or exosuits [16]. Furthermore, in comparison to the PneuNet design, fiber-reinforced actuators are less susceptible to catastrophic damage [17] due to their reinforcement and lower volume expansion. In addition, because the structure of fiber-reinforced actuators has fewer seams compared to PneuNet actuators, the issue of delamination that causes early failure is less likely. While the processing of fiber-reinforced actuators may pose greater challenges compared to PneuNet actuators due to their multi-material design, the ongoing progress in processing techniques, such as multi-material additive manufacturing, is expected to alleviate this issue.
Besides the previously mentioned pneumatic actuators, shape memory alloy (SMA) wires are being extensively utilized as actuation elements in various soft robots [18,19,20]. The high-power density of shape memory alloy wires and their heat activation, occurring through the Joule effect, make them intriguing actuators [21], especially in scenarios where weight is a concern [22], like in untethered robots [23]. However, SMA wires have certain drawbacks, including a slow transition process and a limited stroke. The slow transition is attributed to the low thermal conductivity of the polymers in which the SMA wires are embedded, as well as the viscoelastic effect of the polymers, which is magnified by the increase in temperature and reduces the elastic load of the materials needed to return the SMA wires to their initial state. Solutions are being researched, including the development of thermally conductive polymers [24], and the integration of multiple SMA wires [25]. Another proposed solution to increase the stroke involves integrating longer SMA wires, made possible by extending the wire outside of the matrix [26]. Aside from actuation [27], SMAs are also used for other functionalities in soft robots, including variable stiffness [28], as well as for damage closure to assist in healing in self-healing soft robots [17]. Furthermore, SMA actuators have been employed as assisting elements in pneumatic actuators, enabling functions such as bending in a single McKibben muscle [29], and offering precise control in a bending fiber-reinforced pneumatic actuator [30].
Utilizing the previous actuation technologies, soft bending and extending actuators have been extensively researched, while there has been comparatively less exploration of twisting or torsional actuators [2]. Yan et al. and Sanan et al. developed pure pneumatic torsional actuators by creating pneumatic chambers in a helical manner [31,32]. Li et al. used origami design to create a soft pneumatic twisting actuator, although the twisting comes with either contraction or extension of the actuator [33]. Jiao et al. achieved a vacuum-driven twisting motion by creating seamless chambers with curved and slanted walls [34]. Gorissen et al. stacked two pneumatic balloon actuators to create a twisting motion. Each actuator consists of a silicon layer with a pattern of molded and sealed voids [35]. With varying fiber angles, Connolly et al. demonstrated twisting in fiber-reinforced actuators without simultaneous extension [14]. Embedded SMA wires have also been used to create a twisting motion in soft actuators [36,37,38], as well as multi-modal actuations [39].
In this study, two novel hybrid reinforced actuators are presented in which SMA wires replace the typical reinforcement used in fiber-reinforced actuators. This substitution allows for twisting when electrically stimulated, providing an additional dimension of movement, while still retaining reinforcement for the pneumatic actuation of the actuator. The inspiration for this work stems from a prior study by our group, whereby SMA wires were utilized to reinforce a self-healing soft bending actuator, aiding in damage closure and promoting healing [17]. In that work [17], a single wire was wound clockwise and then wound back counterclockwise. In this work, we build upon that concept, differing in the approach of employing two SMA wires for radial reinforcement of the soft chamber. One wire is wrapped clockwise and the other is wrapped counterclockwise around the chamber. Consequently, in the current study, the activation of each wire induces a twisting motion in two different directions. Furthermore, achieving selectivity between twisting and bending/extending in fiber-reinforced (herein, SMA wire-reinforced) pneumatic actuators becomes possible, a unique characteristic not commonly observed in soft actuators. This capability is attained by integrating SMA wires and imparting hardware multifunctionality [40]. The subsequent section outlines the design, processing, and characterization methods. The results provide insights into the functioning of the actuator in both twisting and bending/extending modes. Following this, we delve into the challenges that must be faced and outline future directions for research.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Typical Fiber-Reinforced Actuators vs. the Proposed Hybrid Actuators
2.1.1. Typical Fiber-Reinforced Actuators
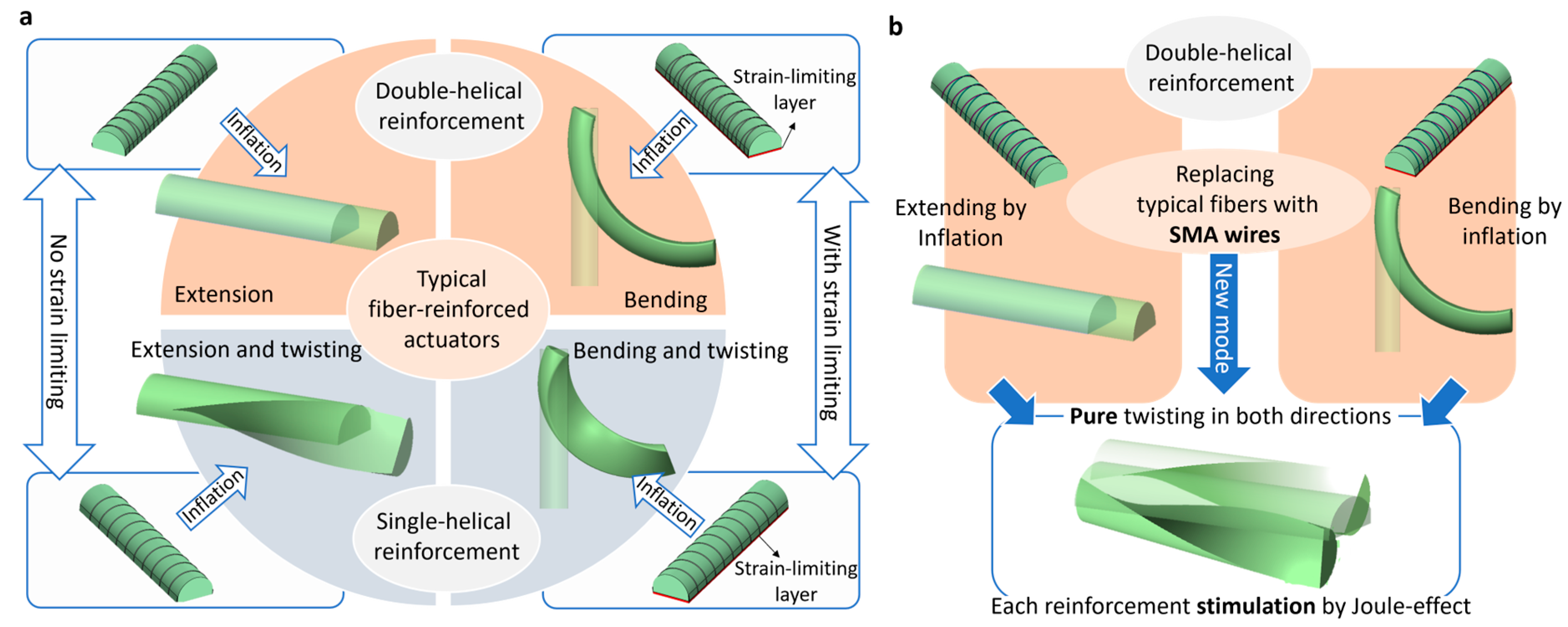
Fiber-reinforced pneumatic actuators are typically constructed using a soft chamber shaped like a cylinder or half cylinder, which is then reinforced with tiny fibers, wires, or strands [11]. Without reinforcement, the chamber expands in all directions upon inflation. However, depending on how the chamber is reinforced, its deformation is restricted in specific directions and the actuator can achieve different motions; typically, extension, bending, and a combination of extension with twisting and bending with twisting [11]. The design and actuation of fiber-reinforced pneumatic actuators are as follows (the readers are referred to https://softroboticstoolkit.com/book/fr-variation-motion (accessed on 12 February 2024)): For extension, the actuator is radially double helically reinforced (Figure 1a). In the case of bending, in addition to radial double helical reinforcement, a strain-limiting layer is embedded within the actuator (Figure 1a). This layer is flexible, yet not stretchable and may consist of materials such as paper or a fabric such as Kevlar. The layer hinders the extension on one side of the actuator, resulting in a bending motion when pressurized. In both the bending and extension actuators, if the radial reinforcement relies solely on a single helix manner, twisting simultaneously occurs in the actuator as well. This twisting motion is a result of the asymmetrical application of force due to the single helical reinforcement (Figure 1a). Hence, to improve the controllability of fiber-reinforced pneumatic actuators, a preference is given to those with double-helical reinforcement that remains untwisted.
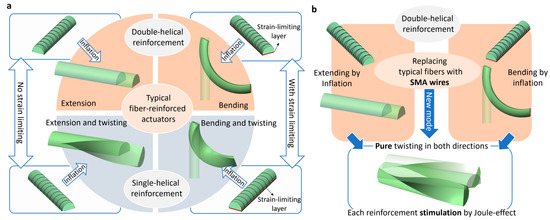
Figure 1.
An overview of the design and motion actuation of (a) typical fiber-reinforced actuators and (b) the SMA-reinforced actuators in the current study. Using SMA wires allows for hybrid pneumatic and electric reinforced actuators capable of either bending or extending and pure twisting. Twisting is possible in both directions in the double-helical reinforcement design.
2.1.2. Concept of Hybrid Actuators
The hybrid principle of the presented actuators refers to their ability to be activated both pneumatically and electrically. Two types of actuators were developed: (i) a bending/twisting actuator and (ii) an extending/twisting actuator (Figure 1b). The key difference between these two actuators lies in the presence of a strain-limiting layer required for the bending motion of the first actuator (Figure 1b).
When the actuators are subjected to pneumatic pressure, the first actuator bends, while the second one extends. This is the pneumatic mode of operation for the actuators. In the electrical mode, attributed to the activation of SMA wires by the Joule effect, the actuators undergo twisting. Typically made from nickel–titanium alloys with a crystalline molecular structure, SMA wires exhibit unique properties. When a load is applied to SMA wires below their transition temperature, in the martensitic phase, the wire is deformed due to the high mobility of interphases of martensite. This strain can be recovered by heating the wires above the transition temperature, inducing the phase transition in the crystalline structure from martensite to austenite [20]. The SMA wires are pre-strained before being embedded within the soft chamber, enabling the initial actuation. During multiple cycles of actuation, when the SMA wires are deactivated (cooling down), the elastic property of the soft chamber restrains them, preparing for the next actuation cycle. Since the chambers are reinforced with double-helical SMA wires, twisting can occur in both directions through the activation of each SMA wire. The twisting motion results from the helical configuration of the SMA wires, which, upon contraction, apply a rotational force to the chamber (Figure 1b).
2.2. Selection of Materials
Three distinct materials were employed in the fabrication of the hybrid soft actuator capable of twisting and bending: a hyperelastic elastomer for the soft chamber material, a fabric as the strain-limiting layer essential for bending performance, and SMA wires for twisting performance, complemented by radial reinforcement necessary for pneumatic actuation. A similar approach was applied for the twisting and extending actuator, omitting the strain-limiting layer. The material constituting the chamber must be inherently soft and flexible, and preferably an elastomer with a nearly purely (hyper)elastic behavior. Additionally, it is vital for this material to possess adequate heat resistance, surpassing the transition temperature of the SMA wires, which is 78 °C. Consequently, we opted for an out-of-shell silicon-based material, specifically Ecoflex-0030 (Amsterdam, Netherland), with a useful temperature range of −53 °C to 232 °C (refer to Smooth-On products, purchased from Form X, Amsterdam, Netherland). Moreover, Ecoflex-0030 exhibits a high fracture strain of 900%, making it an ideal choice for various soft robotic applications. A piece of Kevlar fabric was chosen as the strain-limiting layer (needed for the bending motion) due to its inextensibility compared to Ecoflex-0030. It is thin and flexible, ensuring that it does not compromise the bending and twisting functions of the actuator. The SMA wires, strands of nickel–titanium alloy, were sourced from Dynalloy (Irvine, CA, USA). Following a comparative analysis between SMA wires with diameters of 0.1 mm and 0.3 mm, the 0.3 mm wire with the start heat transition temperature of 68 °C was selected. In addition to the higher force of the 0.3 mm wire (1280 gr for the 0.3 mm SMA wire and 143 gr for the 0.1 mm SMA wire), its larger diameter facilitates enhanced interaction with the soft chamber. However, it is important to note that wrapping the 0.3 mm SMA wire around the chamber presents greater challenges compared to using the 0.1 mm SMA wire. The wires were already pre-strained by 5%. The wire’s properties are detailed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Properties of the 0.3 mm SMA wire sourced from Dynalloy.
2.3. Design and Processing
The design parameters are adjustable according to the application. In this study, we aimed to demonstrate our novel technology by targeting dimensions comparable to those of a human finger for the actuator. The length was set at 90 mm, with a width of approximately 20 mm. Another crucial parameter is the pitch of the radial reinforcement, as a larger pitch size is expected to result in a greater twisting angle. To determine the maximum pitch size while ensuring sufficient reinforcement for pneumatic actuation, finite element simulations were conducted using Abaqus CAE 2019 (Simulia, Dassault Systèmes, Johnston, RI, USA). In the finite element model, the bending performance was taken into consideration. The hyperelastic material modeling, the Neo-Hookean model for Ecoflex-0030, was described in [41]. SMA wires were defined as element B32, while the matrix was represented by element C3D10H. A tie interaction was established between the SMA wires and the matrix. The pressure was applied to the inner surfaces of the actuator. Further detailed information is available in [17]. Based on the finite element analysis, it was determined that the maximum pitch achievable while ensuring adequate reinforcement for pneumatic actuation was 6 mm.
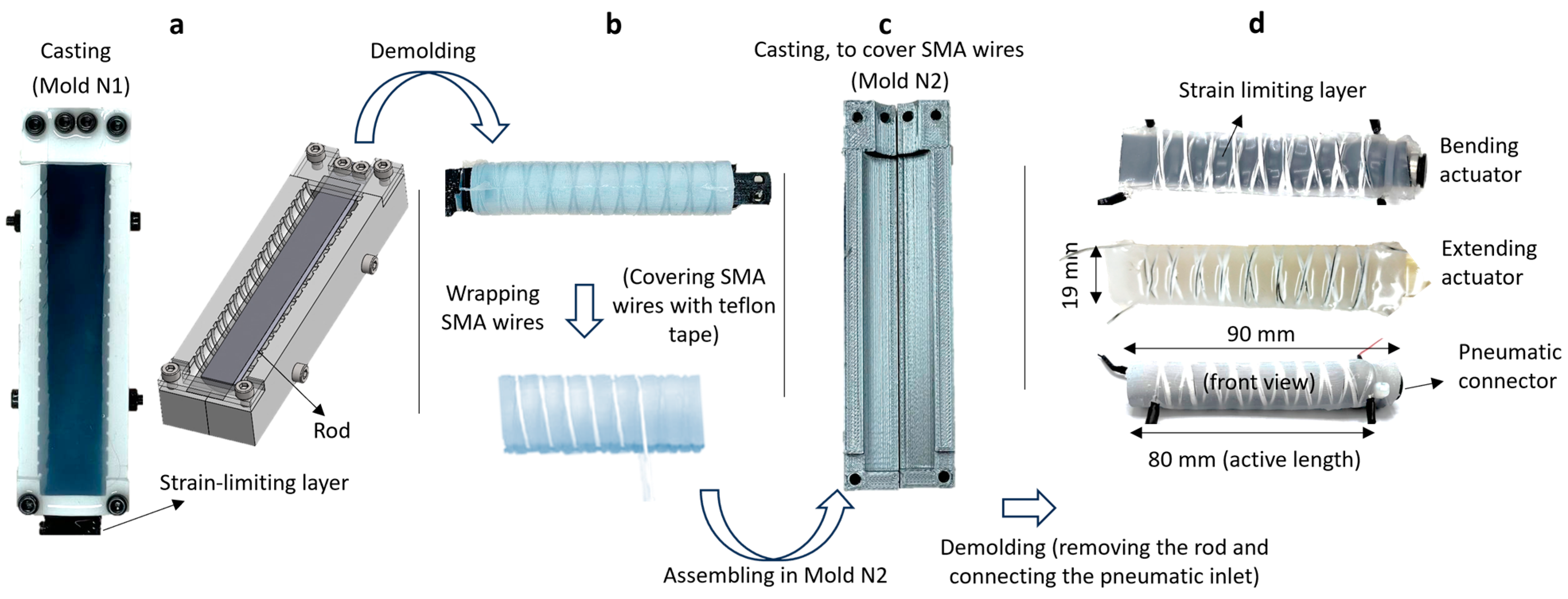
Figure 2 outlines the processing steps involved in creating the actuators. The process utilizes a primary mold (mold N1) and a secondary mold (mold N2) 3D-printed using filament extrusion (Figure 2). The molds were printed in two separate parts for easier demolding. The half-cylinder rod (Figure 2a), spray-coated with a release agent, is positioned in mold N1, and the strain-limiting layer is secured in place using side clamps. It is important to note that the step of adding the strain limiting layer is exclusive to the bending actuator and not applicable to the extending actuator. The material is then poured into mold N1 and cured for four hours at room temperature. Thereafter, the chamber containing the embedded strain-limiting layer and the rod inside is demolded from the mold (Figure 2b). The path for radial reinforcement was considered in mold N1 to ensure even spacing of the radial reinforcements and prevent ballooning upon inflation. This also guarantees that the wires are fully embedded within the actuator, facilitating efficient force transmission during twisting.
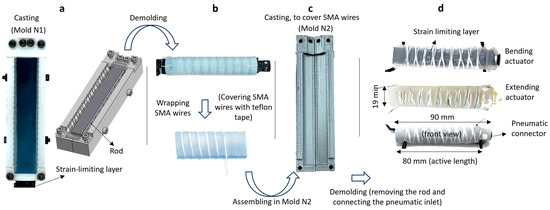
Figure 2.
Processing of the SMA-reinforced actuators. (a) The mold N1 with the half-cylindrical rod and the clamps that are used to secure the rod and the strain-limiting layer. The material is poured into mold N1. (b) The cured chamber is then disassembled and equipped with the SMA wires that are covered with Teflon tape. (c) Thereafter the chamber is placed in mold N2 and, again, the material is poured into the mold to embed the reinforcements. After 4 h, the actuator is demolded, the rod is removed, and the pneumatic connector is connected. (d) Dimensions of the two actuators.
Subsequently, the cured material was then equipped with radial reinforcements covered with Teflon tape (Figure 2b). The use of Teflon tape is to prevent short circuits in the wires when the voltage is applied. Teflon tape is an excellent insulator, can withstand high temperatures, is durable, and due to low friction allows for smooth movement of SMA wires upon activation. Similar to the step in Figure 2a, the chamber with the radial reinforcement was placed into mold N2 (Figure 2c). More material was then poured into mold N2, completely covering and embedding the radial SMA reinforcements. After a four-hour curing process under ambient conditions, the part was demolded. Finally, the half-cylinder rod was removed from the chamber, and the actuator was equipped with the necessary pressure inlet and sealed via clamping (Figure 2d). The actuator’s dimensions are 90 mm in length (10 mm is exploited for the pneumatic connector) and 19 mm in diameter (Figure 2d).
2.4. Experimental Setup
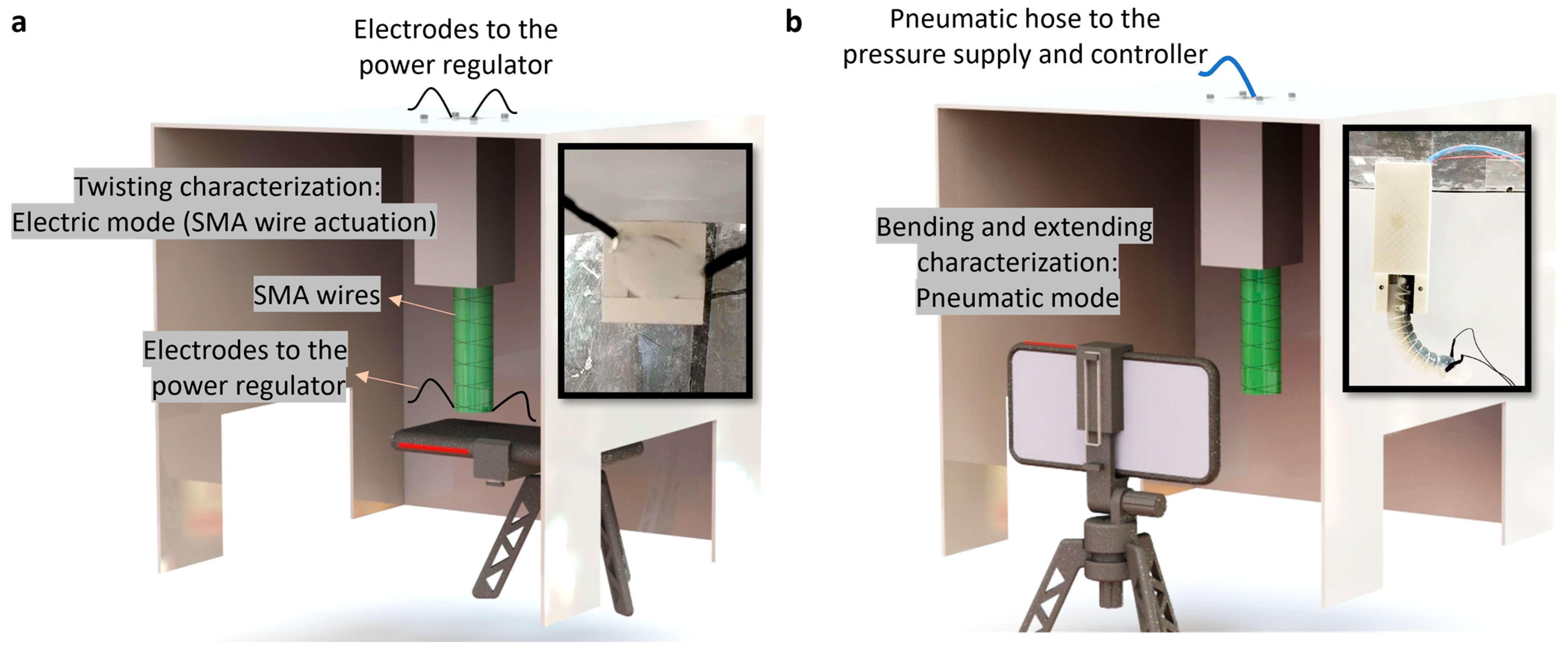
Referring to Table 1, the manufacturer’s data sheet for the SMA wires provided the recommended electrical current necessary for achieving full contraction of the wires. Each radial reinforcement had a length of almost 60 mm, requiring a corresponding electrical voltage/current of 12 V/1.5 A for achieving full contraction. This electrical current was supplied using a laboratory power supply. The actuator was securely mounted within a Plexiglas box (Figure 3a). The actuator’s performance upon wire activation was recorded from the bottom of the box (Figure 3a). The twisting performance of the actuators was later analyzed through video processing.
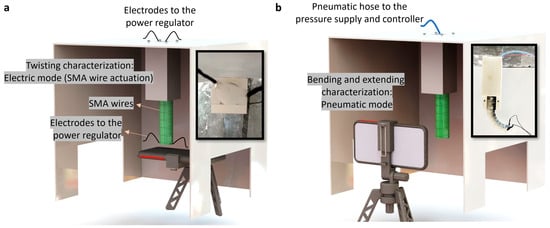
Figure 3.
Setups used for testing the actuators in the (a) electric mode for SMA actuation and the resulting twisting behavior (four electrodes, two pairs, were attached to the two SMA wires for electrical activation) and (b) pneumatic mode. Note that pneumatic setup was used for both the bending actuator and extending actuator.
For pneumatic actuation of the bending and extending actuators, a pressure supply was connected to a FESTO VEAB-L-26-D7-Q4-V1-1R1 pressure controller. The actuator’s performance under varying pressure levels was recorded and subsequently analyzed through front-view video recording and processing, as illustrated in Figure 3b. It is important to note that in this work, the actuators’ performance was kinematically analyzed. The force exertion capabilities were not investigated in this particular study.
3. Results
As mentioned, two different reinforced actuators were developed. A bending/twisting actuator and an extending/twisting actuator. The difference between these two actuators lies in the strain limiting layer which is needed for the bending performance of the first actuator. However, as the strain limiting layer was very thin and flexible, it did not compromise the twisting performance of the bending/twisting actuator. As such, the twisting performance of both actuators was quite similar and the reported results are true for both of them.
3.1. Twisting Performance
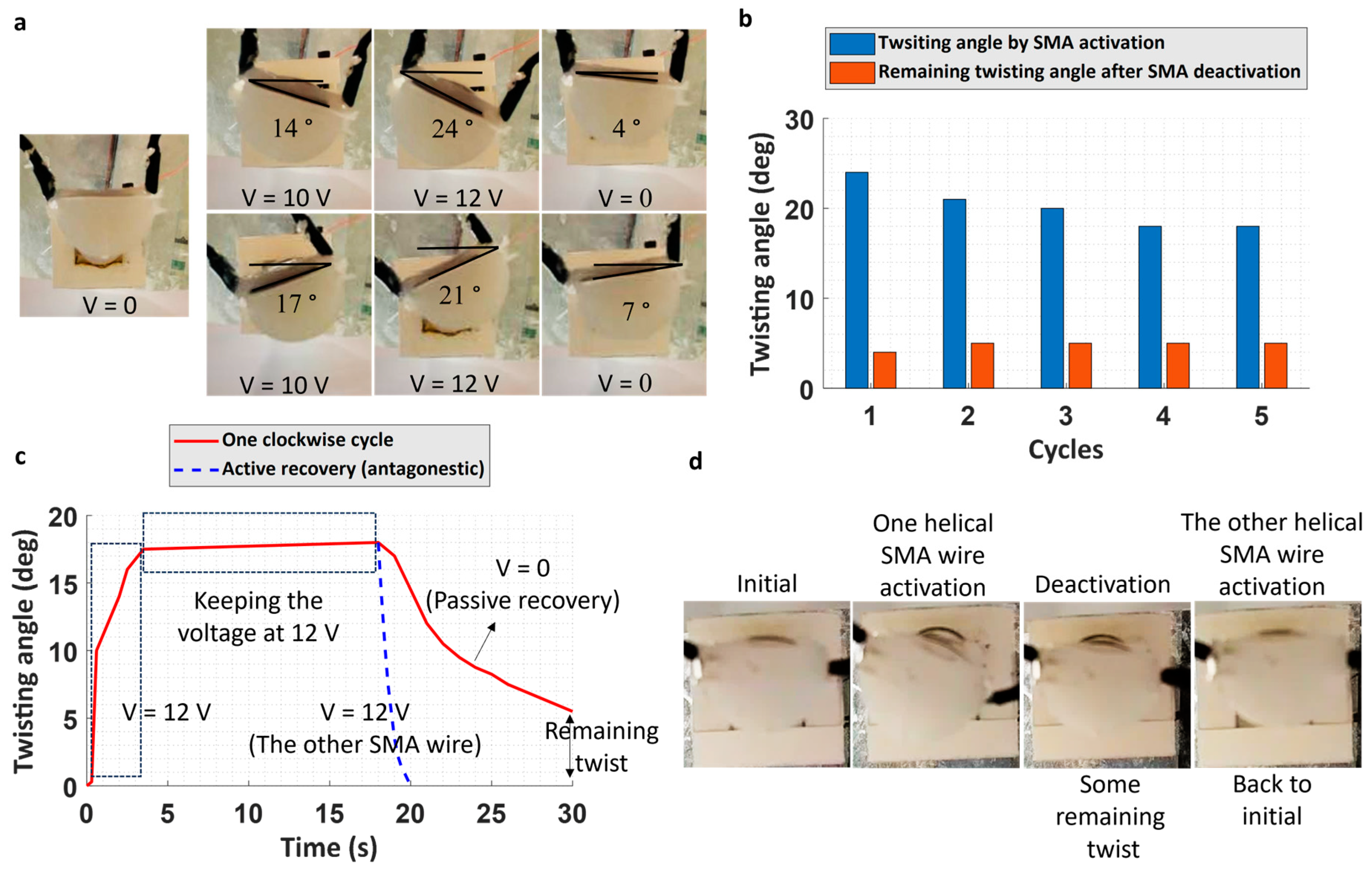
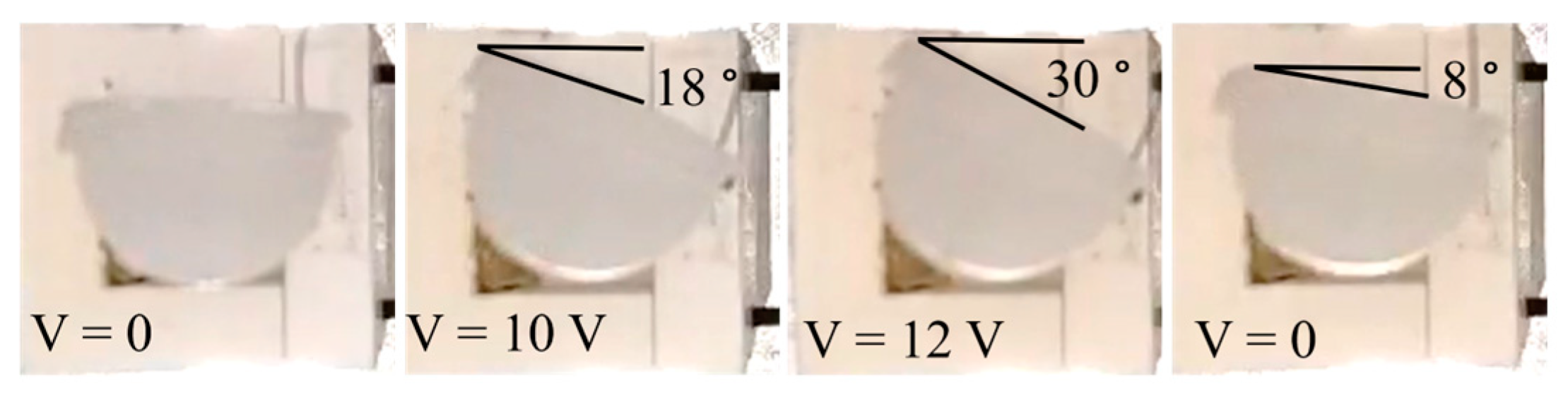
The electric-activated contraction of the SMA wires wrapped around the soft chamber resulted in a pure twisting angle in the soft actuators. Two wires were used for the radial reinforcement of the chamber, creating a double helical reinforcement, allowing for twisting in both clockwise and counterclockwise directions (Figure 4a and Supplementary Video S1). Using different voltage levels, various twisting angles could be achieved (Figure 4a). Figure 4b shows the results of clockwise twisting of the actuator in five consecutive cycles. As observed, without any external intervention, cycles of twisting actuations were possible. The lesser twisting angle in the following cycles compared to the first cycle could be attributed to the viscoelastic property of the soft matrix (via SMA wire activation, the matrix is heated up), some misalignment of the wire after the first activation, and a smaller pre-strain compared to the initial amount provided by the supplier. Multiple cycles of actuation imply that the elastic response of the soft chamber is capable of restraining the wire when it cools down; this is referred to as passive antagonist action from the soft elastomeric chamber (Figure 4c). However, despite the passive antagonistic action, a complete return to the initial position did not occur, and some remaining twisting angles were observed after each deactivation of the SMA wire (Figure 4a–c). Nevertheless, in the presented design, the other SMA wire reinforcement can act as the active antagonistic action (Figure 4c). Another approach to enhance the recovery process involves altering the matrix and examining the impact of the different mechanical properties of the matrix on the twisting and recovery process. Furthermore, the adhesion between the SMA wires and the matrix can be studied [42]. Figure 4c also provides a brief description of the time response of the actuators (the fourth cycle of the twisting test in Figure 4b was selected as the example). By suddenly increasing the voltage to 12 V, more than 90% of the maximum twisting angle is accomplished in almost 2 s. It can roughly be approximated that the actuators twist with a velocity of 10° per second. The actuator was able to maintain its position for longer time periods. After turning off the electricity, it took approximately 10 s for the passive recovery of the actuator. Nevertheless, as seen, this recovery can be actively achieved in 2 s. Figure 4d demonstrates how activation of the second SMA wire (the other radial helical reinforcement) can return the actuator to the full initial position.
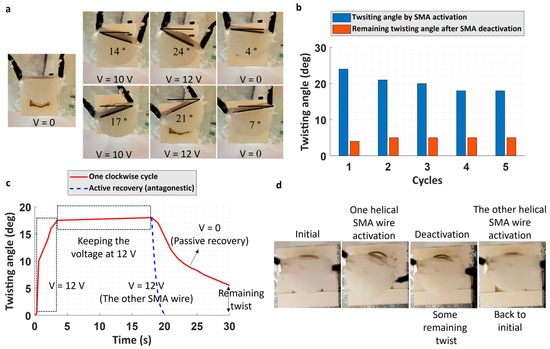
Figure 4.
Twisting performance of the actuators. (a) Twisting in both directions at two different voltages. As seen, after turning the voltage off, some remaining twisting angles exist. (b) Five consecutive clockwise twisting cycles. (c) Time response of the actuators in one of the twisting cycles as well as active recovery. (d) Active recovery (antagonistic action) of the double reinforcements after passive recovery.
Although double helical reinforcement is necessary for the pneumatic bending and extension of the actuators, each helical reinforcement also compromises the twisting actuation of the other reinforcement. The maximum twisting angle of an actuator reinforced with a single helical reinforcement was 30° (Figure 5 and the Supplementary Video S2), while in the case of double helical reinforcement, it was 24° (Figure 4a). Note that in the single helical reinforcement design, a combination of twisting with bending/extending can be achieved upon inflation (Figure 1a), and with SMA activation, single-direction twisting is performed.
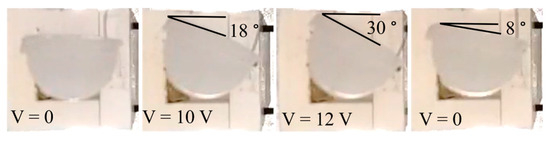
Figure 5.
Clockwise twisting in the single helical reinforcement design. With single helical reinforcement, a greater twisting angle can be achieved through the activation of the SMA wire.
3.2. Pneumatic Actuation
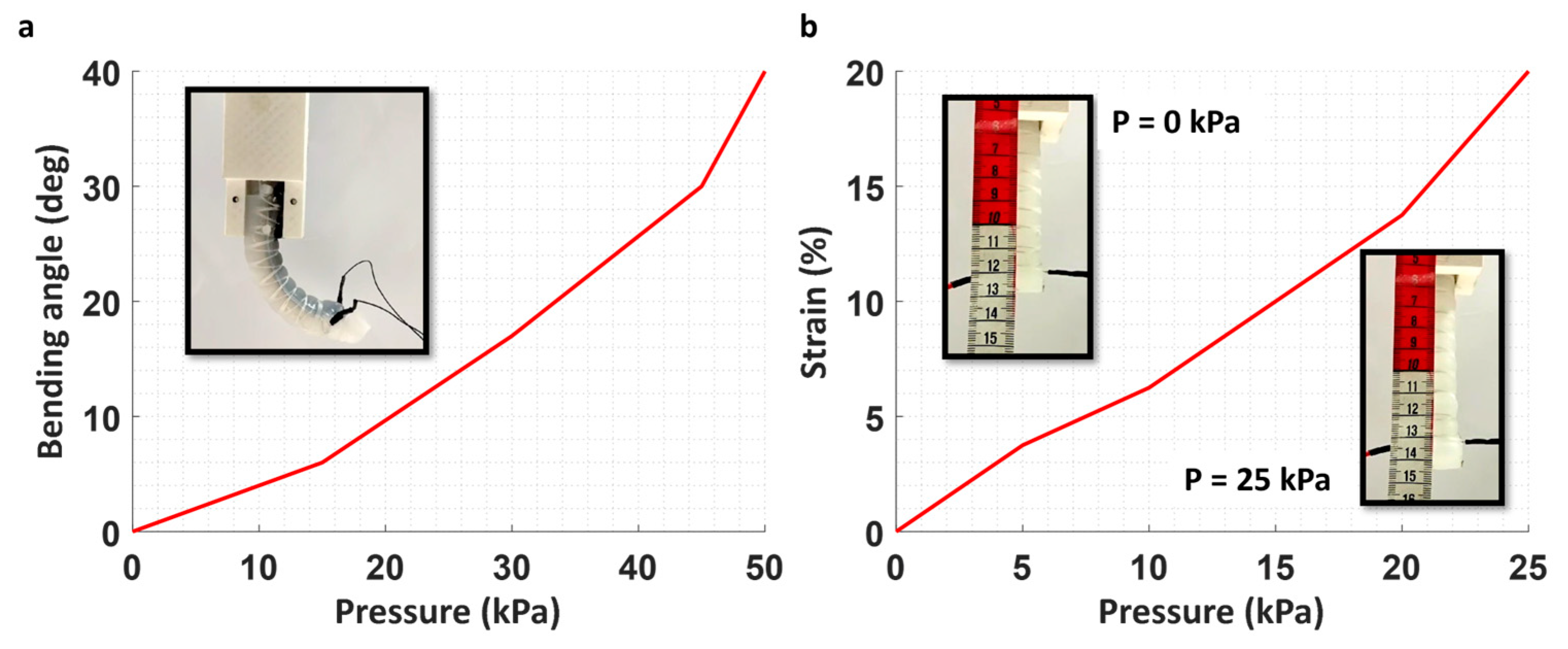
Pneumatic actuation of typical fiber-reinforced soft actuators has been well studied in the literature. In this study, the results demonstrate that utilizing SMA wires as reinforcement with the considered design parameters not only enables electrically driven twisting of the actuators but also allows for effective bending in the bending/twisting and extending in the extending/twisting actuators in pneumatic mode. Figure 6a depicts the bending performance where the bending angle reaches 40° with an input pressure of 50 kPa (Supplementary Video S3). Although higher bending angles can be achieved, the resulting configuration meets the requirements for many applications, such as gripping. The performance of the extending actuator is shown in Figure 6b (Supplementary Video S4). As observed, a 20% longitudinal strain was achieved with an input pressure of 25 kPa. It was observed that a 5 kPa increase in pressure could extend the actuator by 3–4 mm. Above the mentioned amount of pressure in the bending and extending actuators, ballooning happened from the end wall of the actuator. However, by increasing the length of the tip of the actuator (its thickness), more pressure can be applied to the chamber.
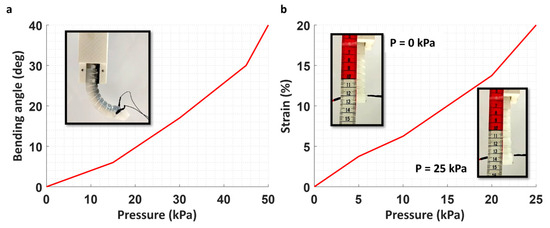
Figure 6.
Pneumatic mode of the actuators. (a) Bending performance in the bending–twisting actuator and (b) extension in the extending/twisting actuator.
4. Conclusions
In this work, two novel hybrid electric/pneumatic actuators capable of twisting and bending/extending are demonstrated. The design of the actuators mimics the well-known fiber-reinforced actuators, in which SMA wires were used as reinforcement instead of typical fibers. As a result, a new capability, which is selectivity between twisting and bending/extending, was introduced. These multifunctional actuators can potentially be utilized for advanced soft robotic applications. For example, the actuators can be used for applications where both bending/extending and twisting are required at different modes of operation. For example, one use case for the bending/twisting actuator can be the wrist of grippers or bionic hands to provide both flexion/extension motion (in the bending mode of the actuator) and pronation/supination motion (in the twisting mode of the actuator). For the extending/twisting case, probably the most highlighted application can be for walking or crawling robots to move forward (in the extending mode of the actuator) and change the contact and friction with the terrain which is needed for moving (in the twisting mode of the actuator). In addition, although not elaborated in this paper, the actuators can have the potential of simultaneous actuation of both modes, which can for instance be used for in-hand manipulation as seen in [3]. The potential use case of this technology can be explored for the closure of areas of damages through self-healing actuators. By employing twisting actuation, it can be investigated whether the actuator can effectively close damage applied in various directions, beyond the transverse damage closure presented in previous studies [17].
However, in this paper, the concept was presented, and a feasibility study was shown. There are still many possibilities to improve the performances of the actuators and address these issues. The primary problem in using SMA wires in the double-helical wrapping design is the risk of a short circuit that can occur if the two wires make contact. Although the wires were covered with Teflon tape, there is a risk of connection between the wires upon activation, leading to overheating and smoking. This necessitates a more robust coating for the wires. Another potential solution could be wrapping the two wires with a noticeable offset, i.e., wrapping the helical reinforcements in different molding steps with sufficient material in between.
Another challenge is understanding the interaction between the embedded wires and the soft matrix. Upon contraction of the wires, some slipping or mislocation in the wires may occur. This can make modeling the twisting performance more challenging and, practically, may alter the reinforcement and lead to ballooning upon inflation. To tackle this issue, research on improving the adhesion of SMA wires with a polymeric matrix can be useful [42]. In the future, it is necessary to develop a valid model for the actuator and study the influence of the size of the chamber and its length and diameter on the twisting angle. The larger the size of the chamber, the longer the reinforcement, resulting in more contraction of the SMA wires upon activation.
Moreover, the force exertion ability of the actuator still needs to be characterized. Clearly, the thicker the SMA wires, the more load they can exert. Nevertheless, activation requires a higher electrical current, and wrapping the wires becomes more difficult. Another characteristic that can be studied is simultaneous pneumatic and electric actuation to determine how the twisting occurs while the actuator is in the bent or extended position.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/act13040125/s1. Video S1: Twisting in double helical reinforcement design; Video S2: Twisting in single helical reinforcement design; Video S3: Pneumatic bending; Video S4: Pneumatic extension.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.K.T.; data curation, S.K.T. and F.C.; formal analysis, S.K.T., S.T. and B.V.; funding acquisition, S.T. and B.V.; investigation, S.K.T. and F.C.; project administration, B.V.; resources, S.K.T., S.T. and B.V.; software, S.K.T. and F.C.; supervision, S.K.T., S.T. and B.V.; validation, F.C.; visualization, S.K.T.; writing—original draft, S.K.T.; writing—review and editing, S.K.T., F.C., S.T. and B.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Sklodowska-Curie grant agreement No 860108 (SMART), as well as the SHINTO project which is funded under the European Innovation Council (EIC) programme of the European Union with grant agreement ID of 101057960.
Data Availability Statement
All information is available in the manuscript and the Supplementary Materials. Any other information can be provided by the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hughes, J.; Culha, U.; Giardina, F.; Guenther, F.; Rosendo, A.; Iida, F. Soft manipulators and grippers: A review. Front. Robot. AI 2016, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintake, J.; Cacucciolo, V.; Floreano, D.; Shea, H. Soft Robotic Grippers. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1707035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abondance, S.; Teeple, C.B.; Wood, R.J. A Dexterous Soft Robotic Hand for Delicate In-Hand Manipulation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 5502–5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calisti, M.; Picardi, G.; Laschi, C. Fundamentals of soft robot locomotion. J. R. Soc. Interface 2017, 14, 20170101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Cao, Y.; Sarparast, M.; Yuan, H.; Dong, L.; Tan, X.; Cao, C. Soft Crawling Robots: Design, Actuation, and Locomotion. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 1900837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubin, C.A.; Heisser, R.H.; Peretz, O.; Timko, J.; Lo, J.; Helbling, E.F.; Sobhani, S.; Gat, A.D.; Shepherd, R.F. Powerful, soft combustion actuators for insect-scale robots. Science 2023, 381, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; O’Brien, K.; Li, S.; Shepherd, R.F. Optoelectronically innervated soft prosthetic hand via stretchable optical waveguides. Sci. Robot. 2016, 1, eaai7529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Xiong, C.; Liu, C.; Li, P.; Chen, Y. Fabrication and Dynamic Modeling of Bidirectional Bending Soft Actuator Integrated with Optical Waveguide Curvature Sensor. Soft Robot. 2019, 6, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ma, J.; Ren, Z.; Gong, Z.; Hao, Y.; Wang, T.; Wen, L. Fiber-reinforced soft robotic anthropomorphic finger. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Robotics and Automation Engineering (ICRAE), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 27–29 August 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedal, A.; Bruder, D.; Bishop-Moser, J.; Vasudevan, R.; Kota, S. A continuum model for fiber-reinforced soft robot actuators. J. Mech. Robot. 2018, 10, 024501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fras, J.; Althoefer, K. Soft Fiber-Reinforced Pneumatic Actuator Design and Fabrication: Towards Robust, Soft Robotic Systems. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference Towards Autonomous Robotic Systems, London, UK, 3–5 July 2019; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, G.; Krishnan, G. Designing Fiber-Reinforced Soft Actuators for Planar Curvilinear Shape Matching. Soft Robot. 2020, 7, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, F.; Walsh, C.J.; Bertoldi, K. Automatic design of fiber-reinforced soft actuators for trajectory matching. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, F.; Polygerinos, P.; Walsh, C.J.; Bertoldi, K. Mechanical programming of soft actuators by varying fiber angle. Soft Robot. 2015, 2, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagoli, A.; Chapelle, F.; Corrales-Ramon, J.-A.; Mezouar, Y.; Lapusta, Y. Review of soft fluidic actuators: Classification and materials modeling analysis. Smart Mater. Struct. 2022, 31, 013001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeder-York, P.; Clites, T.; Boggs, E.; Neff, R.; Polygerinos, P.; Holland, D.; Stirling, L.; Galloway, K.; Wee, C.; Walsh, C. Biologically Inspired Soft Robot for Thumb Rehabilitation1. J. Med. Devices 2014, 8, 020933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizian, S.K.; Terryn, S.; Cornellà, A.C.; Brancart, J.; Legrand, J.; Van Assche, G.; Vanderborght, B. Assisted damage closure and healing in soft robots by shape memory alloy wires. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Han, Y.-J.; Han, M.-W. A Shape Memory Alloy-Based Soft Actuator Mimicking an Elephant’s Trunk. Polymers 2023, 15, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Atab, N.; Mishra, R.B.; Al-Modaf, F.; Joharji, L.; Alsharif, A.A.; Alamoudi, H.; Diaz, M.; Qaiser, N.; Hussain, M.M. Soft Actuators for Soft Robotic Applications: A Review. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 2000128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianchetti, M.; Licofonte, A.; Follador, M.; Rogai, F.; Laschi, C. Bioinspired soft actuation system using shape memory alloys. Actuators 2014, 3, 226–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Heo, J.; Rodrigue, H.; Lee, H.; Pané, S.; Han, M.; Ahn, S. Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) Actuators: The Role of Material, Form, and Scaling Effects. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2208517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Zarepoor, M.; Huang, X.; Sabelhaus, A.P.; Majidi, C. Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) Actuator with Embedded Liquid Metal Curvature Sensor for Closed-Loop Control. Front. Robot. AI 2021, 8, 599650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Kumar, K.; Jawed, M.K.; Nasab, A.M.; Ye, Z.; Shan, W.; Majidi, C. Chasing biomimetic locomotion speeds: Creating untethered soft robots with shape memory alloy actuators. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaau7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Kumar, K.; Jawed, M.K.; Nasab, A.M.; Ye, Z.; Shan, W.; Majidi, C. Highly Dynamic Shape Memory Alloy Actuator for Fast Moving Soft Robots. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.-H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Rodrigue, H.; Choi, I.-S.; Kang, Y.J.; Ahn, S.-H. 35 Hz shape memory alloy actuator with bending-twisting mode. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Chung, Y.S.; Rodrigue, H. Long Shape Memory Alloy Tendon-based Soft Robotic Actuators and Implementation as a Soft Gripper. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigue, H.; Wang, W.; Kim, D.-R.; Ahn, S.-H. Curved shape memory alloy-based soft actuators and application to soft gripper. Compos. Struct. 2017, 176, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschi, C.; Cianchetti, M.; Mazzolai, B.; Margheri, L.; Follador, M.; Dario, P. Soft robot arm inspired by the octopus. Adv. Robot. 2012, 26, 709–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Guo, J.; Chen, Y.; Hao, L.; Davis, S. Development of a SMA-Fishing-Line-McKibben Bending Actuator. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 27183–27189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golchin, M.N.; Hadi, A.; Tarvirdizadeh, B. Development of A New Soft Robotic Module Using Compressed Air and Shape Memory Alloys. In Proceedings of the 9th RSI International Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics, ICRoM 2021, Tehran, Iran, 17–19 November 2021; pp. 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, B.; Zhao, J. A New Spiral-Type Inflatable Pure Torsional Soft Actuator. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanan, S.; Lynn, P.S.; Griffith, S.T. Pneumatic Torsional Actuators for Inflatable Robots. J. Mech. Robot. 2014, 6, 031003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Fan, D.; Zhu, R.; Lei, Q.; Liao, Y.; Yang, X.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; et al. Origami-Inspired Soft Twisting Actuator. Soft Robot. 2023, 10, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Ji, C.; Zou, J.; Yang, H.; Pan, M. Vacuum-Powered Soft Pneumatic Twisting Actuators to Empower New Capabilities for Soft Robots. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorissen, B.; Chishiro, T.; Shimomura, S.; Reynaerts, D.; De Volder, M.; Konishi, S. Flexible pneumatic twisting actuators and their application to tilting micromirrors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2014, 216, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, R.N.; Hartl, D.J.; Boyd, J.G.; Lagoudas, D.C. Modeling and Development of a Twisting Wing Using Inductively Heated Shape Memory Alloy Actuators. In Active and Passive Smart Structures and Integrated Systems 2015; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2015; Volume 9431, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigue, H.; Bhandari, B.; Han, M.-W.; Ahn, S.-H. A shape memory alloy–based soft morphing actuator capable of pure twisting motion. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 26, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.-E.; Quan, Y.-J.; Wang, W.; Rodrigue, H.; Song, S.-H.; Ahn, S.-H. A smart soft actuator using a single shape memory alloy for twisting actuation. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 125033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigue, H.; Wang, W.; Bhandari, B.; Han, M.-W.; Ahn, S.-H. SMA-based smart soft composite structure capable of multiple modes of actuation. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 82, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianchetti, M. Embodied Intelligence in Soft Robotics Through Hardware Multifunctionality. Front. Robot. AI 2021, 8, 724056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polygerinos, P.; Wang, Z.; Overvelde, J.T.B.; Galloway, K.C.; Wood, R.J.; Bertoldi, K.; Walsh, C.J. Modeling of Soft Fiber-Reinforced Bending Actuators. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gapeeva, A.; Vogtmann, J.; Zeller-Plumhoff, B.; Beckmann, F.; Gurka, M.; Carstensen, J.; Adelung, R. Electrochemical Surface Structuring for Strong SMA Wire–Polymer Interface Adhesion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 21924–21935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).