Newly Discovered Rustrela Virus: Current State of Knowledge About the Etiological Agent of Feline “Staggering Disease”
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Etiology of “Staggering Disease”
3. The Origin of Rustrela Virus
3.1. Discovery of Novel Rubiviruses
3.2. General Taxonomy of the Matonaviridae Family
| Realm | Kingdom | Phylum | Class | Order | Family | Genus | Species | Virus Name | Abbrev. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Riboviria | Orthornavirae | Kitrinoviricota | Alsuviricetes | Hepelivirales | Matonaviridae | Rubivirus | Rubivirus rubellae | Rubella virus | RuV |
| Rubivirus strelense | Rustrela virus | RusV | |||||||
| Rubivirus ruteetense | Ruhugu virus | RuhV |
3.3. Host Range and Geographical Distribution of Rustrela Virus
3.4. Potential Reservoirs and Transmission Pathways of Rustrela Virus
3.5. Clinical and Histopathology Features of Rustrela Virus Infection
3.6. Diagnostic Techniques and Challenges for Rustrela Virus Infection
4. Genomic Structure and Sequence Characteristics of Rustrela Virus
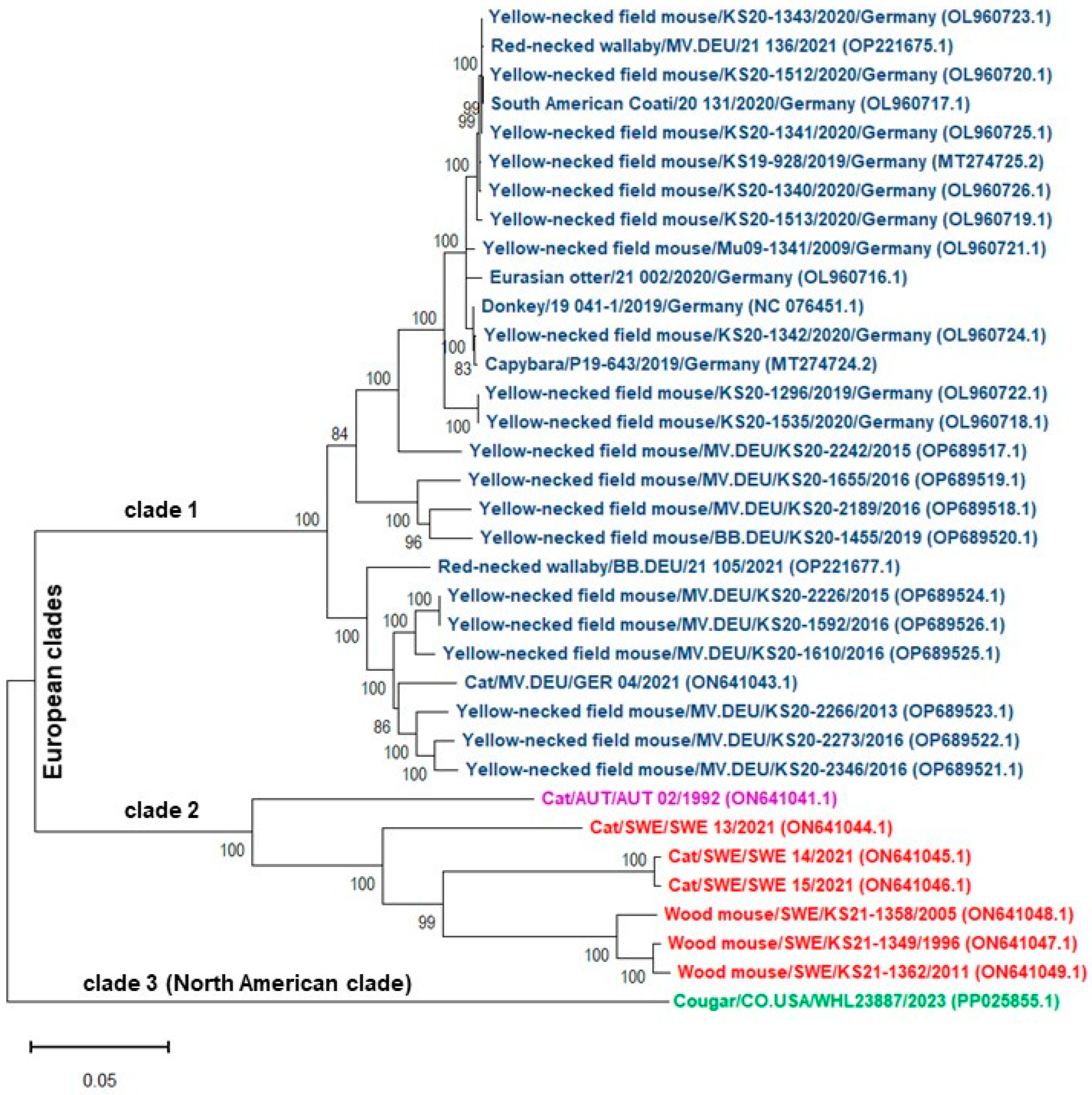
5. Phylogenetic Analysis
6. Potential for Zoonotic Transmission of Rustrela Virus
Comparison of RusV’s Zoonotic Risk with Other Emerging Neurotropic Viruses
7. Future Directions for the Field
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RusV | Rustrela virus |
| SD | Staggering disease |
| RuV | Rubella virus |
| RuhV | Ruhugu virus |
| BoDV | Borna disease virus |
| FFPE | Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded |
| ICTV | International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses |
| ORF | Open reading frame |
| nsPP | Non-structural polyprotein |
| sPP | Structural polyprotein |
| RdRP | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase |
| E1 | Envelope glycoprotein 1 |
| E2 | Envelope glycoprotein 2 |
| C | Capsid protein |
| HTS | High-throughput sequencing |
| VNT | Virus neutralization test |
References
- Kronevi, T.; Nordström, M.; Moreno, W.; Nilsson, P.O. Feline ataxia due to nonsuppurative meningoencephalomyelitis of unknown aetiology. Nord. Vet. Med. 1974, 26, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matiasek, K.; Pfaff, F.; Weissenböck, H.; Wylezich, C.; Kolodziejek, J.; Tengstrand, S.; Ecke, F.; Nippert, S.; Starcky, P.; Litz, B.; et al. Mystery of fatal ‘staggering disease’ unravelled: Novel rustrela virus causes severe meningoencephalomyelitis in domestic cats. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thilén, E.; Rubbenstroth, D.; Tengstrand, S.; Pfaff, F.; Wensman, J.J.; Ley, C. Evidence of rustrela virus-associated feline staggering disease in Sweden since the 1970s. Acta Vet. Scand. 2024, 66, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, V.; Weidinger, P.; Matt, J.; Weissenbacher-Lang, C.; Nowotny, N.; Weissenböck, H. Rustrela Virus-Associated Encephalomyelitis (‘Staggering Disease’) in Cats from Eastern Austria, 1994–2016. Viruses 2023, 15, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowotny, N.; Weissenböck, H. Description of feline nonsuppurative meningoencephalomyelitis (“staggering disease”) and studies of its etiology. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 1668–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissenböck, H.; Nowotny, N.; Zoher, J. Feline Meningoencephalomyelitis (“staggering disease”) in Österreich. Wien. Tierärztl. Mschr. 1994, 81, 195–201. [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren, A.L.; Zimmermann, W.; Bode, L.; Czech, G.; Gosztonyi, G.; Lindberg, R.; Ludwig, H. Staggering disease in cats: Isolation and characterization of the feline Borna disease virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1995, 76, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, A.J.; Paskey, A.C.; Ebinger, A.; Pfaff, F.; Priemer, G.; Höper, D.; Breithaupt, A.; Heuser, E.; Ulrich, R.G.; Kuhn, J.H.; et al. Relatives of rubella virus in diverse mammals. Nature 2020, 586, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Le Roi, M.; Puff, C.; Wohlsein, P.; Pfaff, F.; Beer, M.; Baumgärtner, W.; Rubbenstroth, D. Rustrela virus as putative cause of nonsuppurative meningoencephalitis in lions. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaff, F.; Breithaupt, A.; Rubbenstroth, D.; Nippert, S.; Baumbach, C.; Gerst, S.; Langner, C.; Wylezich, C.; Ebinger, A.; Höper, D.; et al. Revisiting Rustrela Virus: New Cases of Encephalitis and a Solution to the Capsid Enigma. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 10, e0010322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, A.; Schlieben, P.; Gerst, S.; Wylezich, C.; Pfaff, F.; Langner, C.; Niesler, M.; Schad, P.; Beer, M.; Rubbenstroth, D.; et al. Rustrela virus infection—An emerging neuropathogen of red-necked wallabies (Macropus rufogriseus). Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 4016–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nippert, S.; Rubbenstroth, D.; Geers, J.A.; Ebinger, A.; Hoffmann, D.; Breithaupt, A.; Wylezich, C.; Wang, X.; Haring, V.C.; Starcky, P.; et al. Continuous presence of genetically diverse rustrela virus lineages in yellow-necked field mouse reservoir populations in northeastern Germany. Virus Evol. 2023, 9, vead048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoff, E.J.; Vandevelde, M. Non-suppurative encephalomyelitis in cats suggestive of a viral origin. Vet. Pathol. 1981, 18, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niller, H.H.; Angstwurm, K.; Rubbenstroth, D.; Schlottau, K.; Ebinger, A.; Günther, S.; Wunderlich, S.; Banas, B.; Forth, L.F.; Hoffmann, D.; et al. Zoonotic spillover infections with Borna disease virus 1 leading to fatal human encephalitis, 1999–2019: An epidemiological investigation. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, A.L.; Johannisson, A.; Zimmermann, W.; Bode, L.; Rozell, B.; Muluneh, A.; Lindberg, R.; Ludwig, H. Neurological disease and encephalitis in cats experimentally infected with Borna disease virus. Acta Neuropathol. 1997, 93, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wensman, J.J.; Berg, M.; Berg, A.L. Experiences of Borna disease virus infection in Sweden. APMIS Suppl. 2008, 124, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wensman, J.J.; Jäderlund, K.H.; Gustavsson, M.H.; Hansson-Hamlin, H.; Karlstam, E.; Lilliehöök, I.; Oström, I.L.; Belák, S.; Berg, M.; Holst, B.S. Markers of Borna disease virus infection in cats with staggering disease. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2012, 14, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wensman, J.J.; Jäderlund, K.H.; Holst, B.S.; Berg, M. Borna disease virus infection in cats. Vet. J. 2014, 201, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankertz, A.; Chen, M.H.; Goldberg, T.L.; Hübschen, J.M.; Pfaff, F.; Ulrich, R.G.; Ictv Report Consortium. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Matonaviridae 2022. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, A.K.; Moss, W.J. Rubella. Lancet 2022, 399, 1336–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Holmes, E.C. Meta-transcriptomics and the evolutionary biology of RNA viruses. Virus Res. 2018, 243, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoghegan, J.L.; Di Giallonardo, F.; Wille, M.; Ortiz-Baez, A.S.; Costa, V.A.; Ghaly, T.; Mifsud, J.C.O.; Turnbull, O.M.H.; Bellwood, D.R.; Williamson, J.E.; et al. Virome composition in marine fish revealed by meta-transcriptomics. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veab005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimwood, R.M.; Holmes, E.C.; Geoghegan, J.L. A novel rubi-like virus in the Pacific electric ray (Tetronarce californica) reveals the complex evolutionary history of the Matonaviridae. Viruses 2021, 13, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). Available online: https://ictv.global/taxonomy (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Fox, K.A.; Breithaupt, A.; Beer, M.; Rubbenstroth, D.; Pfaff, F. Rustrela Virus in Wild Mountain Lion (Puma concolor) with Staggering Disease, Colorado, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 1664–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staggering Disease Discovered in Colorado Mountain Lion. News Release, 15 August 2024. American Veterinary Medical Association. Available online: https://www.avma.org/news/staggering-disease-discovered-colorado-mountain-lion (accessed on 26 April 2025).
- Wang, F.; Flanagan, J.; Su, N.; Wang, L.-C.; Bui, S.; Nielson, A.; Wu, X.; Vo, H.-T.; Ma, X.-J.; Luo, Y. RNAscope: A novel in situ RNA analysis platform for formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues. J. Mol. Diagn. 2012, 14, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Q.Q.; Yang, R.; Shi, J.F.; Zeng, N.Y.; Liang, D.Y.; Sha, S.; Chang, Q. Effect of preservation time of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues on extractable DNA and RNA quantity. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060520931259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, J.R.; Enns, E.; Marinier, E.; Mandal, A.; Herman, E.K.; Chen, C.; Graham, M.; Van Domselaar, G.; Stothard, P. Proksee: In-depth characterization and visualization of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W484–W492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.K.; Kielian, M. The Enigmatic Capsid Protein of an Encephalitic Rubivirus. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e02294-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA 11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Molecular Evolution and Phylogenetics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Dubé, M.; Etienne, L.; Fels, M.; Kielian, M. Calcium-Dependent Rubella Virus Fusion Occurs in Early Endosomes. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 6303–6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufloo, J.; Andreu-Moreno, I.; Moreno-García, J.; Valero-Rello, A.; Sanjuán, R. Receptor-binding proteins from animal viruses are broadly compatible with human cell entry factors. Nat. Microbiol. 2025, 10, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pörtner, K.; Wilking, H.; Frank, C.; Böhmer, M.M.; Stark, K.; Tappe, D. Risk factors for Borna disease virus 1 encephalitis in Germany-a case-control study. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, e2174778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, A.; Mahapatra, S.; Ray, S.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Islam, M.J.; Garai, S.; Dutta, T.K.; Chattaraj, M.; Chattaraj, S. The rising threat of Nipah virus: A highly contagious and deadly zoonotic pathogen. Virol. J. 2025, 22, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branda, F.; Ceccarelli, G.; Giovanetti, M.; Albanese, M.; Binetti, E.; Ciccozzi, M.; Scarpa, F. Nipah Virus: A Zoonotic Threat Re-Emerging in the Wake of Global Public Health Challenges. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camp, J.V.; Nowotny, N.; Aberle, S.W.; Redlberger-Fritz, M. Retrospective Screening for Zoonotic Viruses in Encephalitis Cases in Austria, 2019-2023, Reveals Infection with Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus but Not with Rustrela Virus or Tahyna Virus. Viruses 2025, 17, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11030–11035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuckerkandl, E.; Pauling, L. Evolutionary divergence and convergence in proteins. In Evolving Genes and Proteins; Bryson, V., Vogel, H.J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1965; pp. 97–166. [Google Scholar]

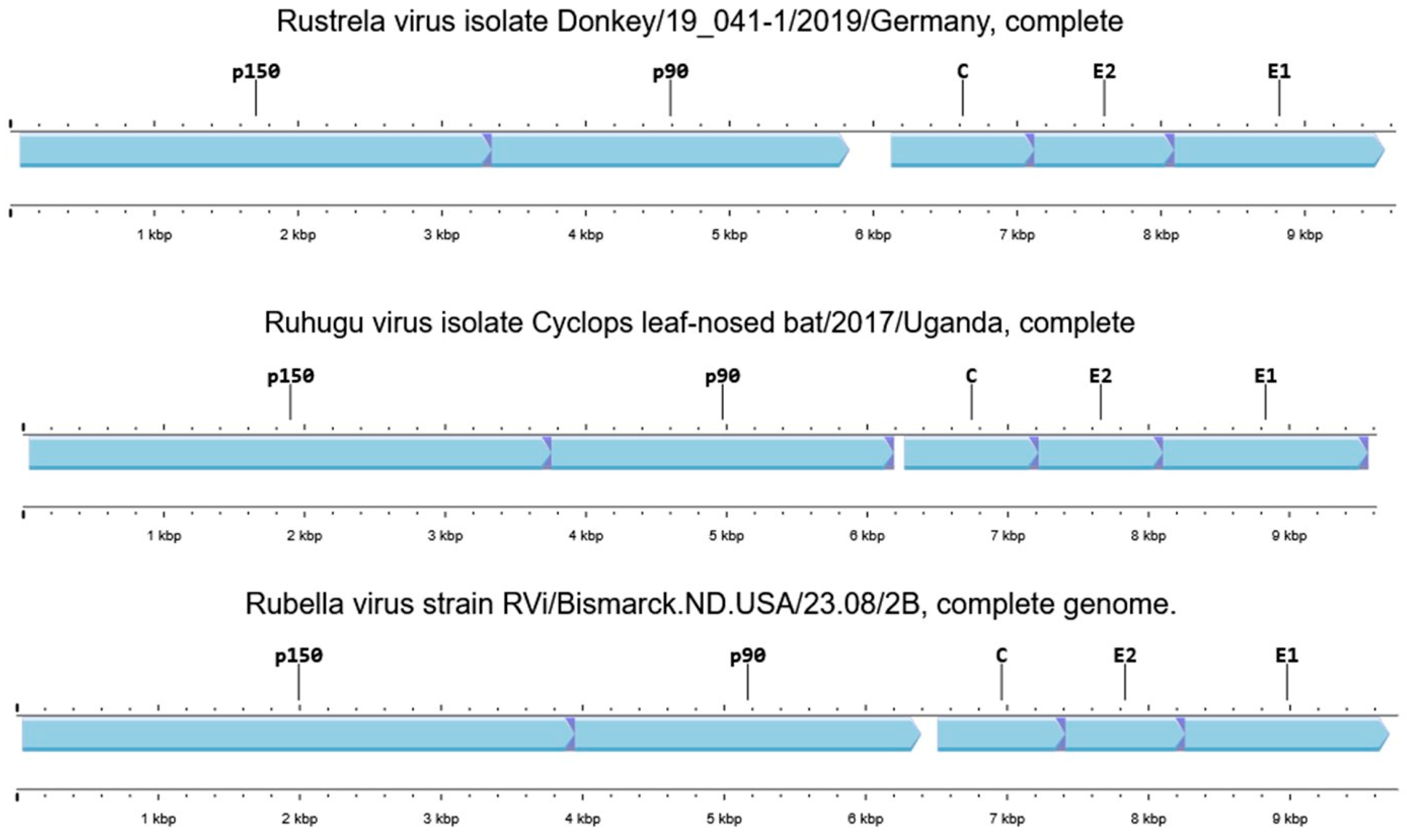
| Comparable Fragment of the Genome | Nucleotide Sequence | Amino Acid Sequence | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identity | Gaps | Identity | Similarity | Gaps | ||
| All isolates * | C | 760/1033 (73.6%) | 71/1033 (6.9%) | 273/333 (82.0%) | 288/333 (86.5%) | 1/333 (0.3%) |
| E1 | 1100/1497 (73.5%) | 57/1497 (3.8%) | 393/487 (80.7%) | 434/487 (89.1%) | 0/487 (0.0%) | |
| E2 | 698/1038 (67.2%) | 135/1038 (13.0%) | 220/324 (67.9%) | 256/324 (79.0%) | 1/324 (0.3%) | |
| p90 | 1930/2535 (76.1%) | 84/2535 (3.3%) | 729/842 (86.6%) | 768/842 (91.2%) | 24/842 (2.9%) | |
| p150 | 2373/3464 (68.5%) | 463/3464 (13.4%) | 765/1107 (69.1%) | 835/1107 (75.4%) | 59/1107 (5.3%) | |
| Clad 1 * | C | 921/996 (92.5%) | 0/996 (0.0%) | 328/332 (98.8%) | 328/332 (98.8%) | 0/332 (0.0%) |
| E1 | 1359/1464 (92.8%) | 0/1464 (0.0%) | 479/487 (98.4%) | 481/487 (98.8%) | 0/487 (0.0%) | |
| E2 | 888/972 (91.4%) | 0/972 (0.0%) | 316/324 (97.5%) | 319/324 (98.5%) | 0/324 (0.0%) | |
| p90 | 2295/2484 (92.4%) | 0/2484 (0.0%) | 812/828 (98.1%) | 817/828 (98.7%) | 0/828 (0.0%) | |
| p150 | 2999/3286 (91.3%) | 14/3286 (0.4%) | 1021/1093 (93.4%) | 1030/1093 (94.2%) | 0/1093 (0.0%) | |
| Clad 2 * | C | 824/1001 (82.3%) | 7/1001 (0.7%) | 314/333 (94.3%) | 318/333 (95.5%) | 1/333 (0.3%) |
| E1 | 1212/1474 (82.2%) | 11/1474 (0.7%) | 464/490 (94.7%) | 474/490 (96.7%) | 3/490 (0.6%) | |
| E2 | 790/1040 (76.0%) | 76/1040 (7.3%) | 289/324 (89.2%) | 307/324 (94.8%) | 0/324 (0.0%) | |
| p90 | 2116/2489 (85.0%) | 10/2489 (0.4%) | 791/828 (95.5%) | 806/828 (97.3%) | 0/828 (0.0%) | |
| p150 | 2642/3320 (79.6%) | 148/3320 (4.5%) | 922/1086 (84.9%) | 952/1086 (87.7%) | 8/1086 (0.7%) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Słońska, A.; Stefańska, I.; Kwiecień, E.; Chrobak-Chmiel, D. Newly Discovered Rustrela Virus: Current State of Knowledge About the Etiological Agent of Feline “Staggering Disease”. Pathogens 2025, 14, 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090851
Słońska A, Stefańska I, Kwiecień E, Chrobak-Chmiel D. Newly Discovered Rustrela Virus: Current State of Knowledge About the Etiological Agent of Feline “Staggering Disease”. Pathogens. 2025; 14(9):851. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090851
Chicago/Turabian StyleSłońska, Anna, Ilona Stefańska, Ewelina Kwiecień, and Dorota Chrobak-Chmiel. 2025. "Newly Discovered Rustrela Virus: Current State of Knowledge About the Etiological Agent of Feline “Staggering Disease”" Pathogens 14, no. 9: 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090851
APA StyleSłońska, A., Stefańska, I., Kwiecień, E., & Chrobak-Chmiel, D. (2025). Newly Discovered Rustrela Virus: Current State of Knowledge About the Etiological Agent of Feline “Staggering Disease”. Pathogens, 14(9), 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090851






