Abstract
This study examines the distributions of the cogging and current forces in a hybrid linear motor and their impact on its performance. Subsequently, using the Maxwell stress tensor to analyze the force acting on the motor, a method has been proposed for calculating the cogging force effect on the mechanical system stiffness. Based on the force profile, it was found that the cogging force was a noncurrent force that could reduce the spring stiffness of a hybrid linear motor when it is in operation. An electromagnetic–mechanical coupling analysis was conducted to calculate the displacement and acceleration of the hybrid linear motor on a dummy jig. The experimental and analytical results were in good agreement, indicating that the proposed method is accurate and reliable.
1. Introduction
Haptic technology [1], also known as haptics, is a form of technology that is used to stimulate touch sensations on a device or interface. This can be achieved through the use of force-feedback mechanisms such as motors, which can create a sense of touch or tactile feedback for the user. Haptics are commonly used in a variety of electronic devices, such as smartphones [2,3,4], tactile displays [5,6], and virtual reality headsets [7], to provide a more immersive and interactive experience. They are also used in a range of other applications, such as robotics and medical simulations. Overall, haptic technology has the potential to significantly improve the way we interact with technology and the world around us. It has already been used in numerous innovative applications, and it is likely that it will continue to be an important area of development in the future. This is an extended and revised version of a preliminary conference report that was presented at the conference on electromagnetic field computation (CEFC) in 2022 [8].
A rotary motor is a type of an electric motor that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy by rotating a shaft [9]. This is achieved through the use of an electromagnet and stator, which create a magnetic field that drives the shaft. Rotary motors are classified into several types, including DC motors [10], AC motors [11], and stepper motors [12], depending on the type of electrical power they use and the way in which they control the rotation of the shaft. On the other hand, a linear motor is a type of an electric motor that converts electrical energy into linear motion, rather than rotational motion. A linear motor consists of a stator and mover, which are arranged in a way that allows the mover to move along a linear path. In summary, the main difference between rotary motors and linear motors is the type of motion they produce. Rotary motors produce rotational motion, while linear motors produce linear motion. Currently, linear motors are also typically more common and widely used than rotary motors because of their simplicity and versatility.
Linear motors can be divided into three main categories based on the type of force they use to produce motion: Lorentz force-based [13,14], solenoid-based [15,16], and hybrid linear motors that use both Lorentz and solenoid forces. Haptic motors can be categorized as shown in Figure 1.
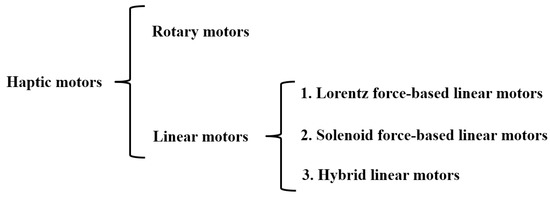
Figure 1.
Categories of haptic motors.
Lorentz-force-based linear motors generate motion by the interaction of a moving charged particle and magnetic field. They usually consist of a stator (coil) and mover. When an electrical current is applied to the coil, a magnetic field is generated around it, which causes the mover to move in a straight line as a result of the Lorentz force acting on the moving charged particles in the mover, as shown in Figure 2a.
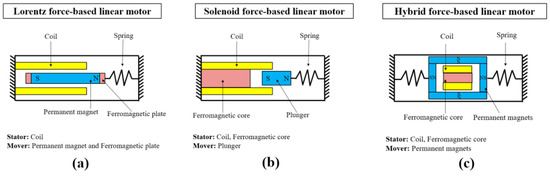
Figure 2.
Typical structures of linear motors based on the type of force: (a) Lorentz force-based linear motor; (b) solenoid force-based linear motor; (c) hybrid force-based linear motor.
Solenoid-based linear motors use the interaction between a magnetic field and ferromagnetic rod or plunger to produce motion. They consist of a stator, which is a coil of wire surrounding a cylindrical core, and a mover, which is a ferromagnetic rod or plunger placed inside the stator. When an electrical current is applied to the stator, a magnetic field is generated around it, which causes the mover to be attracted toward the stator and move in a linear fashion, as shown in Figure 2b.
While many researchers have developed linear motors that use either a Lorentz force or solenoid force, hybrid linear motors that use both Lorentz and solenoid forces are relatively less common. Hybrid linear motors typically consist of a stator that includes both a coil of wire and ferromagnetic core, and a mover. The stator generates a magnetic field that interacts with both the mover and ferromagnetic core, causing the mover to move in a straight line. Hybrid linear motors can offer the benefits of both Lorentz-force- and solenoid-based linear motors, such as high precision and electromagnetic force, as shown in Figure 2c.
The cogging force, which is also known as the cogging torque [17], is the residual force that is exerted on the rotor of a permanent magnet motor when it is stationary. It occurs as a result of the interaction between the permanent magnet and ferromagnetic material in the rotor and stator, and it is typically an undesirable effect in permanent magnet motors because it can cause the motor to vibrate or oscillate. In a previous study, Xu et al. [18] investigated the cogging force on a balanced armature receiver and found that the cogging force is linearly distributed on a part of the armature. It can be considered a negative spring force and helps to reduce the stiffness of the mechanical system. Xu et al. considered the cogging force by modifying the mechanical properties to obtain the same vibration deformation. However, no exact spring stiffness or negative spring stiffness calculations were reported.
This study first considered the working principle of a hybrid linear motor. The force profile of a hybrid linear motor was then obtained using the Maxwell stress tensor [19,20] in order to understand the cogging force effect on the motor and the relationship between the cogging stiffness and spring stiffness. Next, an electromagnetic–mechanical coupling analysis [21,22] was performed to obtain the displacement and acceleration of the hybrid linear motor. The results of this analysis were verified through an experiment.
Compared with existing research, the main contribution of this research is a detailed analysis and verification of the cogging force effect in hybrid linear motors using different magnet settings and the application of an electromagnetic–mechanical coupling analysis to determine the displacement and acceleration of the motor. This study had the goal of providing a new and improved understanding of the cogging force effect and its impact on the performance of a hybrid linear motor, and the results of this research may contribute to the development of more efficient and effective linear motor systems.
The length, width, and height of the hybrid linear motor were 20.0, 6.0, and 3.40 mm, respectively. The full model, top view, X-ray image, and exploded view are shown in Figure 3. The dimensions of the magnetic circuit are shown in Figure 4.
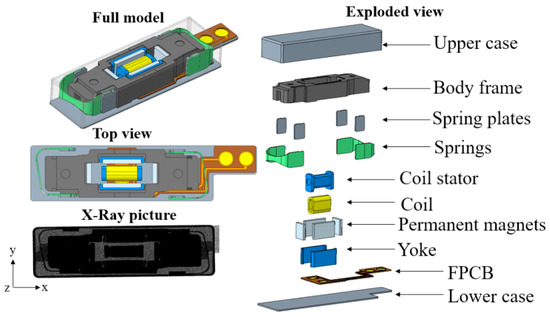
Figure 3.
Hybrid linear motor.
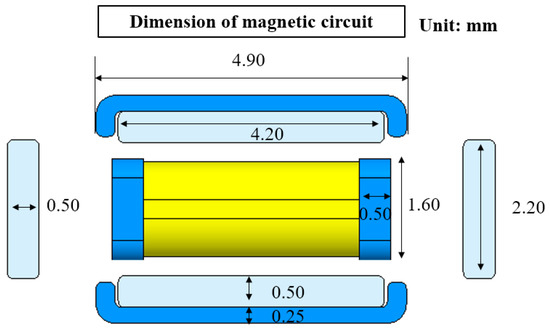
Figure 4.
Dimensions of magnetic circuit.
2. Material Properties
The mover included the body frame, spring plates, spring, permanent magnets, and yokes, while the other parts consisted of a coil, coil stator, case, and flexible printed circuit board (FPCB). The mechanical material properties of linear vibration include density, Young’s modulus, and Poisson’s ratio, as listed in Table 1. The upper and lower parts of the case were made of the same material as the spring. The FPCB is neglected in the following analysis. The yokes, coil stator, permanent magnets, and coils also exhibited electromagnetic properties.

Table 1.
Mechanical material properties.
A B–H curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the magnetic flux density B (T) and magnetic field strength H (A/m) in a material. It is used to understand the behavior of a material when it is subjected to a varying magnetic field. The shape of the B–H curve can vary depending on the type of the material and conditions under which it is measured. For example, some materials may exhibit a linear relationship between B and H, while others may show a nonlinear relationship. The yokes were made of cold-rolled carbon steel (SPCC), which provided nonlinear magnetic permeability.
The remanence of the N52H permanent magnet was 1.45 T, and the magnetic coercivity was 1066 kA/m. The direct-current resistance (DCR) of the 188 turn coil was 8.0 Ω, and the electrical conductivity was 100% IACS. The input voltage of the hybrid linear motor was 1.5 Vrms, which was determined using the smart power amplification circuit of a smartphone. The electrical conductivities of the other materials were neglected.
3. Analysis Method
3.1. Force Profile Analysis
The electromagnetic and mechanical systems of the linear haptic motor were coupled. The magnetization direction of the hybrid linear motor is shown in Figure 5a. Two types of forces exist in a hybrid linear motor: noncurrent and current forces. The noncurrent force, which is also called the cogging force, is the result of the magnetic interaction between the permanent magnet and magnetic material. The cogging force is dependent only on the position. The direction of the cogging force is illustrated in Figure 5b. The current force is defined as the electromagnetic force generated by the electrical current passing through a coil.
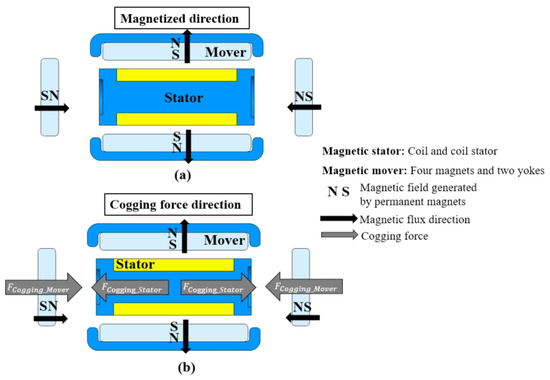
Figure 5.
Cogging force: (a) magnetized direction and (b) cogging force direction.
The solenoid force is directly proportional to the current passing through the coil and the number of turns in the coil. The direction of the solenoid force is determined by the direction of the current and the right-hand rule, which states that if the thumb of the right hand points in the direction of the current and the fingers wrap around the wire in the direction of the magnetic field, the force will be in the direction that the fingers point. In a hybrid linear motor, the solenoid force can be used to generate motion along the axis of the coil by attracting or repelling a ferromagnetic object placed in the field. When an electrical current passes through the coil, it can produce a uniform magnetic field. The solenoid force is one of the current forces; the other current force is the Lorentz force generated by the right-hand rule. The solenoid and Lorentz force directions of a hybrid line motor are illustrated in Figure 6.
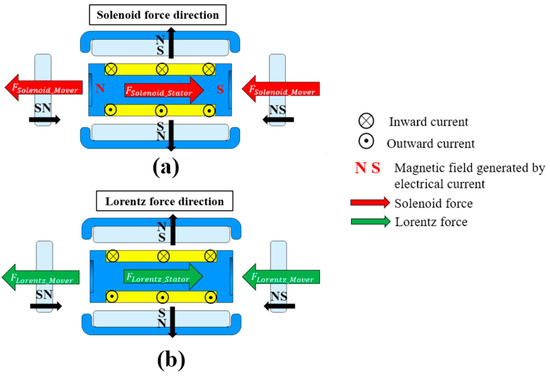
Figure 6.
Current force directions: (a) solenoid and (b) Lorentz force direction.
The Maxwell stress tensor is a matrix that represents the forces acting on a surface element in an electromagnetic field. It can be used to calculate the forces exerted by electromagnetic fields on conductors, insulators, and other materials. The Maxwell stress tensor, , given by Equation (1), was employed for the cogging and current force calculations in this study. The electromagnetic force of a certain body volume is expressed as Equation (2). The indices and refer to the coordinates , , and . The Kronecker delta, , is given by Equation (3).
Here, , , , , , , and denote the permittivity of free space, electric field, magnetic permeability of free space, magnetic field, force generated in the electromagnetic field, divergence operator, and volume integration, respectively.
The parts of the mover, which include four magnets and two yokes, are shown in Figure 7a. According to the analysis results, as shown in Figure 7b, the cogging force of the mover mainly originates from magnet #X1 and magnet #X2. Magnet #Y1 and magnet #Y2 have the same cogging forces in the X direction. Meanwhile, the cogging forces of yoke #1 and yoke #2 are also the same, which are almost equal to zero from −0.6 mm to +0.60 mm. The yokes have the lowest cogging forces because they are made of a material with the same magnetic permeability as the coil stator. The sum of the cogging forces of the various parts is equal to the total cogging force of the mover, taking both the magnets and yokes into account.
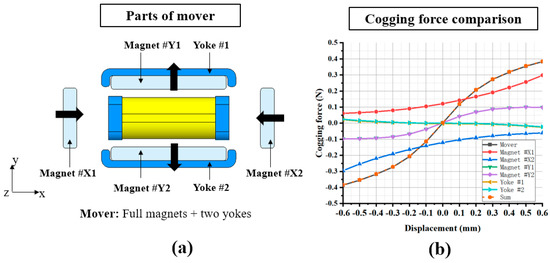
Figure 7.
Magnetic mover: (a) parts of mover and (b) comparison of cogging forces of different parts of mover.
The cogging force of the mover, , and cogging force of the stator, , are the action and reaction forces, respectively. The relationship between the current force, solenoid force, and Lorentz force is given by Equation (4). The total force of the mover, , is defined as the summation of the cogging force and current force, , as shown in Equation (5). Here, is the force factor, as shown in Equation (6).
The force profile of the hybrid linear motor under a constant voltage is shown in Figure 8a, which shows that the cogging force of the mover is linearly fitted to obtain the cogging stiffness, as shown in Figure 8b.
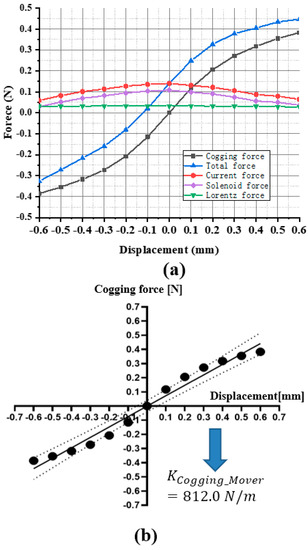
Figure 8.
Force profile: (a) different force distributions and (b) cogging stiffness of linear motor.
According to the above analysis, the cogging force is affected by the magnetic interaction between the mover and stator. Full-magnet, X−magnet−only, and Y−magnet−only models were made to verify the cogging force effect on the total stiffness. The Y−magnet−only model included magnet #Y1, magnet #Y2, and two yokes. The sample preparation, models, and samples are shown in Figure 9.
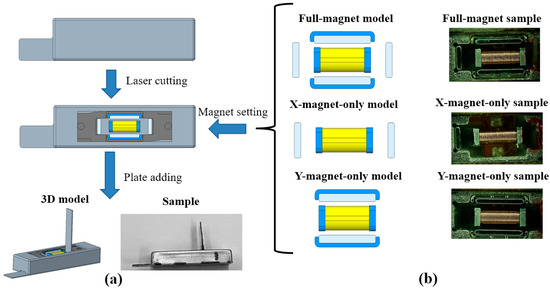
Figure 9.
Samples with open case: (a) sample preparation process and (b) magnet settings.
A comparison of the cogging forces for the full−magnet, X−magnet−only, and Y−magnet−only models is shown in Figure 10. The cogging stiffness values of these models had the following ranking: full-magnet model (812.0 N/m), Y−magnet−only model (370.8 N/m), and X−magnet−only model (129.5 N/m).
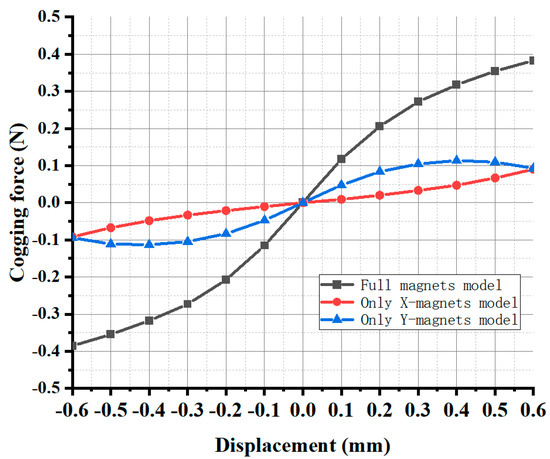
Figure 10.
Comparison of cogging forces of different models.
3.2. Cogging Stiffness Effect
When the hybrid linear motor is set at the initial position, which is the equilibrium position, the spring and cogging forces are zero. The spring and cogging forces change after the motor moves a certain distance, as shown in Figure 11. The net force, , is given by Equation (7). The total mechanical stiffness, , is equal to the spring stiffness, , minus the cogging stiffness, , which suggests that the cogging force has a negative impact on the spring stiffness of the hybrid linear motor. The total mechanical stiffness is given by Equation (8).
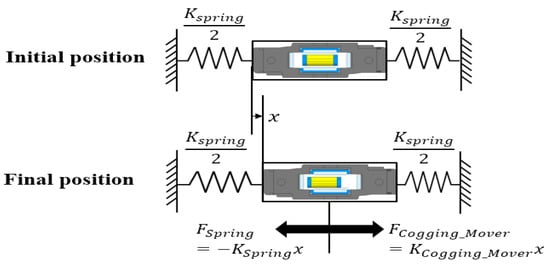
Figure 11.
Initial position and final position of mover.
3.3. Electromagnetic–Mechanical Coupling Analysis Method
The electromagnetic–mechanical (E–M) coupling analysis method [5] was used to calculate the acceleration with a dummy jig, where the accelerometer was on the side of the dummy jig. The E–M coupling equations include voltage and forced-vibration equations. The voltage equation of the linear motor is given by Equation (9), where , , , and denote the input voltage, DCR of the coil, inductance, and mechanical vibration velocity, respectively. The mover of a linear motor is driven by the current force generated by the interaction between the magnetic field and electrical current. Simultaneously, the movement of the mover generates a back-electromotive force on the coil, as shown in Equation (10). The forced-vibration equation of the linear motor was solved using the finite-element method, as shown in Equation (11), where , , , , , , and denote the mass matrix, acceleration vector, damping coefficient matrix, velocity vector, stiffness matrix, displacement vector, and current force acting on the mover, respectively. The E–M coupling model is shown in Figure 12.
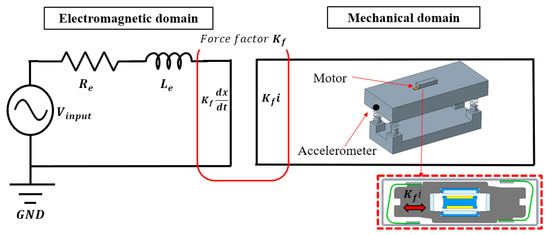
Figure 12.
E–M coupling model.
In a motor system, mechanical damping is a type of energy dissipation that occurs in mechanical systems due to friction, air resistance, and other forms of viscous drag. It is a property of the physical components of the system and arises from the interactions between these components and their surroundings. Electromagnetic damping is a type of energy dissipation that occurs in electrical and electromagnetic systems due to the resistance of conductors and the conversion of electromagnetic energy into heat. This type of damping is particularly important in motors and is a result of the interaction between the magnetic fields generated by the conductors and the resistance of the conductors themselves.
The method of modeling the mechanical damping of the system is to adjust the mechanical damping ratio to match the observed displacement amplitude at the resonance frequency after considering electromagnetic damping. Electromagnetic damping is automatically considered by the E–M coupling system. By considering both mechanical and electromagnetic damping in the modeling process, it is possible to obtain a more accurate analysis result of the system.
The software employed for the E–M coupling analysis was COMSOL Multiphysics, which uses a 3D numerical approach to solve governing equations. The E–M coupling analysis involved the interplay between the electromagnetic and mechanical effects in the system. The coupling from the electromagnetic to mechanical domain manifested as forces, while the coupling from the mechanical to electromagnetic domain resulted in a back-electromotive force (back-emf). The aim of the E–M coupling analysis was to accurately model and predict the overall behavior of the system under various conditions, taking into account the mutual influence of electromagnetic and mechanical phenomena.
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Experimental Setups
In order to study the performance of the hybrid linear motor, a series of experiments was conducted using two different experimental setups. The first setup used a Klippel measurement system, which is a specialized system designed for the precise measurement of the displacement of a linear motor or other electromechanical device. It consisted of numerous components, including a monitor, host computer, controller, distortion analyzer, and power amplifier (PLX 1802). The system also included a laser, which was used to measure the displacement of the motor with high accuracy, as shown in Figure 13a,b. The laser on the mover of the hybrid linear motor is shown in Figure 13c.
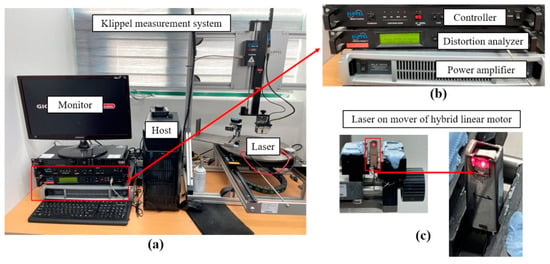
Figure 13.
Klippel measure system: (a) monitor, host, and laser; (b) controller, distortion analyzer, and power amplifier; and (c) laser on mover of hybrid linear motor.
The second setup was an acceleration measurement system, which included a monitor, vibration analyzer, and dummy jig, as shown in Figure 14a. The system used accelerometers to measure the acceleration of the motor on the dummy jig, which allowed the motor to freely move and allowed its acceleration to be accurately measured. Two motor positions (center and side) were used to obtain the acceleration of the hybrid linear motor on the dummy jig, as shown in Figure 14b,c.
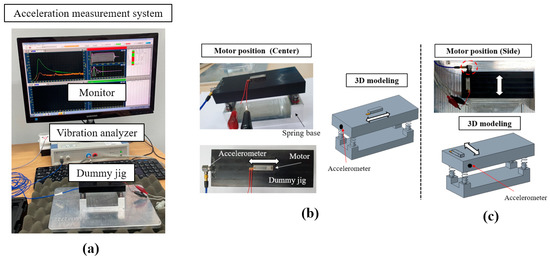
Figure 14.
Acceleration measurement system: (a) monitor, vibration analyzer, and dummy jig; (b) motor position (center); and (c) motor position (side).
4.2. Total Stiffness Results
The results of the analyses of the total stiffness values of the full-magnet, X-magnet-only, and Y-magnet-only models could be calculated based on the relationship between the cogging stiffness, spring stiffness, and total stiffness. The experimental results for the total stiffness could be obtained from the T/S parameters using the Klippel measurement system. Samples with different magnet settings are shown in Figure 15, along with the laser position. Three samples were used for each model, and the result for the total stiffness was the average value.
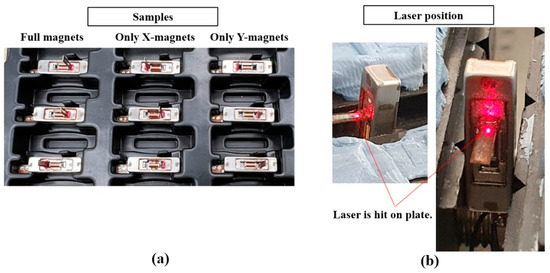
Figure 15.
Samples for total stiffness testing: (a) samples with different magnet settings and (b) laser position.
A comparison of the stiffness values of the different models is given in Table 2. As can be seen, a smaller cogging stiffness was associated with a higher total stiffness, which made the resonance frequency increase. Thus, the total stiffness testing verified the cogging force effect, which was used to reduce the spring stiffness of the mechanical system. The experimental total stiffness results were in good agreement with the analysis results.

Table 2.
Comparison of stiffness values of full-magnet, X-magnet-only, and Y-magnet-only models.
4.3. Displacement and Acceleration Results
The data collected from these experiments were used to validate the accuracy of the E–M coupling analysis method. The results of this comparison are shown in Figure 16, which illustrates the good agreement between the experimental data and predictions made by the E–M coupling method. This suggests that the E–M coupling method is an effective tool for analyzing the performance of a hybrid linear motor and can be used to accurately predict its displacement.
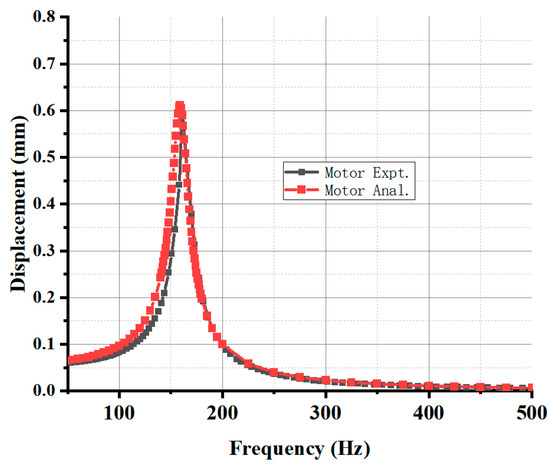
Figure 16.
Comparison of displacement values from experiment and analysis.
Figure 17a shows a comparison of the experimental accelerations obtained with different motor positions. In Figure 17b, a comparison of the acceleration results from the experiment and analysis is shown for the center position. It appears that the experimental results are in good agreement with the analytical results, indicating that the acceleration values obtained through experimentation matched well those predicted by the E–M coupling analysis.
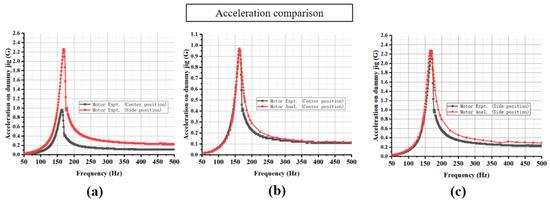
Figure 17.
Acceleration comparisons: (a) experimental acceleration comparison (center position vs. side position); (b) center position (experiment vs. analysis); and (c) side position (experiment vs. analysis).
Similarly, a comparison of the acceleration results from the experiment and analysis is shown for the side position. The observed discrepancies at frequencies higher than the resonance, as shown in Figure 17c, could have been caused by the accelerometer’s wire. The presence of the wire may have made the dummy jig heavier on one side, leading to a lower acceleration measurement. However, it also appears that the experimental results were in good agreement with the analytical results for most frequencies.
Overall, the experimental results were in good agreement with the analysis results for both the center and side positions, indicating that the analysis was accurate and reliable.
5. Conclusions
This study focused on understanding the different types of forces that act on a hybrid linear motor and how they impact its performance. To do this, the Maxwell stress tensor was used to analyze the force profile and understand the relationship between the different forces. In addition to analyzing the forces acting on a hybrid linear motor, a method for calculating the cogging stiffness was also proposed. This calculation method allowed for a better understanding of the effect of the cogging stiffness on the mechanical systems and how it can impact their performance. To validate the results of the analysis, experiments were conducted on a dummy jig, and the results were compared with the theoretical calculations. This showed good agreement between the experimental and analytical results, indicating that the analysis method used in this study was accurate and reliable. Overall, the novelty and scientific contribution of the study lie in the thorough investigation of the cogging force effect and application of the electromagnetic–mechanical coupling analysis method.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.J. and S.H.; methodology, Z.J.; software, Z.J. and J.P.; validation, Z.J., J.P. and D.X.; formal analysis, Z.J. and J.P.; investigation, Z.J. and J.P.; resources, Z.J.; data curation, Z.J. and J.P.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.J.; writing—review and editing, Z.J., J.P. and D.X.; visualization, Z.J.; supervision, S.H.; project administration, S.H.; funding acquisition, S.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sreelakshmi, M.; Subash, T.D. Haptic technology: A comprehensive review on its applications and future prospects. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 4182–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.U.; Hwang, G.Y.; Hwang, S.M.; Kang, B.S.; Kim, H.G. Development of brushless and sensorless vibration motor used for mobile phone. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2002, 38, 3000–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.H.; Lee, J. Analysis of flat-type vibration motor for mobile phone. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 4018–4020. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, S.M.; Lee, H.J.; Chung, S.U.; Hwang, G.Y.; Kang, B.S. Development of solenoid-type vibrators used for mobile phones. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2003, 39, 3262–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.X.; Park, K.H.; Kim, J.H.; Jiang, Y.W.; Xu, D.P.; Hwang, S.M. Analysis and design of a new linear vibration motor used to reduce magnetic flux leakage in in-vehicle infotainment. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.X.; Park, K.H.; Hwang, S.M. Design of a Width Slim Linear Vibration Motor Used for Automotive LCD Display Panel. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2022, 58, 8200405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, P. Virtual Reality Headsets—A Theoretical and Pragmatic Approach, 1st ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.X.; Park, J.H.; Xu, D.P.; Hwang, S.M. Electromagnetic-Mechanical Coupling Analysis of Linear Haptic Motor Considering Cogging Force Effect. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 20th Biennial Conference on Electromagnetic Field Computation (CEFC), Virtual, Denver, CO, USA, 24–26 October 2022; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Guarnieri, M. The development of ac rotary machines. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2018, 12, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.S.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Ramli, R. Optimal parameter estimation for a DC motor using genetic algorithm. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 2020, 11, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Jiang, M.; Xiang, Z.; Quan, L.; Hua, W.; Cheng, M. Design and optimization of a flux-modulated permanent magnet motor based on an airgap-harmonic-orientated design methodology. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 5337–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendjedia, M.; Ait-Amirat, Y.; Walther, B.; Berthon, A. Position control of a sensorless stepper motor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 27, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.B.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H. Horizontal linear vibrating actuator to reduce smart phone thickness. J. Vibroengineering. 2013, 15, 2003–2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Park, K.; Hwang, S. Novel Magnetic Circuit Design and Acceleration Calculation of Horizontal Linear Vibration Motor. Actuators 2022, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Tao, Z.; Li, H.; Zhu, K.; Wang, D.; Wu, H.; Xu, T. A MEMS Voice Coil Motor with a 3D Solenoid Coil. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 16th International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems (NEMS), Xiamen, China, 25–29 April 2021; pp. 1745–1748. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, B.; Xu, H.; Liu, B.; Dai, M.; Zhu, C.; Li, S. Novel magnetic circuit topology of linear force motor for high energy utilization of permanent magnet: Analytical modelling and experiment. Actuators 2021, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Li, S.; Pan, X.; Wu, S.; Tang, R. Analytical model for cogging torque calculation in surface-mounted permanent magnet motors with rotor eccentricity and magnet defects. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 2191–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.P.; Jiang, Y.W.; Kwon, J.H.; Hwang, S.M. Analysis of the effects of electromagnetic circuit variables on sound pressure level and total harmonic distortion in a balanced armature receiver. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 8001504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meessen, K.J.; Paulides, J.J.H.; Lomonova, E.A. Force calculations in 3-D cylindrical structures using Fourier analysis and the Maxwell stress tensor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 49, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.K.; Koh, C.S.; Ryu, J.S.; Xie, D. Comparison of Force Calculation Methods in 2D and 3D Finite Element Method. KIEE Int. Trans. Electr. Mach. Energy Convers. Syst. 2001, 11, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Zaouia, M.; Benamrouche, N.; Rachek, M. Electromagnetic-mechanical coupled model of tubular linear stepping motors. Electromotion 2011, 18, 331–339. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Jiang, Y.W.; Hwang, S.M. Analysis of a vibrating motor considering electrical, magnetic, and mechanical coupling effect. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).