The Rise, Fall, and Rethink of (Fluoro)quinolones: A Quick Rundown
Abstract
1. Introduction
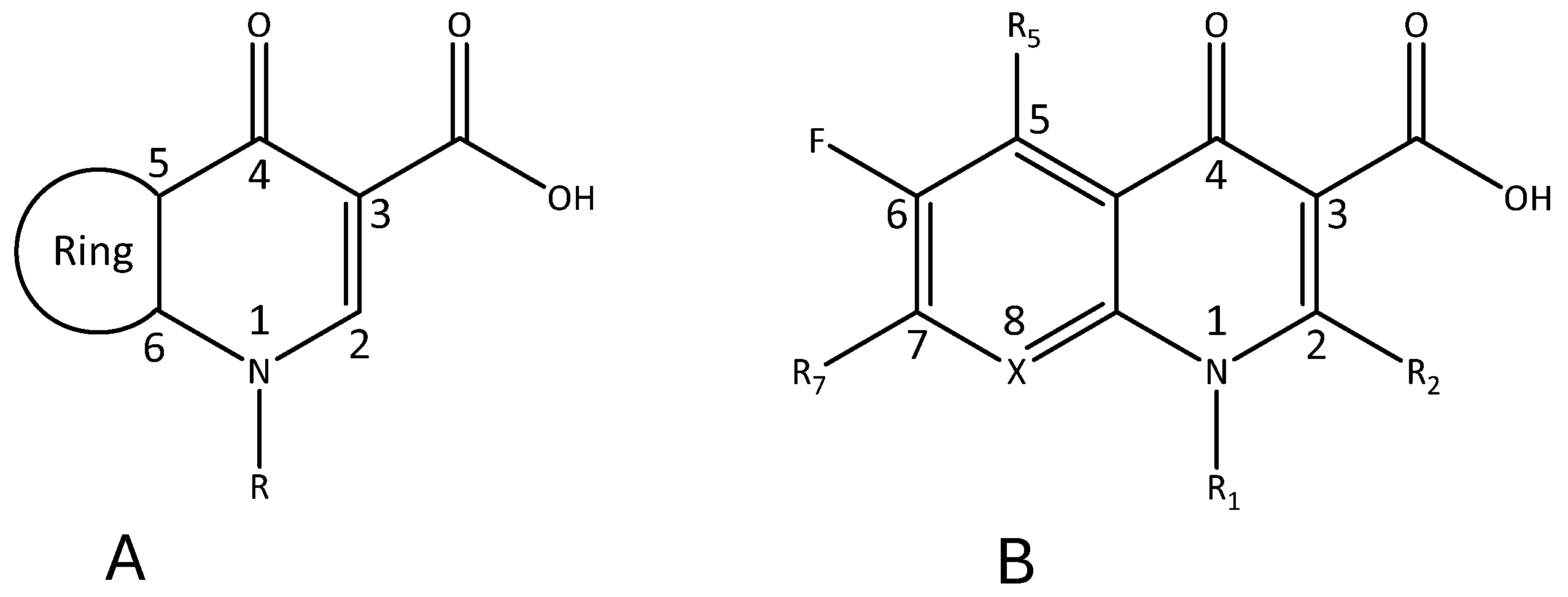
2. (Fluoro)quinolones: Main Molecules, Structures, and Applications
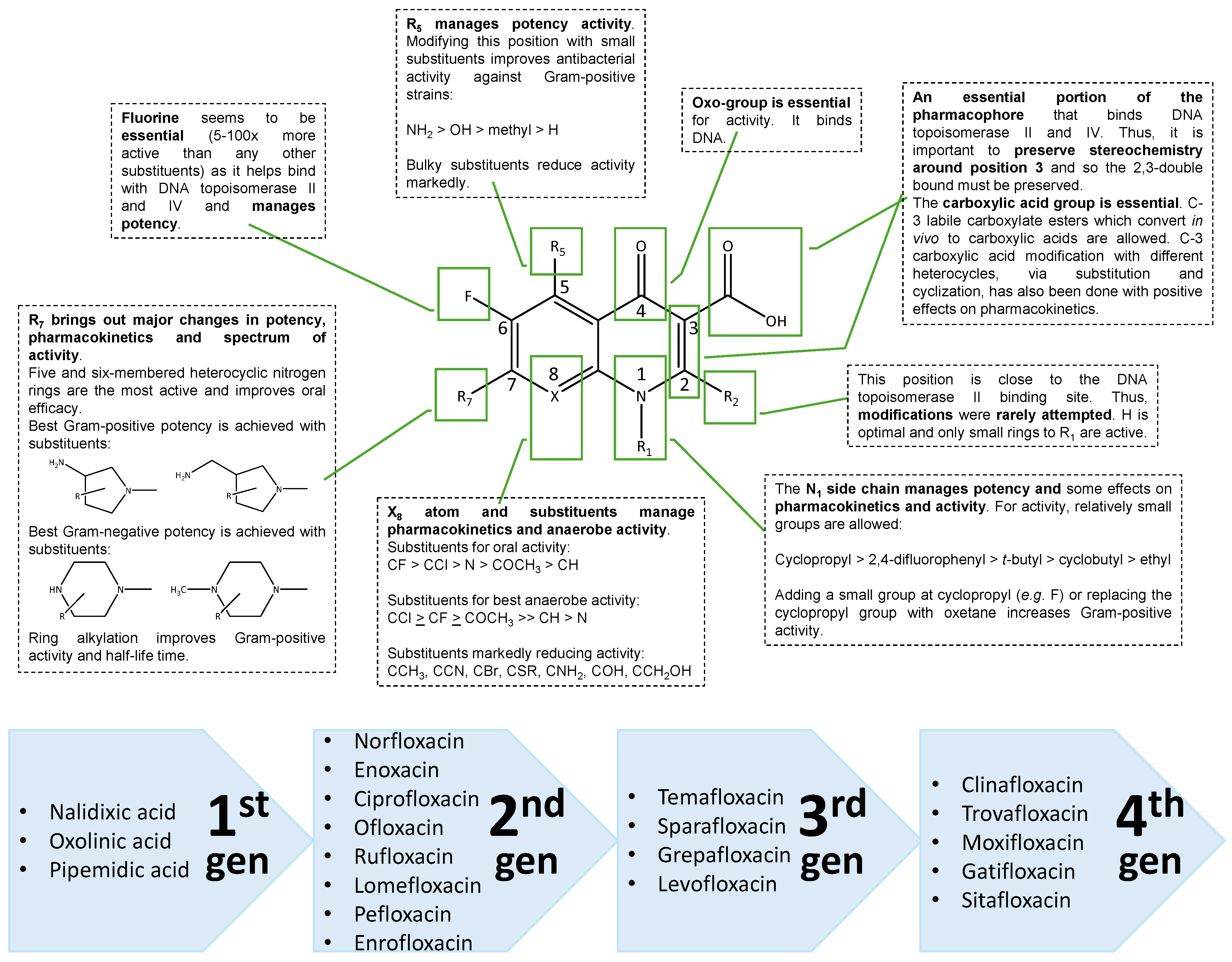
2.1. Medicinal Chemistry
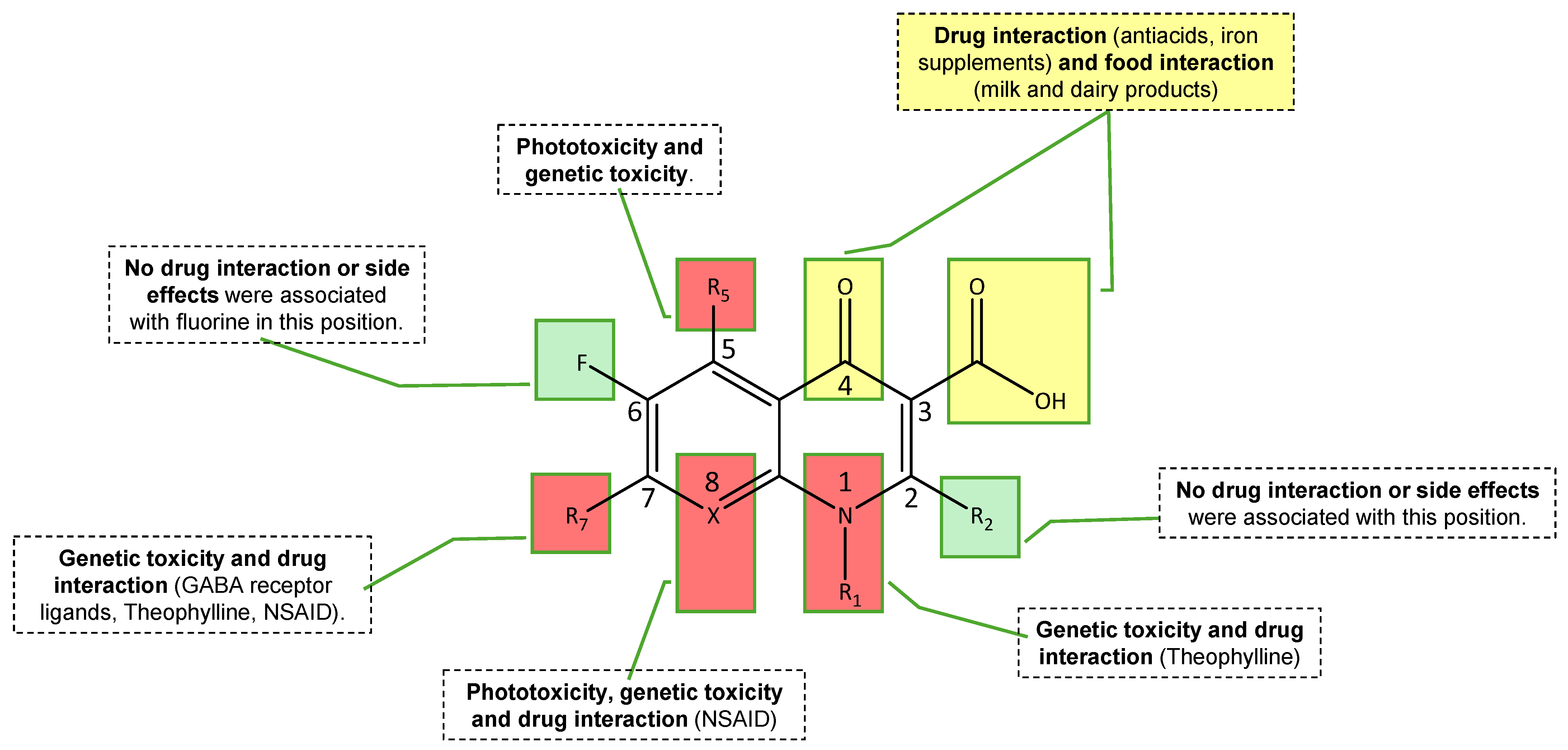
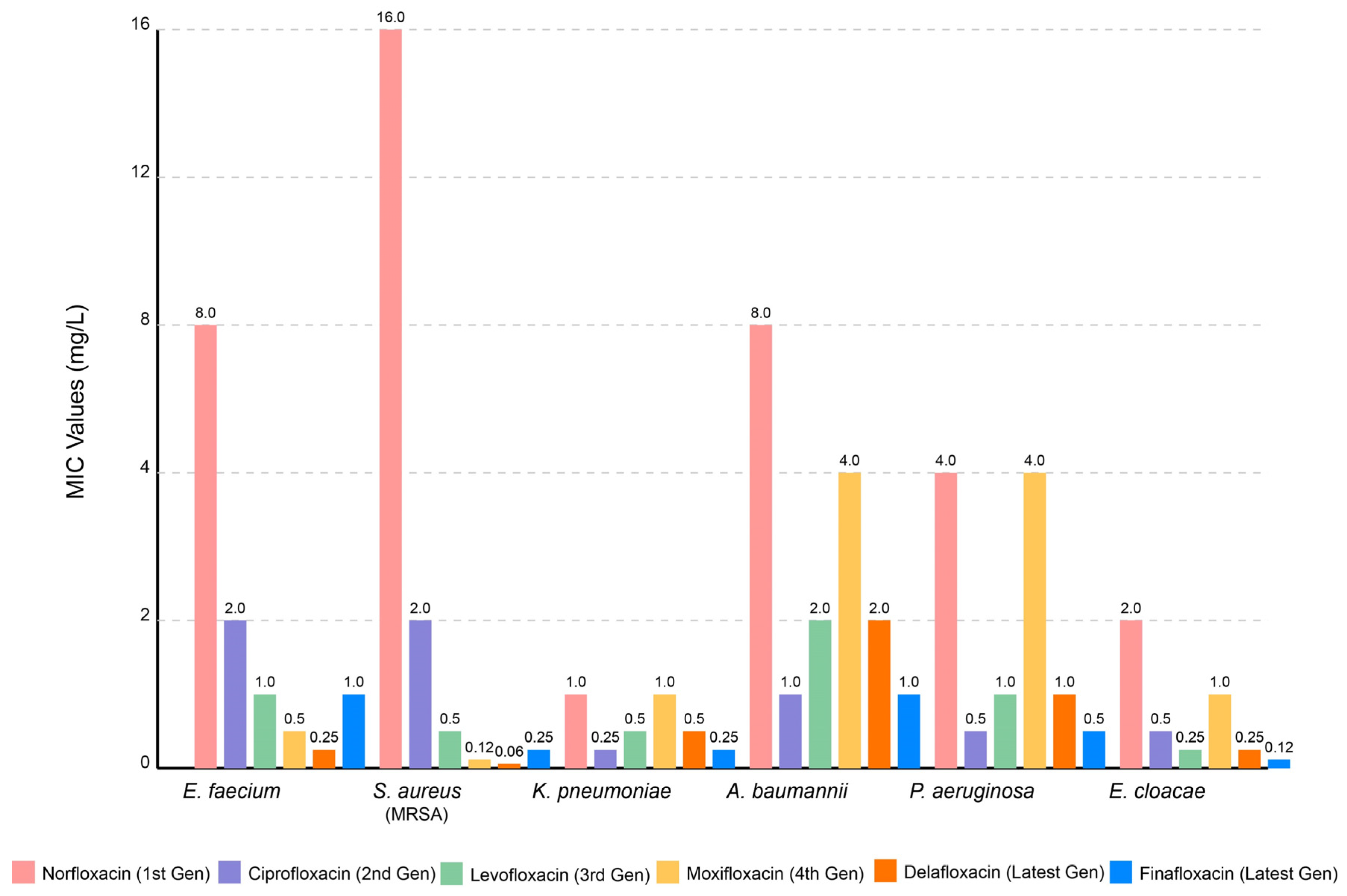
2.2. Clinical Applications, Pharmacokinetics, Toxicology, and Resistance Concerns
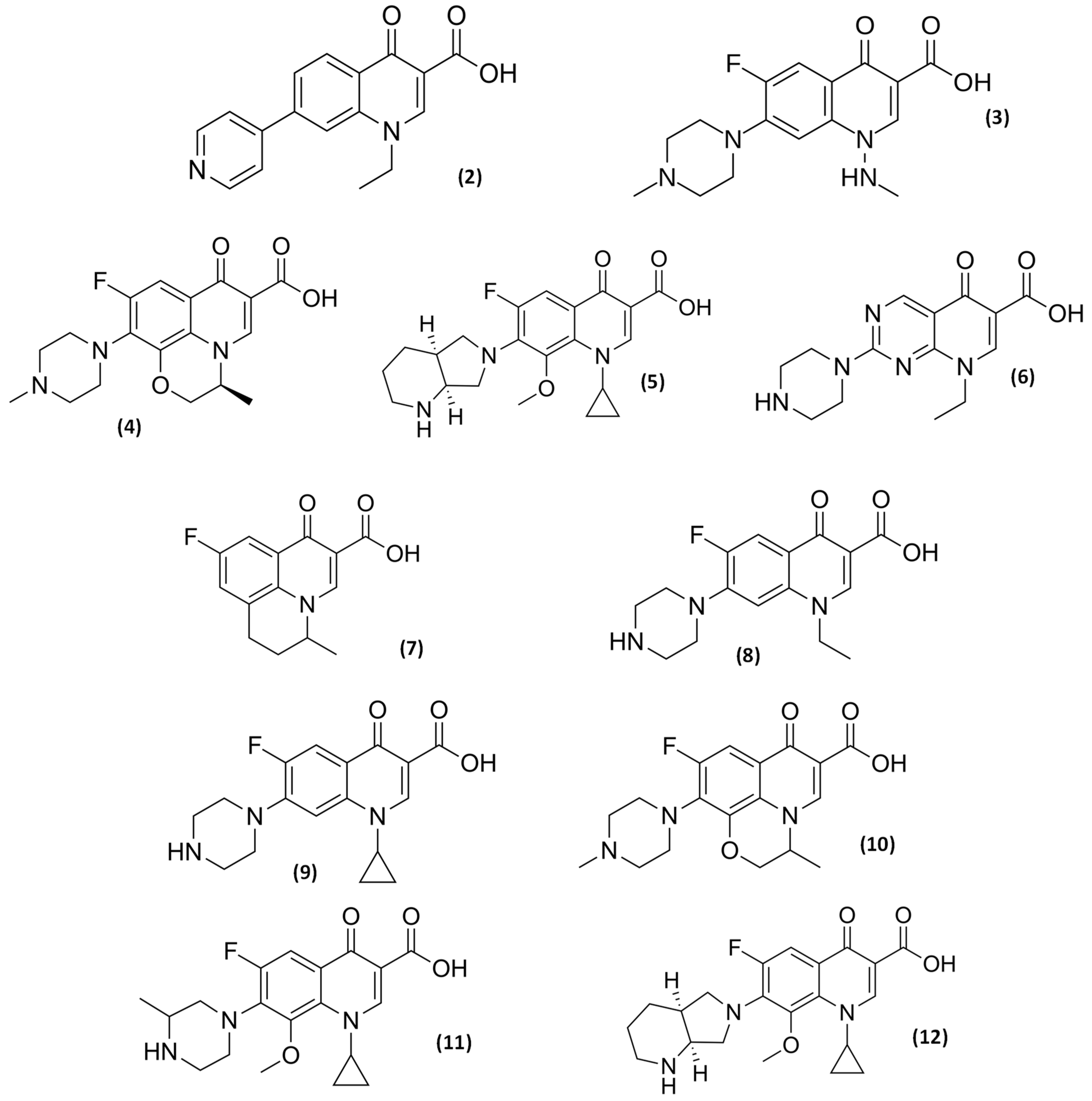
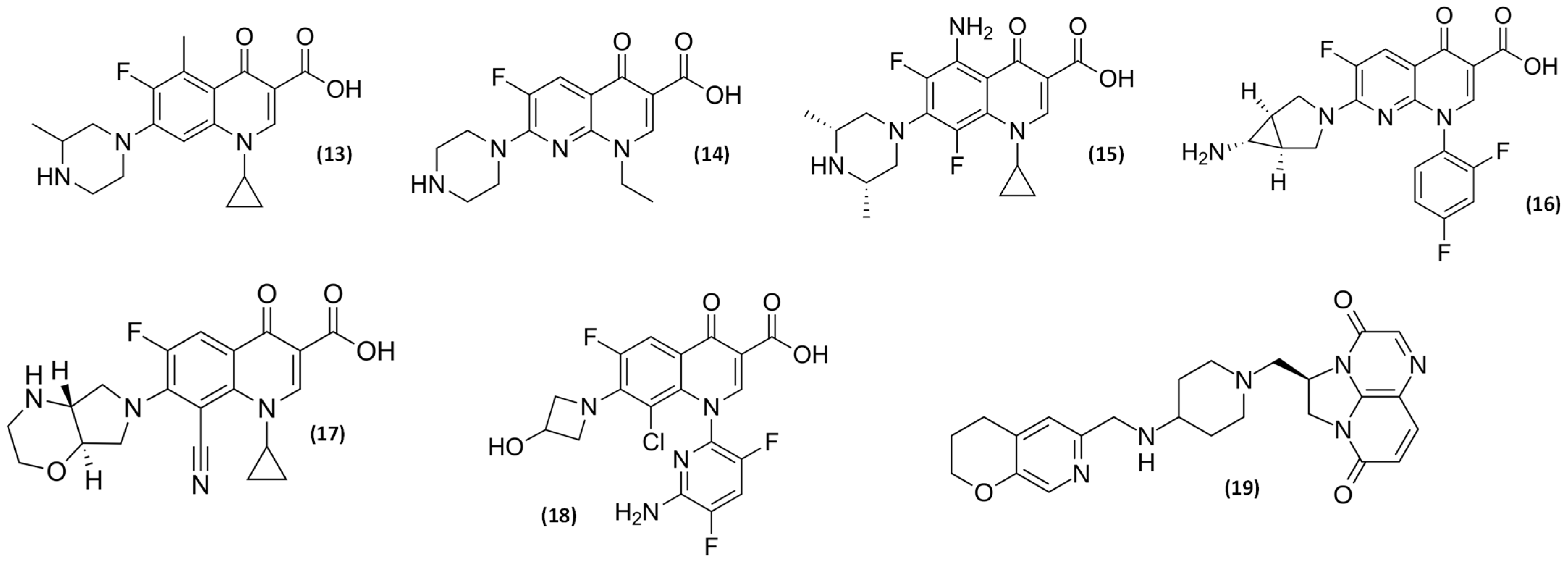
2.3. Older and Novel (Fluoro)quinolones
2.4. Tolerance and Resistance Mechanisms Related to (Fluoro)quinolones
| Feature | Description | Reference(s) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistance | Main Mechanisms of Resistance |
| [4,8,9,19,57,58,64] |
| Key Targets for Resistance |
| ||
| Species with Most Documented Resistance |
| ||
| Drivers of Resistance |
| ||
| Tolerance | Mechanisms of Tolerance |
| [18,94] |
| Approach | Narrative | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Combination Therapy | Pairing (fluoro)quinolones with complementary antimicrobials has shown synergistic effects against resistant pathogens. The combination of levofloxacin with colistin demonstrates enhanced activity against multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa through increased bacterial membrane permeability. | [95,96,97,98,99] |
| Efflux Pump Inhibitors | Co-administration of efflux pump inhibitors with (fluoro)quinolones reverses resistance in ESKAPE pathogens. Compounds like phenylalanine-arginine β-naphthylamide (PAβN) restore ciprofloxacin susceptibility in resistant A. baumannii by blocking efflux mechanisms. | [99,100,101,102,103] |
| Nanocarrier Delivery Systems | Lipid and polymer nanoparticles improve (fluoro)quinolone pharmacokinetics and target delivery. Ciprofloxacin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles demonstrate enhanced biofilm penetration and increased antibacterial activity against intracellular pathogens. | [104,105,106] |
| Biofilm-Targeting Strategies | Modified (fluoro)quinolones with anti-biofilm properties address persistent infections. Ciprofloxacin conjugated with iron chelators disrupts established biofilms in chronic respiratory infections through coordinated antimicrobial and iron sequestration mechanisms. | [107,108,109,110] |
| (Fluoro)quinolone Hybrids | Novel hybrid molecules combining (fluoro)quinolone pharmacophores with other antimicrobial moieties enhance spectrum and potency. Ciprofloxacin-triazole hybrids demonstrate improved activity against (fluoro)quinolone-resistant S. aureus while maintaining Gram-negative coverage. | [111,112,113,114] |
| Photodynamic Antimicrobial Therapy | Light-activated (fluoro)quinolone derivatives generate reactive oxygen species for enhanced bactericidal activity. Photoactivated ciprofloxacin conjugates demonstrate efficacy against resistant pathogens through mechanisms distinct from conventional antibiotic action. | [114,115,116,117,118] |
| Pulmonary and Topical Delivery Systems | Alternative administration routes optimize (fluoro)quinolone delivery to specific infection sites. Inhaled levofloxacin formulations achieve higher local concentrations in respiratory infections while minimizing systemic exposure and toxicity. | [119,120,121,122,123] |
| pH-Responsive Delivery Systems | Smart delivery platforms release (fluoro)quinolones specifically under infection-associated acidic conditions. pH-sensitive hydrogels delivering delafloxacin provide enhanced activity in the acidic microenvironment of abscesses and infected tissues. | [78,124] |
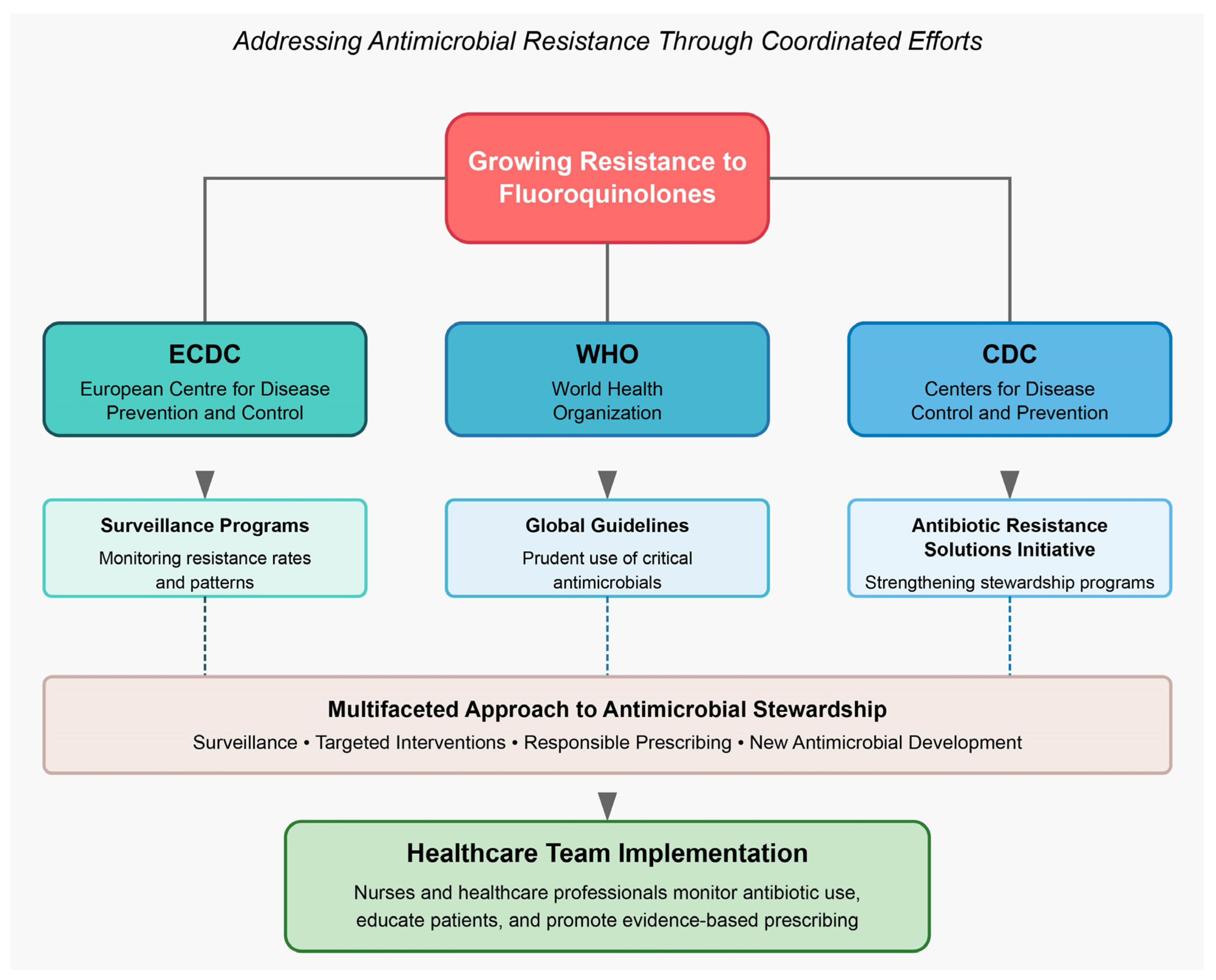
2.5. Where Are We Presently on (Fluoro)quinolone Stewardship?
3. Bibliographic Search
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, Y.; Zhao, L. The Antibacterial Activity of Fluoroquinolone Derivatives: An Update (2018–2021). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 224, 113741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, P.; Anuradha; Chandra, A.; Tanwar, T.; Sahu, S.K.; Mittal, A. Emerging Quinoline- and Quinolone-Based Antibiotics in the Light of Epidemics. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2022, 100, 765–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Jacome, L.E.; Mercado-Casillas, Y.M.; Méndez-Sotelo, B.J.; Jiménez-Cortes, J.G.; Tovar-García, A.; Estrada-Velasco, A.Y.; Almeida-Villegas, J.A.; Martínez, J.D.P.; García-Contreras, R. Anti-Bacterial Agents. In Encyclopedia of Infection and Immunity; Rezaei, N., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) Group. Opinion of the Scientific Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ) Related to Campylobacter in Animals and Foodstuffs. EFSA J. 2005, 3, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Kumar, A.; Malik, A.K.; Singh, B.; Rao, A.L.J. Spectrophotometric Methods for the Determination of Fluoroquinolones: A Review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2008, 38, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Kim, E.Y.; Kim, Y.J. Systemic Use of Fluoroquinolone in Children. Korean J. Pediatr. 2013, 56, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Goldman, J.L. Safety Concerns Surrounding Quinolone Use in Children. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 56, 1060–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.R.; Arias, C.A. ESKAPE pathogens: Antimicrobial resistance, epidemiology, clinical impact and therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 598–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulani, M.S.; Kamble, E.E.; Kumkar, S.N.; Tawre, M.S.; Pardesi, K.R. Emerging Strategies to Combat ESKAPE Pathogens in the Era of Antimicrobial Resistance: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 403107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, J.A.; Attallah, D.; Al-Rabia, M.W.; Alqarni, M.A.; Alkuwaity, K.K.; Almoghrabi, Y.; Daghistani, H.; Ismail, M.A.; Sharif, A.T.; Redwan, B.; et al. Epidemiology and Clinical Impact of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus at King Abdulaziz University Hospital (2015–2022): Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Mortality. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2025, 18, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, A.A.; Birhanu, A.G. Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus: Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Drug Resistance Development and Novel Strategies to Combat. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 7641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyres, K.L.; Lam, M.M.C.; Holt, K.E. Population Genomics of Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 344–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imperi, F.; Foglia, F.; Ambrosino, A.; Bashir, S.; Finamore, E.; Zannella, C.; Donnarumma, G.; De Filippis, A.; Galdiero, M. Prevalence of Acinetobacter Baumannii Multidrug Resistance in University Hospital Environment. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfadadny, A.; Ragab, R.F.; AlHarbi, M.; Badshah, F.; Ibáñez-Arancibia, E.; Farag, A.; Hendawy, A.O.; De los Ríos-Escalante, P.R.; Aboubakr, M.; Zakai, S.A.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa: Navigating Clinical Impacts, Current Resistance Trends, and Innovations in Breaking Therapies. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1374466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Villodres, Á.; Soto-Gallego, C.; Ortiz De La Rosa, J.M.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, M.; Casimiro-Soriguer, C.S.; Gimeno-Gascón, A.; Cisneros, J.M.; Lepe, J.A. Impact of the Inoculum Effect on Cefepime Activity against AmpC-Hyperproducing Enterobacter Spp.: Insights into Resistance Mechanisms. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2025; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, Research, and Development of New Antibiotics: The WHO Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sproston, E.L.; Wimalarathna, H.M.L.; Sheppard, S.K. Trends in Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Campylobacter. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, e000198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falzon, D.; Gandhi, N.; Migliori, G.B.; Sotgiu, G.; Cox, H.S.; Holtz, T.H.; Hollm-Delgado, M.G.; Keshavjee, S.; DeRiemer, K.; Centis, R.; et al. Resistance to Fluoroquinolones and Second-Line Injectable Drugs: Impact on Multidrug-Resistant TB Outcomes. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastida, T.; Pérez-Vázquez, M.; Campos, J.; Cortés-Lletget, M.C.; Román, F.; Tubau, F.; De la Campa, A.G.; Alonso-Tarrés, C. Levofloxacin Treatment Failure in Haemophilus Influenzae Pneumonia—Volume 9, Number 11—November 2003—Emerging Infectious Diseases Journal-CDC. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 1475–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swingler, E.A.; Song, M.; Moore, S.E.; Bohn, B.C.; Schulz, P.S.; Junkins, A.D.; Wilde, A.M. Fluoroquinolone stewardship at a community health system: A decade in review. Antimicrob. Steward. Healthc. Epidemiol. 2022, 2, e186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiesh, B.M.; Zuhour, A.; Omar, M.A.; Hamad, M.H.; Abutaha, A.; Al-Jabi, S.W.; Sabateen, A.; Zyoud, S.H. Patterns of fluoroquinolone utilization and resistance in a tertiary care hospital: A retrospective cross-sectional analysis study from a developing country. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliotti, C.; Buttazzi, R.; Sforza, S.; Moro, M.L. Resistance to Fluoroquinolones and Treatment Failure/Short-Term Relapse of Community-Acquired Urinary Tract Infections Caused by Escherichia Coli. J. Infect. 2008, 57, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, J.D.; Low, D.E. A Review of Streptococcus Pneumoniae Infection Treatment Failures Associated with Fluoroquinolone Resistance. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suda, K.J.; Garey, K.W.; Danziger, L.H. Treatment Failures Secondary to Drug Interactions with Divalent Cations and Fluoroquinolone. Pharm. World Sci. 2005, 27, 81–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics: Reminder of Measures to Reduce the Risk of Long-Lasting, Disabling and Potentially Irreversible Side Effects|European Medicines Agency (EMA). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/fluoroquinolone-antibiotics-reminder-measures-reduce-risk-long-lasting-disabling-potentially-irreversible-side-effects (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Pérez-Trallero, E.; Marimon, J.M.; Iglesias, L.; Larruskain, J. Fluoroquinolone and Macrolide Treatment Failure in Pneumococcal Pneumonia and Selection of Multidrug-Resistant Isolates. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maragakis, L.L.; Perl, T.M. Acinetobacter Baumannii: Epidemiology, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Treatment Options. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-ferreira, N.; Ferreira, V.; Teixeira, P. Occurrence and Multidrug Resistance of Campylobacter in Chicken Meat from Different Production Systems. Foods 2022, 11, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Nelson, J.M.; Barrett, T.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Rossiter, S.P.; Friedman, C.R.; Joyce, K.W.; Smith, K.E.; Jones, T.F.; Hawkins, M.A.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance among Campylobacter Strains, United States, 1997–2001—Volume 10, Number 6—June 2004—Emerging Infectious Diseases Journal-CDC. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hryhoriv, H.; Kovalenko, S.M.; Georgiyants, M.; Sidorenko, L.; Georgiyants, V. A Comprehensive Review on Chemical Synthesis and Chemotherapeutic Potential of 3-Heteroaryl Fluoroquinolone Hybrids. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suaifan, G.A.R.Y.; Mohammed, A.A.M. Fluoroquinolones Structural and Medicinal Developments (2013–2018): Where Are We Now? Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 3005–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Pan, B.; Liu, M.L. Ciprofloxacin Derivatives and Their Antibacterial Activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 146, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoor, A.F.; Yousaf, M.; Siddique, R.; Ahmad, S.; Naqvi, S.A.R.; Rizvi, S.M.A. Synthetic Strategies toward the Synthesis of Enoxacin-, Levofloxacin-, and Gatifloxacin-Based Compounds: A Review. Synth. Commun. 2017, 47, 1021–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oniga, S.; Palage, M.; Araniciu, C.; Marc, G.; Oniga, O.; Vlase, L.; Prisăcari, V.; Valica, V.; Curlat, S.; Uncu, L. Design, Synthesis, Molecular Docking, and Antibacterial Activity Evaluation of Some Novel Norfloxacin Analogues. Farmacia 2018, 66, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesher, G.Y.; Froelich, E.J.; Gruett, M.D.; Bailey, J.H.; Brundage, R.P. 1,8-Naphthyridine Derivatives. A New Class of Chemotherapeutic Agents. J. Med. Pharm. Chem. 1962, 5, 1063–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaumann, R.; Rodloff, A.C. Activities of Quinolones against Obligately Anaerobic Bacteria. Antiinfect. Agents Med. Chem. 2007, 6, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, P.S.; Legoabe, L.J.; Beteck, R.M. Quinolone: A Versatile Therapeutic Compound Class. Mol. Divers. 2022, 27, 1501–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, A.; El-mrabet, A.; Haoudi, A.; Kandri-Rodi, Y.; Mazzah, A. An Overview of Quinolones as Potential Drugs: Synthesis, Reactivity and Biological Activities. Organics 2025, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bambeke, F.; Michot, J.M.; Van Eldere, J.; Tulkens, P.M. Quinolones in 2005: An Update. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2005, 11, 256–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, J.A.; Gelone, S.P. The Newer Fluoroquinolones. Infect. Dis. Clin. North. Am. 2004, 18, 691–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillotson, G.S. Quinolones: Structure-Activity Relationships and Future Predictions. J. Med. Microbiol. 1996, 44, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.D.M.; Ziora, Z.M.; Blaskovich, M.A.T. Quinolone antibiotics. MedChemComm 2019, 10, 1719–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mitscher, L.A. Bacterial Topoisomerase Inhibitors: Quinolone and Pyridone Antibacterial Agents. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 559–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massa, S.; Corelli, F.; Mai, A.; Artico, M.; Panico, S.; Simonetti, N. Research on Antibacterial and Antifungal Agents. XI. New Antibacterial Quinolones Related to Pirfloxacin. Farmaco 1989, 44, 779–793. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, N.; Kumar, S.; Satti, N.K.; Ali, A.; Gupta, P.; Katoch, M. A Strain of Streptomyces Sp. Isolated from Rhizospheric Soil of Crataegus Oxycantha Producing Nalidixic Acid, a Synthetic Antibiotic. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 1393–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisacchi, G.S. Origins of the Quinolone Class of Antibacterials: An Expanded “Discovery Story”. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4874–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, P. Quinolone Generations: Natural History or Natural Selection? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2000, 46 (Suppl. T1), 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.C.; Jain, A.; Jain, S. Fluoroquinolone Antibacterials: A Review on Chemistry, Microbiology and Therapeutic Prospects-PubMed. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2009, 66, 587–604. [Google Scholar]
- Lucia, P.; Lucia, P.; Quinolones: Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity. Antimicrobial Agents. 2012. Available online: https://cdn.intechopen.com/pdfs/38653/intech-quinolones_synthesis_and_antibacterial_activity.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Patel, N.B.; Shaikh, A.R.; Soni, H.I.; Parmar, R.B.; Patel, J.A. In Vitro Antimicrobial, Antimycobacterial Evalution and Synthesis of Substituted 1, 2, 4-Triazole Motifs. Chem. Biol. Interface 2018, 8, 184–193. [Google Scholar]
- Hryhoriv, H.; Mariutsa, I.; Kovalenko, S.M.; Sidorenko, L.; Perekhoda, L.; Filimonova, N.; Geyderikh, O.; Georgiyants, V. Structural Modification of Ciprofloxacin and Norfloxacin for Searching New Antibiotics to Combat Drug-Resistant Bacteria. ScienceRise Pharm. Sci. 2021, 33, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, I.; King, A.; Shannon, K. Comparative In-Vitro Properties of the Quinolones. In The Quinolones; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 99–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheld, W.M. Maintaining Fluoroquinolone Class Efficacy: Review of Influencing Factors. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, E.J.C. Intra-Abdominal Anaerobic Infections: Bacteriology and Therapeutic Potential of Newer Antimicrobial Carbapenem, Fluoroquinolone, and Desfluoroquinolone Therapeutic Agents. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 35, S106–S111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, R. Etymologia: Fluoroquinolone—Volume 23, Number 5—May 2017—Emerging Infectious Diseases Journal-CDC. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budd, E.; Cramp, E.; Sharland, M.; Hand, K.; Howard, P.; Wilson, P.; Wilcox, M.; Muller-Pebody, B.; Hopkins, S. Adaptation of the WHO Essential Medicines List for National Antibiotic Stewardship Policy in England: Being AWaRe. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 3384–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, D.C.; Xie, W.L.; Cheng, G.Y.; Yue, M.; Du, X.Y.; Jiang, J. Pregnancy Related Adverse Events and Congenital Disorders Associated with Fluoroquinolones: A Real-World Pharmacovigilance Study of the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS). Heliyon 2024, 10, e37547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, M.A.; Schutze, G.E.; Byington, C.L.; Maldonado, Y.A.; Barnett, E.D.; Campbell, J.D.; Davies, H.D.; Lynfield, R.; Munoz, F.M.; Nolt, D.; et al. The Use of Systemic and Topical Fluoroquinolones. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20162706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, M.L. Vancomycin Pharmacokinetics in Neonates Receiving Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 1998, 18, 1082–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondeau, J.M. Expanded Activity and Utility of the New Fluoroquinolones: A Review. Clin. Ther. 1999, 21, 3–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthymiopoulos, C.; Bramer, S.L.; Maroli, A.; Blum, B. Theophylline and Warfarin Interaction Studies with Grepafloxacin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1997, 33 (Suppl. 1), 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggio, D.; Ananda-Rajah, M.R. Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics and Adverse Events. Aust. Prescr. 2021, 44, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliphant, C.M.; Green, G.M. Quinolones: A Comprehensive Review. Am. Fam. Physician 2002, 65, 455–465. [Google Scholar]
- Mandell, L.; Tillotson, G. Safety of Fluoroquinolones: An Update. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2002, 13, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.I.; MacGowan, A.P. Development of the Quinolones. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 51, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millanao, A.R.; Mora, A.Y.; Villagra, N.A.; Bucarey, S.A.; Hidalgo, A.A. Biological Effects of Quinolones: A Family of Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Agents. Molecules 2021, 26, 7153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, E.J.C.; Citron, D.M. Comparative Activity of Ciprofloxacin, Ofloxacin, Sparfloxacin, Temafloxacin, CI-960, CI-990, and WIN 57273 against Anaerobic Bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1992, 36, 1158–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhala, R.H.; Rao, B.; Marshall, R.; Bansal, M.B.; Thadepalli, H. In Vitro Susceptibility of Anaerobic Bacteria to Ciprofloxacin (Bay o 9867). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1984, 26, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelbaum, P.C. Quinolone Activity against Anaerobes. Drugs 1999, 58, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimings, C.; Riley, T.V. Antibiotics and Hospital-Acquired Clostridium Difficile Infection: Update of Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, I. Fever and Rash in a Husband and Wife Returning from the Cook Islands. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejo-Cancho, I.; Bosch, J.; Vergara, A.; Mascaro, J.M.; Marco, F.; Vila, J. Dermatitis by Dermatophilus Congolensis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, e73–e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifan, A.; Stanciu, C.; Girleanu, I.; Stoica, O.C.; Singeap, A.M.; Maxim, R.; Chiriac, S.A.; Ciobica, A.; Boiculese, L. Proton Pump Inhibitors Therapy and Risk of Clostridium Difficile Infection: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 6500–6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miflin, J.K.; Templeton, J.M.; Blackall, P.J. Antibiotic Resistance in Campylobacter Jejuni and Campylobacter Coli Isolated from Poultry in the South-East Queensland Region. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 59, 775–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McDonald, L.C.; Gerding, D.N.; Johnson, S.; Bakken, J.S.; Carroll, K.C.; Coffin, S.E.; Dubberke, E.R.; Garey, K.W.; Gould, C.V.; Kelly, C.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Clostridium Difficile Infection in Adults and Children: 2017 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassetti, M.; Righi, E.; Pecori, D.; Tillotson, G. Delafloxacin: An Improved Fluoroquinolone Developed through Advanced Molecular Engineering. Future Microbiol. 2018, 13, 1081–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, N.; Jansone, I.; Obidenova, T.; Simanis, R.; Meisters, J.; Straupmane, D.; Reinis, A. Antimicrobial Resistance in Nosocomial Isolates of Gram-Negative Bacteria: Public Health Implications in the Latvian Context. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Hou, H.; Gao, F. Current Scenario of Quinolone Hybrids with Potential Antibacterial Activity against ESKAPE Pathogens. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 247, 115026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Póvoa, P.; Moniz, P.; Pereira, J.G.; Coelho, L. Optimizing Antimicrobial Drug Dosing in Critically Ill Patients. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaglione, F.; Paraboni, L. Pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics of antibacterials in the Intensive Care Unit: Setting appropriate dosing regimens. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2008, 32, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kherroubi, L.; Bacon, J.; Rahman, K.M. Navigating Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Gram-Negative Bacteria: A Comprehensive Evaluation. JAC Antimicrob. Resist. 2024, 6, dlae127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Z.; Plésiat, P.; Nikaido, H. The Challenge of Efflux-Mediated Antibiotic Resistance in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luscher, A.; Moynie, L.; Auguste, P.S.; Bumann, D.; Mazza, L.; Pletzer, D.; Naismith, J.H.; Köhlera, T. TonB-Dependent Receptor Repertoire of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa for Uptake of Siderophore-Drug Conjugates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00097-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Miyajima, F.; Roberts, P.; Ellison, L.; Pickard, D.J.; Martin, M.J.; Connor, T.R.; Harris, S.R.; Fairley, D.; Bamford, K.B.; et al. Emergence and global spread of epidemic healthcare-associated Clostridium difficile. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tängdén, T.; Carrara, E.; Hellou, M.M.; Yahav, D.; Paul, M. Introducing New Antibiotics for Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria: Obstacles and the Way Forward. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2024, 31, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papp-Wallace, K.M.; Bonomo, R.A. New β-Lactamase Inhibitors in the Clinic. Infect. Dis. Clin. North. Am. 2016, 30, 441–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman Prieto, A.M.; van Schaik, W.; Rogers, M.R.C.; Coque, T.M.; Baquero, F.; Corander, J.; Willems, R.J.L. Global Emergence and Dissemination of Enterococci as Nosocomial Pathogens: Attack of the Clones? Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 198281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; p. 72. [Google Scholar]
- Shealy, S.C.; Brigmon, M.M.; Justo, J.A.; Brandon Bookstaver, P.; Kohn, J.; Al-Hasan, M.N. Impact of Reappraisal of Fluoroquinolone Minimum Inhibitory Concentration Susceptibility Breakpoints in Gram-Negative Bloodstream Isolates. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Forde, B.M.; Kidd, T.J.; Harris, P.N.A.; Schembri, M.A.; Beatson, S.A.; Paterson, D.L.; Walker, M.J. Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00181-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, T.T.; Minejima, E.; Chiu, C.A.; Butler-Wu, S.M. Don’t Get Wound Up: Revised Fluoroquinolone Breakpoints for Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, 2072–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defife, R.; Scheetz, M.H.; Feinglass, J.M.; Postelnick, M.J.; Scarsr, K.K. Effect of Differences in MIC Values on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Bloodstream Infections Caused by Gram-Negative Organisms Treated with Levofloxacin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bergh, B.; Fauvart, M.; Michiels, J. Formation, Physiology, Ecology, Evolution and Clinical Importance of Bacterial Persisters. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 219–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Gu, J.; Zhang, Y. Bacterial Persisters: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Development. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarika, A.; Galani, I.; Pistiki, A.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J. Time–Kill Effect of Levofloxacin on Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and Acinetobacter Baumannii: Synergism with Imipenem and Colistin. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Yang, H.; Hu, L.; Ye, Y.; Li, J. Activity of Levofloxacin in Combination with Colistin against Acinetobacter Baumannii: In Vitro and in a Galleria Mellonella Model. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2017, 50, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Momenzadeh, M.; Soltani, R.; Shafiee, F.; Hakamifard, A.; Pourahmad, M.; Abbasi, S. The Effectiveness of Colistin/Levofloxacin Compared to Colistin/Meropenem in the Treatment of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (VAP) Caused by Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 18, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogfelt, A.; Cláudio Nascimento Da Silva, L.; Gomes-Abreu, A.; Arshad, N.; Azzam, W.; Zilberberg, M.D.; Shorr, A.F. Acinetobacter Baumannii Complex Infections: New Treatment Options in the Antibiotic Pipeline. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compagne, N.; Vieira Da Cruz, A.; Müller, R.T.; Hartkoorn, R.C.; Flipo, M.; Pos, K.M. Update on the Discovery of Efflux Pump Inhibitors against Critical Priority Gram-Negative Bacteria. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, K. Efflux-Mediated Resistance to Fluoroquinolones in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.L.A.R.; Pereira, R.L.S.; Rocha, J.E.; Farias, P.A.M.; Freitas, T.S.; Caldas, F.R.d.L.; Figueredo, F.G.; Sampaio, N.F.L.; Oliveira-Tintino, C.D.d.M.; Tintino, S.R.; et al. Unlocking Bacterial Defense: Exploring the Potent Inhibition of NorA Efflux Pump by Coumarin Derivatives in Staphylococcus Aureus. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 190, 106608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Ahn, J. Advances in the Discovery of Efflux Pump Inhibitors as Novel Potentiators to Control Antimicrobial-Resistant Pathogens. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türeli, N.G.; Torge, A.; Juntke, J.; Schwarz, B.C.; Schneider-Daum, N.; Türeli, A.E.; Lehr, C.M.; Schneider, M. Ciprofloxacin-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles against Cystic Fibrosis P. Aeruginosa Lung Infections. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 117, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, A.; Ali, S.M.; Rana, N.F.; Tanweer, T.; Batool, A.; Webster, T.J.; Menaa, F.; Riaz, S.; Rehman, Z.; Batool, F.; et al. Ciprofloxacin-Loaded Gold Nanoparticles against Antimicrobial Resistance: An in Vivo Assessment. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Zou, J.; Xin, H.; Sun, J.; Han, T.; Sun, M.; Niu, M. Nanomedicines as Disruptors or Inhibitors of Biofilms: Opportunities in Addressing Antimicrobial Resistance. J. Control. Release 2025, 381, 113589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, A.G.; Yousef, A.E. Combating Bacterial Biofilms: Current and Emerging Antibiofilm Strategies for Treating Persistent Infections. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roszkowski, P.; Bielenica, A.; Stefańska, J.; Majewska, A.; Markowska, K.; Pituch, H.; Koliński, M.; Kmiecik, S.; Chrzanowska, A.; Struga, M. Antibacterial and Anti-Biofilm Activities of New Fluoroquinolone Derivatives Coupled with Nitrogen-Based Heterocycles. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 179, 117439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.; Perry, A.; Perry, J.D.; Gould, F.K.; Samuel, J. In Vitro Effects of Combined Iron Chelation, Antibiotics and Matrix Disruption on Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Luo, B.Z.; Li, C.M.; Liang, J.L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, W.M.; Guo, J.L. Discovery of 3-Hydroxypyridin-4(1H)-Ones Ester of Ciprofloxacin as Prodrug to Combat Biofilm-Associated Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 289, 117396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samir, M.; Ramadan, M.; Abdelrahman, M.H.; Abdelbaset, M.S.; Abdel-Aziz, M.; Halby, H.M.; Gamal El-Din, A.; Abuo-Rahma, G.E.-D.A. New Ciprofloxacin-Pyrazolopyrimidine Hybrids as Topoisomerase IV and Gyrase Inhibitors against MRSA AUMC 261. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202303672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plech, T.; Kaproń, B.; Paneth, A.; Kosikowska, U.; Malm, A.; Strzelczyk, A.; Stączek, P.; Świątek, Ł.; Rajtar, B.; Polz-Dacewicz, M. Determination of the Primary Molecular Target of 1,2,4-Triazole-Ciprofloxacin Hybrids. Molecules 2015, 20, 6254–6272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lungu, I.A.; Moldovan, O.L.; Biriș, V.; Rusu, A. Fluoroquinolones Hybrid Molecules as Promising Antibacterial Agents in the Fight against Antibacterial Resistance. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Kulkarni, A.; Sharma, A.K.; Chakrapani, H. Visible-Light Controlled Release of a Fluoroquinolone Antibiotic for Antimicrobial Photopharmacology. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 2155–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorowicz, J.; Sączewski, J. Modifications of Quinolones and Fluoroquinolones: Hybrid Compounds and Dual-Action Molecules. Monatshefte Chem.-Chem. Mon. 2018, 149, 1199–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, L.; Zeng, J.; Qiu, H.; Tan, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhao, H.; Gu, Y. Enhanced Antimicrobial Activity through the Combination of Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy and Low-Frequency Ultrasonic Irradiation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 183, 114168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.; Feng, G.; Zhuo, J.; Sun, G. UV Light-Induced Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species and Antimicrobial Properties of Cellulose Fabric Modified by 3,3′,4,4′-Benzophenone Tetracarboxylic Acid. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 27918–27924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, S.; Schito, G.C.; Schito, A.M.; Zuccari, G. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-Mediated Antibacterial Oxidative Therapies: Available Methods to Generate ROS and a Novel Option Proposal. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panthi, V.K.; Fairfull-Smith, K.E.; Islam, N. Ciprofloxacin-Loaded Inhalable Formulations against Lower Respiratory Tract Infections: Challenges, Recent Advances, and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elborn, J.S.; Flume, P.A.; Van Devanter, D.R.; Procaccianti, C. Management of Chronic Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection with Inhaled Levofloxacin in People with Cystic Fibrosis. Future Microbiol. 2021, 16, 1087–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardikasari, S.A.; Sipos, B.; Csóka, I.; Katona, G. Nasal Route for Antibiotics Delivery: Advances, Challenges and Future Opportunities Applying the Quality by Design Concepts. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 77, 103887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.; Alves, G.; Oliveira, P.; Fortuna, A.; Falcão, A. Intranasal Delivery of Ciprofloxacin to Rats: A Topical Approach Using a Thermoreversible in Situ Gel. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 97, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Xu, K. Advancements and Prospects of PH-Responsive Hydrogels in Biomedicine. Gels 2025, 11, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Reporting Protocol 2024. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/AMR-reporting-protocol-2024.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2025).
- Antimicrobial Resistance Solutions Initiative|Antimicrobial Resistance|CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/antimicrobial-resistance/programs/index.html (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Wiley, K.C.; Villamizar, H.J. Antibiotic Resistance Policy and the Stewardship Role of the Nurse. Policy Polit. Nurs. Pract. 2018, 20, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.; Xu, J.; Ischia, J.; Bolton, D. Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Urinary Tract Infections: Epidemiology, Mechanisms of Action and Management Strategies. BJUI Compass 2024, 5, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenover, F.C. Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, S3–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodrigues, C.F.; Silva, F. The Rise, Fall, and Rethink of (Fluoro)quinolones: A Quick Rundown. Pathogens 2025, 14, 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060525
Rodrigues CF, Silva F. The Rise, Fall, and Rethink of (Fluoro)quinolones: A Quick Rundown. Pathogens. 2025; 14(6):525. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060525
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodrigues, Célia Fortuna, and Francisco Silva. 2025. "The Rise, Fall, and Rethink of (Fluoro)quinolones: A Quick Rundown" Pathogens 14, no. 6: 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060525
APA StyleRodrigues, C. F., & Silva, F. (2025). The Rise, Fall, and Rethink of (Fluoro)quinolones: A Quick Rundown. Pathogens, 14(6), 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060525