Abstract
Novel miniature-scale bistable actuators are developed, which consist of two antagonistically coupled buckling shape memory alloy (SMA) beams. Two SMA films are designed as buckling SMA beams, whose memory shapes are adjusted to have opposing buckling states. Coupling the SMA beams in their center leads to a compact bistable actuator, which exhibits a bi-directional snap-through motion by selectively heating the SMA beams. Fabrication involves magnetron sputtering of SMA films, subsequent micromachining by lithography, and systems integration. The stationary force–displacement characteristics of monostable actuators consisting of single buckling SMA beams and bistable actuators are characterized with respect to their geometrical parameters. The dynamic performance of bistable actuation is investigated by selectively heating the SMA beams via direct mechanical contact to a low-temperature heat source in the range of 130–190 °C. The bistable actuation is characterized by a large stroke up to 3.65 mm corresponding to more than 30% of the SMA beam length. Operation frequencies are in the order of 1 Hz depending on geometrical parameters and heat source temperature. The bistable actuation at low-temperature differences provides a route for waste heat recovery.
1. Introduction
Bistable mechanical systems exhibit the unique property of two stable equilibrium states characterized by local minima of potential energy [1]. The stable positions are retained without power supply and, thus, power consumption is only required upon switching between the positions. When subjected to specific stimuli or loading conditions, a snap-through buckling motion can occur resulting in a rapid transition between the stable states. Bistable microactuators are basic components in engineering applications, such as micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) [2,3,4], microfluidics [5], and constitute key building blocks in emerging digital mechanical microsystems based on multistable microactuation [6].
In the past, bistable mechanisms have been developed consisting of compliant beams and plates, e.g., [7,8]. In this case, bistable actuation relies on the design of the movable compliant structures and the method of external loading. In particular, an external force needs to be applied to trigger the snap-through of the bistable structures. Considerable effort has been devoted to the design and fabrication of bistable MEMS devices including microvalves [9], micro-switches and relays [10,11,12], as well as fiber-optic switches [13]. In recent years, the development of smart materials such as shape memory [14,15] and piezoelectric materials [16,17] has led to the development of bistable mechanisms that do no longer rely on an external load but utilize their intrinsic transducer properties to induce bistability. Thus, novel smart bistable actuators have been developed making use of an extended range of stimuli including electrical [18,19], magnetic [20,21], thermal [22], and coupled fields [5,23].
Among the thermally responsive actuators, shape memory alloy (SMA) actuators are of special interest as they can convert small amounts of heat into mechanical work output in a narrow temperature interval. Depending on the SMA material, shape recovery can be induced well below 200 °C, enabling the conversion of low temperature waste heat. Due to the high power/weight ratio and ease-of-micromachining, film-basedSMA actuators have been widely implemented in microsystems, e.g., [24,25], and in robotics, e.g., [26]. The drawback of an external triggering force in conventional bistable systems can be avoided by the design of buckling SMA actuators with a predefined shape that is memorized by thermo-mechanical treatment (memory shape) and the use of the intrinsic thermally induced shape-recovery force [27]. As the one-way shape memory effect can only cause one-way snap-through behavior, a reset mechanism is required. Although the two-way shape memory effect could be implemented to switch between the stable states, the recovery stress upon cooling is much lower compared to the one-way shape memory effect and, thus, the switching force might be too low in most cases.
In the following, we present the design, fabrication, and characterization of novel miniature-scale bistable actuators consisting of two antagonistically coupled buckling SMA beams. In order to enable flexible downscaling, the fabrication technology is based on SMA films that are deposited by magnetron sputtering and micromachined by lithography. Thermal actuation is performed by direct mechanical contact between the SMA beams and a low-temperature heat source. The stationary and dynamic performance of the actuators are investigated to assess the influence of geometrical parameters and heat source temperature.
2. Material Characterization
The base material for this study was Ti53.9Ni30.4Cu15.7 films of 15 µm thickness fabricated by magnetron sputtering and subsequent crystallization by rapid thermal annealing at 700 °C for 15 min [28,29]. The phase transformation between austenite and martensite state of the films was investigated by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Therefore, the temperature of a SMA test sample was ramped at a constant cooling and heating rate of 10 °C/min. Figure 1a shows a DSC measurement indicating that the phase transformation occurred in the temperature range between 30 and 70 °C. The tangential method was used to determine the critical phase transformation temperatures, i.e., martensite start and finish temperatures; Ms = 41.9 °C and Mf = 31.9 °C, as well as the austenite start and finish temperatures; As = 58.6 °C and Af = 70.3 °C, respectively. In a martensitic state at a temperature below Mf, the SMA film could be deformed easily by mechanical loading. When the SMA film was heated above Af, the remanent strain after loading could be reset and, thus, the SMA film restored its initial memory shape.
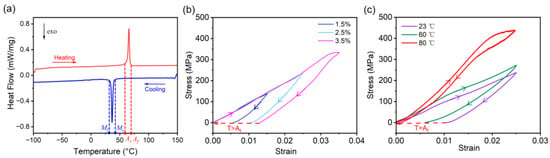
Figure 1.
(a) Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) measurement of a TiNiCu film of 15 µm thickness; (b) stress–strain characteristics of a TiNiCu tensile test specimen at different maximum strain in the range of from 1.5 to 3.5% at a low strain rate of 10−3/s at room temperature; (c) stress–strain characteristics of a TiNiCu tensile test specimen at different temperatures in the range of from 23 to 80 °C at a strain rate of 10−3/s.
A tensile test set-up was used to investigate the stress–strain characteristics of TiNiCu test specimens with the dimensions length l × width w of 15 × 2 mm2. Therefore, the strain was ramped step-wise and stress was monitored within a sufficiently long time interval to allow for quasi-stationary conditions. A temperature chamber was utilized for control of the ambient temperature. Figure 1b shows the stress–strain characteristics at room temperature (23 °C) at a strain rate of 10−3 s−1 for a maximum strain up to 3.5%. As the SMA film was in a martensitic state, the stress–strain characteristics show the typical nonlinear quasi-plastic behavior, reflecting the accommodation of martensite variants into the external load. After reaching the strain limit and subsequent load release, a remanent strain occurred depending on the maximum strain, which could be reset by heating above Af. Figure 1c shows the corresponding stress–strain characteristics at elevated temperatures. When the specimen was heated from ambient temperature to 60 °C, partial phase transformation occurred resulting in an initial increase in the slope of the stress–strain curve and a reduction in remanent strain. At 80 °C, the strain was fully reset upon unloading and the length of the sample returned to the initial state due to the reversible-stress-induced martensitic phase transition. Taking the difference in stress between martensite (23 °C) and austenite (80 °C) at 2% strain, a maximum shape recovery stress of about 150 MPa was determined. At larger strain, stress-induced martensite causes a stress plateau (Figure 1c) and, thus, the shape recovery stress saturates and does not increase further.
3. Actuator Design and Fabrication
Buckling beam structures are an effective way to design bistable devices, but they require an external force to overcome the energy barrier between the two stable states. Here, we design buckling SMA beams with a predefined memory shape to utilize the intrinsic thermally induced shape recovery force instead of an external force. Figure 2 shows the layout of the bistable SMA actuator, which is sketched in its two equilibrium positions. The major components were two SMA beams of TiNiCu, whose memory shapes were adjusted to be opposing buckling states, a spacer separating the SMA beams, and two heat sources located above and below the SMA beams. When SMA beam 1 came into contact with heat source 1 (Figure 2a), it was heated selectively and transformed from martensite to an austenite state. Due to the shape memory effect, SMA beam 1 returned to the opposing buckling state and, therefore, pushed SMA beam 2 towards heat source 2. This motion was supported by the snap-through motion towards the second equilibrium position. In this case, SMA beam 2 came into contact with heat source 2 (Figure 2b) and was heated above its Af temperature, while SMA beam 1 cooled back down below its Mf temperature. Consequently, the actuator was reset to its initial state, where the actuation cycle started again. Alternately heating the SMA beams resulted in an oscillatory snap-through motion.
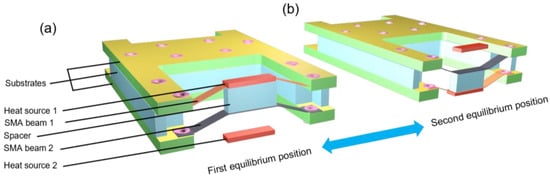
Figure 2.
Layout of the bistable SMA actuator. At sufficiently high temperature of the heat sources 1 and 2 an oscillatory motion occurs between the two equilibrium positions shown in (a,b).
Figure 3 illustrates the shape setting and assembly process of the bistable actuator. Flat SMA beams were placed in customized molds and deformed in opposite bending directions as shown in Figure 3a. Subsequent heat treatment was performed in a tube furnace in constraint condition for 30 min at 465 °C to obtain pairs of SMA beams with opposing buckling memory shapes. By setting the geometrical parameters of the mold, the heat treatment resulted in a pre-deformed shape that matched the specific mold with spacer length s and pre-deflection h. Figure 3b shows a photo of an SMA beam before and after the heat treatment. The SMA beams were fabricated by micromachining the magnetron-sputtered TiNiCu films using optical lithography. The width of the SMA beams was 1 mm and the distance between the two clamping sides of each SMA beam was 10 mm. The spacer height was adjusted to 3 mm, which enabled sufficient thermal isolation between the SMA beams.
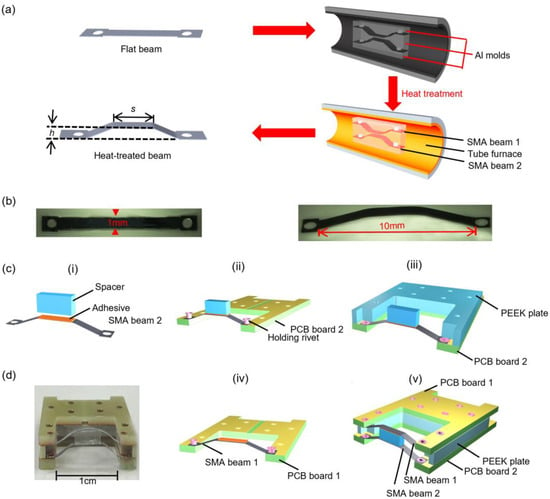
Figure 3.
Shape-setting and assembly process of the bistable actuator. (a) Schematic of heat treatment in a vacuum tube furnace; (b) photos of the SMA beam before and after heat treatment; (c) schematic assembly process; (d) photo of the bistable SMA actuator. Heat sources 1 and 2 are not shown for clarity. Legend: s—spacer length, h—pre-deflection.
Bistable actuators were fabricated by coupling the pairs of SMA beams in their center by a spacer. As illustrated in Figure 3c, the assembly process started with bonding the spacer on SMA beam 2 (i). Then, both SMA beam 2 and the attached spacer were then mounted on milled PCB board 2 and fixed by rivets (ii). Subsequently, a PEEK plate was positioned on PCB board 2 (iii), while SMA beam 1 was mounted on PCB board 1 (iv). The final assembly is sketched in (v). The PEEK plate between the two PCBs was designed to prevent short circuits and to reduce heat transfer between the SMA beams. A photo of the bistable SMA actuator is shown in Figure 3d without heat sources.
4. Stationary Force–Displacement Characteristics
4.1. Monostable SMA Actuators
A series of monostable SMA actuators consisting of a single SMA beam with buckling memory shape were investigated for different spacer lengths s and pre-deflection h. Therefore, the center of the SMA beam was deflected in out-of-plane direction under quasi-static loading conditions using a tensile test system to characterize the force–displacement characteristics in a martensite and an austenite state. The single SMA beam shows monostable behavior as it adopts one stable deflection after heating. Figure 4a illustrates the measurement setup. A spacer of length s was attached at the beam center, which complied with the interface of the load cell of the tensile test system. In a martensitic state, the measurement of force FM started in the undeflected state of the SMA beam center at displacement z = 0. Therefore, FM denotes the mechanical loading force of the tensile testing machine required to deform the SMA beam at room temperature in martensitic condition. This deformation was partly elastic and partly quasi-plastic due to reorientation of martensite variants. The shape recovery force FA was determined by the mechanical loading force required to deform the SMA beam in austenitic condition after Joule heating to austenitic state. By comparing the resistive and ambient heating conditions shown in Figure S1 in the Supplementary Information, we conclude that an electrical power of >430 mW is required to increase the average temperature above Af temperature.
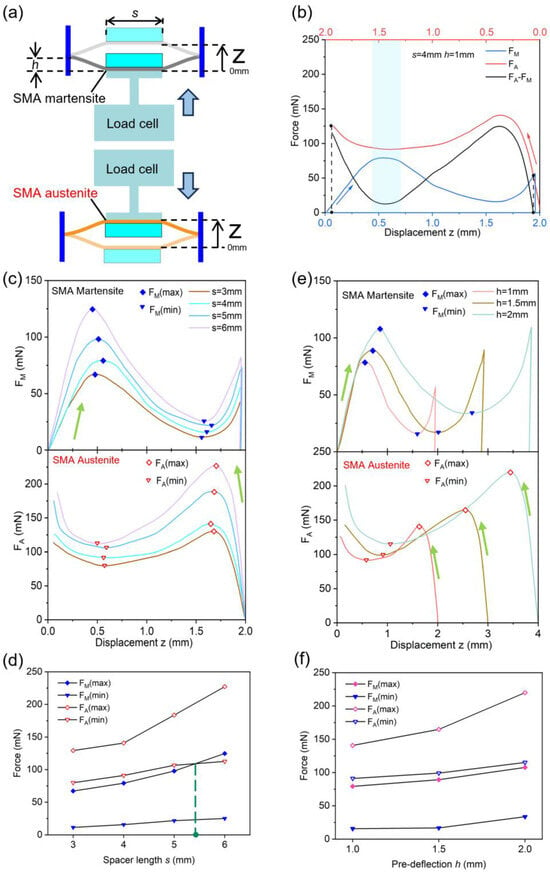
Figure 4.
(a) Schematic of force–displacement measurement of monostable SMA actuators. (b) Force–displacement characteristics of a monostable SMA actuator with an SMA beam in a martensitic state FM (blue) and in an austenitic state FA (red) with the memory shape corresponding to the deflected state at 2 mm displacement. The combined force FA–FM is shown in black. (c) Force–displacement characteristics for different spacer lengths s at a pre-deflection h of 1 mm. (d) Summary of maximum/minimum forces in martensitic and an austenitic state FM(max)/FM(min) and FA(max)/FA(min), respectively, determined from (c). (e) Force–displacement characteristics for different pre-deflections h at a spacer length s of 4 mm. (f) Summary of maximum/minimum forces in a martensitic and an austenitic state FM(max)/FM(min) and FA(max)/FA(min), respectively, determined from (e). The arrows in (b–e) indicate the direction of loading by the load cell.
In this case, the measurement started in fully deflected state at maximum displacement of the SMA beam center, which depends on the pre-deflection h. The forces FM and FA were determined whilst increasing and decreasing displacement using displacement-control under quasi-stationary conditions, respectively.
Typical force–displacement characteristics of a monostable SMA actuator are shown in Figure 4b for the case of spacer length s and pre-deflection h of 4 and 1mm, respectively. In a martensitic state, the force FM pointed in a negative z-direction acting against the force of the load cell (positive direction). It initially increased strongly with increasing deflection until a maximum was reached. When further increasing the deflection, the force decreased up to a minimum and then increased again. After release of the applied deflection load near the maximum displacement, the SMA beam stayed quasi-plastically deformed due to the self-accommodation behavior of the martensite variants. Figure 4b also shows that the course of shape recovery force FA in the case of the memory shape corresponds to the deflected state at 2 mm displacement. Therefore, FA was zero at 2 mm and pointed in a positive z-direction acting against the force of the load cell (negative z-direction). FA increased during decreasing displacement and exhibited a large maximum followed by a shallow minimum. For all displacements, FA was larger compared to FM, in this case indicating that any deflection of the SMA beam in a martensitic state could be reset by an SMA beam in an austenitic state. In particular, the sum of positive force FA and negative force FM (FA − FM) stayed positive for all displacements except for the maximum displacement close to the memory shape. This result has important consequences for coupled SMA beam systems, as it indicates that selective heating of one of the two SMA beams always causes a sufficiently high shape recovery force at any deflection to induce a snap-through motion back to the corresponding memory shape. In particular, bistable snap-through should occur between the two stable deflection states when heating the two SMA beams alternately. Figure 4b also indicates that two coupled SMA beams may only show bistability for those geometrical parameters, for which the force minimum in an austenitic state is larger compared to the force maximum in a martensitic state.
Figure 4c shows the effect of spacer length s on the stationary force–displacement characteristics of monostable SMA actuators for a pre-deflection h of 1 mm. In a martensitic state, the maximum force increases from 67 to 98 mN when increasing the spacer length s from 3 to 5 mm. At the same time, the force minimum also increases from 11 to 22 mN. Again, the SMA beams stay quasi-plastically deformed after the release of the deflection load near the maximum displacement. In an austenitic state, the maximum force increases from 129 to 184 mN with s increasing from 3 to 5 mm, while the force minimum FA rises from 80 to 106 mN. These trends of maximum and minimum force values are summarized in Figure 4d. When increasing spacer length s, the difference in force minimum in an austenitic state FA(min) and the force maximum in a martensitic state FM(max) decrease and eventually becomes negative between 5 and 6 mm. At a spacer length s of 6 mm, FM(max) exceeds FA(min), indicating that the shape recovery force is no longer sufficient to induce a snap-through motion back to the memory shape and, thus, the coupled SMA beam system is not bistable.
Figure 4e shows the effect of pre-deflection h on the stationary force–displacement characteristics of the monostable SMA actuators for a spacer length s of 4 mm. In a martensitic state, the maximum force FM(max) increases from 79.1 to 107.7 mN when increasing pre-deflection h from 1 to 2 mm, while the minimum force in an austenitic state FA(min) increases from 91.1 to 115.1 mN. Thus, FM(max) remains below FA(min) in the investigated parameter range, as summarized in Figure 4f, indicating that the coupled SMA beam system displays bistable performance in all cases.
The effects of the parameters s and h on the maximum and minimum forces of single SMA beams show a similar trend and, thus, add up. Figure S2 summarizes the effects of all parameter combinations of s and h in the Supplementary Information.
4.2. Bistable SMA Actuators
In the following, we investigate the performance of a series of bistable actuators for different spacer lengths s and pre-deflections h. The center of the coupled SMA beams is deflected in the out-of-plane direction under quasi-static conditions using a tensile test system. Force–displacement characteristics were determined by selectively heating one SMA beam and measuring the resulting net-force Fn at discrete displacement steps by controlling the travel distance of the load cell. The measurement setup shown in Figure 5a illustrates a case in which SMA beams 1 and 2 are in a martensitic and an austenitic state, respectively. In this case, Fn points in a positive direction in the first equilibrium position at zero displacement. Similarly, Fn points in a negative direction in the second equilibrium position at maximum displacement, when the states of SMA beams 1 and 2 are reversed.
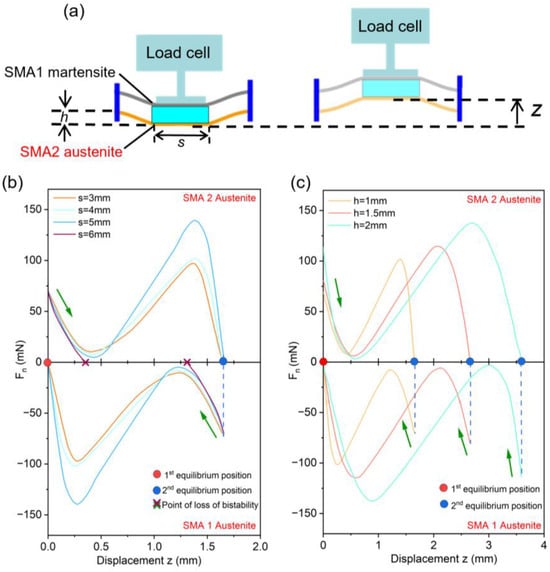
Figure 5.
(a) Schematic of force–displacement measurement of bistable SMA actuators for the case of selectively heating SMA beam 2. (b) Force–displacement characteristics for different spacer length s at a pre-deflection h of 1 mm. The upper panel shows the case of selectively heating SMA beam 2 to an austenitic state keeping SMA beam 1 in a martensitic state, and in the lower panel vice versa. (c) Force–displacement characteristics for different pre-deflections h at a spacer length s of 4 mm. The upper panel shows the case of selectively heating SMA beam 2 to an austenitic state keeping SMA beam 1 in a martensitic state, and in the lower panel vice versa. The arrows in (b,c) indicate the direction of loading by the load cell.
The upper part of Figure 5b shows the force–displacement characteristics of bistable SMA actuators for the case illustrated in (a) for different spacer length s at a pre-deflection h of 1 mm. For small-enough spacer lengths s in the range of 3 to 5 mm, Fn decreases and passes through a minimum. Then, it strongly increases to a maximum and finally decreases to zero at the second equilibrium position of the actuator. The minimal net force decreases with increasing s and eventually becomes zero for spacer lengths s exceeding 5 mm. In particular, for s = 6 mm, Fn decreases to zero after a small displacement of 0.3 mm, indicating that the actuator cannot reach the second equilibrium position. Evidently, the actuator is no longer bistable when the spacer length s becomes too large. This performance is in line with the course of the combined forces of the monostable actuator FA–FM displayed in Figure 4b and the trend of maximum and minimum force values summarized in Figure 4d. We conclude that the shape recovery force becomes too low to induce a snap-through motion back to the memory shape and, thus, the coupled SMA beam system looses bistability at large spacer lengths. A similar performance is observed in the lower part of Figure 5b, in which the states of SMA beams 1 and 2 are reversed. In this case, the actuator starts at the second equilibrium position, whereby Fn drives the actuator towards the first equilibrium position at zero displacement.
Figure 5c shows the effect of pre-deflection h on the stationary force–displacement characteristics of the bistable SMA actuators for a spacer length s of 4 mm. Again, the upper part displays the case wherein SMA beams 1 and 2 are in martensitic and an austenitic state, respectively. When increasing h from 1 to 2 mm, the maximum displacement increases to 3.6 mm. This large bistable actuation stroke corresponds to more than 30% of the SMA beam length. Fn decreases but stays positive, indicating that the actuators display bistable performance in all cases. A similar performance is observed during actuation in the reverse direction in the lower part of Figure 5c. This performance is in line with the course of the combined forces of the monostable actuator FA-FM displayed in Figure 4e,f, showing that the shape recovery forces dominate the forces in a martensitic state at all displacements. The effect of all parameter combinations of s and h on minimum net-forces Fn(min) is presented in Figure 6, providing an overview of their combined effect on bistability.
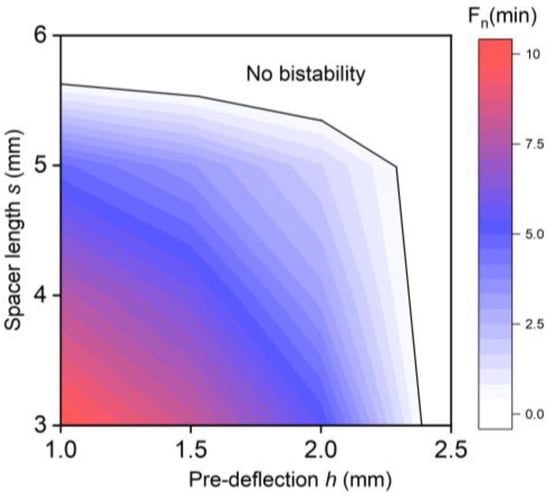
Figure 6.
The combined effects of spacer length s and pre-deflection h on the minimum net-force Fn(min) of the bistable SMA actuator. The limit of bistability is reached when Fn(min) becomes zero, as indicated by the solid line.
5. Dynamic Actuation Performance
In addition to direct Joule heating of the SMA beams, thermal actuation via direct mechanical contact of the SMA beams to a low-temperature heat source is an attractive alternative. In the following, we investigate the performance of a bistable SMA actuator, which is driven by additional heat sources above and below the SMA beams, as sketched in Figure 2. The spacer height in between the SMA beams of 3 mm enables sufficient thermal isolation. This has been verified by electrical resistance measurements of both beams, in which the electrical heating power correlates with the average temperature of the beams, as shown in the new Figure S1 in the Supplementary Information. Figure 7a presents the typical time-resolved switching performance of a bistable SMA actuator with spacer length s and pre-deflection h of 5 and 1 mm, respectively. The time-resolved displacement was determined using a laser displacement sensor. The heat sources were set to 160 °C using temperature sensors attached to the heat sources and closed-loop feedback control. In this case, an oscillatory snap-through motion of about 1 Hz occurred, reflecting the periodic heating and cooling of the two antagonistic SMA beams. The time constants required for heating τh and for switching between equilibrium positions τsw were determined to be 0.21 and 0.36 s, respectively.
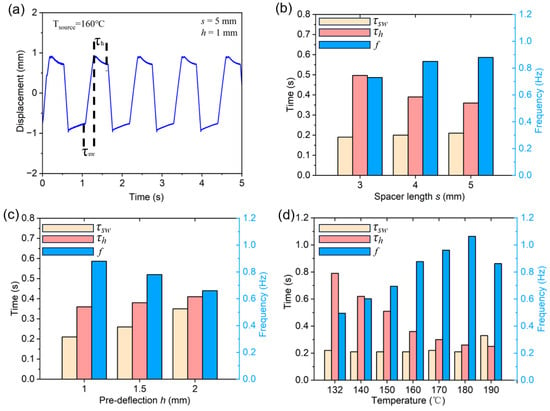
Figure 7.
(a) Typical time-resolved switching performance of a bistable SMA actuator with a spacer length s of 5 mm and pre-deflection h of 1 mm at a heat source temperature of 160 °C. (b) Switching time τsw, heating time τh, and frequency for different spacer lengths s at h = 1 mm. (c) Switching time τsw, heating time τh, and frequency for different pre-deflections h at s = 5 mm. (d) Switching time τsw, heating time τh, and frequency for different heat source temperatures at s = 5 mm and h = 1 mm.
The dynamic performance depended on the spacer length s, pre-deflection h, and heat source temperatures. When the spacer length s was increased from 3 to 5 mm, the switching time τsw remained almost unchanged, while the heating time τh decreased from 0.5 to 0.36 s, as shown in Figure 7b. The increasing spacer length resulted in a larger contact area between the SMA beam and the heat source, which allowed for enhanced heat transfer and, thus, reduced the time required for phase transformation from martensite to austenite. Therefore, the frequency of the oscillatory motion increased by about 20%. Figure 7c illustrates the time-resolved switching performance of the bistable actuator, when increasing the pre-deflection h from 1 to 2 mm at a spacer length s of 4 mm and temperature of heat source of 160 °C. As h increased from 1 to 2 mm, the switching time τsw increased from 0.21 to 0.35 s. The slight increase in heating time from 0.39 to 0.41 s was due to the change in beam length. The oscillation frequency decreased from 0.88 to 0.66 Hz, while the actuation stroke increased by a factor of 2. Despite the larger stroke, the switching speed of the SMA beams increased due to the larger net force Fn. The higher switching speed ensured that there was only a minor decrease in frequency. Figure 7d summarizes the effect of increasing the heat source temperature on the dynamic response of the bistable SMA actuator. When the heat source temperature increased from 132 to 180 °C, the switching time τsw remained almost constant, while the heating time decreased from 0.79 to 0.26 s. The higher temperature of the heat source enhanced the heat transfer between SMA beam and heat source, while the contact area and contact force remained about the same. The reduced heating time to induce the phase transformation caused an increase in the frequency of the oscillatory motion by about a factor of 2. The optimal temperature range is 160–180 °C. Below 160 °C, heating times increase substantially until no oscillation is observed below 132 °C. Above 180 °C, the oscillation frequency decreases again due to overheating caused by limited heat transfer. Consequently, continuous oscillation is lost above 190 °C.
6. Conclusions
We present the design, fabrication, and performance of miniature-scale bistable SMA actuators which consist of two antagonistically coupled buckling SMA beams. The SMA beams were fabricated by magnetron sputtering, lithography, and a dedicated heat treatment to set their memory shapes to adopt opposing buckling states. Coupling the SMA beams in their center leads to compact bistable actuators, which exhibit a bi-directional snap-through motion between two equilibrium positions by selectively heating the SMA beams.
The stationary performance of the actuators is strongly affected by the spacer length and pre-deflection of the SMA beams. The stationary force–displacement characteristics of monostable SMA actuators consisting of a single SMA beam with buckling memory shape reveal minimal shape recovery forces in an austenitic state FA(min) and maximal forces in a martensitic state FM(max), which pose important constraints on the design of bistable coupled SMA beam systems. Bistability is only achieved if the FA(min) of one SMA beam exceeds the FM(max) of the antagonistic SMA beam at any displacement to enable a snap-through motion in between the corresponding memory shapes. This result is confirmed by the stationary force–displacement characteristics of the bistable SMA actuators showing bistable switching in between two equilibrium positions only for spacer lengths up to 5 mm, where the net force of the coupled SMA beams stays positive throughout the displacement range. We demonstrate that this condition is no longer fulfilled at a larger spacer length of 6 mm, where the net force decreases to zero after a small displacement and, thus, the actuator cannot reach the second equilibrium position. Increasing the pre-deflection of the SMA beams from 1 to 2 mm gives rise to an enhanced actuation stroke by a factor of 2, while the bistable performance is retained. The presented bistable SMA actuator can be operated thermally through direct heat transfer at mechanical contact between the SMA beams and a heat source, which is an effective means to convert low-temperature waste heat below 200 °C into mechanical energy. We present dynamic measurements of thermally driven bistable SMA actuators operating at frequencies of up to 1.1 Hz and actuation strokes of up to 3.65 mm, corresponding to more than 30% of the SMA beam length. This performance provides an interesting route for the design of novel thermal bistable actuators that are driven by waste-heat at low-temperature differences.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/act12110422/s1, Figure S1: Normalized electrical resistance of the monostable SMA actuator determined under Joule heating conditions (yellow). For comparison, the normalized electrical resistance of the SMA film material was determined under ambient heating conditions (blue) in a thermostat. Normalization was performed using the expression (R − Rmin)/(Rmax − Rmin). Comparing both measurements indicates that an electrical power of >430 mW was required to increase the average temperature above Af temperature; Figure S2: The combined effects of spacer length s and pre-deflection h on the minimum and maximum forces of monostable SMA actuators in martensite (FM(min), FM(max)) (a) and austenite condition (FA(min), FA(max)) (b) as well as on the corresponding force difference FA(min) − FM(max). Both parameters s and h affect the forces in a similar way and, thus, both effects add up.
Author Contributions
X.C. designed, fabricated the bistable SMA actuator, performed the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the original draft. L.B. and E.Q. designed, fabricated, and optimized TiNiCu films. M.K. conceived the concept, designed the bistable SMA actuator, supervised the experiments, and wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
X.C. received financial support from the China Scholarship Council (CSC201908140104). L.B. and E.Q. acknowledge funding by the German Science Foundation (DFG) through project (413288478).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available, because they are used in ongoing research.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the expertise of Christof Megnin in interconnection technology.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Qiu, J.; Lang, J.H.; Slocum, A.H. A Curved-Beam Bistable Mechanism. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2004, 13, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorfmeister, M.; Schneider, M.; Schmid, U. Static and Dynamic Performance of Bistable MEMS Membranes. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 282, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.A.; Chen, J.H.; Pham, H.T. A Constant-Force Bistable Micromechanism. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 189, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.; Younis, M.I. Analytical Study of the Snap-Through and Bistability of Beams with Arbitrarily Initial Shape. J. Mech. Robot. 2020, 12, 041001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megnin, C.; Barth, J.; Kohl, M. A Bistable SMA Microvalve for 3/2-Way Control. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 188, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, M.; Seelecke, S.; Wallrabe, U. (Eds.) . Cooperative Microactuator Systems; MDPI: Basel, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Howell, L.L.; Rao, S.S.; Midha, A. Reliability-Based Optimal Design of a Bistable Compliant Mechanism. J. Mech. Design 1994, 116, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsay, J.; Su, L.Q.; Sung, C.K. Design of a Linear Micro-Feeding System Featuring Bistable Mechanisms. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2005, 15, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, B.; Schomburg, W.K. A Thermopneumatically Actuated Bistable Microvalve. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2010, 20, 095024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, M.; Saif, A. On a Tunable Bistable MEMS-Theory and Experiment. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2000, 9, 157. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, M.S.; Howell, L.L. On-Chip Actuation of an in-Plane Compliant Bistable Micromechanism. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2002, 11, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, N.D.; Howell, L.L. A Self-Retracting Fully Compliant Bistable Micromechanism. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2003, 12, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieri, F.; Piotto, M. A Micromachined Bistable 1 x 2 Switch for Optical Fibers. Microelectron. Eng. 2000, 53, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Shea, K. An Autonomous Programmable Actuator and Shape Reconfigurable Structures Using Bistability and Shape Memory Polymers. 3D Print Addit. Manuf. 2018, 5, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.Y.; Lee, E.; Ha, S.; Kim, N.; Jun, Y.C. Multistable Thermal Actuators Via Multimaterial 4D Printing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, A.F.; Van Gemmeren, V.; Anderson, A.J.; Weaver, P.M. Dynamics and Control of Twisting Bi-Stable Structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 025006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giddings, P.F.; Kim, H.A.; Salo, A.I.T.; Bowen, C.R. Modelling of Piezoelectrically Actuated Bistable Composites. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 1261–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouche, W.; Maurini, C.; Vidoli, S.; Vincenti, A. Multi-Parameter Actuation of a Neutrally Stable Shell: A Flexible Gear-Less Motor. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2017, 473, 20170364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Wei, S.; Jiang, X.; Holmes, D.P.; Ghosh, T.K. Bioinspired Electrically Activated Soft Bistable Actuators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1802999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukaides, E.G.; Smoukov, S.K.; Seffen, K.A. Magnetic Actuation and Transition Shapes of a Bistable Spherical Cap. Int. J. Smart Nano Mater. 2014, 5, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Liu, Y.; Wan, G.; Xu, Z.; Wen, C.; Yu, H.; Zhang, J.X.J.; Li, J.; Chen, Z. Magneto-Sensitive Bistable Soft Actuators: Experiments, Simulations, and Applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 221902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.; Khan, F.; Younis, M.I. A Monolithic Tunable Symmetric Bistable Mechanism. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 075033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.A.; Betts, D.N.; Salo, A.I.T.; Bowen, C.R. Shape Memory Alloy-Piezoelectric Active Structures for Reversible Actuation of Bistable Composites. AIAA J. 2010, 48, 1265–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, M. Shape Memory Microactuators; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; ISBN 3-540-20635-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kohl, M.; Ossmer, H.; Gueltig, M.; Megnin, C. SMA Foils for MEMS: From Material Properties to the Engineering of Microdevices. Shape Mem. Superelasticity 2018, 4, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzeh, A.; Paik, J. Robogami: A Fully Integrated Low-Profile Robotic Origami. J. Mech. Robot. 2015, 7, 021009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Bumke, L.; Quandt, E.; Kohl, M. A Thermal Energy Harvester Based on Bistable SMA Microactuation. In Proceedings of the ACTUATOR 2022, Mannheim, Germany, 29–30 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, H.; Bumke, L.; Chluba, C.; Quandt, E.; James, R.D. Phase Engineering and Supercompatibility of Shape Memory Alloys. Mater. Today 2018, 21, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miranda, R.L.; Zamponi, C.; Quandt, E. Micropatterned Freestanding Superelastic TiNi Films. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2013, 15, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).