Development and Validation of a Rapid Turbidimetric Assay to Determine the Potency of Cefuroxime Sodium in Powder for Dissolution for Injection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
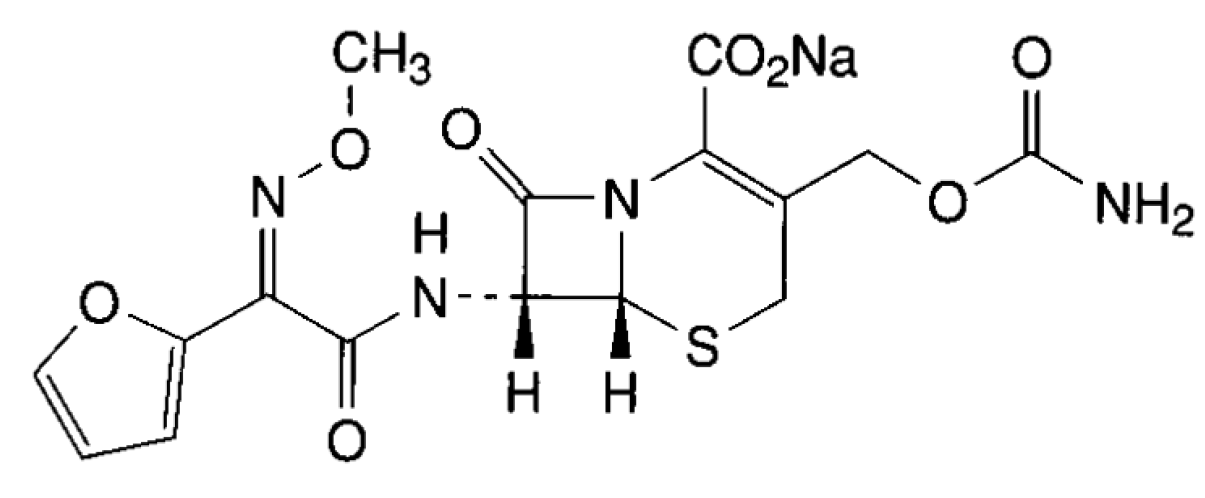
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Solutions
2.4. Turbidimetric Assay
2.5. Method Validation
2.5.1. Linearity
2.5.2. Precision
2.5.3. Accuracy
2.5.4. Robustness
2.6. HPLC Method
2.7. Comparison of Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Validation of the Analytical Method
3.1.1. Linearity

3.1.2. Precision
3.1.3. Accuracy
| Added Cefuroxime Reference Standard (µg/mL) | Cefuroxime Reference Standarda Found (µg/mL) | Recovery (%) | Average Recovery (%) ± RSD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 4.5 | 4.58 | 101.77 | 100.21 ± 0.41 |
| R2 | 24.5 | 24.01 | 98.00 | |
| R3 | 44.5 | 44.89 | 100.87 |
3.1.4. Robustness
| Variable | Range Investigated | Cefuroxime Content (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| incubation time of the inoculum | 18 h | 99.39 | 0.49 |
| 24 h | 100.56 | 0.46 | |
| volume culture medium | 10 mL | 99.39 | 0.49 |
| 12 mL | 100.52 | 0.42 |
3.2. Comparison of Methods

| Method | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameters | HPLC | Turbidimetric |
| Average cefuroxime content (%) | 99.84 ± 0.24 | 99.37 ± 0.47 |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kessler, R.E.; Bies, M.; Chisbolm, D.R.; Pursiano, T.A.; Tsai, Y.H.; Misiek, M. Comparison of a new cephalosporin, BMY 28142, with other broad-spectrum β-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1985, 27, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunton, L.; Chabner, B.; Knollman, B. Goodman and Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics; McGraw-Hill Book Co.: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, M.P.; Nakahiro, R.K.; Chin, A.; Bedikian, A.; Gill, M.A. Cefepime: A new fourth-generation cephalosporin. Am. J. Hosp. Pharm. 1994, 51, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, A.; Andrasi, M.; Kardos, S. Application of capillary zone electrophoresis to the analysis and to a stability study of cephalosporins. J. Chromatogr. B 2002, 775, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefnawy, M.; EL-Shabrawy, Y.; Belal, F. Spectrofluorometric determination of alpha-aminocephalosporins in biological fluids and pharmaceutical preparations. J. Biomed. Anal. 1999, 21, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivaska, A.; Nordstrom, F. Determination of some cephalosporins by differential pulse polarography and linear scan voltammetry. Anal. Chim. Acta 1983, 146, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, A.H.; Salgado, H.R.N. Spectrophotometric determination of ceftazidime in pharmaceutical preparations using neocuproin as a complexing agent. Anal Lett. 2008, 41, 2143–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, A.H.; Salgado, H.R.N. Development and validation of HPLC method for determination of ceftazidime. J AOAC Int. 2008, 91, 739–743. [Google Scholar]
- Mrestani, Y. Application of capillary zone electrophoresis in cephalosporin analysis. J. Chromatogr. B. 1997, 690, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.H.; Askal, H. Colourimetric and AAS determination of cephalosporins using Reineck’s salt. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 29, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, H.R.N.; Lopes, C.C.G.O. Determination of gatifloxacin in bulk and tablet preparations by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. AOAC Int. 2006, 89, 642–645. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schulman, S.G. Determination of cephalothin sodium by a chemiluminescence method. Anal. Chim. Acta 1991, 255, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.J.; Rolim, C.M.B.; Melo, J.; Souza, P.S.; Bergold, A.M. Development of a microbiological assay to determine the potency of ceftiofur sodium powder. J. AOAC Int. 2007, 90, 1724–1728. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tozo, G.C.G.; Salgado, H.R.N. Determination of lomefloxacin in raw material and tablet preparations by liquid chromatography. J. AOAC Int. 2006, 89, 1305–1308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lourenço, F.R.; Barbosa, A.; Pinto, T.J.A. Microbiological Assay for Apramycin Soluble Powder. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2011, 30, 554–557. [Google Scholar]
- Barot, T.G.; Patidar, K.; Kshartri, N.; Vyas, N. Development and validation of LC method for the determination of ampicillin and dicloxacillin in pharmaceutical formulation using an experimental design. E-J. Chem. 2009, 6, 955–964. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Z.; Liu, Y. Simultaneous content determination of ampicillin and cloxacillin for injection by HPLC. Heilongjiang Yiyao 2009, 22, 442–443. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Hu, C. Determination of related substances in ampicillin sodium and sulbactam sodium for injection by RP-HPLC gradient elution method. Chin. J. Antibiot. 2009, 34, 158–162. [Google Scholar]
- Cione, A.P.P.; Liberale, M.J.; Silva, P.M. Development and validation of analytical method for determination of an association of ampicillins in lyophilized powder for injection by HPLC. Quim. Nova 2010, 33, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.J.M.C.L.; Farias, T.A.L.; Filho, J.A.R.; Francelino, L.; Oliveira, E.J.A. Validation of a high-performance liquid chromatography method for determination of injectable sodium ampicillin used at public hospitals in Recife, Brasil. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2010, 29, 72–78. [Google Scholar]
- Rambla-Alegre, M.; Martí-Centelles, R.; Esteve-Romero, J.; Carda-Broch, S. Application of a liquid chromatographic procedure for the analysis of penicillin antibiotics in biological fluids and pharmaceutical formulations using sodium dodecyl sulphate/propanol mobile phases and direct injection. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 4972–4981. [Google Scholar]
- Ganjali, M.R.; Faridbod, F.; Saboury, A.A.; Norouzi, P. Pico-level monitoring of ampicillin by using a novel cerium fluorescence probe. Anal. Lett. 2010, 43, 2193–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavendra, G.P.A.; Suryanarayana, R.V. Spectrophotometric method for the determination of ampicillin and amoxicillin. J. Pharm. Res. 2010, 3, 869–872. [Google Scholar]
- Kurian, T.; Kurien, J. Simultaneous multicomponent spectrophotometric analysis of ampicillin and probenecid in pharmaceutical formulation by derivative spectroscopy, Hygeia. J. Drugs Med. 2011, 3, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Tótoli, E.G.; Salgado, H.R.N. Development and validation of the quantitative analysis of ampicillin sodium in powder for injection by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). Phys. Chem. 2012, 2, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorouraddin, M.H.; Iranifam, M.; Imani-Nabiyyi, A. Study of the enhancement of a new chemiluminescence reaction and its application to determination of b-lactam antibiotics. Luminescence. 2009, 24, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, A.H.; Salgado, H.R.N. Microbiological assay for ceftiazidime injection. J. AOAC Int. 2007, 90, 1379–1382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vieira, D.C.M.; Ricarte, P.C.; Salgado, H.R.N. Validation of Microbiological Assay for Determination of Cefuroxime in Injectable Preparations. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2012, 31, 746–750. [Google Scholar]
- The United States Pharmacopoeia; United States Pharmacopoeial Convention, Inc.: Rockville, MD, USA, 2014.
- Vieira, D.C.M.; Salgado, H.R.N. Comparison of HPLC and UV Spectrophotometric Methods for the Determination of Cefuroxime Sodium in Pharmaceutical Products. J. Chromat. Sci. 2011, 49, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazilian Pharmacopeia, 5th ed.; ANVISA, fundação Osvaldo Cruz: Brasília, Brazil, 2010; pp. 75–87, 261–269.
- Brazil, Ministério da Saúde. Resolução RDC no. 899, de 29 de maio de 2003. Approves the guide for validation of analytical and bioanalytical methods. Diário Oficial da União : Brasília, DF, 2 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Validation of Analytical Procedures. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Harmonization, Text and Methodology Q2 (R1), Geneva, Switzerland, 1 March 2005.
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Official Methods of Analysis, 17th ed.; AOAC: Gaithesburg, MD, USA, 2002; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- British Pharmacopoeia; The Stationary Office: London, UK, 2010; Volume 155–163, pp. 2373–2375.
- European Pharmacopoeia, 7th ed.; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2011; pp. 1393–1399.
- Hewitt, W. Microbiological Assay for Pharmaceutical Analysis: A Rational Approach; Interpharm/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Vieira, D.C.M.; Fiuza, T.F.M.; Salgado, H.R.N. Development and Validation of a Rapid Turbidimetric Assay to Determine the Potency of Cefuroxime Sodium in Powder for Dissolution for Injection. Pathogens 2014, 3, 656-666. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens3030656
Vieira DCM, Fiuza TFM, Salgado HRN. Development and Validation of a Rapid Turbidimetric Assay to Determine the Potency of Cefuroxime Sodium in Powder for Dissolution for Injection. Pathogens. 2014; 3(3):656-666. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens3030656
Chicago/Turabian StyleVieira, Daniela C. M., Thalita F. M. Fiuza, and Hérida R.N. Salgado. 2014. "Development and Validation of a Rapid Turbidimetric Assay to Determine the Potency of Cefuroxime Sodium in Powder for Dissolution for Injection" Pathogens 3, no. 3: 656-666. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens3030656
APA StyleVieira, D. C. M., Fiuza, T. F. M., & Salgado, H. R. N. (2014). Development and Validation of a Rapid Turbidimetric Assay to Determine the Potency of Cefuroxime Sodium in Powder for Dissolution for Injection. Pathogens, 3(3), 656-666. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens3030656




