The Role of the Microbiome in the Metabolic Health of People with Schizophrenia and Related Psychoses: Cross-Sectional and Pre-Post Lifestyle Intervention Analyses
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (i)
- To conduct a pilot study to characterize the gut microbiota in two patient groups, those with first-episode psychosis and those with established schizophrenia, compared with matched controls.
- (ii)
- To examine gut microbiota diversity and composition before and after treatment with lifestyle intervention in enhanced clinical settings.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Participants
2.2.1. Group 1. First Episode Psychosis
2.2.2. Group 2. Established illness (Patients on Clozapine)
2.2.3. Group 3. Matched Controls (MCs)
2.3. Sample Size
2.4. Procedure
2.5. Blood Collection
2.6. Stool Collection and Sequencing
2.7. Explanatory Outcomes and Clinical/Demographic Details
2.8. Data Analysis
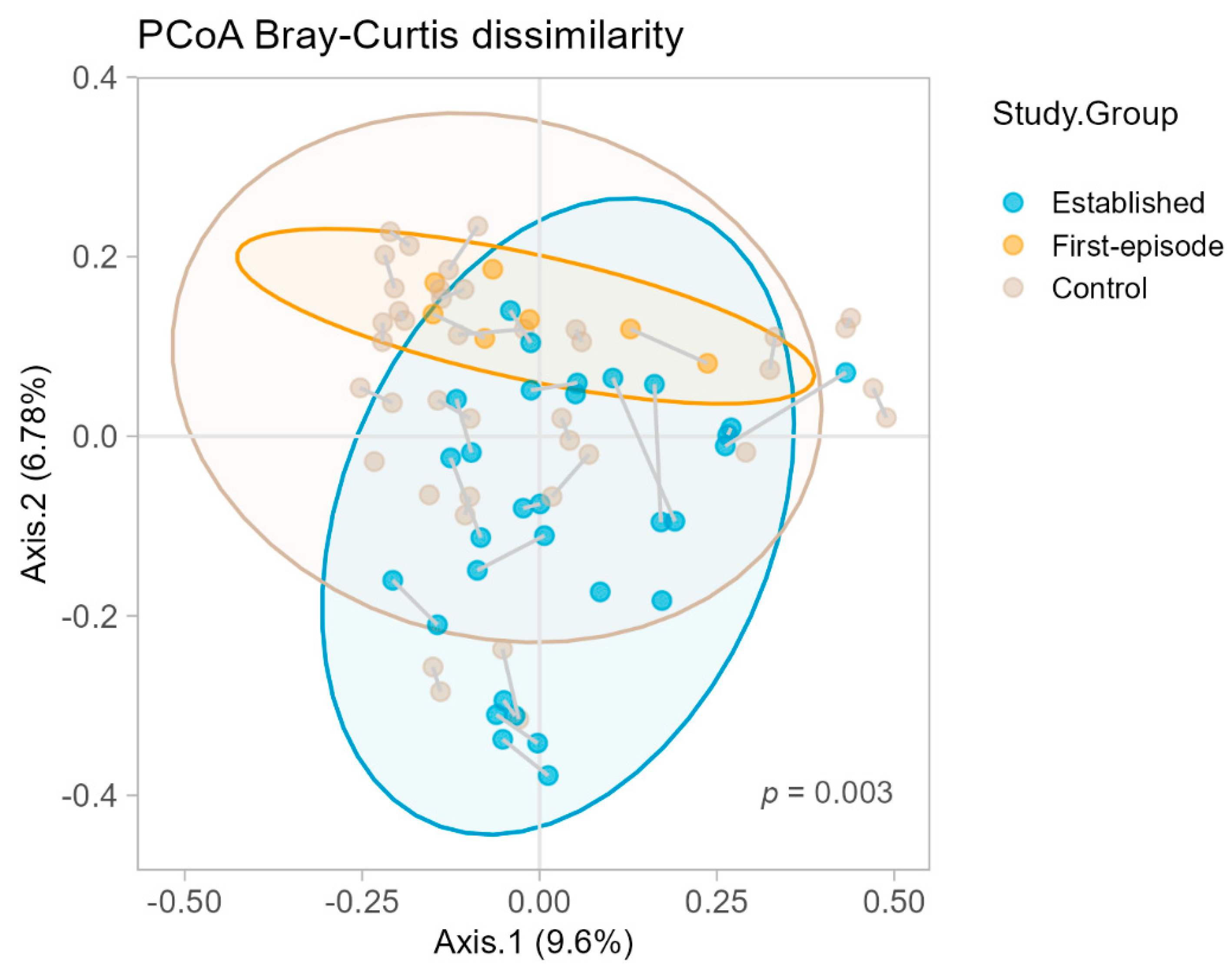
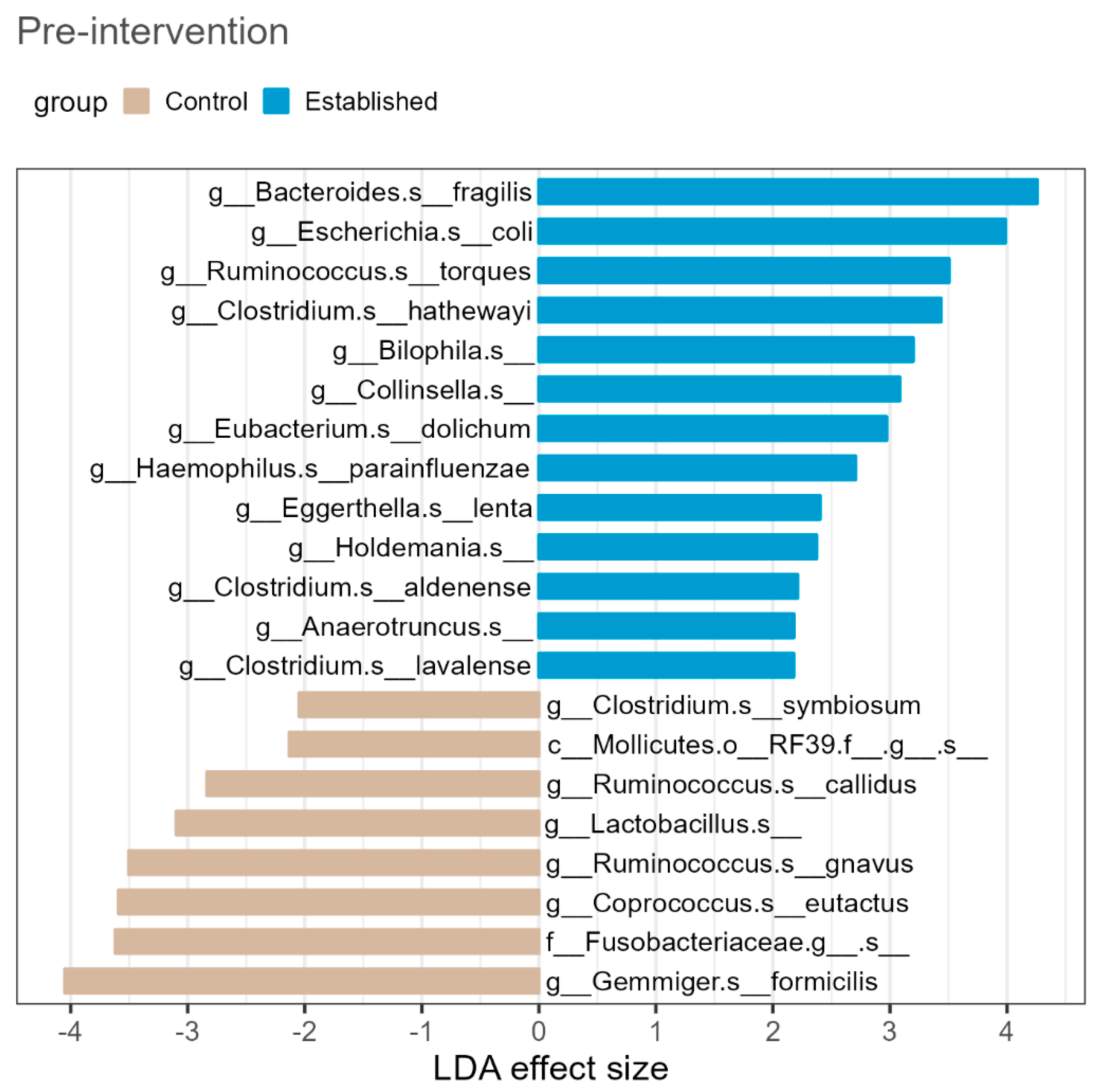
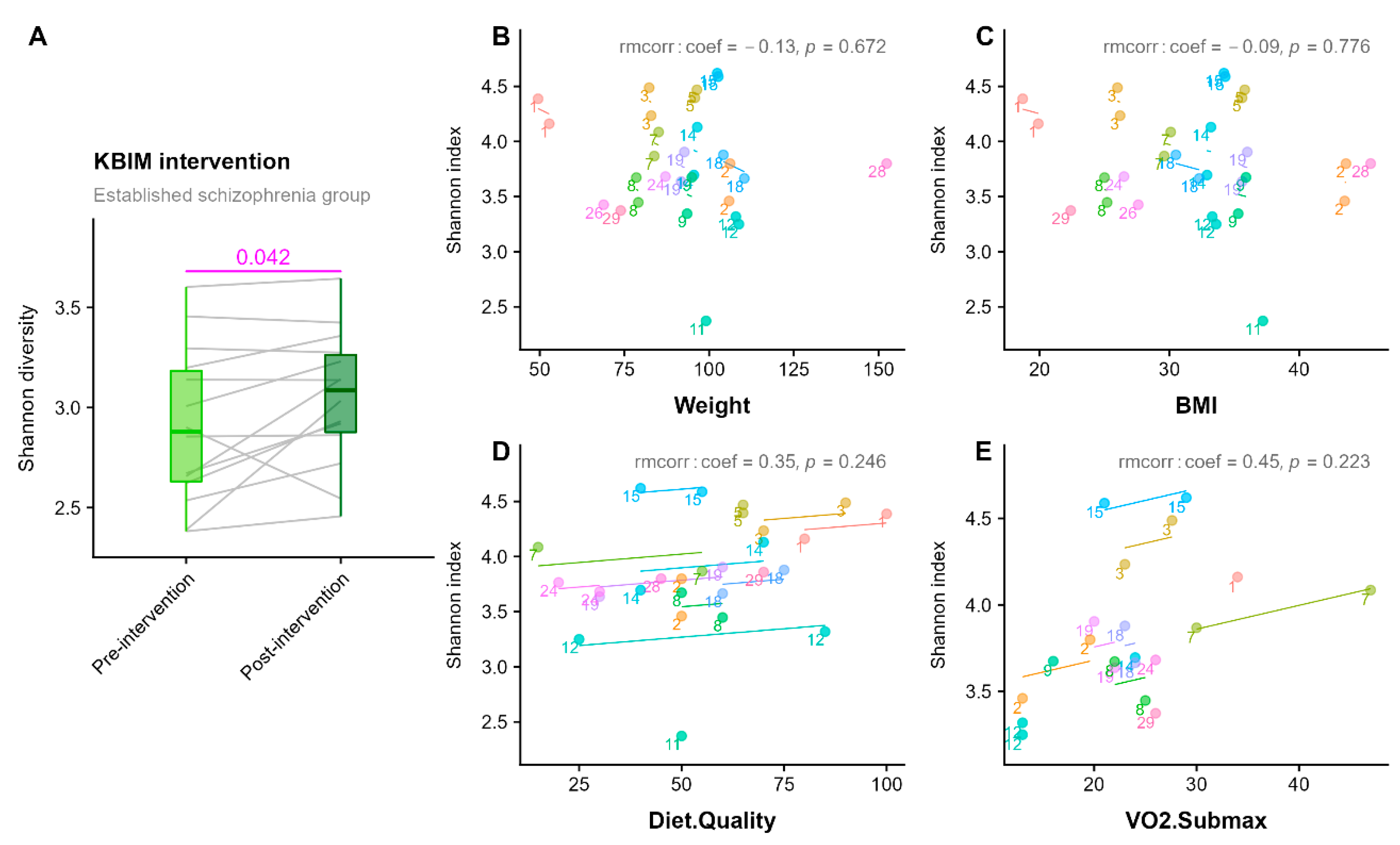
3. Results
3.1. Baseline
3.2. 12-Week Follow-Up
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Whiteford, H.A.; Ferrari, A.J.; Degenhardt, L.; Feigin, V.; Vos, T. The global burden of mental, neurological and substance use disorders: An analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjorthøj, C.; Stürup, A.E.; McGrath, J.J.; Nordentoft, M. Years of potential life lost and life expectancy in schizophrenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 2017, 4, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correll, C.U.; Solmi, M.; Veronese, N.; Bortolato, B.; Rosson, S.; Santonastaso, P.; Thapa-Chhetri, N.; Fornaro, M.; Gallicchio, D.; Collantoni, E. Prevalence, incidence and mortality from cardiovascular disease in patients with pooled and specific severe mental illness: A large-scale meta-analysis of 3,211,768 patients and 113,383,368 controls. World Psychiatry 2017, 16, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correll, C.U.; Manu, P.; Olshanskiy, V.; Napolitano, B.; Kane, J.M.; Malhotra, A.K. Cardiometabolic risk of second-generation antipsychotic medications during first-time use in children and adolescents. JAMA 2009, 302, 1765–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teasdale, S.B.; Ward, P.B.; Samaras, K.; Firth, J.; Stubbs, B.; Tripodi, E.; Burrows, T.L. Dietary intake of people with severe mental illness: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Psychiatry 2019, 214, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stubbs, B.; Firth, J.; Berry, A.; Schuch, F.B.; Rosenbaum, S.; Gaughran, F.; Veronesse, N.; Williams, J.; Craig, T.; Yung, A.R. How much physical activity do people with schizophrenia engage in? A systematic review, comparative meta-analysis and meta-regression. Schizophr. Res. 2016, 176, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Chatelier, E.; Nielsen, T.; Qin, J.; Prifti, E.; Hildebrand, F.; Falony, G.; Almeida, M.; Arumugam, M.; Batto, J.-M.; Kennedy, S. Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with metabolic markers. Nature 2013, 500, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Fuentes, C.; Schellekens, H.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The microbiota–gut–brain axis in obesity. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, A.; Davis, J.; Dawson, S.; Loughman, A.; Collier, F.; O’Hely, M.; Simpson, C.; Green, J.; Marx, W.; Hair, C. A systematic review of gut microbiota composition in observational studies of major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 1920–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchia, M.; Fontana, A.; Panebianco, C.; Paribello, P.; Arzedi, C.; Cossu, E.; Garzilli, M.; Montis, M.A.; Mura, A.; Pisanu, C.; et al. Involvement of Gut Microbiota in Schizophrenia and Treatment Resistance to Antipsychotics. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Kosciolek, T.; Maldonado, Y.; Daly, R.E.; Martin, A.S.; McDonald, D.; Knight, R.; Jeste, D.V. Differences in gut microbiome composition between persons with chronic schizophrenia and healthy comparison subjects. Schizophr. Res. 2019, 204, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Wu, B.; Liang, J.; He, F.; Gu, W.; Li, K.; Luo, Y.; Chen, J.; Gao, Y.; Wu, Z. Altered gut microbiota and mucosal immunity in patients with schizophrenia. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 85, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Łoniewski, I.; Misera, A.; Stachowska, E.; Maciejewska, D.; Marlicz, W.; Galling, B. Second-generation antipsychotics and metabolism alterations: A systematic review of the role of the gut microbiome. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 1491–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Lee, I.S.; Choue, R. Obesity, inflammation and diet. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2013, 16, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillman, S.; Cloonan, N.; Catts, V.; Miller, L.; Wong, J.; McCrossin, T.; Cairns, M.; Weickert, C.S. Increased inflammatory markers identified in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of individuals with schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacomb, I.; Stanton, C.; Vasudevan, R.; Powell, H.; O’Donnell, M.; Lenroot, R.; Bruggemann, J.; Balzan, R.; Galletly, C.; Liu, D. C-reactive protein: Higher during acute psychotic episodes and related to cortical thickness in schizophrenia and healthy controls. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileva, S.S.; Tucker, J.; Siskind, D.; Eyles, D. Does the gut microbiome mediate antipsychotic-induced metabolic side effects in schizophrenia? Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2022, 21, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zong, G.; Li, S.; Rimm, E.B.; Hu, F.B.; Manson, J.E.; Rexrode, K.M.; Shin, H.J. Influence of lifestyle on incident cardiovascular disease and mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2867–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.B.; Schmader, K.E.; Hanlon, J.T.; Abernethy, D.R.; Gray, S.; Dunbar-Jacob, J.; Holmes, H.M.; Murray, M.D.; Roberts, R.; Joyner, M. Pharmacotherapy in older adults with cardiovascular disease: Report from an American College of Cardiology, American Geriatrics Society, and National Institute on Aging Workshop. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2019, 67, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, J.; Siddiqi, N.; Koyanagi, A.; Siskind, D.; Rosenbaum, S.; Galletly, C.; Allan, S.; Caneo, C.; Carney, R.; Carvalho, A.F. The Lancet Psychiatry Commission: A blueprint for protecting physical health in people with mental illness. Lancet Psychiatry 2019, 6, 675–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.-x.; Lau, W.; Ma, E.P.; Hung, K.S.; Chen, S.-y.; Cheng, K.-s.; Cheung, E.F.; Lui, S.S.; Chan, R.C. The Important Role of Motivation and Pleasure Deficits on Social Functioning in Patients With Schizophrenia: A Network Analysis. Schizophr. Bull. 2022, 63, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, J.; Henry, C.; Watkins, A.; Newall, H.; Samaras, K.; Ward, P.B. Metabolic abnormalities in an early psychosis service: A retrospective, naturalistic cross-sectional study. Early Interv. Psychiatry 2011, 5, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lappin, J.M.; Wijaya, M.; Watkins, A.; Morell, R.; Teasdale, S.; Lederman, O.; Rosenbaum, S.; Dick, S.; Ward, P.; Curtis, J. Cardio-metabolic risk and its management in a cohort of clozapine-treated outpatients. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 199, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morell, R.; Curtis, J.; Watkins, A.; Poole, J.; Fibbins, H.; Rossimel, E.; Gerrard, M.; White, A.; Teasdale, S.; Ward, P.B. Cardio-metabolic risk in individuals prescribed long-acting injectable antipsychotic medication. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 281, 112606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, J.; Watkins, A.; Rosenbaum, S.; Teasdale, S.; Kalucy, M.; Samaras, K.; Ward, P.B. Evaluating an individualized lifestyle and life skills intervention to prevent antipsychotic-induced weight gain in first-episode psychosis. Early Interv. Psychiatry 2016, 10, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, J.; Watkins, A.; Teasdale, S.; Lederman, O.; Kalucy, M.; Lappin, J.; Samaras, K.; Rosenbaum, S.; Ward, P.B. 2-year follow-up: Still keeping the body in mind. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2018, 52, 602–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Bull. World Health Organ. 2007, 85, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.-J.; Paramsothy, R.; Wu, N.; Ghaly, S.; Leach, S.; Paramsothy, S.; Corte, C.; O’Brien, C.; Burke, C.; Wark, G. Australia IBD Microbiome (AIM) Study: Protocol for a multicentre longitudinal prospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e042493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amplicon, P.; Clean-Up, P.; Index, P. 16s Metagenomic Sequencing Library Preparation; Illumina: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Hugenholtz, P.; Larsen, N.; Rojas, M.; Brodie, E.L.; Keller, K.; Huber, T.; Dalevi, D.; Hu, P.; Andersen, G.L. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5069–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorpe, M.G.; Milte, C.M.; Crawford, D.; McNaughton, S.A. A revised Australian Dietary Guideline Index and its association with key sociodemographic factors, health behaviors and body mass index in peri-retirement aged adults. Nutrients 2016, 8, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vancampfort, D.; Guelinckx, H.; De Hert, M.; Stubbs, B.; Soundy, A.; Rosenbaum, S.; De Schepper, E.; Probst, M. Reliability and clinical correlates of the Astrand–Rhyming sub-maximal exercise test in patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2014, 220, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakdash, J.Z.; Marusich, L.R. Repeated Measures Correlation. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance (PERMANOVA). In Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’hara, R.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Szoecs, E.; Wagner, H. vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.6-4. 2022. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vegan/vegan.pdf (accessed on 23 October 2022).
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, F.; Ju, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, Q.; Guo, R.; Ma, Q.; Sun, Q.; Fan, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yang, Z.; et al. Metagenome-wide association of gut microbiome features for schizophrenia. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Zeng, B.; Liu, M.; Chen, J.; Pan, J.; Han, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, K.; Zhou, C.; Wang, H.; et al. The gut microbiome from patients with schizophrenia modulates the glutamate-glutamine-GABA cycle and schizophrenia-relevant behaviors in mice. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau8317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Hu, S.; Liang, Y. Analysis of gut microbiota diversity and auxiliary diagnosis as a biomarker in patients with schizophrenia: A cross-sectional study. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 197, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F.; Petito, V.; Gasbarrini, A. Commensal Clostridia: Leading players in the maintenance of gut homeostasis. Gut Pathog. 2013, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Meng, X.; Li, D.; Calderone, R.; Mao, D.; Sui, B. Commensal homeostasis of gut microbiota-host for the impact of obesity. Front. Physiol. 2018, 8, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natividad, J.M.; Lamas, B.; Pham, H.P.; Michel, M.-L.; Rainteau, D.; Bridonneau, C.; Da Costa, G.; van Hylckama Vlieg, J.; Sovran, B.; Chamignon, C. Bilophila wadsworthia aggravates high fat diet induced metabolic dysfunctions in mice. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Long, W.; Hao, B.; Ding, D.; Ma, X.; Zhao, L.; Pang, X. A human stool-derived Bilophila wadsworthia strain caused systemic inflammation in specific-pathogen-free mice. Gut Pathog. 2017, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devkota, S.; Chang, E.B. Interactions between Diet, Bile Acid Metabolism, Gut Microbiota, and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Dig. Dis. 2015, 33, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laitinen, K.; Mokkala, K. Overall dietary quality relates to gut microbiota diversity and abundance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minichino, A.; Brondino, N.; Solmi, M.; Del Giovane, C.; Fusar-Poli, P.; Burnet, P.; Cipriani, A.; Lennox, B.R. The gut-microbiome as a target for the treatment of schizophrenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials of add-on strategies. Schizophr. Res. 2021, 234, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liu, C.; Yang, Y.; Kang, D.; Xiao, J.; Long, Y.; Lang, B.; Peng, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, X. The effects of probiotics plus dietary fiber on antipsychotic-induced weight gain: A randomized clinical trial. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Kang, D.; Zhang, F.; Yang, Y.; Liu, C.; Xiao, J.; Long, Y.; Lang, B.; Peng, X.; Wang, W. Probiotics Plus Dietary Fiber Supplements Attenuate Olanzapine-Induced Weight Gain in Drug-Naïve First-Episode Schizophrenia Patients: Two Randomized Clinical Trials. Schizophr. Bull. 2022, 48, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, R.; Rani, A.; Metwally, A.; McGee, H.S.; Perkins, D.L. Analysis of the microbiome: Advantages of whole genome shotgun versus 16S amplicon sequencing. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 469, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovel, J.; Patterson, J.; Wang, W.; Hotte, N.; O’Keefe, S.; Mitchel, T.; Perry, T.; Kao, D.; Mason, A.L.; Madsen, K.L. Characterization of the gut microbiome using 16S or shotgun metagenomics. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| First-Episode Psychosis (n = 5) | Established Illness (n = 17) | Total with Psychosis (n = 22) | Matched Controls (n = 22) | Statistical Test | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female (n, %) | 1 (20) | 9 (53) | 10 (45) | 10 (45) | X2 = 1.69 | 0.43 |
| Age (mean, SD) | 21.8 ± 3.3 | 44.2 ± 9.7 | 39.5 ± 14.8 | 38.7 ± 14.9 | Z = 118 | 0.80 |
| Ethnicity (n, %) | ||||||
| Europid | 4 (80) | 13 (76) | 17 (77) | 17 (77) | ||
| South American | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | ||
| Asian | 0 (0) | 2 (12) | 2 (9) | 4 (18) | X2 = 13.0 | 0.22 |
| North African/Middle Eastern | 0 (0) | 1 (6) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | ||
| Polynesian | 1 (20) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | ||
| Other | 0 (0) | 1 (6) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | ||
| Weight (kg) (mean, SD) | 60.4 ± 11.1 | 92.9 ± 21.2 | 85.5 ± 23.7 | 81.6 ± 15.3 | t (21) = −0.68 | 0.51 |
| BMI (kg/m2) (mean, SD) | 20.3 ± 2.8 | 31.9 ± 6.9 | 29.2 ± 7.9 | 27.8 ± 5.0 | t (21) = −0.83 | 0.41 |
| BMI Classification (n, %) | ||||||
| Underweight | 2 (40) | 0 (0) | 2 (9) | 0 (0) | ||
| Normal | 3 (60) | 2 (12) | 5 (23) | 9 (41) | ||
| Overweight | 0 (0) | 5 (29) | 5 (23) | 5 (23) | X2 = 6.21 | 0.29 |
| Obese Class I | 0 (0) | 4 (23.5) | 4 (18) | 6 (27) | ||
| Obese Class II | 0 (0) | 4 (23.5) | 4 (18) | 2 (9) | ||
| Obese Class III | 0 (0) | 2 (12) | 2 (9) | 0 (0) | ||
| Diet Quality | 47.0 ± 16.0 | 51.1 ± 17.3 | 50.0 ± 16.7 | NA | - | - |
| V02 Submax | 47.5 ± 5.0 | 23.4 ± 6.3 | 26.6 ± 10.4 | NA | - | - |
| Antipsychotic Medication | ||||||
| Clozapine (and other antipsychotic) | 0 (0) | 9 (53) | 9 (41) | NA | - | - |
| Clozapine (only) | 0 (0) | 8 (47) | 8 (36) | NA | - | - |
| Olanzapine | 1 (20) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | NA | - | - |
| Risperidone | 1 (20) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | NA | - | - |
| Aripiprazole | 3 (60) | 0 (0) | 3 (14) | NA | - | - |
| Mood Stabiliser (n, %) | 0 (0) | 4 (24) | 4 (18) | NA | - | - |
| Antidepressant (n, %) | 0 (0) | 8 (47) | 8 (36) | NA | - | - |
| Metformin (n, %) | 0 (0) | 11 (65) | 11 (50) | NA | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
O’Donnell, M.; Teasdale, S.B.; Chua, X.-Y.; Hardman, J.; Wu, N.; Curtis, J.; Samaras, K.; Bolton, P.; Morris, M.J.; Shannon Weickert, C.; et al. The Role of the Microbiome in the Metabolic Health of People with Schizophrenia and Related Psychoses: Cross-Sectional and Pre-Post Lifestyle Intervention Analyses. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111279
O’Donnell M, Teasdale SB, Chua X-Y, Hardman J, Wu N, Curtis J, Samaras K, Bolton P, Morris MJ, Shannon Weickert C, et al. The Role of the Microbiome in the Metabolic Health of People with Schizophrenia and Related Psychoses: Cross-Sectional and Pre-Post Lifestyle Intervention Analyses. Pathogens. 2022; 11(11):1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111279
Chicago/Turabian StyleO’Donnell, Maryanne, Scott B. Teasdale, Xin-Yi Chua, Jamie Hardman, Nan Wu, Jackie Curtis, Katherine Samaras, Patrick Bolton, Margaret J. Morris, Cyndi Shannon Weickert, and et al. 2022. "The Role of the Microbiome in the Metabolic Health of People with Schizophrenia and Related Psychoses: Cross-Sectional and Pre-Post Lifestyle Intervention Analyses" Pathogens 11, no. 11: 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111279
APA StyleO’Donnell, M., Teasdale, S. B., Chua, X.-Y., Hardman, J., Wu, N., Curtis, J., Samaras, K., Bolton, P., Morris, M. J., Shannon Weickert, C., Purves-Tyson, T., El-Assaad, F., Jiang, X.-T., Hold, G. L., & El-Omar, E. (2022). The Role of the Microbiome in the Metabolic Health of People with Schizophrenia and Related Psychoses: Cross-Sectional and Pre-Post Lifestyle Intervention Analyses. Pathogens, 11(11), 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111279










