Serum Resistance of Mycoplasma agalactiae Strains and Mutants Bearing Different Lipoprotein Profiles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
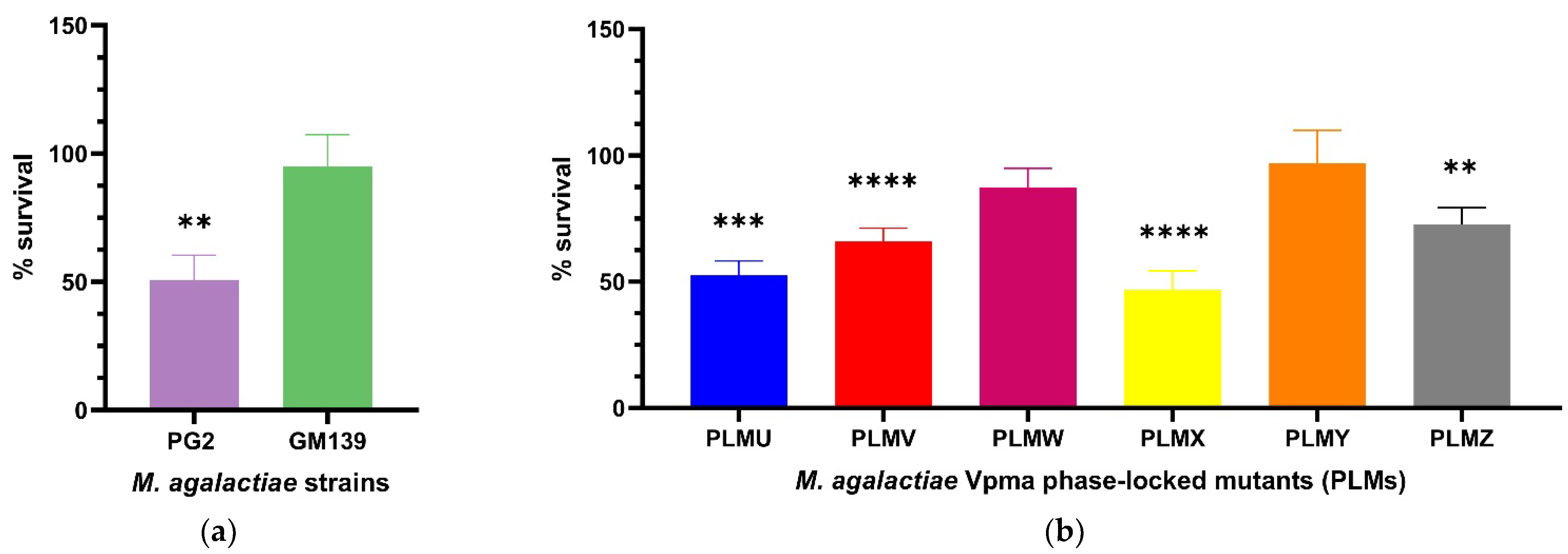
2.1. Bactericidal Assays with Sheep Sera and Guinea Pig Serum Complement Reveal Significant Differences in Susceptibilty and Relative Survival
2.1.1. Sensitized Sheep Serum
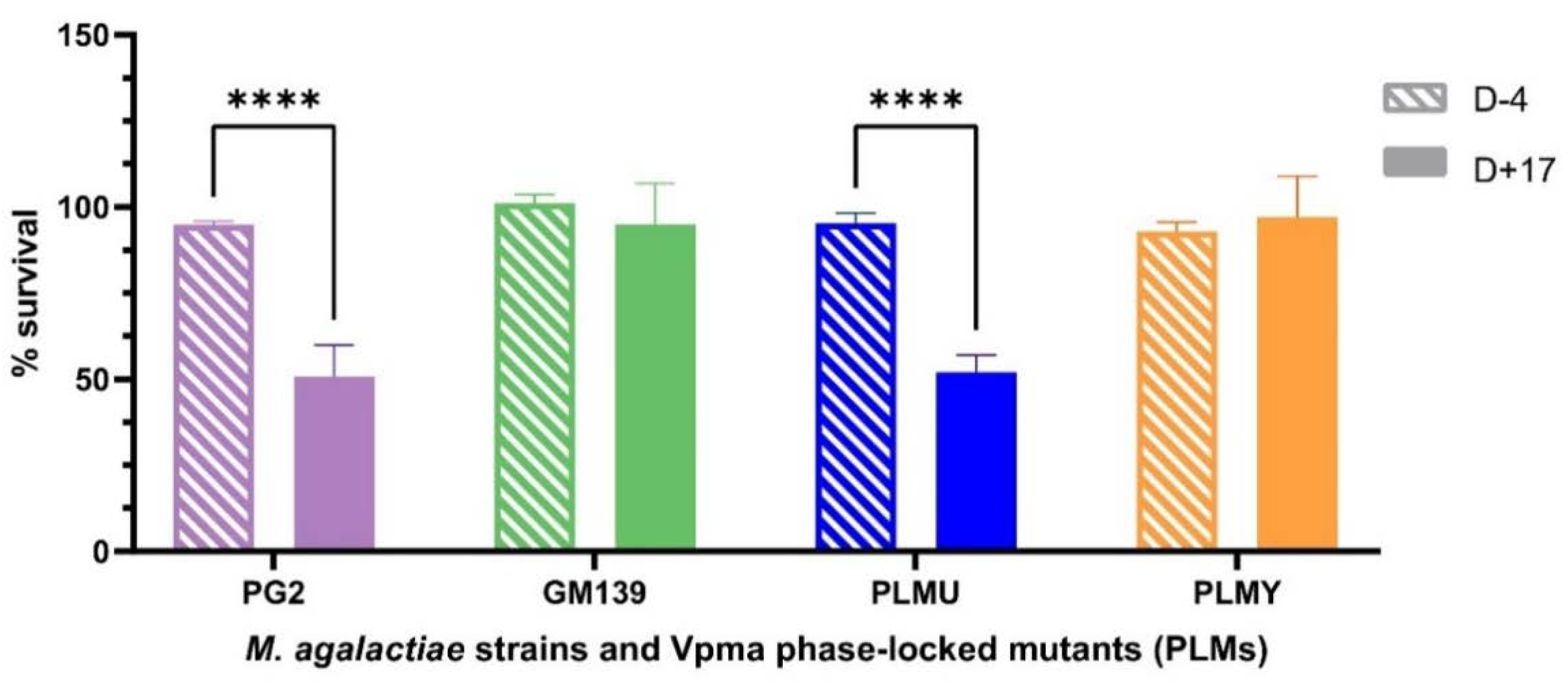
2.1.2. Comparison of Non-Sensitized and Sensitized Sheep Serum
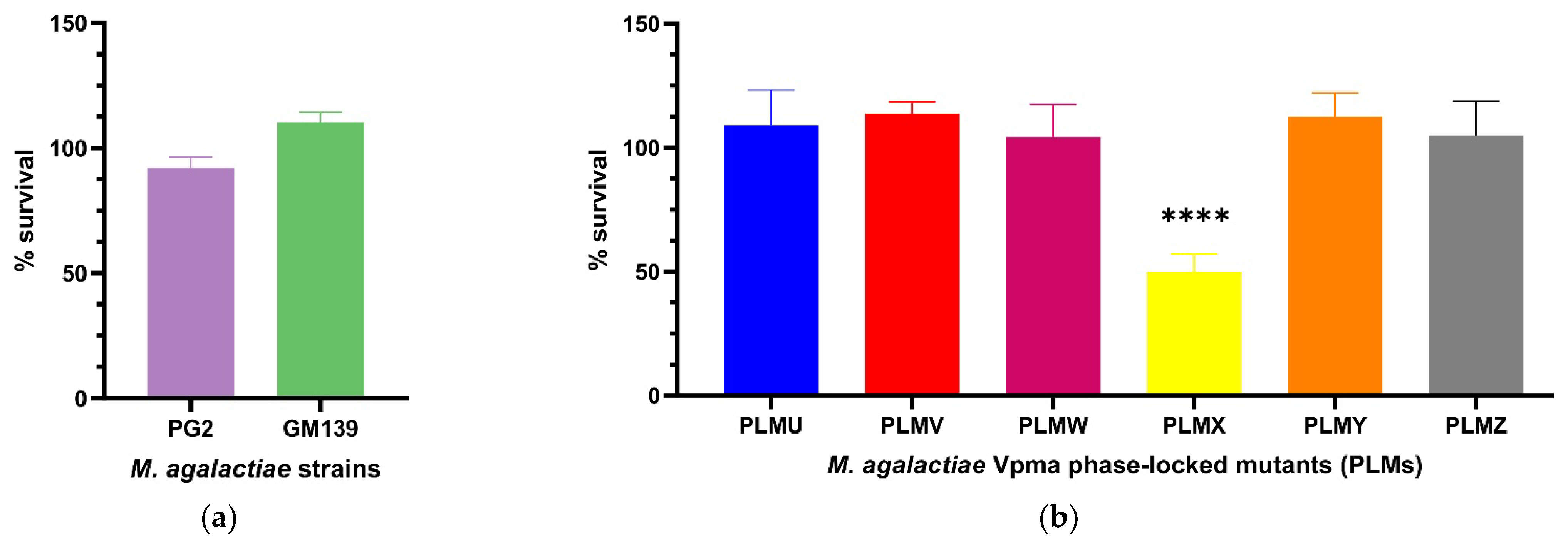
2.1.3. Guinea Pig Serum Complement
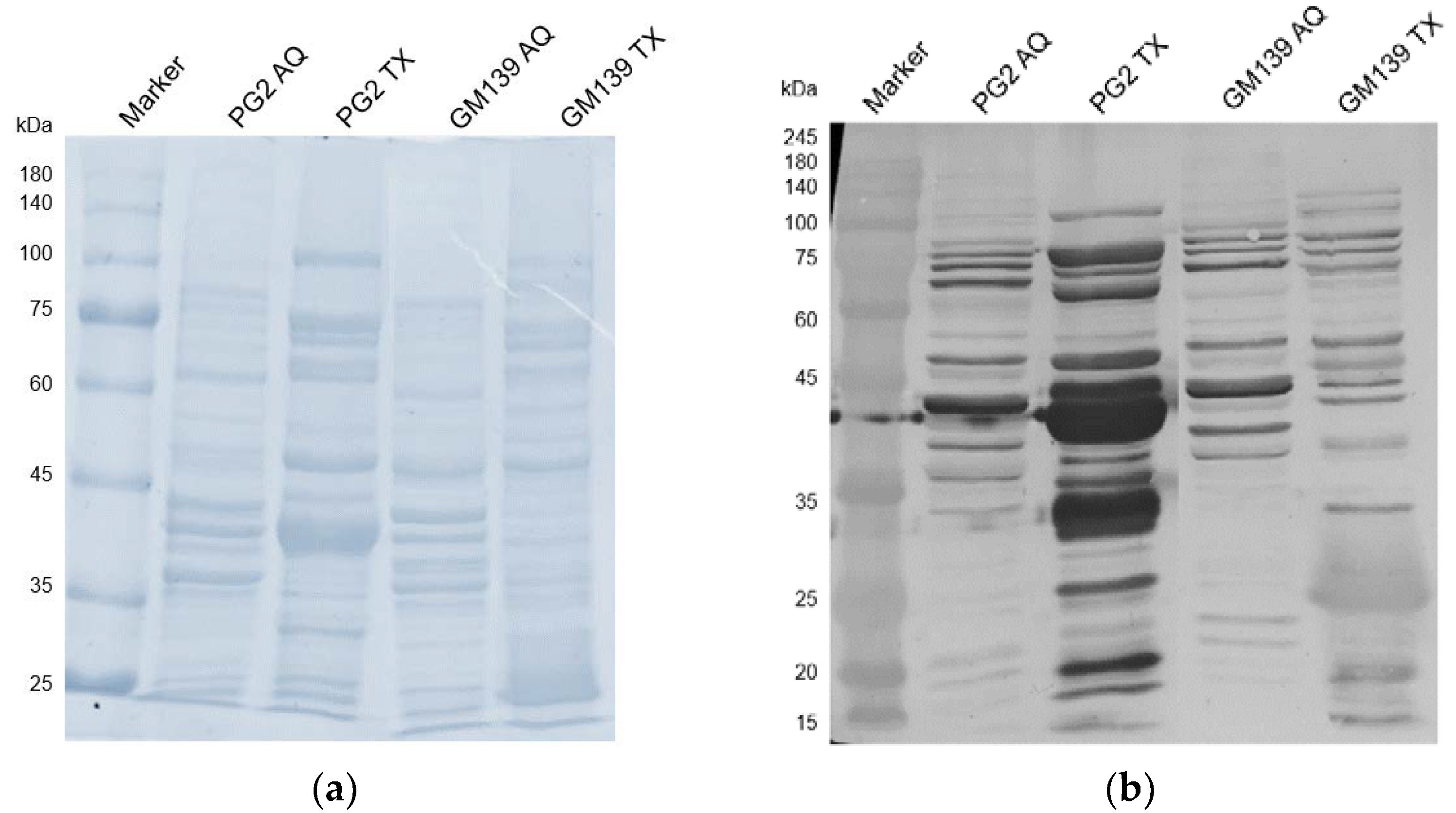
2.2. Western Blot with Sheep Serum D+17
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
4.2. Bactericidal Assay
4.3. Calculation of Percentage Survival
4.4. Statistical Analysis
4.5. Triton X-114 Phase Extraction & Blotting
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Razin, S. Mycoplasmas. In Medical Microbiology, 4th ed.; Baron, S., Ed.; University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996; pp. 861–892. ISBN 9780585417967. [Google Scholar]
- Razin, S.; Yogev, D.; Naot, Y. Molecular Biology and Pathogenicity of Mycoplasmas. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 1094–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citti, C.; Nouvel, L.X.; Baranowski, E. Phase and Antigenic Variation in Mycoplasmas. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 1073–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamu, J.Y.; Wawegama, N.K.; Browning, G.F.; Markham, P.F. Membrane Proteins of Mycoplasma bovis and Their Role in Pathogenesis. Res. Vet. Sci. 2013, 95, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosengarten, R.; Citti, C.; Glew, M.; Lischewski, A.; Droeße, M.; Much, P.; Winner, F.; Brank, M.; Spergser, J. Host-Pathogen Interactions in Mycoplasma Pathogenesis: Virulence and Survival Strategies of Minimalist Prokaryotes. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2000, 290, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra-Dewasthaly, R.; Citti, C.; Glew, M.D.; Zimmermann, M.; Rosengarten, R.; Jechlinger, W. Phase-Locked Mutants of Mycoplasma agalactiae: Defining the Molecular Switch of High-Frequency Vpma Antigenic Variation. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 67, 1196–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flitman-Tene, R.; Mudahi-Orenstein, S.; Levisohn, S.; Yogev, D. Variable Lipoprotein Genes of Mycoplasma agalactiae Are Activated In Vivo by Promoter Addition via Site-Specific DNA Inversions. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glew, M.D.; Papazisi, L.; Poumarat, F.; Bergonier, D.; Rosengarten, R.; Citti, C. Characterization of a Multigene Family Undergoing High-Frequency DNA Rearrangements and Coding for Abundant Variable Surface Proteins in Mycoplasma agalactiae. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 4539–4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, S.; Zimmermann, M.; Rosengarten, R.; Chopra-Dewasthaly, R. Novel Role of Vpmas as Major Adhesins of Mycoplasma agalactiae Mediating Differential Cell Adhesion and Invasion of Vpma Expression Variants. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 308, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czurda, S.; Hegde, S.M.; Rosengarten, R.; Chopra-Dewasthaly, R. Xer1-Independent Mechanisms of Vpma Phase Variation in Mycoplasma agalactiae Are Triggered by Vpma-Specific Antibodies. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 307, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glew, M.D.; Marenda, M.; Rosengarten, R.; Citti, C. Surface Diversity in Mycoplasma agalactiae Is Driven by Site-Specific DNA Inversions within the Vpma Multigene Locus. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra-Dewasthaly, R.; Spergser, J.; Zimmermann, M.; Citti, C.; Jechlinger, W.; Rosengarten, R. Vpma Phase Variation Is Important for Survival and Persistence of Mycoplasma agalactiae in the Immunocompetent Host. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouvel, L.X.; Marenda, M.; Sirand-Pugnet, P.; Sagné, E.; Glew, M.; Mangenot, S.; Barbe, V.; Barré, A.; Claverol, S.; Citti, C. Occurrence, Plasticity, and Evolution of the Vpma Gene Family, a Genetic System Devoted to High-Frequency Surface Variation in Mycoplasma agalactiae. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 4111–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, M.S.; Spergser, J.; Marques, L.M.; Timenetsky, J.; Rosengarten, R.; Chopra-Dewasthaly, R. Predominant Single Stable VpmaV Expression in Strain GM139 and Major Differences with Mycoplasma agalactiae Type Strain PG2. Animals 2022, 12, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra-Dewasthaly, R.; Baumgartner, M.; Gamper, E.; Innerebner, C.; Zimmermann, M.; Schilcher, F.; Tichy, A.; Winter, P.; Jechlinger, W.; Rosengarten, R.; et al. Role of Vpma Phase Variation in Mycoplasma agalactiae Pathogenesis. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 66, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà-Cuéllar, M.; Aragon, V. Serum-Resistance in Haemophilus parasuis Is Associated with Systemic Disease in Swine. Vet. J. 2008, 175, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, W.L.; Denison, A.M.; Dybvig, K. Resistance of Mycoplasma pulmonis to Complement Lysis Is Dependent on the Number of Vsa Tandem Repeats: Shield Hypothesis. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 6846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, B.M.; Simmons, W.L.; Dybvig, K. The vsa Shield of Mycoplasma pulmonis Is Antiphagocytic. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Han, R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, A.Y.; Xin, J.; Li, S.; Zeng, Y.; Shao, G.; et al. Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae Evades Complement Activation by Binding to Factor H via Elongation Factor Thermo Unstable (EF-Tu). Virulence 2020, 11, 1059–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.J.; Morlin, G.; Valentine, N.; Smith, A.L. Serum Resistance in an Invasive, Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae Strain. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkelberger, J.R.; Song, W.C. Complement and Its Role in Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaurivaud, P.; Baranowski, E.; Pau-Roblot, C.; Sagné, E.; Citti, C.; Tardy, F. Mycoplasma agalactiae Secretion of β-(1→6)-Glucan, a Rare Polysaccharide in Prokaryotes, Is Governed by High-Frequency Phase Variation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 3370–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowald, S. Testing and Comparing the Serum Resistance of Different Strains and Mutants of Mycoplasma agalactiae. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Veterinary Medicine, Vienna, Austria, July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Feng, S.; Xu, C.; Zhou, S.; He, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Guo, L.; Liao, M. Serum Resistance in Haemophilus parasuis SC096 Strain Requires Outer Membrane Protein P2 Expression. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012, 326, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, F.; Wang, Z.; Wua, W. Antibodies Specific to Membrane Proteins Are Effective in Complement-Mediated Killing of Mycoplasma bovis. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e00740-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joiner, K.A.; Goldman, R.C.; Hammer, C.H.; Leive, L.; Frank, M.M. Studies of the Mechanism of Bacterial Resistance to Complement-Mediated Killing. V. IgG and F(Ab’)2 Mediate Killing of E. coli 0111B4 by the Alternative Complement Pathway without Increasing C5b-9 Deposition. J. Immunol. 1983, 131, 2563–2569. [Google Scholar]
- Rautemaa, S.M.R. Complement-Resistance Mechanisms of Bacteria. Microbes Infect. 1999, 1, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, S.; Hegde, S.; Spergser, J.; Brunthaler, R.; Rosengarten, R.; Chopra-Dewasthaly, R. In vitro and in vivo Cell Invasion and Systemic Spreading of Mycoplasma agalactiae in the Sheep Infection Model. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodin, P.; Davis, M.M. Human Immune System Variation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorduijn, D.J.; Rooijakkers, S.H.M.; van Schaik, W.; Bardoel, B.W. Complement Resistance Mechanisms of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Immunobiology 2016, 221, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edward, D.G.; Freundt, E.A. Type Strains of Species of the Order Mycoplasmatales, Including Designation of Neotypes for Mycoplasma mycoides Subsp. mycoides, Mycoplasma agalactiae Subsp. agalactiae, and Mycoplasma arthritidis. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1973, 23, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- DaMassa, A.J. Recovery of Mycoplasma agalactiae from Mastitic Goat Milk. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1983, 183, 548–549. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chopra-Dewasthaly, R.; Zimmermann, M.; Rosengarten, R.; Citti, C. First Steps towards the Genetic Manipulation of Mycoplasma agalactiae and Mycoplasma bovis Using the Transposon Tn4001mod. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. IJMM 2005, 294, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboklaish, A.F.; Dordet-Frisoni, E.; Citti, C.; Toleman, M.A.; Glass, J.I.; Spiller, O.B. Random Insertion and Gene Disruption via Transposon Mutagenesis of Ureaplasma parvum Using a Mini-Transposon Plasmid. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pomakova, D.K.; Hsiao, C.-B.; Beanan, J.M.; Olson, R.; Macdonald, U.; Keynan, Y.; Russo, T.A. Clinical and Phenotypic Differences between Classic and Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumonia: An Emerging and under-Recognized Pathogenic Variant. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 31, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, K.S.; Kim, M.F.; Watson-McKown, R. Molecular and Diagnostic Procedures. In Mycoplasmology Volume I Molecular Characterization; Razin, S., Tully, J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995; p. 483. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sommer, K.; Kowald, S.; Chopra-Dewasthaly, R. Serum Resistance of Mycoplasma agalactiae Strains and Mutants Bearing Different Lipoprotein Profiles. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11091036
Sommer K, Kowald S, Chopra-Dewasthaly R. Serum Resistance of Mycoplasma agalactiae Strains and Mutants Bearing Different Lipoprotein Profiles. Pathogens. 2022; 11(9):1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11091036
Chicago/Turabian StyleSommer, Katja, Saskia Kowald, and Rohini Chopra-Dewasthaly. 2022. "Serum Resistance of Mycoplasma agalactiae Strains and Mutants Bearing Different Lipoprotein Profiles" Pathogens 11, no. 9: 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11091036
APA StyleSommer, K., Kowald, S., & Chopra-Dewasthaly, R. (2022). Serum Resistance of Mycoplasma agalactiae Strains and Mutants Bearing Different Lipoprotein Profiles. Pathogens, 11(9), 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11091036




