Do or Die: HPV E5, E6 and E7 in Cell Death Evasion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. HPV Genome Organization and Life Cycle
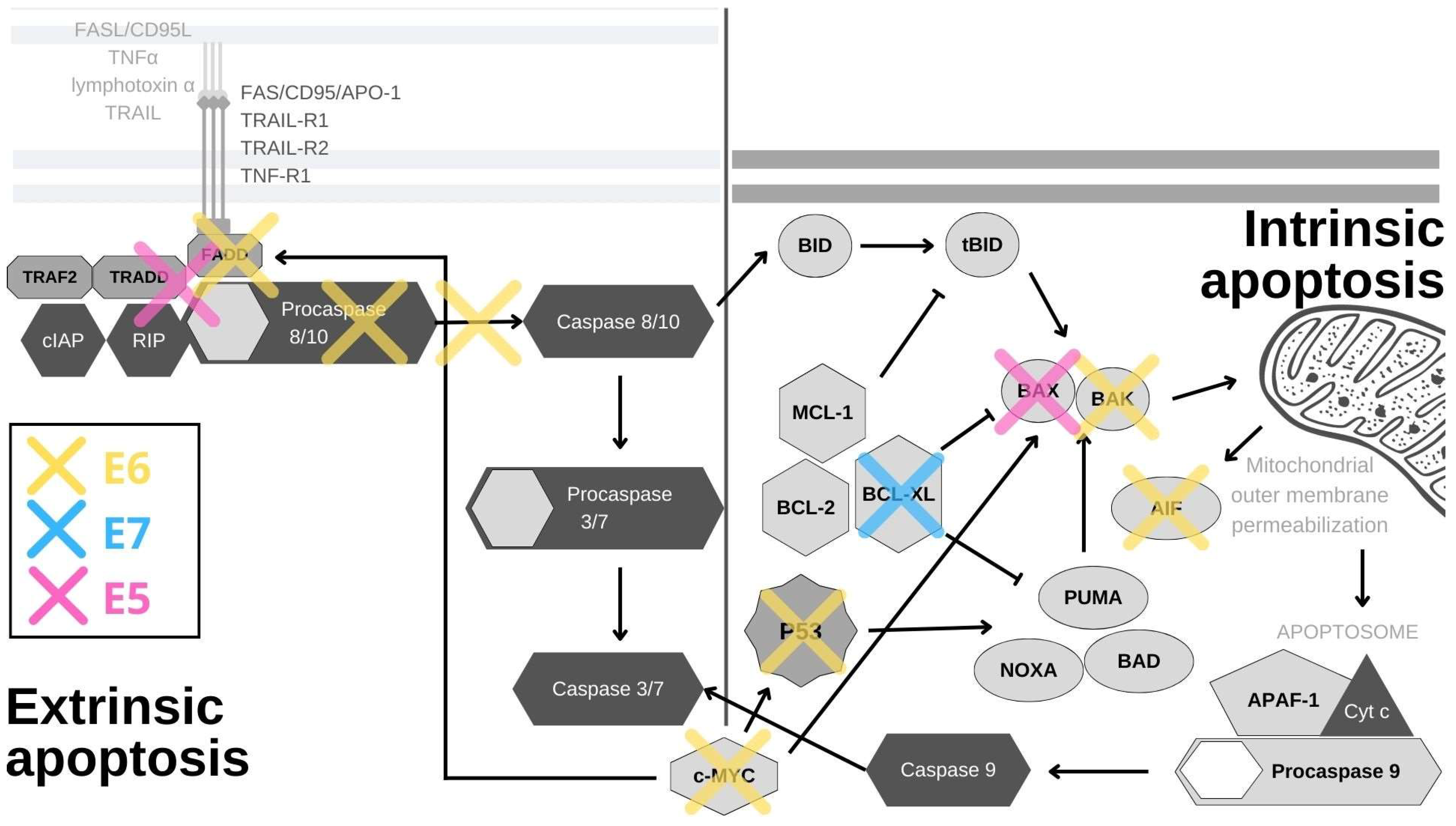
3. Apoptosis
4. Autophagy
5. Anoikis and Pyroptosis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bernard, H.-U.; Burk, R.D.; Chen, Z.; van Doorslaer, K.; zur Hausen, H.; de Villiers, E.-M. Classification of Papillomaviruses (PVs) Based on 189 PV Types and Proposal of Taxonomic Amendments. Virology 2010, 401, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bzhalava, D.; Eklund, C.; Dillner, J. International Standardization and Classification of Human Papillomavirus Types. Virology 2015, 476, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaić, V. Functional Roles of E6 and E7 Oncoproteins in HPV-Induced Malignancies at Diverse Anatomical Sites. Cancers 2016, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Đukić, A.; Lulić, L.; Thomas, M.; Skelin, J.; Saidu, N.E.B.; Grce, M.; Banks, L.; Tomaić, V. HPV Oncoproteins and the Ubiquitin Proteasome System: A Signature of Malignancy? Pathogens 2020, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organisation International Agency for Research on Cancer Iarc Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans Volume 90 Human Papillomaviruses; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon Cedex, France, 2007; Volume 90, ISBN 9789283212904.
- Bouvard, V.; Baan, R.; Straif, K.; Grosse, Y.; Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Freeman, C.; Galichet, L.; et al. A Review of Human Carcinogens--Part B: Biological Agents. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 321–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lont, A.P.; Kroon, B.K.; Horenblas, S.; Gallee, M.P.W.; Berkhof, J.; Meijer, C.J.L.M.; Snijders, P.J.F. Presence of High-Risk Human Papillomavirus DNA in Penile Carcinoma Predicts Favorable Outcome in Survival. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 1078–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, B.S.; Jensen, H.L.; Van Den Brule, A.J.C.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Frisch, M. Risk Factors for Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Vulva and Vagina-Population-Based Case-Control Study in Denmark. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 2827–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Franceschi, S.; Howell-Jones, R.; Snijders, P.J.F.; Clifford, G.M. Human Papillomavirus Type Distribution in 30,848 Invasive Cervical Cancers Worldwide: Variation by Geographical Region, Histological Type and Year of Publication. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doorbar, J.; Quint, W.; Banks, L.; Bravo, I.G.; Stoler, M.; Broker, T.R.; Stanley, M.A. The Biology and Life-Cycle of Human Papillomaviruses. Vaccine 2012, 30 (Suppl. 5), F55–F70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.V.; Faizo, A.A.A. Control of Human Papillomavirus Gene Expression by Alternative Splicing. Virus Res. 2017, 231, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorbar, J. Model Systems of Human Papillomavirus-Associated Disease. J. Pathol. 2016, 238, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglennon, G.A.; McIntosh, P.; Doorbar, J. Persistence of Viral DNA in the Epithelial Basal Layer Suggests a Model for Papillomavirus Latency Following Immune Regression. Virology 2011, 414, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, A.A. Mechanisms and Strategies of Papillomavirus Replication. Biol. Chem. 2017, 398, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Xicotencatl, L.; Pedroza-Saavedra, A.; Chihu-Amparan, L.; Salazar-Piña, A.; Maldonado-Gama, M.; Esquivel-Guadarrama, F. Cellular Functions of HPV16 E5 Oncoprotein during Oncogenic Transformation. Mol. Cancer Res. 2021, 19, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahara, T.; Peh, W.L.; Doorbar, J.; Lee, D.; Lambert, P.F. Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E1circumflexE4 Contributes to Multiple Facets of the Papillomavirus Life Cycle. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 13150–13165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarth, J.A.; Patterson, M.R.; Morgan, E.L.; Macdonald, A. The Human Papillomavirus Oncoproteins: A Review of the Host Pathways Targeted on the Road to Transformation. J. Gen. Virol. 2021, 102, 001540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, A.A.; Warburton, A. The Role of Integration in Oncogenic Progression of HPV-Associated Cancers. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosper, P.F.; Bradley, S.; Luo, L.; Kimple, R.J. Biology of HPV Mediated Carcinogenesis and Tumor Progression. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 31, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzon, L.; Mazzetta, F.; Venuti, A.; Frega, A.; Torrisi, M.R.; French, D. In Vivo HPV 16 E5 MRNA: Expression Pattern in Patients with Squamous Intra-Epithelial Lesions of the Cervix. J. Clin. Virol. 2011, 52, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaresi, S.; Cortese, M.S.; Quinn, J.; Ashrafi, G.H.; Graham, S.V.; Campo, M.S. Effects of Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E5 Deletion Mutants on Epithelial Morphology: Functional Characterization of Each Transmembrane Domain. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoler, M.H.; Rhodes, C.R.; Whitbeck, A.; Wolinsky, S.M.; Chow, L.T.; Broker, T.R. Human Papillomavirus Type 16 and 18 Gene Expression in Cervical Neoplasias. Hum. Pathol. 1992, 23, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arcy, M.S. Cell Death: A Review of the Major Forms of Apoptosis, Necrosis and Autophagy. Cell Biol. Int. 2019, 43, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, S.; Mu, T.; Wang, G.; Jiang, X. Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis in Mammals. Protein Cell 2014, 5, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorstyn, L.; Akey, C.W.; Kumar, S. New Insights into Apoptosome Structure and Function. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 1194–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, H. Death Receptor-Ligand Systems in Cancer, Cell Death, and Inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, P.; Myles, I.A. Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptors: Pleiotropic Signaling Complexes and Their Differential Effects. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 585880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessler, T.; Healy, S.; Samali, A.; Szegezdi, E. Structural Determinants of DISC Function: New Insights into Death Receptor-Mediated Apoptosis Signalling. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 140, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Vitale, I.; Aaronson, S.A.; Abrams, J.M.; Adam, D.; Agostinis, P.; Alnemri, E.S.; Altucci, L.; Amelio, I.; Andrews, D.W.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Cell Death: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 486–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roufayel, R.; Younes, K.; Al-Sabi, A.; Murshid, N. BH3-Only Proteins Noxa and Puma Are Key Regulators of Induced Apoptosis. Life 2022, 12, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafner, A.; Bulyk, M.L.; Jambhekar, A.; Lahav, G. The Multiple Mechanisms That Regulate P53 Activity and Cell Fate. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huibregtse, J.M.; Scheffner, M.; Howley, P.M. Localization of the E6-AP Regions That Direct Human Papillomavirus E6 Binding, Association with P53, and Ubiquitination of Associated Proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 4918–4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffner, M.; Huibregtse, J.M.; Vierstra, R.D.; Howley, P.M. The HPV-16 E6 and E6-AP Complex Functions as a Ubiquitin-Protein Ligase in the Ubiquitination of P53. Cell 1993, 75, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaić, V.; Pim, D.; Banks, L. The Stability of the Human Papillomavirus E6 Oncoprotein Is E6AP Dependent. Virology 2009, 393, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kranjec, C.; Tomaić, V.; Massimi, P.; Nicolaides, L.; Doorbar, J.; Banks, L. The High-Risk HPV E6 Target Scribble (HScrib) Is Required for HPV E6 Expression in Cervical Tumour-Derived Cell Lines. Papillomavirus Res. 2016, 2, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massimi, P.; Shai, A.; Lambert, P.; Banks, L. HPV E6 Degradation of P53 and PDZ Containing Substrates in an E6AP Null Background. Oncogene 2008, 27, 1800–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, M.S.; Laimins, L.A. Inhibition of P53 DNA Binding by Human Papillomavirus E6 Proteins. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 4262–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, H.; Degenkolbe, R.; Bernard, H.U.; O’Connor, M.J. The Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E6 Oncoprotein Can Down-Regulate P53 Activity by Targeting the Transcriptional Coactivator CBP/P300. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 6209–6219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekaric, P.; Shamanin, V.A.; Luo, J.; Androphy, E.J. HAda3 Regulates P14ARF-Induced P53 Acetylation and Senescence. Oncogene 2007, 26, 6261–6268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.; Vande Pol, S.; Banerjee, N.S.; Dutta, A.B.; Chow, L.T.; Dutta, A. Destabilization of TIP60 by Human Papillomavirus E6 Results in Attenuation of TIP60-Dependent Transcriptional Regulation and Apoptotic Pathway. Mol. Cell 2010, 38, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.C.; Chiang, C.-M. E6 Oncoprotein Represses P53-Dependent Gene Activation via Inhibition of Protein Acetylation Independently of Inducing P53 Degradation. Mol. Cell 2005, 17, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajay, A.K.; Meena, A.S.; Bhat, M.K. Human Papillomavirus 18 E6 Inhibits Phosphorylation of P53 Expressed in HeLa Cells. Cell Biosci. 2012, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Gong, C.; Ge, L.; Song, L.; Chen, F.; Jin, C.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, G. Orphan Nuclear Receptor Nurr1 as a Potential Novel Marker for Progression in Human Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Basheeth, N.; Patil, N. Biomarkers in Head and Neck Cancer an Update. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head neck Surg. Off. Publ. Assoc. Otolaryngol. India 2019, 71, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, L.; Duru, N.; Kong, X.; Zhang, P.; Wan, B.; Sui, L.; et al. YY1 Is a Novel Potential Therapeutic Target for the Treatment of HPV Infection-Induced Cervical Cancer by Arsenic Trioxide. Int. J. Gynecol. cancer Off. J. Int. Gynecol. Cancer Soc. 2011, 21, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warowicka, A.; Broniarczyk, J.; Węglewska, M.; Kwaśniewski, W.; Goździcka-Józefiak, A. Dual Role of YY1 in HPV Life Cycle and Cervical Cancer Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borbély, Á.A.; Murvai, M.; Kónya, J.; Beck, Z.; Gergely, L.; Li, F.; Veress, G. Effects of Human Papillomavirus Type 16 Oncoproteins on Survivin Gene Expression. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branca, M.; Giorgi, C.; Santini, D.; Di Bonito, L.; Ciotti, M.; Costa, S.; Benedetto, A.; Casolati, E.A.; Favalli, C.; Paba, P.; et al. Survivin as a Marker of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia and High-Risk Human Papillomavirus and a Predictor of Virus Clearance and Prognosis in Cervical Cancer. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 124, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Roberts, J.; Dakic, A.; Zhang, Y.; Schlegel, R. HPV E7 Contributes to the Telomerase Activity of Immortalized and Tumorigenic Cells and Augments E6-Induced HTERT Promoter Function. Virology 2008, 375, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross-Mesilaty, S.; Reinstein, E.; Bercovich, B.; Tobias, K.E.; Schwartz, A.L.; Kahana, C.; Ciechanover, A. Basal and Human Papillomavirus E6 Oncoprotein-Induced Degradation of Myc Proteins by the Ubiquitin Pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 8058–8063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Banks, L. Inhibition of Bak-Induced Apoptosis by HPV-18 E6. Oncogene 1998, 17, 2943–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kübler, K.; Heinenberg, S.; Rudlowski, C.; Keyver-Paik, M.-D.; Abramian, A.; Merkelbach-Bruse, S.; Büttner, R.; Kuhn, W.; Schildhaus, H.-U. C-Myc Copy Number Gain Is a Powerful Prognosticator of Disease Outcome in Cervical Dysplasia. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, W.; Lou, W.; Hong, Z.; Qiu, L.; Di, W. Genomic Amplification of HPV, H-TERC and C-MYC in Liquid-based Cytological Specimens for Screening of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Cancer. Oncol Lett 2019, 17, 2099–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, M.; Yamashita, A.; Saito, M.; Ichino, M.; Kinjo, T.; Mizuki, N.; Klinman, D.M.; Okuda, K. The Human Papillomavirus E6 Protein Targets Apoptosis-Inducing Factor (AIF) for Degradation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabeça, T.K.; de Mello Abreu, A.; Andrette, R.; de Souza Lino, V.; Morale, M.G.; Aguayo, F.; Termini, L.; Villa, L.L.; Lepique, A.P.; Boccardo, E. HPV-Mediated Resistance to TNF and TRAIL Is Characterized by Global Alterations in Apoptosis Regulatory Factors, Dysregulation of Death Receptors, and Induction of ROS/RNS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippova, M.; Song, H.; Connolly, J.L.; Dermody, T.S.; Duerksen-Hughes, P.J. The Human Papillomavirus 16 E6 Protein Binds to Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) R1 and Protects Cells from TNF-Induced Apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 21730–21739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippova, M.; Parkhurst, L.; Duerksen-Hughes, P.J. The Human Papillomavirus 16 E6 Protein Binds to Fas-Associated Death Domain and Protects Cells from Fas-Triggered Apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 25729–25744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnett, T.O.; Filippova, M.; Duerksen-Hughes, P.J. Accelerated Degradation of FADD and Procaspase 8 in Cells Expressing Human Papilloma Virus 16 E6 Impairs TRAIL-Mediated Apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 1915–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Ding, S.; Yu, L.; Shen, H.; Wan, Y.; Wu, Y. Effects of HPV16 E6 Protein on Daxx-Induced Apoptosis in C33A Cells. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2020, 25, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaykalova, D.A.; Manola, J.B.; Ozawa, H.; Zizkova, V.; Morton, K.; Bishop, J.A.; Sharma, R.; Zhang, C.; Michailidi, C.; Considine, M.; et al. NF-ΚB and Stat3 Transcription Factor Signatures Differentiate HPV-Positive and HPV-Negative Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 1879–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Shen, Z. The Clinical Value of HPV E6/E7 and STAT3 MRNA Detection in Cervical Cancer Screening. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2018, 214, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, E.L.; Macdonald, A. Autocrine STAT3 Activation in HPV Positive Cervical Cancer through a Virus-Driven Rac1—NFκB—IL-6 Signalling Axis. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, E.L.; Wasson, C.W.; Hanson, L.; Kealy, D.; Pentland, I.; McGuire, V.; Scarpini, C.; Coleman, N.; Arthur, J.S.C.; Parish, J.L.; et al. STAT3 Activation by E6 Is Essential for the Differentiation-Dependent HPV18 Life Cycle. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.; Narayan, N.; Pim, D.; Tomaić, V.; Massimi, P.; Nagasaka, K.; Kranjec, C.; Gammoh, N.; Banks, L.; Thomas, M.; et al. Human Papillomaviruses, Cervical Cancer and Cell Polarity. Oncogene 2008, 27, 7018–7030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pim, D.; Bergant, M.; Boon, S.S.; Ganti, K.; Kranjec, C.; Massimi, P.; Subbaiah, V.K.; Thomas, M.; Tomaić, V.; Banks, L. Human Papillomaviruses and the Specificity of PDZ Domain Targeting. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 3530–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganti, K.; Broniarczyk, J.; Manoubi, W.; Massimi, P.; Mittal, S.; Pim, D.; Szalmas, A.; Thatte, J.; Thomas, M.; Tomaić, V.; et al. The Human Papillomavirus E6 PDZ Binding Motif: From Life Cycle to Malignancy. Viruses 2015, 7, 3530–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranjec, C.; Massimi, P.; Banks, L. Restoration of MAGI-1 Expression in Human Papillomavirus-Positive Tumor Cells Induces Cell Growth Arrest and Apoptosis. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 7155–7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, M.A.; Lee, J.H.; Klingelhutz, A.J. Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E6 Activates NF-KappaB, Induces CIAP-2 Expression, and Protects against Apoptosis in a PDZ Binding Motif-Dependent Manner. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5301–5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Ravanan, P.; Talwar, P. Death Associated Protein Kinase 1 (DAPK1): A Regulator of Apoptosis and Autophagy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banzai, C.; Nishino, K.; Quan, J.; Yoshihara, K.; Sekine, M.; Yahata, T.; Tanaka, K. Promoter Methylation of DAPK1, FHIT, MGMT, and CDKN2A Genes in Cervical Carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 19, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanatatsaneejit, P.; Chalertpet, K.; Sukbhattee, J.; Nuchcharoen, I.; Phumcharoen, P.; Mutirangura, A. Promoter Methylation of Tumor Suppressor Genes Induced by Human Papillomavirus in Cervical Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanayake Weeramange, C.; Tang, K.D.; Vasani, S.; Langton-Lockton, J.; Kenny, L.; Punyadeera, C. DNA Methylation Changes in Human Papillomavirus-Driven Head and Neck Cancers. Cells 2020, 9, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazzi, R.; Cusenza Ylenia, V.; Pistoni, M.; Canovi, L.; Cascione, L.; Bertoni, F.; Merli, F. KLF4, DAPK1 and SPG20 Promoter Methylation Is Not Affected by DNMT1 Silencing and Hypomethylating Drugs in Lymphoma Cells. Oncol Rep 2022, 47, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Balasubramanian, A.; Hawes, S.E.; Toure, P.; Sow, P.S.; Dem, A.; Dembele, B.; Critchlow, C.W.; Xi, L.; Lu, H.; et al. Detection of Hypermethylated Genes in Women with and without Cervical Neoplasia. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2005, 97, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Tan, W.; Yang, H.; Zhang, S.; Dai, Y. Detection of Host Cell Gene/HPV DNA Methylation Markers: A Promising Triage Approach for Cervical Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 831949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Choi, M.Y.; Cho, G.J.; Choi, W.S. UHRF1 Silences Gelsolin to Inhibit Cell Death in Early Stage Cervical Cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 526, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Qiao, L.; Wang, X.; Ding, C.; Chen, J.J. UHRF1 Epigenetically Down-Regulates UbcH8 to Inhibit Apoptosis in Cervical Cancer Cells. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, K.; Zhou, X.; Hayakawa, H.; Cho, J.-Y.; Libermann, T.A.; Jin, J.; Harper, J.W.; Munger, K. Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E7 Oncoprotein Associates with the Cullin 2 Ubiquitin Ligase Complex, Which Contributes to Degradation of the Retinoblastoma Tumor Suppressor. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 9737–9747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alunni-Fabbroni, M.; Littlewood, T.; Deleu, L.; Caldeira, S.; Giarrè, M.; Dell’ Orco, M.; Tommasino, M. Induction of S Phase and Apoptosis by the Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E7 Protein Are Separable Events in Immortalized Rodent Fibroblasts. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2277–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Lemarroy, A.; Gariglio, P.; Whitaker, N.J.; Eichhorst, S.T.; Hausen, H.z.; Krammer, P.H.; Rösl, F. Restoration of P53 Expression Sensitizes Human Papillomavirus Type 16 Immortalized Human Keratinocytes to CD95-Mediated Apoptosis. Oncogene 2002, 21, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, J.R.; Zacny, V.; Münger, K. The Cytokines Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α) and TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand Differentially Modulate Proliferation and Apoptotic Pathways in Human Keratinocytes Expressing the Human Papillomavirus-16 E7 Oncoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 22522–22528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.A.; Zacny, V.; Belinsky, G.S.; Classon, M.; Jones, D.L.; Schlegel, R.; Münger, K. The HPV E7 Oncoprotein Inhibits Tumor Necrosis Factor α-Mediated Apoptosis in Normal Human Fibroblasts. Oncogene 2001, 20, 3629–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santer, F.R.; Moser, B.; Spoden, G.A.; Jansen-Dürr, P.; Zwerschke, W. Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E7 Oncoprotein Inhibits Apoptosis Mediated by Nuclear Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein-3 by Enhancing Its Ubiquitin/Proteasome-Dependent Degradation. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 2511–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shim, J.-H.; Cho, K.-J.; Lee, K.-A.; Kim, S.-H.; Myung, P.-K.; Choe, Y.-K.; Yoon, D.-Y. E7-Expressing HaCaT Keratinocyte Cells Are Resistant to Oxidative Stress-Induced Cell Death via the Induction of Catalase. Proteomics 2005, 5, 2112–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Yu, X.; Chen, J.J.; Zhao, W. Cancerous Inhibitor of Protein Phosphatase 2A Contributes to Human Papillomavirus Oncoprotein E7-Induced Cell Proliferation via E2F1. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 5253–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, A.; Abbruzzese, C.; Manente, L.; Valderas, Á.A.; Mattarocci, S.; Federico, A.; Starace, G.; Chersi, A.; Mileo, A.M.; Paggi, M.G. Human Papillomavirus-16 E7 Interacts with Siva-1 and Modulates Apoptosis in HaCaT Human Immortalized Keratinocytes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 212, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longworth, M.S.; Laimins, L.A. The Binding of Histone Deacetylases and the Integrity of Zinc Finger-like Motifs of the E7 Protein Are Essential for the Life Cycle of Human Papillomavirus Type 31. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 3533–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finzer, P.; Krueger, A.; Stöhr, M.; Brenner, D.; Soto, U.; Kuntzen, C.; Krammer, P.H.; Rösl, F. HDAC Inhibitors Trigger Apoptosis in HPV-Positive Cells by Inducing the E2F-P73 Pathway. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4807–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvas, K.; Rosenberger, S.; Brenner, D.; Fritsch, C.; Gmelin, N.; Krammer, P.H.; Rösl, F. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor-Induced Sensitization to TNFalpha/TRAIL-Mediated Apoptosis in Cervical Carcinoma Cells Is Dependent on HPV Oncogene Expression. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 1384–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.-M.; Kim, S.-H.; Cho, E.-A.; Song, Y.-S.; Kim, W.-H.; Juhnn, Y.-S. Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E5 Protein Inhibits Hydrogen-Peroxide-Induced Apoptosis by Stimulating Ubiquitin-Proteasome-Mediated Degradation of Bax in Human Cervical Cancer Cells. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Spandau, D.F.; Roman, A. E5 Protein of Human Papillomavirus Type 16 Protects Human Foreskin Keratinocytes from UV B-Irradiation-Induced Apoptosis. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabsch, K.; Mossadegh, N.; Kohl, A.; Komposch, G.; Schenkel, J.; Alonso, A.; Tomakidi, P. The HPV-16 E5 Protein Inhibits TRAIL- and FasL-Mediated Apoptosis in Human Keratinocyte Raft Cultures. Intervirology 2004, 47, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudarshan, S.R.; Schlegel, R.; Liu, X. The HPV-16 E5 Protein Represses Expression of Stress Pathway Genes XBP-1 and COX-2 in Genital Keratinocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 399, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.L.; Tsao, Y.P.; Liu, D.W.; Huang, S.J.; Lee, W.H.; Chen, S.L. The Expression of HPV-16 E5 Protein in Squamous Neoplastic Changes in the Uterine Cervix. J. Biomed. Sci. 2001, 8, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Um, S.H.; Mundi, N.; Yoo, J.; Palma, D.A.; Fung, K.; MacNeil, D.; Wehrli, B.; Mymryk, J.S.; Barrett, J.W.; Nichols, A.C. Variable Expression of the Forgotten Oncogene E5 in HPV-Positive Oropharyngeal Cancer. J. Clin. Virol. 2014, 61, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandia, R.; Dadar, M.; Munjal, A.; Dhama, K.; Karthik, K.; Tiwari, R.; Yatoo, M.I.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Singh, K.P.; Joshi, S.K.; et al. A Comprehensive Review of Autophagy and Its Various Roles in Infectious, Non-Infectious, and Lifestyle Diseases: Current Knowledge and Prospects for Disease Prevention, Novel Drug Design, and Therapy. Cells 2019, 8, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, S.; Cuervo, A.M. The Coming of Age of Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, J.; Bao, J. Microautophagy: Lesser-Known Self-Eating. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vescovo, T.; Pagni, B.; Piacentini, M.; Fimia, G.M.; Antonioli, M. Regulation of Autophagy in Cells Infected With Oncogenic Human Viruses and Its Impact on Cancer Development. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, L.; Mostowy, S.; Sancho-Shimizu, V. Autophagy-Virus Interplay: From Cell Biology to Human Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surviladze, Z.; Sterk, R.T.; DeHaro, S.A.; Ozbun, M.A. Cellular Entry of Human Papillomavirus Type 16 Involves Activation of the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt/MTOR Pathway and Inhibition of Autophagy. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 2508–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, L.M.; Cicchini, L.; Pyeon, D. Human Papillomavirus Infection Is Inhibited by Host Autophagy in Primary Human Keratinocytes. Virology 2013, 437, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanning, J.E.; Saini, H.K.; Murray, M.J.; Caffarel, M.M.; van Dongen, S.; Ward, D.; Barker, E.M.; Scarpini, C.G.; Groves, I.J.; Stanley, M.A.; et al. Depletion of HPV16 Early Genes Induces Autophagy and Senescence in a Cervical Carcinogenesis Model, Regardless of Viral Physical State. J. Pathol. 2013, 231, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattoscio, D.; Medda, A.; Chiocca, S. Human Papilloma Virus and Autophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Tomaić, V.; Pim, D.; Myers, M.P.; Tommasino, M.; Banks, L. Interactions between E6AP and E6 Proteins from Alpha and Beta HPV Types. Virology 2013, 435, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, M.; Pagni, B.; Vescovo, T.; Ellis, R.; Cosway, B.; Rollo, F.; Bordoni, V.; Agrati, C.; Labus, M.; Covello, R.; et al. HPV Sensitizes OPSCC Cells to Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis by Inhibiting Autophagy through E7-Mediated Degradation of AMBRA1. Autophagy 2021, 17, 2842–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Münger, K. Expression of the Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E7 Oncoprotein Induces an Autophagy-Related Process and Sensitizes Normal Human Keratinocytes to Cell Death in Response to Growth Factor Deprivation. Virology 2009, 385, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pim, D.; Massimi, P.; Dilworth, S.M.; Banks, L. Activation of the Protein Kinase B Pathway by the HPV-16 E7 Oncoprotein Occurs through a Mechanism Involving Interaction with PP2A. Oncogene 2005, 24, 7830–7838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menges, C.W.; Baglia, L.A.; Lapoint, R.; McCance, D.J. Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E7 Up-Regulates AKT Activity through the Retinoblastoma Protein. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5555–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinolo, A.A.; Marsh, C.; El Dinali, M.; Gangane, N.; Jennison, K.; Hewitt, S.; Patel, V.; Seiwert, T.Y.; Gutkind, J.S. MTOR as a Molecular Target in HPV-Associated Oral and Cervical Squamous Carcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 2558–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, J.; Ling, M.T.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, K.-N. The Role of the PI3K/Akt/MTOR Signalling Pathway in Human Cancers Induced by Infection with Human Papillomaviruses. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezazadeh, D.; Norooznezhad, A.H.; Mansouri, K.; Jahani, M.; Mostafaie, A.; Mohammadi, M.H.; Modarressi, M.H. Rapamycin Reduces Cervical Cancer Cells Viability in Hypoxic Condition: Investigation of the Role of Autophagy and Apoptosis. Onco. Targets. Ther. 2020, 13, 4239–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, R.J.; Oleinik, N.; Panneer Selvam, S.; Vaena, S.G.; Dany, M.; Nganga, R.N.; Depalma, R.; Baron, K.D.; Kim, J.; Szulc, Z.M.; et al. HPV/E7 Induces Chemotherapy-Mediated Tumor Suppression by Ceramide-Dependent Mitophagy. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017, 9, 1030–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belleudi, F.; Nanni, M.; Raffa, S.; Torrisi, M.R. HPV16 E5 Deregulates the Autophagic Process in Human Keratinocytes. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 9370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Pan, X.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X. Expression of Beclin 1 and LC3 in FIGO Stage I-II Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Relationship to Survival. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodevelopmental Biol. Med. 2012, 33, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Zhou, J.; Wang, F.; Shi, H.; Li, Y.; Li, B. HPV-16 E6/E7 Promotes Cell Migration and Invasion in Cervical Cancer via Regulating Cadherin Switch in Vitro and in Vivo. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2015, 292, 1345–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carchman, E.H.; Matkowskyj, K.A.; Meske, L.; Lambert, P.F. Dysregulation of Autophagy Contributes to Anal Carcinogenesis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoli, P.; Giannoni, E.; Chiarugi, P. Anoikis Molecular Pathways and Its Role in Cancer Progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 3481–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangarajan, A.; Syal, R.; Selvarajah, S.; Chakrabarti, O.; Sarin, A.; Krishna, S. Activated Notch1 Signaling Cooperates with Papillomavirus Oncogenes in Transformation and Generates Resistance to Apoptosis on Matrix Withdrawal through PKB/Akt. Virology 2001, 286, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.K.-T.; Leung, T.H.-Y.; Siu, M.K.-Y.; Mo, X.-T.; Tang, H.W.-M.; Chan, K.K.-L.; Cheung, A.N.-Y.; Ngan, H.Y.-S. HPV-Induced Nurr1 Promotes Cancer Aggressiveness, Self-Renewal, and Radioresistance via ERK and AKT Signaling in Cervical Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2021, 497, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henken, F.E.; Banerjee, N.S.; Snijders, P.J.F.; Meijer, C.J.L.M.; De-Castro Arce, J.; Rösl, F.; Broker, T.R.; Chow, L.T.; Steenbergen, R.D.M. PIK3CA-Mediated PI3-Kinase Signalling Is Essential for HPV-Induced Transformation in Vitro. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaty, B.T.; Moon, D.H.; Shen, C.J.; Amdur, R.J.; Weiss, J.; Grilley-Olson, J.; Patel, S.; Zanation, A.; Hackman, T.G.; Thorp, B.; et al. PIK3CA Mutation in HPV-Associated OPSCC Patients Receiving Deintensified Chemoradiation. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2020, 112, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwin, T.R.; Clarke, M.A.; Dean, M.; Wentzensen, N. Somatic Host Cell Alterations in HPV Carcinogenesis. Viruses 2017, 9, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backsch, C.; Rudolph, B.; Steinbach, D.; Scheungraber, C.; Liesenfeld, M.; Häfner, N.; Hildner, M.; Habenicht, A.; Runnebaum, I.B.; Dürst, M. An Integrative Functional Genomic and Gene Expression Approach Revealed SORBS2 as a Putative Tumour Suppressor Gene Involved in Cervical Carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z. Comprehensive Analysis Reveals Novel Gene Signature in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Predicting Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Patients. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 5882–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, W.; Huang, S.; Yang, Z.; Xu, L.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Shen, Q.; Wang, C.; et al. The RNA Binding Protein SORBS2 Suppresses Metastatic Colonization of Ovarian Cancer by Stabilizing Tumor-Suppressive Immunomodulatory Transcripts. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Peng, Z.; Xing, C. SORBS2, Mediated by MEF2D, Suppresses the Metastasis of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Inhibitiing the c-Abl-ERK Signaling Pathway. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 2706–2718. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, A.C.; Ray, A.-M.; Ramolu, L.; Macabre, C.; Simon, F.; Noulet, F.; Blandin, A.-F.; Renner, G.; Lehmann, M.; Choulier, L.; et al. Caveolin-1-Negative Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Primary Tumors Display Increased Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition and Prometastatic Properties. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 41884–41901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razani, B.; Altschuler, Y.; Zhu, L.; Pestell, R.G.; Mostov, K.E.; Lisanti, M.P. Caveolin-1 Expression Is down-Regulated in Cells Transformed by the Human Papilloma Virus in a P53-Dependent Manner. Replacement of Caveolin-1 Expression Suppresses HPV-Mediated Cell Transformation. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 13916–13924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suprynowicz, F.A.; Disbrow, G.L.; Krawczyk, E.; Simic, V.; Lantzky, K.; Schlegel, R. HPV-16 E5 Oncoprotein Upregulates Lipid Raft Components Caveolin-1 and Ganglioside GM1 at the Plasma Membrane of Cervical Cells. Oncogene 2008, 27, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanos, W.C.; Hoover, A.; Harris, G.F.; Wu, S.; Strand, G.L.; Anderson, M.E.; Klingelhutz, A.J.; Hendriks, W.; Bossler, A.D.; Lee, J.H. The PDZ Binding Motif of Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E6 Induces PTPN13 Loss, Which Allows Anchorage-Independent Growth and Synergizes with Ras for Invasive Growth. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 2493–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalmás, A.; Tomaić, V.; Basukala, O.; Massimi, P.; Mittal, S.; Kónya, J.; Banks, L. The PTPN14 Tumor Suppressor Is a Degradation Target of Human Papillomavirus E7. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00057-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatterschide, J.; Bohidar, A.E.; Grace, M.; Nulton, T.J.; Kim, H.W.; Windle, B.; Morgan, I.M.; Munger, K.; White, E.A. PTPN14 Degradation by High-Risk Human Papillomavirus E7 Limits Keratinocyte Differentiation and Contributes to HPV-Mediated Oncogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7033–7042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Zhang, X.; Liu, N.; Tang, L.; Peng, C.; Chen, X. Pyroptosis: Mechanisms and Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, D.; Shin, H.-W.; Kim, J.; Lee, M.; Myeong, J.; Chun, Y.-S.; Park, J.-W. Cervical Cancer Is Addicted to SIRT1 Disarming the AIM2 Antiviral Defense. Oncogene 2018, 37, 5191–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez-Perez, A.; Wang, X.I.; Li, M.; Zhang, S. SIRT1 Overexpression in Cervical Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions and Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 59, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wu, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Zou, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, B.; Hua, C.; Rui, H.; et al. HPV E7 Inhibits Cell Pyroptosis by Promoting TRIM21-Mediated Degradation and Ubiquitination of the IFI16 Inflammasome. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2924–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skelin, J.; Sabol, I.; Tomaić, V. Do or Die: HPV E5, E6 and E7 in Cell Death Evasion. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11091027
Skelin J, Sabol I, Tomaić V. Do or Die: HPV E5, E6 and E7 in Cell Death Evasion. Pathogens. 2022; 11(9):1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11091027
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkelin, Josipa, Ivan Sabol, and Vjekoslav Tomaić. 2022. "Do or Die: HPV E5, E6 and E7 in Cell Death Evasion" Pathogens 11, no. 9: 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11091027
APA StyleSkelin, J., Sabol, I., & Tomaić, V. (2022). Do or Die: HPV E5, E6 and E7 in Cell Death Evasion. Pathogens, 11(9), 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11091027







