EBV Reactivation in Transplant Recipients following SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
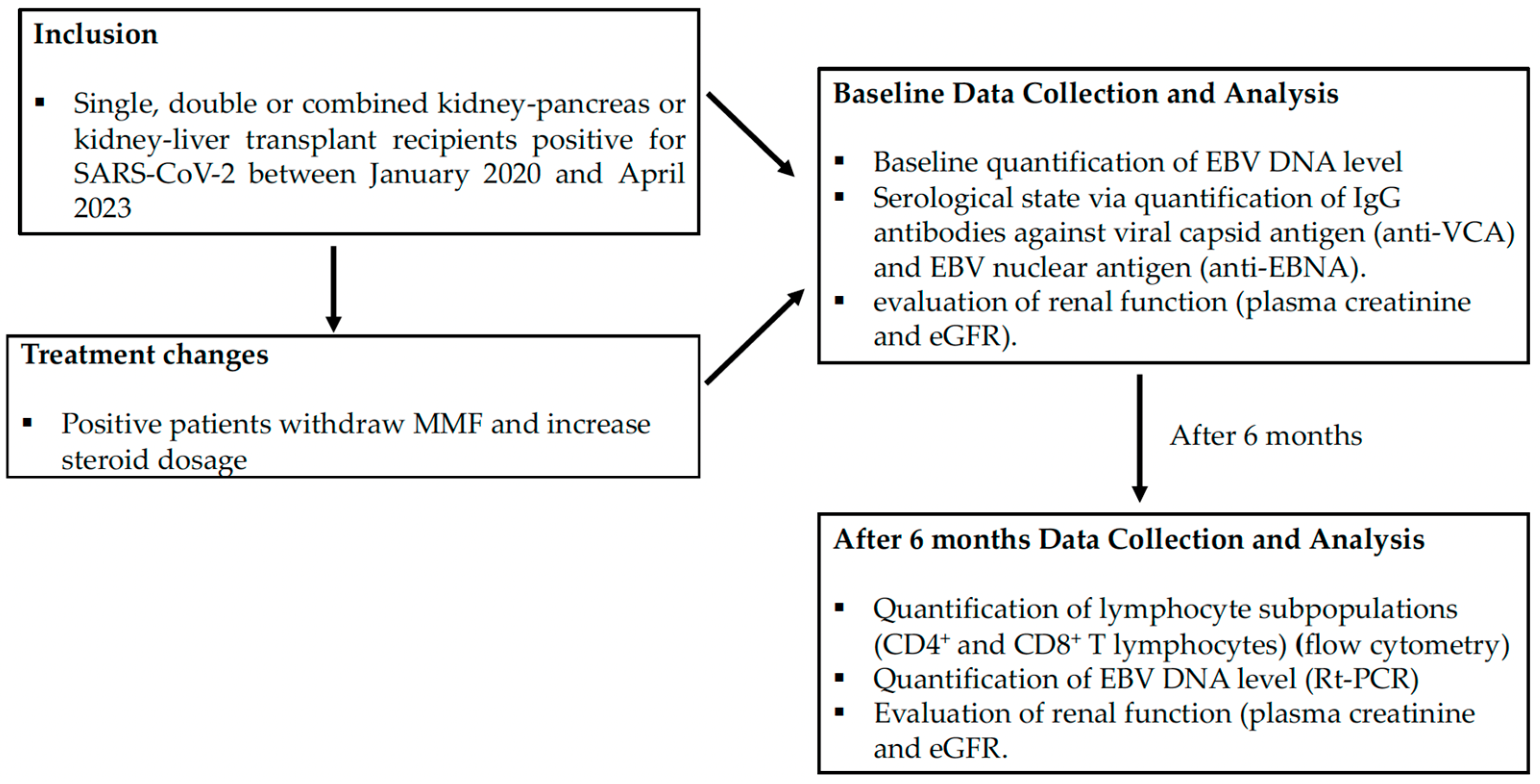
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Methods
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Cohort
3.2. EBV DNA Detection and Outcomes
3.3. Lymphocyte Subpopulation Count and Viral Serology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pakfetrat, M.; Malekmakan, L.; Jafari, N.; Sayadi, M. Survival Rate of Renal Transplant and Factors Affecting Renal Transplant Failure. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2022, 20, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, J.A. Infection in organ transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 17, 856–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, A.; Ison, M.G.; Danziger-Isakov, L. Long-term infectious complications of Kidney transplantation. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 17, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, J.; Durand, C.M.; Agha, I.; Brennan, D.C. Epstein-Barr virus and renal transplantation. Transplant. Rev. 2017, 31, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamoulid, J.; Courivaud, C.; Coaquette, A.; Chalopin, J.M.; Gaiffe, E.; Saas, P.; Ducloux, D. Subclinical Epstein-Barr virus viremia among adult renal transplant recipients: Incidence and consequences. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprangers, B.; Riella, L.V.; Dierickx, D. Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder Following Kidney Transplantation: A Review. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 78, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, D.E.; Douglas, L.; Andreadis, C.; Vogl, D.T.; Arnoldi, S.; Kotloff, R.; Svoboda, J.; Bloom, R.D.; Olthoff, K.M.; Brozena, S.C.; et al. EBV PCR in the diagnosis and monitoring of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder: Results of a two-arm prospective trial. Am. J. Transplant. 2008, 8, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, C.J.; Karger, A.B.; Mullan, B.D.; Brundage, R.C.; Balfour, H.H., Jr. Quantitative Epstein-Barr virus shedding and its correlation with the risk of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder. Clin. Transplant. 2012, 26, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, E.; Shenton, B.K.; Green, K.; Jackson, G.; Gould, F.K.; Yap, C.; Talbot, D. Dynamic EBV gene loads in renal, hepatic, and cardiothoracic transplant recipients as determined by real-time PCR light cycler. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2004, 6, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.; Bowles, K.; Bradley, J.A.; Emery, V.; Featherstone, C.; Gupte, G.; Marcus, R.; Parameshwar, J.; Ramsay, A.; Newstead, C. Haemato-oncology Task Force of the British Committee for Standards in Haematology and British Transplantation Society. Management of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder in adult solid organ transplant recipients—BCSH and BTS Guidelines. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 149, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, U.D.; Preiksaitis, J.K. Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders, Epstein-Barr virus infection, and disease in solid organ transplantation: Guidelines from the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Zheng, B.; Daines, L.; Sheikh, A. Long-term sequelae of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of one-year follow-up studies on post COVID symptoms. Pathogens 2022, 11, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalbandian, A.; Sehgal, K.; Gupta, A.; Madhavan, M.V.; McGroder, C.; Stevens, J.S.; Cook, J.R.; Nordvig, A.S.; Shalev, D.; Sehrawat, T.S.; et al. Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, J.E.; Okyay, R.A.; Licht, W.E.; Hurley, D.J. Investigation of long COVID prevalence and its relationship to Epstein-Barr virus reactivation. Pathogens 2021, 10, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilbrands, L.B.; Duivenvoorden, R.; Vart, P.; Franssen, C.F.M.; Hemmelder, M.H.; Jager, K.J.; Kieneker, L.M.; Noordzij, M.; Pena, M.J.; Vries, H.; et al. COVID-19-related mortality in kidney transplant and dialysis patients: Results of the ERACODA collaboration. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponticelli, C. Herpes viruses and tumours in kidney transplant recipients. The role of immunosuppression. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 1769–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalck, S.; Rooney, C.M.; Heslop, H. Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders. Annu. Rev. Med. 2005, 56, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steven, N.M.; Annels, N.E.; Kumar, A.; Leese, A.M.; Kurilla, M.G.; Rickinson, A.B. Immediate early and early lytic cycle proteins are frequent targets of the Epstein-Barr virus-induced cytotoxic T cell response. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 1605–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunn, A.V.W.; Guy, G.W.; Botchway, S.W.; Bell, J.D. SARS-CoV-2 and EBV; the cost of a second mitochondrial “whammy”? Immun. Ageing 2021, 18, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Song, J.; Liu, H.; Zheng, H.; Chen, C. Positive Epstein-Barr virus detection in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basic-Jukic, N.; Juric, I.; Furic-Cunko, V.; Katalinic, L.; Radic, J.; Bosnjak, Z.; Jelakovic, B.; Kastelan, Z. Follow-up of renal transplant recipients after acute COVID-19 -A prospective cohort single-center study. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2021, 9, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musialik, J.; Kolonko, A.; Wiecek, A. Increased EBV DNAemia after Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Solid Organ Transplants. Vaccines 2022, 10, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolucci, S.; Cassaniti, I.; Novazzi, F.; Fiorina, L.; Piralla, A.; Comolli, G.; Bruno, R.; Maserati, R.; Gulminetti, R.; Novati, S.; et al. EBV DNA increase in COVID-19 patients with impaired lymphocyte subpopulation count. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 104, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehner, G.F.; Klein, S.J.; Zoller, H.; Peer, A.; Bellmann, R.; Joannidis, M. Correlation of interleukin-6 with Epstein-Barr virus levels in COVID-19. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naendrup, J.H.; Borrega, G.J.; Eichenauer, D.A.; Shimabukuro-Vornhagen, A.; Kochanek, M.; Boll, B. Reactivation of EBV and CMV in severe COVID-19-epiphenomena or trigger of hyperinflammation in need of treatment? A large case series of critically ill patients. J. Intensive Care Med. 2022, 37, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Total Number of Patients | 166 |
|---|---|
| Demographic | |
| 104 (62.6%) |
| 62 (37.4%) |
| 56 y (23–88) |
| Comorbidity | |
| 116 (69%) |
| 26 (15.7%) |
| 21 (12.7%) |
| 29 (17.5%) |
| Type of treatment | |
| 162 (7.6%) |
| 137 (82.5%) |
| 142 (85.5%) |
| Withdrawal of treatment | |
| 19 (11.4%) |
| 93 (56%) |
| 6 (11.4%) |
| Increase of treatment | |
| 103 (62%) |
| Patients positive for COVID-19 | |
| 25 (14.45%) |
| 41 (23.70%) |
| 100 (60.2%) |
| Patients with vaccination for SARS-CoV-2 | |
| 130 (78.3%) |
| Statistical Significance | ||
|---|---|---|
| Patient median age | ||
| >60 y vs. <60 y | p < 0.05 | |
| EBV Reactivation | ||
| Hospitalization for severe COVID-19 vs. home-managed | ||
| p < 0.001 | ||
| More recent transplant vintage vs. older transplant vintage | ||
| p < 0.01 | ||
| CD4+/CD8+ Ratio | ||
| Steroid dose increased vs. unchanged | ||
| p < 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stefanelli, L.F.; Alessi, M.; Di Bella, C.; Billo, M.E.; Viola, L.; Gnappi, M.; Bettin, E.; Cacciapuoti, M.; Calò, L.A. EBV Reactivation in Transplant Recipients following SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Retrospective Study. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121435
Stefanelli LF, Alessi M, Di Bella C, Billo ME, Viola L, Gnappi M, Bettin E, Cacciapuoti M, Calò LA. EBV Reactivation in Transplant Recipients following SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Retrospective Study. Pathogens. 2023; 12(12):1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121435
Chicago/Turabian StyleStefanelli, Lucia Federica, Marianna Alessi, Caterina Di Bella, Maria Elena Billo, Ludovica Viola, Maddalena Gnappi, Elisabetta Bettin, Martina Cacciapuoti, and Lorenzo A. Calò. 2023. "EBV Reactivation in Transplant Recipients following SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Retrospective Study" Pathogens 12, no. 12: 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121435
APA StyleStefanelli, L. F., Alessi, M., Di Bella, C., Billo, M. E., Viola, L., Gnappi, M., Bettin, E., Cacciapuoti, M., & Calò, L. A. (2023). EBV Reactivation in Transplant Recipients following SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Retrospective Study. Pathogens, 12(12), 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12121435






