Survey of Piroplasmids in Wild Mammals, Unconventional Pets, and Ticks from Goiás State, Midwestern Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Aspects
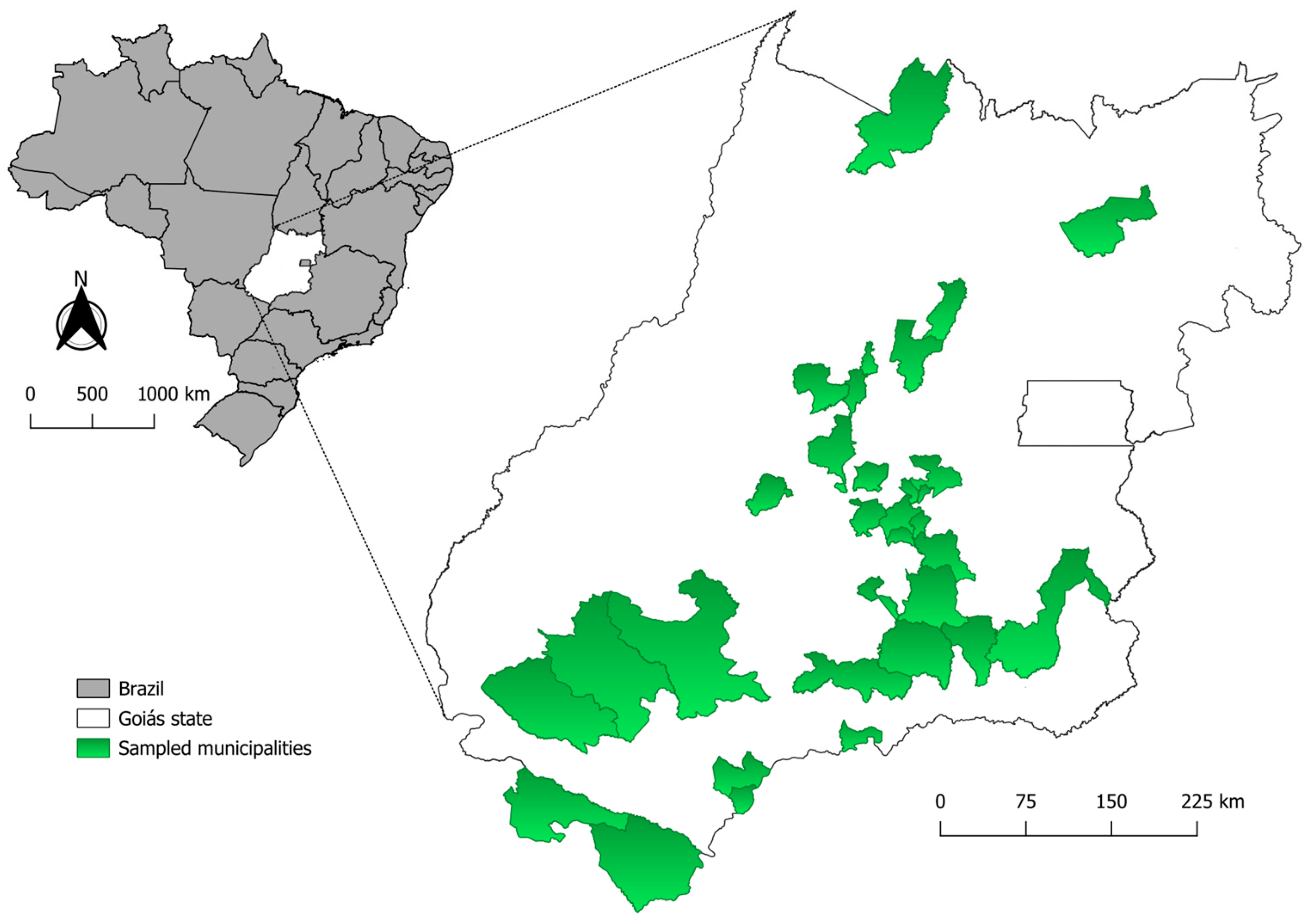
2.2. Study Area
2.3. Sampling
2.4. Microscopic Analysis of Blood Smear Samples
2.5. Tick Collection
2.6. DNA Extraction
2.7. Molecular Analyses
2.8. Amplicon Purification, Sequencing, and Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Blood Smear Analysis
3.2. Tick Identification
3.3. Molecular Detection of Piroplasmids in Ticks, Blood, and Tissue Samples
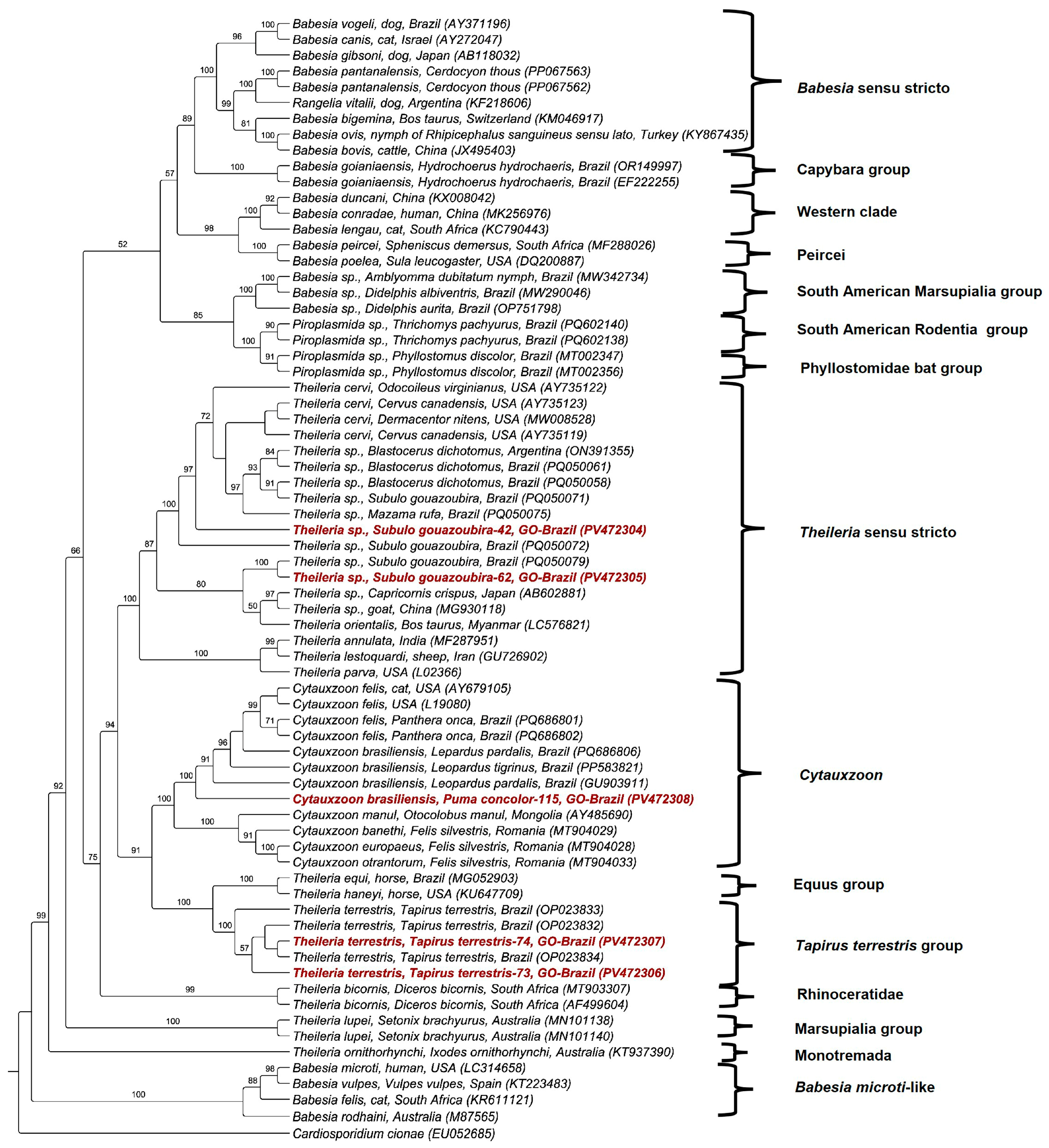
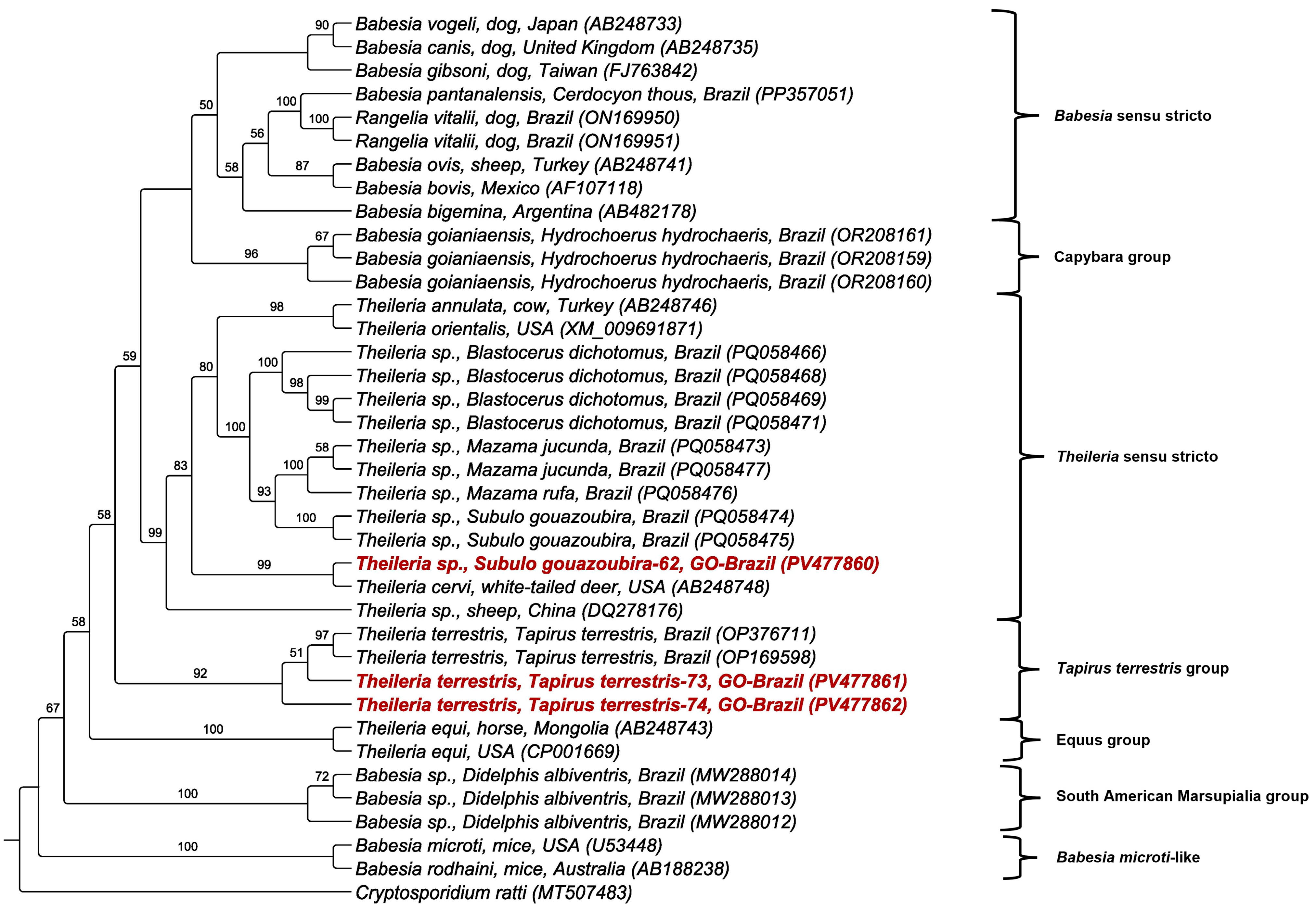
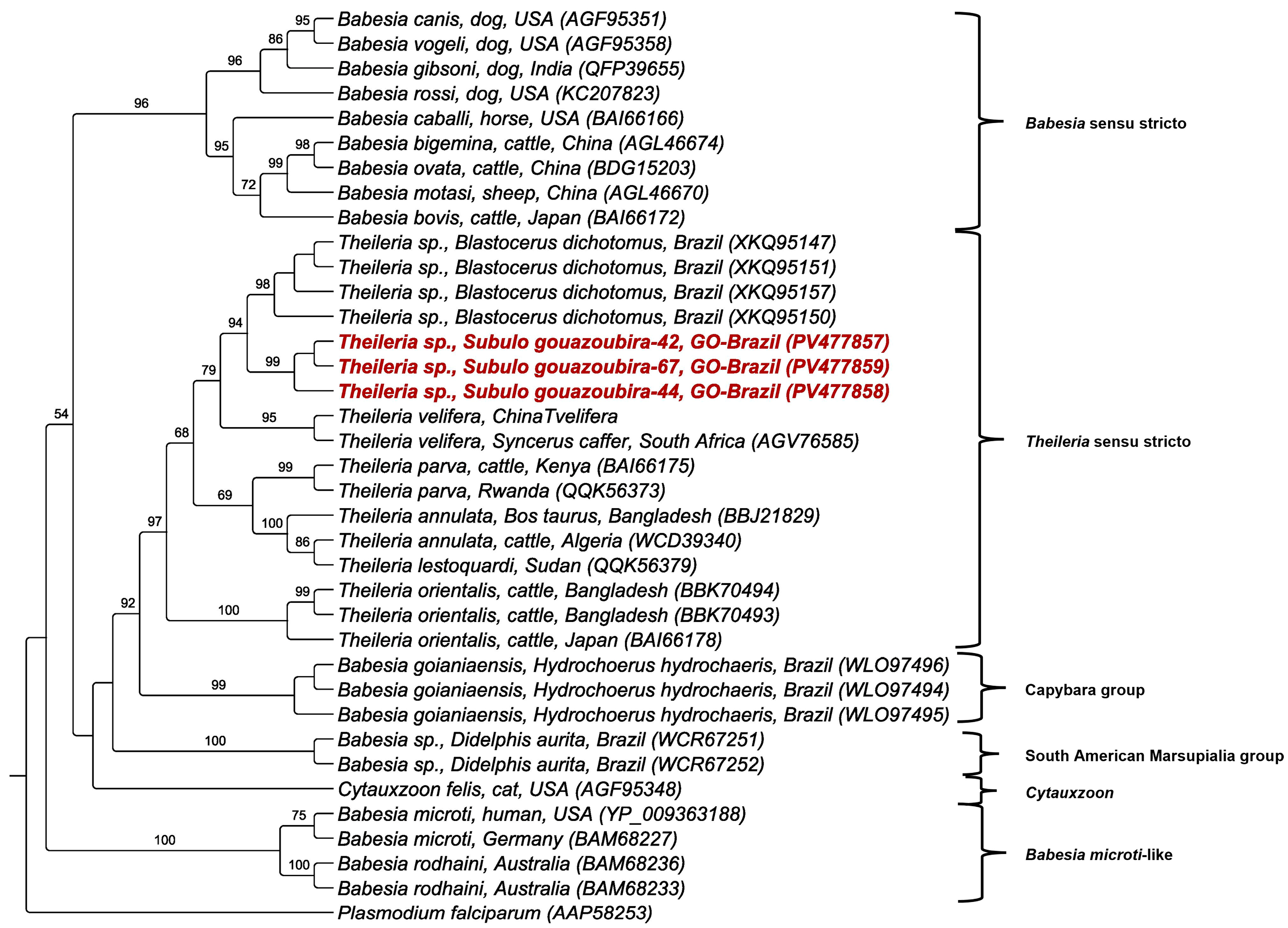
3.4. Phylogenetic and BLASTn Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fava, N.M.N.; Alves, T.S.; Lopes, M.G.; Labruna, M.B.; Santos, A.Q.; Cury, M.C. Occurrence and Molecular Identification of Hemoparasites in Wild Mammals Kept in Rehabilitation Centers in Brazil. Acta Parasitol. 2022, 67, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Paula, L.G.F.; Weck, B.C.; Neves, L.C.; Paula, W.V.D.F.; Araújo, L.B.D.M.; Martins, D.B.; Peres, P.C.D.O.; Labruna, M.B.; Krawczak, F.D.S. Natural Infection and Molecular Detection of Cytauxzoon felis in a Free-Ranging Puma concolor in the State of Goiás, Brazil. Cienc. Rural 2022, 52, e20210577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penzhorn, B.L. Babesiosis of Wild Carnivores and Ungulates. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 138, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnittger, L.; Ganzinelli, S.; Bhoora, R.; Omondi, D.; Nijhof, A.M.; Florin-Christensen, M. The Piroplasmida Babesia, Cytauxzoon, and Theileria in Farm and Companion Animals: Species Compilation, Molecular Phylogeny, and Evolutionary Insights. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 121, 1207–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabsley, M.J.; Shock, B.C. Natural History of Zoonotic Babesia: Role of Wildlife Reservoirs. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2013, 2, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.A. Parasite Zoonoses and Wildlife: One Health, Spillover and Human Activity. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotondano, T.E.D.F.; Almeida, H.K.A.; Krawczak, F.D.S.; Santana, V.L.; Vidal, I.F.; Labruna, M.B.; de Azevedo, S.S.; de Almeida, A.M.P.; de Melo, M.A. Pesquisa de Ehrlichia canis, Babesia spp. e Hepatozoon spp. em cães de uma Região Semiárida do Brasil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Veterinaria 2015, 24, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas-Torres, F. Canine Vector-Borne Diseases in Brazil. Parasites Vectors 2008, 1, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perles, L.; Moraes, M.F.; Xavier da Silva, M.; Vieira, R.F.C.; Machado, R.Z.; Lux Hoppe, E.G.; André, M.R. Co-Infection by Multiple Vector-Borne Agents in Wild Ring-Tailed Coatis (Nasua nasua) from Iguaçu National Park, Southern Brazil. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Chomel, B.B.; Otranto, D. Ticks and Tick-Borne Diseases: A One Health Perspective. Trends Parasitol. 2012, 28, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongruel, A.C.B.; Medici, E.P.; da Costa Canena, A.; Calchi, A.C.; Perles, L.; Rodrigues, B.C.B.; Soares, J.F.; Machado, R.Z.; André, M.R. Theileria terrestris nov. sp.: A Novel Theileria in Lowland Tapirs (Tapirus terrestris) from Two Different Biomes in Brazil. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawczak, F.D.S.; Calchi, A.C.; Neves, L.C.; Dias, S.A.; da Silva, B.B.F.; Paula, W.V.D.F.; de Paula, L.G.F.; Tavares, M.A.; Pádua, G.T.; de Lima, N.J.; et al. Phylogenetic Inferences Based on Distinct Molecular Markers Confirm a Novel Babesia Species (Babesia goianiaensis nov. sp.) in Capybaras (Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris and Associated Ticks. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, L.R.; Paludo, G.; Bisol, T.B.; Perles, L.; de Oliveira, L.B.; de Oliveira, C.M.; da Silva, T.M.V.; Nantes, W.A.G.; Duarte, M.A.; Santos, F.M.; et al. Molecular Detection of Piroplasmids in Synanthropic Rodents, Marsupials, and Associated Ticks from Brazil, with Phylogenetic Inference of a Putative Novel Babesia sp. from White-Eared Opossum (Didelphis albiventris). Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 3537–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, Á.F.X.D.; Calchi, A.C.; Stocco, A.V.; Stocco, N.V.; Costa, A.C.; Mureb, E.N.; Pires, J.R.; Guimarães, A.; Raimundo, J.M.; de Almeida Balthazar, D.; et al. Expanding the Universe of Piroplasmids: Morphological Detection and Phylogenetic Positioning of Putative Novel Piroplasmids in Black-Eared Opossums (Didelphis aurita) from Southeastern Brazil, with Description of “South American Marsupialia Group” of Piroplasmida. Parasitol. Res. 2023, 122, 1519–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, P.V.; Soares, C.O.; Scofield, A.; Santiago, C.D.; França, T.N.; Barros, S.S. Fatal Cytauxzoonosis in Captive-Reared Lions in Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 145, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.M.C.; Lacher, T.E. Cerrado—South America. In Encyclopedia of the World’s Biomes; Goldstein, M.I., DellaSala, D.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 546–553. ISBN 978-0-12-816097-8. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, T.F.; Onofrio, V.C.; Barros-Battesti, D.M.; Labruna, M.B. Nymphs of the Genus Amblyomma (Acari: Ixodidae) of Brazil: Descriptions, Redescriptions, and Identification Key. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2010, 1, 75–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Fernandes Martins, T.; Muñoz-Leal, S.; Onofrio, V.C.; Barros-Battesti, D.M. Ticks (Ixodida: Argasidae, Ixodidae) of Brazil: Updated Species Checklist and Taxonomic Keys. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, C.M.; Anastos, G.; Elbl, A. The Larval Ixodid Ticks of the Eastern United States. Misc. Publ. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1961, 2, 213–237. [Google Scholar]
- Sangioni, L.A.; Horta, M.C.; Vianna, M.C.B.; Gennari, S.M.; Soares, R.M.; Galvão, M.A.M.; Schumaker, T.T.S.; Ferreira, F.; Vidotto, O.; Labruna, M.B. Rickettsial Infection in Animals and Brazilian Spotted Fever Endemicity. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocher, T.D.; Thomas, W.K.; Meyer, A.; Edwards, S.V.; Pääbo, S.; Villablanca, F.X.; Wilson, A.C. Dynamics of Mitochondrial DNA Evolution in Animals: Amplification and Sequencing with Conserved Primers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 6196–6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangold, A.J.; Bargues, M.D.; Mas-Coma, S. Mitochondrial 16S rDNA Sequences and Phylogenetic Relationships of Species of Rhipicephalus and other Tick genera among Metastriata (Acari: Ixodidae). Parasitol. Res. 1998, 84, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birkenheuer, A.J.; Marr, H.; Alleman, A.R.; Levy, M.G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Development and Evaluation of a PCR Assay for the Detection of Cytauxzoon felis DNA in Feline Blood Samples. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 137, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greay, T.L.; Zahedi, A.; Krige, A.S.; Owens, J.M.; Rees, R.L.; Ryan, U.M.; Oskam, C.L.; Irwin, P.J. Endemic, Exotic and Novel Apicomplexan Parasites Detected during a National Study of Ticks from Companion Animals in Australia. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quillfeldt, P.; Martínez, J.; Bugoni, L.; Mancini, P.L.; Merino, S. Blood Parasites in Noddies and Boobies from Brazilian Offshore Islands—Differences Between Species and Influence of Nesting Habitat. Parasitology 2014, 141, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreeg, M.E.; Marr, H.S.; Tarigo, J.L.; Cohn, L.A.; Bird, D.M.; Scholl, E.H.; Levy, M.G.; Wiegmann, B.M.; Birkenheuer, A.J. Mitochondrial Genome Sequences and Structures Aid in the Resolution of Piroplasmida Phylogeny. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.D.; Austen, J.; Portas, T.J.; Friend, J.A.; Ahlstrom, L.A.; Oskam, C.L.; Ryan, U.M.; Irwin, P.J. Sequence Analyses at Mitochondrial and Nuclear Loci Reveal a Novel Theileria sp. and aid in the Phylogenetic Resolution of Piroplasms from Australian Marsupials and Ticks. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.F.; Girotto, A.; Brandão, P.E.; Da Silva, A.S.; França, R.T.; Lopes, S.T.A.; Labruna, M.B. Detection and Molecular Characterization of a Canine Piroplasm from Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 180, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shock, B.C.; Birkenheuer, A.J.; Patton, L.L.; Olfenbuttel, C.; Beringer, J.; Grove, D.M.; Peek, M.; Butfiloski, J.W.; Hughes, D.W.; Lockhart, J.M.; et al. Variation in the ITS-1 and ITS-2 RRNA Genomic Regions of Cytauxzoon felis from Bobcats and Pumas in the Eastern United States and Comparison with Sequences from Domestic Cats. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 190, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panait, L.C.; Mihalca, A.D.; Modrý, D.; Juránková, J.; Ionică, A.M.; Deak, G.; Gherman, C.M.; Heddergott, M.; Hodžić, A.; Veronesi, F.; et al. Three New Species of Cytauxzoon in European Wild Felids. Vet. Parasitol. 2021, 290, 109344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreeg, M.E.; Marr, H.S.; Tarigo, J.; Cohn, L.A.; Levy, M.G.; Birkenheuer, A.J. Pharmacogenomics of Cytauxzoon felis Cytochrome b: Implications for Atovaquone and Azithromycin Therapy in Domestic Cats with Cytauxzoonosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, B.; Hillier, L.D.; Wendl, M.C.; Green, P. Base-Calling of Automated Sequencer Traces Using Phred. I. Accuracy Assessment. Genome Res. 1998, 8, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT Online Service: Multiple Sequence Alignment, Interactive Sequence Choice and Visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A Fast Online Phylogenetic Tool for Maximum Likelihood Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W232–W235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöver, B.C.; Muller, K.F. TreeGraph 2: Combining and Visualizing Evidence from Different Phylogenetic Analyses. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calchi, A.C.; Duarte, J.M.B.; Castro-Santiago, A.C.; Bassini-Silva, R.; Barros-Battesti, D.M.; Machado, R.Z.; André, M.R. Genetic Diversity of Theileria spp. in Deer (Artiodactyla: Cervidae) from Brazil. Parasitol. Res. 2024, 123, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, H.S.; Marcili, A.; Barbieri, A.R.M.; Minervino, A.H.H.; Moreira, T.R.; Gennari, S.M.; Labruna, M.B. Novel Piroplasmid and Hepatozoon Organisms Infecting the Wildlife of Two Regions of the Brazilian Amazon. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2017, 6, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morner, T.; Obendorf, D.L.; Artois, M.; Woodford, M.H. Surveillance and Monitoring of Wildlife Diseases. Rev. Sci. Tech. Off. Int. Epiz. 2002, 21, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas-Torres, F.; de Sousa-Paula, L.C.; Otranto, D. The Rhipicephalus sanguineus group: Updated List of Species, Geographical Distribution, and Vector Competence. Parasites Vectors 2024, 17, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labruna, M.B.; Jorge, R.S.P.; Sana, D.A.; Jácomo, A.T.A.; Kashivakura, C.K.; Furtado, M.M.; Ferro, C.; Perez, S.A.; Silveira, L.; Santos, T.S.; et al. Ticks (Acari: Ixodida) on Wild Carnivores in Brazil. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2005, 36, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Ferreira, D.R.A.; de Melo, L.M.; Lima, P.A.C.P.; Siqueira, D.B.; Rameh-de-Albuquerque, L.C.; de Melo, A.V.; Ramos, J.A.C. Ticks on Captive and Free-Living Wild Animals in Northeastern Brazil. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2010, 50, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witter, R.; Martins, T.F.; Campos, A.K.; Melo, A.L.T.; Corrêa, S.H.R.; Morgado, T.O.; Wolf, R.W.; May-Júnior, J.A.; Sinkoc, A.L.; Strüssmann, C.; et al. Rickettsial Infection in Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) of Wild Animals in Midwestern Brazil. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, M.S.; Bahiense, T.C.; Silva, A.A.B.; Onofrio, V.C.; Barral, T.D.; Souza, B.M.P.; Lira-da-Silva, R.M.; Biondi, I.; Meyer, R.; Portela, R.W. Ticks and Associated Pathogens From Rescued Wild Animals in Rainforest Fragments of Northeastern Brazil. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caminade, C.; McIntyre, K.M.; Jones, A.E. Impact of Recent and Future Climate Change on Vector-Borne Diseases. Ann. Acad. N. Y. Sci. 2019, 1436, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastos, T.S.A.; de Carvalho Madrid, D.M.; Faria, A.M.; Freitas, T.M.S.; Linhares, G.F.C. Carrapatos Em Animais Silvestres Do Bioma Cerrado Triados Pelo Cetas, Ibama-Goiás. Cienc. Anim. Bras. 2016, 17, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Peña, A.; Binder, L.C.; Nava, S.; Szabó, M.P.J.; Labruna, M.B. Exploring the Ecological and Evolutionary Relationships between Rickettsia and Hard Ticks in the Neotropical Region. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, J.; Carreira, A.; Bueno, C.; Machado Da Silva, A.V. Wild Mammal Translocations: A Public Health Concern. Open J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 10, 64–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.A.; de Oliveira, C.M.; Honorato, S.M.; do Rosario Batista, L.M.; Mendonça, J.T.; de Sousa, D.E.R.; Hirano, L.Q.L.; André, M.R.; de Castro, M.B.; Paludo, G.R. Cytauxzoon brasiliensis sp. nov. (Apicomplexa: Theileriidae), a New Species Infecting a Little-Spotted-Cat (Leopardus tigrinus) (Carnivora: Felidae) from Brazil. Syst. Parasitol. 2024, 101, 78–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labruna, M.B.; Martins, T.F.; Acosta, I.C.L.; Serpa, M.C.A.; Soares, H.S.; Teixeira, R.H.F.; Fernandes-Santos, R.C.; Medici, E.P. Ticks and Rickettsial Exposure in Lowland Tapirs (Tapirus terrestris) of Three Brazilian Biomes. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calchi, A.C.; May-Júnior, J.A.; Baggio-Souza, V.; Berger, L.; Fagundes-Moreira, R.; Mallmann-Bohn, R.; de Queiroz Viana Braga, L.; Kirnew, M.D.; Silveira, M.F.; Ampuero, R.A.N.; et al. Diversity of Cytauxzoon spp. (Piroplasmida: Theileriidae) in Wild Felids from Brazil and Argentina. Pathogens 2025, 14, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, M.R.; Adania, C.H.; Machado, R.Z.; Allegretti, S.M.; N Felippe, P.A.; Silva, K.F.; H Nakaghi, A.C.; Dagnone, A.S. Molecular Detection of Cytauxzoon spp. in Asymptomatic Brazilian Wild Captive Felids. J. Wildl. Dis. 2009, 45, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagundes-Moreira, R.; Souza, U.A.; May-Junior, J.A.; Baggio-Souza, V.; Berger, L.; Wagner, P.G.C.; Mazim, F.D.; Peters, F.B.; Favarini, M.O.; Tortato, M.A.; et al. Epidemiological Compatibility of Amblyomma sculptum as Possible Vector and Panthera onca as Reservoir of Cytauxzoon spp. in Midwestern Brazil. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 102021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, K.C.M.; Fernandes, M.P.; Herrera, H.M.; Freschi, C.R.; Machado, R.Z.; André, M.R. Diversity of Piroplasmids among Wild and Domestic Mammals and Ectoparasites in Pantanal Wetland, Brazil. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Mammal Species | CETAS-GO | CETRAS-CN | SMA | Vet Clinics | ZOO GYN | Total Number of Animals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alouatta caraia | 11 | - | - | - | - | 11 |
| Callithrix penicillata | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 |
| Cavia porcellus | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| Cerdocyon thous | 11 | - | - | - | - | 11 |
| Chrysocyon brachyurus | 6 | - | - | - | - | 6 |
| Coendou prehensilis | 5 | 1 | - | - | - | 6 |
| Didelphys albiventris | 3 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 5 |
| Euphractus sexcinctus | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris | 3 | - | 1 | - | - | 4 |
| Leopardus pardalis | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| Mazama americana | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| Myrmecophaga tridactyla | 21 | - | - | - | - | 21 |
| Nasua nasua | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 |
| Oryctolagus cuniculus | - | - | 1 | 4 | - | 5 |
| Pecari tajacu | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 |
| Puma concolor | 6 | - | - | - | - | 6 |
| Rattus norvegicus f. domestica | - | - | - | - | 2 | 2 |
| Sapajus libidinosus | 4 | - | - | - | - | 4 |
| Subulo gouazoubira | 11 | 1 | - | - | - | 12 |
| Tamandua tetradactyla | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| Tapirus terrestris | 2 | - | - | - | 2 | 4 |
| Total | 87 | 5 | 2 | 6 | 5 | 105 |
| Tick Species | Tick Stage (No. of Specimens) | Host Species (No. of Animals) | Samples Tested by PCR * | Piroplasmid DNA-Positive/No. Tested (% of Positives) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amblyomma sculptum | Nymph (123) | A. caraya (1), C. prehensilis (1), C. thous (1), H. hydrochaeris (2), S. gouazoubira (1), M. tridactyla (5), T. terrestris (2), T. tetradactyla (3) | 37 | 2/37 (5.4%) |
| Males (40) | M. tridactyla (8), T. terrestris (2) | 15 | 0/15 (0%) | |
| Females (33) | H. hydrochaeris (1), M. tridactyla (4); T. terrestris (2) | 7 | 0/7 (0%) | |
| Amblyomma dubitatum | Males (32) | H. hydrochaeris (2) | 5 | 1/5 (20%) |
| Females (6) | H. hydrochaeris (2) | 0 | - | |
| Rhipicephalus microplus | Females (3) | S. gouazoubira (1), T. terrestris (1) | 0 | - |
| Amblyomma nodosum | Males (17) | M. tridactyla (4), T. tetradactyla (4) | 5 | 0/5 (0%) |
| Females (8) | M. tridactyla (5), T. tetradactyla (2) | 0 | - | |
| Dermacentor nitens | Males (2) | P. concolor (1) | 0 | - |
| Amblyomma longirostre | Females (1) | C. prehensilis (1) | 0 | - |
| Males (3) | C. prehensilis (1) | 0 | - | |
| Amblyomma ovale | Males (2) | P. concolor (1) | 0 | - |
| Females (2) | P. concolor (1) | 0 | - | |
| Amblyomma calcaratum | Males (4) | M. tridactyla (1), T. tetradactyla (1) | 0 | - |
| Amblyomma spp. | Larvae (24) | M. tridactyla (1), P. concolor (3), T. terrestris (1) | 0 | - |
| Total | 300 | 69 | 3/69 (4.3%) |
| Mammal Species | No. per Species (% of Mammals Collected) | Piroplasmid DNA-Positive/No. of Tested (% of Positives) |
|---|---|---|
| Alouatta caraia | 11 (10.5%) | 0/11 (0%) |
| Callithrix penicillata | 1 (0.9%) | 0/1 (0%) |
| Cavia porcellus | 1 (0.9%) | 0/1 (0%) |
| Cerdocyon thous | 11 (10.5%) | 2/11 (18.2%) |
| Chrysocyon brachyurus | 6 (5.7%) | 2/6 (33.4%) |
| Coendou prehensilis | 6 (5.7%) | 1/6 (16.7%) |
| Didelphys albiventris | 5 (4.8%) | 0/5 (0%) |
| Euphractus sexcinctus | 1 (0.9%) | 0/1 (0%) |
| Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris | 4 (3.9%) | 2/4 (50%) |
| Leopardus pardalis | 1 (0.9%) | 0/1 (0%) |
| Mazama americana | 1 (0.9%) | 1/1 (100%) |
| Myrmecophaga tridactyla | 21 (20%) | 2/21 (9.5%) |
| Nasua nasua | 1 (0.9%) | 0/1 (0%) |
| Oryctolagus cuniculus | 5 (4.8%) | 0/5 (0%) |
| Pecari tajacu | 1 (0.9%) | 0/1 (0%) |
| Puma concolor | 6 (5.7%) | 4/6 (66.7%) |
| Rattus norvegicus | 2 (1.9%) | 0/2 (0%) |
| Sapajus libidinosus | 4 (3.9%) | 0/4 (0%) |
| Subulo gouazoubira | 12 (11.5%) | 9/12 (75%) |
| Tamandua tetradactyla | 1 (0.9%) | 0/1 (0%) |
| Tapirus terrestris | 4 (3.9%) | 4/4 (100%) |
| Total | 105 (100%) | 27/105 (25.7%) |
| Sample No. (GenBank Accession No.) Wild Mammal Species | Molecular Marker | Size (bp) | Percent Identity | Query Cover (%)/E-Value | Sequence Best Match Location/Host (GenBank Accession No.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 42 (PV472304/PV477857/PV476206) Subulo gouazoubira | 18S rRNA | 1352 | 99.93% | 100%/0.0 | Theileria cervi Wisconsin—USA/elk blood (AY735123.1) |
| cox-3 | 650 | 87.50% | 100%/0.0 | Theileria sp. Brazil/Blastocerus dichotomus (PQ058478.1) | |
| ITS-1 | 566 | 89.60% | 100%/0.0 | Theileria sp. Tennessee—USA/Amblyomma americanum from Odocoileus virginianus (KC122621.1) | |
| Sample 44 (PV477858/PV476207) Subulo gouazoubira | cox-3 | 650 | 87.62% | 99%/0.0 | Theileria sp. Brazil/Blastocerus dichotomus (PQ058488.1) |
| ITS-1 | 534 | 89.17% | 100%/0.0 | Theileria sp. Georgia—USA/Amblyomma americanum (KC119626.1) | |
| Sample 45 (PV544933) Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris | 18S rRNA | 565 | 100% | 100%/0.0 | Babesia goianiaensis Goiás—Brazil/Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris (OR149999.1) |
| Sample 62 (PV472305/PV477860) Subulo gouazoubira | 18S rRNA | 1358 | 99.41% | 100%/0.0 | Theileria cervi Texas—EUA/Dermacentor nitens from Odocoileus virginianus (MW008521.1) |
| hsp70 | 810 | 92.92% | 100%/0.0 | Theileria cervi Georgia—USA/Odocoileus virginianus (AB248748.1) | |
| Sample 67 (PV477859) Subulo gouazoubira | cox-3 | 650 | 87.62% | 99%/0.0 | Theileria sp. Brazil/Blastocerus dichotomus (PQ058488.1) |
| Sample 73 (PV472306/PV477861) Tapirus terrestris | 18S rRNA | 1350 | 100% | 100%/0.0 | Theileria sp. Brazil/Tapirus terrestris (OP023832.1) |
| hsp70 | 893 | 99.22% | 86%/0.0 | Theileria sp. Brazil/Tapirus terrestris (OP376711.1) | |
| Sample 74 (PV472307/PV477862) Tapirus terrestris | 18S rRNA | 1397 | 100% | 100%/0.0 | Theileria sp. Brazil/Tapirus terrestris (OP023832.1) |
| hsp70 | 739 | 99.04% | 99%/0.0 | Theileria sp. Brazil/Tapirus terrestris (OP169598.1) | |
| Sample 108 PV544934 Subulo gouazoubira | 18S rRNA | 437 | 100% | 100%/0.0 | Theileria cervi Indiana—EUA/elk blood (AY735119.1) |
| Sample 115 (PV472308) Puma concolor | 18S rRNA | 1270 | 99.76% | 100%/0.0 | Cytauxzoon brasiliensis Brazil/Leopardus pardalis (PP583821.1) |
| Sample 128 (PV544935) Coendou prehensilis | 18S rRNA | 304 | 100% | 100%/1e-155 | Babesia vogeli Brazil/Canis lupus familiaris (MN912657.1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bittencourt, R.B.M.; Calchi, A.C.; Neves, L.C.; de Lima, N.J.; dos Santos, G.C.; Cardoso, E.R.N.; Paula, W.V.d.F.; Araújo, L.B.d.M.; Gonçalves, J.R.; Sobreira, E.d.A.; et al. Survey of Piroplasmids in Wild Mammals, Unconventional Pets, and Ticks from Goiás State, Midwestern Brazil. Pathogens 2025, 14, 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060585
Bittencourt RBM, Calchi AC, Neves LC, de Lima NJ, dos Santos GC, Cardoso ERN, Paula WVdF, Araújo LBdM, Gonçalves JR, Sobreira EdA, et al. Survey of Piroplasmids in Wild Mammals, Unconventional Pets, and Ticks from Goiás State, Midwestern Brazil. Pathogens. 2025; 14(6):585. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060585
Chicago/Turabian StyleBittencourt, Raphaela Bueno Mendes, Ana Cláudia Calchi, Lucianne Cardoso Neves, Nicolas Jalowitzki de Lima, Gabriel Cândido dos Santos, Ennya Rafaella Neves Cardoso, Warley Vieira de Freitas Paula, Luciana Batalha de Miranda Araújo, Jessica Rocha Gonçalves, Elisângela de Albuquerque Sobreira, and et al. 2025. "Survey of Piroplasmids in Wild Mammals, Unconventional Pets, and Ticks from Goiás State, Midwestern Brazil" Pathogens 14, no. 6: 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060585
APA StyleBittencourt, R. B. M., Calchi, A. C., Neves, L. C., de Lima, N. J., dos Santos, G. C., Cardoso, E. R. N., Paula, W. V. d. F., Araújo, L. B. d. M., Gonçalves, J. R., Sobreira, E. d. A., Baptista, L. A. M. L., Luz, H. R., André, M. R., Dantas-Torres, F., & Krawczak, F. d. S. (2025). Survey of Piroplasmids in Wild Mammals, Unconventional Pets, and Ticks from Goiás State, Midwestern Brazil. Pathogens, 14(6), 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060585






