Neuraminidase in Virus-like Particles Contributes to the Protection against High Dose of Avian Influenza Virus Challenge Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Gene Cloning and VLP Characterization
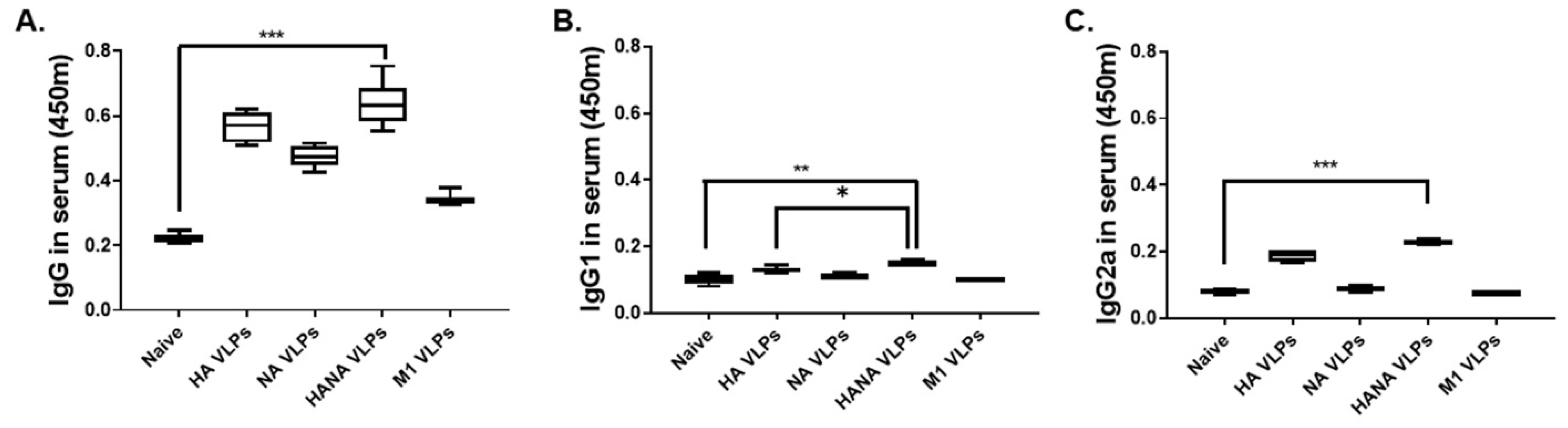
2.2. Virus-Specific Antibody Responses from the Sera of Immunized Mice
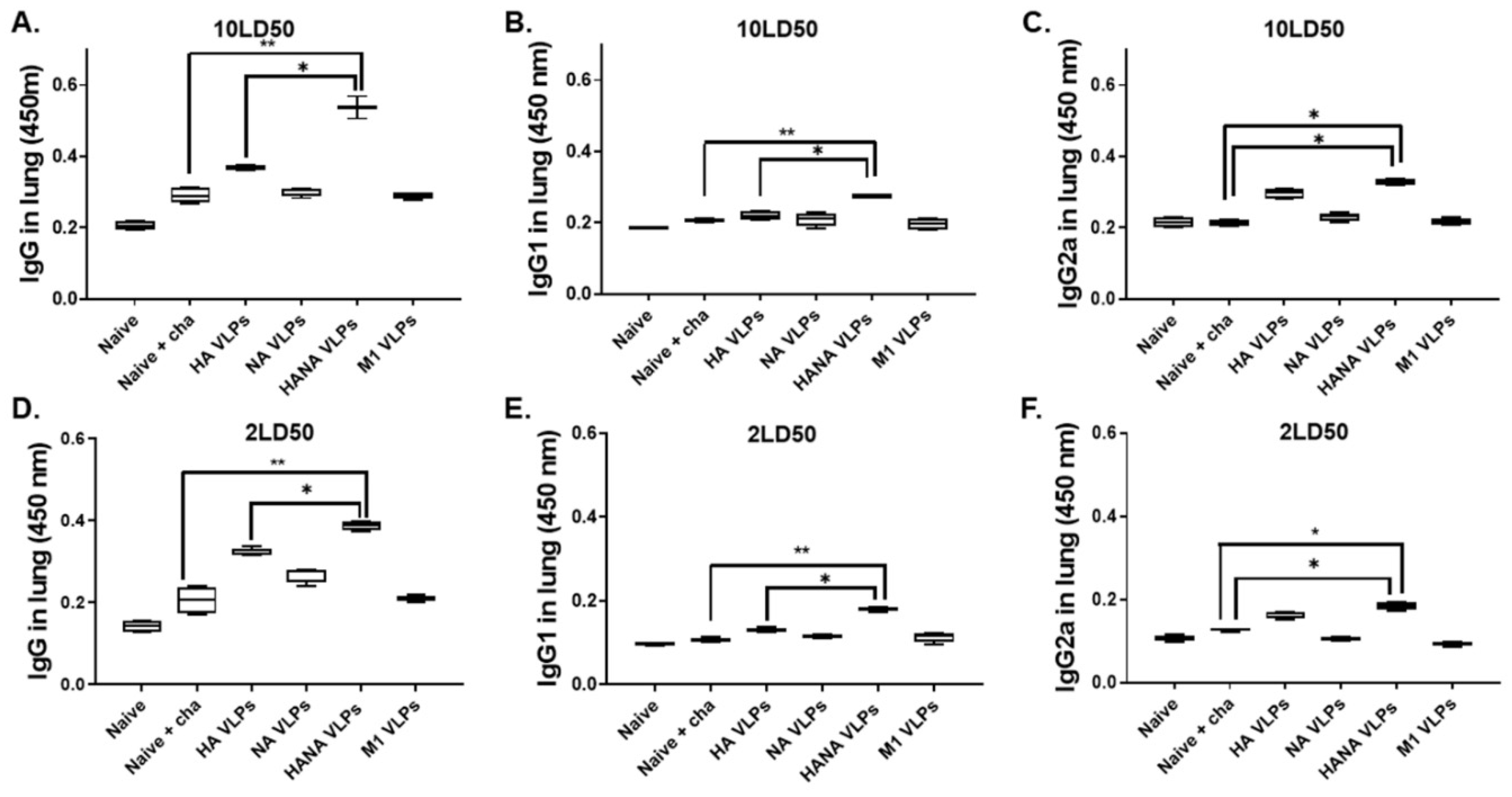
2.3. VLP Immunization Induces Strong Antibody Responses against Lethal Doses of Influenza Virus Challenge Infection
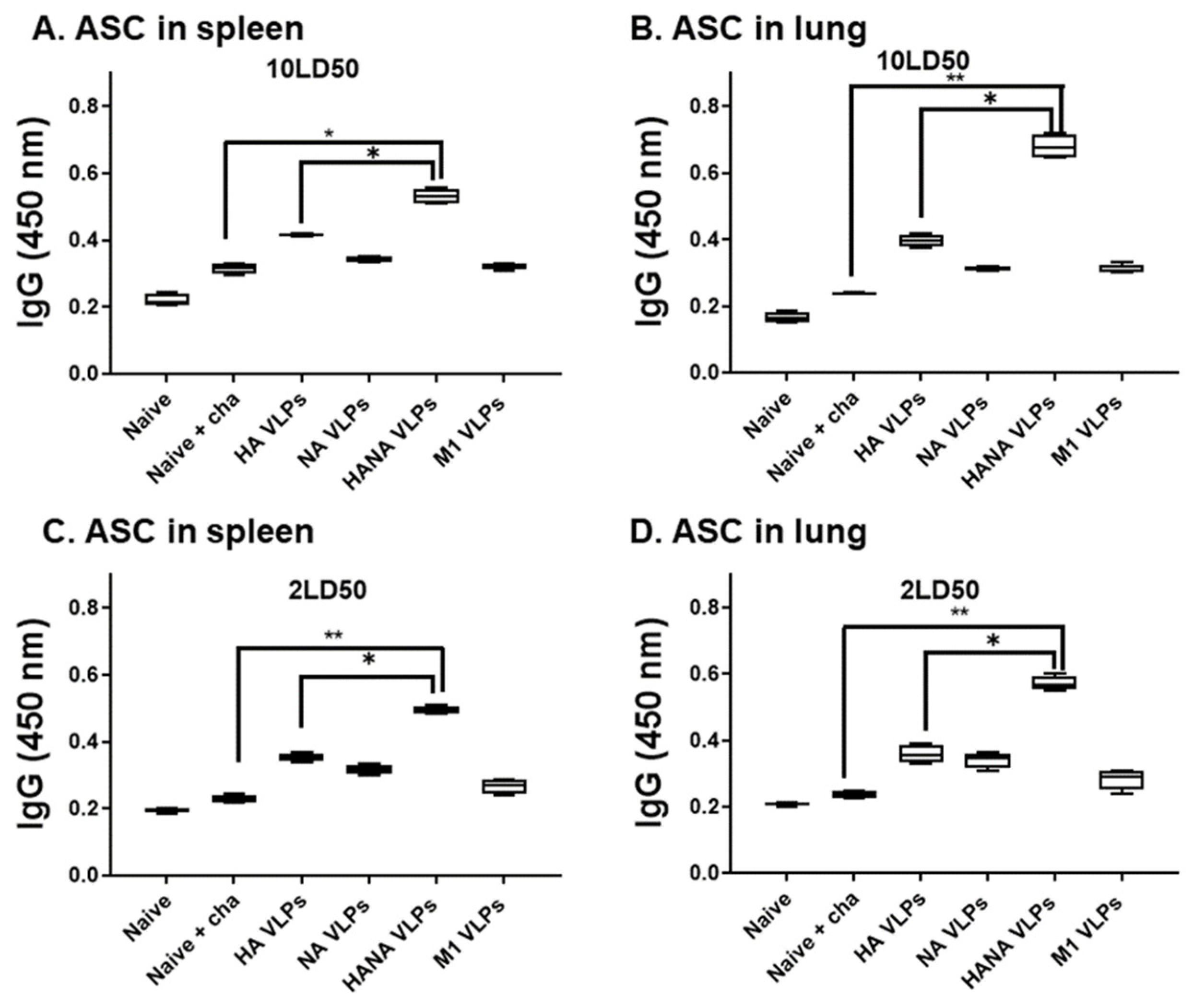
2.4. Single Immunization with the VLPs Elicited Strong Antibody-Secreting Cell (ASC) Responses in Mice
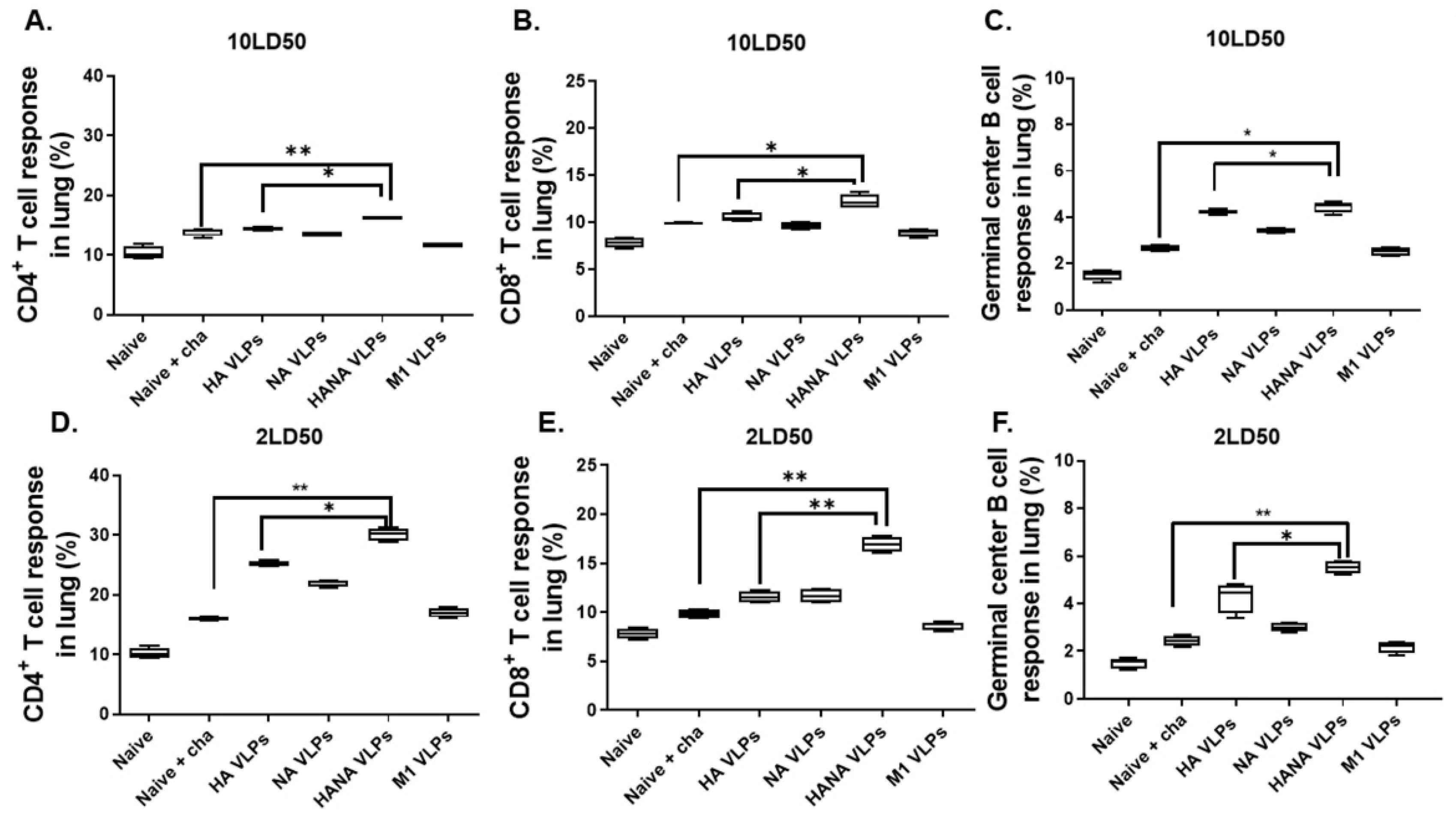
2.5. VLPs Induced Robust Cellular Imune Responses in Mice
2.6. Single Immunization with the VLP Vaccines Suppresses Pulmonary Inflammation
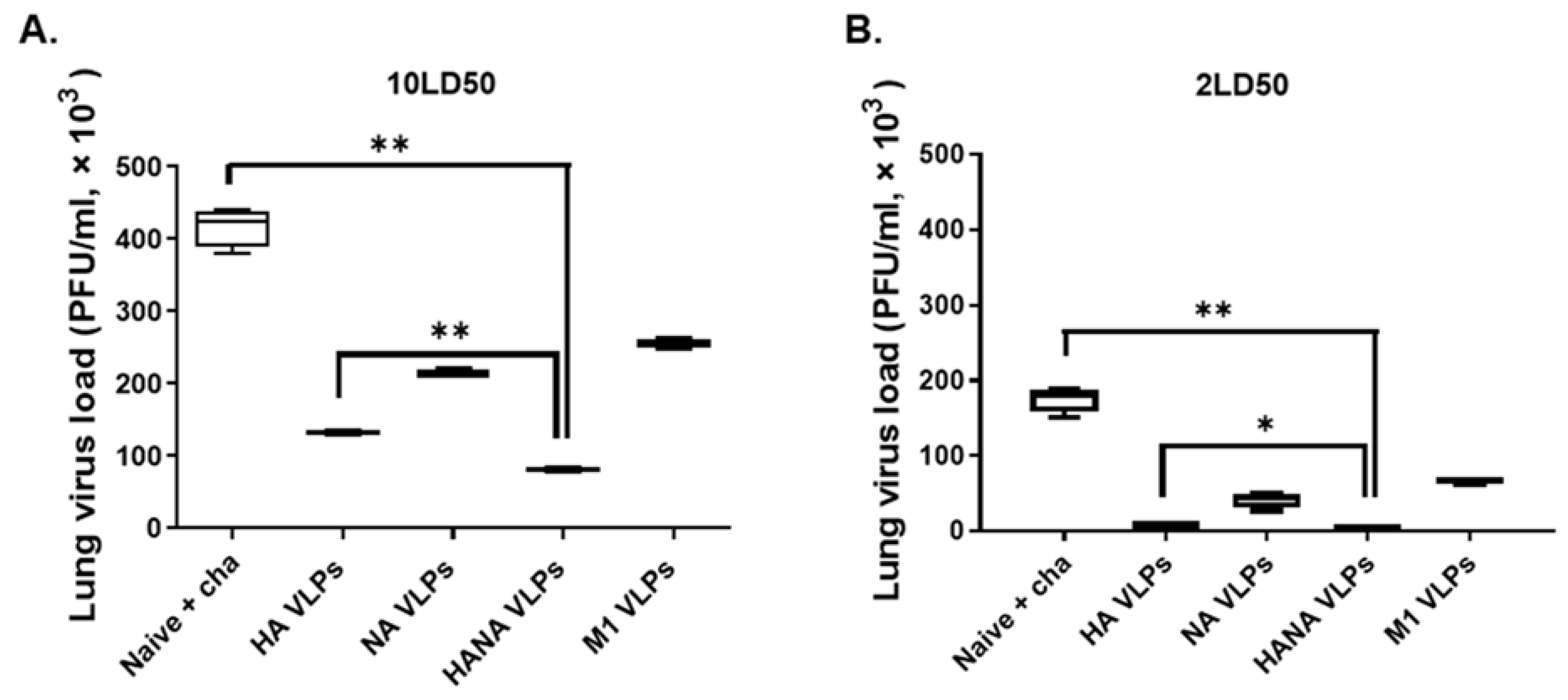
2.7. A Single VLP Immunization Lowers Lung Virus Load and Contributes to Protection
2.8. NA Antigen Is Critical in Inducing Protection against High Challenge Dose Infection
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals, Cells, and Viruses
4.2. Cloning of Avian Influenza Antigens and Generation of rBVs and VLPs
4.3. Characterization of VLPs
4.4. HA and NA Activity Assessment
4.5. Mouse Immunization and Challenge Infection
4.6. Virus-Specific Antibody Responses in Sera
4.7. Pulmonary and Splenic Antibody-Secreting Cell (ASC) Responses
4.8. Flow Cytometry, Cytokine Assays, and Lung Virus Titer
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lai, S.; Qin, Y.; Cowling, B.; Ren, X.; A Wardrop, N.; Gilbert, M.; Tsang, T.K.L.; Wu, P.; Feng, L.; Jiang, H.; et al. Global epidemiology of avian influenza A H5N1 virus infection in humans, 1997–2015: A systematic review of individual case data. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, e108–e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, K.; Richard, M.; Verhagen, J.H.; van Riel, D.; Schrauwen, E.J.; Brand, J.M.V.D.; Mänz, B.; Bodewes, R.; Herfst, S. One health, multiple challenges: The inter-species transmission of influenza A virus. One Health 2015, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.-S.; DeBeauchamp, J.; Zanin, M.; Sun, Y.; Tang, L.; Webby, R. H5N1 influenza vaccine induces a less robust neutralizing antibody response than seasonal trivalent and H7N9 influenza vaccines. npj Vaccines 2017, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, F.; Fouchier, R.; Eichelberger, M.C.; Webby, R.J.; Shaw-Saliba, K.; Wan, H.; Wilson, P.C.; Compans, R.W.; Skountzou, I.; Monto, A.S. NAction! How Can Neuraminidase-Based Immunity Contribute to Better Influenza Virus Vaccines? mBio 2018, 9, e02332-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, F.; Palese, P. Advances in the development of influenza virus vaccines. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.-M.; Cho, H.-K.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.J.; Park, S.-J.; Kim, D.-Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, J.-W.; Lee, M.-H.; Kim, M.-C.; et al. Single dose of multi-clade virus-like particle vaccine protects chickens against clade 2.3.2.1 and clade 2.3.4.4 highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Lu, J.; Zhang, X.; Mei, M.; Feng, L.; Peng, D.; Hou, J.; Kang, S.-M.; Liu, X.; Tang, Y. Single Dose of Consensus Hemagglutinin-Based Virus-Like Particles Vaccine Protects Chickens against Divergent H5 Subtype Influenza Viruses. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.; O’Kennedy, M.M.; Wandrag, D.B.; Adeyemi, M.; Abolnik, C. Efficacy of a plant-produced virus-like particle vaccine in chickens challenged with Influenza A H6N2 virus. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 18, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillet, S.; Racine, T.; Nfon, C.; Di Lenardo, T.; Babiuk, S.; Ward, B.; Kobinger, G.; Landry, N. Plant-derived H7 VLP vaccine elicits protective immune response against H7N9 influenza virus in mice and ferrets. Vaccine 2015, 33, 6282–6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monto, A.S.; Petrie, J.G.; Cross, R.T.; Johnson, E.; Liu, M.; Zhong, W.; Levine, M.; Katz, J.M.; Ohmit, S.E. Antibody to Influenza Virus Neuraminidase: An Independent Correlate of Protection. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skarlupka, A.L.; Bebin-Blackwell, A.-G.; Sumner, S.F.; Ross, T.M. Universal Influenza Virus Neuraminidase Vaccine Elicits Protective Immune Responses against Human Seasonal and Pre-pandemic Strains. J. Virol. 2021, 95, JVI0075921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushko, P.; Tretyakova, I.; Hidajat, R.; Zsak, A.; Chrzastek, K.; Tumpey, T.M.; Kapczynski, D.R. Virus-like particles displaying H5, H7, H9 hemagglutinins and N1 neuraminidase elicit protective immunity to heterologous avian influenza viruses in chickens. Virology 2016, 501, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretyakova, I.; Pearce, M.B.; Florese, R.; Tumpey, T.M.; Pushko, P. Intranasal vaccination with H5, H7 and H9 hemagglutinins co-localized in a virus-like particle protects ferrets from multiple avian influenza viruses. Virology 2013, 442, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-Y.; Yeh, Y.-C.; Chan, J.-T.; Yang, Y.-C.; Yang, J.-R.; Liu, M.-T.; Wu, H.-S.; Hsiao, P.-W. A VLP Vaccine Induces Broad-Spectrum Cross-Protective Antibody Immunity against H5N1 and H1N1 Subtypes of Influenza A Virus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyson, C.; Youk, S.; Smith, D.; Dimitrov, K.; Lee, D.-H.; Larsen, L.E.; Swayne, D.E.; Pantin-Jackwood, M.J. Pathogenicity and genomic changes of a 2016 European H5N8 highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (clade 2.3.4.4) in experimentally infected mallards and chickens. Virology 2019, 537, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherwood, R.L.; Thomas, P.T.; Kawanishi, C.Y.; Fenters, J.D. Comparison of Streptococcus zooepidemicus and influenza virus pathogenicity in mice by three pulmonary exposure routes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1988, 54, 1744–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulo, A.C.; Correia-Neves, M.; Domingos, T.; Murta, A.G.; Pedrosa, J. Influenza Infectious Dose May Explain the High Mortality of the Second and Third Wave of 1918–1919 Influenza Pandemic. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, J.E.; Kelly, H.A.; Mercer, G.N.; Glass, K. Systematic review of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus shedding: Duration is affected by severity, but not age. Influ. Other Respir. Viruses 2013, 8, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlleben, G.; Müller, J.; Tatsch, U.; Hambrecht, C.; Herz, U.; Renz, H.; Schmitt, E.; Moll, H.; Erb, K.J. Influenza A virus infection inhibits the efficient recruitment of Th2 cells into the airways and the development of airway eosinophilia. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 4601–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, R.A.; Carter, D.M.; Daniluk, S.; Toapanta, F.R.; Ahmad, A.; Gavrilov, V.; Massare, M.; Pushko, P.; Mytle, N.; Rowe, T.; et al. Influenza virus-like particles elicit broader immune responses than whole virion inactivated influenza virus or recombinant hemagglutinin. Vaccine 2007, 25, 3871–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant, A.J.; DiPiazza, A.; Nayak, J.L.; Rattan, A.; Richards, K.A. CD4 T cells in protection from influenza virus: Viral antigen specificity and functional potential. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 284, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowthaman, V.; Vanamayya, P.R.; Nagarajan, S.; Suba, S.; Bhatia, S.; Jain, R.; Behera, P.; Tosh, C.; Murugkar, H.V.; Dubey, S.C. Influence of Dose of Inocula on Outcome of Clinical Disease in Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (H5N1) Infections—An Experimental Study. Avian Dis. 2010, 54, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Gruta, N.; Turner, S.J. T cell mediated immunity to influenza: Mechanisms of viral control. Trends Immunol. 2014, 35, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, N.; Van Tin, N.; Sato, Y.; Thach, H.N.; Katano, H.; Diep, P.H.; Kumasaka, T.; Thuy, N.T.; Hasegawa, H.; San, L.T.; et al. Pathological study of archival lung tissues from five fatal cases of avian H5N1 influenza in Vietnam. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 26, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Lu, M.; Korteweg, C.; Gao, Z.; McNutt, M.; Ye, J.; Zhang, T.; Gu, J. Distinctly different expression of cytokines and chemokines in the lungs of two H5N1 avian influenza patients. J. Pathol. 2008, 216, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienz, O.; Rud, J.G.; Eaton, S.M.; A Lanthier, P.; Burg, E.; Drew, A.; Bunn, J.; Suratt, B.T.; Haynes, L.; Rincon, M. Essential role of IL-6 in protection against H1N1 influenza virus by promoting neutrophil survival in the lung. Mucosal Immunol. 2012, 5, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggert, D.; Swayne, D. Single Vaccination Provides Limited Protection to Ducks and Geese Against H5N1 High Pathogenicity Avian Influenza Virus. Avian Dis. 2010, 54, 1224–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelissen, L.A.H.M.; de Vries, R.; De Boer-Luijtze, E.A.; Rigter, A.; Rottier, P.J.M.; de Haan, C. A Single Immunization with Soluble Recombinant Trimeric Hemagglutinin Protects Chickens against Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus H5N1. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noad, R.; Roy, P. Virus-like particles as immunogens. Trends Microbiol. 2003, 11, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiblhofer, S.; Laimer, J.; Machado, Y.; Weiss, R.; Thalhamer, J. Influence of protein fold stability on immunogenicity and its implications for vaccine design. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2017, 16, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone, L.A.; Ahmad, A.; Veguilla, V.; Lu, X.; Smith, G.; Katz, J.M.; Pushko, P.; Tumpey, T.M. Intranasal Vaccination with 1918 Influenza Virus-Like Particles Protects Mice and Ferrets from Lethal 1918 and H5N1 Influenza Virus Challenge. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 5726–5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.-M.; Hossain, J.; Yoo, D.-G.; Lipatov, A.S.; Davis, C.T.; Quan, F.-S.; Chen, L.-M.; Hogan, R.J.; Donis, R.O.; Compans, R.W.; et al. Protective immunity against H5N1 influenza virus by a single dose vaccination with virus-like particles. Virology 2010, 405, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.-M.; Yoo, D.-G.; Lipatov, A.S.; Song, J.-M.; Davis, C.T.; Quan, F.-S.; Chen, L.-M.; Donis, R.O.; Compans, R.W. Induction of Long-Term Protective Immune Responses by Influenza H5N1 Virus-Like Particles. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.-J.; Chu, K.-B.; Lee, D.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Park, B.R.; Kim, M.-C.; Kang, S.-M.; Quan, F.-S. Influenza M2 virus-like particle vaccination enhances protection in combination with avian influenza HA VLPs. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.-B.; Kang, H.-J.; Yoon, K.-W.; Lee, H.-A.; Moon, E.-K.; Han, B.-K.; Quan, F.-S. Influenza Virus-like Particle (VLP) Vaccines Expressing the SARS-CoV-2 S Glycoprotein, S1, or S2 Domains. Vaccines 2021, 9, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, E.-K.; Kang, H.-J.; Chu, K.-B.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, D.-H.; Soh, Y.; Quan, F.-S. Immune Correlates of Protection Induced by Virus-Like Particles Containing 2009 H1N1 Pandemic Influenza HA, NA or M1 Proteins. Immunol. Investig. 2018, 48, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Manual on Animal Influenza Diagnosis and Surveillance. Available online: https://www.who.int/csr/resources/publications/influenza/whocdscsrncs20025rev.pdf (accessed on 22 July 2021).
- Kim, K.-H.; Lee, Y.-T.; Park, S.; Jung, Y.-J.; Lee, Y.; Ko, E.-J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Li, X.; Kang, S.-M. Neuraminidase expressing virus-like particle vaccine provides effective cross protection against influenza virus. Virology 2019, 535, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kwon, Y.-M.; Lee, Y.-T.; Kim, M.-C.; Hwang, H.S.; Ko, E.-J.; Lee, Y.; Choi, H.-J.; Kang, S.-M. Virus-Like Particles Are a Superior Platform for Presenting M2e Epitopes to Prime Humoral and Cellular Immunity against Influenza Virus. Vaccines 2018, 6, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, F.-S.; Huang, C.; Compans, R.W.; Kang, S.-M. Virus-Like Particle Vaccine Induces Protective Immunity against Homologous and Heterologous Strains of Influenza Virus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 3514–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, H.-J.; Chu, K.-B.; Yoon, K.-W.; Eom, G.-D.; Mao, J.; Kim, M.-J.; Lee, S.-H.; Moon, E.-K.; Quan, F.-S. Neuraminidase in Virus-like Particles Contributes to the Protection against High Dose of Avian Influenza Virus Challenge Infection. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101291
Kang H-J, Chu K-B, Yoon K-W, Eom G-D, Mao J, Kim M-J, Lee S-H, Moon E-K, Quan F-S. Neuraminidase in Virus-like Particles Contributes to the Protection against High Dose of Avian Influenza Virus Challenge Infection. Pathogens. 2021; 10(10):1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101291
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Hae-Ji, Ki-Back Chu, Keon-Woong Yoon, Gi-Deok Eom, Jie Mao, Min-Ju Kim, Su-Hwa Lee, Eun-Kyung Moon, and Fu-Shi Quan. 2021. "Neuraminidase in Virus-like Particles Contributes to the Protection against High Dose of Avian Influenza Virus Challenge Infection" Pathogens 10, no. 10: 1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101291
APA StyleKang, H.-J., Chu, K.-B., Yoon, K.-W., Eom, G.-D., Mao, J., Kim, M.-J., Lee, S.-H., Moon, E.-K., & Quan, F.-S. (2021). Neuraminidase in Virus-like Particles Contributes to the Protection against High Dose of Avian Influenza Virus Challenge Infection. Pathogens, 10(10), 1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101291





