Occurrence and Characteristics of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli from Dairy Cattle, Milk, and Farm Environments in Peninsular Malaysia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Sample Collection
4.2. Isolation and Identification of ESBL-Producing E. coli
4.3. Phenotypic Confirmation of ESBL-Producing E. coli
4.4. Genomic DNA Extraction
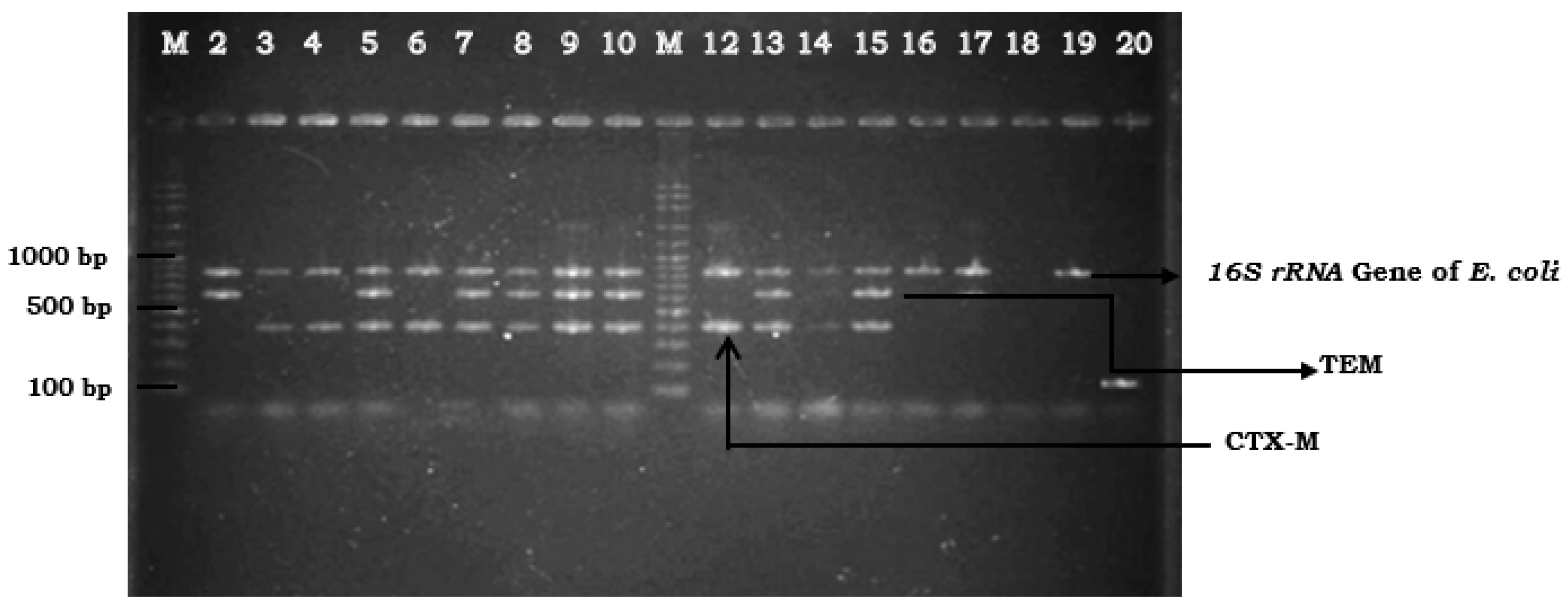
4.5. Genotypic Detection of ESBL Genes by mPCR
4.6. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Food Safety Authority. Technical specifications on the harmonised monitoring and reporting of antimicrobial resistance in Salmonella, Campylobacter and indicator Escherichia coli and Enterococcus spp. bacteria transmit-ted through food. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thu, W.P.; Sinwat, N.; Bitrus, A.A.; Angkittitrakul, S.; Prathan, R.; Chuanchuen, R. Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, virulence gene, and class 1 integrons of Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis from pigs, pork and humans in Thai-Laos border provinces. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 18, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilani, H.; Abbassi, M.S.; Ferjani, S.; Mansouri, R.; Sghaier, S.; Ben Salem, R.; Ben Chehida, N. Occurrence of blaCTX-M-1, qnrB1 and virulence genes in avian ESBL-producing Escherichia coli isolates from Tunisia. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, S.D.; Shang, X.F.; Wang, X.R.; Wang, L.; Yan, Z.T.; Li, H.S. Prevalence and characteristics of extended spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli from bovine mastitis cases in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 1246–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassuna, N.A.; Khairalla, A.S.; Farahat, E.M.; Hammad, A.M.; Abdel-Fattah, M. Molecular characterization of Extended-spectrum β lactamase-producing E. coli recovered from community-acquired urinary tract infections in Upper Egypt. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, L.; Sharp, H.; Hille, K.; Seibt, U.; Fischer, J.; Pfeifer, Y.; Friese, A. Subgrouping of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli from animal and human sources: An approach to quantify the distribution of ESBL types between different reservoirs. Int. J. Med Microbiol. 2014, 304, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitrus, A.A.; Chuanchuen, R.; Luangtongkum, T. Emergence of colistin resistance in extended-spectrum beta lactamase producing Enterobacteriaceae isolated from food animals and its public health implication: A review. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2018, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwoji, I.D.; Musa, J.A.; Daniel, N.; Mohzo, D.L.; Bitrus, A.A.; Ojo, A.A.; Ezema, K.U. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in chickens from small-scale (backyard) poultry farms in Maiduguri, Nigeria. Int. J. One Health 2019, 5, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitrus, A.A.; Mshelia, P.A.; Kwoji, I.D.; Goni, M.D.; Jajere, S.M. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase and ampicillin Class C beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli from food animals: A review. Int. J. One Health 2019, 5, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijazi, S.M.; Fawzi, M.A.; Ali, F.M.; Abd El Galil, K.H. Multidrug-resistant ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae and associated risk factors in community infants in Lebanon. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2016, 10, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.N.; Wang, J.; Ho, H.; Wang, Y.T.; Huang, S.N.; Han, R.W. Prevalence and antimicrobial-resistance phenotypes and genotypes of Escherichia coli isolated from raw milk samples from mastitis cases in four regions of China. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 22, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, J.F.; Moulin, G.; Page, S.W.; Pastoret, P.P. Antimicrobial resistance in animal and public health: Introduction and classification of antimicrobial agents. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2012, 31, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, A.; Hörmansdorfer, S.; Messelhäusser, U.; Käsbohrer, A.; Sauter-Louis, C.; Mansfeld, R. Prevalence of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli on Bavarian dairy and beef cattle farms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 3027–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, E.; Jeckel, S.; Snow, L.; Stubbs, R.; Teale, C.; Wearing, H.; Coldham, N. Epidemiology of extended spectrum beta-lactamase E. coli (CTX-M-15) on a commercial dairy farm. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 154, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.; Amoureux, L.; Locatelli, A.; Depret, G.; Jolivet, C.; Gueneau, E.; Neuwirth, C. Occurrence of CTX-M producing Escherichia coli in soils, cattle, and farm environment in France (Burgundy region). Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamang, M.D.; Nam, H.M.; Kim, S.R.; Chae, M.H.; Jang, G.C.; Jung, S.C.; Lim, S.K. Prevalence and molecular characterization of CTX-M β-lactamase–producing Escherichia coli isolated from healthy swine and cattle. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A. Animal reservoirs for extended spectrum β-lactamase producers. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 14, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.A.; Randall, L.P.; Snary, E.L.; Cockrem, H.; Lotz, S.; Wearing, H.; La Ragione, R.M. Fecal carriage and shedding density of CTX-M extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in cattle, chickens, and pigs: Implications for environmental contamination and food production. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3715–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroi, M.; Matsui, S.; Kubo, R.; Iida, N.; Noda, Y.; Kanda, T.; Ohashi, N. Factors for occurrence of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in broilers. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2012, 74, 1635–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zheng, H.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Q.; Deng, Y.; Liu, J.H. Prevalence and characterisation of CTX-M β-lactamases amongst Escherichia coli isolates from healthy food animals in China. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2012, 39, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Rösler, U.; Riese, A.; Baumann, M.; Zhao, J.; Wei, H.; Kreusukon, K. First findings on the prevalence of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases producing Escherichia coli (ESBL-producing E. coli) and risk factors in dairy farms in Beijing area, China. In Proceedings of the 10th Year Anniversary of Veterinary Public Health Centre for Asia Pacific, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 3–6 July 2013; pp. 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- Reist, M.; Geser, N.; Hächler, H.; Schärrer, S.; Stephan, R. ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae: Occurrence, risk factors for faecal carriage and strain traits in the Swiss slaughter cattle population younger than 2 years sampled at abattoir level. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouini, A.; Vinué, L.; Slama, K.B.; Saenz, Y.; Klibi, N.; Hammami, S.; Torres, C. Characterization of CTX-M and SHV extended-spectrum β-lactamases and associated resistance genes in Escherichia coli strains of food samples in Tunisia. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 60, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geser, N.; Stephan, R.; Hächler, H. Occurrence and characteristics of extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) producing Enterobacteriaceae in food producing animals, minced meat and raw milk. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, S.P.; Jayarao, B.M.; Almeida, R.A. Foodborne pathogens in milk and the dairy farm environment: Food safety and public health implications. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2005, 2, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.S.; Balan, G.; Puthucheary, S.; Kong, B.H.; Lim, K.T.; Tan, L.K.; Thong, K.L. Prevalence and characterization of multidrug-resistant and extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli from paediatric wards of a Malaysian hospital. Microb. Drug Resist. 2012, 18, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.T.; Yasin, R.; Yeo, C.C.; Puthucheary, S.; Thong, K.L. Characterization of multidrug resistant ESBL-producing Escherichia coli isolates from hospitals in Malaysia. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallensten, A.; Hernandez, J.; Ardiles, K.; Gonzalez-Acuna, D.; Drobni, M.; Olsen, B. Extended spectrum beta-lactamases detected in Escherichia coli from gulls in Stockholm, Sweden. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2011, 1, 7030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofte, D.; Maciuca, I.E.; Evans, N.J.; Williams, H.; Wattret, A.; Fick, J.C.; Williams, N.J. Detection and molecular characterization of Escherichia coli CTX-M-15 and Klebsiella pneumoniae SHV-12 β-lactamases from bovine mastitis isolates in the United Kingdom. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissera, S.; Lee, S.M. Isolation of extended spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) producing bacteria from urban surface waters in Malaysia. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 20, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Geng, S.N.; Li, T.Y.; Ye, Z.M.; Zhang, D.S.; Zhou, H.W. High diversity of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing bacteria in an urban river sediment habitat. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 5972–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, S.; Ewers, C.; Wieler, L.H. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases producing E. coli in wildlife, yet another form of environmental pollution. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyles, C.; Boerlin, P. Horizontally transferred genetic elements and their role in pathogenesis of bacterial disease. Vet. Pathol. 2014, 51, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Qu, Y.; Hu, D.; Shi, Y.X. Comparison of extended spectrum β-lactamases-producing Escherichia coli with non-ESBLs-producing E. coli: Drug-resistance and virulence. World J. Emerg. Med. 2012, 3, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wayne, P. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing: Twentieth informational supplement. CLSI document M100-S20. Clin. Lab. Stand. Inst. 2010. Available online: https://clsi.org/media/1469/m100s27_sample.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2020).
| Farms | No. of Samples Collected | Sample Type | No. of Positive ESBL-Producing E. coli (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faecal Samples n = 229 | Farm Environment n = 77 | Milk n = 71 | |||
| 1 | 38 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 (2.6) |
| 2 | 42 | 0 | 1 | - | 1 (2.4) |
| 3 | 44 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 3 (6.8) |
| 4 | 44 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 7 (15.9) |
| 5 | 26 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 (7.7) |
| 6 | 44 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 (0) |
| 7 | 28 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 (3.6) |
| 8 | 35 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 (0) |
| 9 | 39 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 (7.7) |
| 10 | 37 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 (0) |
| TOTAL | 377 | 1 (0.27%) | 5 (1.32%) | 12 (3.18%) | 18 (4.8) |
| Sample Type | No. of Samples Collected | No. of Positive ESBL-Producing E. coli (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Floor, feed, and water trough swabs | 20 | 0 (0) |
| Drinking water | 16 | 3 (18.6) |
| Source of drinking water | 10 | 1 (10) |
| Feed | 17 | 0 (0) |
| House flies (Musca domestica) | 14 | 1 (7.1) |
| TOTAL | 77 | 5 (6.5) |
| Farms | Sample ID (18 Isolates) | Sample Type | ESBL Genotype | Genetic Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F1M3 | Milk | TEM | I |
| 2 | F2WS | Source of drinking water | CTX-M | II |
| 3 | F2M8 | Milk | CTX-M | II |
| F3DW1 | Drinking water | TEM, CTX-M | III | |
| F3DW2 | Drinking water | CTX-M | II | |
| 4 | F4M1 | Milk | Not detected | IV |
| F4M3 | Milk | TEM, CTX-M | III | |
| F4M4 | Milk | TEM, CTX-M | III | |
| F4M5 | Milk | TEM, CTX-M | III | |
| F4M6 | Milk | TEM, CTX-M | III | |
| F4M7 | Milk | CTX-M | II | |
| F4M4 | Faeces | TEM, CTX-M | III | |
| 5 | F5M4 | Milk | Not detected | IV |
| F5Hf 2 | House flies | Not detected | IV | |
| 7 | F7DW2 | Drinking water | TEM, CTX-M | III |
| 9 | F7M5 | Milk | TEM, CTX-M | III |
| F9M7 | Milk | Not detected | IV | |
| F9M8 | Milk | TEM | I |
| Gene | Primer Sequence (5′–3′ Direction) | Product Size (bp) | Gene Accession No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| TEM | Forward—TCCTTGAGAGTTTTCGCCCC Reverse—TGACTCCCCGTCGTGTAGAT | 643 | EU352903 |
| SHV | Forward—CAATCACGACGGCGGAATCT Reverse—GTGGGTCATGTCGGTACCAT | 168 | AB731686 |
| CTX-M | Forward—AAGCACGTCAATGGGACGAT Reverse—GTTGGTGGTGCCATAGCCA | 402 | JN411912 |
| OXA | Forward—TTGCACTTGATAGTGGTGTGA Reverse—AGTGAGTTGTCAAGCCAAAAAGT | 250 | JN003412 |
| E. coli | Forward—TGACGTTACCCGCAGAAGAA Reverse—CTCCAATCCGGACTACGACG | 832 | X80724 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kamaruzzaman, E.A.; Abdul Aziz, S.; Bitrus, A.A.; Zakaria, Z.; Hassan, L. Occurrence and Characteristics of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli from Dairy Cattle, Milk, and Farm Environments in Peninsular Malaysia. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9121007
Kamaruzzaman EA, Abdul Aziz S, Bitrus AA, Zakaria Z, Hassan L. Occurrence and Characteristics of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli from Dairy Cattle, Milk, and Farm Environments in Peninsular Malaysia. Pathogens. 2020; 9(12):1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9121007
Chicago/Turabian StyleKamaruzzaman, Emelia Aini, Saleha Abdul Aziz, Asinamai Athliamai Bitrus, Zunita Zakaria, and Latiffah Hassan. 2020. "Occurrence and Characteristics of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli from Dairy Cattle, Milk, and Farm Environments in Peninsular Malaysia" Pathogens 9, no. 12: 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9121007
APA StyleKamaruzzaman, E. A., Abdul Aziz, S., Bitrus, A. A., Zakaria, Z., & Hassan, L. (2020). Occurrence and Characteristics of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli from Dairy Cattle, Milk, and Farm Environments in Peninsular Malaysia. Pathogens, 9(12), 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9121007





