A Novel High Discriminatory Protocol for the Detection of Borrelia afzelii, Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Stricto and Borrelia garinii in Ticks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genomes Download and Annotation Revision
2.2. Target Genes Selection
2.3. Primer Design
2.4. Real-Time PCR Assay Set Up
2.5. Protocol Validation
3. Results
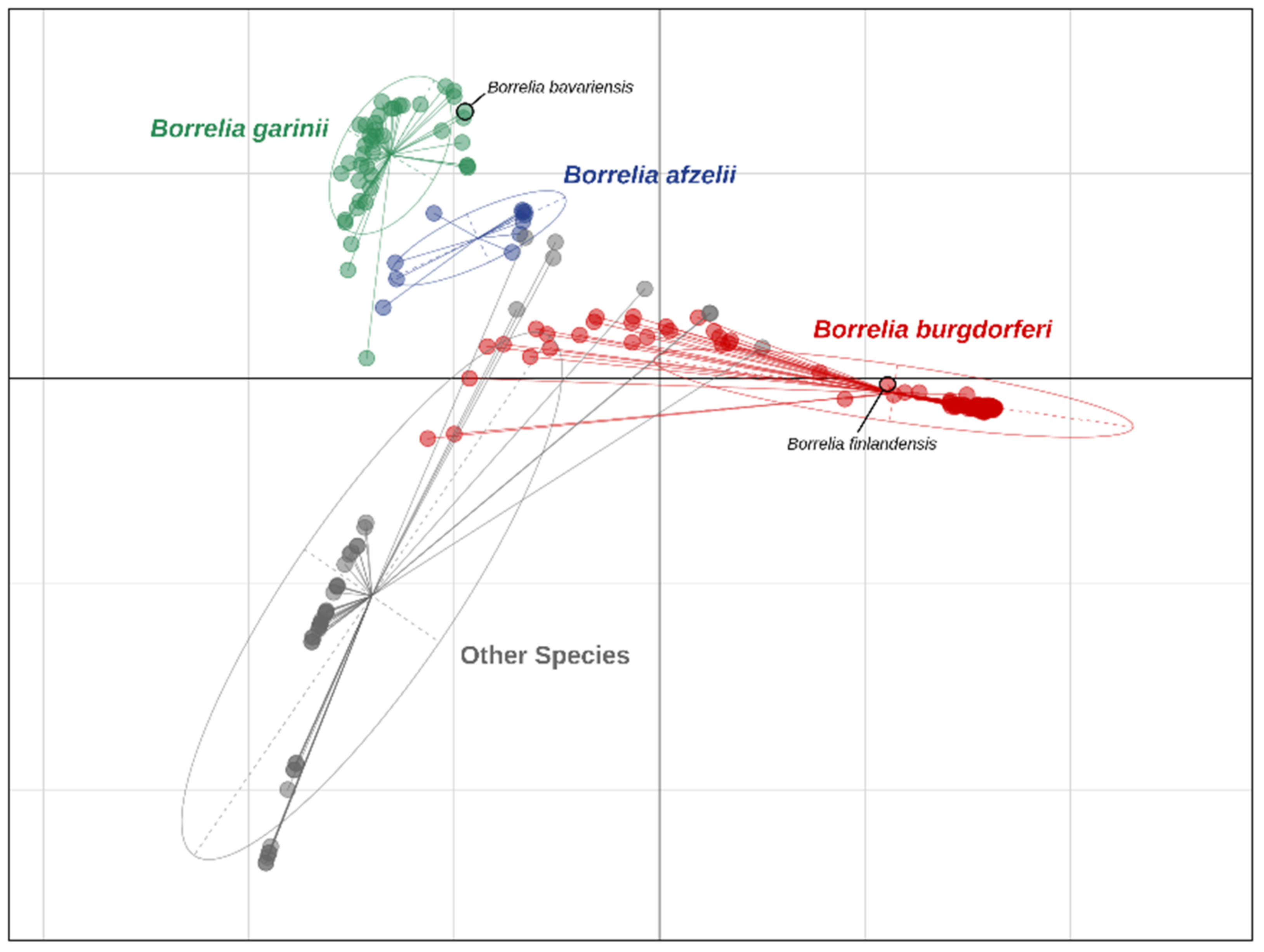
3.1. Bioinformatics Results: Validating PATRIC Annotation
3.2. Bioinformatics Results: Target Genes Selection and Primers Design
3.3. Protocol Validation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gould, L.H.; Nelson, R.S.; Griffith, K.S.; Hayes, E.B.; Piesman, J.; Mead, P.S.; Cartter, M.L. Knowledge, Attitudes, and Behaviors Regarding Lyme Disease Prevention among Connecticut Residents, 1999–2004. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2008, 8, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, A.R. Lyme Disease: A Review. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2010, 10, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumic, I.; Severnini, E. “Ticking Bomb”: The Impact of Climate Change on the Incidence of Lyme Disease. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 2018, 5719081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Estrada-Peña, A.; Cutler, S.; Potkonjak, A.; Vassier-Tussaut, M.; Van Bortel, W.; Zeller, H.; Fernández-Ruiz, N.; Mihalca, A.D. An Updated Meta-Analysis of the Distribution and Prevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi s.l. in Ticks in Europe. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2018, 17, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adrion, E.R.; Aucott, J.; Lemke, K.W.; Weiner, J.P. Health Care Costs, Utilization and Patterns of Care Following Lyme Disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritt, B.S.; Mead, P.S.; Johnson, D.K.H.; Neitzel, D.F.; Respicio-Kingry, L.B.; Davis, J.P.; Schiffman, E.; Sloan, L.M.; Schriefer, M.E.; Replogle, A.J.; et al. Identification of a Novel Pathogenic Borrelia Species Causing Lyme Borreliosis with Unusually High Spirochaetaemia: A Descriptive Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubiak, K.; Dziekońska-Rynko, J.; Szymańska, H.; Kubiak, D.; Dmitryjuk, M.; Dzika, E. Questing Ixodes ricinus Ticks (Acari, Ixodidae) as a Vector of Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato and Borrelia miyamotoi in an Urban Area of North-Eastern Poland. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2019, 78, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizzoli, A.; Hauffe, H.; Carpi, G.; Vourc, H.G.; Neteler, M.; Rosa, R. Lyme Borreliosis in Europe. Eurosurveillance 2011, 16, 19906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omazic, A.; Berggren, C.; Thierfelder, T.; Koch, A.; Evengard, B. Discrepancies in Data Reporting of Zoonotic Infectious Diseases across the Nordic Countries—A Call for Action in the Era of Climate Change. Int. J. Circumpolar Health 2019, 78, 1601991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franke, J.; Hildebrandt, A.; Dorn, W. Exploring Gaps in Our Knowledge on Lyme Borreliosis Spirochaetes—Updates on Complex Heterogeneity, Ecology, and Pathogenicity. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2013, 4, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaenson, T.G.T.; Jaenson, D.G.E.; Eisen, L.; Petersson, E.; Lindgren, E. Changes in the Geographical Distribution and Abundance of the Tick Ixodes ricinus during the Past 30 Years in Sweden. Parasit. Vectors 2012, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurtenbach, K.; Peacey, M.; Rijpkema, S.G.; Hoodless, A.N.; Nuttall, P.A.; Randolph, S.E. Differential Transmission of the Genospecies of Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato by Game Birds and Small Rodents in England. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Dam, A.P. Diversity of Ixodes-Borne Borrelia Species—Clinical, Pathogenetic, and Diagnostic Implications and Impact on Vaccine Development. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2002, 2, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanek, G.; Strle, F. Lyme Borreliosis: A European Perspective on Diagnosis and Clinical Management. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 22, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdin, J.; Cerar, T.; Strle, F.; Ruzić-Sabljić, E. Evaluation of Real-Time PCR Targeting Hbb Gene for Borrelia Species Identification. J. Microbiol. Methods 2010, 82, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margos, G.; Vollmer, S.A.; Ogden, N.H.; Fish, D. Population Genetics, Taxonomy, Phylogeny and Evolution of Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 1545–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poland, G.A. Prevention of Lyme Disease: A Review of the Evidence. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2001, 76, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capelli, G.; Ravagnan, S.; Montarsi, F.; Ciocchetta, S.; Cazzin, S.; Porcellato, E.; Babiker, A.M.; Cassini, R.; Salviato, A.; Cattoli, G.; et al. Occurrence and Identification of Risk Areas of Ixodes ricinus-Borne Pathogens: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis in North-Eastern Italy. Parasit. Vectors 2012, 5, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haddad, V.; Haddad, M.R.; Santos, M.; Cardoso, J.L.C. Skin Manifestations of Tick Bites in Humans. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2018, 93, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzic Sabljic, E.; Cerar, T. Borrelia Genotyping in Lyme Disease. Open Dermatol. J. 2016, 10, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casjens, S.R.; Mongodin, E.F.; Qiu, W.-G.; Luft, B.J.; Schutzer, S.E.; Gilcrease, E.B.; Huang, W.M.; Vujadinovic, M.; Aron, J.K.; Vargas, L.C.; et al. Genome Stability of Lyme Disease Spirochetes: Comparative Genomics of Borrelia burgdorferi Plasmids. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, W.-G.; Martin, C.L. Evolutionary Genomics of Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato: Findings, Hypotheses, and the Rise of Hybrids. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 27, 576–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Margos, G.; Gatewood, A.G.; Aanensen, D.M.; Hanincová, K.; Terekhova, D.; Vollmer, S.A.; Cornet, M.; Piesman, J.; Donaghy, M.; Bormane, A.; et al. MLST of Housekeeping Genes Captures Geographic Population Structure and Suggests a European Origin of Borrelia burgdorferi. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 8730–8735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gevers, D.; Dawyndt, P.; Vandamme, P.; Willems, A.; Vancanneyt, M.; Swings, J.; De Vos, P. Stepping Stones towards a New Prokaryotic Taxonomy. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 361, 1911–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.J.; Aanensen, D.M.; Jordan, G.E.; Kilian, M.; Hanage, W.P.; Spratt, B.G. Assigning Strains to Bacterial Species via the Internet. BMC Biol. 2009, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilhelmsson, P.; Fryland, L.; Börjesson, S.; Nordgren, J.; Bergström, S.; Ernerudh, J.; Forsberg, P.; Lindgren, P.-E. Prevalence and Diversity of Borrelia Species in Ticks That Have Bitten Humans in Sweden. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 4169–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiappa, G.; Cafiso, A.; Monza, E.; Serra, V.; Olivieri, E.; Romeo, C.; Bazzocchi, C. Development of a PCR for Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato, Targeted on the GroEL Gene. Folia Parasitol. 2020, 67, 2020.026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piesman, J.; Schneider, B.S.; Zeidner, N.S. Use of Quantitative PCR to Measure Density of Borrelia burgdorferi in the Midgut and Salivary Glands of Feeding Tick Vectors. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 4145–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivacic, L.; Reed, K.D.; Mitchell, P.D.; Ghebranious, N. A LightCycler TaqMan Assay for Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato in Clinical Samples. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007, 57, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiegala, A.; Król, N.; Oltersdorf, C.; Nader, J.; Pfeffer, M. The Enzootic Life-Cycle of Borrelia burgdorferi (Sensu Lato) and Tick-Borne Rickettsiae: An Epidemiological Study on Wild-Living Small Mammals and Their Ticks from Saxony, Germany. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raileanu, C.; Tauchmann, O.; Vasić, A.; Wöhnke, E.; Silaghi, C. Borrelia miyamotoi and Borrelia burgdorferi (Sensu Lato) Identification and Survey of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus in Ticks from North-Eastern Germany. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parola, P.; Raoult, D. Ticks and Tickborne Bacterial Diseases in Humans: An Emerging Infectious Threat. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 897–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koś, W.; Wodecka, B.; Anklewicz, M.; Skotarczak, B. Rapid Identification of Borrelia by High Resolution Melting Analysis of the GroEL Gene. Folia Biol. 2013, 61, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michelet, L.; Delannoy, S.; Devillers, E.; Umhang, G.; Aspan, A.; Juremalm, M.; Chirico, J.; van der Wal, F.J.; Sprong, H.; Boye Pihl, T.P.; et al. High-Throughput Screening of Tick-Borne Pathogens in Europe. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klitgaard, K.; Kjær, L.J.; Isbrand, A.; Hansen, M.F.; Bødker, R. Multiple Infections in Questing Nymphs and Adult Female Ixodes ricinus Ticks Collected in a Recreational Forest in Denmark. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjær, L.J.; Klitgaard, K.; Soleng, A.; Edgar, K.S.; Lindstedt, H.E.H.; Paulsen, K.M.; Andreassen, Å.K.; Korslund, L.; Kjelland, V.; Slettan, A.; et al. Spatial Patterns of Pathogen Prevalence in Questing Ixodes ricinus Nymphs in Southern Scandinavia, 2016. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.J.; Wattam, A.R.; Aziz, R.K.; Brettin, T.; Butler, R.; Butler, R.M.; Chlenski, P.; Conrad, N.; Dickerman, A.; Dietrich, E.M.; et al. The PATRIC Bioinformatics Resource Center: Expanding Data and Analysis Capabilities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D606–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, I.; Ouk Kim, Y.; Park, S.-C.; Chun, J. OrthoANI: An Improved Algorithm and Software for Calculating Average Nucleotide Identity. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1100–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, C.; Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Phillippy, A.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Aluru, S. High Throughput ANI Analysis of 90K Prokaryotic Genomes Reveals Clear Species Boundaries. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.K.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.G.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid Large-Scale Prokaryote Pan Genome Analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jombart, T. Adegenet: A R Package for the Multivariate Analysis of Genetic Markers. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 1403–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jombart, T.; Devillard, S.; Balloux, F. Discriminant Analysis of Principal Components: A New Method for the Analysis of Genetically Structured Populations. BMC Genet. 2010, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perini, M.; Piazza, A.; Panelli, S.; Di Carlo, D.; Corbella, M.; Gona, F.; Vailati, F.; Marone, P.; Cirillo, D.M.; Farina, C.; et al. EasyPrimer: User-Friendly Tool for Pan-PCR/HRM Primers Design. Development of an HRM Protocol on Wzi Gene for Fast Klebsiella Pneumoniae Typing. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madden, T.L. 2002 The BLAST sequence analysis tool. In The NCBI Handbook; McEntyre, J., Ed.; Bethesda, MD National Library of Medicine (US); National Center for Biotechnology Information: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gyllemark, P.; Wilhelmsson, P.; Elm, C.; Hoornstra, D.; Hovius, J.W.; Johansson, M.; Tjernberg, I.; Lindgren, P.-E.; Henningsson, A.J.; Sjöwall, J. Are Other Tick-Borne Infections Overlooked in Patients Investigated for Lyme Neuroborreliosis? A Large Retrospective Study from South-Eastern Sweden. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjellander, P.L.; Aronsson, M.; Bergvall, U.A.; Carrasco, J.L.; Christensson, M.; Lindgren, P.-E.; Åkesson, M.; Kjellander, P. Validating a Common Tick Survey Method: Cloth-Dragging and Line Transects. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2021, 83, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, I.; Margos, G.; Casjens, S.R.; Qiu, W.-G.; Eggers, C.H. Multipartite Genome of Lyme Disease Borrelia: Structure, Variation and Prophages. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 42, 409–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, S.; Tyson, S.; Dibernardo, A.; Drebot, M.; Feil, E.J.; Graham, M.; Knox, N.C.; Lindsay, L.R.; Margos, G.; Mechai, S.; et al. Whole Genome Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis of Strains of the Agent of Lyme Disease Borrelia burgdorferi from Canadian Emergence Zones. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raileanu, C.; Moutailler, S.; Pavel, I.; Porea, D.; Mihalca, A.D.; Savuta, G.; Vayssier-Taussat, M. Borrelia Diversity and Co-Infection with Other Tick Borne Pathogens in Ticks. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cosson, J.-F.; Michelet, L.; Chotte, J.; Le Naour, E.; Cote, M.; Devillers, E.; Poulle, M.-L.; Huet, D.; Galan, M.; Geller, J.; et al. Genetic Characterization of the Human Relapsing Fever Spirochete Borrelia miyamotoi in Vectors and Animal Reservoirs of Lyme Disease Spirochetes in France. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primers | Sequence (5’–3’) | Tm Oligo (°C) | Amplicon Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bafzelii_qPCR_F | ATTCTTGTGGTCCTGGTT | 51.4 | 263 |
| Bafzelii_qPCR_R | TGAATCAATCTGCCCTAG | 51.4 | |
| Bafzelii_qPCR_F | ATTCTTGTGGTCCTGGTT | 51.4 | 263 |
| Bafzelii_qPCR_R | TGAATCAATCTGCCCTAG | 51.4 | |
| Bbss_qPCR_F | TGTATTCAAGAAACTAAAGCC | 52.0 | 128 |
| Bbss_qPCR_R | GCTCAACTTTTGAATAAATGC | 52.0 | |
| Bgarinii_qPCR_F | AAAAAGTGATAGAGAGTTCC | 51.1 | 75 |
| Bgarinii_qPCR_R | CCCTCTTCAAATTCATTGTC | 53.2 |
| LyDet | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. afzelii | B. burgdorferi s.s. | B. garinii | NEG | |||
| Total (120) | 14 | 1 | 23 | 82 | ||
| Fluidigm | B. miyamotoi | 9 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 8 |
| B. spielmanii | 10 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 9 | |
| B. valasiana | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | |
| B. afzelii | 24 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 12 | |
| B. burgdorferi s.s. | 9 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 8 | |
| B. garinii | 22 | 0 | 0 | 19 | 3 | |
| Borrelia spp. | 22 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 18 | |
| NEG | 21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 21 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiappa, G.; Perini, M.; Cafiso, A.; Nodari, R.; Wilhelmsson, P.; Lindgren, P.-E.; Omazic, A.; Ullman, K.; Moutailler, S.; Kjellander, P.; et al. A Novel High Discriminatory Protocol for the Detection of Borrelia afzelii, Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Stricto and Borrelia garinii in Ticks. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111234
Chiappa G, Perini M, Cafiso A, Nodari R, Wilhelmsson P, Lindgren P-E, Omazic A, Ullman K, Moutailler S, Kjellander P, et al. A Novel High Discriminatory Protocol for the Detection of Borrelia afzelii, Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Stricto and Borrelia garinii in Ticks. Pathogens. 2022; 11(11):1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111234
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiappa, Giulia, Matteo Perini, Alessandra Cafiso, Riccardo Nodari, Peter Wilhelmsson, Per-Eric Lindgren, Anna Omazic, Karin Ullman, Sara Moutailler, Petter Kjellander, and et al. 2022. "A Novel High Discriminatory Protocol for the Detection of Borrelia afzelii, Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Stricto and Borrelia garinii in Ticks" Pathogens 11, no. 11: 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111234
APA StyleChiappa, G., Perini, M., Cafiso, A., Nodari, R., Wilhelmsson, P., Lindgren, P.-E., Omazic, A., Ullman, K., Moutailler, S., Kjellander, P., Bazzocchi, C., & Grandi, G. (2022). A Novel High Discriminatory Protocol for the Detection of Borrelia afzelii, Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Stricto and Borrelia garinii in Ticks. Pathogens, 11(11), 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111234










