Analysis of Donor to Recipient Pathogen Transmission in Relation to Cold Ischemic Time and Other Selected Aspects of Lung Transplantation—Single Center Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microbiological Testing
- Donor bronchial aspirate (DBA)—during the final bronchoscopic organ assessment by the surgeon in the operating theater of the donor home hospital.
- Graft endobronchial swab (GES, surgical material)—during its preparation before implantation in the recipient’s operating theater.
- Recipient cultures (RC) before transplantation (nose and throat swabs, sputum, and urine)—after the recipient arrives at the hospital.
- Recipient bronchial aspirate (RBA)—during the first and subsequent bronchofiberoscopies performed within 7 days after the transplant procedure.
2.2. Graft Preservation
2.3. Antimicrobial Therapy
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
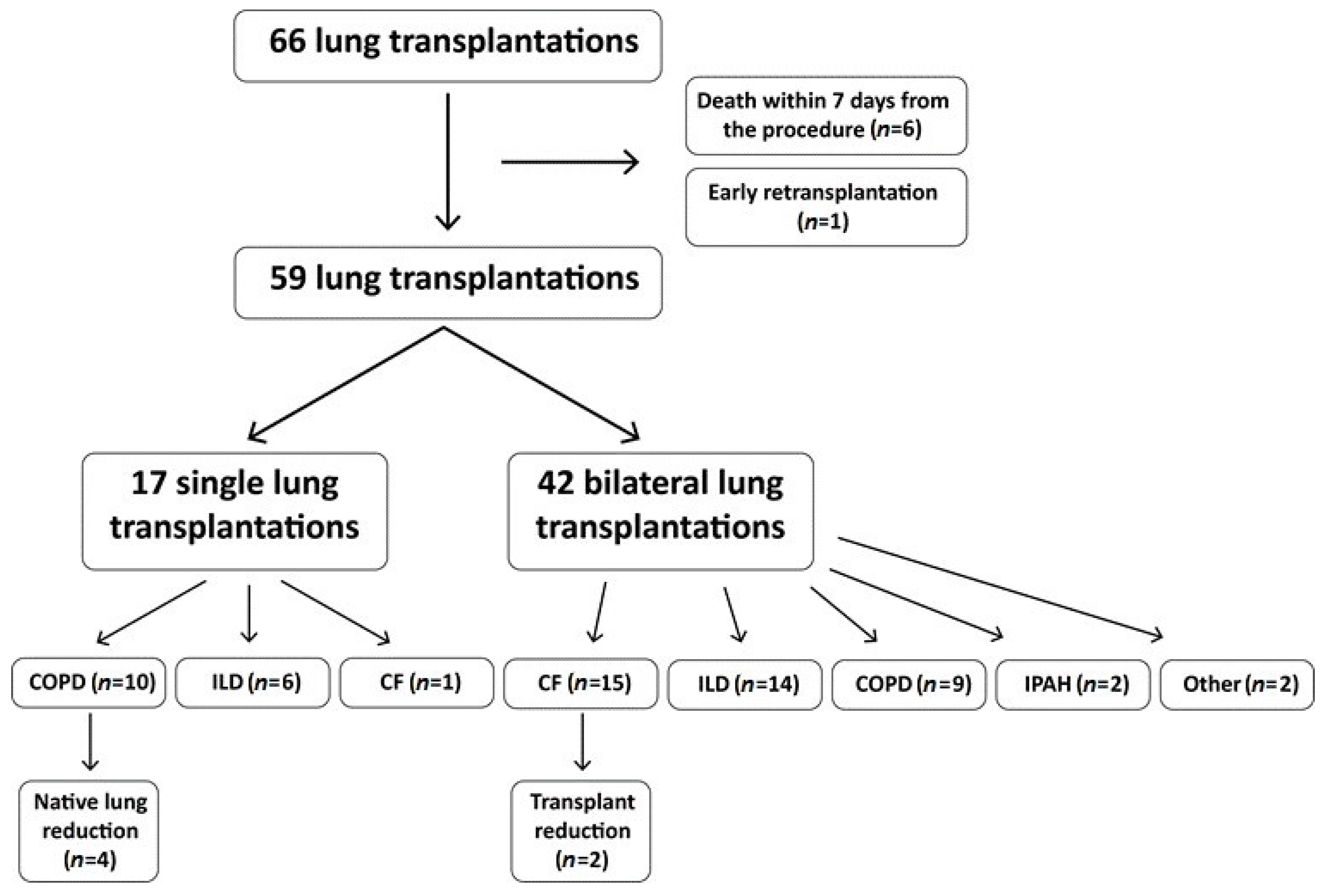
3.1. Recipients
3.2. Donors
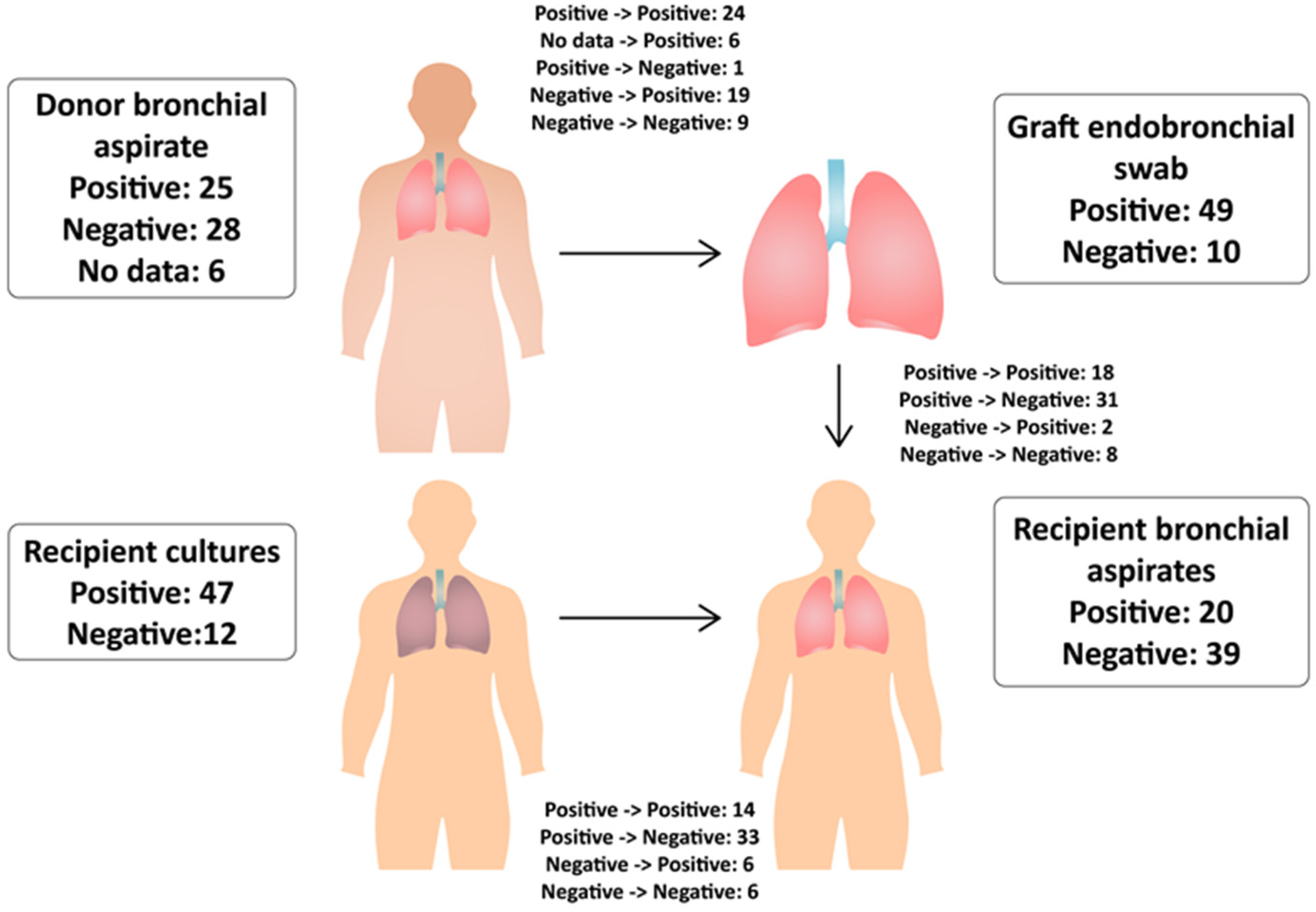
3.3. Donor Bronchial Aspirates
3.4. Graft Endobronchial Swab (Surgical Material)
3.5. Recipient Cultures before Transplantation
3.6. Recipient’s Bronchial Aspirates
3.7. Postoperative Course
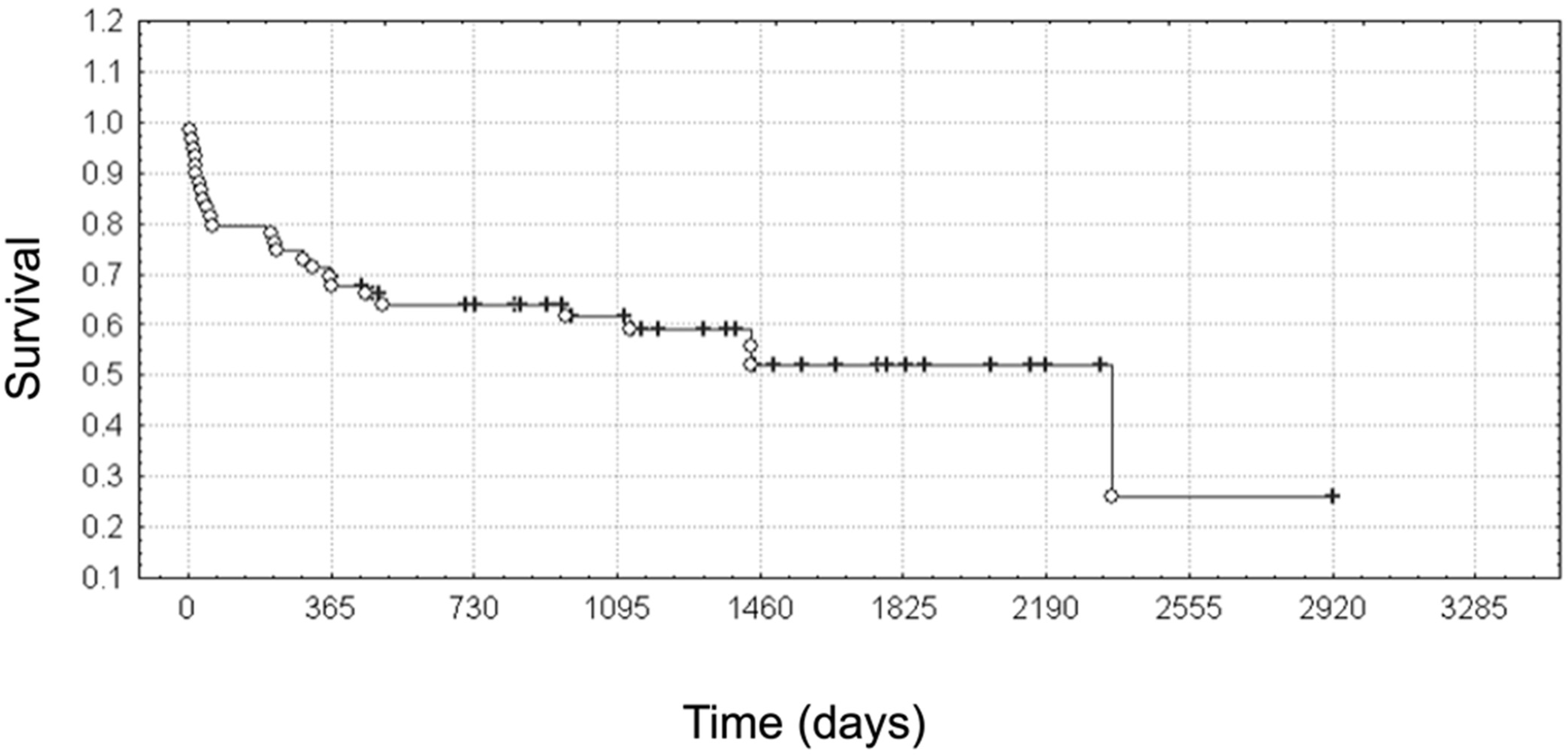
3.8. Survival
3.9. Analysis of Antimicrobial Therapy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sithamparanathan, S.; Thirugnanasothy, L.; Clark, S.; Dark, J.H.; Fisher, A.J.; Gould, K.F.; Hasan, A.; Lordan, J.L.; Meachery, G.; Parry, G.; et al. Observational Study of Lung Transplant Recipients Surviving 20 Years. Respir. Med. 2016, 117, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munshi, L.; Keshavjee, S.; Cypel, M. Donor Management and Lung Preservation for Lung Transplantation. Lancet Respir. Med. 2013, 1, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leard, L.E.; Holm, A.M.; Valapour, M.; Glanville, A.R.; Attawar, S.; Aversa, M.; Campos, S.V.; Christon, L.M.; Cypel, M.; Dellgren, G.; et al. Consensus Document for the Selection of Lung Transplant Candidates: An Update from the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2021, 40, 1349–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raskin, J.; Vanstapel, A.; Verbeken, E.K.; Beeckmans, H.; Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; Verleden, S.E.; Neyrinck, A.P.; Ceulemans, L.J.; Van Raemdonck, D.E.; Verleden, G.M.; et al. Mortality after Lung Transplantation: A Single-centre Cohort Analysis. Transpl. Int. 2019, 33, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, I.; Gavalda, J.; Monforte, V.; Len, O.; Roman, A.; Bravo, C.; Ferrer, A.; Tenorio, L.; Roman, F.; Maestre, J.; et al. Donor-To-Host Transmission of Bacterial and Fungal Infections in Lung Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2006, 6, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunsow, E.; Los-Arcos, I.; Martin-Gómez, M.T.; Bello, I.; Pont, T.; Berastegui, C.; Ferrer, R.; Nuvials, X.; Deu, M.; Peghin, M.; et al. Donor-Derived Bacterial Infections in Lung Transplant Recipients in the Era of Multidrug Resistance. J. Infect. 2020, 80, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainstein, E.J.; Smud, A.; Mañez, N.; Orazi, M.L.; Barcan, L.; Svetliza, G.N.; Quinteros, C.; Dietrich, A.; Da Lozzo, A.; Beveraggi, E.; et al. Donor to Host Transmission of Infection in Lung Transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2019, 38, S316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Len, O.; Garzoni, C.; Lumbreras, C.; Molina, I.; Meije, Y.; Pahissa, A.; Grossi, P. Recommendations for Screening of Donor and Recipient Prior to Solid Organ Transplantation and to Minimize Transmission of Donor–Derived Infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranghino, A.; Diena, D.; Simonato, F.; Messina, M.; Burdese, M.; Piraina, V.; Fop, F.; Segoloni, G.P.; Biancone, L. Clinical Impact of Bacterial Contamination of Perfusion Fluid in Kidney Transplantation. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samardžija, D.; Zamberlin, Š.; Pogacic, T. Psychrotrophic bacteria and milk and dairy products quality. Mljekarsivo 2012, 62, 77–95. Available online: https://hrcak.srce.hr/file/124020 (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- Chaney, J.; Suzuki, Y.; Cantu, E., III; van Berkel, V. Lung Donor Selection Criteria. J. Thorac. Dis. 2014, 6, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannon, J.D.; Ball, A.; Yonan, N.; Clark, S.; Mascaro, J.; Catarino, P.; Simon, A.; Dark, J.H. The Effect of Cold and Warm Ischemia Time on Survival After Lung Transplantation in a Large National Cohort. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2014, 33, S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, D.C.; Yusen, R.D.; Cherikh, W.S.; Goldfarb, S.B.; Kucheryavaya, A.Y.; Khusch, K.; Levvey, B.J.; Lund, L.H.; Meiser, B.; Rossano, J.W.; et al. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-Fourth Adult Lung And Heart-Lung Transplantation Report—2017; Focus Theme: Allograft Ischemic Time. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2017, 36, 1047–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammie, J.S.; Stukus, D.R.; Pham, S.M.; Hattler, B.G.; McGrath, M.F.; McCurry, K.R.; Griffith, B.P.; Keenan, R.J. Effect of Ischemic Time on Survival in Clinical Lung Transplantation. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1999, 68, 2015–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, J.C.; Valero, V., III; Kilic, A.; Magruder, J.T.; Merlo, C.A.; Shah, P.D.; Shah, A.S. Association Between Prolonged Graft Ischemia and Primary Graft Failure or Survival Following Lung Transplantation. JAMA Surg. 2015, 150, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thabut, G.; Mal, H.; Cerrina, J.; Dartevelle, P.; Dromer, C.; Velly, J.-F.; Stern, M.; Loirat, P.; Lesèche, G.; Bertocchi, M.; et al. Graft Ischemic Time and Outcome of Lung Transplantation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennessy, S.A.; Hranjec, T.; Emaminia, A.; LaPar, D.J.; Kozower, B.D.; Kron, I.L.; Jones, D.R.; Lau, C.L. Geographic Distance Between Donor and Recipient Does Not Influence Outcomes After Lung Transplantation. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 92, 1847–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaidan, H.; Fakhro, M.; Lindstedt, S. Impact of Allograft Ischemic Time on Long-Term Survival in Lung Transplantation: A Swedish Monocentric Study. Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 2020, 54, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Raemdonck, D.; Neyrinck, A.; Verleden, G.M.; Dupont, L.; Coosemans, W.; Decaluwe, H.; Decker, G.; De Leyn, P.; Nafteux, P.; Lerut, T. Lung Donor Selection and Management. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2009, 6, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ison, M.G.; Nalesnik, M.A. An Update on Donor-Derived Disease Transmission in Organ Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, F.; Page, C.; Rossolini, G.M.; Pallecchi, L.; Matera, M.G.; Rogliani, P.; Cazzola, M. The Effect of N -Acetylcysteine on Biofilms: Implications for the Treatment of Respiratory Tract Infections. Respir. Med. 2016, 117, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.; Geneve, C.; Tebano, G.; Grall, N.; Piednoir, P.; Bronchard, R.; Godement, M.; Atchade, E.; Augustin, P.; Mal, H.; et al. Morbidity and Mortality Related to Pneumonia and TRACHEOBRONCHITIS in ICU after Lung Transplantation. BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Guisado, M.; Givaldá, J.; Ussetti, P.; Ramos, A.; Morales, P.; Blanes, M.; Bou, G.; de la Torre-Cisneros, J.; Román, A.; Borro, J.M.; et al. Pneumonia After Lung Transplantation in the Resitra Cohort: A Multicenter Prospective Study. Am. J. Transplant. 2007, 7, 1989–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riera, J.; Caralt, B.; López, I.; Augustin, S.; Roman, A.; Gavalda, J.; Rello, J. Ventilator-Associated Respiratory Infection Following Lung Transplantation. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 45, 726–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, M.; Dworniczak, S.; Dworniczak, A.; Kozielski, J. Occurrence of Alert Pathogens in Patients Hospitalised in the Department of Lung Diseases. Adv. Respir. Med. 2015, 83, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remund, K.F.; Best, M.; Egan, J.J. Infections Relevant to Lung Transplantation. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2009, 6, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Duin, D.; van Delden, C. Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria Infections in Solid Organ Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, L.J.; Noone, P.G. Respiratory Infections in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis Undergoing Lung Transplantation. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, T.C.; Cockburn, A.E.; Yung, H.; Karimi, E.; Dirmantaite, L.; Khan, M.; Perry, A.; Gell, R.; Al-Aloul, M.; Thompson, R.D.; et al. Management of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection After Lung Transplantation Across the UK and the Impact on Long-Term Survival. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2017, 36, S322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinkamp, G.; Schmitt-Grohe, S.; Döring, G.; Staab, D.; Pfründer, D.; Beck, G.; Schubert, R.; Zielen, S. Once-Weekly Azithromycin in Cystic Fibrosis with Chronic Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection. Respir. Med. 2008, 102, 1643–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaume, M.; Köhler, T.; Greub, G.; Manuel, O.; Aubert, J.-D.; Baerlocher, L.; Farinelli, L.; Buckling, A.; van Delden, C. Rapid Adaptation Drives Invasion of Airway Donor Microbiota by Pseudomonas after Lung Transplantation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, J.; Sunny, S.S.; Hester, K.L.M.; Parry, G.; Kate Gould, F.; Dark, J.H.; Clark, S.C.; Meachery, G.; Lordan, J.; Fisher, A.J.; et al. Outcomes of Lung Transplantation in Adults with Bronchiectasis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosotti, M.; Tarsia, P.; Morlacchi, L.C. Infections after Lung Transplantation. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 3849–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rello, J.; Lisboa, T.; Koulenti, D. Respiratory Infections in Patients Undergoing Mechanical Ventilation. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raviv, Y.; Shitrit, D.; Amital, A.; Fox, B.; Bakal, I.; Tauber, R.; Bishara, J.; Kramer, M.R. Multidrug-ResistantKlebsiella Pneumoniaeacquisition in Lung Transplant Recipients. Clin. Transplant. 2012, 26, E388–E394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.H.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, E.J.; Jung, I.Y.; Jeong, S.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, M.S.; Kim, A.; Lee, J.G.; Paik, H.C. Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii Infection in Lung Transplant Recipients: Risk Factors and Prognosis. Infect. Dis. 2019, 51, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazleen, A.; Parmar, J. Pre-Transplant C-Reactive Protein (CRP) as a Marker of Post-Transplant Outcomes in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis (CF). Thorax 2016, 71 (Suppl. 3), A137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rello, J.; Bello, I.; de Vicente, R.; Hermira Anchuelo, A.; Ballesteros, M.Á.; Iranzo, R.; Rellán, L.; Riera, J.; Robles, J.C. Risk Factors for Mortality in 272 Patients With Lung Transplant: A Multicenter Analysis of 7 Intensive Care Units. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2017, 53, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.H.; Krupnick, A.S. Perioperative Antibiotics in Thoracic Surgery. Thorac. Surg. Clin. 2012, 22, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.; Niederman, M.S.; Chastre, J.; Ewig, S.; Fernandez-Vandellos, P.; Hanberger, H.; Kollef, M.; Li Bassi, G.; Luna, C.M.; Martin-Loeches, I.; et al. International ERS/ESICM/ESCMID/ALAT Guidelines for the Management of Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia and Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Population (n = 59) | Mean | SD | Median | Lower Quartile | Upper Quartile | Range | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 49.66 | 13.33 | 57 | 39 | 59 | 20–65 | <0.001 | |
| ICU stay * (days) | n = 46 78.0% | 13.15 | 15.12 | 7 | 4.75 | 14.5 | 2–62 | <0.001 |
| Hospitalization (days) | 33.97 | 14.83 | 31 | 24 | 41 | 7–73 | <0.001 | |
| Survival on 21 December 2019 | n = 33 55.9% | 921.37 | 757.85 | 848 | 277 | 1445 | 7–2922 | <0.01 |
| Population (n = 59) | Mean | SD | Median | Lower Quartile | Upper Quartile | Range | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 39.78 | 13.12 | 41 | 30 | 50 | 11–61 | p = 0.08 | |
| ICU stay (hours) | 105.92 | 77.02 | 109 | 42 | 142 | 8–334 | p < 0.01 | |
| CIT 1 (min) | 59/100% | 403.27 | 107.02 | 400 | 330 | 480 | 150–630 | p = 0.69 |
| CIT 2 (min) | 42/71.2% | 541.74 | 114.14 | 540 | 477.5 | 600 | 270–740 | p = 0.38 |
| Donor Bronchial Aspirate (n = 53) | Graft Endobronchial Swabs (n = 59) | Recipient Bronchial Aspirates (n = 59) | Recipient Cultures (n = 59) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram-positive bacteria | ||||
| Staphylococcus aureus MSSA | 8 | 15 | 2 | 13 |
| Staphylococcus aureus MRSA | 1 | |||
| Staphylococcus auricularis | 1 | |||
| Staphylococcus haemolyticus MRCNS, MLS | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis MRCNS, MRSE, MLS | 4 | 4 | ||
| Staphylococcus lugudensis | 1 | |||
| Staphylococcus hominis MSCNS | 1 | |||
| Streptococcus anginosus | 1 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactea MLS | 1 | |||
| Enterococcus faecalis | 2 | 3 | ||
| Enterococcus fecium | 1 | 1 | ||
| Enterococcus casseliflavus | 1 | |||
| Corynebacterium ulcerans | 1 | |||
| Gram-negative bacteria | ||||
| Enterobacter cloace | 2 | 4 | 4 | |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | 4 | 5 | 2 | 7 |
| Klebsiella oxytoca | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Escherichia coli | 2 | 5 | 2 | |
| Proteus mirabilis | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Haemofilus influenzae | 1 | 1 | ||
| Citrobacter freundii | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Moraxella catharralis | 1 | |||
| Serratia odorifera | 1 | 1 | ||
| Serratia marcescens | 1 | |||
| Stenotrophomonas maltophilia | 1 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 2 | 5 | 9 | |
| Acinetobacter baumannii | 4 | 7 | 5 | |
| Achromobacter xylosoxidans | 1 | |||
| Fungi | ||||
| Candida glabrata | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| Candida albicans | 5 | 17 | 6 | 29 |
| Candida crusei | 2 | 1 | ||
| Candida tropicalis | 1 | |||
| Candida parapsylosis | 1 | |||
| Candida fumata | 1 |
| Number of Strains | 1 | 2 a | 3 a | 4 a | 5 a | 6 a | 7 a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material collection | (-)/ GES | DBA/ GES | DBA/ GES/ RBA | DBA/ GES/ RBA | DBA/ GES/ RBA | GES/ RBA | GES/ RBA |
| Drug sensitivity | |||||||
| Piperacillin+ tazobactam | R | R | R | R | |||
| Ticarcillin + clavulanic acid | S | R | |||||
| Ampicillin+ sulbactam | S | R | R | MIC 16 | MS | R | S MS |
| Ceftazidime | R | ||||||
| Cefepime | S | R | R | MS | R | MS | R |
| Cefotaxime | R | R | |||||
| Ciprofloxacin | S | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| Levofloxacin | R | R | R | ||||
| Imipenem | S | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| Meropenem | R | R | R | R | R | R | |
| Gentamicin | S | R | R | R | S | S MS S | R |
| Tobramycin | R | R | |||||
| Amikacin | R | R MS | S | R | R MS | R MS | |
| Colistin | S | S | S | S | S | S | |
| Tetracycline | R | ||||||
| Trimethoprim + sulfamethoxazole | S | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| Parameter | Prolonged Intubation | Non-Prolonged Intubation | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean SD (Range) | Median (Range) | n | Mean SD (Range) | Median (Range) | ||
| Age (years) | 26 | 45 13.88 (21–65) | 43 (33–58) | 33 | 52 12.15 (20–64) | 57 (50–59.75) | 0.049 |
| CIT 1 (min) | 26 | 440 102.48 (245–630) | 420 (360–519) | 33 | 374.09 102.77 (150–570) | 360 (303.75–435) | 0.029 |
| CIT 2 (min) | 21 | 584 101.45 (380–740) | 600 (495–660) | 21 | 498 111.82 (277–690) | 495 (412.5–580) | 0.016 |
| ICU stay (days) | 22 | 21 18.36 (5–62) | 13 (7.5–29.5) | 24 | 5 3.20 (2–16) | 5 (3–6) | <0.001 |
| Hospitalization (days) | 26 | 40 19.08 (7–73) | 35 (73–23.5) | 33 | 29 7.79 (16–53) | 27 (24–32.75) | 0.032 |
| p Value | HR (95%CI) | |
|---|---|---|
| DBA+ | 0.37 | 0.690 (0.309–1.539) |
| GES+ | 0.02 * | 0.348 (0.144–0.842) |
| DBA-/GES+ | 0.03 * | 0.322 (0.115–0.908) |
| RC+ | 0.84 | 0.911 (0.362–2.291) |
| RBA+ | 0.44 | 1.369 (0.619–3.028) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piotrowska, M.; Wojtyś, M.E.; Kiełbowski, K.; Bielewicz, M.; Wasilewski, P.; Safranow, K.; Grodzki, T.; Kubisa, B. Analysis of Donor to Recipient Pathogen Transmission in Relation to Cold Ischemic Time and Other Selected Aspects of Lung Transplantation—Single Center Experience. Pathogens 2023, 12, 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12020306
Piotrowska M, Wojtyś ME, Kiełbowski K, Bielewicz M, Wasilewski P, Safranow K, Grodzki T, Kubisa B. Analysis of Donor to Recipient Pathogen Transmission in Relation to Cold Ischemic Time and Other Selected Aspects of Lung Transplantation—Single Center Experience. Pathogens. 2023; 12(2):306. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12020306
Chicago/Turabian StylePiotrowska, Maria, Małgorzata Edyta Wojtyś, Kajetan Kiełbowski, Michał Bielewicz, Piotr Wasilewski, Krzysztof Safranow, Tomasz Grodzki, and Bartosz Kubisa. 2023. "Analysis of Donor to Recipient Pathogen Transmission in Relation to Cold Ischemic Time and Other Selected Aspects of Lung Transplantation—Single Center Experience" Pathogens 12, no. 2: 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12020306
APA StylePiotrowska, M., Wojtyś, M. E., Kiełbowski, K., Bielewicz, M., Wasilewski, P., Safranow, K., Grodzki, T., & Kubisa, B. (2023). Analysis of Donor to Recipient Pathogen Transmission in Relation to Cold Ischemic Time and Other Selected Aspects of Lung Transplantation—Single Center Experience. Pathogens, 12(2), 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12020306





