Genomic and Pangenomic Insights into Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. oncorhynchi subsp. nov.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Genome Sequencing and Analysis
2.3. Multilocus Phylogenetic Analysis (MLPA)
2.4. Comparative and Functional Genome Analysis
2.5. Morphological, Biochemical, and Physiological Tests
2.5.1. Biochemical Features
2.5.2. Growth Characteristics and Environmental Tolerance
2.6. Assessment of Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Susceptibility
3. Results
3.1. Phenotypic Characteristics
3.2. Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Susceptibility
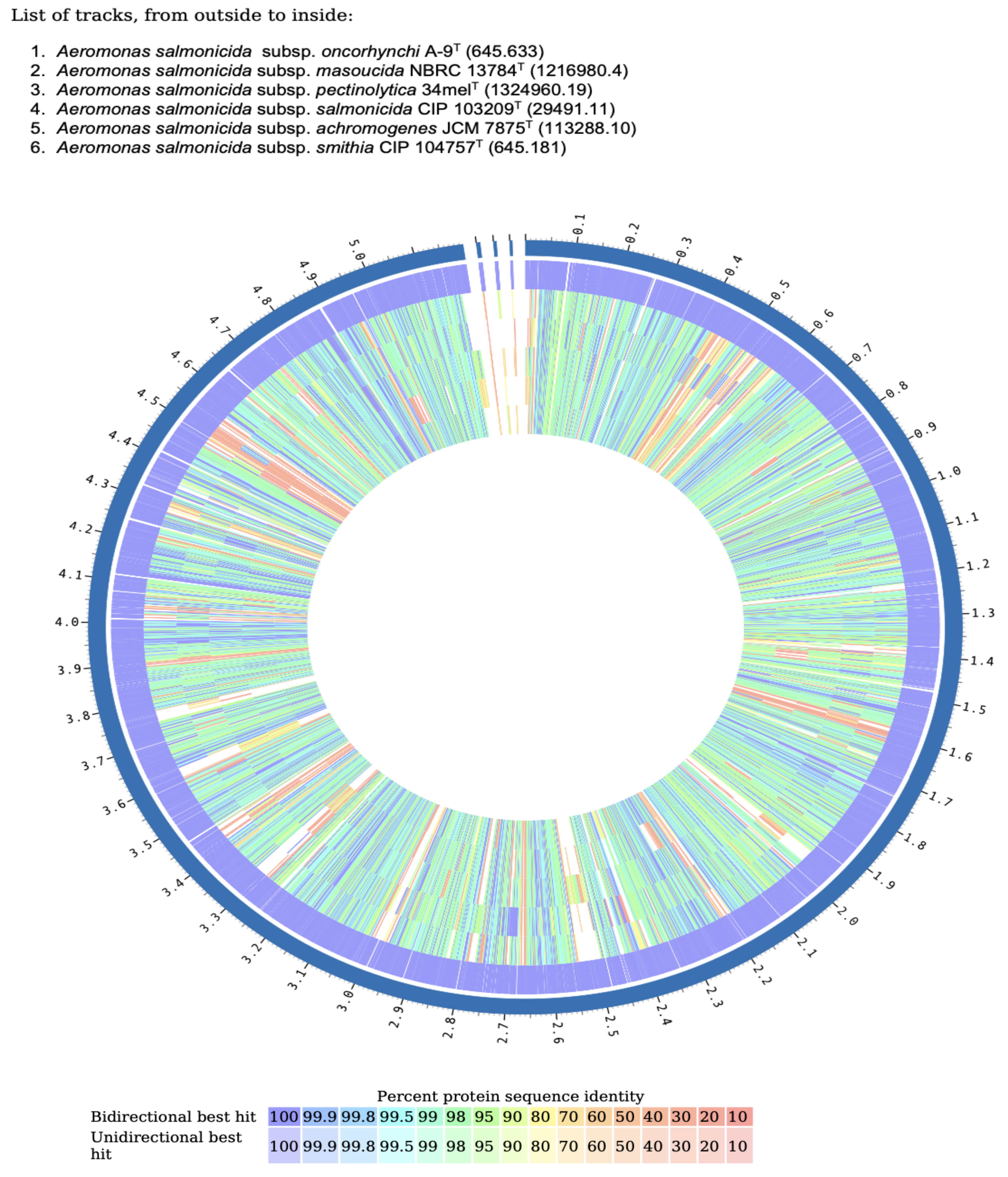
3.3. Genome Analysis
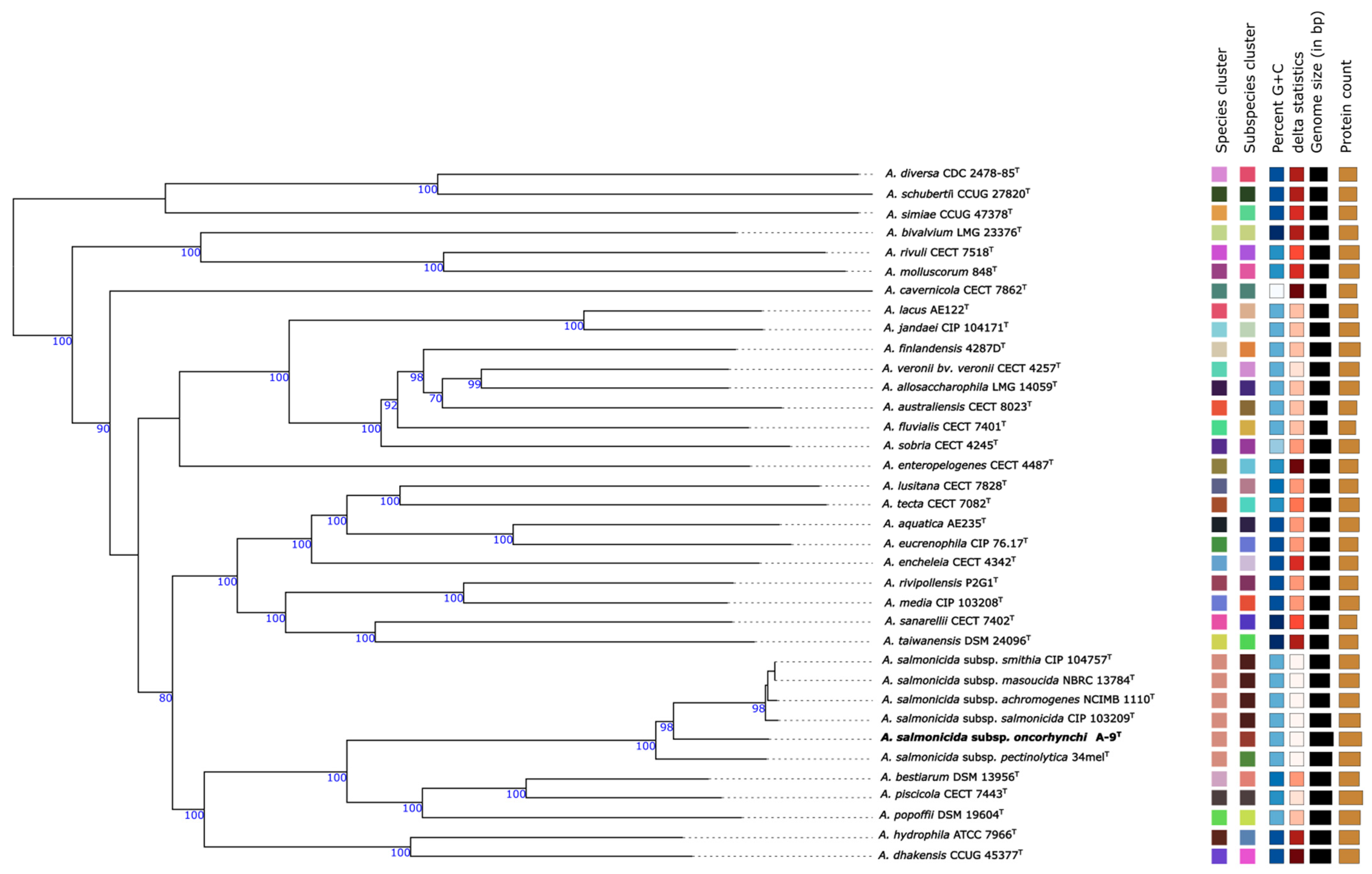
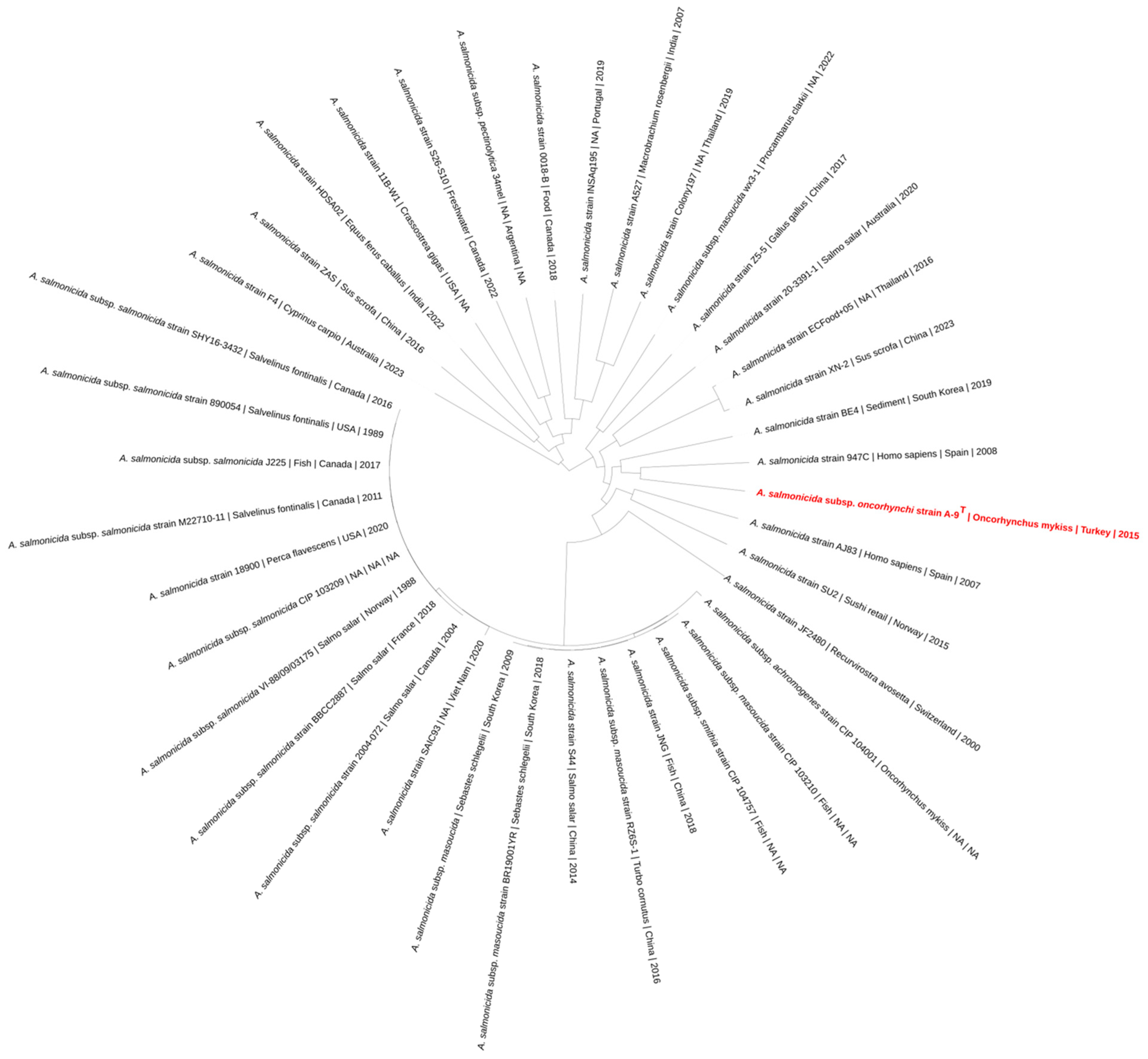
3.4. MLPA-Based Phylogenetic Results
3.5. Virulence Factors
3.6. Antimicrobial Resistance Gene Analysis
3.7. Genome-Based Phylogeny and Subspecies Delineation
3.8. Comparative Proteome Analysis
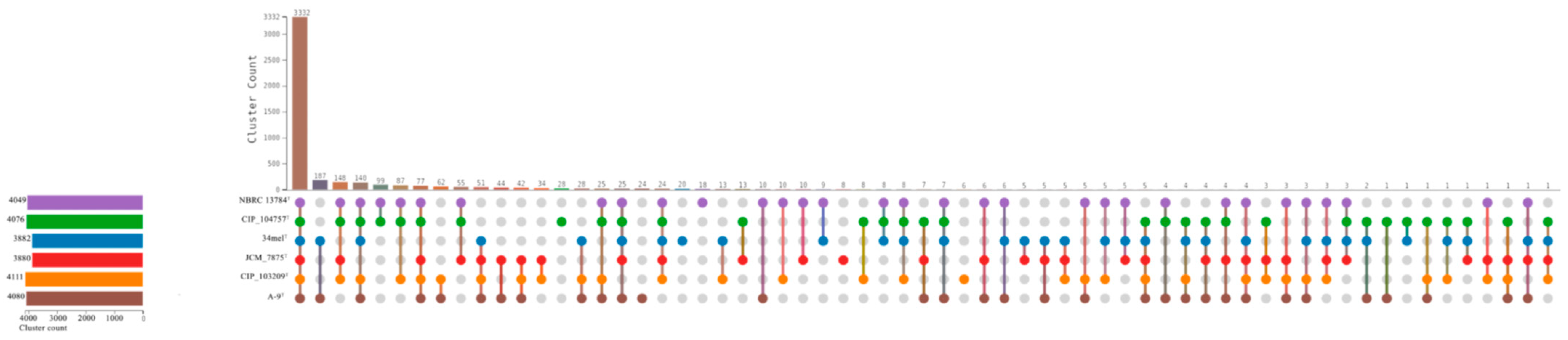
3.9. Pangenome Analysis
3.10. Description of Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. oncorhynchi subsp. nov.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Austin, B.; Austin, D.A. Enterobacteriaceae Representatives. In Bacterial Fish Pathogens: Disease of Farmed and Wild Fish; Austin, B., Austin, D.A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 323–396. ISBN 978-3-319-32674-0. [Google Scholar]
- Reith, M.; Singh, R.K.; Curtis, B.A.; Boyd, J.M.; Bouevitch, A.; Kimball, J.; Munholland, J.; Murphy, C.; Sarty, D.; Williams, J.S.; et al. The Genome of Aeromonas salmonicida Subsp. Salmonicida A449: Insights Into the Evolution of a Fish Pathogen. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, A.T.; Trudel, M.V.; Paquet, V.E.; Boyle, B.; Tanaka, K.H.; Dallaire-Dufresne, S.; Daher, R.; Frenette, M.; Derôme, N.; Charette, S.J. Detection of Variants of the pRAS3, pAB5S9, and pSN254 Plasmids in Aeromonas salmonicida Subsp. Salmonicida: Multidrug Resistance, Interspecies Exchanges, and Plasmid Reshaping. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 7367–7374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Merino, S.; Tomás, J.M. The Aeromonas salmonicida Lipopolysaccharide Core From Different Subspecies: The Unusual Subsp. Pectinolytica. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björnsdóttir, B.; Guðmundsdóttir, S.; Bambir, S.H.; Gudmundsdóttir, B.K. Experimental Infection of Turbot, Scophthalmus maximus (L.), by Aeromonas salmonicida Subsp. Achromogenes and Evaluation of Cross Protection Induced by a Furunculosis Vaccine. J. Fish Dis. 2005, 28, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudel, M.V.; Vincent, A.T.; Attéré, S.A.; Labbé, M.; Derôme, N.; Culley, A.I.; Charette, S.J. Diversity of Antibiotic-Resistance Genes in Canadian Isolates of Aeromonas salmonicida Subsp. Salmonicida: Dominance of pSN254b and Discovery of pAsa8. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burr, S.E.; Pugovkin, D.; Wahli, T.; Segner, H.; Frey, J. Attenuated Virulence of an Aeromonas salmonicida Subsp. Salmonicida Type III Secretion Mutant in a Rainbow Trout Model. Microbiology 2005, 151, 2111–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebanks, R.O.; Goguen, M.; Knickle, L.; Dacanay, A.; Leslie, A.; Ross, N.W.; Pinto, D.M. Analysis of a Ferric Uptake Regulator (Fur) Knockout Mutant in Aeromonas salmonicida Subsp. Salmonicida. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 162, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, S.B.; Marcoux, P.-É.; Paquet, V.E.; Zoubaï, S.; Vy Can, T.N.; Attéré, S.A.; Vincent, A.T.; Charette, S.J. Expansion of the Tetracycline Resistome in Aeromonas salmonicida With a Tet(D) Gene Found in Plasmids pAsa-2900 and pAsa-2900b. Front. Bacteriol. 2024, 3, 1418706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, F.; Zamora-Lagos, M.-A.; Blettinger, M.; Yeroslaviz, A.; Dahl, A.; Gruber, S.; Habermann, B.H. The Complete and Fully Assembled Genome Sequence of Aeromonas salmonicida Subsp. Pectinolytica and Its Comparative Analysis with Other Aeromonas Species: Investigation of the Mobilome in Environmental and Pathogenic Strains. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B. Methods for the Diagnosis of Bacterial Fish Diseases. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2019, 1, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, F. TrimGalore: A Wrapper Around Cutadapt and FastQC to Consistently Apply Adapter and Quality Trimming to FastQ Files, with Extra Functionality for RRBS Data; GitHub: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2017; Available online: https://github.com/FelixKrueger/TrimGalore (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving Bacterial Genome Assemblies from Short and Long Sequencing Reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, R.D.; Assaf, R.; Brettin, T.; Conrad, N.; Cucinell, C.; Davis, J.J.; Dempsey, D.M.; Dickerman, A.; Dietrich, E.M.; Kenyon, R.W.; et al. Introducing the Bacterial and Viral Bioinformatics Resource Center (BV-BRC): A Resource Combining PATRIC, IRD and ViPR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D678–D689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatusova, T.; DiCuccio, M.; Badretdin, A.; Chetvernin, V.; Nawrocki, E.P.; Zaslavsky, L.; Lomsadze, A.; Pruitt, K.D.; Borodovsky, M.; Ostell, J. NCBI Prokaryotic Genome Annotation Pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6614–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Carbasse, J.S.; Peinado-Olarte, R.L.; Göker, M. TYGS and LPSN: A Database Tandem for Fast and Reliable Genome-Based Classification and Nomenclature of Prokaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D801–D807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, M.; Rosselló-Móra, R.; Oliver Glöckner, F.; Peplies, J. JSpeciesWS: A Web Server for Prokaryotic Species Circumscription Based on Pairwise Genome Comparison. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 929–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alperi, A.; Figueras, M.; Inza, I.; Martinez-Murcia, A. Analysis of 16S rRNA Gene Mutations in a Subset of Aeromonas Strains and Their Impact in Species Delineation. Int. Microbiol. Off. J. Span. Soc. Microbiol. 2008, 11, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Murcia, A.J.; Monera, A.; Saavedra, M.J.; Oncina, R.; Lopez-Alvarez, M.; Lara, E.; Figueras, M.J. Multilocus Phylogenetic Analysis of the Genus Aeromonas. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 34, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Bravo, A.; Figueras, M.J. An Update on the Genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, Epidemiology, and Pathogenicity. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, N.D.; Lund, S.P.; Colman, R.E.; Foster, J.T.; Sahl, J.W.; Schupp, J.M.; Keim, P.; Morrow, J.B.; Salit, M.L.; Zook, J.M. Best Practices for Evaluating Single Nucleotide Variant Calling Methods for Microbial Genomics. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML Version 8: A Tool for Phylogenetic Analysis and Post-Analysis of Large Phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v6: Recent Updates to the Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation Tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W78–W82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Zheng, D.; Zhou, S.; Chen, L.; Yang, J. VFDB 2022: A General Classification Scheme for Bacterial Virulence Factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D912–D917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcock, B.P.; Huynh, W.; Chalil, R.; Smith, K.W.; Raphenya, A.R.; Wlodarski, M.A.; Edalatmand, A.; Petkau, A.; Syed, S.A.; Tsang, K.K.; et al. CARD 2023: Expanded Curation, Support for Machine Learning, and Resistome Prediction at the Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D690–D699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid Prokaryotic Genome Annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, V.; Afgan, E.; Gu, Q.; Clements, D.; Blankenberg, D.; Goecks, J.; Taylor, J.; Nekrutenko, A. The Galaxy Platform for Accessible, Reproducible and Collaborative Biomedical Analyses: 2020 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W395–W402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.K.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid Large-Scale Prokaryote Pan Genome Analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lu, F.; Luo, Y.; Bie, L.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y. OrthoVenn3: An Integrated Platform for Exploring and Visualizing Orthologous Data across Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W397–W403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantalapiedra, C.P.; Hernández-Plaza, A.; Letunic, I.; Bork, P.; Huerta-Cepas, J. eggNOG-Mapper v2: Functional Annotation, Orthology Assignments, and Domain Prediction at the Metagenomic Scale. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 5825–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An Information Aesthetic for Comparative Genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, N. Identification of Pseudomonas Pyocyanea by the Oxidase Reaction. Nature 1956, 178, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiner, K. Catalase Test Protocol. Am. Soc. Microbiol. 2010, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kwasny, S.M.; Opperman, T.J. Static Biofilm Cultures of Gram-positive Pathogens Grown in a Microtiter Format Used for Anti-biofilm Drug Discovery. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2010, 50, 13A.8.1–13A.8.23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hossary, D.; Mahdy, A.; Elariny, E.Y.; Askora, A.; Merwad, A.M.; Saber, T.; Dahshan, H.; Hakami, N.Y.; Ibrahim, R.A. Antibiotic Resistance, Virulence Gene Detection, and Biofilm Formation in Aeromonas spp. Isolated from Fish and Humans in Egypt. Biology 2023, 12, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VET03/VET04-S2; CLSI Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Bacteria Isolated From Aquatic Animals. Second Informational Supplement; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2014.
- Austin, B.; Austin, D.A. Bacterial Fish Pathogens. Disease in Farmed and Wild Fish; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1986; p. 434. [Google Scholar]
- Pavan, M.; Abbott, S.; Zorzopulos, J.; Janda, J. Aeromonas salmonicida Subsp. Pectinolytica Subsp. Nov., a New Pectinase-Positive Subspecies Isolated from a Heavily Polluted River. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänninen, M.-L.; Hirvelä-Koski, V. Molecular and Phenotypic Methods for the Characterization of Atypical Aeromonas salmonicida. Vet. Microbiol. 1997, 56, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalsgaard, I.; Gudmundsdóttir, B.K.; Helgason, S.; Høie, S.; Thoresen, O.F.; Wichardt, U.P.; Wiklund, T. Identification of Atypical Aeromonas salmonicida: Inter-laboratory Evaluation and Harmonization of Methods. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 84, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popoff, M. Genus III. Aeromonas Kluyver and Van Niel 1936, 389 A^L. Bergy’s Man. Syst. Bacteriol. 1984, 1, 545–548. [Google Scholar]
- Hahnel, G.; Gould, R. Effects of Temperature on Biochemical Reactions and Drug Resistance of Virulent and a Virulent Aeromonas salmonicida. J. Fish Dis. 1982, 5, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T. A New Subspecies of Aeromonas salmonicida as an Etiological Agent of Furunculosis on “Sakuramasu”(Oncorhynchus masou) and Pink Salmon (O. gorbuscha) Rearing for Maturity Part 1. On the Morphological and Physiological Properties. Fish Pathol. 1969, 3, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Klenk, H.-P.; Göker, M. Taxonomic Use of DNA G+C Content and DNA–DNA Hybridization in the Genomic Age. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.J.; Kim, D.; Kim, W.; Kim, C.; Jung, S.; Oh, M.; Kim, D. Atypical Aeromonas salmonicida Infection in the Black Rockfish, Sebastes schlegeli Hilgendorf, in Korea. J. Fish Dis. 2010, 34, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, M.; Rodrigues, J.; Matias, R.; Jordao, L. Aeromonas spp. in Freshwater Bodies: Antimicrobial Resistance and Biofilm Assembly. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen-Ivey, C.R.; Hossain, M.J.; Odom, S.E.; Terhune, J.S.; Hemstreet, W.G.; Shoemaker, C.A.; Zhang, D.; Xu, D.-H.; Griffin, M.J.; Liu, Y.-J. Classification of a Hypervirulent Aeromonas Hydrophila Pathotype Responsible for Epidemic Outbreaks in Warm-Water Fishes. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcoux, P.-É.; Attéré, S.A.; Paquet, V.E.; Paquet, M.F.; Girard, S.B.; Farley, J.; Frenette, M.; Vincent, A.T.; Charette, S.J. Host Dependent-Transposon for a Plasmid Found in Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida That Bears a catB3 Gene for Chloramphenicol Resistance. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.H.; Dallaire-Dufresne, S.; Daher, R.; Frenette, M.; Charette, S.J. An Insertion Sequence-Dependent Plasmid Rearrangement in Aeromonas salmonicida Causes the Loss of the Type Three Secretion System. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacanay, A.; Boyd, J.M.; Fast, M.D.; Knickle, L.C.; Reith, M. Aeromonas salmonicida Type I Pilus System Contributes to Host Colonization but Not Invasion. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2010, 88, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawari, N. Aeromonas salmonicida: A Very Rare but Potential Threat to Human. Indian J. Child Health 2024, 10, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagar, V.; Godambe, L.P.; Bandekar, J.R.; Shashidhar, R. Biofilm Formation by Aeromonas Strains Under Food-Related Environmental Stress Conditions. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2017, 41, e13182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Ji, X.; Jiang, B.; Yuan, T.; Gerile, C.L.M.; Zhu, L.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Guo, X.; et al. Virulence, Antibiotic Resistance, and Phylogenetic Relationships of Aeromonas spp. Carried by Migratory Birds in China. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, K.J.; Okamoto, T.; Bongulto, K.A.; Gandalera, E.E.; Kagia, N.; Watanabe, K. Natural Compound-Induced Downregulation of Antimicrobial Resistance and Biofilm-Linked Genes in Wastewater Aeromonas Species. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1456700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.J.; Swift, S.; Kirke, D.; Keevil, C.W.; Dodd, C.E.R.; Williams, P. The Regulation of Biofilm Development by Quorum Sensing in Aeromonas hydrophila. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 4, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.H.; Vincent, A.T.; Emond-Rhéault, J.-G.; Adamczuk, M.; Frenette, M.; Charette, S.J. Plasmid Composition in Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. Salmonicida 01-B526 Unravels Unsuspected Type Three Secretion System Loss Patterns. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbehiry, A.; Marzouk, E.; Abdeen, E.; Aldubaib, M.; Alsayeqh, A.F.; Ibrahem, M.D.; Hamada, M.; Alenzi, A.; Moussa, I.M.; Hemeg, H.A. Proteomic Characterization and Discrimination of Aeromonas Species Recovered From Meat and Water Samples With a Spotlight on the Antimicrobial Resistance of Aeromonas hydrophila. Microbiologyopen 2019, 8, e782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, W.; Lu, J.; Liu, Z.; Lin, X.; Liu, Y. Quantitative Proteomics Analysis Reveals the Effect of a MarR Family Transcriptional Regulator AHA_2124 on Aeromonas hydrophila. Biology 2023, 12, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maistrenko, O.M.; Mende, D.R.; Luetge, M.; Hildebrand, F.; Schmidt, T.S.; Li, S.S.; Rodrigues, J.F.M.; von Mering, C.; Pedro Coelho, L.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; et al. Disentangling the Impact of Environmental and Phylogenetic Constraints on Prokaryotic Within-Species Diversity. Isme J. 2020, 14, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh Truong, N.H.; Nguyen, Q.; Voong, P.V.; Chau, V.; Thanh Nguyen, N.H.; Thi Nguyen, T.H.; Vo, P.; Nguyen, L.T.; Phuong Ha, T.T.; Huong Nguyen, L.P.; et al. Genomic Characterization of Aeromonas spp. Isolates From Striped Catfish With Motile Aeromonas Septicemia and Human Bloodstream Infections in Vietnam. Microb. Genom. 2024, 10, 001248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| 1 | 2 * | 3 ** | 4 *** | 5 **** | 6 ***** | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 4–45 °C | 4–25 °C | 5–37 °C | 5–30 °C | 5–35 °C | 5–37 °C |
| NaCl (%) (w/v) | 0–4 | 0–2 | ND | ND | ND | 0–4 |
| Motility | − | − | − | + | + | + |
| Hydrolysis of | ||||||
| DNase | − | + | + | + | + | + |
| Tween 80 | + | − | ND | + | + | ND |
| L-Tyrosin | − | ND | ND | ND | ND | + |
| Growth ability on | ||||||
| McConkey Agar | + | − | + | + | ND | |
| Indole | − | − | + | + | − | + |
| Anaerobic environment | + | + | ND | − | ND | + |
| API 20 NE | ||||||
| Indole Production | − | + | + | + | − | + |
| Fermentation (D-Glucose) | + | + | + | − | + | + |
| Arginine Dihydrolase | − | − | − | + | + | + |
| Urease | − | − | − | + | + | + |
| Hydrolysis of Aesculin | + | − | − | − | + | ND |
| Assimilation of | ND | |||||
| L-Arabinose | + | + | + | − | + | + |
| D-Mannose | + | − | + | + | + | + |
| D-Mannitol | + | − | + | + | + | + |
| N-acetyl-D-Glucosamine | + | − | + | ND | ND | + |
| D-Maltose | + | − | ND | + | + | + |
| Potassium Gluconate | + | ND | ND | − | − | − |
| API 20 E | ||||||
| ONPG: Ortho-Nitrophenyl-β-galactoside (tests for β-galactosidase activity) | + | ND | + | − | − | + |
| IND: Indole Production | − | ND | + | + | ND | + |
| VP: Voges–Proskauer Test | + | ND | + | − | ND | − |
| SOR: Sorbitol Fermentation | + | ND | + | − | − | − |
| SAC: Sucrose Fermentation | + | ND | + | + | − | + |
| ARA: Arabinose Fermentation | + | ND | + | − | − | |
| BIOLOG GENIII | ||||||
| Carbon source utilization assays | ||||||
| D-Raffinose | + | ND | − | − | − | − |
| D-Melibiose | + | ND | − | − | − | − |
| Sucrose | + | ND | + | + | − | + |
| D-Turanose | + | ND | − | − | − | − |
| Strain | AMR Genes Detected |
|---|---|
| A. salmonicida subsp. achromogenes JCM 7875T | OXA-956, cphA5, FOX-18 |
| A. salmonicida subsp. masoucida NBRC 13784T | OXA-956, FOX-18 |
| A. salmonicida subsp. pectinolytica 34melT | OXA-956, cphA5, FOX-20 |
| A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida CIP 103209T | cphA5, FOX-18 |
| A. salmonicida subsp. smithia CIP 104757T | OXA-956, FOX-18 |
| A. salmonicida subsp. oncorhynchi A-9T | OXA-956, cphA5, FOX-20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ajmi, N.; Duman, M.; Ay, H.; Saticioglu, I.B. Genomic and Pangenomic Insights into Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. oncorhynchi subsp. nov. Pathogens 2025, 14, 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060523
Ajmi N, Duman M, Ay H, Saticioglu IB. Genomic and Pangenomic Insights into Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. oncorhynchi subsp. nov. Pathogens. 2025; 14(6):523. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060523
Chicago/Turabian StyleAjmi, Nihed, Muhammed Duman, Hilal Ay, and Izzet Burcin Saticioglu. 2025. "Genomic and Pangenomic Insights into Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. oncorhynchi subsp. nov." Pathogens 14, no. 6: 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060523
APA StyleAjmi, N., Duman, M., Ay, H., & Saticioglu, I. B. (2025). Genomic and Pangenomic Insights into Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. oncorhynchi subsp. nov. Pathogens, 14(6), 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060523







