Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Children in Hangzhou (2022–2023)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Laboratory Assay
2.2.1. Nucleic Acid Extraction and Amplification
2.2.2. Capillary Electrophoresis
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
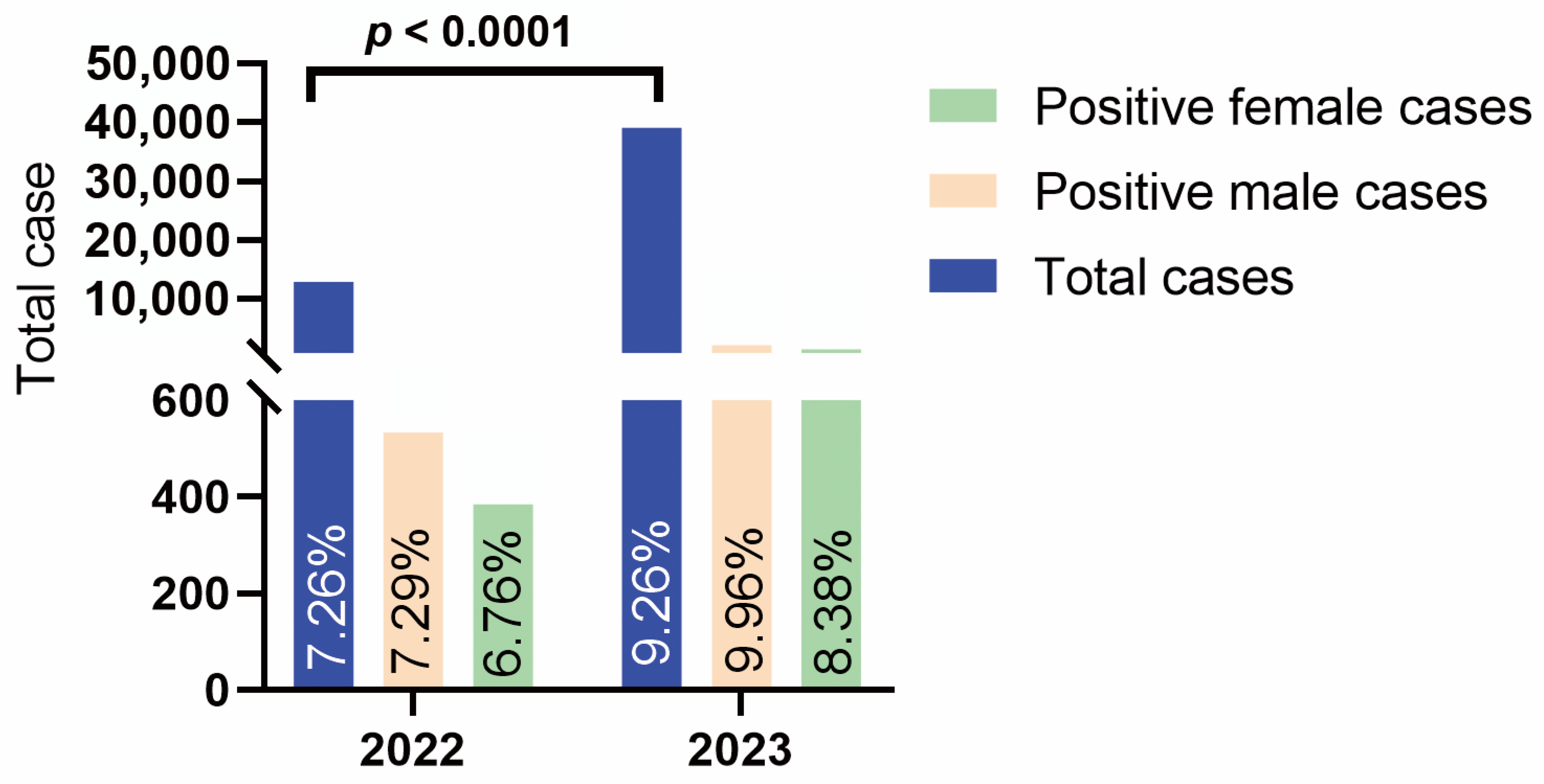
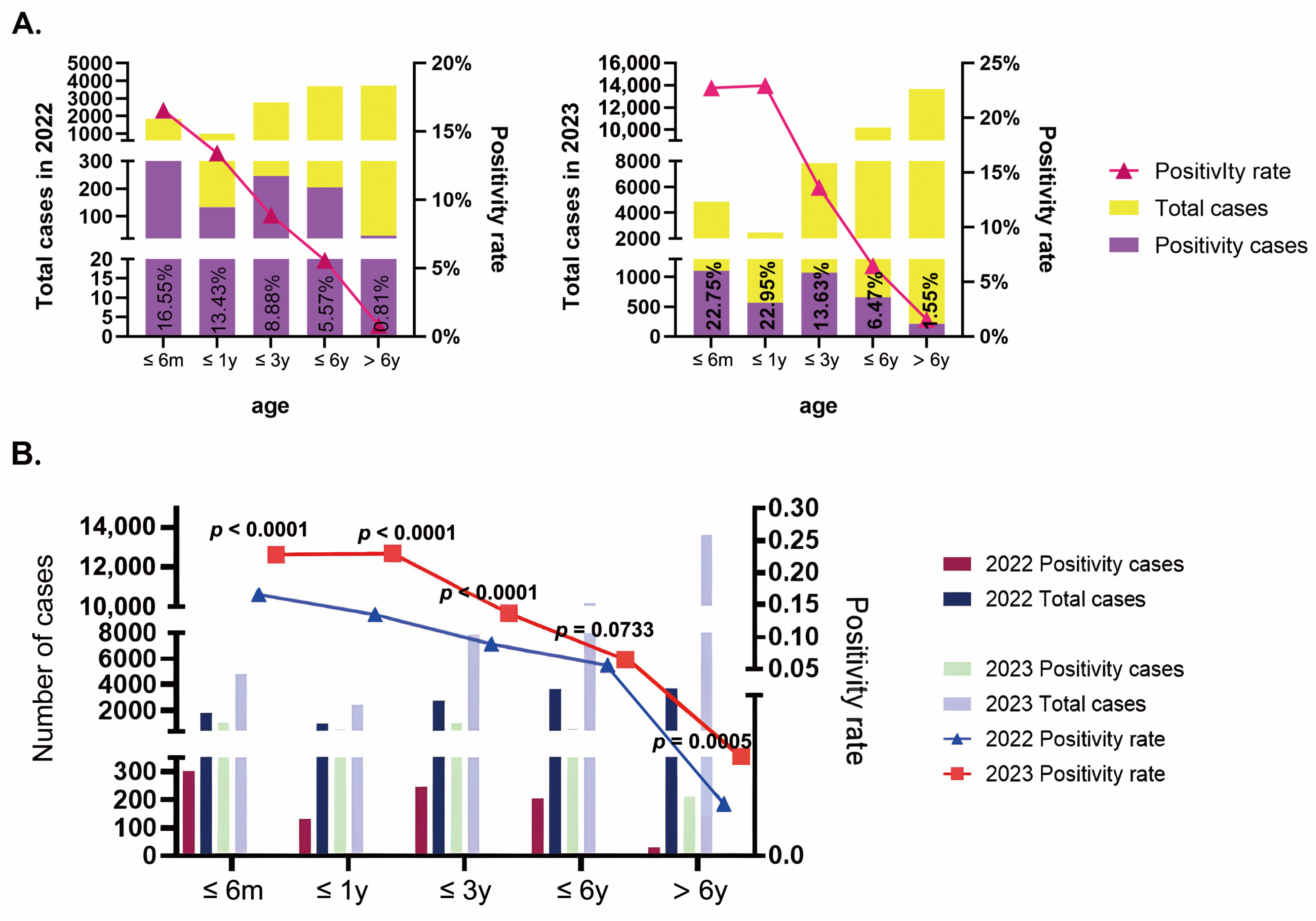
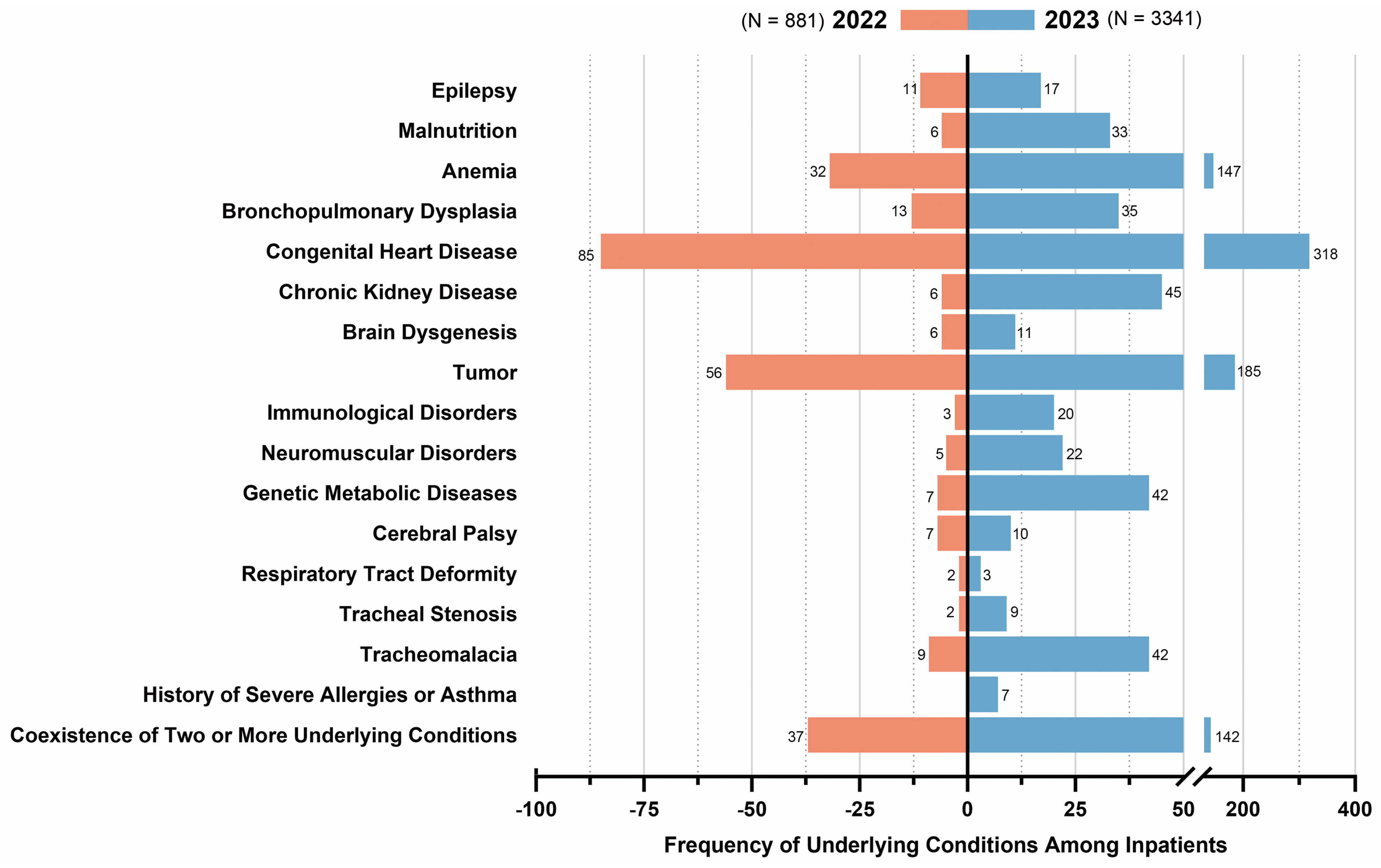
3.1. Epidemiology Characteristics
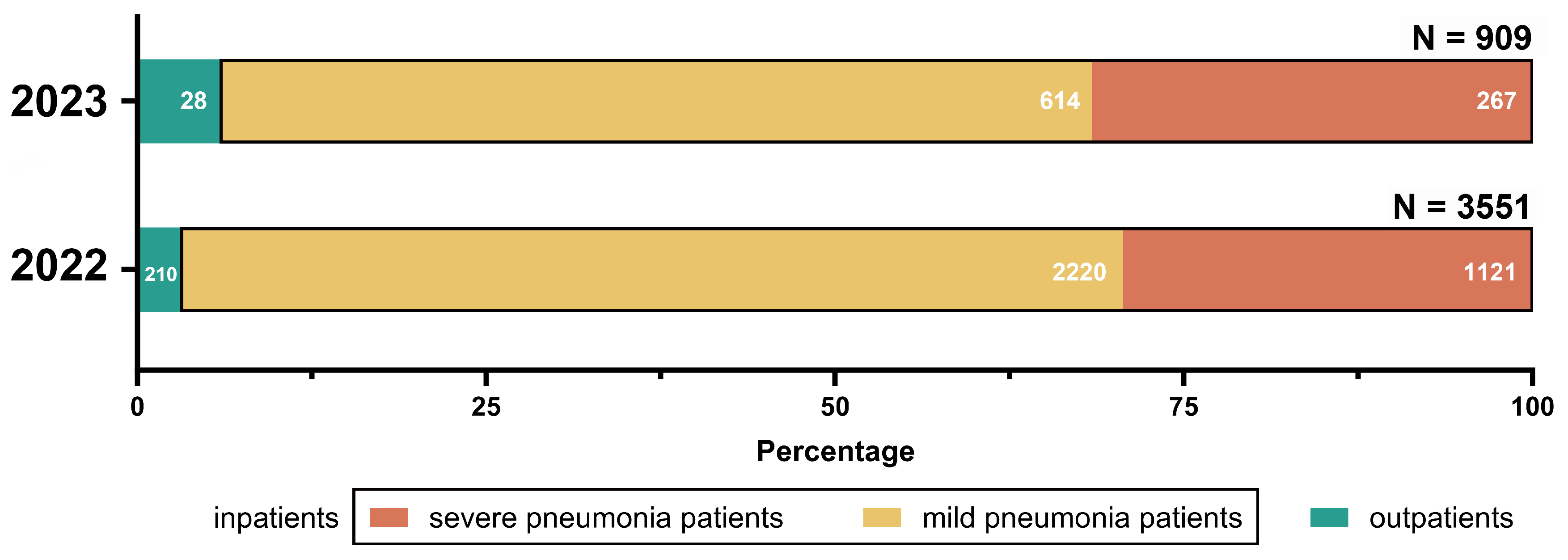
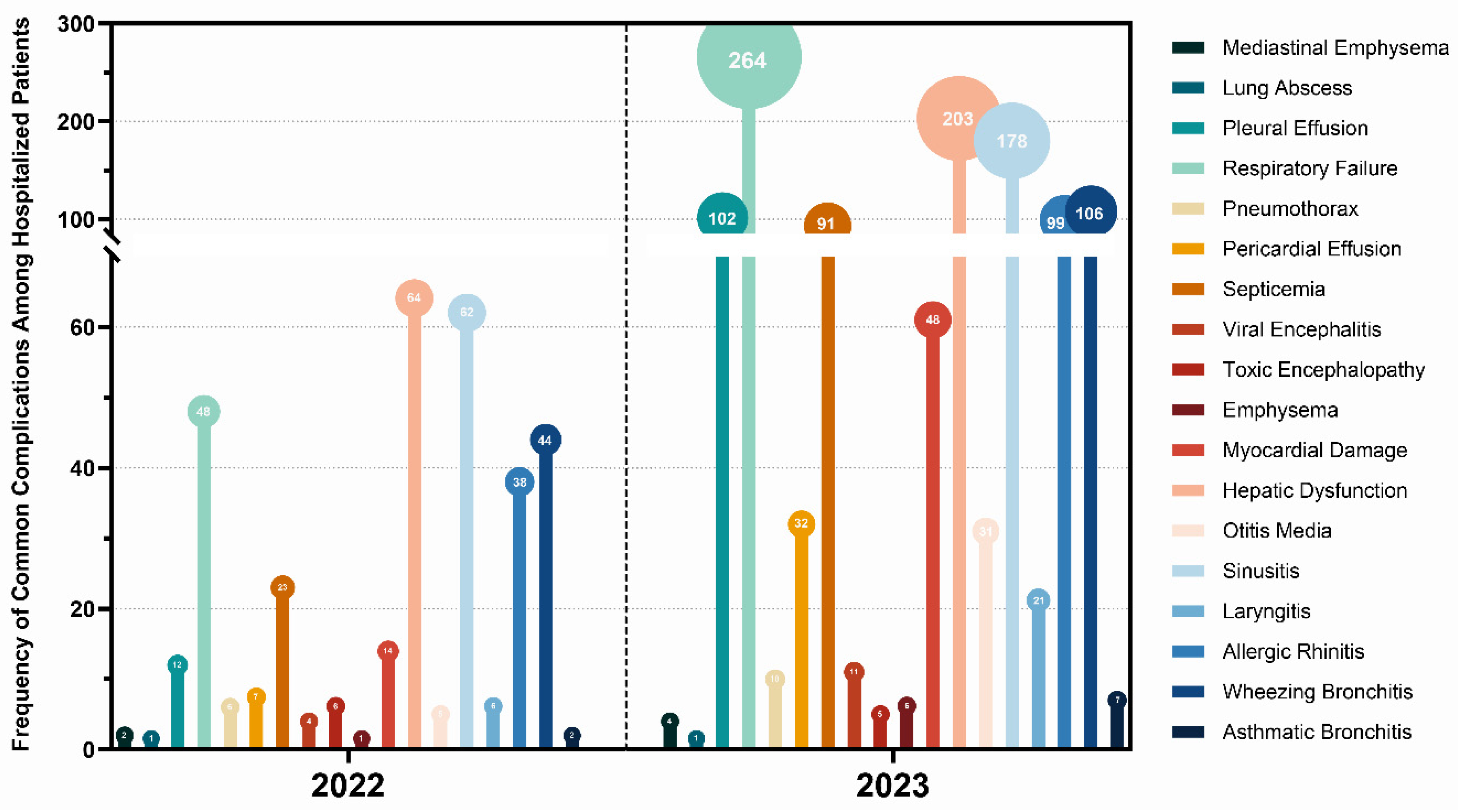
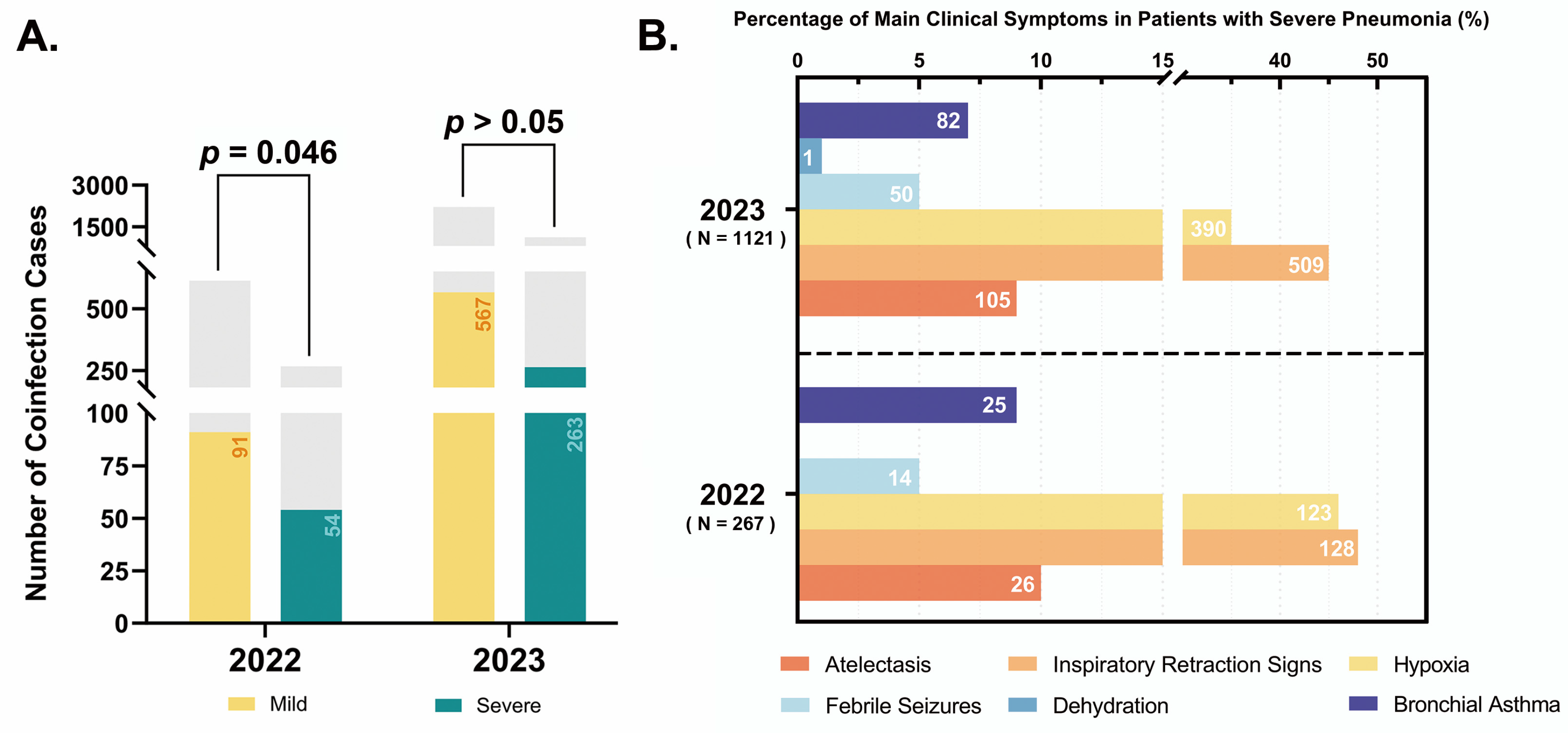
3.2. Clinical Characteristics
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, J.; Shi, M.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.; Li, A.; Wu, S.Y.; Chiang, C.M.; Zhang, Y. The matrix protein of respiratory syncytial virus suppresses interferon signaling via RACK1 association. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0074723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blount, R.E., Jr.; Morris, J.A.; Savage, R.E. Recovery of cytopathogenic agent from chimpanzees with coryza. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1956, 92, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanock, R.; Roizman, B.; Myers, R. Recovery from infants with respiratory illness of a virus related to chimpanzee coryza agent (CCA). I. Isolation, properties and characterization. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1957, 66, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchers, A.T.; Chang, C.; Gershwin, M.E.; Gershwin, L.J. Respiratory syncytial virus—A comprehensive review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 45, 331–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sockrider, M.; Katkin, J. What is respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, P3–P4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.L.; Shao, X.J.; Wang, J.; Guo, W.L. Temporal characteristics of respiratory syncytial virus infection in children and its correlation with climatic factors at a public pediatric hospital in Suzhou. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 58, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, M.; Tan, H.; Tie, Y.; et al. Epidemiology of respiratory pathogens in patients with acute respiratory infections during the COVID-19 pandemic and after easing of COVID-19 restrictions. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0116124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Blau, D.M.; Caballero, M.T.; Feikin, D.R.; Gill, C.J.; Madhi, S.A.; Omer, S.B.; Simões, E.A.F.; Campbell, H.; et al. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in children younger than 5 years in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 2047–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estimates of the global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of lower respiratory infections in 195 countries, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1191–1210. [CrossRef]
- Soni, A.; Kabra, S.K.; Lodha, R. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection: An Update. Indian. J. Pediatr. 2023, 90, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-N.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Xu, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Lu, Q.-B.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.-A.; Lin, S.-H.; Lv, C.-L.; Jiang, B.-G.; et al. Infection and co-infection patterns of community-acquired pneumonia in patients of different ages in China from 2009 to 2020: A national surveillance study. Lancet Microbe 2023, 4, e330–e339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, R.; Fan, C.; Zhang, J.; Wen, B.; Lei, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, C.; Qu, X. Respiratory syncytial virus subtype ON1/NA1/BA9 predominates in hospitalized children with lower respiratory tract infections. J. Med. Virol. 2017, 89, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddadin, Z.; Schuster, J.E.; Spieker, A.J.; Rahman, H.; Blozinski, A.; Stewart, L.; Campbell, A.P.; Lively, J.Y.; Michaels, M.G.; Williams, J.V.; et al. Acute Respiratory Illnesses in Children in the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic: Prospective Multicenter Study. Pediatrics 2021, 148, e2021051462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Pan, Z.; Dong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, W.; Hao, C. Inhibition, transition, and surge: Dynamic evolution of pediatric respiratory pathogen trends amid COVID-19 pandemic policy adjustments. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1420929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, M.; Lu, Q.; Tu, Y. The circulating characteristics of common respiratory pathogens in Ningbo, China, both before and following the cessation of COVID-19 containment measures. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogilvie, M.M.; Vathenen, A.S.; Radford, M.; Codd, J.; Key, S. Maternal antibody and respiratory syncytial virus infection in infancy. J. Med. Virol. 1981, 7, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacimustafaoglu, M.; Celebi, S.; Aynaci, E.; Sinirtas, M.; Koksal, N.; Kucukerdogan, A.; Ercan, I.; Goral, G.; Ildirim, I. The progression of maternal RSV antibodies in the offspring. Arch. Dis. Child. 2004, 89, 52–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, C.; Mao, L.; Li, Y.; Yuan, L.; Li, Z. A rapid, sensitive, and high-throughput pathogen detection method and application of identifying pathogens based on multiplex PCR technology combined with capillary electrophoresis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2025, 111, 116563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health Commission of China. Diagnosis and Treatment Guidelines for Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Children (2019 Edition). Chin. J. Pract. Rural. Dr. 2019, 26, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, E.J.; Uyeki, T.M.; Chu, H.Y. The effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on community respiratory virus activity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muňoz, F.M.; Swamy, G.K.; Hickman, S.P.; Agrawal, S.; Piedra, P.A.; Glenn, G.M.; Patel, N.; August, A.M.; Cho, I.; Fries, L. Safety and Immunogenicity of a Respiratory Syncytial Virus Fusion (F) Protein Nanoparticle Vaccine in Healthy Third-Trimester Pregnant Women and Their Infants. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 1802–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonsenso, D. Bivalent Prefusion F Vaccine in Pregnancy to Prevent RSV Illness in Infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, M.; Kyaw, M.H. Burden of respiratory syncytial virus infections in China: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Glob. Health 2015, 5, 020417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.J.; Huang, X.B.; Zhong, H.L.; Ye, C.X.; Tan, X.; Zhou, K.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, S.F.; Zhu, X.; Lin, C.J.; et al. Epidemiological characteristics and phylogenic analysis of human respiratory syncytial virus in patients with respiratory infections during 2011–2016 in southern China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 90, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirimi, N.; Miligkos, M.; Koutouzi, F.; Petridou, E.; Siahanidou, T.; Michos, A. Respiratory syncytial virus activity and climate parameters during a 12-year period. J. Med. Virol. 2016, 88, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusuf, S.; Piedimonte, G.; Auais, A.; Demmler, G.; Krishnan, S.; Van Caeseele, P.; Singleton, R.; Broor, S.; Parveen, S.; Avendano, L.; et al. The relationship of meteorological conditions to the epidemic activity of respiratory syncytial virus. Epidemiol. Infect. 2007, 135, 1077–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranhos-Baccalà, G.; Komurian-Pradel, F.; Richard, N.; Vernet, G.; Lina, B.; Floret, D. Mixed respiratory virus infections. J. Clin. Virol. 2008, 43, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, C.; Sun, P.; Zeng, F.; Wang, Q.; Wu, J.; Fang, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Gu, Y.; et al. Epidemic features and megagenomic analysis of childhood Mycoplasma pneumoniae post COVID-19 pandemic: A 6-year study in southern China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2353298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirin, B.K.; Topić, R.Z.; Dodig, S. Hepatitis during respiratory syncytial virus infection—A case report. Biochem. Med. 2013, 23, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.B.; Simőes, E.A.; Anderson, L.J. Clinical and epidemiologic features of respiratory syncytial virus. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 372, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedimonte, G.; Perez, M.K. Respiratory syncytial virus infection and bronchiolitis. Pediatr. Rev. 2014, 35, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, H.; Nokes, D.J.; Gessner, B.D.; Dherani, M.; Madhi, S.A.; Singleton, R.J.; O’Brien, K.L.; Roca, A.; Wright, P.F.; Bruce, N.; et al. Global burden of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 1545–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.; Bottle, A.; Sharland, M.; Modi, N.; Aylin, P.; Majeed, A.; Saxena, S. Risk factors for hospital admission with RSV bronchiolitis in England: A population-based birth cohort study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, C.; García-García, M.L.; Pozo, F.; Paula, G.; Molinero, M.; Calderón, A.; González-Esguevillas, M.; Casas, I. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Coinfections With Rhinovirus and Human Bocavirus in Hospitalized Children. Medicine 2015, 94, e1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Pillai, P.; Miyake, F.; Nair, H. The role of viral co-infections in the severity of acute respiratory infections among children infected with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV): A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 010426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stobbelaar, K.; Mangodt, T.C.; Van der Gucht, W.; Delhaise, L.; Andries, J.; Gille, V.; Barbezange, C.; Smet, A.; De Winter, B.Y.; De Dooy, J.J.; et al. Risk Factors Associated with Severe RSV Infection in Infants: What Is the Role of Viral Co-Infections? Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0436822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinello, R.A.; Chen, M.D.; Weibel, C.; Kahn, J.S. Correlation between respiratory syncytial virus genotype and severity of illness. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 186, 839–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Year | Coinfection Virus Types | Number of Cases [N (%)] |
|---|---|---|
| 2022 (N = 153) | HRV | 32 (20.92) |
| HPIV | 28 (18.3) | |
| Mp | 28 (18.3) | |
| HBoV | 22 (14.37) | |
| AdV | 10 (6.54) | |
| CoV | 6 (3.92) | |
| HMPV | 5 (3.27) | |
| AdV + Mp | 4 (2.61) | |
| Cp | 3 (1.96) | |
| HRV + Mp | 3 (1.96) | |
| HRV + HBoV | 2 (1.31) | |
| FluA H1N1 | 1 (0.65) | |
| FluA H3N2 | 1 (0.65) | |
| HRV + HPIV | 1 (0.65) | |
| HRV + FluB | 1 (0.65) | |
| HBoV + HPIV | 1 (0.65) | |
| HPIV + CoV | 1 (0.65) | |
| HBoV + FluA H3N2 | 1 (0.65) | |
| Mp + HPIV | 1 (0.65) | |
| HRV + Mp + Cp | 1 (0.65) | |
| HRV + Mp + HPIV + HBoV + HMPV | 1 (0.65) | |
| 2023 (N = 923) | Mp | 232 (25.14) |
| HRV | 211 (22.86) | |
| HPIV | 124 (13.43) | |
| HMPV | 49 (5.31) | |
| AdV | 31 (3.36) | |
| HBoV | 30 (3.25) | |
| HRV + Mp | 29 (3.14) | |
| CoV | 27 (2.93) | |
| HPIV + HRV | 26 (2.82) | |
| HPIV + Mp | 22 (2.38) | |
| FluA H3N2 | 21 (2.28) | |
| FluB | 18 (1.95) | |
| HBoV + Mp | 9 (0.98) | |
| AdV + Mp | 9 (0.98) | |
| HRV + HMPV | 7 (0.76) | |
| HMPV | 6 (0.65) | |
| AdV + HRV | 6 (0.65) | |
| HBoV + HRV | 5 (0.54) | |
| Cp | 4 (0.43) | |
| HPIV + HMPV | 4 (0.43) | |
| CoV + Mp | 4 (0.43) | |
| FluA H3N2 + Mp | 4 (0.43) | |
| HRV + CoV | 3 (0.33) | |
| HPIV + CoV | 3 (0.33) | |
| HPIV + AdV | 3 (0.33) | |
| FluA H1N1 | 2 (0.22) | |
| FluB + Mp | 2 (0.22) | |
| HPIV + HBoV | 2 (0.22) | |
| HPIV + Cp | 2 (0.22) | |
| HRV + HMPV | 2 (0.22) | |
| HBoV + HRV + Mp | 2 (0.22) | |
| HRV + Cp | 1 (0.11) | |
| H1N1 + HPIV | 1 (0.11) | |
| HMPV + Cp | 1 (0.11) | |
| AdV + HBoV | 1 (0.11) | |
| AdV + CoV | 1 (0.11) | |
| AdV + HMPV | 1 (0.11) | |
| Flu B + HMPV | 1 (0.11) | |
| HPIV + HRV + Mp | 1 (0.11) | |
| HPIV + HRV + HMPV | 1 (0.11) | |
| HPIV + HBoV + HRV | 1 (0.11) | |
| HPIV + HBoV + HMPV | 1 (0.11) | |
| HPIV + AdV + HRV | 1 (0.11) | |
| HPIV + AdV + Mp | 1 (0.11) | |
| FluA H3N2 + HRV | 1 (0.11) | |
| FluA H3N2 + HMPV | 1 (0.11) | |
| FluA H3N2 + Flu B | 1 (0.11) | |
| AdV + HRV + Mp | 1 (0.11) | |
| AdV + HMPV + Mp | 1 (0.11) | |
| Flu B + HMPV + Mp | 1 (0.11) | |
| HPIV + HBoV + HRV + Mp | 1 (0.11) | |
| HPIV + HBoV + HRV + HMPV | 1 (0.11) | |
| FluA H3N2 + HBoV + HRV | 1 (0.11) | |
| FluA H3N2 + HBoV + Mp | 1 (0.11) | |
| FluA H3N2 + AdV + HRV | 1 (0.11) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, Q.-R.; Chu, X.-L.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Li, W.; Guo, Y.-J.; Shang, S.-Q. Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Children in Hangzhou (2022–2023). Pathogens 2025, 14, 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060603
Lai Q-R, Chu X-L, Chen Y-Y, Li W, Guo Y-J, Shang S-Q. Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Children in Hangzhou (2022–2023). Pathogens. 2025; 14(6):603. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060603
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Qin-Rui, Xiao-Li Chu, Ying-Ying Chen, Wei Li, Ya-Jun Guo, and Shi-Qiang Shang. 2025. "Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Children in Hangzhou (2022–2023)" Pathogens 14, no. 6: 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060603
APA StyleLai, Q.-R., Chu, X.-L., Chen, Y.-Y., Li, W., Guo, Y.-J., & Shang, S.-Q. (2025). Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Children in Hangzhou (2022–2023). Pathogens, 14(6), 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060603





