Effect of Non-Concentrated and Concentrated Vaporized Hydrogen Peroxide on Scrapie Prions
Abstract
1. Introduction
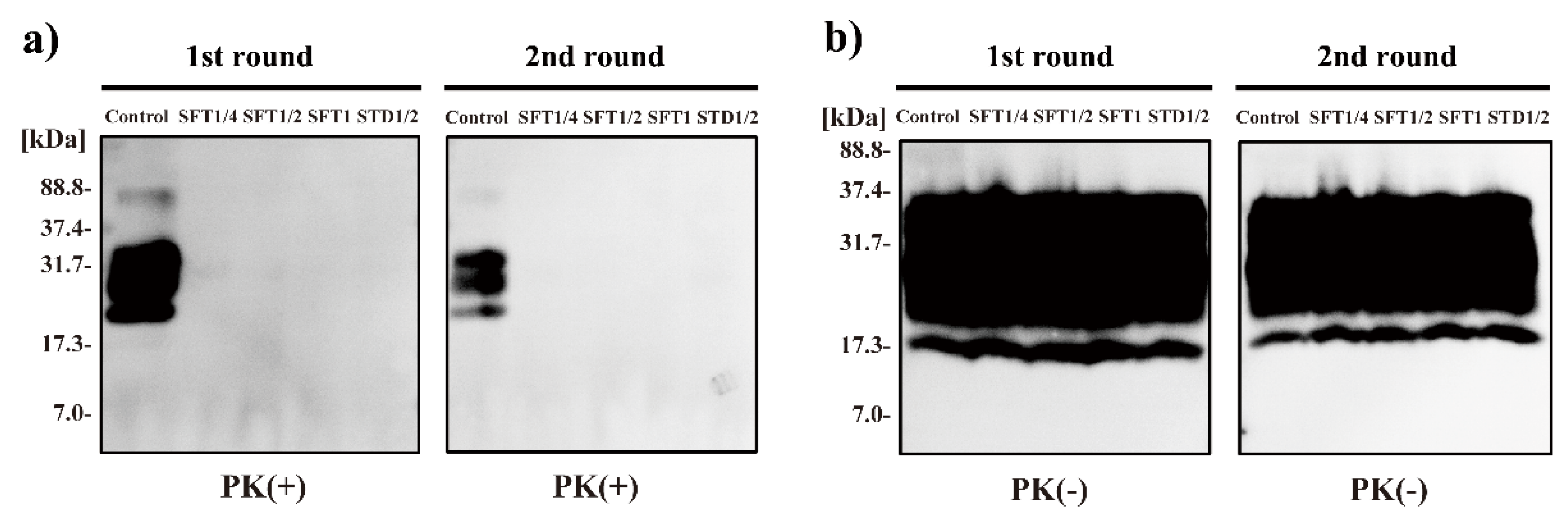
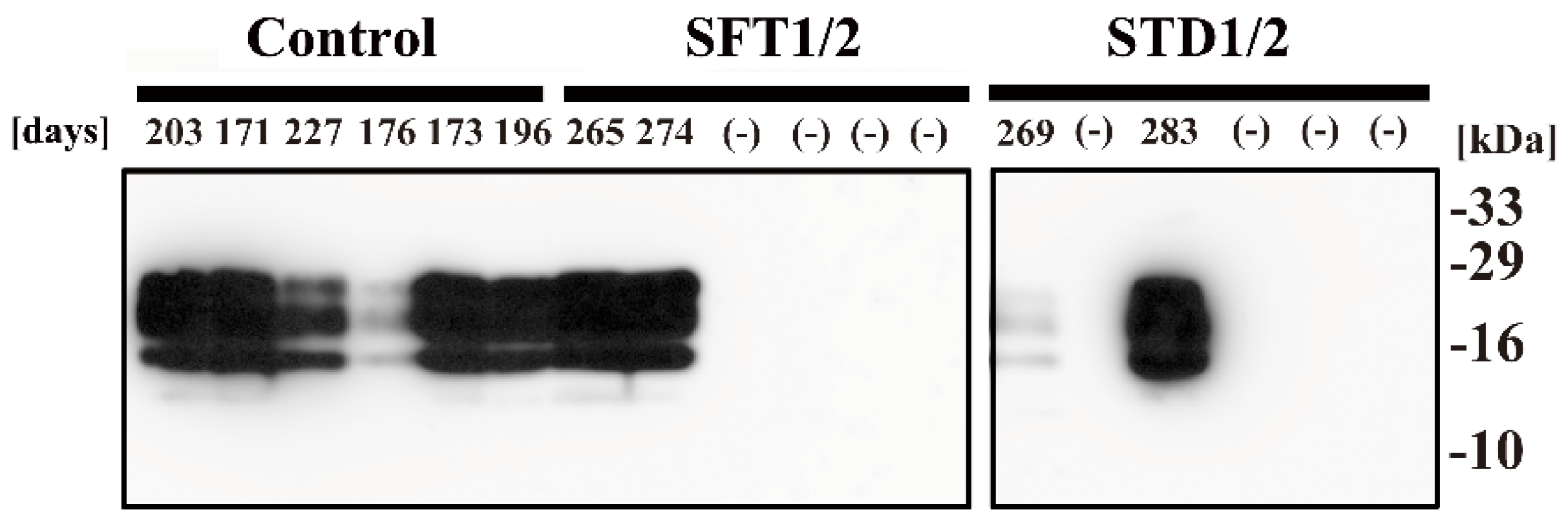
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Mouse Brain Homogenate
4.2. ES-700 Treatment of Prions
4.3. Prion Inoculation
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Protein Misfolding Cyclic Amplification
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prusiner, S.B. Prions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13363–13383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prusiner, S.B. Molecular biology of prion diseases. Science 1991, 252, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakudo, A.; Ikuta, K. Fundamentals of prion diseases and their involvement in the loss of function of cellular prion protein. Protein Pept. Lett. 2009, 16, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakudo, A.; Ikuta, K. Prion protein functions and dysfunction in prion diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorini, M.; Bongianni, M.; Monaco, S.; Zanusso, G. Biochemical characterization of prions. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 150, 389–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, K.M.; Baldwin, M.; Nguyen, J.; Gasset, M.; Serban, A.; Groth, D.; Mehlhorn, I.; Huang, Z.; Fletterick, R.J.; Cohen, F.E.; et al. Conversion of alpha-helices into beta-sheets features in the formation of the scrapie prion proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 10962–10966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, F.E.; Prusiner, S.B. Pathologic conformations of prion proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 793–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla, J.; Saa, P.; Morales, R.; Abid, K.; Maundrell, K.; Soto, C. Protein misfolding cyclic amplification for diagnosis and prion propagation studies. Methods Enzym. 2006, 412, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, C.; Saborio, G.P.; Anderes, L. Cyclic amplification of protein misfolding: Application to prion-related disorders and beyond. Trends Neurosci. 2002, 25, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla, J.; Saa, P.; Hetz, C.; Soto, C. In vitro generation of infectious scrapie prions. Cell 2005, 121, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritzkow, S.; Wagenfuhr, K.; Daus, M.L.; Boerner, S.; Lemmer, K.; Thomzig, A.; Mielke, M.; Beekes, M. Quantitative detection and biological propagation of scrapie seeding activity in vitro facilitate use of prions as model pathogens for disinfection. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belondrade, M.; Nicot, S.; Beringue, V.; Coste, J.; Lehmann, S.; Bougard, D. Rapid and highly sensitive detection of variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease abnormal prion protein on steel surfaces by protein misfolding cyclic amplification: Application to prion decontamination studies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belondrade, M.; Jas-Duval, C.; Nicot, S.; Bruyere-Ostells, L.; Mayran, C.; Herzog, L.; Reine, F.; Torres, J.M.; Fournier-Wirth, C.; Beringue, V.; et al. Correlation between bioassay and protein misfolding cyclic amplification for variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease decontamination studies. mSphere 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakudo, A. Inactivation methods for prions. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2020, 36, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakudo, A.; Ano, Y.; Onodera, T.; Nitta, K.; Shintani, H.; Ikuta, K.; Tanaka, Y. Fundamentals of prions and their inactivation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 27, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutala, W.A.; Weber, D.J. Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America. Guideline for disinfection and sterilization of prion-contaminated medical instruments. Infect Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2010, 31, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, P.T.; Lin, S.M. Hydrogen Peroxide Plasma Sterilization System. U.S. Patent 4,756,882, 27 January 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Krebs, M.C.; Bécasse, P.; Verjat, D.; Darbord, J.C. Gas plasma sterilization: Relative efficacy of the hydrogen peroxide phase compared with that of the plasma phase. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 160, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakudo, A.; Shintani, H. Nova Medical: Sterilization and Disinfection by Plasma: Sterilization Mechanisms, Biological and Medical Applications (Medical Devices and Equipment); Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shintani, H. Is SteradR from J&J is truly plasma gas sterilizer? Pharm. Reg. Aff. 2013, 3, e124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eveland, R.W. Disinfection and Sterilization with Hydrogen Peroxide. In Block’s Disinfection, Sterilization, and Preservation, 6th ed.; McDonnell, G., Hansen, J., Eds.; Wolters Kluwer: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 671–683. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Department of Transportation. Packaging Your Dangerous Goods. Available online: https://www.faa.gov/hazmat/safecargo/how_to_ship/package_for_shipping/ (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- Bentley, K.; Dove, B.K.; Parks, S.R.; Walker, J.T.; Bennett, A.M. Hydrogen peroxide vapour decontamination of surfaces artificially contaminated with norovirus surrogate feline calicivirus. J. Hosp. Infect. 2012, 80, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckert, R.A.; Best, M.; Jordan, L.T.; Dulac, G.C.; Eddington, D.L.; Sterritt, W.G. Efficacy of vaporized hydrogen peroxide against exotic animal viruses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 3916–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrie, E.; Andrews, L.; Yezli, S.; Otter, J.A. Hydrogen peroxide vapour (HPV) inactivation of adenovirus. Lett. Appl. Microbiol 2011, 52, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otter, J.A.; Budde-Niekiel, A. Hydrogen peroxide vapor: A novel method for the environmental control of lactococcal bacteriophages. J. Food. Prot. 2009, 72, 412–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottage, T.; Richardson, C.; Parks, S.; Walker, J.T.; Bennett, A.M. Evaluation of hydrogen peroxide gaseous disinfection systems to decontaminate viruses. J. Hosp. Infect. 2010, 74, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, S.M.; Chander, Y.; Yezli, S.; Otter, J.A. Evaluating the virucidal efficacy of hydrogen peroxide vapour. J. Hosp. Infect. 2014, 86, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichet, G.; Antloga, K.; Comoy, E.; Deslys, J.P.; McDonnell, G. Prion inactivation using a new gaseous hydrogen peroxide sterilisation process. J. Hosp. Infect. 2007, 67, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichet, G.; Comoy, E.; Duval, C.; Antloga, K.; Dehen, C.; Charbonnier, A.; McDonnell, G.; Brown, P.; Lasmezas, C.I.; Deslys, J.P. Novel methods for disinfection of prion-contaminated medical devices. Lancet 2004, 364, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEvoy, B.; Rowan, N.J. Terminal sterilization of medical devices using vaporized hydrogen peroxide: A review of current methods and emerging opportunities. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 1403–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, H.; Taylor, D.; Dickinson, J.; Walker, J.T.; Perrett, D.; Raven, N.D.; Sutton, J.M. Surface decontamination of surgical instruments: An ongoing dilemma. J. Hosp. Infect. 2006, 63, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merritt, K.; Hitchins, V.M.; Brown, S.A. Safety and cleaning of medical materials and devices. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 53, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.M.; Fernie, K.; Steele, P.J.; McConnell, I.; Somerville, R.A. Thermostability of mouse-passaged BSE and scrapie is independent of host PrP genotype: Implications for the nature of the causal agents. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 3199–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, M.W.; Ironside, J.W. Review: Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: Prion protein type, disease phenotype and agent strain. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2012, 38, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parchi, P.; Saverioni, D. Molecular pathology, classification, and diagnosis of sporadic human prion disease variants. Folia Neuropathol. 2012, 50, 20–45. [Google Scholar]
- Parchi, P.; Cescatti, M.; Notari, S.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J.; Capellari, S.; Giese, A.; Zou, W.Q.; Kretzschmar, H.; Ghetti, B.; Brown, P. Agent strain variation in human prion disease: Insights from a molecular and pathological review of the National Institutes of Health series of experimentally transmitted disease. Brain 2010, 133, 3030–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, M.T.; Will, R.G.; Manson, J.C. Defining sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease strains and their transmission properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12005–12010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moda, F.; Suardi, S.; Di Fede, G.; Indaco, A.; Limido, L.; Vimercati, C.; Ruggerone, M.; Campagnani, I.; Langeveld, J.; Terruzzi, A.; et al. MM2-thalamic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: Neuropathological, biochemical and transmission studies identify a distinctive prion strain. Brain Pathol. 2012, 22, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fichet, G.; Comoy, E.; Dehen, C.; Challier, L.; Antloga, K.; Deslys, J.P.; McDonnell, G. Investigations of a prion infectivity assay to evaluate methods of decontamination. J. Microbiol. Methods 2007, 70, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattison, I.H. The relative susceptibility of sheep, goats and mice to two types of the goat scrapie agent. Res. Vet. Sci. 1966, 7, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusiner, S.B.; Cochran, S.P.; Groth, D.F.; Downey, D.E.; Bowman, K.A.; Martinez, H.M. Measurement of the scrapie agent using an incubation time interval assay. Ann. Neurol. 1982, 11, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipscomb, I.P.; Pinchin, H.; Collin, R.; Keevil, C.W. Effect of drying time, ambient temperature and pre-soaks on prion-infected tissue contamination levels on surgical stainless steel: Concerns over prolonged transportation of instruments from theatre to central sterile service departments. J. Hosp. Infect. 2007, 65, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canon Lifecare Solutions Inc. Low-Temperature Sterilization: Hydrogen Peroxide Gas Sterilizer ES-700. Available online: https://lifecare.medical.canon/overseas/product/es-700.html (accessed on 19 October 2020).
- Sakudo, A.; Iwamaru, Y.; Furusaki, K.; Haritani, M.; Onishi, R.; Imamura, M.; Yokoyama, T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Onodera, T. Inactivation of scrapie prions by the electrically charged disinfectant CAC-717. Pathogens 2020, 9, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakudo, A.; Imanishi, Y.; Hirata, A.; Koga, Y.; Shintani, H. Effect of nitrogen gas plasma generated by a fast-pulsed power supply using a static induction thyristor on scrapie prion. Pathogens 2020, 9, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

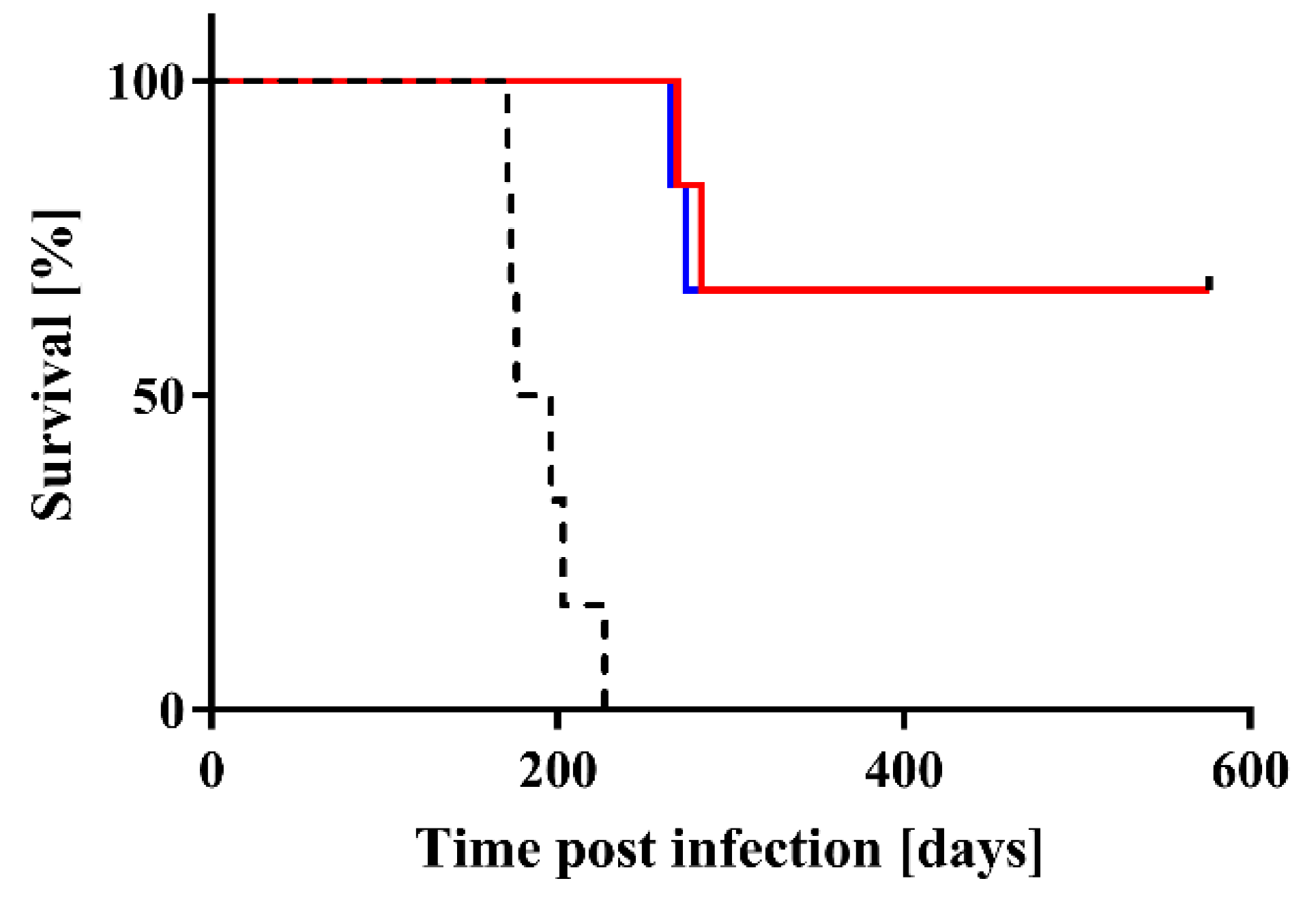
| Treatment | Mean Incubation Time ± SEM 1 | N/N02 |
|---|---|---|
| Control 3 | 191.0 ± 9.0 days | 6/6 |
| SFT1/2 | >265 days 4 | 2/6 |
| STD1/2 | >269 days 5 | 2/6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sakudo, A.; Yamashiro, R.; Harata, C. Effect of Non-Concentrated and Concentrated Vaporized Hydrogen Peroxide on Scrapie Prions. Pathogens 2020, 9, 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9110947
Sakudo A, Yamashiro R, Harata C. Effect of Non-Concentrated and Concentrated Vaporized Hydrogen Peroxide on Scrapie Prions. Pathogens. 2020; 9(11):947. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9110947
Chicago/Turabian StyleSakudo, Akikazu, Risa Yamashiro, and Chihiro Harata. 2020. "Effect of Non-Concentrated and Concentrated Vaporized Hydrogen Peroxide on Scrapie Prions" Pathogens 9, no. 11: 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9110947
APA StyleSakudo, A., Yamashiro, R., & Harata, C. (2020). Effect of Non-Concentrated and Concentrated Vaporized Hydrogen Peroxide on Scrapie Prions. Pathogens, 9(11), 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9110947





