Family-Run Pig Farms: Research and Extension Activities for Parasite Control in a Municipality in the State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
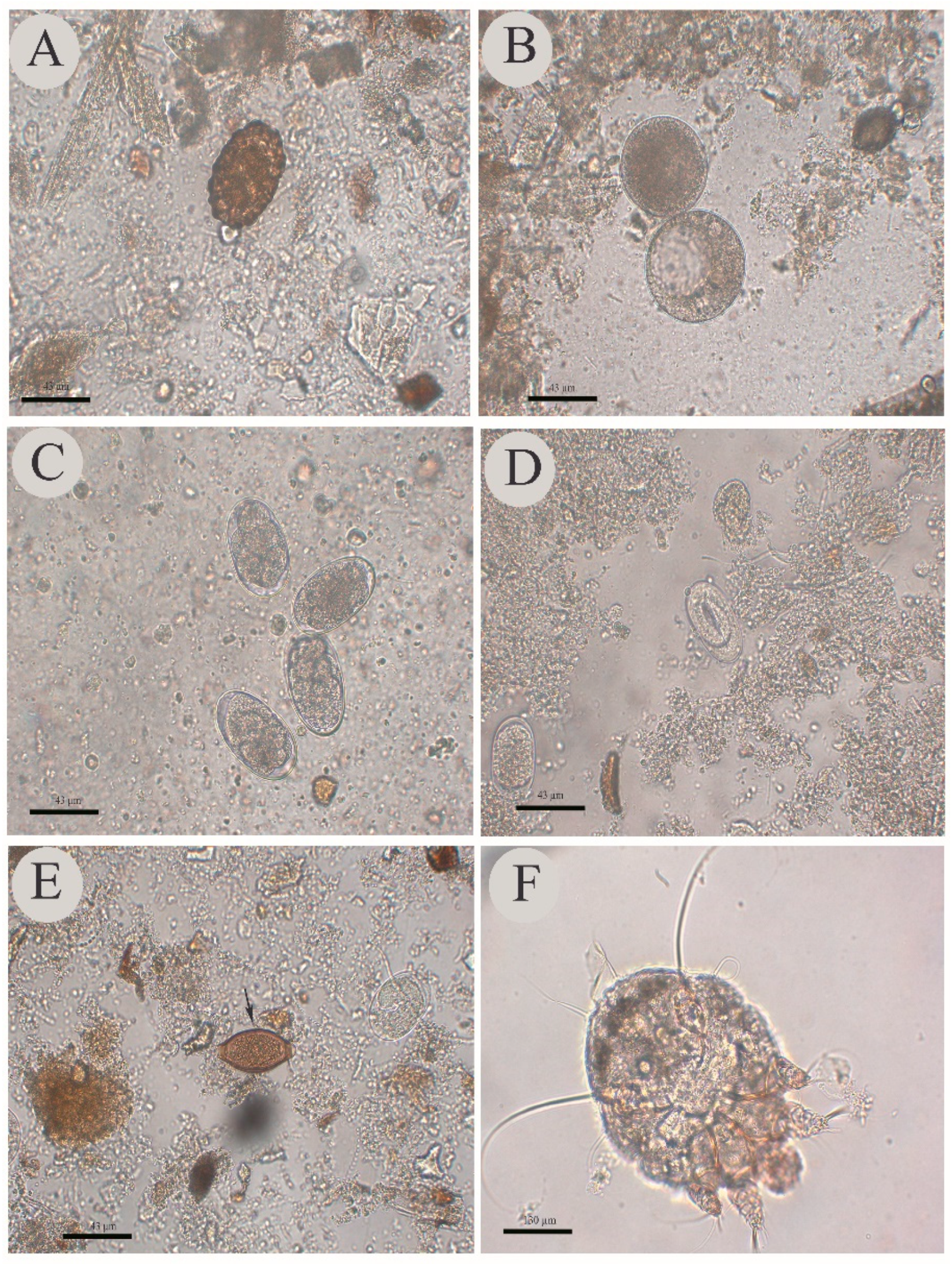
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Location
4.2. Study Design and Collection of Biological Samples
4.3. Laboratory Processing
4.4. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ribeiro-Silva, R.C.; Pereira, M.; Aragão, É.; Guimarães, J.M.M.; Ferreira, A.J.F.; Rocha, A.S.; Silva, N.J.; Teixeira, C.S.S.; Falcão, I.R.; Paixao, E.S.; et al. COVID-19, Food Insecurity and Malnutrition: A Multiple Burden for Brazil. Front. Nutr. 2021, 15, 751715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Com Preço Recorde, Consumo de Carne é o Menor em 16 Anos. In BBC News. 2021. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/portuguese/brasil-59653752 (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Mekuriaw, Y.; Asmare, B. Assessment of Pig Production and Constraints in Mecha District, Amhara Region, Northwestern Ethiopia. Adv. Agric. 2014, 2014, 329254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekule, F.P.; Kyvsgaard, N.C. Improving pig husbandry in tropical resource-poor communities and its potential to reduce risk of porcine cysticercosis. Acta Trop. 2003, 87, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebisi, O.R. Gastro-intestinal helminths and public health: Overview of a neglected sector. J. Vet. Med. 2008, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Embrapa. Estatísticas—Brasil 2021. Available online: https://www.embrapa.br/suinos-e-aves/cias/estatisticas (accessed on 22 May 2022).
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. Censo Agropecuário Resultados Definitivos 2017. Available online: https://sidra.ibge.gov.br/pesquisa/censo-agropecuario/censo-agropecuario-2017 (accessed on 22 May 2022).
- Silva Filha, O.L.; Barbosa, E.J.R.; Lima, A.D.; Melo, A.G.P.; Melo Filho, A.J.; Sá, M.S. Os produtores de suínos no Município de Floresta, Estado de Pernambuco, Brasil. Actas Iberoam. Conserv. Anim. 2011, 1, 416–418. [Google Scholar]
- Silva Filha, O.L. Caracterização da criação de suínos locais no Curimataú Paraibano. Ph.D. Thesis, Centro de Ciências Agrárias da Universidade Federal da Paraíba, Paraíba, Brazil, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bordin, E.L. Relações entre infecções por parasitas internos de suínos e o custo de alimentação—Uma revisão. A Hora Veterinária 1987, 7, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Roepstorff, A.; Nilsson, O.; Oksanen, A.; Gjerde, B.; Richter, S.H.; Ortenberg, E.; Christensson, D.; Martinsson, K.B.; Bartlett, P.C.; Nansen, P.; et al. Intestinal parasites in swine in the Nordic countries: Prevalence and geographical distribution. Vet. Parasitol. 1998, 76, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nansen, P.; Roepstorff, A. Parasitic helminths of the pig: Factors influencing transmission and infection levels. Int. J. Parasitol. 1999, 29, 877–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.; Bastos, O.M.P.; Dib, L.V.; Siqueira, M.P.; Cardozo, M.L.; Ferreira, L.C.; Chaves, W.T.; Fonseca, A.B.M.; Uchôa, C.M.A.; Amendoeira, M.R.R. Gastrointestinal parasites of swine raised in different management systems in the State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2015, 35, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaymani-Mohammadi, S.; Petri, W.A., Jr. Zoonotic implications of the swine-transmitted protozoal infections. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 140, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, K.J.L.; Calegar, D.A.; Santos, J.P.; Bacelar, P.A.A.; Coronato-Nunes, B.; Reis, E.R.C.; Boia, M.N.; Carvalho-Costa, F.A.; Jaeger, L.H. Genetic diversity of Ascaris spp. infecting humans and pigs in distinct Brazilian regions, as revealed by mitochondrial DNA. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumsa, B.; Kifle, E. Internal parasites and health management of pigs in Burayu District, Oromia Regional State, Ethiopia. J. South Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2014, 85, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Class, C.S.C.; Silveira, R.L.; Palmer, J.P.S.; Fialho, P.A.; Lobão, L.F.; Dib, L.V.; Uchôa, C.M.A.; Barbosa, A.S. Research and extension action for parasitic control in pig breeding families located in Tanguá, Rio de Janeiro. Pesq Vet Bras. 2020, 40, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, R.C.; Carrazza, L.G.; Sant’ana, D.S.; Oliveira, M.T.; Carrazza, T.G. Prevalência de parasitos gastrintestinais em leitões de terminação relacionada com densidade de alojamento e sexo. Pubvet 2011, 5, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.G.T.; Fonseca, Z.A.A.S.; Coelho, W.A.C.; Ahid, S.M.M. Endoparasitose em suínos (Sus domesticus) criados em confinamento no Município de Mossoró, Rio Grande do Norte. Pubvet 2011, 5, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreiro, C.; Coelho, C.D.; Jorge, J.L.B.P.; Costa, N.O.G.; Paiva, R.V.; Filho, W.L.T.; Rosa, A.G.; Jesus, V.L.T. Parasitos intestinais em suínos confinados em uma criação no município de Pinheiral, RJ. Braz. J. Vet. Med. 2016, 38, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, H.G.; Silva, J.T.; Álvares, F.B.V.; Ferreira, L.C.; Azevedo, S.S.; Vilela, V.L.R. Prevalence and risk factors associated with swine gastrointestinal nematodes and coccidia in the semi-arid region of northeastern Brazil. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2019, 52, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattos, M.J.T.; Marques, S.T.; Juffo, E.; Ramos, M.; Silveira, E.; Ribeiro, V.L.S. Parasitoses em suínos de criatórios familiares na região metropolitana de Porto Alegre, RS, Brasil. Rev. Agr. Acad. 2020, 3, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfetti, D.J.C.; Quintero, M.E.A.; Low, J.L.T.; Moreno, P.M. Prevalencia de enteroparásitos porcinos en una comunidad rural de la península de Paraguaná, Estado Falcón, Venezuela. Rev. Científica. 2013, 23, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Dadas, S.; Mishra, S.; Jawalagatti, V.; Gupta, S.; Vinary, T.S.; Gudewar, J. Prevalence of gastro-intestinal parasites in pigs (Sus scrofa) of Mumbai Region. Int. J. Sci. Environ. Technol. 2016, 5, 822–826. [Google Scholar]
- Roesel, K.; Dohoo, I.; Baumann, M.; Dione, M.; Grace, D.; Clausen, P.H. Prevalence and risk factors for gastrointestinal parasites in small-scale pig enterprises in Central and Eastern Uganda. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumusiime, M.; Ntampaka, P.; Niragire, F.; Sindikubwabo, T.; Habineza, F. Prevalence of Swine Gastrointestinal Parasites in Nyagatare District, Rwanda. J. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 2020, 8814136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puicón, V.; López-Flores, A.; Fabian-Dominguez, F.; Sánchez-Cárdenas, H. Prevalencia coprológica de parásitos gastrointestinales en humanos y porcinos de crianza de traspatio del distrito de Zapatero, San Martín. Rev. Vet. Zoot. Amaz. 2021, 1, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, A.M.; Gennari, S.M.; Lisboa, M.N.T.S.; Silvestrim, A.; Caproni, L., Jr.; Umehara, O. Parasitas intestinais em suínos confinados nos Estados de São Paulo e Minas Gerais. Arq. Inst. Biol. 2000, 67, 199–203. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, Y.B.; Hu, Y.J.; Li, Y.; Li, B.S.; Lin, R.Q.; Xie, D.H.; Gasser, R.B.; Zhu, X.Q. Survey of intestinal parasites in pigs from intensive farms in Guangdong Province, People’s Republic of China. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 3–4, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, H.A.H.A.; Jeon, H.; Yu, Y.; Do, C.; Lee, Y. Intestinal parasite infections in pigs and beef cattle in rural areas of Chungcheongnam-do, Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 2010, 48, 347–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beloeil, P.A.; Chauvin, C.; Fablet, C.; Jolly, J.P.; Eveno, E.; Madec, F.; Reperant, J.M. Helminth control practices and infections in growing pigs in France. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2003, 81, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, G.G.; Santos, T.B.; Melo, C.M.; Jeraldo, V.L.S. Ocorrência de enteroparasitas em amostras fecais de suínos do município de Simão Dias—SE. Cad. Grad. —Ciências Biológicas Saúde 2012, 1, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, E.S.; Cruz, A.C.M.; Class, C.S.C.; Barbosa, A.S.; Machado, S.J.; Silva, G.V.O.; Knackfuss, F.B.; Silveira, R.L. Parasitos gastrointestinais de suínos criados em uma granja em Nova Iguaçu, Rio de Janeiro. Pubvet 2020, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoruyi, Z.; Agbinone, I. Gastrointestinal parasites among swine bred in Edo State, Nigeria. Afr. J. Clin. Exper. Microbiol. 2020, 21, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinilla, J.C.; Morales, E.; Delgado, N.U.; Florez, A.A. Prevalence and risk factors of gastrointestinal parasites in backyard pigs reared in the Bucaramanga Metropolitan Area, Colombia. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2020, 29, e015320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alencar, A.S.; Farias, M.P.O.; Rosas, E.O.; Lima, M.M.; Alves, L.C.; Faustino, M.A.G. Influência do manejo higiênico-sanitário na infecção por helmintos gastrintestinais em suínos de granjas tecnificadas e de subsistência abatidos na Região Metropolitana de Recife e Zona da Mata do Estado de Pernambuco, Brasil. Arq. Inst. Biol. 2011, 78, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, E.; Sjölund, M.; Wallgren, T.; Lind, E.O.; Höglund, J.; Wallgren, P. Management practices related to the control of gastrointestinal parasites on Swedish pig farms. Porcine Health Manag. 2021, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, D.M.; Cruz, J.F.; Neto, M. Uso preventivo do toltrazuril para controle da coccidiose em cabritos de corte criados em região semiárida. Rev. Bras. Saúde Prod. Anim. 2015, 16, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.L.R.; Moreira, J.P.; Nascimento, S.; Mota, L.C.; Silva, A.D.L. Dinâmica da produção de suínos nos municípios de Nísia Floresta e São José do Mipibu—Rio Grande do Norte. In Proceedings of the 49ª Reunião Anual da Sociedade Brasileira de Zootecnia, Brasília, Brazil, 23–26 July 2012; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha, L.O.; Oliveira, R.M.; Hellmeister Filho, P.; Gomes, N.A.; Carneiro, M.F.; Silva, O.M.; Fernandes, L.C. Diagnóstico Participativo/Rural aplicado à criação de aves e suínos caipiras em regiões periurbanas no município de Senador Canedo (GO). Front. J. Soc. Technol. Environ. Sci. 2016, 5, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motsa’A, J.S.; Defang, H.F.; Keambou, C.T. Socio-economic and technical characteristics of pig (Sus scrofa domesticus) production system in the humid forest with monomodal rainfall agroecological zone of Cameroon. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2018, 12, 2318–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, F.L.; Ramirez-Ávila, L. Current world status of Balantidium coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.K.M.; Dib, L.V.; Amendoeira, M.R.; Class, C.C.; Pinheiro, J.L.; Fonseca, A.B.M.; Barbosa, A.S. Balantidiasis in humans: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Trop. 2021, 233, 106069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, C.R.; Nessi, A.P.; González, O.H.; Hernández, M.O.; Galindo, M.; Dorta, A.; Wagner, C.; Vethencourt, M.A.; Pérez de, G.M.V. Balantidium spp. en cerdos y sus criadores: Prevalencia em comunidades de dos Estados de Venezuela. Vitae 2013, 54, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, A.S.; Bastos, O.M.P.; Uchôa, C.M.A.; Dib, L.V.; Amendoeira, M.R.R. Avaliação da frequência de Balantidium coli em suínos, tratadores de suínos e primatas não humanos no estado do Rio de Janeiro. Rev. Patol. Trop. 2016, 45, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.M.S.; Costa, J.O.; Souza, J.C.A. Ocorrência de endoparasitos em suínos criados em Itabuna, Bahia, Brasil. Ciência Veterinária Nos Trópicos 2007, 10, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, C.R.; Macêdo, E.S.; Brandão, E.M.; Pereira, P.V.M.; Santos, A.C.G. Avaliação Parasitária de suínos nativos da região da baixada Maranhense. Arch. Vet. Sci. 2015, 20, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, C.; Joachim, A.; Daugschies, A. Occurrence of Isospora suis in larger piglet production units and on specialized piglet rearing farms. Vet. Parasitol. 1999, 82, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roepstorff, A.; Nansen, P. FAO Animal Health Manual: Epidemiology, Diagnosis and Control of Helminth Parasites of Swine; Food and Agricultural Organization of United States Press: Rome, Italy, 1996; pp. 1–171. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, M.; Zhou, R.Q.; Huang, H.C.; Hu, S.J. Prevalence and risk factors associated with intestinal parasites in pigs in Chongqing, China. Res. Vet. Sci. 2011, 91, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.V.; Sobestiansky, J.; Linhares, G.F.C.; Vieira, R.C.; Oliveira, J.P.; Vieira, M.C.M. Prevalência de sarna sarcóptica em suínos mantidos em criações intensivas na microrregião de Goiânia—GO—Brasil. Rev. Patol. Trop. 2002, 31, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sobestiansky, J.; Linhares, G.F.C.; Silva, E.V.; Linhares, D. Aspectos clínicos e epidemiológicos de um foco de sarna sarcóptica em um sistema intensivo de produção de suínos localizado no município de Teresópolis GO, Brasil. Rev. Patol. Trop. 2005, 34, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laha, R. Sarcoptic mange infestation in pigs: An overview. J. Parasit. Dis. 2015, 39, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruas, E.D.; Brandão, I.M.M.; Carvalho, M.A.T.; Soares, M.H.P.; Matias, R.F.; Gava, R.C. Metodologia Participativa de Extensão Rural para o Desenvolvimento Sustentável—MEXPAR; Bárbara Bela Editora Gráfica: Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2006; p. 68. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. Cachoeiras de Macacu. 2021. Available online: https://cidades.ibge.gov.br/brasil/rj/cachoeiras-de-macacu/panorama (accessed on 29 September 2021).
- Palmeira, L.; Agenda 21 Local de Cachoeiras de Macacu, Brasil. In Démarches Territoriales de Développement Durab. 2013. Available online: http://demarchesterritorialesdedeveloppementdurable.org/cachoeiras-de-macacu-brasil/ (accessed on 29 September 2021).
- Ritchie, L.S. An ether sedimentation technique for routine stool examinations. Bull. US Army Med. Dep. 1948, 8, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Young, K.H.; Bullock, S.L.; Melvin, D.M.; Spruill, C.L. Ethyl acetate as a substitute for diethyl ether in the formalin-ether sedimentation technique. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1979, 10, 852–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheather, A.T. The detection of intestinal protozoa and mange parasites by a floatation technique. J. Comp. Pathol.Therap. 1923, 36, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, F.; Bomfim, T.C.; Gomes, R.S. Comparação da eficiência da técnica de sedimentação pelo formaldeído-éter e da técnica de centrífugo flutuação modificada na detecção de cistos de Giardia sp. e oocistos de Cryptosporidium sp. em amostras fecais de bezerros. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2003, 12, 135–137. [Google Scholar]
- Lutz, A.O. Schistosomum mansoni e a Schistosomatose segundo observações, feitas no Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 1919, 11, 121–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parasites | Family Pig-Farming Properties | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (n = 36) | B (n = 3) | C (n = 6) | D (n = 27) | E (n = 8) | F (n = 4) | G (n = 15) | H (n = 28) | I (n = 41) | J (n = 12) | Total (n = 180) | p Value | |
| Phylum Ciliophora | 19 (52.8%) | 2 (66.7%) | 1 (16.7%) | 25 (92.6%) | 7 (87.5%) | 3 (75%) | 14 (93.3%) | 25 (89.3%) | 20 (48.8%) | 11 (91.7%) | 127 (70.5%) | 0.00 * |
| Coccidia oocysts | 16 (44.4%) | 0 | 1 (16.7%) | 10 (37%) | 5 (62.5%) | 0 | 10 (66.7%) | 13 (46.4%) | 4 (9.7%) | 10 (83.3%) | 69 (38.3%) | 0.00 * |
| Amoebids | 1 (2.8%) | 0 | 0 | 2 (7.4%) | 0 | 0 | 1 (6.7%) | 1 (3.6%) | 0 | 0 | 5 (2.8%) | 1 |
| Blastocystis sp. | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (25%) | 0 | 0 | 2 (7.1%) | 5 (12.2%) | 0 | 7 (3.9%) | 0.61 |
| A. suum | 24 (66.7%) | 3 (100%) | 4 (66.7%) | 0 | 3 (37.5%) | 0 | 2 (13.3%) | 16 (57.15%) | 2 (4.9%) | 4 (33.3%) | 58 (32.2%) | 0.00 * |
| T. suis | 6 (16.7%) | 2 (66.7%) | 0 | 8 (29.6%) | 2 (25%) | 0 | 2 (13.3%) | 3 (10.7%) | 0 | 8 (66.7%) | 31 (17.2%) | 0.009 * |
| Strongyles | 19 (52.7%) | 1 (33.3%) | 5 (83.3%) | 19 (70.4%) | 8 (100%) | 4 (100%) | 10 (66.7%) | 24 (89.3%) | 1 (2.4%) | 11 (91.7%) | 102 (56.7%) | 0.00 * |
| S. ransomi | 18 (50%) | 1 (33.3%) | 3 (50%) | 16 (59.2%) | 5 (63.5%) | 0 | 6 (40%) | 20 (71.4%) | 0 | 11 (91.7%) | 80 (44.4%) | 0.00 * |
| Nematode larvae | 2 (5.5%) | 0 | 1 (16.7%) | 0 | 1 (12.5%) | 0 | 0 | 1 (3.5%) | 0 | 2 (16.7%) | 7 (3.9%) | 0.59 |
| Capillaria sp. | 1 (2.8%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.5%) | 1 |
| Subtotal | 32 (88.9%) | 3 (100%) | 6 (100%) | 25 (92.6%) | 8 (100%) | 4 (100%) | 14 (93.3%) | 27 (96.4%) | 25 (61%) | 11 (91.7%) | 155 (86.1%) | |
| Ectoparasites | A (n = 35) | B (n = 3) | C (n = 5) | D (n = 19) | E (n = 8) | F (n = 3) | G (n = 7) | H (n = 21) | I (n = 32) | J (n = 9) | Total (n = 142) | p Value |
| S. scabiei var. suis | 0 | 0 | 2 (40%) | 0 | 1 (12.5%) | 0 | 1 (14.3%) | 1 (4.8%) | 0 | 0 | 5 (3.5%) | 1 |
| D. phylloides | 1 (2.9%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.7%) | 1 |
| Arthropod egg | 0 | 0 | 1 (20%) | 0 | 3 (37.5%) | 0 | 2 (28.6%) | 1 (4.8%) | 2 (6.2%) | 0 | 9 (6.3%) | 1 |
| Subtotal | 1 (2.8%) | 0 | 2 (4%) | 0 | 4 (50%) | 0 | 2 (28.6%) | 2 (9.5%) | 2 (6.2%) | 0 | 13 (9.1%) | |
| Information | Parasite | Phylum Ciliophora | Coccidia Oocysts | A. suum | T. suis | Strongyles | S. ransomi | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | p Value | % | p Value | % | p Value | % | p Value | % | p Value | % | p Value | % | p Value | |
| Sex | ||||||||||||||
| Male (n = 71) | 84.5 | 0.6623b | 67.6 | 0.5067b | 35.2 | 0.5324b | 25.3 | 0.1419b | 16.9 | 1b | 47.9 | 0.06b | 35.2 | 0.0476b * |
| Female (n = 109) | 87.1 | 72.5 | 40.4 | 36.7 | 19.4 | 62.4 | 50.4 | |||||||
| Age range | ||||||||||||||
| Initiation (n = 79) | 72.1 | 0.0000a * | 55.7 | 0.005a * | 39.2 | 0.4986a | 27.8 | 0.1924a | 24 | 0.0616a | 40.5 | 0.006a * | 38 | 0.3026a |
| Growing (n = 28) | 100 | 85.7 | 28.6 | 46.4 | 17.9 | 67.8 | 50 | |||||||
| Fatteners (n = 73) | 95.9 | 80.8 | 41.1 | 86.3 | 9.6 | 69.9 | 49.3 | |||||||
| Property type | ||||||||||||||
| Backyard of the homes (n = 47) | 91.5 | 0.3257b | 59.6 | 0.06b * | 44.6 | 1b | 63.8 | 0.0000b * | 21.3 | 1b | 59.6 | 0.1472b | 51.06 | 0.6305b |
| Little farm (n = 133) | 84.2 | 74.4 | 36.1 | 21.1 | 15.7 | 55.6 | 42.1 | |||||||
| Stocking and categorization of animals by pig pen | ||||||||||||||
| There is no set number (n = 99) | 92.9 | 0.0058a * | 76.8 | 0.111a | 54.5 | 0.000a * | 49.5 | 0.0000a * | 21.2 | 0.2338a | 72.7 | 0.0000a * | 60.1 | 0.0000a * |
| Divide pigs by age group (n = 77) | 76.6 | 62.3 | 19.5 | 11.7 | 12.9 | 36.7 | 25.9 | |||||||
| Only one pig per pen (n = 4) | 100 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | |||||||
| Facilities type | ||||||||||||||
| Collective bays with cement wall (n = 100) | 81 | 0.06a | 73 | 0.0238a * | 27 | 0.003a * | 18 | 0.0000a * | 11 | 0.0275a * | 48 | 0.0005a * | 36 | 0.0211a * |
| Collective bays with cement wall, wooden or bamboo fence (n = 41) | 95.1 | 80.5 | 63.4 | 31.7 | 29.3 | 82.9 | 60.9 | |||||||
| Collective bays with cement and wood wall (n = 39) | 89.7 | 70.6 | 41.03 | 69 | 20.5 | 51.3 | 48.7 | |||||||
| Roof pen | ||||||||||||||
| Totally covered with fiber cement tile, galvanized or PVC (n = 168) | 85.7 | 1b | 69 | 0.1140b | 35.1 | 0.001b * | 32.1 | 1b | 13.7 | 0.0001b * | 54.1 | 0.0135b * | 41.1 | 0.0006b * |
| Partially covered with fiber cement tile (n = 12) | 91.7 | 91.7 | 83.3 | 33.3 | 66.7 | 91.6 | 91.7 | |||||||
| Floor of the buildings | ||||||||||||||
| Naked soil or deteriorated cement (n = 33) | 93.4 | 0.262b | 78.8 | 0.2958b | 63.6 | 0.001b * | 30.3 | 0.8399b | 30.3 | 0.0397b * | 78.8 | 0.005b * | 60.6 | 0.051b |
| Cemented or concreted (n = 147) | 84.4 | 68.7 | 32.6 | 32.7 | 14.3 | 51.7 | 40.8 | |||||||
| Water to cool the pig | ||||||||||||||
| Yes (n = 36) | 88.9 | 0.788b | 52.8 | 0.0134b * | 44.4 | 0.445b | 66.7 | 0.0000b * | 16.7 | 1b | 52.7 | 0.7073b | 50 | 0.4056b |
| No (n = 144) | 85.4 | 75 | 36.8 | 23.7 | 17.4 | 57.6 | 43.06 | |||||||
| Habit of throwing water on the body of pigs to refresh them | ||||||||||||||
| Yes (n = 180) | 86.1 | NA | 70.5 | NA | 38.3 | NA | 32.2 | NA | 17.2 | NA | 56.7 | NA | 44.4 | NA |
| Supply of drinking water | ||||||||||||||
| Ad libitum (n = 159) | 84.9 | 0.316b | 71 | 0.7992b | 36.5 | 0.231b | 29.6 | 0.0467b * | 13.2 | 0.0005b * | 53.5 | 0.019b * | 40.8 | 0.100b |
| Provided two or three times a day (n = 21) | 95.2 | 66.7 | 52.4 | 52.4 | 47.6 | 80.9 | 71.4 | |||||||
| Type of drinking fountains | ||||||||||||||
| Cement fountain (n = 52) | 96.15 | 0.004a * | 80.8 | 0.1250a | 46.1 | 0.0002a * | 48.1 | 0.0000a * | 13.5 | 0.0564a | 76.9 | 0.000a * | 57.7 | 0.0000a * |
| Nipple type (n = 72) | 75 | 66.7 | 19.4 | 2.7 | 11.1 | 33.3 | 22.2 | |||||||
| Cut tire and plastic bowls (n = 8) | 100 | 87.5 | 62.5 | 37.5 | 25 | 100 | 62.5 | |||||||
| Cement lame and plastic bowls (48) | 89.6 | 62.5 | 54.2 | 58.3 | 29.2 | 62.5 | 60.4 | |||||||
| Food provided to pig | ||||||||||||||
| Remains of human and agricultural food, wheat bran and/or barley (n = 63) | 95.2 | 0.000a * | 90.5 | 0.000a * | 60.3 | 0.0000a * | 39.7 | 0.0000a * | 23.8 | 0.0067a * | 84.1 | 0.0000a * | 66.7 | 0.0000a * |
| Remains of human and agricultural food, maize or rice flour (n = 45) | 91.1 | 48.9 | 37.8 | 68.9 | 17.8 | 55.6 | 48.9 | |||||||
| Agricultural remainder and specific pig feed and wheat bran (n = 41) | 60.9 | 48.8 | 9.8 | 4.9 | 0 | 2.4 | 0 | |||||||
| Horse feed, wheat bran, corn flour or rice and corn (n = 27) | 92.6 | 92.6 | 37 | 0 | 29.6 | 70.4 | 59.3 | |||||||
| Corn bran for pig (n = 4) | 100 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | |||||||
| Feeder | ||||||||||||||
| Cement feeder on the floor (n = 123) | 83.7 | 0.462a | 76.4 | 0.001a * | 34.1 | 0.0022a * | 18.7 | 0.0000a * | 12.2 | 0.000a * | 53.6 | 0.0710a | 38.2 | 0.0042a * |
| Directly on the floor (n = 36) | 88.9 | 52.8 | 44.4 | 66.7 | 16.7 | 52.8 | 50 | |||||||
| Floor and feeder (n = 9) | 100 | 33.3 | 11.1 | 77.8 | 22.2 | 66.7 | 44.4 | |||||||
| Floor, plastic bowls and tire (n = 12) | 91.7 | 91.7 | 83.3 | 33.3 | 66.7 | 91.7 | 91.7 | |||||||
| Information | Parasites | Phylum Ciliophora | Coccidia oocysts | A. suum | Trichuris suis | Strongylus | S. ransomi | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | p Value | % | p Value | % | p Value | % | p Value | % | p Value | % | p Value | % | p Value | |
| Presence of fly | ||||||||||||||
| Yes (n = 137) | 82.5 | 0.010b * | 65.7 | 0.0121b * | 37.2 | 0.594b | 26.3 | 0.0045b * | 17.5 | 1b | 47.4 | 0.0000b * | 39.4 | 0.0216b * |
| No (n = 43) | 97.7 | 86.1 | 41.9 | 51.2 | 16.3 | 86.1 | 60.5 | |||||||
| Blood in pig feces | ||||||||||||||
| No (n = 180) | 86.1 | NA | 70.5 | NA | 38.3 | NA | 32.2 | NA | 17.2 | NA | 56.7 | NA | 44.4 | NA |
| Anti-parasitic medicine | ||||||||||||||
| Yes (n = 180) | 86.1 | NA | 70.5 | NA | 38.3 | NA | 32.2 | NA | 17.2 | NA | 56.7 | NA | 44.4 | NA |
| Caring for the piglets | ||||||||||||||
| Breastfeeding after birth and/or teeth cutting (n = 105) | 93.3 | 0.0017b * | 73.3 | 0.4071b * | 52.4 | 0.000b * | 50.5 | 0.0000b * | 20 | 0.3173b | 73.3 | 0.0000b * | 60 | 0.0000b * |
| Breastfeeding after birth, vaccination, iron supplementation and sterilization (n = 75) | 76 | 66.7 | 18.7 | 6.6 | 13.3 | 33.3 | 22.7 | |||||||
| Accumulation of excreta in the pig enclosure | ||||||||||||||
| Yes (n = 31) | 96.8 | 0.05b | 75 | 0.6702b | 50 | 0.1615b | 37.5 | 0.5332b | 18.7 | 0.7984b | 75 | 0.0294b * | 46.9 | 0.8451b |
| No (n = 148) | 83.8 | 69.6 | 35.8 | 31.1 | 16.9 | 52.7 | 43.9 | |||||||
| How to wash the environment | ||||||||||||||
| Water (n = 168) | 85.7 | 1b | 69.1 | 0.114b | 35.1 | 0.0013b * | 32.1 | 1b | 13.7 | 0.0001b * | 54.1 | 0.0135b * | 41.1 | 0.0000b * |
| Not clean the environment, uses straw bedding (n = 12) | 91.7 | 91.7 | 83.3 | 33.3 | 66.7 | 91.7 | 91.7 | |||||||
| Sanitary break/Use of the flamethrower as a broom | ||||||||||||||
| No (n = 180) | 86.1 | NA | 70.5 | NA | 38.3 | NA | 32.2 | NA | 17.2 | NA | 56.7 | NA | 44.4 | NA |
| Cleaning utensils intended only for cleaning the pig facility | ||||||||||||||
| Yes (n = 177) | 85.8 | 1b | 70.6 | 1b | 38.9 | 0.2868b | 31.07 | 0.0322b * | 16.4 | 0.077b * | 57.6 | 0.5796b | 44.6 | 1b |
| No (n = 3) | 100 | 66.7 | 0 | 100 | 66.7 | 33.3 | 33.3 | |||||||
| Specific clothing only for handling pigs | ||||||||||||||
| Yes (n = 8) | 100 | 0.332a | 87.5 | 0.062a | 62.5 | 0.017a * | 37.5 | 0.2564a | 25 | 0.779a | 100 | 0.0251a * | 62.5 | 0.5511a |
| No (n = 157) | 84.7 | 67.5 | 34.4 | 33.7 | 17.02 | 53.5 | 43.9 | |||||||
| Sporadically (n = 15) | 93.3 | 93.3 | 66.7 | 13.33 | 13.3 | 66.7 | 40 | |||||||
| Information | Multivariate Logistic Regression | |
|---|---|---|
| p-Value (p ≤ 0.05) | OR Adjusted (95% CI) | |
| Gastrointestinal parasite | ||
| Age range | 0.0003 | 3.9153 (1.8810–8.1497) |
| Form of the Phylum Ciliophora | ||
| Age range | 0.0096 | 1.6960 (1.1372–2.5294) |
| Coccidia oocysts | ||
| Food provided to pig | 0.008 | 5.6971 (1.5761–20.593) |
| How to wash the environment | 0.0391 | 5.4707 (1.0884–27.496) |
| Caring for the piglets | 0.0004 | 3.9851 (1.8515–8.5773) |
| Ascaris suum | ||
| Facilities type | 0.0087 | 8.9037 (1.7374–45.6286) |
| Strongyles | ||
| Age range | 0.0109 | 1.7479 (1.1371–2.6870) |
| How to wash the environment | 0.0469 | 8.6966 (1.0302–73.4132) |
| Floor of the buildings | 0.0465 | 8.6587 (1.0341–72.4980) |
| Strongyloides ransomi | ||
| Food provided to pig | 0.0001 | 9.7365 (3.0710–30.8694) |
| Caring for the piglets | 0.0004 | 3.6347 (1.7915–7.3744) |
| How to wash the environment | 0.0253 | 11.0733 (1.3465–91.0613) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Class, C.; Silveira, R.; Fialho, P.; Silva, L.; Lobão, L.; Amendoeira, M.R.; Barbosa, A. Family-Run Pig Farms: Research and Extension Activities for Parasite Control in a Municipality in the State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Pathogens 2022, 11, 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11090971
Class C, Silveira R, Fialho P, Silva L, Lobão L, Amendoeira MR, Barbosa A. Family-Run Pig Farms: Research and Extension Activities for Parasite Control in a Municipality in the State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Pathogens. 2022; 11(9):971. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11090971
Chicago/Turabian StyleClass, Camila, Renato Silveira, Priscila Fialho, Letícia Silva, Lucas Lobão, Maria Regina Amendoeira, and Alynne Barbosa. 2022. "Family-Run Pig Farms: Research and Extension Activities for Parasite Control in a Municipality in the State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil" Pathogens 11, no. 9: 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11090971
APA StyleClass, C., Silveira, R., Fialho, P., Silva, L., Lobão, L., Amendoeira, M. R., & Barbosa, A. (2022). Family-Run Pig Farms: Research and Extension Activities for Parasite Control in a Municipality in the State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Pathogens, 11(9), 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11090971






