Abstract
Yersinia enterocolitica is a zoonotic proto-microbe that is widespread throughout the world, causes self-limiting diseases in humans or animals and even leads to sepsis and death in patients with severe cases. In this study, a real-time recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) assay for pathogenic Y. enterocolitica was established based on the ail gene. The results showed that the RPA detection for Y. enterocolitica could be completed within 20 min at an isothermal temperature of 38 °C by optimizing the conditions in the primers and Exo probe. Moreover, the sensitivity of the current RT-RPA was 10−4 ng/μL, and the study found that the assay was negative in the application of the genomic DNA of other pathogens. These suggest the establishment of a rapid and sensitive real-time RPA method for the detection of pathogenic Y. enterocolitica, which can provide new understandings for the early diagnosis of the pathogens.
1. Introduction
Yersinia enterocolitica, a member of the Enterobacteriaceae family, is a kind of zoonotic pathogen that exists widely all over the world [1,2]. It can infect humans or animals through contaminated food or water, causing self-limiting disease, lymphadenitis and terminal ileal inflammation, sepsis and even death in severe cases [3,4].
Y. enterocolitica can be classified into six biotypes: 1A, 1B, 2~5, and more than 70 different serotypes [5]. All biotypes, except for type 1A, are pathogenic to varying degrees in any animal. Because biotype 1A does not have the virulence plasmid pYV and chromosomal virulence gene, it is usually considered to be non-pathogenic [6,7]. The major virulence genes of pathogenic Y. enterocolitica are distributed in ail, fyuA, ystA, virF and yadA. While the plasmid virulence genes virF and yadA are easily lost during passage, the ail gene is an important virulence marker of Yersinia enterocolitica and is widely used in pathogenicity analysis [8].
Yersinia, caused by the bacterium Y. enterocolitica, is now the third most common zoonosis in Europe after campylobacteriosis and salmonellosis [9]. Previous reports showed a 166% increase in Yersinia patients in 2017 compared to 2014–2016 [10]. The detection rate of Y. enterocolitica in common food was 2.33% and in frozen food was 6.72% [11]. At present, Y. enterocolitica has become an important pathogen detected in many countries.
The traditional isolation method of Y. enterocolitica requires a lot of time, and most isolates are non-pathogenic strains [12]. The molecular methods of the PCR, multiplex PCR, real-time PCR and loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) have been reported for the diagnosis of pathogenic Y. enterocolitica [8,13,14,15,16]. The molecular detection method is able to detect Y. enterocolitica in a shorter period of time compared to the traditional method, which takes a lot of time. Since the introduction of the classic PCR in 1983, nucleic acid amplification–based pathogen detection has been widely used for disease surveillance [17]. However, it has only been used in laboratories because it requires sophisticated thermal cycling apparatuses and trained personnel. Although the PCR and real-time PCR display high sensitivity, accuracy and specificity, these methods require specialized equipment and experienced operators, thus limiting their application [18]. The LAMP assay for Y. enterocolitica allows for more sensitive analysis than does PCR detection, although it requires the design of multiple primer pairs and takes more time [15]. Therefore, a simpler and faster test is necessary for the quick diagnosis of pathogenic Y. enterocolitica.
Many strategies to achieve amplification at a constant temperature have emerged as potential alternatives to PCR, with the recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) being the fastest growing in recent years [19]. The RPA assay is a highly specific and sensitive detection technique compared with other existing detection techniques, requiring only 10–20 minutes to complete the reaction with only a primer of 30–35 bp to complete the amplification between 25–42 ℃ [16,20,21]. Therefore, the RPA replaces the thermal cycling required for PCR by using recombinant enzyme proteins, single-stranded DNA binding proteins for primer annealing and a strand-swapping DNA polymerase for amplifying nucleic acid sequences [22]. The RPA reaction has been widely used in the detection of various pathogens due to its advantages of simple operation, strong specificity, high sensitivity and fast detection speed [21,23,24,25]. Real-time RPA has been successfully used to detect a variety of pathogens, including Vibrio vulnificus [26], Avian reovirus [27], and Schistosoma haematobium [22]. Hence, this study focused on the development and validation of a novel RT-RPA assay for the simple and effective detection of pathogenic Y. enterocolitica.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Condition
Seventeen bacterial strains were applied in this study, including the five pathogenic Y. enterocolitica, five non-pathogenic Y. enterocolitica and seven non-Y. enterocolitica bacterial species (Table 1). The pathogenic Y. enterocolitica ATCC 23715 was obtained from the China Institute of Veterinary Drug Control (CIVDC), Beijing, China. The other strains were isolated from Qinghai province, China, and stored in our laboratory. Y. enterocolitica strains were incubated at 25 °C for 24 h in Luria–Bertani broth (LB) under constant shaking. All other strains were cultured for 18 h in LB broth at 37 °C under constant shaking.

Table 1.
All strains used in the study.
2.2. Extraction of Genomic DNA
All bacteria genomic DNA were extracted using the TIANamp Bacteria DNA kit (Tiangen, Beijing, China) following the instructions provided by the manufacturer, and the quantities and qualities were determined by measuring A260 and the A260/A280 ratio with a micro-spectrophotometer (KAIAO, Shanghai, China). All the bacteria genomic DNA were uniformly adjusted to 100 ng/μL and stored at −20 °C until use.
2.3. RPA Primer and Probe Designs
In accordance with the reference sequences of Y. enterocolitica (accession numbers CP009846), four pairs of primers were designed targeting the conserved region of the ail gene. The Exo probe was designed based on this primer amplicon after the primers with high sensitivity were screened by the basal RPA test. The primers and Exo probe were designed following the TwistDx instruction manual (TwistDx, Cambridge, UK). All the primers and the Exo probe were synthesized and provided by Sangon (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Real-time RPA primers and probes.
2.4. Real-Time RPA Assay
The real-time RPA reactions were performed in a 50 μL volume using a kit (Amp Future, Weifang, China) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Briefly, 2.0 μL of 10 μM of both forward and reverse primer, 0.6 μL of 10 μM Probe (RPA-Probe-5), 29.4 μL of A buffer, 10.0 μL DNase-free water, 3.5 μL of the DNA template and 2.5 μL of B buffer were added to a lyophilized RPA reaction pellet. The RPA reactions were run for 30 min at 38 °C, and fluorescence signals were read with a real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA). The RPA-Probe 6 is performed under the same conditions.
2.5. Analytical Sensitivity and Specificity
To determine the sensitivity of the RPA assay, the bacterial genomic DNA (100 ng/μL) was diluted in a 10-fold ratio, and six dilution gradients from 10 to 10−4 ng/μL were selected for the test. All the samples were tested in duplicate and the whole assay was carried out for three times.
To test the specificity of RPA, DNA was extracted from a group of bacterial chants, described in Table 1, for testing. Three independent reactions were performed.
2.6. Repeatability Testing
The bacterial genomic DNA was replicated three times each for inter-batch and intra-batch DNA in three concentration gradients of high (10 ng/μL), medium (10−1 ng/μL) and low (10−5 ng/μL) concentrations, for a total of nine replicates of the same concentration of DNA.
2.7. Validation with Artificially Contaminated Samples
Samples of yak dung were used to assess the potential use and suitability of the real-time RPA assay. All samples were collected from locally farmed yaks and identified as negative for Y. enterocolitica by traditional culture assay and PCR. Then, 00 CFU of different Y. enterocolitica strains were added to samples without Y. enterocolitica. The contaminated samples were added to 5 mL of LB broth and incubated for 24 h at 25 °C to enrich the bacterial concentration. The samples were boiled for 15 min to collect DNA after the enrichment and the RPA reactions were performed.
2.8. Data Analysis
Results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD), and all statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS 20.0 software package. The significance of the experimental data was determined by Dunn’s multiple comparisons procedure.
3. Results
3.1. Optimal Combination Primers and Probes for Real-Time RPA Assay
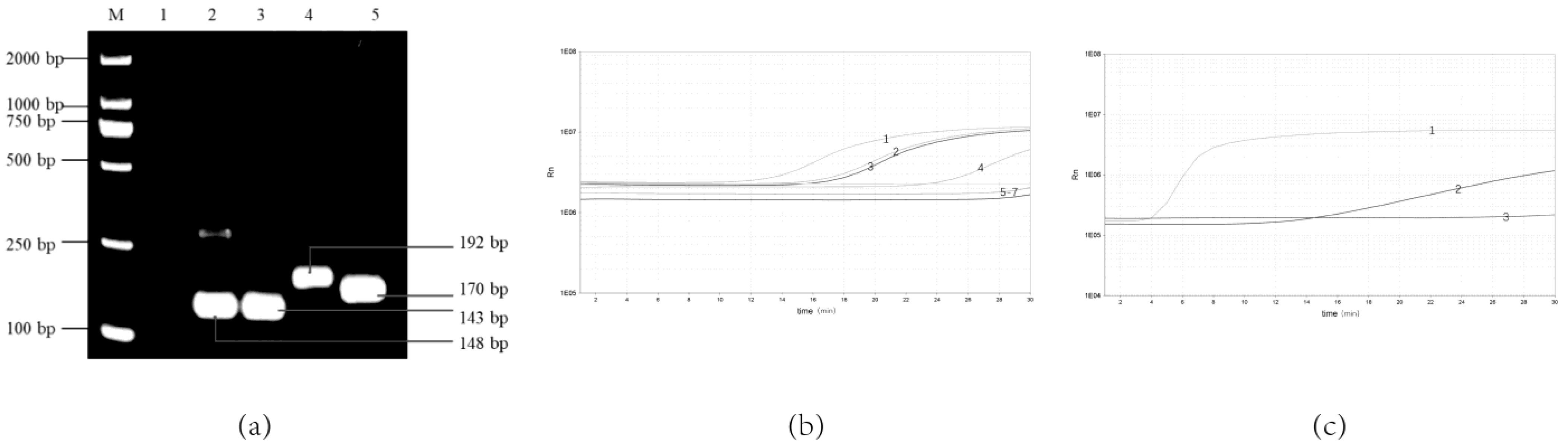
As the results show, four pairs of primer sets could recognize and amplify Y. enterocolitica (Figure 1a,b). It can be seen in Figure 1b that primer F3/R3 has the highest amplification efficiency compared with the three other pairs of primers that can be amplified. Lane 3 in Figure 1a has an indistinct non-specific strip at about 200 bp. In Figure 1a, lane 5 has clearer bands of primer dimers below 100 bp. Therefore, primers F3/R3 with high amplification efficiency and non-specific bands were selected. Comparing the different probes, the probe RPA-Probe-5 amplifies with higher efficiency and sensitivity, as shown in Figure 1c. Therefore, the primer–probe combinations used in this experiment were determined to be RPA-F-3, RPA-R-3 and RPA-Probe-5, respectively. They amplified the target gene fragment size of 192 bp at 38 °C.
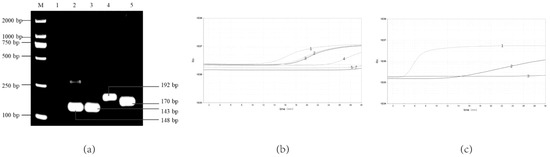
Figure 1.
Screening of optimal real-time RPA primer–probe combinations. (a) Screening the optimal primers for the real-time RPA by the basic RPA: 1, NTC; 2, F1/R1; 3. F2/R2; 4, F3/R3; 5, F1/R2; (b) Screening the optimal primers for the real-time RPA: 1, F3/R3; 2, F1/R1; 3, F2/R2; 4, F1/R2; 5, F1/R3; 6, F2/R3; 7, NTC; (c) Screening the optimal probe for the real-time RPA: 1, Probe-5; 2, Probe-6; 3. NCT.
3.2. Analytical Sensitivity and Specificity of the Real-Time RPA Assay
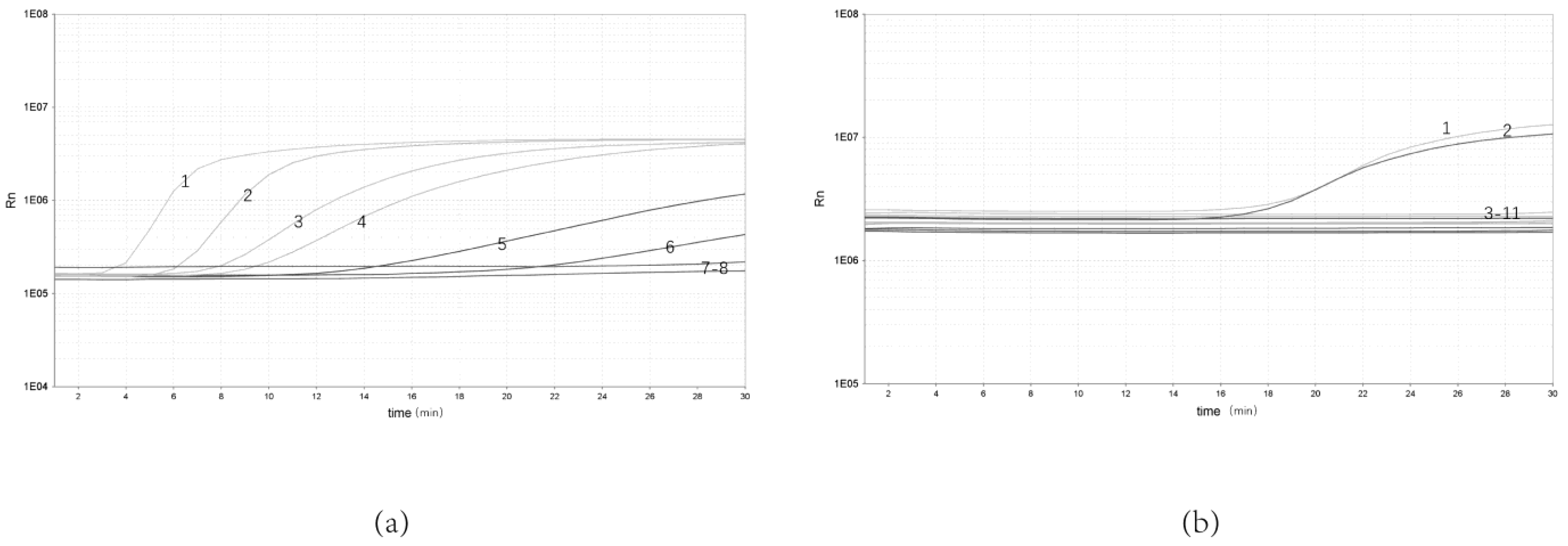
To determine the sensitivity of the real-time RPA assay, bacterial genomic DNA from 10 to10−5 ng/μL were selected for the test. The results showed that the real-time RPA could be detected at a minimum concentration of 10−4 ng/μL. The real-time RPA assay could be detected in as little as 3 min (Figure 2a).
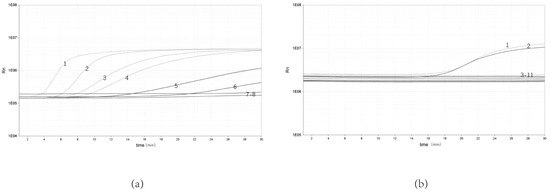
Figure 2.
Sensitivity and specificity of real-time RPA assay. (a) Sensitivity test of real-time RPA assay: 1, 10 ng/μL; 2, 100 ng/μL; 3, 10−1 ng/μL; 4, 10−2 ng/μL; 5, 10−3 ng/μL; 6, 10−4 ng/μL; 7, 10−5 ng/μL; 8, NTC. (b) Specificity test of real-time RPA assay: 1, Y. enterocolitica ATCC 23715; 2, Y. enterocolitica ZDN6; 3, Pasteurella P0810; 4, Shigella Castellani 06-01-03; 5, Slmonella 06-03-01; 6, Escherichia coli 03-03; 7, Aeromonas hydrophila AH 1302; 8, Bacillus cereus 06-05-02; 9, non-pathogenic Y. enterocolitica GN 22; 10, Staphylococcus aureus 04-011; 11, NTC.
The genomic DNA from Y. enterocolitica and other bacterial strains was amplified to evaluate the specificity of real-time RPA. The results showed that only pathogenic Y. enterocolitica showed significant amplification, with no amplification curve for either non- pathogenic Y. enterocolitica or Y. enterocolitica (Figure 2b).
This section may be divided by subheadings. It should provide a concise and precise description of the experimental results, their interpretation as well as the experimental conclusions that can be drawn.
3.3. Analytical Repeatability of the Real-Time RPA Assay
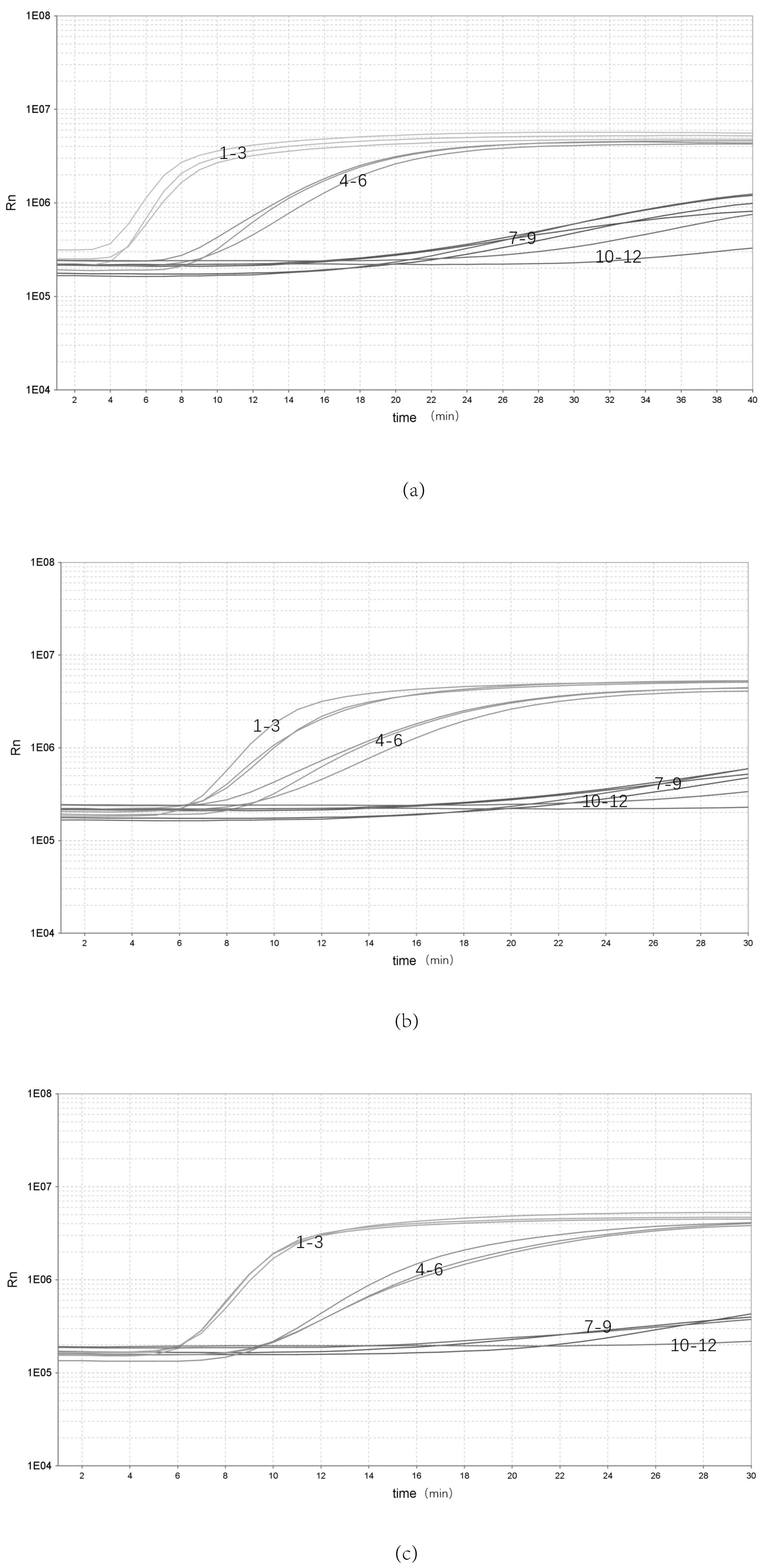
The bacterial genomic DNA was replicated three times at each of three concentrations: high (10 ng/μL), medium (10−1 ng/μL) and low (10−5 ng/μL) (Figure 3). Three batches of inter-group replicates were selected to extract DNA separately, using the same kit. The results showed that the high (10 ng/μL), medium (10−1 ng/μL) and low (10−5 ng/μL) concentrations were stably detected, indicating that the assay has good stability.
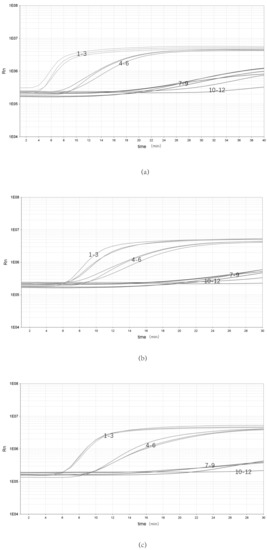
Figure 3.
Repeatability of the real-time RPA assay. (a–c) Repeatability of the real-time RPA assay with different groups: 1–3, 100 ng/μL; 4–6, 10−2 ng/μL; 7–9, 10−5 ng/μL; 10–12, NTC.
3.4. Validation of the Real-Time RPA Assay on Artificially Contaminated Samples
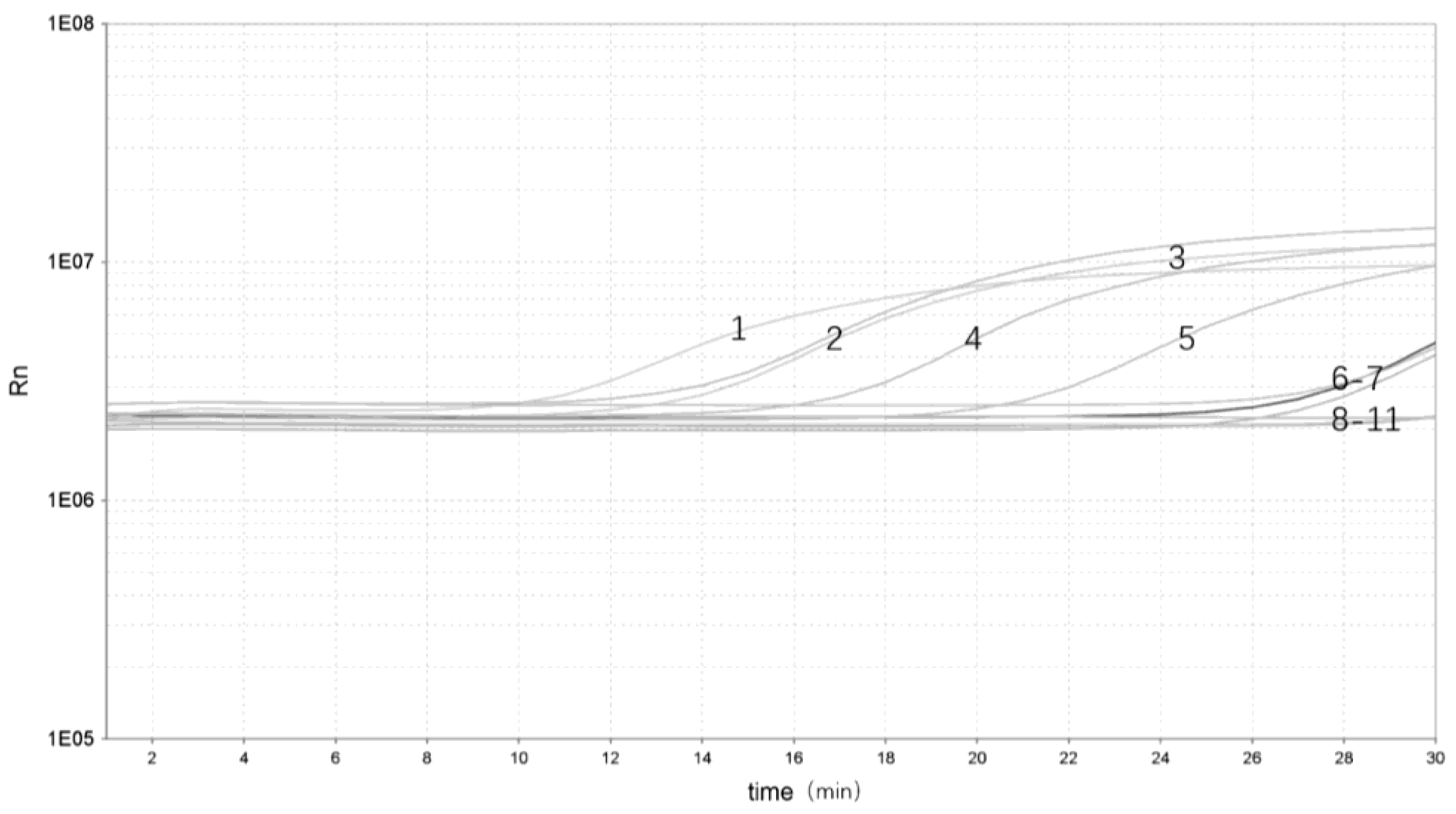
To evaluate the performance of the real-time RPA in yak stool samples, the different Y. enterocolitica strains were added to different samples. There were five samples identified as Y. enterocolitica DNA–positive [Threshold time (Tt) value ranging from 3.17 to 22.47] and five as negative (Tt value undetermined) (Figure 4). Real-time RPA can show significant amplification within 3 min with a clear fluorescent signal for rapid detection of pathogenic Y. enterocolitica.
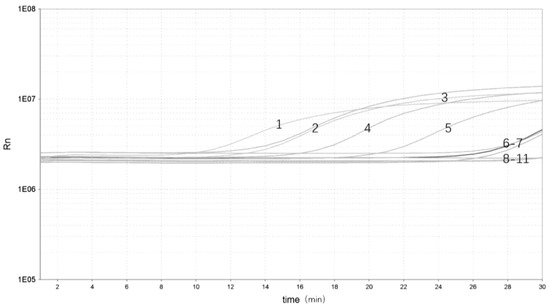
Figure 4.
Validation of the real-time RPA assay: 1, pathogenic Y. enterocolitica ZDN 6 (Tt 3.17); 2, pathogenic Y. enterocolitica ATCC 23715 (Tt 9.51); 3, pathogenic Y. enterocolitica 08-01 (Tt 10.02); 4, pathogenic Y. enterocolitica GN 22 (Tt 18.55); 5, pathogenic Y. enterocolitica ZDN 22 (Tt 22.47); 6, non-pathogenic Y. enterocolitica GLN 1 (Tt undetermined); 7, non-pathogenic Y. enterocolitica HNN 18 (Tt undetermined); 8, non-pathogenic Y. enterocolitica HNN 47 (Tt undetermined); 9, non-pathogenic Y. enterocolitica ZDN 37 (Tt undetermined); 10, non-pathogenic Y. enterocolitica HNN 63 (Tt undetermined); 11, NTC (Tt undetermined).
4. Discussion
The detection rate of Y. enterocolitica has been largely underestimated worldwide because of the difficulties in recovering Yersinia strains from the flora of stool samples [28]. Even though some selective media for Yersinia strains have been developed and isolation of Y. enterocolitica has been improved, these selective media are not yet available and therefore cannot be routinely used by clinical laboratories [29,30]. Nowadays, Cepulodin Irgasan Novobiocin Agar (CIN) can be used for the isolation of Y. enterocolitica, which contains cefsulodin, irgasen and eosporin as selective antimicrobial agents that inhibit the growth of many members of the Enterobacteriaceae family and favor slower growing bacteria [31]. This culture method relies on standard enrichment and selective plating protocols, but this requires additional time, money and work. Here, we developed a real-time RPA method by targeting the ail gene for the detection of Y. enterocolitica. In our experiment, we selected a sequence specific to the ail gene of pathogenic Y. enterocolitica for the design of primers and probes. The primers and probes can detect pathogenic Y. enterocolitis but not non-pathogenic Y. enterocolitica.
The real-time RPA sensitivity experiments can detect a minimum concentration of 10−4 ng/μL, which is almost identical to RT-PCR [4] and LAMP [15] sensitivity. It is 10 times more sensitive compared to RPA-SYBR Green I [32] and normal PCR. When the amount of DNA is 35 ng, it can show significant amplification within 3 min with an obvious fluorescence signal, which can rapidly detect Y. enterocolitica. The real-time RPA assay in this study did not cross-react with eight other species of pathogens tested, including one species of non-pathogenic Y. enterocolitica, or seven clinically common species. Of note, we employed two species of pathogenic Y. enterocolitica (Y. enterocolitica ATCC 23715 and Y. enterocolitica ZDN6) and one non-pathogenic Y. enterocolitica species (Y. enterocolitica GN 22) to verify the specificity of the method, and the results showed that this method can effectively distinguish between pathogenic Y. enterocolitica and non-pathogenic Y. enterocolitica.
Existing rapid detection methods (RT-PCR and LAMP) for Y. enterocolitica require at least 50 min to complete [4,15]. The detection time of DNA in this study was less than 20 min, and the detection results can be viewed in real time, which greatly improves the detection efficiency of Y. enterocolitica. In addition, compared to PCR methods, real-time RPA does not require sophisticated thermal cycling apparatuses and trained personnel. The real-time RPA can detect Y. enterocolitica at 38 °C in as little as 3 min. For this study, we used an RT-PCR machine to read the fluorescence signal, but a portable tube scanner can also give satisfactory results [25]. Compared to previous methods, the real-time RPA method is suitable for field testing, and the reagents can be stored at room temperature for long periods of time in the lyophilized format.
The occurrence of pathogenic Y. enterocolitica in the conventional environment is not very common, so we applied different Y. enterocolitica in order to contaminate samples that tested negative by conventional methods. The real-time RPA reactions can detect different Y. enterocolitica species and can accurately distinguish between pathogenic Y. enterocolitica and non-pathogenic Y. enterocolitica. The real-time RPA reactions are well tolerated for crude samples. In our samples, DNA was released by simple boiling and used directly in the assay without affecting the detection limit or accuracy. This makes the entire assay process simpler. Therefore, the real-time RPA method consists of the two steps of sample boiling and isothermal amplification, and therefore it is easy to operate and has wide application value.
5. Conclusions
The present study established a real-time RPA method for the rapid detection of pathogenic Y. enterocolitica based on ail genes and demonstrated that it could detect pathogenic Y. enterocolitica within 20 min. Further study will develop the concept that portable devices based on the current real-time RPA method should be an important tool for early diagnosis of the pathogenic Y. enterocolitica outbreak sites in resource-limited settings.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Z. and M.Z..; methodology, H.Z., L.T.; software, M.Z.; validation, H.Z., M.Z. and S.H.; formal analysis, H.Z.; investigation, M.Z., X.W. and K.M.; resources, H.Z.; data curation, M.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, M.Z.; writing—review and editing, H.Z., J.L. and J.Z.; visualization, H.Z., M.Z. and S.L.; supervision, H.Z.; project administration, H.Z. and J.Z.; funding acquisition, H.Z and J.Z.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number “31560695” and the National Natural Science Foundation of Qinghai (2020-HZ-801 and 2021-HZ-803).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bottone, E.J. Yersinia enterocolitica: Revisitation of an Enduring Human Pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Newsl. 2015, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusak, L.A.; Pereira, R.D.C.L.; Freitag, I.G.; Hofer, C.B.; Hofer, E.; Asensi, M.D.; Vallim, D.C. Rapid detection of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:3 using a duplex PCR assay. J. Microbiol. Methods 2018, 154, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, C.L.; Rosenzweig, J.A.; Kirtley, M.L.; Chopra, A.K. Pathogenesis of Y. enterocolitica and Y. pseudotuberculosis in Human Yersiniosis. J. Pathog. 2011, 2011, 182051. [Google Scholar]
- Stachelska, M. Detection of Yersinia Enterocolitica Species in Pig Tonsils and Raw Pork Meat by the Real-Time Pcr and Culture Methods. Pol. J. Veter. Sci. 2017, 20, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Gulati, P.; Bhagat, N.; Dhar, M.S.; Virdi, J.S. Detection of Yersinia enterocolitica in food: An overview. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 34, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt-Samoraj, A.; Syczyło, K.; Szczerba-Turek, A.; Bancerz-Kisiel, A.; Jabłoński, A.; Łabuć, S.; Pajdak, J.; Oshakbaeva, N.; Szweda, W. Presence of ail and ystB genes in Yersinia enterocolitica biotype 1A isolates from game animals in Poland. Veter. J. 2017, 221, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraushaar, B.; Dieckmann, R.; Wittwer, M.; Knabner, D.; Konietzny, A.; Mäde, D.; Strauch, E. Characterization of a Yersinia enterocolitica biotype 1A strain harbouring an ail gene. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 111, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.H.; Ikeuchi, S.; O’Brien, Y.S.; Niwa, T.; Hara-Kudo, Y.; Taniguchi, T.; Hayashidani, H. Multiplex PCR method for differentiating highly pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica and low pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica, and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. J. Veter. Med. Sci. 2021, 83, 1982–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, A.; Hammerl, J.A.; Appel, B.; Dieckmann, R.; Al Dahouk, S. Differential detection of pathogenic Yersinia spp. by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Food Microbiol. 2017, 62, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tack, D.M.; Marder, E.; Griffin, P.; Cieslak, P.; Dunn, J.; Hurd, S.; Scallan, E.; Lathrop, S.; Muse, A.; Ryan, P.; et al. Preliminary Incidence and Trends of Infections with Pathogens Transmitted Commonly Through Food-Foodborne Diseases Active Surveillance Network, 10 US Sites, 2015–2018. Mmwr-Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2019, 68, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, H.; Wu, Q.; Ding, Y.; Xu, T.; Ma, G.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, M.; et al. Occurrence, molecular characterization, and antimicrobial susceptibility of Yersinia enterocolitica isolated from retail food samples in China. LWT 2021, 150, 111876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldová, E.; Švandová, E.; Votýpka, J.; Šourek, J. Comparative Study of Culture Methods to Detect Yersinia enterocolitica Serogroup O3 on Swine Tongues. Zent. Bakteriol. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 1990, 272, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwaga, J.; Iversen, J.O.; Misra, V. Detection of pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica by polymerase chain reaction and digoxigenin-labeled polynucleotide probes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 2668–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambertz, S.T.; Nilsson, C.; Hallanvuo, S.; Lindblad, M. Real-Time PCR Method for Detection of Pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica in Food. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 6060–6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, R.; Afshar, D. Development of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for rapid detection of Yersinia enterocolitica via targeting a conserved locus. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2015, 7, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luciani, M.; Schirone, M.; Portanti, O.; Visciano, P.; Armillotta, G.; Tofalo, R.; Suzzi, G.; Sonsini, L.; Di Febo, T. Development of a rapid method for the detection of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:8 from food. Food Microbiol. 2018, 73, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullis, K.; Faloona, F.; Scharf, S.; Saiki, R.; Horn, G.; Erlich, H. Specific enzymatic amplification of DNA in vitro: The polymerase chain reaction. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1986, 51 Pt 1, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Ma, J.; Li, X.; Wang, R.; Chen, S. A real-time recombinase polymerase amplification assay for fast and accurate detection of Ditylenchus destructor. Mol. Cell. Probes 2021, 61, 101788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.D.; Jaykus, L.-A. Development of a Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for Detection of Epidemic Human Noroviruses. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, M.A.; Reed, A.N.; Jin, L.; Pastey, M.K. Rapid Detection of Cyprinid Herpesvirus 3 in Latently Infected Koi by Recombinase Polymerase Amplification. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2016, 28, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato, I.M.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Recombinase polymerase amplification: Basics, applications and recent advances. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 98, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frimpong, M.; Kyei-Tuffuor, L.; Fondjo, L.A.; Ahor, H.S.; Adjei-Kusi, P.; Maiga-Ascofare, O.; Phillips, R.O. Evaluation of a real-time recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid detection of Schistosoma haematobium infection in resource-limited setting. Acta Trop. 2021, 216, 105847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hou, P.; Zhao, G.; Yu, L.; Gao, Y.-W.; He, H. Development and evaluation of serotype-specific recombinase polymerase amplification combined with lateral flow dipstick assays for the diagnosis of foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype A, O and Asia1. BMC Veter. Res. 2018, 14, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Hou, P.; Huan, Y.; He, C.; Wang, H.; He, H. Development of a recombinase polymerase amplification combined with a lateral flow dipstick assay for rapid detection of the Mycoplasma bovis. BMC Veter. Res. 2018, 14, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, L.; Deng, Q.; Zhao, L.; Sun, X.X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, B.; Wang, J. Real-time recombinase polymerase amplification assay for the rapid and sensitive detection of Campylobacter jejuni in food samples. J. Microbiol. Methods 2018, 157, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Shen, H.; Jiang, G.; Dong, J.; Zhao, P.; Gao, S. A Real-Time Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Method for Rapid Detection of Vibrio vulnificus in Seafood. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 586981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Shi, H.; Zhang, M.; Song, Y.; Zhang, K.; Cong, F. Establishment of a Real-Time Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for the Detection of Avian Reovirus. Front. Veter. Sci. 2020, 7, 551350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laporte, J.; Savin, C.; Lamourette, P.; Devilliers, K.; Volland, H.; Carniel, E.; Créminon, C.; Simon, S. Fast and Sensitive Detection of Enteropathogenic Yersinia by Immunoassays. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Noyen, R.; Vandepitte, J.; Wauters, G. Nonvalue of cold enrichment of stools for isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica serotypes 3 and 9 from patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1980, 11, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, M.; Meyer, A.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; Gaarslev, K.; Espersen, F. Evaluation of Statens Serum Institut enteric medium for detection of enteric pathogens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 2312–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petsios, S.; Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M.; Sakkas, H.; Papadopoulou, C. Conventional and molecular methods used in the detection and subtyping of Yersinia enterocolitica in food. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 237, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Hu, P.; Ren, H.; Wang, H.; Cao, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. RPA-SYBR Green I based instrument-free visual detection for pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica in meat. Anal. Biochem. 2021, 621, 114157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).